- Review Article
- Allergy
- Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels can predict allergic disease development and atopic march in children
- Zak Callaway, Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):398-405. Published online February 3, 2025
-
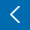
· Allergic march occurs in a subset of children, beginning with atopic dermatitis and progressing to food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and/or asthma. Its early diagnosis is important to slowing its progression.
· Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN), an excellent biomarker of eosinophil activity, is often elevated in allergic diseases.
· EDN levels have been used to predict allergic disease development and diagnose, treat, and monitor allergic diseases.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation and sedation requirements in the pediatric intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ambrus Szemere, Alíz Fazekas, Anna Réka Sebestyén, Rani Ezzeddine, Veronika Upor, Marie Anne Engh, Péter Hegyi, Zsolt Molnár, Klára Horváth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):406-416. Published online February 19, 2025
-
Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation requirements, pediatric intensive care unit length of stay, and sedative exposure. However, it may increase the likelihood of unplanned extubation, highlighting the importance of incorporating preventive measures to mitigate this risk.
- Endocrinology
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Other
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumors in the head and neck in patients with APC gene deletion mutations: a case report and scoping review of the literature
- Koral M. Blunt, Monirah Albathi, Miriam Conces, Tendy Chiang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):428-433. Published online January 13, 2025
-
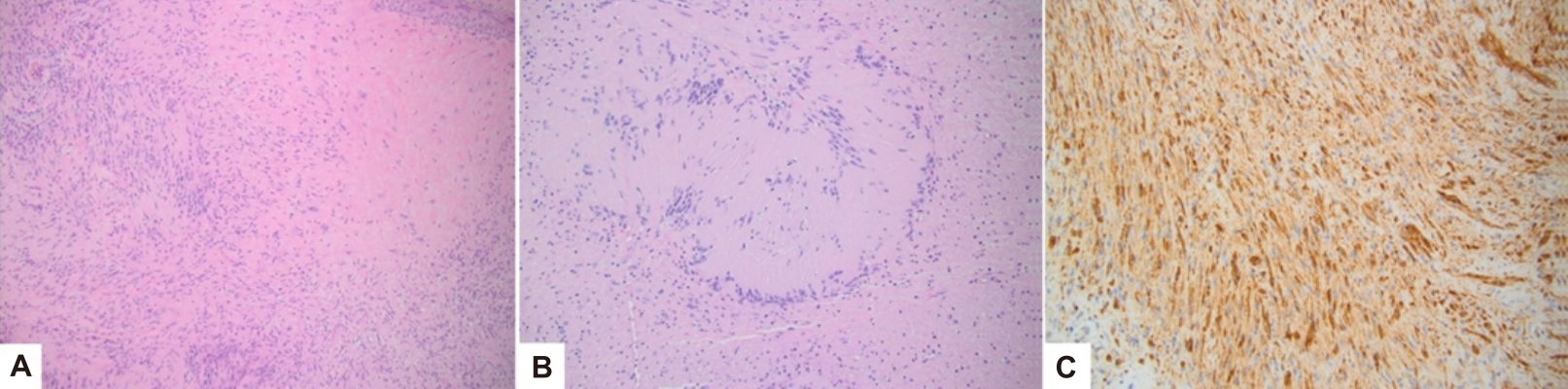
In this report, we describe our experience with a patient with an APC-related genetic syndrome who presented with a rare palatal lesion with characteristics of a schwannoma. We discuss the role of immunohistochemical staining in discerning the differential diagnosis.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Screen time and neurodevelopment in preschoolers: addressing a growing concern in pediatric practice
- Soongang Park, Hyewon Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):434-436. Published online January 13, 2025
-
· Excessive screen time in preschoolers is associated with neurodevelopmental delays, particularly during the early years of life.
· Parental supervision and national guidelines are critical in mitigating the negative impacts of excessive screen time and fostering healthy media habits in preschoolers.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Impact of Xmn1 polymorphism on hydroxyurea therapy in children with HbE-β non-transfusion dependent thalassemia: a cohort study
- Saheli Roy, Paramita Bhattacharya, Atanu Kumar Dutta, Mrinal Kanti Das
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):437-444. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: Does the T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influence hydroxyurea efficacy in children of Eastern descent with fetal hemoglobin (HbE)-β nontransfusion dependent thalassemia (NTDT)?
Finding: Decrease in transfusion requirement and increase in height following hydroxyurea therapy was noted in both groups, however, change in CT was more critical than that in CC genotype.
Meaning: T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influences hydroxyurea efficacy in children with HbE-β NTDT.
- Oncology
- Prognostic role of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in predicting infection in pediatric cancer with febrile neutropenia
- Seham M. Ragab, Sara Mahmoud El-Deeb, Ahmed Saeed, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):445-453. Published online January 13, 2025
-

· Infection remains a leading cause of death in febrile neutropenia (FN).
· Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-ProADM) levels are higher among patients with FN and a bacterial infection.
· A longer FN duration and hospital stay length as well as elevated C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and MR-ProADM levels are significant risk factors for mortality.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):454-462. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: What is the acceptance rate for coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Finding: One-third of parents were hesitant to vaccinate their child. Parental willingness to vaccinate themselves, older patient age, and belief in the vaccine's potency were associated with vaccine acceptance.
Meaning: These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions to improve vaccine acceptance among parents of children with SLE.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Differential roles of interleukin-6 and adrenomedullin in early diagnosis and mortality predictions in late-onset neonatal sepsis
- Emilly Henrique dos Santos, Gabriel Acca Barreira, Mariana Okay Saippa, Maria Carolina Pires Cruz, Karen Alessandra Rodrigues, Ronaldo Arkader, Thelma Suely Okay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):463-471. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: Can adrenomedullin (ADM) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) detect late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) at admission (area under the curve [AUC]>0.90) as an early diagnostic marker?
Finding: Only IL-6 consistently distinguished survivors from nonsurvivors (AUC>0.90) on admission and antibiotic treatment days 3 and 7. C-reactive protein level identified infections from day 3 but failed to predict outcomes (AUC<0.70).
Meaning: IL-6 level can improve LOS diagnosis and prognosis.
- Clinical Note
- General Pediatrics
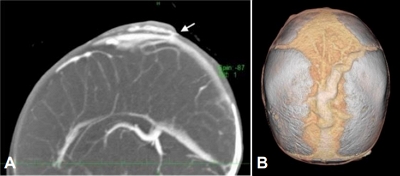
- Aplasia cutis congenita with unique vascular malformation and cranial hypoplasia: a case in a preterm infant
- Yasufumi Sakata, Natsumi Fujii, Sadahiro Nomura, Yoshihiro Azuma, Hiroki Hamano, Hidenobu Kaneyasu, Seigo Okada, Kazumasa Takahashi, Shunji Hasegawa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):472-474. Published online March 11, 2025
-