- Perspective
- Neurology
- How can pediatricians treat neurodevelopmental disorders
- Young-Hoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):1-2. Published online July 27, 2020
-
∙ Recently neurodevelopmental therapy for preschool-aged children with neurodevelopmental disorders is paid for by health insurance in Korea.
∙ There are good evidences that parenting programs and neurodevelopmental therapy can work in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder.
∙ Pediatricians must be able to pass away important information to parents.
- Review Articles
- Other
- Review of epidemiological studies on air pollution and health effects in children
- Jong-Tae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):3-11. Published online June 10, 2020
-
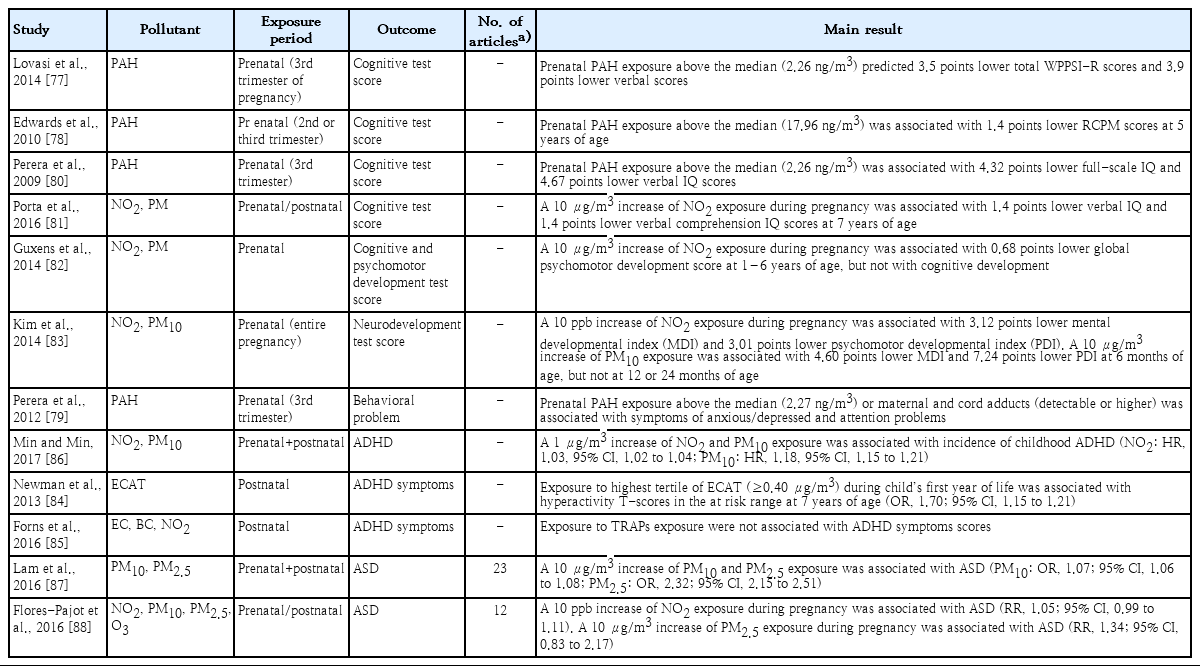
This review summarized the accumulated epidemiologic evidence with emphasis on studies conducted in Korea and heterogeneity in the literature. Based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses, there is consistent evidence on the association between exposure to ambient air pollution and children’s health, especially respiratory health and adverse birth outcomes, and growing evidence on neurodevelopmental outcomes.
- Endocrinology
- Early menarche and its consequence in Korean female: reducing fructose intake could be one solution
- Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Sub Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):12-20. Published online May 14, 2020
-
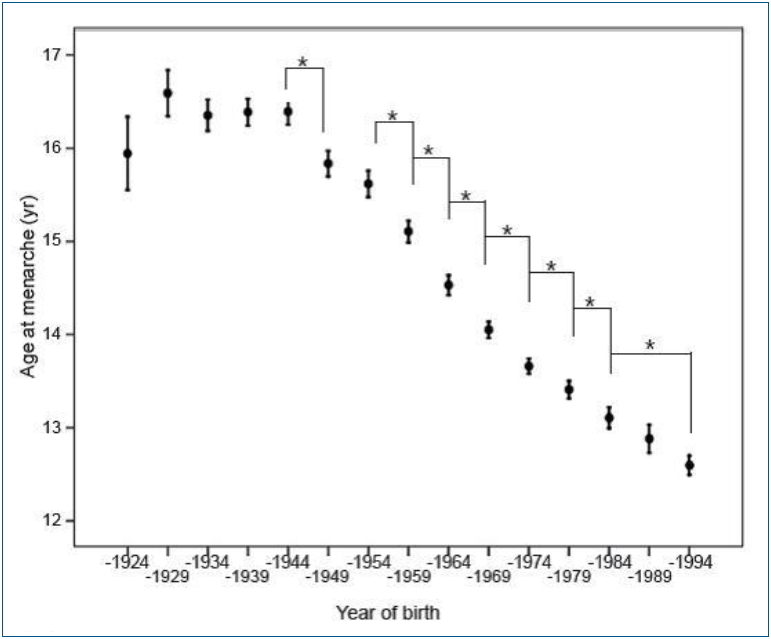
In Korea, the average age of menarche has declined sharply. Early menarche is associated with psychosocial and behavioral problems and cardiometabolic disease. Excess fructose intake has been suggested as one cause of early menarche in recent studies, so reducing fructose intake may be one solution.
- Gastroenterology
- Changing prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents
- Ji Sook Park, Jin Su Jun, Ji-Hyun Seo, Hee-Shang Youn, Kwang-Ho Rhee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):21-25. Published online July 15, 2020
-
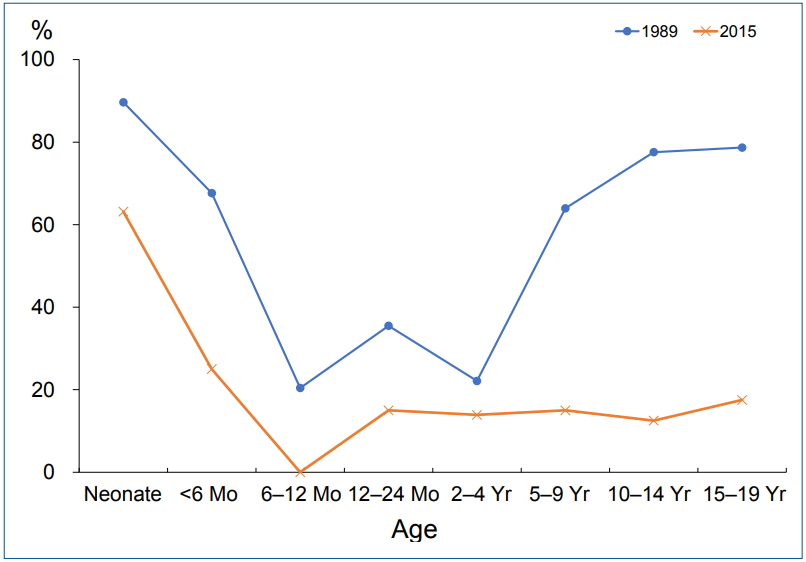
Although Helicobacter pylori infection rate in children is unclear due to diversity and limitation of diagnostic tests unlike in adults, investigation the childhood prevalence is important for predicting H. pylori-related diseases in the future.
H. pylori infection occurred in early childhood, and declined during 30 years in our study.
Change in risk factors of H. pylori transmission and consensus for eradication therapy in children might further reduce the infection rate.
- Editorials
- General Pediatrics
- Why should we be concerned about early menarche?
- Hae Sang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):26-27. Published online July 13, 2020
-
· Early menarche is associated with several health problems in later life.
· Early menarche can be caused by environmental factors such as increased subcutaneous fat, a high body mass index, and sugar-sweetened beverages as well as genetic factors.
· Health education can prevent early menarche by aiming to reduce the consumption of fructose, high concentrations of which are present in sugar-sweetened beverages.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neutrophil CD11b as a promising marker for early detection of neonatal sepsis
- Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):28-30. Published online September 1, 2020
-

· Neonatal sepsis is a global problem and significant cause of neonatal mortality and adverse short- and long-term outcomes.
· Due to severe limitations diagnosing neonatal sepsis, there is a critical need to identify reliable specific biomarkers for early detection.
· nCD11b might be an accurate and rapid biomarker for the early detection of neonatal sepsis.
- Original Articles
- Gastroenterology
- Noninvasive markers for esophageal varices in children with cirrhosis
- Parisa Rahmani, Fatemeh Farahmand, Ghobad Heidari, Azadeh Sayarifard
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):31-36. Published online July 21, 2020
-
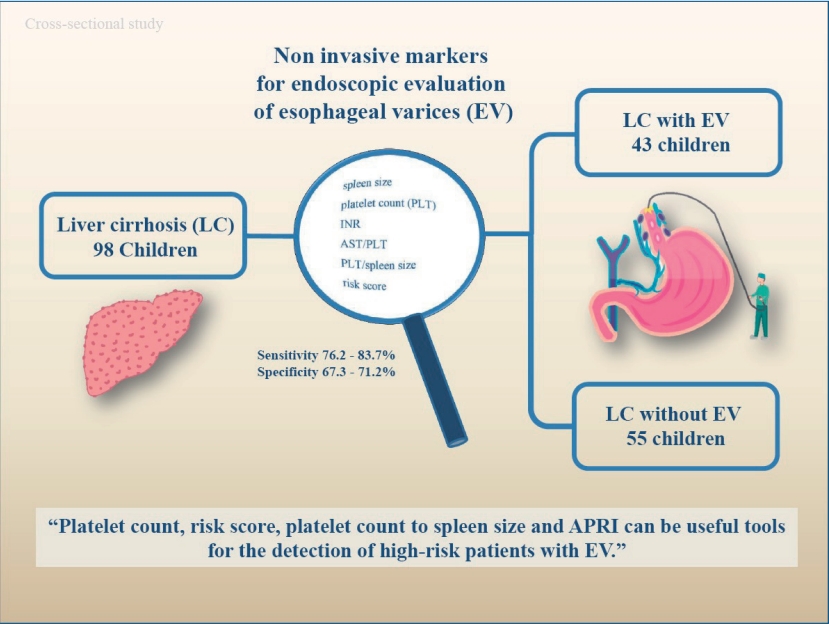
Question: Can noninvasive biomarkers identify esophageal varices among children with esophageal cirrhosis?
Finding: The spleen size, platelet count, international normalized ratio, aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index, platelet count to spleen size ratio, and risk score differed significantly between the patients with and those without esophageal varices.
Meaning: These biological parameters can predict esophageal varices among pediatric patients and indicate the need for esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The protective effect of CXC chemokine receptor 2 antagonist on experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia induced by postnatal systemic inflammation
- Seung Hyun Lee, Chang Won Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):37-43. Published online July 15, 2020
-

Question: Can CXC chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) antagonist preserve alveolarization by attenuating the inflammation induced by systemic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)?
Finding: CXCR2 antagonist significantly decreased neutrophil counts in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood induced by systemic LPS administration and restored alveolarization in newborn rats.
Meaning: CXCR2 antagonist protected the lungs from the inflammation in a rat model of BPD.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Role of neutrophil CD11b expression in diagnosis of earlyonset neonatal sepsis in full-term infant
- Safaa ELMeneza, Walaa Mohamed, Iman Elbagoury, Karima Bahagat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):44-45. Published online April 14, 2020
-
Question: Can CD11b detect sepsis in full-term infants with suspected sepsis?
Finding: The percentage of neutrophils expressing CD11b was significantly upregulated in the sepsis and suspected sepsis groups versus the control group.
Meaning: CD11b is a sensitive marker for sepsis and suspected sepsis in full-term neonates and it may be added to sepsis markers. This information would allow the neonatologist to confidently discontinue antibiotic use as long as the neonate is clinically stable.