- Review Articles
- Neurology
- Recent update on reading disability (dyslexia) focused on neurobiology
- Sung Koo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):497-503. Published online March 2, 2021
-
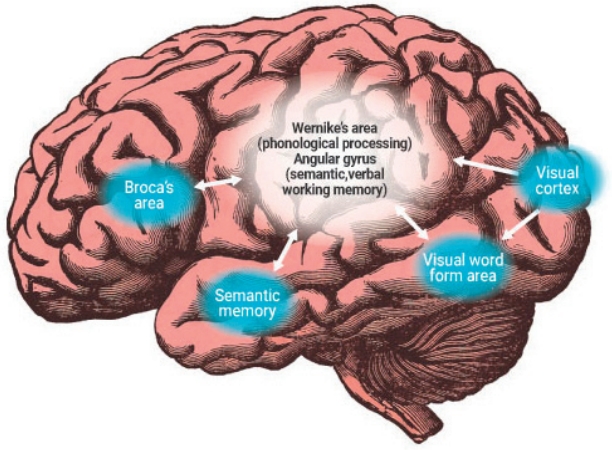
·Neurobiological studies using functional brain imaging have uncovered the reading pathways, brain regions involved in reading, and neurobiological abnormalities of dyslexia.
·An accurate diagnosis and timely specialized intervention are important in children with dyslexia. When national infant development screening tests have been conducted as in Korea, if a language developmental delay and early predictors of dyslexia are detected, the progression to dyslexia should be carefully observed and early intervention provided.
- Immunology
- Modern diagnostic capabilities of neonatal screening for primary immunodeficiencies in newborns
- Evgenia Olegovna Khalturina, Natalia Dmitrievna Degtyareva, Anastasiia Vasi’evna Bairashevskaia, Alena Valerievna Mulenkova, Anna Vladimirovna Degtyareva
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):504-510. Published online March 25, 2021
-
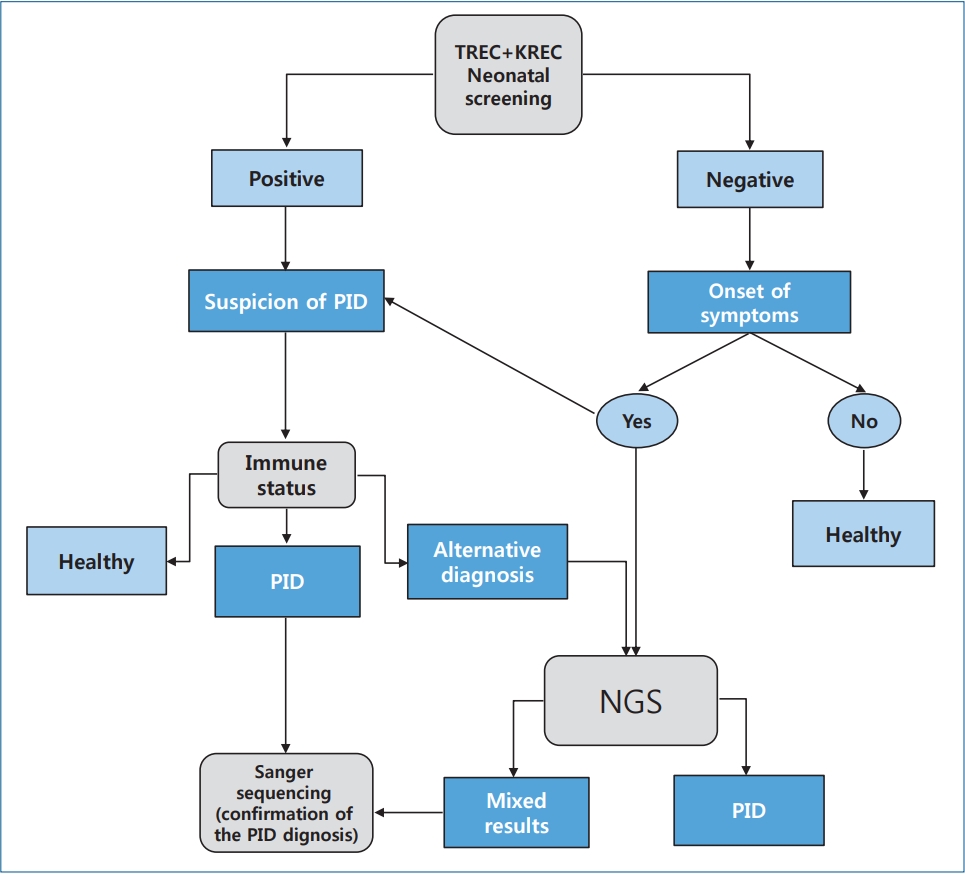
· Neonatal screening for primary immunodeficiency diseases (PIDs) enables early diagnosis and subsequent initiation of therapy.
· Excision of T-cell receptors and kappa-recombination excision circles are cheaper alternative PID screening methods.
· Sanger DNA sequencing remains the reference method for detecting PID; however, next-generation sequencing technology is increasingly used to diagnose it.
· Here we developed a graphical algorithm for diagnosing primary immunodeficiency syndrome based on modern methods of screening for primary immunodeficiencies in newborns.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Obesity and chronic kidney disease: prevalence, mechanism, and management
- Hyung Eun Yim, Kee Hwan Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):511-518. Published online April 6, 2021
-
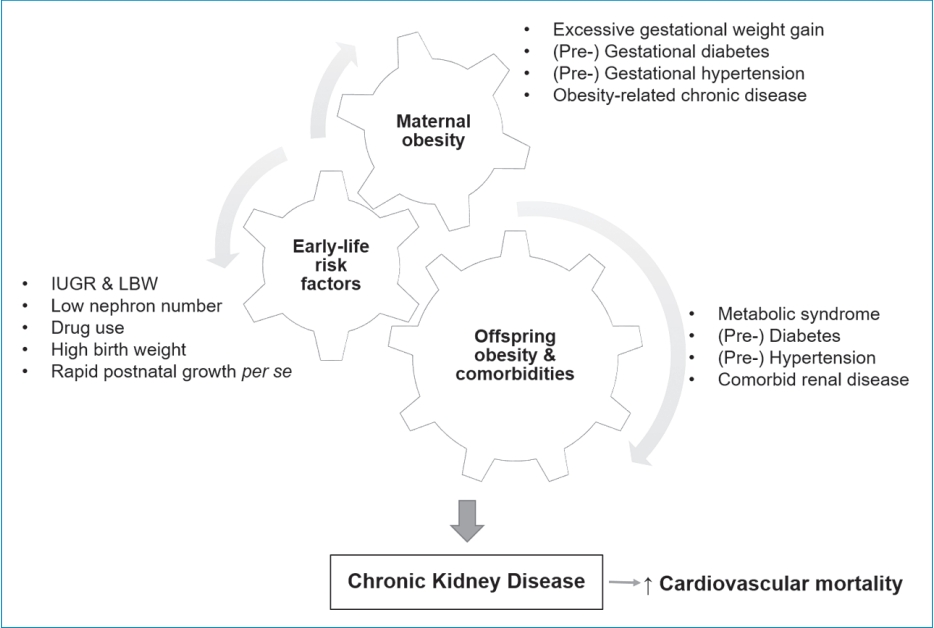
· Obesity is strongly associated with the development and progression of chronic kidney disease.
· Altered renal hemodynamics, metabolic effects, and lipid nephrotoxicity may play a key role in the development of obesity-related kidney disease.
· Children born to obese mothers are at increased risk of developing obesity and chronic kidney disease later in life.
· A multilevel approach is needed to prevent obesity and related chronic diseases.
- Editorials
- Immunology
- Importance of neonatal screening for primary immunodeficiencies
- Jung Woo Rhim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):519-520. Published online May 4, 2021
-
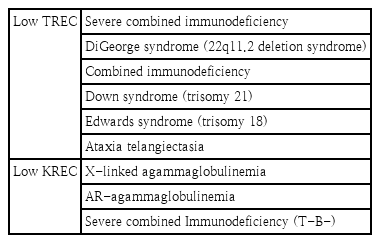
· Early detection of asymptomatic infants with primary immunodeficiencies before the onset of infections enables effective treatment and intervention to prevent serious sequelae.
· T-cell receptor excision circles and kappa-deleting recombination excision circles have recently been used to detect T- or B-cell lymphopenia in neonates.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Obesity and chronic kidney disease: what should pediatric nephrologists know?
- Jung Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):521-522. Published online June 1, 2021
-
• Obesity is not only a comorbidity of hypertension, it may be a riskfactorfor chronickidneydisease.
• Renal impairment associated with obesity is believed to start early in childhood and continue into adulthood, implying a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
• The identification of kidney injury, implementation of preventive strategies, and prompt treatment are essential to improving clinical outcomes in obese children with early kidney disease.
- Endocrinology
- Ambient air pollution and pediatric diabetes
- Jae Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):523-534. Published online March 12, 2021
-
· Epidemiological studies have shown that ambient air pollution is associated with diabetes mellitus in children and adults.
· The mechanism of ambient air pollution causing diabetes mellitus is unclear.
· A study of the association between diabetes and air pollution in Korean pediatric populations is required.
- Original Articles
- Endocrinology
- Correlation between total air pollutant emissions and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the Russian Federation
- Hoon Sung Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Ji-Young Seo, Faina Linkov, Evgeniy Shubnikov, Hong Kyu Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):525-530. Published online January 18, 2021
-
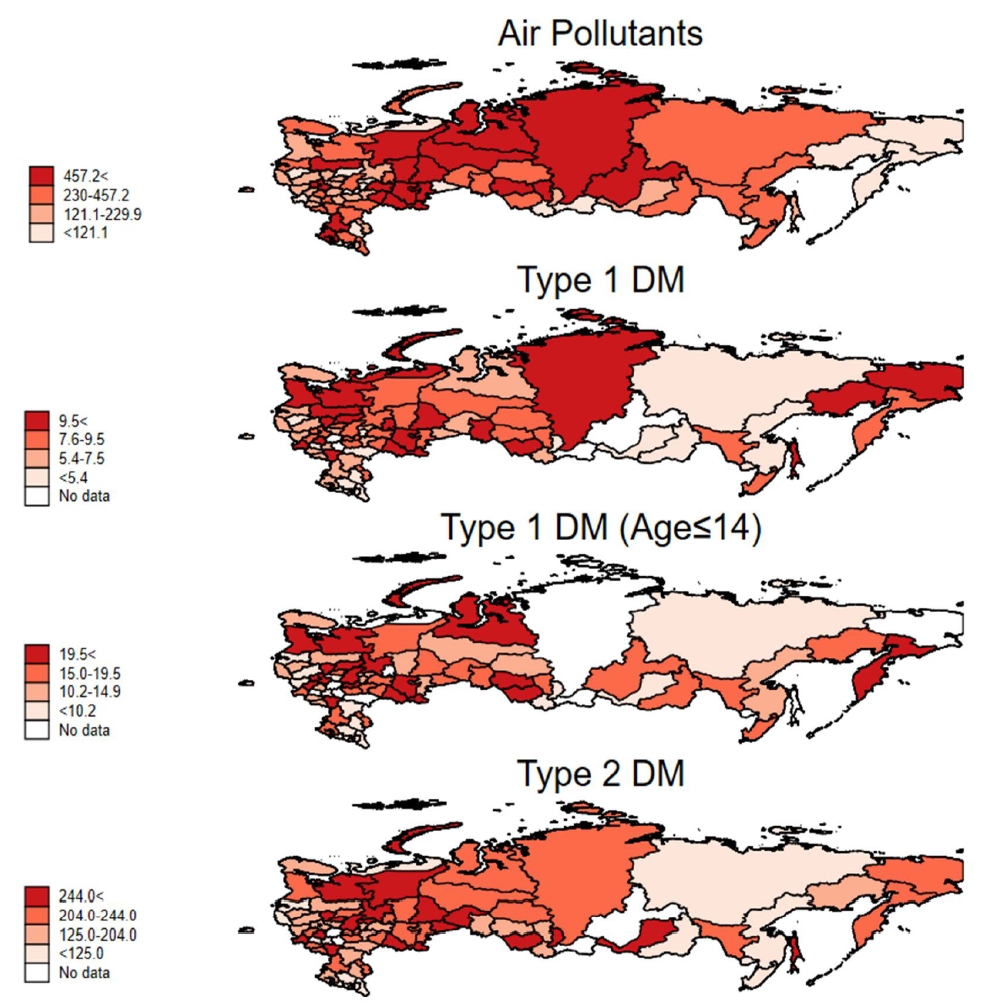
Question: Is there a quantitative relationship between air pollutant emissions and the incidence of type 1 diabetes (T1D)?
Finding: The incidence of T1D in each region of the Russian Federation correlated with the total air pollutants emitted each year.
Meaning: These findings suggest that air pollution contributes to the development of T1D.
- Other
- Clinical spectrum and short-term outcomes of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in a south Indian hospital
- Muruganantham Balagurunathan, Thrilok Natarajan, Jothilakshmi Karthikeyan, Venkateshwaran Palanisamy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):531-537. Published online August 4, 2021
-

Question: What are the clinical spectrum, course, and short-term outcomes of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C)?
Finding: MIS-C can have variable clinical manifestations. Fever is most common, followed by gastrointestinal and cardiovascular symptoms. Early identification and appropriate management lead to favorable outcomes.
Meaning: MIS-C can present in a myriad of ways and severities. High suspicion is necessary to ensure its early identification and appropriate management and favorable patient outcomes.
- Neurobehavior
- Association between small for gestational age and risk of autism spectrum disorders: a meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Zahra Asali, Mahdieh Seyedi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):538-542. Published online January 28, 2021
-
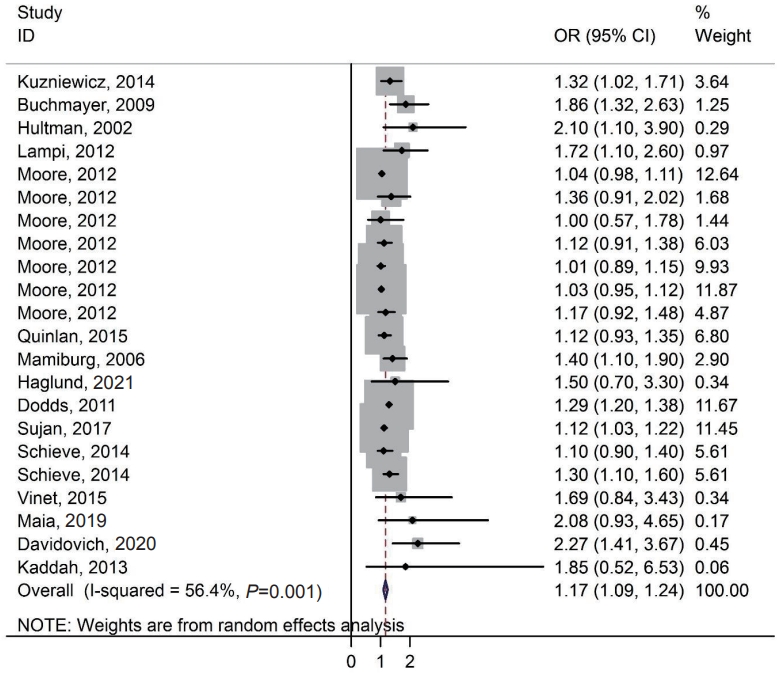
• The relationship between small for gestational age (SGA) and autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and remains conflicting.
• We showed based on odds ratio reports in epidemiological studies that SGA can increase the risk of ASD and SGA is a risk factor for ASD.
• The association between SGA and the risk of ASD has further momentum to the current public health emphasis on appropriate prepregnancy weight and weight gain during pregnancy