- Perspective
- Infection
- Statement on healthcare system preparedness in response to COVID-19 Omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5 surge in Korea from the Korean Pediatric Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases
- Eun Young Cho, Dong Hyun Kim, Soo-Han Choi, Ki Wook Yun, Jong Gyun Ahn, Hye-Kyung Cho, Hyunju Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Yae-Jean Kim; Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):510-511. Published online September 23, 2022
-
In order to respond to the recent surge in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases and the continuously changing epidemiology of COVID-19, a sustainable and flexible pediatric healthcare system must be prepared considering the specificity of pediatric care. We demand a more proactive response from the health authorities to check the current state of pediatric COVID-19 patient care and to ensure that pediatric patients receive appropriate and timely management.
- Review Articles
- General Pediatrics
- Motor performance of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: focus on the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency
- Khushboo Prashant Adhvaryu, Suruliraj Karthikbabu, Pratiksha Tilak Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):512-520. Published online February 17, 2022
-
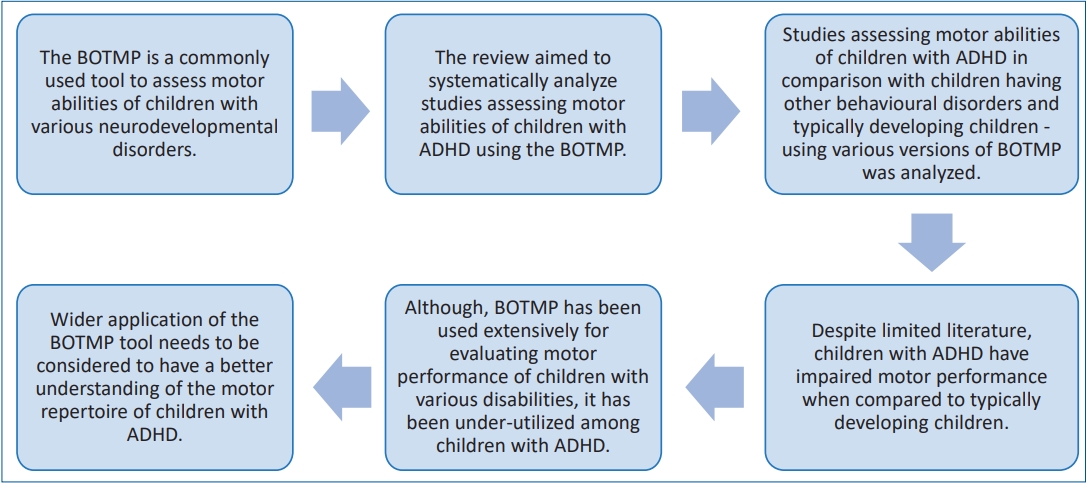
· Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) tend to have impaired motor performance that may affect their growth and development.
· Although widely used among children with developmental disorders, the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOTMP) is used sparsely among children with ADHD.
· Assessment by the BOTMP increases our understanding of the motor repertoire of children with ADHD.
· Wider usage of the BOTMP will enable more comprehensive planning of rehabilitation goals to enhance the motor abilities of children with ADHD.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal seizures: stepping outside the comfort zone
- Menna Hashish, Mohamed Reda Bassiouny
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):521-528. Published online April 4, 2022
-
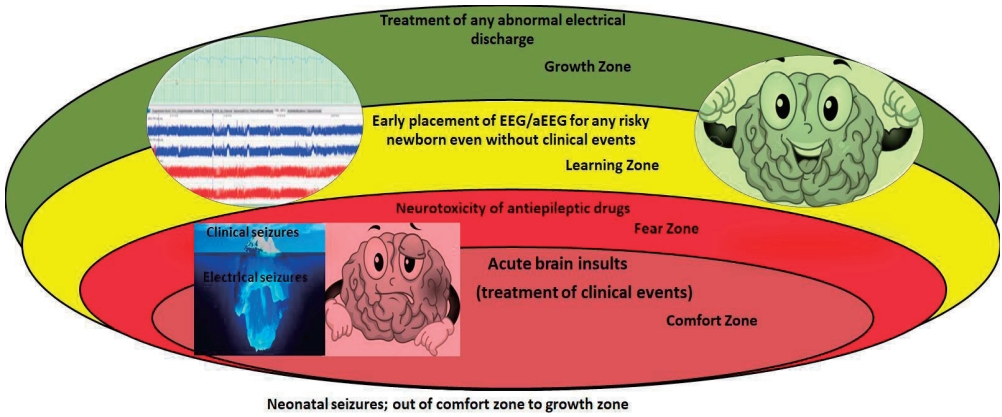
· Use conventional and amplitude-integrated electroencephalography to confirm clinical seizures and screen high-risk newborns.
· Select an explicit clear elective event to be treated with less toxic and more effective antiepileptics.
- Allergy
- Management of patients with allergic diseases in the era of COVID-19
- Eun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):529-535. Published online September 23, 2022
-
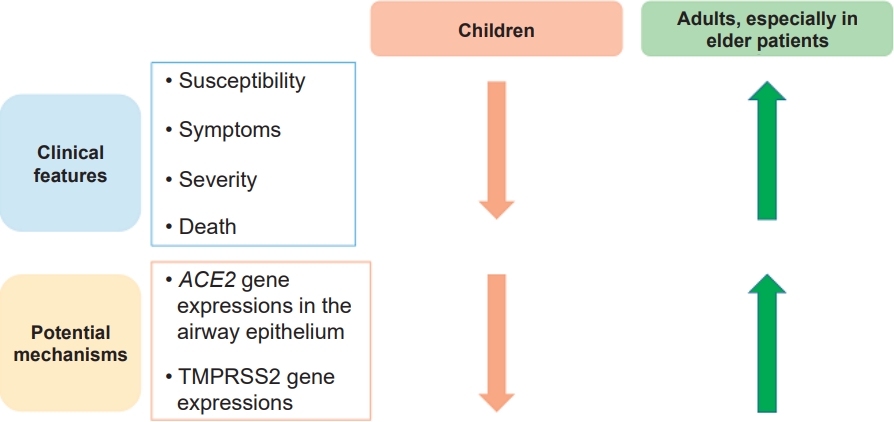
In the early days of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, allergic diseases, especially asthma, were considered to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. These concerns stemmed from the idea that individuals with allergic diseases are generally more susceptible to respiratory virus infections, which are major causes of exacerbation of allergic diseases. However, epidemiologic data with...
- Editorials
- Neurology
- Increasing our understanding of rotavirus-induced central nervous system manifestations
- Jon Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):536-537. Published online May 6, 2022
-

· Diverse clinicoradiological features of central nervous system (CNS) complications in rotavirus infection can be identified with the rapid and wide use of various brain magnetic resonance imaging protocols.
· An increased understanding of the various pathophysiological mechanisms of rotavirus-induced CNS manifestations will enable precise management in the future.
- Cardiology
- Recent research trends in Kawasaki disease-related infection
- Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):538-539. Published online July 22, 2022
-
The incidence of Kawasaki disease has reportedly decreased since the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) quarantine. However, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children has reportedly occurred more frequently in areas where COVID-19 was prevalent than in previous years. Research into the etiology of childhood and adolescent systemic vasculitis in infection-related immune responses during the COVID-19 pandemic has increased accordingly.
- Original Articles
- Nutrition
- Survey of Korean pediatrician’s perceptions of barriers to and improvements in breastfeeding
- Seong Phil Bae, Woo Ryoung Lee, Won-Ho Hahn, Hye-Jung Shin, Young Min Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Yong Joo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Youn Jeong Shin, Dae Yong Yi, Soon Min Lee, Juyoung Lee, Jin A Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Euiseok Jung, Eui Kyung Choi, Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):540-546. Published online July 29, 2022
-
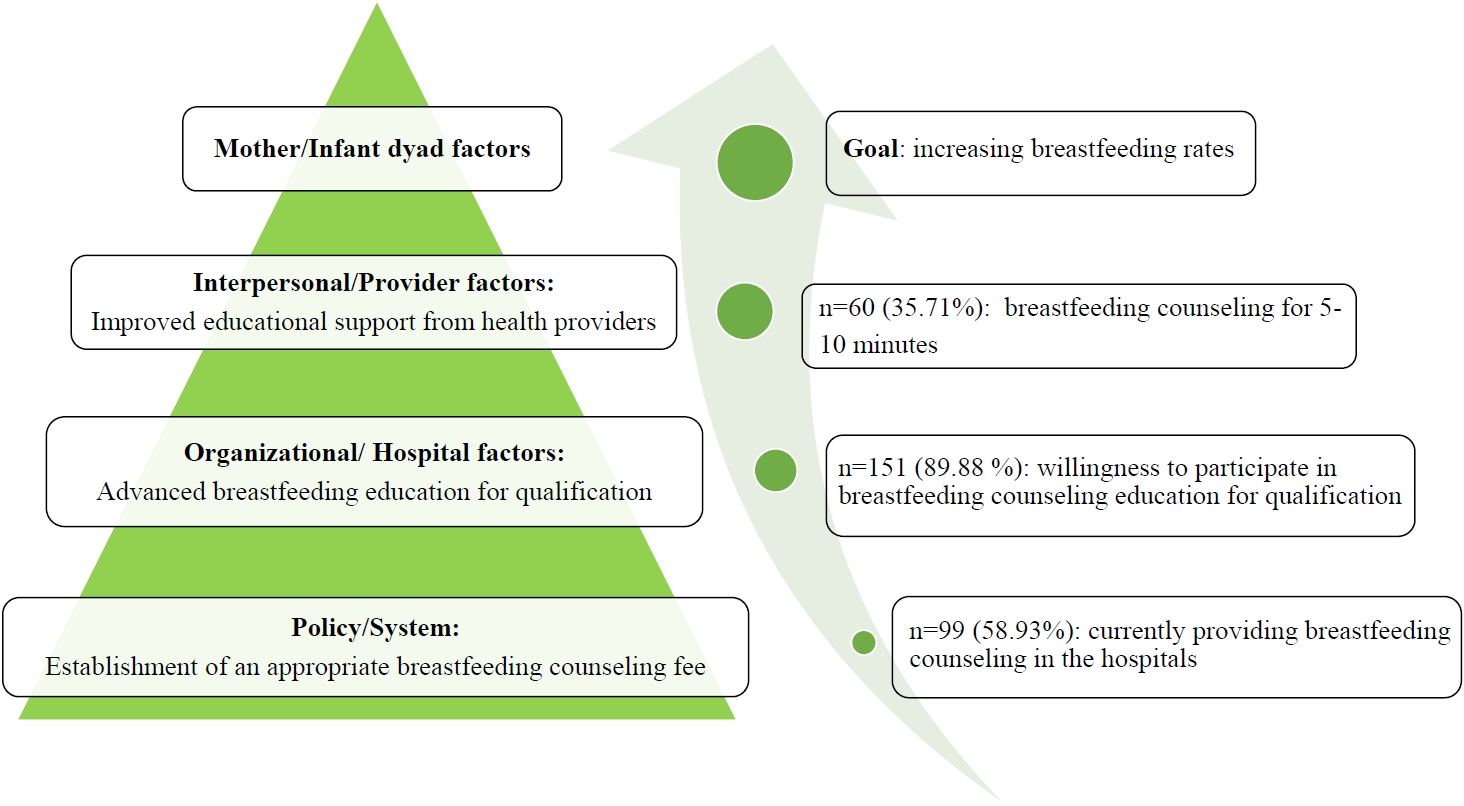
Question: What barriers to breastfeeding do Korean pediatricians perceive?
Finding: Regardless of medical institution, breastfeeding counseling for parents is currently limited, and breastfeeding is commonly discontinued due to various maternal and neonatal factors.
Meaning: To promote breastfeeding, increasing pediatrician participation in breastfeeding counseling with the establishment of appropriate breastfeeding counseling fees and the expansion of practical and high-quality breastfeeding education for medical staff should be considered.
- Gastroenterology
- Probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect ınfantile colic symptoms and fecal microbiota profile: a single-blind randomized controlled study
- Aysu Yıldız Karaahmet, Gülümser Dolgun, Metehan Özen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):547-554. Published online September 23, 2022
-

Question: Do probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect infantile colic symptoms and intestinal microbiota?
Finding: Infants whose mothers ingested probiotics demonstrated decreased crying frequency and intensity and significantly increased bacterial diversity in the stools. The bacterial variety was substantially affected by the added probiotic product.
Meaning: The addition of probiotics to maternal nutrition in early infancy could play an important role in preventing infantile colic.