- Review Articles
- Infection
- Etiological and pathophysiological enigmas of severe coronavirus disease 2019, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease
- Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):153-166. Published online November 23, 2021
-
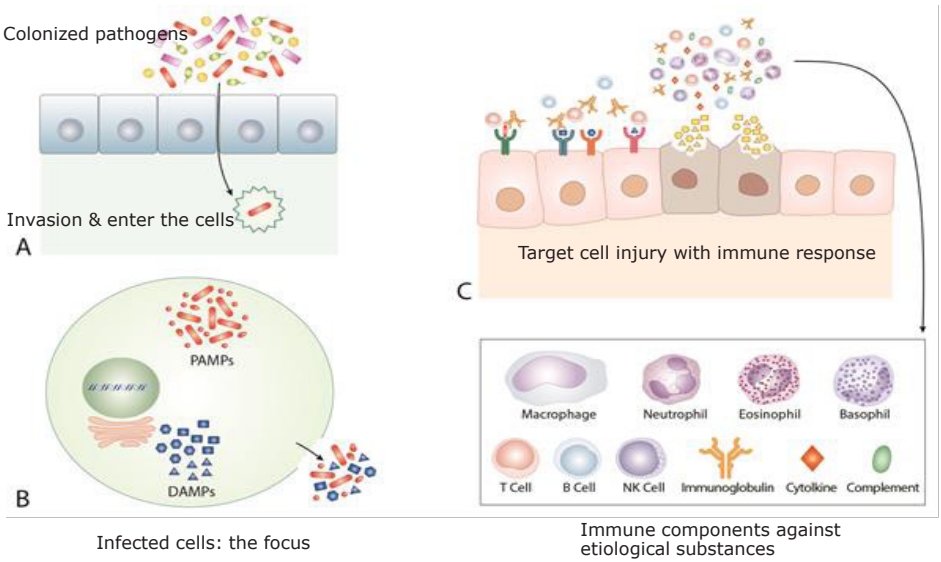
· Severe cases of coronavirus disease, Kawasaki disease (KD), and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) share similar findings: a protracted clinical course, multiorgan involvement, and similar activated biomarkers.
· Here we propose etiological agents in KD and MIS-C as species in the microbiota and introduce a common pathogenesis through the protein-homeostasis-system hypothesis.
· Early proper dose of corticosteroids and/or intravenous immunoglobulin may help to reduce morbidity and mortality in these diseases.
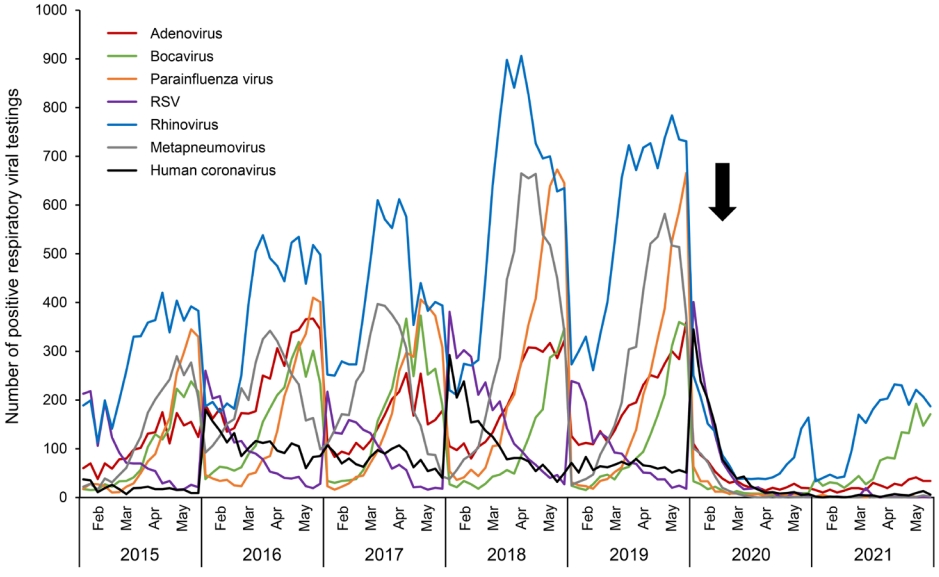
- Epidemiological changes in infectious diseases during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea: a systematic review
- Jong Gyun Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):167-171. Published online November 30, 2021
-
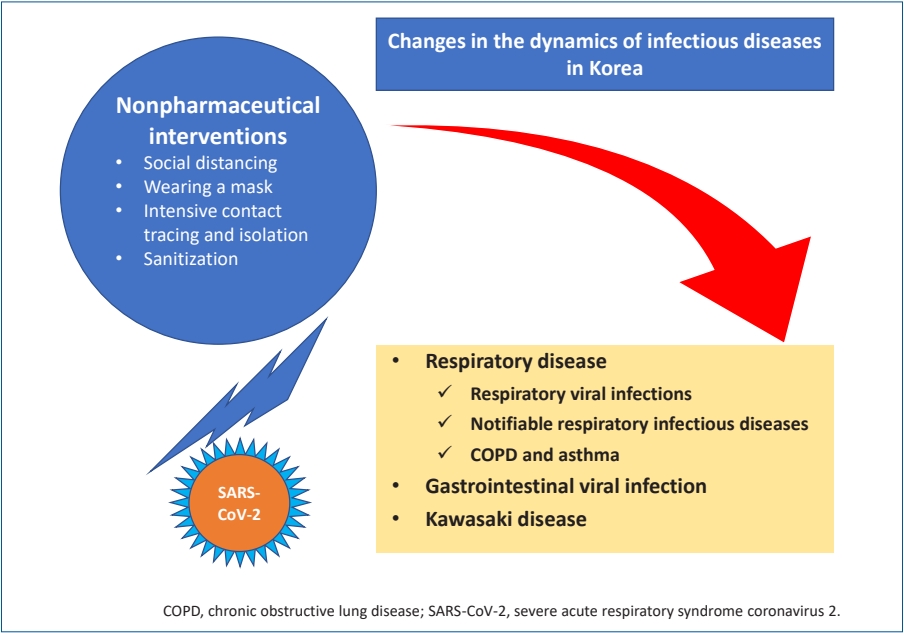
· Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have had a major impact on the epidemiology of various infectious diseases in Korea.
· Respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal viral diseases were significantly reduced during the NPI period.
· The decrease in Kawasaki disease after the introduction of NPI is an unintended result.
· Infectious diseases that decreased during NPI use may re-emerge.
· We must continuously monitor the epidemiology of various infectious diseases during the coronavirus era
- Endocrinology
- Genetic factors in precocious puberty
- Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):172-181. Published online October 18, 2021
-
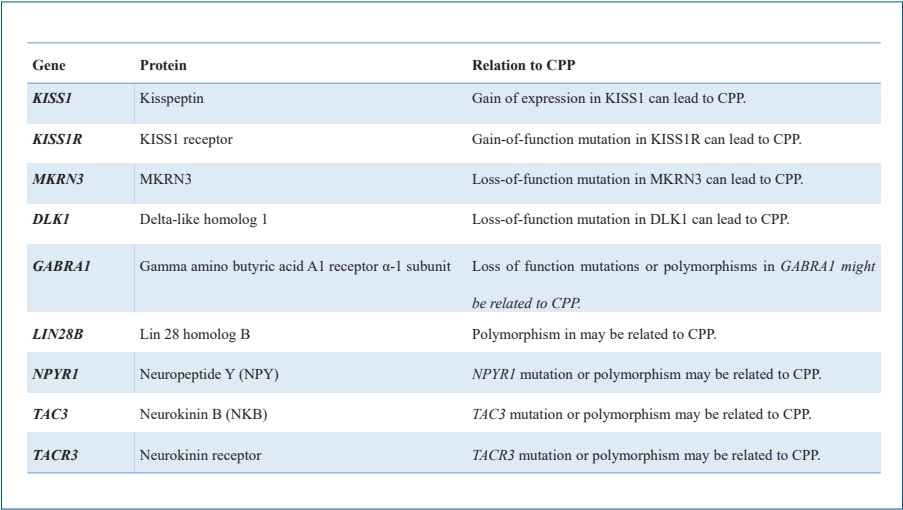
· Mutations in the kisspeptin (KISS1), kisspeptin receptor (KISS1R), makorin ring finger protein 3 (MKRN3), and delta-like homolog 1 (DLK1) genes are associated with idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP).
· A few genes related to pubertal onset have been implicated in ICPP.
· Epigenetic factors such as DNA methylation, histone posttranslational modifications, and noncoding ribonucleic acids may be related to ICPP
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pathophysiology, classification, and complications of common asymptomatic thrombocytosis in newborn infants
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):182-187. Published online October 18, 2021
-
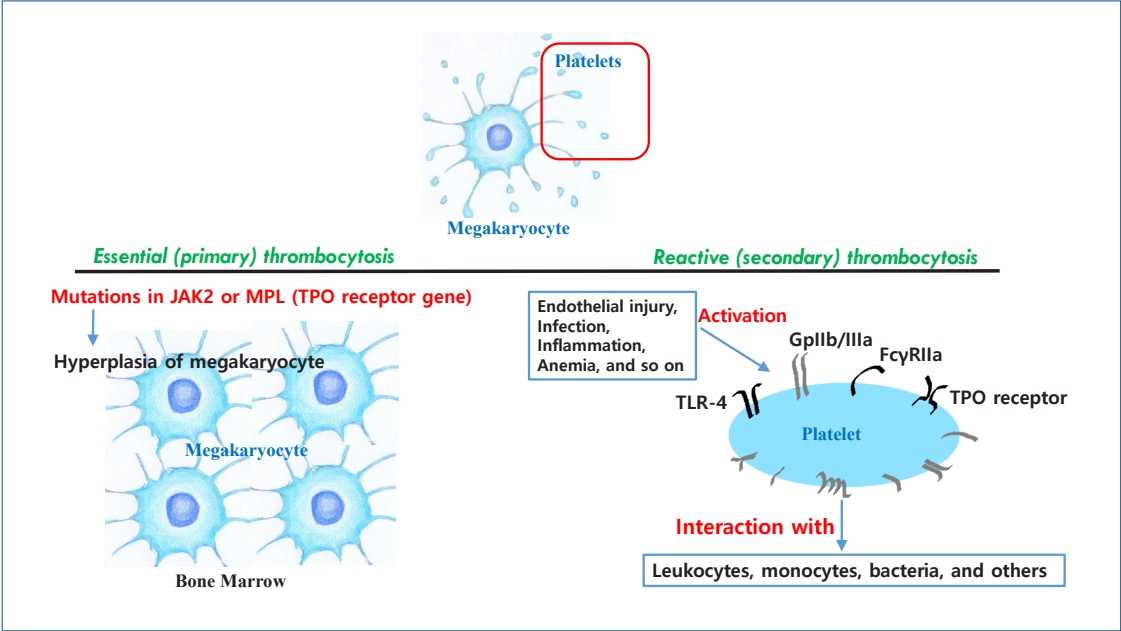
· Thrombocytosis, common in newborns and infants (<2 years) (3%–13%), is caused by elevated thrombopoietin (TPO) concentrations.
· Serum TPO levels are significantly higher immediately to 1 month postnatal and decrease with age.
· Platelet counts are positively correlated with gestational age at birth and postnatal age.
· Thrombocytosis is more common in preterm than in term infants.
· Thrombocytosis in newborns is reactive and resolves spontaneously without complications.
- Original Articles
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Comparison of minimally invasive surfactant therapy with intubation surfactant administration and extubation for treating preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized clinical trial
- Mohammad Kazem Sabzehei, Behnaz Basiri, Maryam Shokouhi, Sajad Ghahremani, Ali Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):188-193. Published online July 28, 2021
-
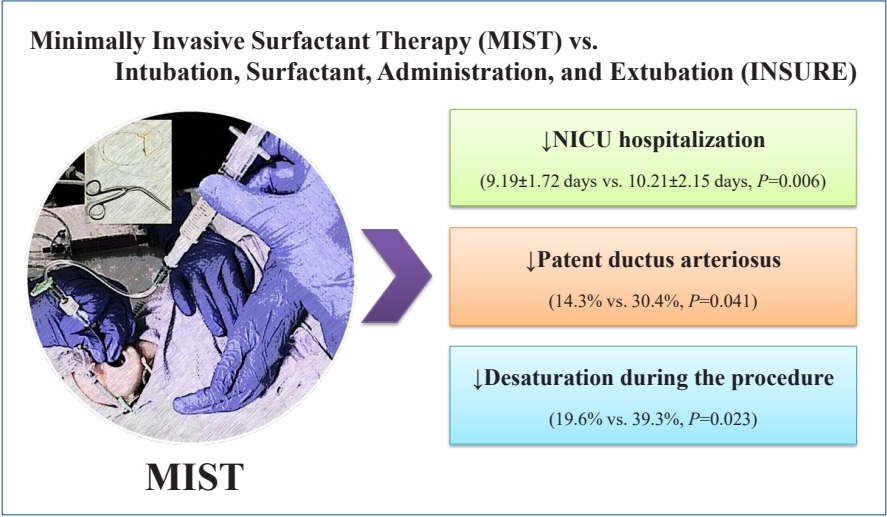
Question: Are the short-term outcomes of minimally invasive surfactant therapy (MIST) relatively superior to those of INtubation, SURfactant administration, and Extubation (INSURE) in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)?
Finding: MIST could be an appropriate substitution for INSURE in preterm infants with RDS since it reduced hospitalization time and number of side effects.
Meaning: MIST is recommended for surfactant administration for its proven advantages over the INSURE technique.
- Emergency Medicine
- Nonfatal injuries in Korean children and adolescents, 2007–2018
- Gyu Min Yeon, Yoo Rha Hong, Seom Gim Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):194-200. Published online September 9, 2021
-
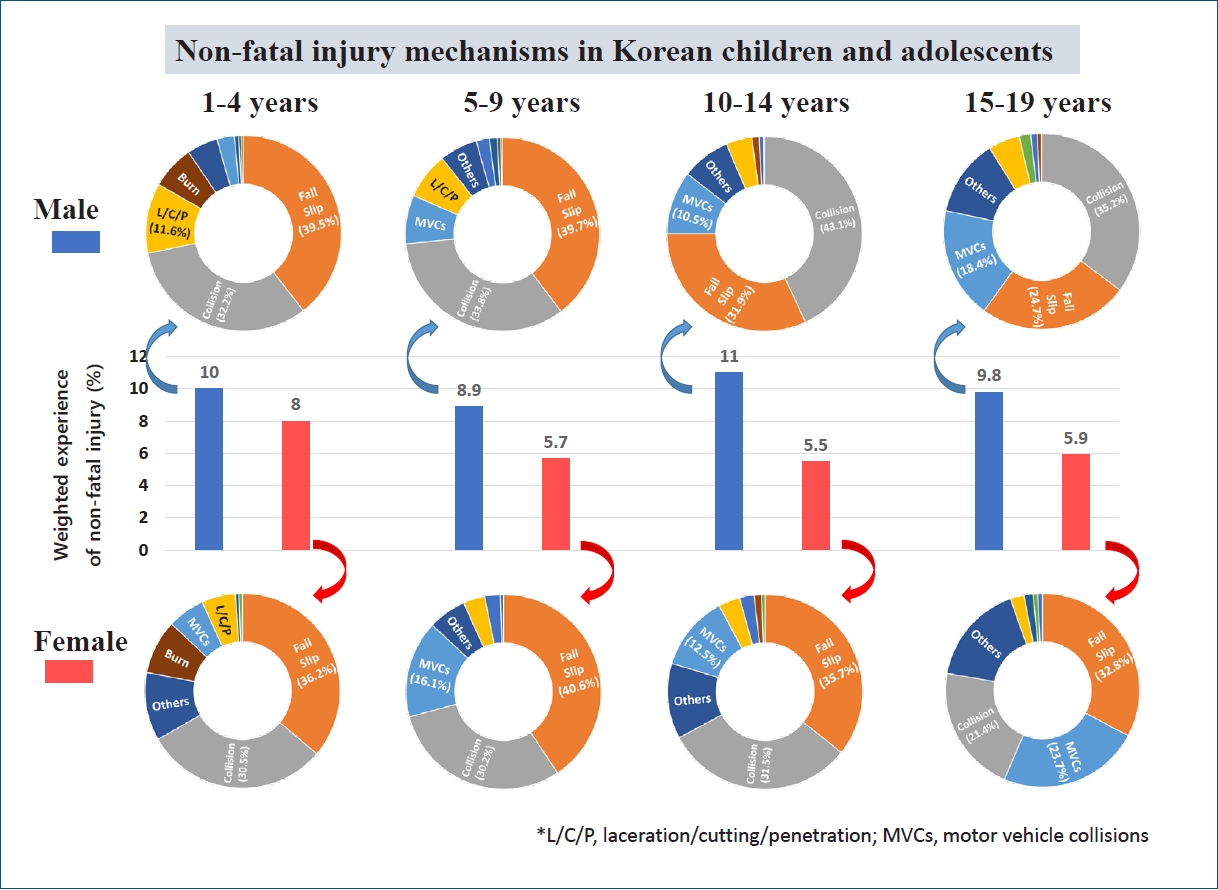
Question: How many children and adolescents have experienced nonfatal injuries in the previous year?
Finding: Among Korean children and adolescents, 8.1% experienced at least one injury per year. We found no significant change in the incidence of injuries over the previous 12 years.
Meaning: The incidence of injuries is higher than this estimation; therefore, more attention and effort are needed to prevent injuries among children and adolescents.
- General Pediatrics
- Early initiation of breastfeeding and factors associated with its delay among mothers at discharge from a single hospital
- J. Jenifer Florence Mary, R. Sindhuri, A. Arul Kumaran, Amol R. Dongre
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):201-208. Published online October 18, 2021
-

Background: According to the National Family Health Survey– 4, in India, 78.9% of deliveries occur in institutions, although only 42.6% of new mothers initiate breastfeeding within 1 hour of delivery.
Purpose: To estimate the proportion of early initiation of breastfeeding (EIBF) among new mothers at discharge from a tertiary care hospital and identify the determinants of delayed initiation of breastfeeding among...
- Clinical note
- General Pediatrics
- Diabetic ketoacidosis in children induced by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) diabetic ketoacidosis post-COVID-19 in children
- Neha Thakur, Narendra Rai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):209-210. Published online November 30, 2021
-
- Letter to the Editor
- Other
- Changes in air pollution and childhood respiratory viral infections in Korea post-COVID-19 outbreak
- Hyung Kyu Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):211-213. Published online February 17, 2022
-