- Review Articles
- Allergy
- Global burden of asthma among children and adolescents with projections to 2050: a comprehensive review and forecasted modeling study
- Tae Hyeon Kim, Hyunjee Kim, Jiyeon Oh, Soeun Kim, Michael Miligkos, Dong Keon Yon, Nikolaos G Papadopoulos
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):329-343. Published online April 22, 2025
-

Pediatric asthma can persist to adulthood and must be effectively managed. This review examined the prevalence of asthma among individuals younger than 20 years and revealed a decline from 1990 to 2021, higher rates in males, and a peak in children aged 5–9 years. Despite a projected continued decrease in prevalence by 2050, asthma will remain a significant health concern for children and adolescents.
- Gastroenterology
- Anxiety disorders presenting as gastrointestinal symptoms in children – a scoping review
- Anjali Kumar, Pramodh Vallabhaneni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):344-351. Published online January 13, 2025
-

A positive bidirectional relationship between gastrointestinal disorders and anxiety, but with no clear aetiology, was identified. Factors such as somatisation and pain catastrophising resulted in poorer pain-related outcomes in children. Further studies are required to understand this relationship in order to have targeted treatments and ensure better long term outcomes.
- Nutrition
- The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey (KIPGroS): a study protocol
- Jong Woo Hahn, MinSoo Shin, Jin Gyu Lim, Yoon-Joo Kim, Ki Soo Kang, Narae Lee, Seong Hee Jeong, Mun Hui Jeong, Yeoun Joo Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Jung Ok Shim, Jee Yoon Park, Chan-Wook Park, Joo Young Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Young Hwa Jung, Jaehyun Kim, Chang Won Choi, Ju Whi Kim, Seung Han Shin, Yun Jeong Lee, Young Ah Lee, Choong-Ho Shin, Seung-sik Hwang, Young Eun Kim, Youn Ha Kang, Kyungwon Oh, Sungha Yun, Jae Sung Ko, Jin Soo Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):352-358. Published online February 13, 2025
-
The suitability of World Health Organization (WHO) growth charts for assessing the growth of children under 3 years of age in all countries remains controversial, and their applicability must be evaluated based on country-specific growth data. The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey evaluated the suitability of WHO growth charts to contribute to the next revision of growth charts in Korea.
- Editorial
- Other
- Further research on impact of microplastics on children's health is essential to protecting future generations
- Jongin Lee, Dong-Wook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):359-361. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The ecological impacts of microplastics have been documented. It was recently recognized that they can directly or indirectly cause diseases in humans.
· There are few established methods for assessing human exposure to microplastics.
· Standardization of exposure assessments and large-scale epidemiological studies are required to explore the human effects of microplastics.
- Original Articles
- Immunology
- Serum bactericidal activity against meningococcus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Soyoung Lee, Kyung-Hyo Kim, Ji Hyen Lee, Han Wool Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):362-369. Published online January 13, 2025
-
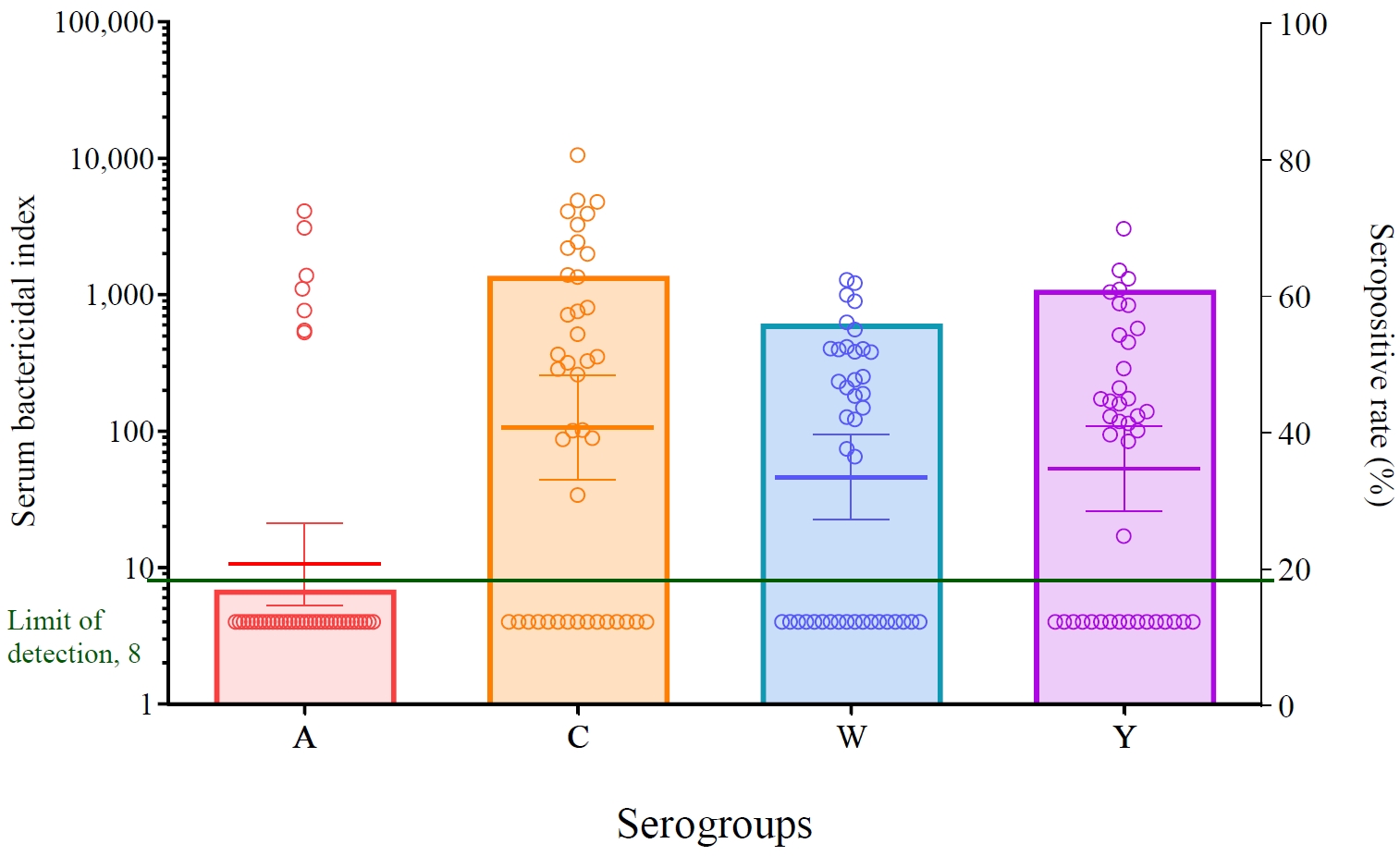
Question: What is the level of immunity against meningococcal infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) under the age of 19, and is vaccination against meningococcus necessary for these patients, given their susceptibility to infections due to immunosuppressive treatments and disease characteristics?
Finding: Although some of our study patients exhibited serum bactericidal activity against meningococci, most remained seronegative.
Meaning: These findings suggest that patients with SLE who are at risk of meningococcal infection receive appropriate vaccinations.
- Nutrition
- Differential effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on adiposity of children with obesity
- Anekchoke Tangtongsoong, Chonnikant Visuthranukul, Yuda Chongpison, Sirinuch Chomtho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):370-378. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: How do dietary intake and physical activity affect body mass index (BMI) z scores and adiposity among children with obesity?
Finding: Higher dietary protein and fiber intakes were significantly associated with a decrease in BMI z scores and adiposity among children with obesity.
Meaning: Optimizing dietary interventions by focusing on protein and fiber intakes could be an effective strategy for managing childhood obesity.
- Infection
- Enteric pathogens implicated in acute infectious diarrhea among young children in resource-limited region with rapidly growing population: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
- Aseel Mahmood Ibrahim Al-Mashahedah, Randa Mohammed Dhahi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):379-387. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: What are the most common enteric pathogens in acute diarrhea among children younger than 5 years of age, and which age group is most susceptible?
Finding: Bacteria were the most common causative microorganisms of diarrhea, followed by viruses, parasites, and fungi. The 1–2-year age group was the most commonly affected.
Meaning: There is a need to formulate preventive strategies targeting children exposed to enteric pathogens to limit diarrhea.
- General Pediatrics
- The role of serum zinc and selenium levels in etiology of febrile seizures
- Yavuz Ataş, Hatice Gamze Poyrazoğlu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):388-394. Published online January 13, 2025
-

Zinc may play a key role in preventing febrile seizures by increasing the seizure threshold and reducing oxidative stress. Incorporating zinc supplements into treatment could help protect children from the adverse effects of febrile seizures and improve their overall outcomes.
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
- Abdominal pain in a young girl: a twist in the tale
- Upasana Ghosh, Ankit Agrawal, Umesh Shukla, Vikas Jain, Deeksha Bhalla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):395-397. Published online March 11, 2025
-
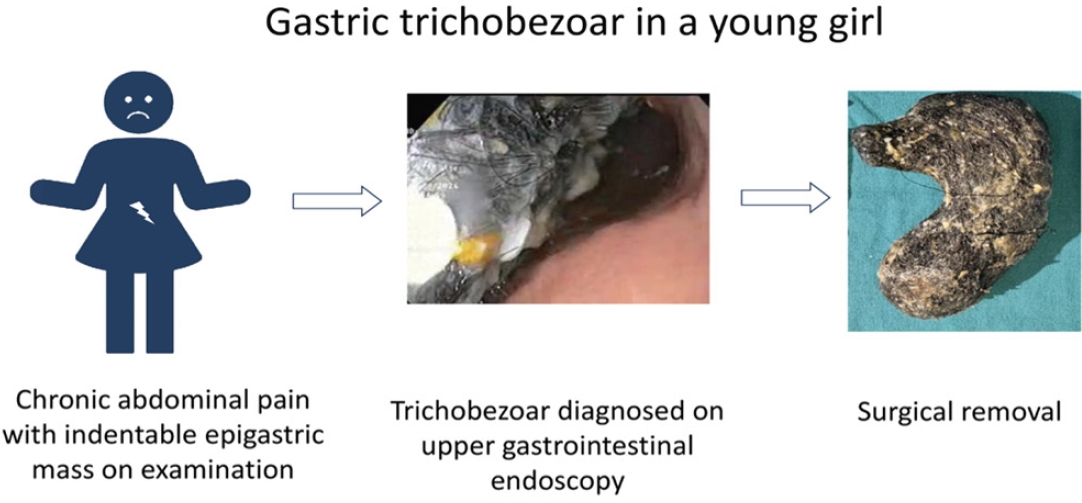
· Chronic abdominal pain caused by a gastric trichobezoar is extremely rare among children.
· An indentable epigastric mass is characteristic and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is diagnostic of a gastric trichobezoar.
· Symptomatic large trichobezoars usually require surgery.
· Neuropsychiatric disorders are often associated with gastric trichobezoar, making a psychiatric evaluation of paramount importance.