- Review Articles
- Nutrition
- Protein substitutions as new-generation pharmanutrition approach to managing phenylketonuria
- Fatma Nur Keskin, Teslime Özge Şahin, Raffaele Capasso, Duygu Ağagündüz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):320-331. Published online November 1, 2022
-
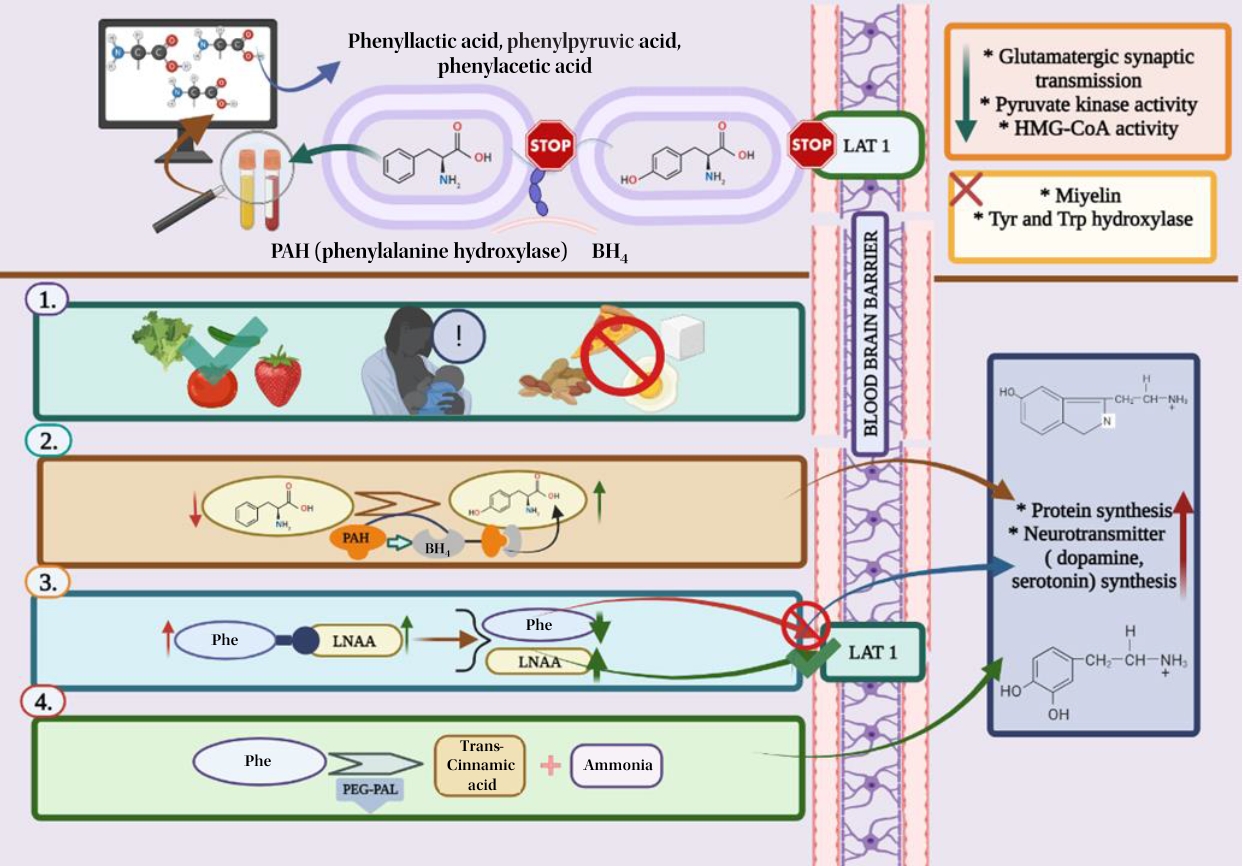
Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disease that results from the inability to metabolize phenylalanine, is currently treated with medical nutrition therapy. New treatment approaches such as tetrahydrobiopterin, glycomacropeptide, large neutral amino acids, pegvaliase, and gene therapy significantly impact disease management and dietary enrichment. This article also reviews animal and human studies that have evaluated the efficacy and safety of these new protein substitutes.
- Cardiology
- Environmental changes surrounding congenital heart disease
- Eun-Young Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):332-338. Published online January 2, 2023
-
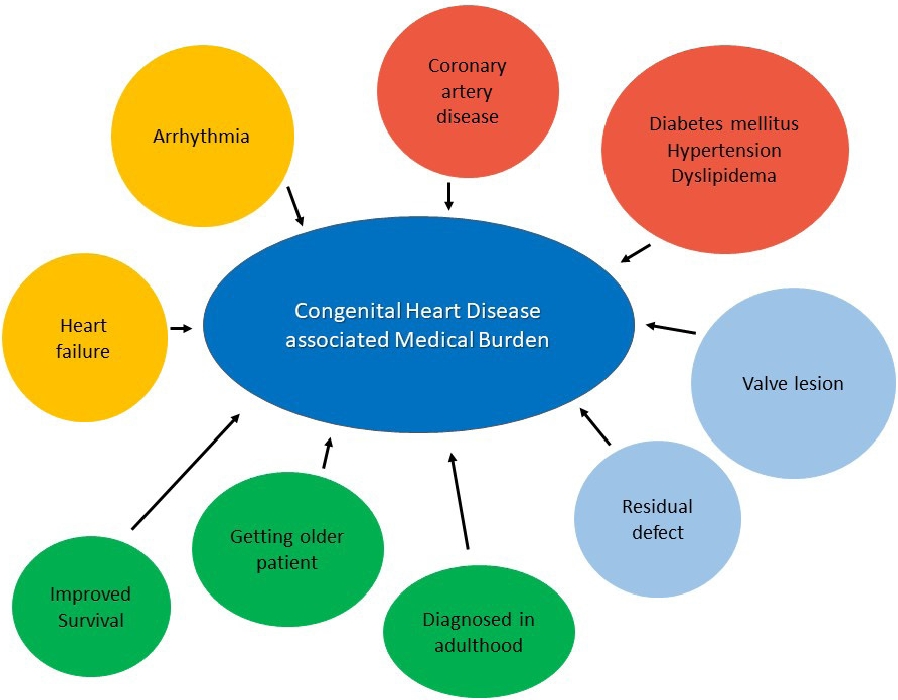
· As the number of patients with congenital heart disease increases, the medical burden increases.
· Various fusion imaging techniques using percutaneous procedures have been introduced.
· With advances in technology, convenient ambulatory devices have been introduced.
· A well-organized team approach is required to resolve advanced heart failure in patients with congenital heart disease.
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
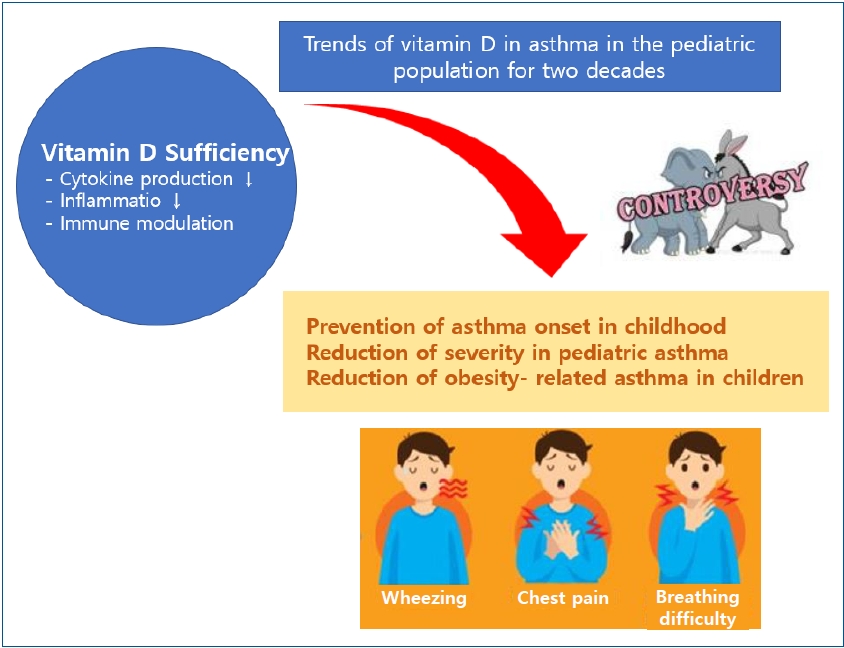
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmias in pediatric patients with COVID-19
- Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):348-349. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Childrens with coronavirus disease 2019 less commonly display life-threatening arrhythmias, including premature atrial or ventricular beats, or conduction disturbances such as first-degree atrioventricular blocks.
· Life-threatening arrhythmias (e.g., nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block) occur in children with sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection suffering from myocarditis or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
· Monitoring clinical status and assessing and managing arrhythmias are crucial in MIS-C.
- Original Articles
- Neurology
- Need for palliative care from birth to infancy in pediatric patients with neurological diseases
- Raffaele Falsaperla, Silvia Marino, Carla Moscheo, Lucia Giovanna Tardino, Simona Domenica Marino, Concetta Sciuto, Piero Pavone, Giovanna Vitaliti, Federica Sullo, Martino Ruggieri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):350-356. Published online June 14, 2023
-
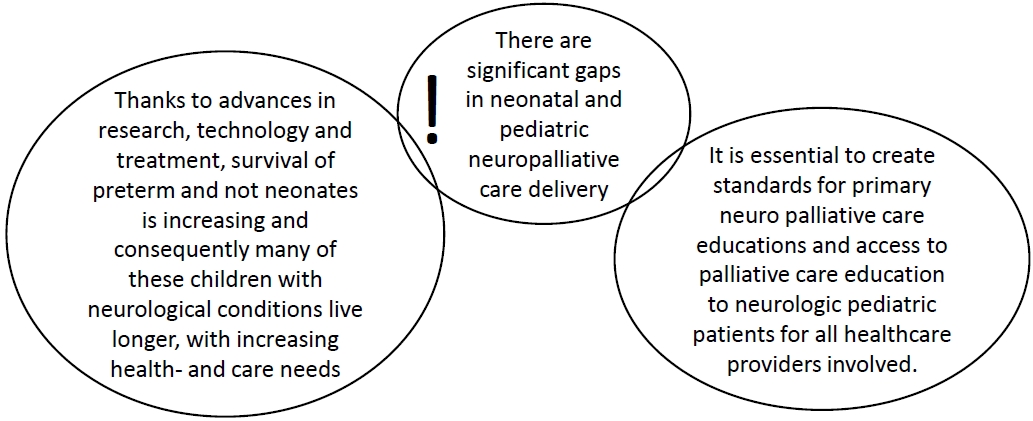
Question: What are the current palliative care protocols, palliative course, and implementable palliative care programs for hospitalized pediatric patients with neurological diseases in Italy?
Finding: We studied 34 newborns with nervous system diseases, all of whom had a poor prognosis.
Meaning: Despite current legislation in Italy, no palliative care network has been implemented. Given the vast number of patients with neurological conditions, standardized palliative care guidelines and protocols are required.
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
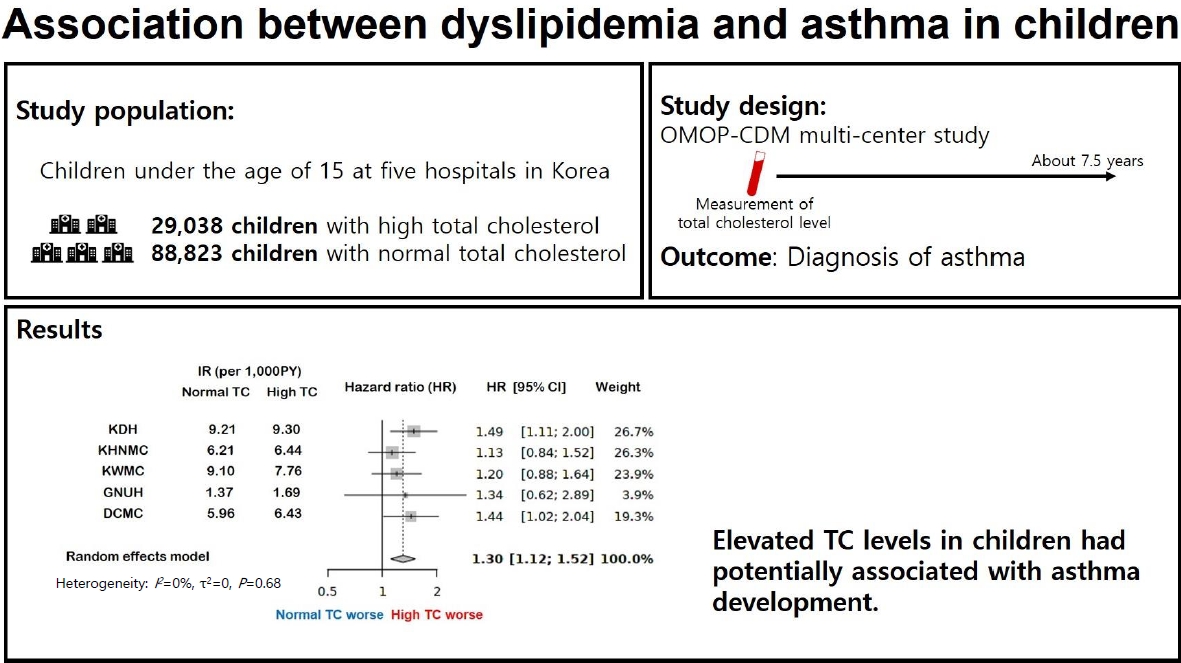
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
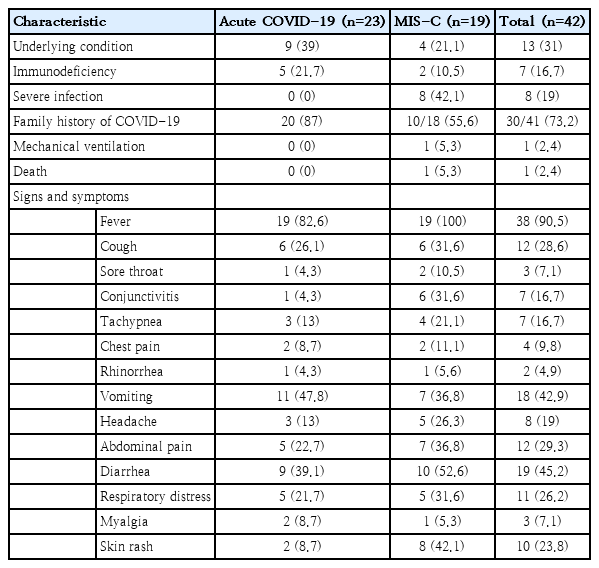
- SARS-CoV-2 fecal shedding pattern in pediatric patients with acute COVID-19 or COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome
- Setareh Mamishi, Fatemeh Jalali, Sepideh Benvari, Babak Pourakbari, Mohammad Reza Abdolsalehi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Mohammad Shahbabaie, Amene Navaeian, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):366-368. Published online June 14, 2023
-