Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six months.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study (27 times)
- Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-
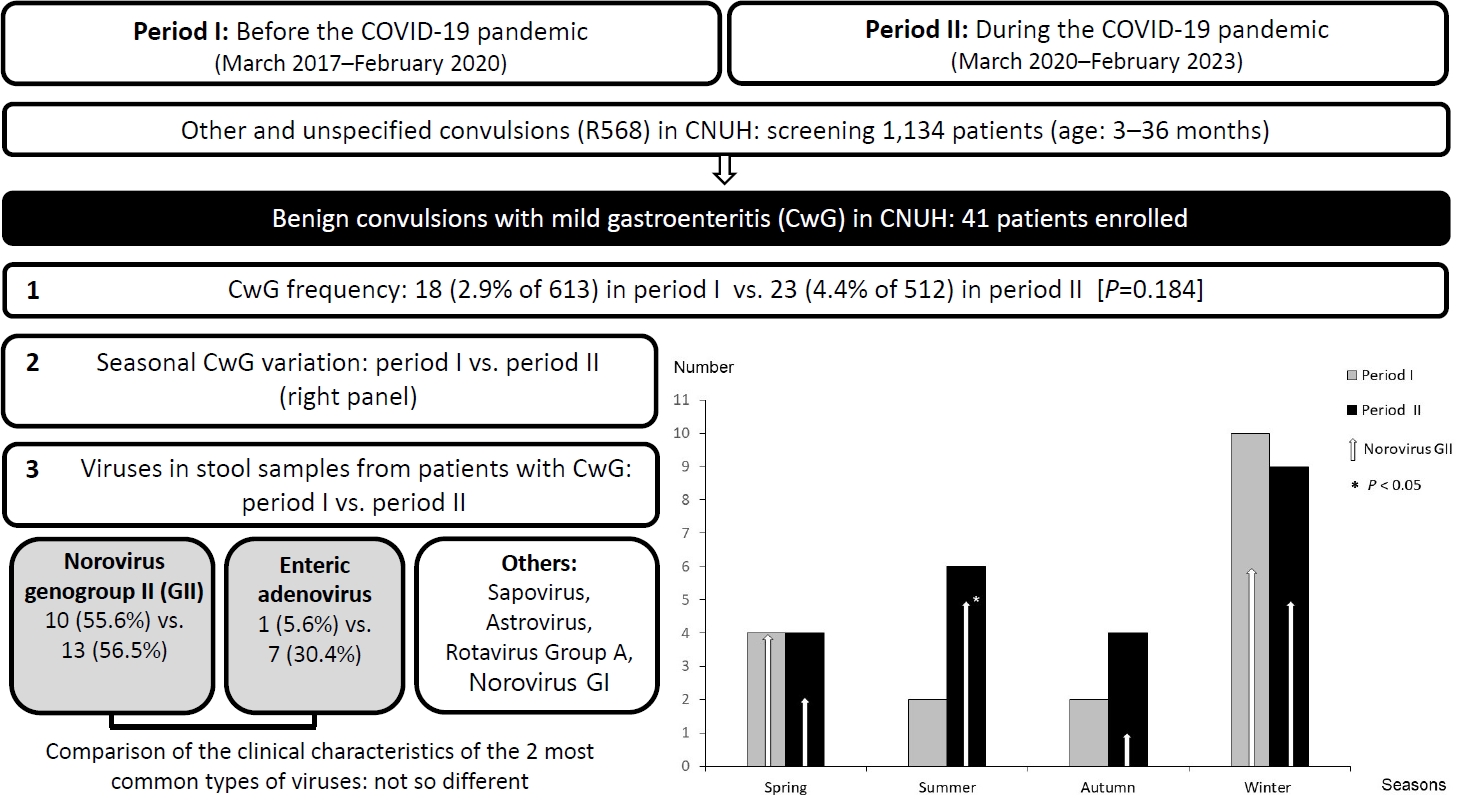
Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG.
- Endocrinology
- Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial (26 times)
- Thushara Rodrigo, Samaranayake Dulani, Sumudu Nimali Seneviratne, Arjuna P. De Silva, Jerad Fernando, H. Janaka De Silva, Jayasekera , V. Pujitha Wickramasinghe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):304-311. Published online November 11, 2021
-
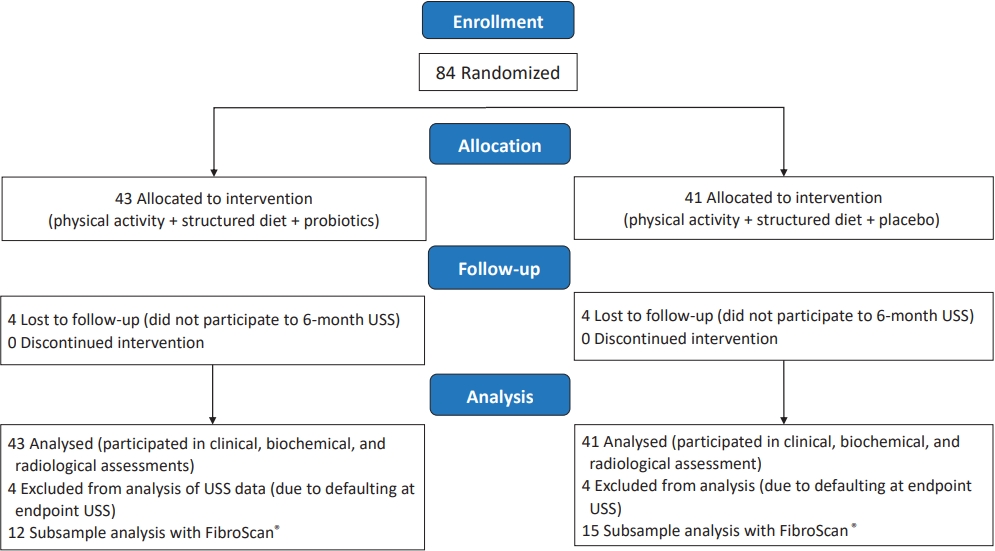
Question: Could probiotics be used as a therapeutic modality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?
Finding: There seem no added advantages over lifestyle modifications compared to Probiotics.
Meaning: There does not seem to be an advantage of probiotics over lifestyle modifications in improving obesity-associated metabolic derangement in children.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmia and COVID-19 in children (26 times)
- Mi Kyoung Song, Bryan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):190-200. Published online April 18, 2023
-
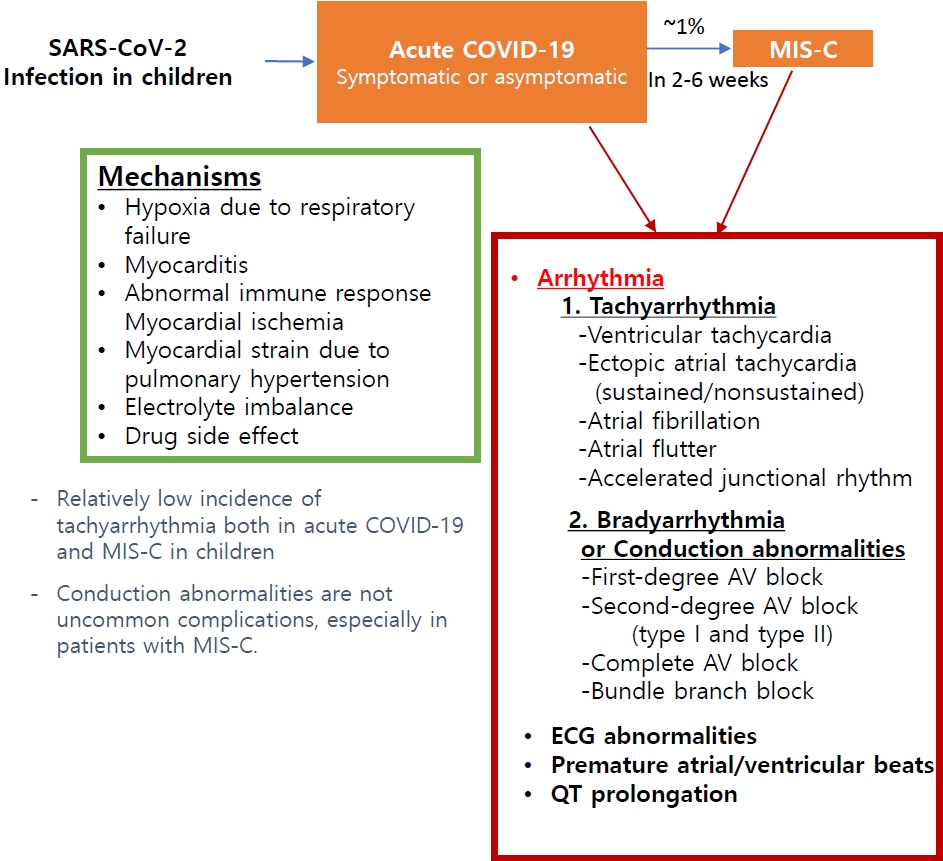
· Pediatric patients have a relatively low incidence of tachyarrhythmia both in acute coronavirus disease 2019 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), but it was associated with an increased risk of poor outcomes.
· Conduction abnormalities were not uncommon, especially in those with MIS-C. Most patients recovered to normal sinus rhythm; however, some progressed to advanced atrioventricular block and rarely required permanent pacemaker implantation.
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of kidney complications in children after COVID-19 infection or vaccination (26 times)
- Jiwon Jung, Joo Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):35-36. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· The proper monitoring for and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced acute kidney injury, which is common in critically ill children, are recommended.
· Glomerulopathy associated with COVID-19 or its vaccination has been reported, and the overall clinical course is similar to that of non-COVID-19-associated diseases.
· Additional COVID-19 vaccinations are recommended; however, careful and individualized decisions should be made in patients with COVID-19- or vaccination-associated glomerulopathy.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes and comorbidities of children with congenital muscular torticollis: evaluation using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children database (25 times)
- Og Hyang Kim, Seung Won Lee, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Yun Hye Jo, Seongyeong Rhie, Man Yong Han, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):312-319. Published online December 9, 2021
-

Question: What comorbidities are increased in children with congenital muscular torticollis (CMT)? Are there differences in the neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with CMT who received physical therapy versus those who did not?
Finding: The risk of congenital musculoskeletal deformities is increased in CMT. Children who did not receive physical therapy were at greater risk of neurodevelopmental delay.
Meaning: In CMT, musculoskeletal comorbidities should be identified and active early treatment provided.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Dietary restriction misconceptions and food allergy education in children with atopic dermatitis (25 times)
- You Hoon Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):83-84. Published online January 27, 2022
-
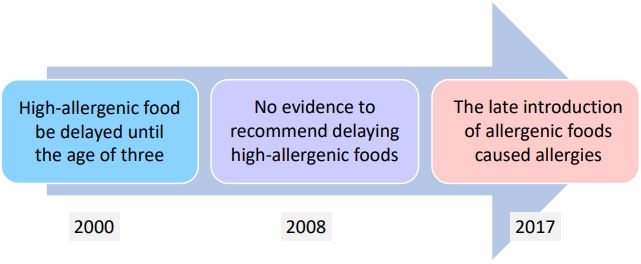
∙ Food intake strategies for preventing food allergies have undergone major changes over the past 20 years.
∙ In children with atopic dermatitis, indiscriminate food restrictions without diagnostic testing leads to nutritional imbalance and poor growth.
∙ When determining food restrictions for pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis, an accurate food allergy diagnosis must be preceded, and continuous parental education about food intake is required.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect ınfantile colic symptoms and fecal microbiota profile: a single-blind randomized controlled study (25 times)
- Aysu Yıldız Karaahmet, Gülümser Dolgun, Metehan Özen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):547-554. Published online September 23, 2022
-

Question: Do probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect infantile colic symptoms and intestinal microbiota?
Finding: Infants whose mothers ingested probiotics demonstrated decreased crying frequency and intensity and significantly increased bacterial diversity in the stools. The bacterial variety was substantially affected by the added probiotic product.
Meaning: The addition of probiotics to maternal nutrition in early infancy could play an important role in preventing infantile colic.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Upper gastrointestinal tract involvement of Crohn disease: clinical implications in children and adolescents (24 times)
- Eun Sil Kim, Mi Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):21-28. Published online September 10, 2021
-
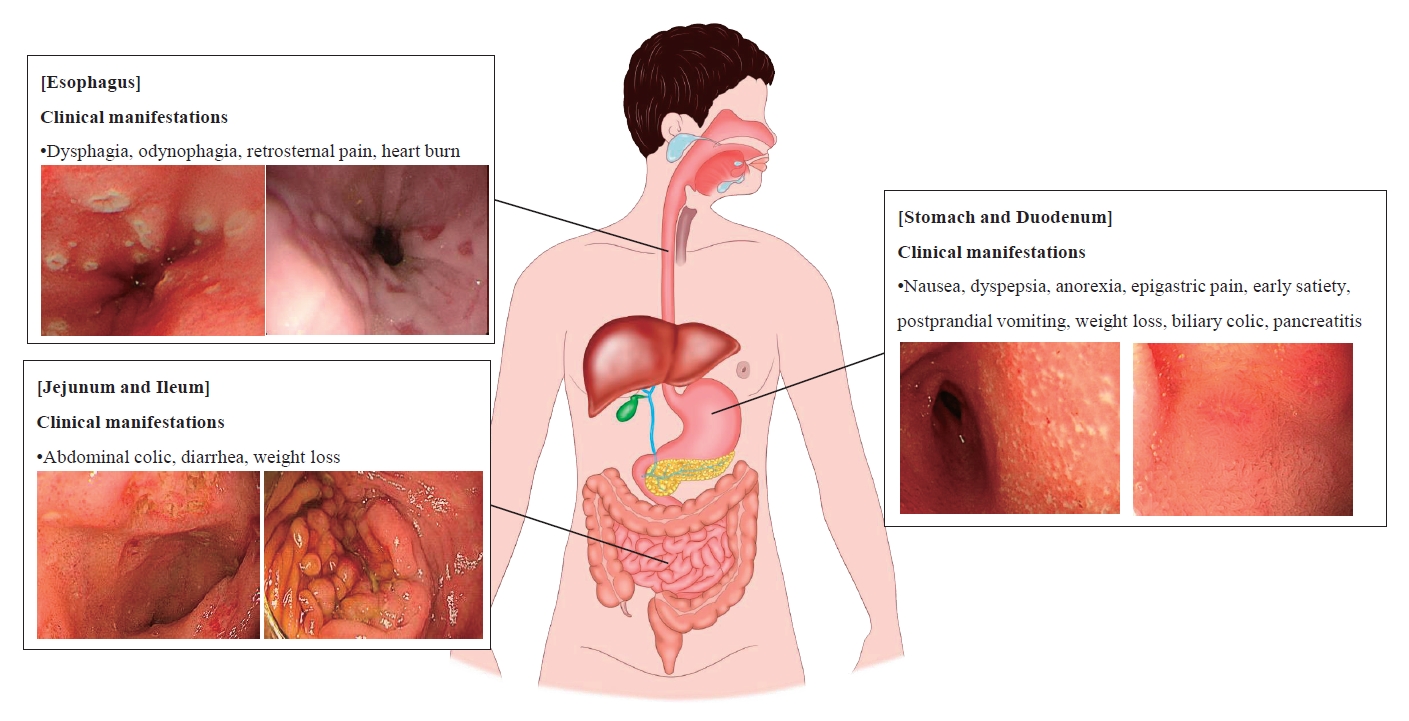
· Clinical manifestations of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) tract involvement in Crohn's disease (CD) are common but often clinically underestimated.
· Diagnosing CD by confirming inflammation of the UGI tract histologically is challenging because macroscopic and microscopic findings overlap with those of other diseases.
· Ongoing efforts are needed to enable a standardized assessment of UGI CD in the future.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal seizures: stepping outside the comfort zone (24 times)
- Menna Hashish, Mohamed Reda Bassiouny
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):521-528. Published online April 4, 2022
-
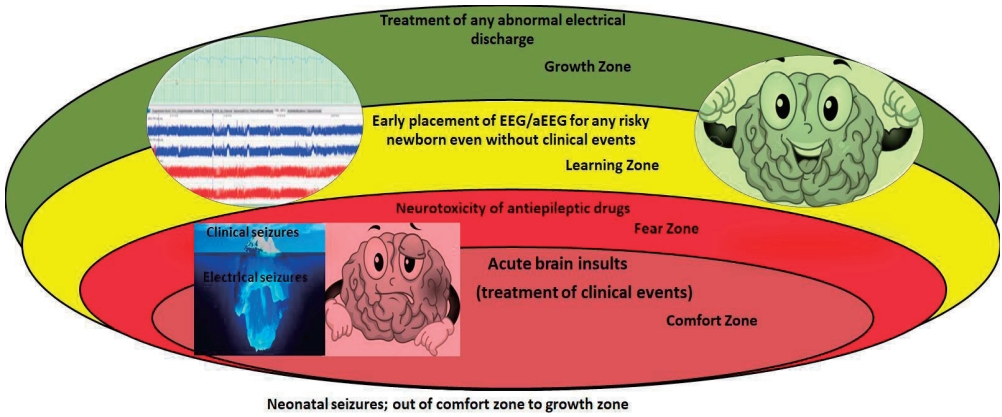
· Use conventional and amplitude-integrated electroencephalography to confirm clinical seizures and screen high-risk newborns.
· Select an explicit clear elective event to be treated with less toxic and more effective antiepileptics.
- Nutrition
- Total energy expenditure measured by doubly labeled water method in children and adolescents: a systematic review (24 times)
- Nahyun Kim, Jonghoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):54-65. Published online October 17, 2022
-
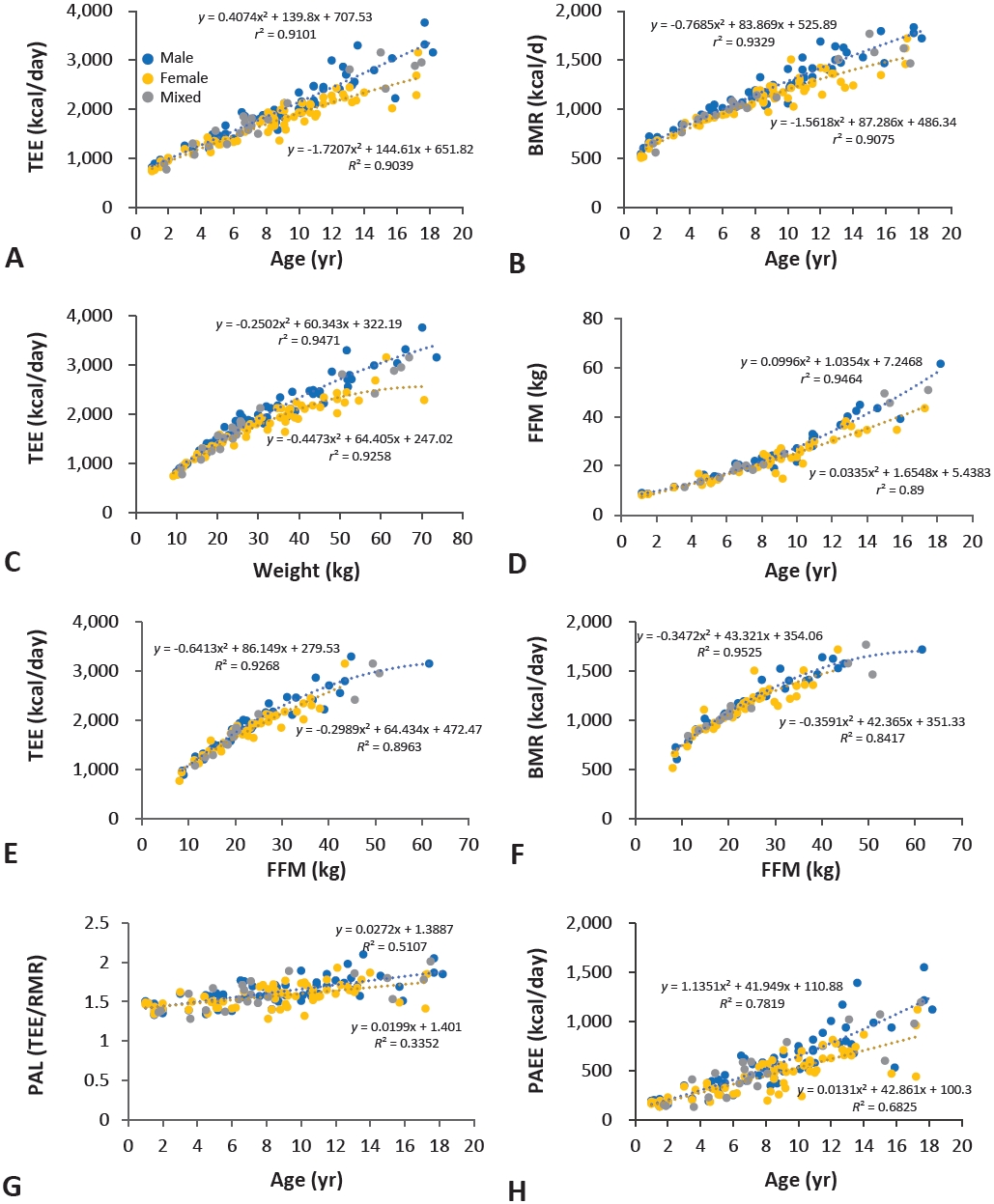
This systematic review summarizes convincing evidence that total energy expenditure (TEE) measured using the doubly labeled water technique increased with age from 1 to 18 years, while fat-free mass (FFM) increased with growth. TEE and in normal-weight participants, while physical activity level did not differ from that of normal-weight participants.
- Protein substitutions as new-generation pharmanutrition approach to managing phenylketonuria (24 times)
- Fatma Nur Keskin, Teslime Özge Şahin, Raffaele Capasso, Duygu Ağagündüz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):320-331. Published online November 1, 2022
-
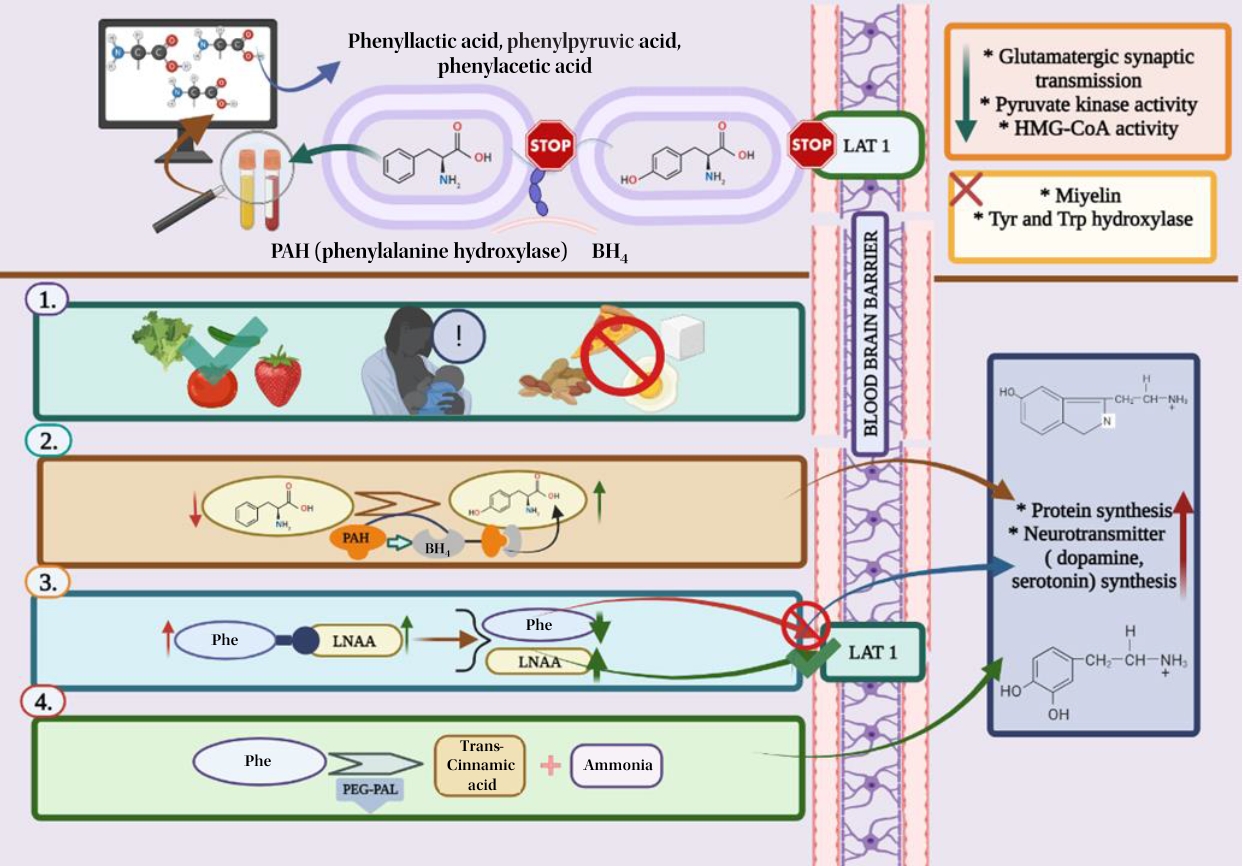
Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disease that results from the inability to metabolize phenylalanine, is currently treated with medical nutrition therapy. New treatment approaches such as tetrahydrobiopterin, glycomacropeptide, large neutral amino acids, pegvaliase, and gene therapy significantly impact disease management and dietary enrichment. This article also reviews animal and human studies that have evaluated the efficacy and safety of these new protein substitutes.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an umbrella review (24 times)
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Sajjad Farashi, Saeid Bashirian, Fereshteh Mehri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):441-446. Published online July 14, 2023
-
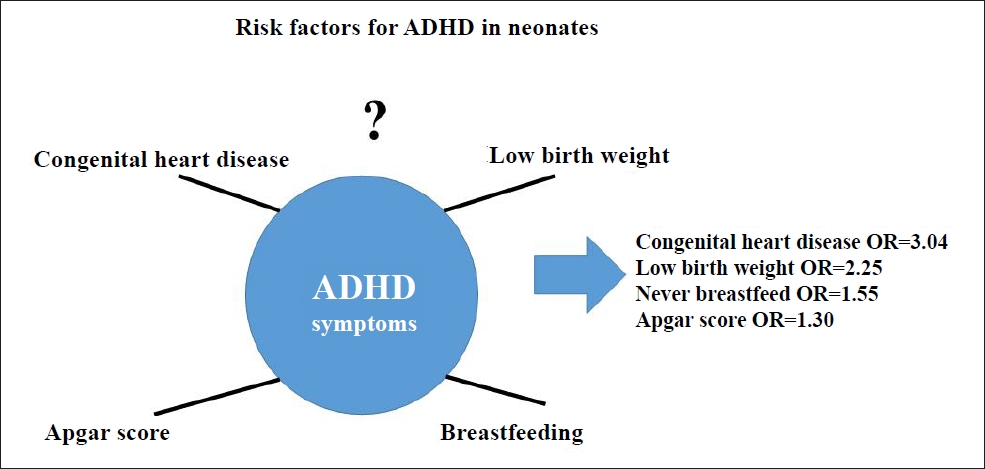
Question: The risk factors for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), such as breastfeeding, congenital heart disease, and low birth weight, in neonates are not well understood.
Finding: This umbrella review obtained significant effect sizes for ADHD for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 3.04), low birth weight (OR, 2.25), never breastfed (OR, 1.55), and Apgar score (OR, 1.30).
Meaning: Congenital heart disease, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, and Apgar scores were significant factors for ADHD.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents (24 times)
- Hae Sang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):90-91. Published online January 24, 2024
-
· With the increase in childhood obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a concern in recent years.
· NAFLD is strongly associated with insulin resistance.
· Lifestyle modifications are the mainstay treatment for NAFLD.
- Review Article
- Oncology
- Application of 3-dimensional printing implants for bone tumors (23 times)
- Jong Woong Park, Hyun Guy Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):476-482. Published online December 23, 2021
-

∙ The application of 3-dimensional (3D) printing in orthopedic oncology is summarized into bone and tumor modeling, patient-specific instruments (PSIs), custom-made implants, and tissue engineering.
∙ The 3D-printed customized implant is the most central application, while modeling and PSI often play adjunct roles.
∙ Short-term surgical outcomes of custom-made 3D-printed implants are promising.
- Editorial
- Pulmonology
- Community-acquired pneumonia in Korean children: time to read between the lines (23 times)
- Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):22-23. Published online November 10, 2022
-
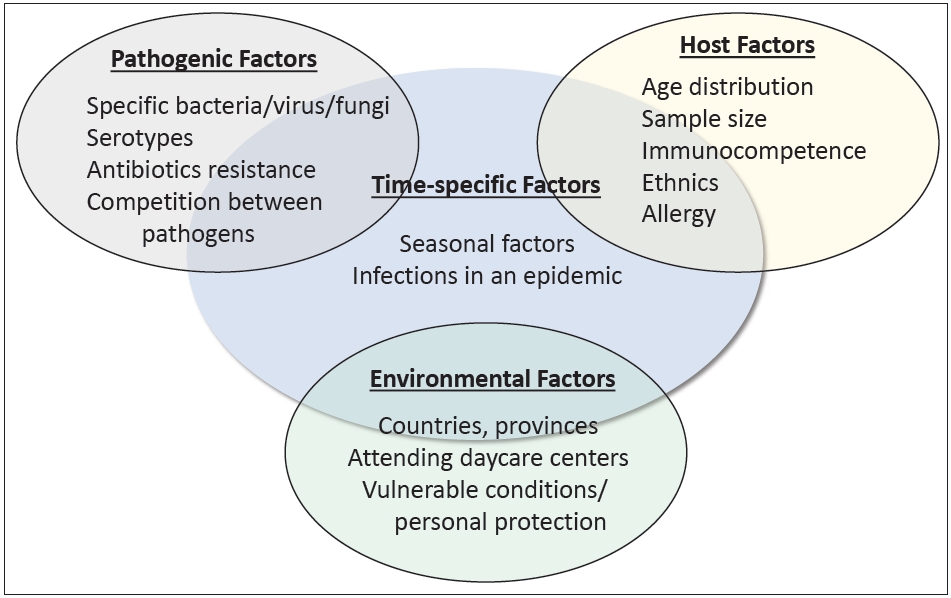
· Various studies have reported the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in Korean children
· Factors other than etiology are equally important to a compre hensive understanding of CAP
· Knowledge from archived reports is no longer directly applicable to the current CAP and requires careful modification
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Optimal hemodialysis treatment for pediatric kidney failure patients (23 times)
- Yo Han Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):125-126. Published online February 15, 2023
-
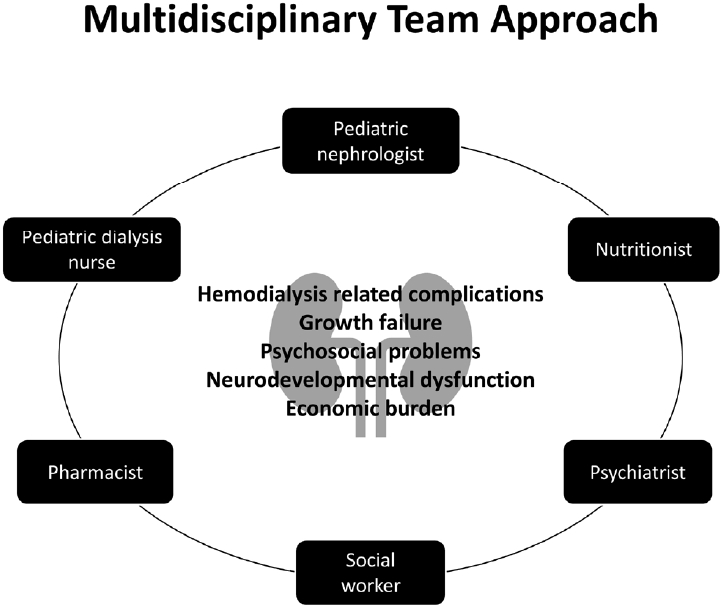
· Although the basic concept of hemodialysis (HD) is similar in adults and children, specific factors must be considered in the latter, including the small dialyzer and circuit, difficult vascular access, and frequent complications.
· HD-associated complications include catheter-related problems, hemodynamic instability, and neurodevelopmental and cognitive dysfunction.
· Pediatric HD is challenging, and steady efforts are needed to perform it safely and reduce its complications, thereby improving clinical outcomes.
- Infection
- Impact and role of vitamins as immunonutrition in children during COVID-19 pandemic (23 times)
- Yoo Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):212-214. Published online April 18, 2023
-

· Vitamins have effector mechanisms in the innate and adaptive immune systems and potential roles in preventing and reducing the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
· Vitamins may be immunonutrients in the treatment of COVID-19 infections and prevention of patient deterioration due to critical illness, thus demonstrating the significance of a nutritious, well-balanced diet.
- Review Article
- Neurobehavior
- Psychological aspects in children and parents of children with chronic kidney disease and their families (22 times)
- Alemsungla Aier, Priya Pais, Vijaya Raman
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):222-229. Published online November 10, 2021
-
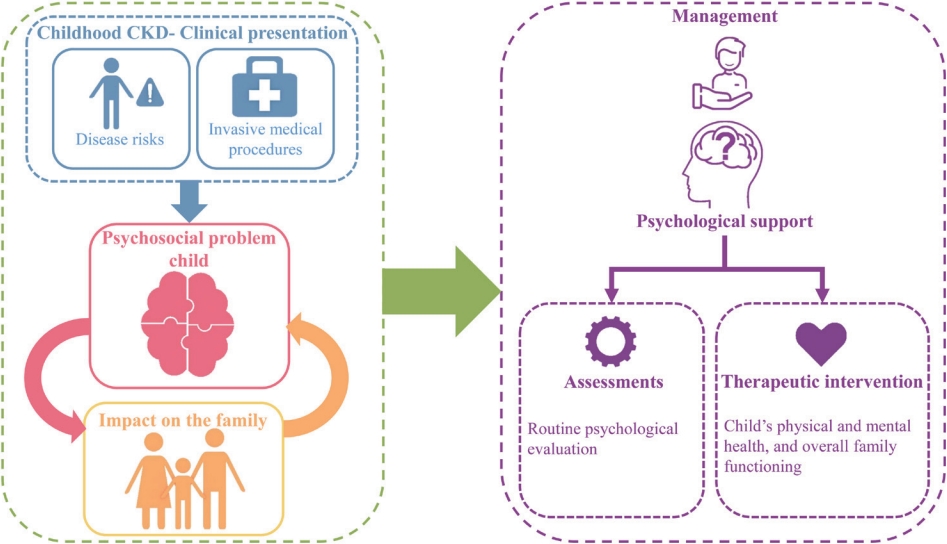
· Childhood chronic kidney disease (CKD) is complex and requires lifetime medical treatment.
· Children with CKD are at risk for emotional, behavioral, social, and academic difficulties that significantly affect their quality of life.
· Caring for children with CKD is stressful for families.
· These unique challenges are crucial and can negatively impact treatment outcomes.
· Awareness of and addressing these evolving psychosocial issues can foster their developing needs.
- Letter to the Editor
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- The influence of parental eating behaviors, child-feeding practices, and infants’ temperaments upon infants’ eating behaviors (22 times)
- Goh Woon Lim, Kyoung Min Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):466-468. Published online June 27, 2022
-

- Pulmonology
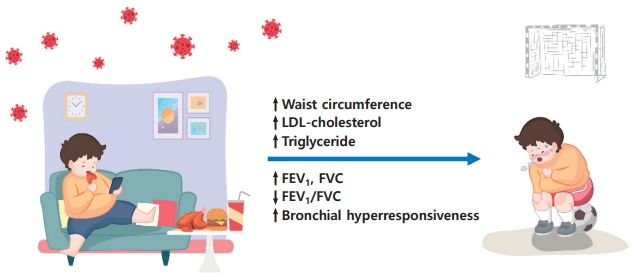
- Metabolic syndrome and pulmonary dysfunction in asthmatic children during the COVID-19 pandemic (22 times)
- Jue Seong Lee, Sang Hyun Park, Yoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):168-170. Published online February 19, 2024
-
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- A thickened formula reduces feeding-associated oxygen desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants (21 times)
- Gayoung Lee, Juyoung Lee, Ga Won Jeon, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):32-37. Published online December 15, 2022
-
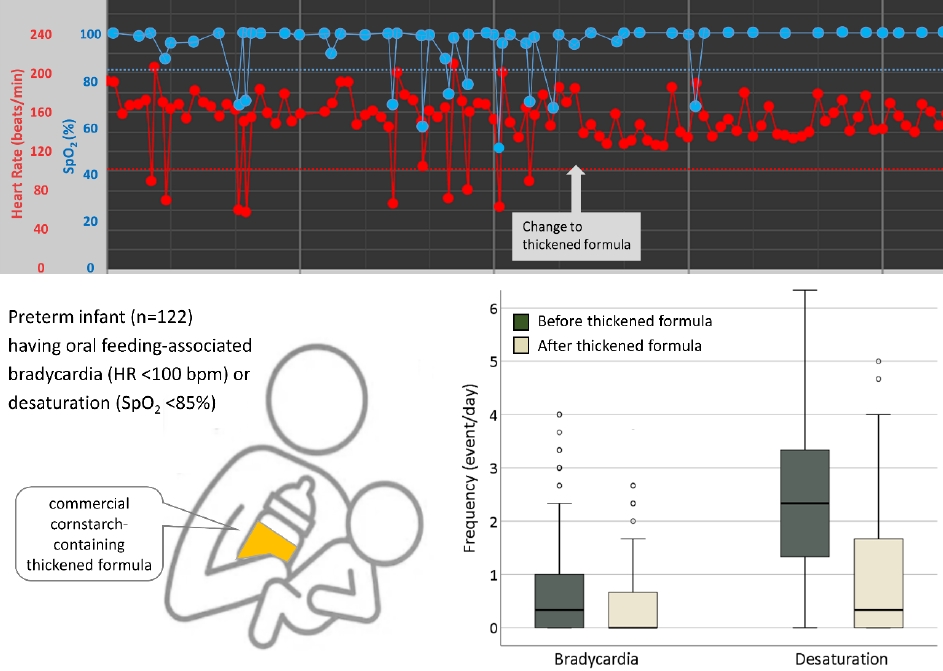
Question: Is a commercial thickened formula able to alleviate oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants?
Finding: Thickened formula feeding significantly reduced oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants.
Meaning: Thickened formula feeding stabilizes oxygen saturation and heart rate during oral feeding among preterm infants with feeding difficulties.
- Review Article
- Infection
- COVID-19 in immunocompromised children and adolescents (21 times)
- Byung Ok Kwak, Byung Wook Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):182-189. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Most immunocompromised children and adolescents are not at increased risk of developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). COVID-19 outcomes for low- or medium-risk immunocompromised children are favorable, while more serious illness reportedly occurs in high-risk immunocompromised children by underlying disease, its treatments, and other factors. Therefore, the early detection and timely management of severe COVID-19 and treatment of underlying disease are important. Hospitalization and COVID-19 vaccination should be carefully considered.
- Editorial
- Infection
- COVID-19 infection and vaccination among children (21 times)
- Amnuay Kleebayoon, Viroj Wiwanitkit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):531-532. Published online August 30, 2023
-
· Coronavirus disease 2019 (OVID-19) infection and immunization have been linked with kidney problems; however, causality has not been proven.
· Concern about confounders is usually needed.
· Correspondence about a published article on the COVID-19 vaccine
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Worldwide national intervention of developmental screening programs in infant and early childhood (20 times)
- Seunghyo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):10-20. Published online September 30, 2021
-

∙ Prevalence rate of developmental disabilities has been reported from 8% to 15% and its rate is increasing worldwide.
∙ The critical period of intervention for developmental delay is before the child reaches 3 years of age.
∙ All primary care pediatricians should conduct developmental surveillance and screening tests to infants and children at scheduled visits. Through this, they are liable for providing early identification and timely intervention.
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution esophageal manometry in children (20 times)
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):155-160. Published online October 17, 2022
-

High-resolution esophageal manometry can be safely performed in children where recurrent vomiting and persistent dysphagia is the working diagnosis after excluding nonluminal and structural obstructive pathologies using pediatric upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Normal manometry values are available. Clinical picture, biochemical tests, radiological interpretation, and endoscopic findings with manometry completes the analysis of patients with recurrent vomiting and dysphagia.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study (19 times)
- In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-

Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Cardiology
- Vasovagal syncope with mild versus moderate autonomic dysfunction: a 13-year single-center experience (18 times)
- Han Eoul Lee, Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):47-52. Published online June 1, 2021
-
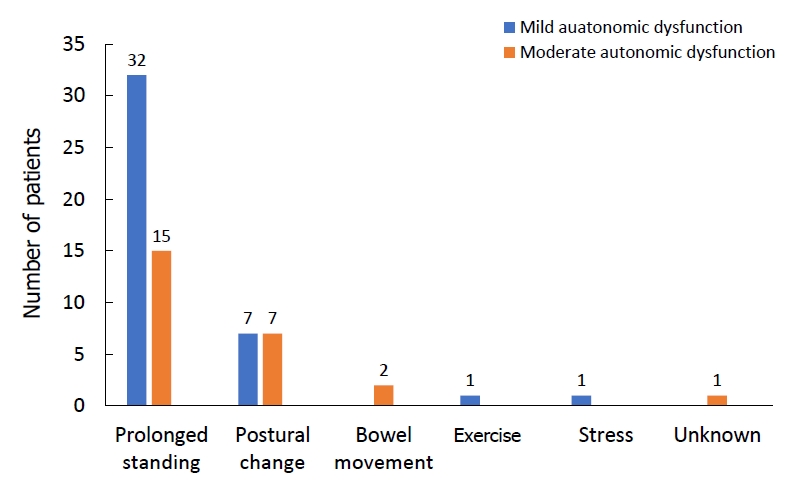
Question: It is well known that autonomic dysfunction contributes to vasovagal syncope (VVS). Does the degree of autonomic dysfunction contribute to clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prognosis?
Finding: The clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prognosis differ between patients with mild and moderate degrees of autonomic dysfunction.
Meaning: VVS is caused by autonomic dysfunction, but autonomic dysfunction severity need not be classified.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Promising candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of seizure disorder, infection, inflammation, tumor, and traumatic brain injury in pediatric patients (18 times)
- Seh Hyun Kim, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):56-64. Published online August 23, 2021
-
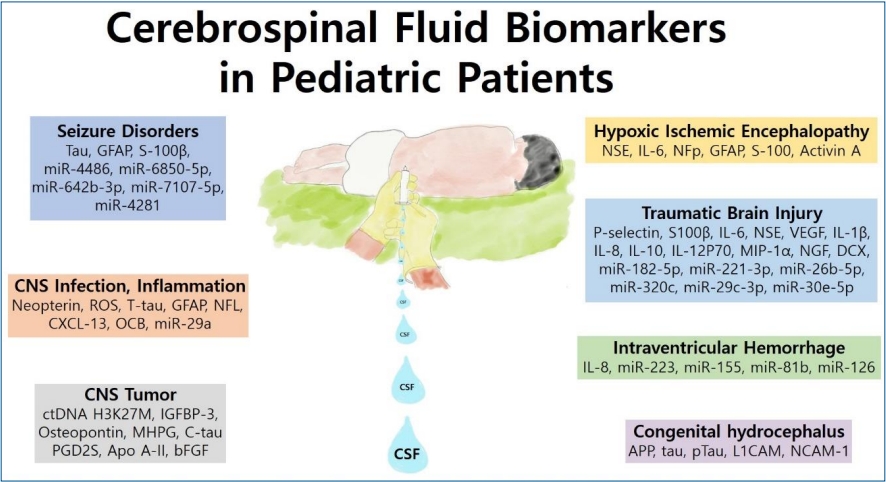
· Pediatric cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) components have been extensively evaluated as biomarkers of various neurologic diseases.
· Several promising candidate CSF biomarkers, including Tau, glial fibrillary acidic protein, neuron-specific enolase, S100β, and interleukins, have been studied in pediatric patients with seizure disorders, central nervous system infections, inflammation, tumors, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, traumatic brain injuries, intraventricular hemorrhage, and congenital hydrocephalus.
· Circulating microRNAs in the CSF are a promising class of biomarkers for various neurological diseases.
- Infection
- Changes in age-specific seroprevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus and impact of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Korea (18 times)
- Byung Ok Kwak, Young Jin Hong, Dong Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):108-114. Published online September 24, 2021
-

Since the introduction of a universal Japanese encephalitis (JE) vaccination program and urbanization, the incidence of JE has dramatically decreased in Korea. However, recent JE cases have occurred, predominantly among unvaccinated adults and with a shift in age distribution. Continuous surveillance of the seroprevalence of JE is required to establish a proper immunization policy in Korea.
- Endocrinology
- Pediatric hypertension based on Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines (JSH 2019) with actual school blood pressure screening data in Japan (18 times)
- Toru Kikuchi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):283-290. Published online November 26, 2021
-
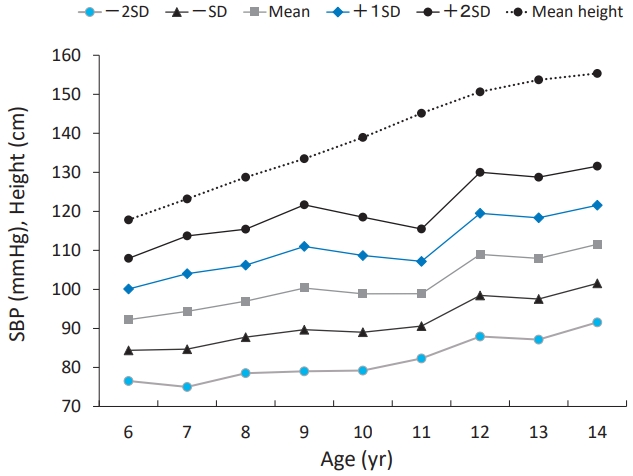
The prevalence of Japanese pediatric hypertension is 0.9% based on proper measurement protocols. Hypertensive children tend to be hypertensive adults. Pediatric essential hypertension is characterized by an absence of symptoms, obesity, a family history of hypertension, and a low birth weight. The most common causes of pediatric secondary hypertension are renal parenchymal and renovascular diseases. Important factors controlling pediatric hypertension include healthy lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







