Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six months.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
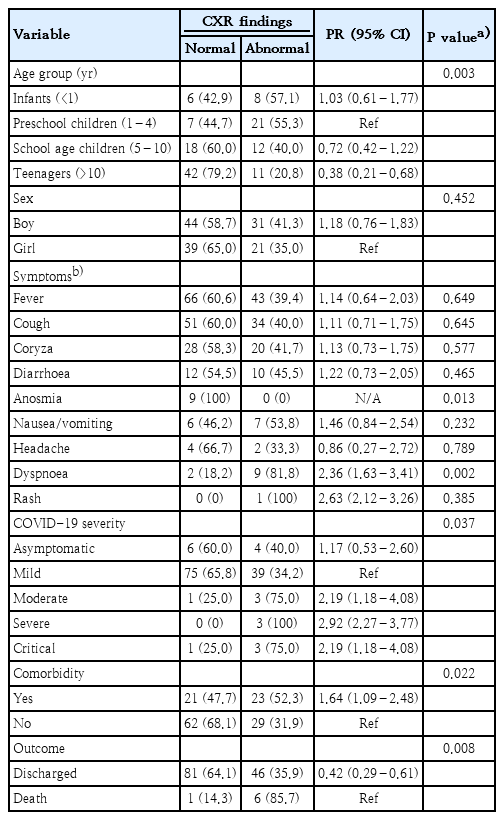
- Chest x-ray findings in children with COVID-19: lesson learned from referral hospitals in Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia (13 times)
- Andrew Limavady, Eka Airlangga, Ririe Fachrina Malisie, Ayodhia Pitaloka Pasaribu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):317-319. Published online May 16, 2023
-
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Does cord blood cortisol have a mediating effect on maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight? (13 times)
- Gyu Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):24-25. Published online November 30, 2022
-

· A high prepregnancy body mass index (pre-BMI) is associated with large for gestational age (LGA) and macrosomia, whereas a low pre-BMI is associated with small for gestational age (SGA) and low birth weight (LBW).
· The identification of the role of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in the effect of pre-BMI and maternal gestational weight gain on birth weight could reduce the frequency of LGA, macrosomia, SGA, or LBW through maternal diet optimization.
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmias in pediatric patients with COVID-19 (13 times)
- Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):348-349. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Childrens with coronavirus disease 2019 less commonly display life-threatening arrhythmias, including premature atrial or ventricular beats, or conduction disturbances such as first-degree atrioventricular blocks.
· Life-threatening arrhythmias (e.g., nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block) occur in children with sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection suffering from myocarditis or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
· Monitoring clinical status and assessing and managing arrhythmias are crucial in MIS-C.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Epidemiological changes in infectious diseases during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea: a systematic review (12 times)
- Jong Gyun Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):167-171. Published online November 30, 2021
-
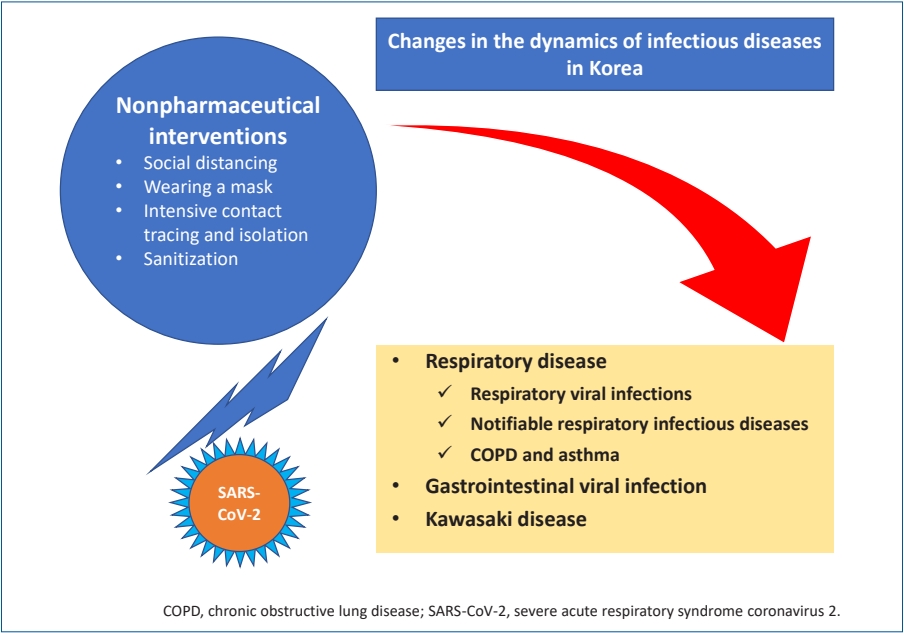
· Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have had a major impact on the epidemiology of various infectious diseases in Korea.
· Respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal viral diseases were significantly reduced during the NPI period.
· The decrease in Kawasaki disease after the introduction of NPI is an unintended result.
· Infectious diseases that decreased during NPI use may re-emerge.
· We must continuously monitor the epidemiology of various infectious diseases during the coronavirus era
- Original Article
- Other
- Plastic bottle feeding produces changes in biochemical parameters in human infants – A pilot study (12 times)
- Mahendra K. Pant, Abul. H. Ahmad, Manisha Naithani, Jayanti Pant
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):459-465. Published online May 19, 2022
-

Question: Plastic feeding bottles are used commonly to feed infants who cannot be breastfeed. Does plastic bottle feeding produce biochemical changes in infants?
Finding: The plastic bottles leach out endocrine disruptors and affects bodily functions in terms of biochemical alterations like increased blood urea, raised creatine-kinase–MB levels, and altered lipid profile in infants exposed to bottle feeding.
Meaning: Plastic bottles feeding alters bodily functions in infants.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Therapeutics for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and adolescents (12 times)
- Soo-Han Choi, Jae Hong Choi, Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):377-386. Published online June 27, 2022
-
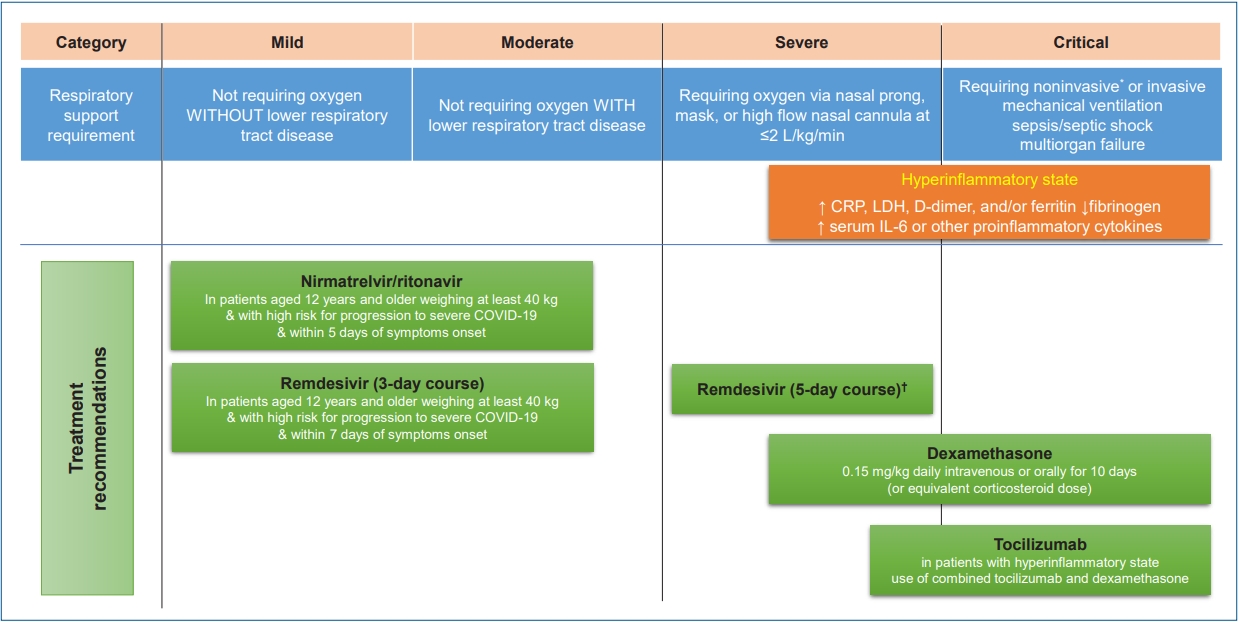
· Children and adolescents with high risks for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be identified and proper treatment should be provided promptly according to the patient’s condition.
· Remdesivir can be considered for pediatric patients of all ages with COVID-19 who have an emergent or increase in supplemental oxygen.
· The use of corticosteroids is not recommended for patients with nonsevere COVID-19. Corticosteroids are recommended in children and adolescents with severe and critical COVID-19.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Survey of Korean pediatrician’s perceptions of barriers to and improvements in breastfeeding (12 times)
- Seong Phil Bae, Woo Ryoung Lee, Won-Ho Hahn, Hye-Jung Shin, Young Min Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Yong Joo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Youn Jeong Shin, Dae Yong Yi, Soon Min Lee, Juyoung Lee, Jin A Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Euiseok Jung, Eui Kyung Choi, Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):540-546. Published online July 29, 2022
-
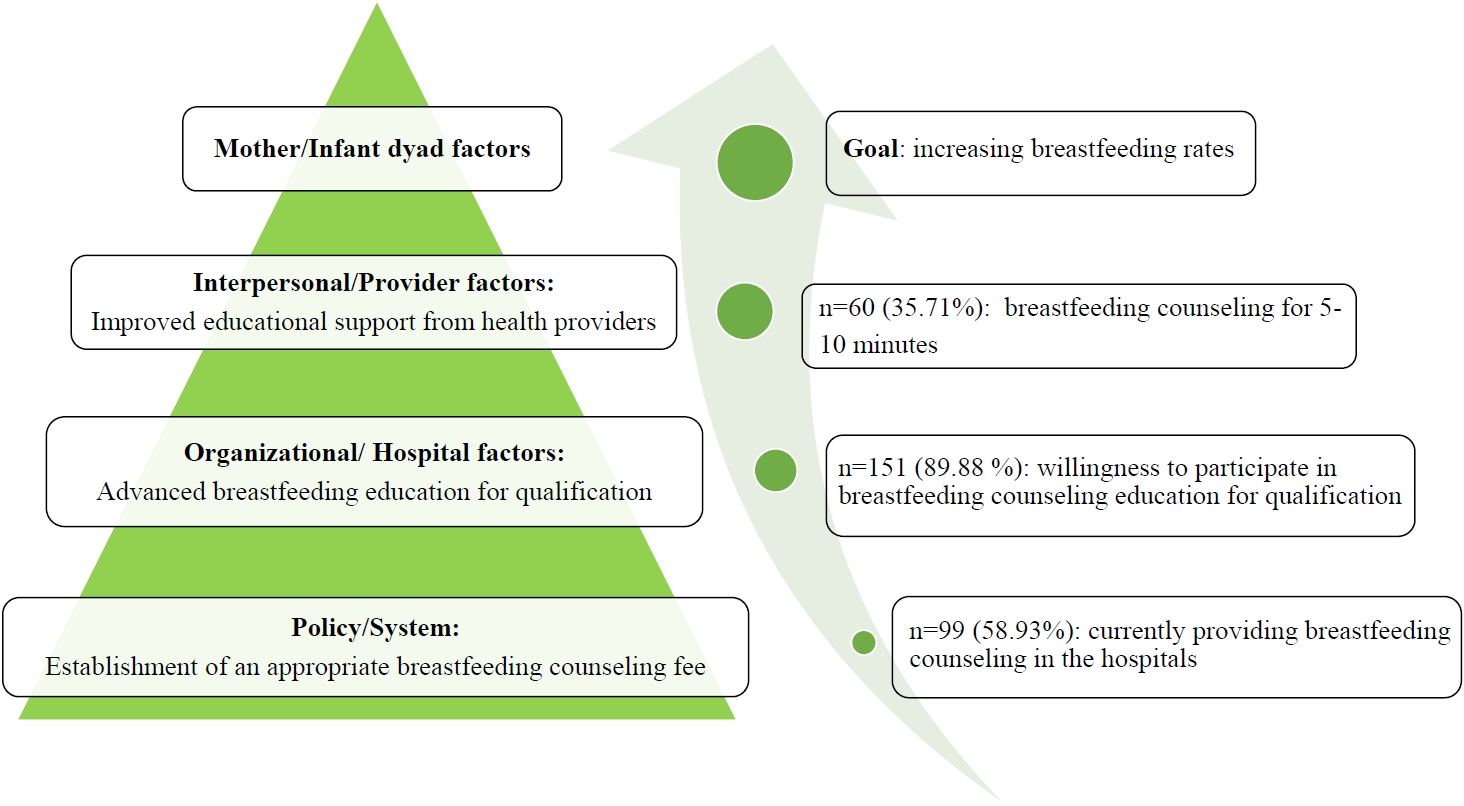
Question: What barriers to breastfeeding do Korean pediatricians perceive?
Finding: Regardless of medical institution, breastfeeding counseling for parents is currently limited, and breastfeeding is commonly discontinued due to various maternal and neonatal factors.
Meaning: To promote breastfeeding, increasing pediatrician participation in breastfeeding counseling with the establishment of appropriate breastfeeding counseling fees and the expansion of practical and high-quality breastfeeding education for medical staff should be considered.
- Gastroenterology
- Association between maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child’s body mass index at preschool age (12 times)
- Jeewon Shin, Yoowon Kwon, Ju Hee Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):76-81. Published online November 30, 2022
-
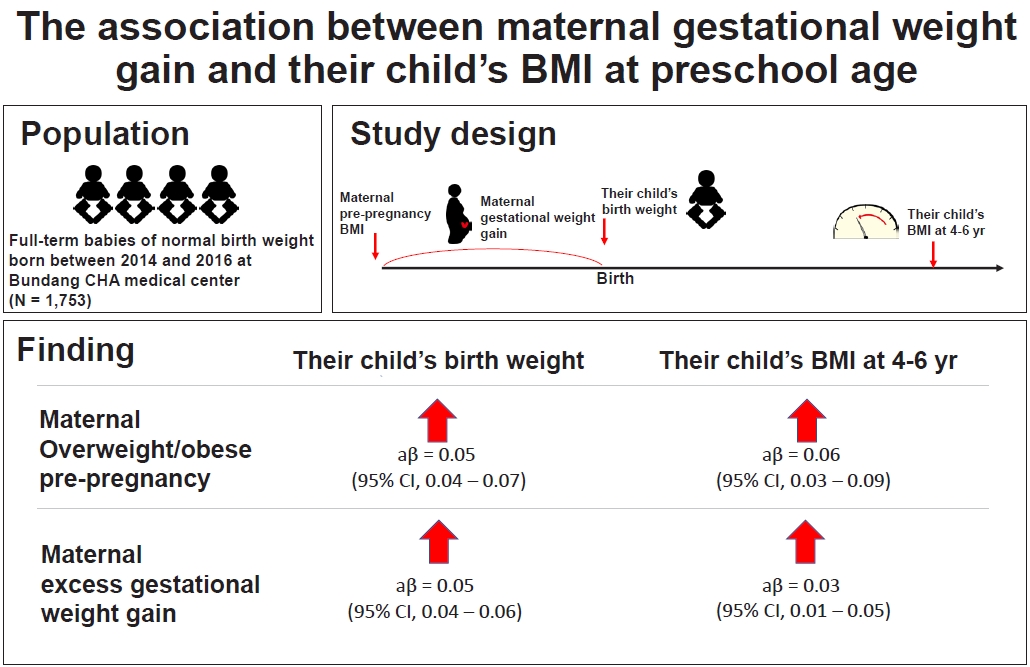
Question: What are the risk factors of newborn birth weight? Does gestational weight gain and prepregnancy body mass index affect childhood weight?
Finding: Excess maternal weight gain increases the risk of overweight/obesity, newborn birth weight, and child body mass index at 4–6 years.
Meaning: Maternal weight control before and during pregnancy should be well controlled.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
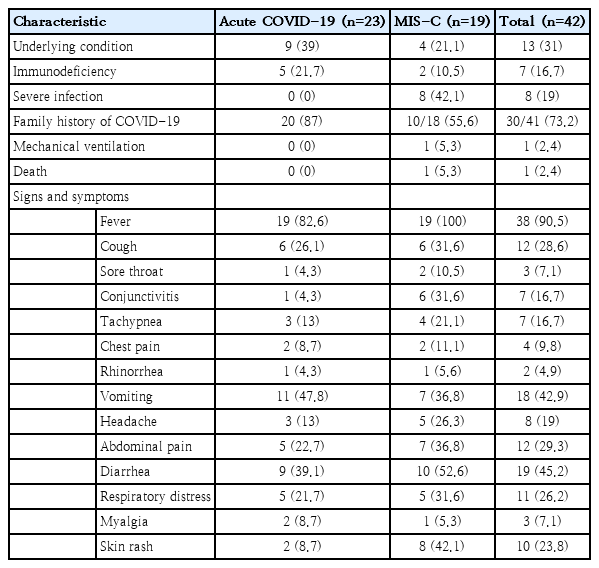
- SARS-CoV-2 fecal shedding pattern in pediatric patients with acute COVID-19 or COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome (12 times)
- Setareh Mamishi, Fatemeh Jalali, Sepideh Benvari, Babak Pourakbari, Mohammad Reza Abdolsalehi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Mohammad Shahbabaie, Amene Navaeian, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):366-368. Published online June 14, 2023
-
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Factors to consider before implementing telemedicine protocols to manage neonatal jaundice (11 times)
- Heui Seung Jo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):403-404. Published online April 12, 2022
-
In the rapidly changing environmental situation during the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak, neonatal centers have developed telemedicine systems with extended coverage for neonatal monitoring and high-risk follow-up programs including neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. At this point, electronic health technology and noncontact medical system increase the effectiveness of rather than replacing the face-to-face visit and the opinions of experienced neonatologists.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mediation effect of cord blood cortisol levels between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight: a hospital-based cross-sectional study (11 times)
- Nisanth Selvam, Jayashree K, Prasanna Mithra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):500-506. Published online July 29, 2022
-

Question: What is the association between cord blood cortisol and maternal weight, birth weight, and cord blood lipid profile?
Finding: Cord blood cortisol levels did not influence the relationship between maternal weight changes or birth weight. Maternal weight changes, birth weight, and cortisol levels altered the cord blood lipid profile.
Meaning: Our findings may aid United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-Being) achievement by 2030.
- Neurobehavior
- Association between previous abortion history and risk of autism spectrum disorders among offspring: a meta-analysis (11 times)
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Saeid Bashirian, Mahdieh Seyedi, Mohammad Rezaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):70-75. Published online August 17, 2022
-

Question: This study aimed to determine whether there is an association between previous abortion history and the risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) among children.
Finding: We found that the risk of ASD associated with previous abortion history had an odds ratio of 1.64 (95% confidence interval, 1.28–2.0; I2=61.7%).
Meaning: These findings suggest a positive and significant association between history of previous abortion and risk of ASD in children.
- Editorial
- Emergency Medicine
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children: teamwork approach (11 times)
- Ji-Hyun Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):66-67. Published online September 1, 2022
-
· The successful and safe enema reduction of intussusception depends primarily on the experience and preference of the radiologists and the availability of resources.
· The establishment of a standardized manual or protocol for reduction and pre-reduction treatment of intussusception, along with the collaboration of pediatricians, radiologists, and surgeons, is expected to improve the treatment success rate.
- Correspondence
- Cardiology
- The authors reply: Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6–18 years, Iran (11 times)
- Seyedeh Mahdieh Namayandeh, Nastran Ahmadi, Seyed Mahmood Sadr
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):414-414. Published online June 14, 2023
-
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Growth patterns of preterm infants in Korea (10 times)
- Joohee Lim, So Jin Yoon, Soon Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):1-9. Published online July 8, 2021
-
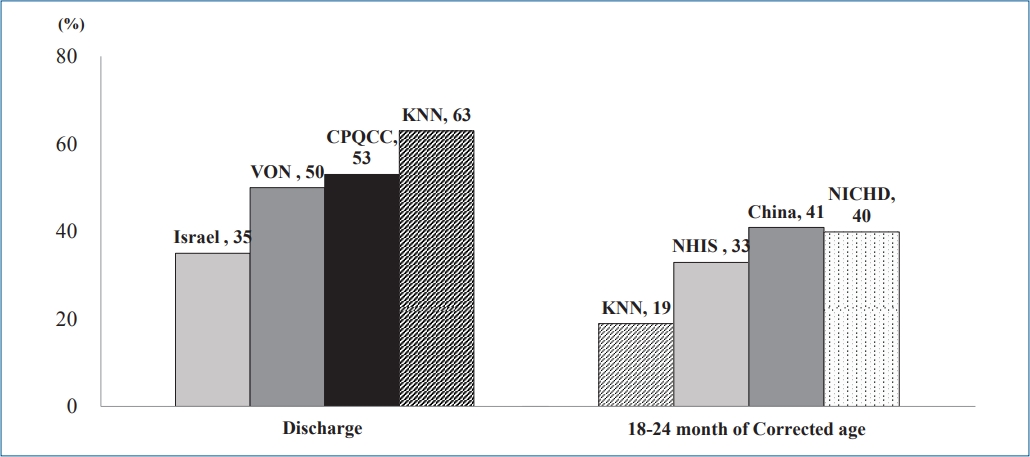
∙ The growth of preterm infants is a main focus of neonatology.
∙ Preterm infants in Korea, especially those with a very low birth weight, achieve retarded growth.
∙ Careful growth monitoring and early intervention will contribute to better development outcomes and quality of life for preterm infants and improve public health.
- Original Article
- Emergency Medicine
- Nonfatal injuries in Korean children and adolescents, 2007–2018 (10 times)
- Gyu Min Yeon, Yoo Rha Hong, Seom Gim Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):194-200. Published online September 9, 2021
-
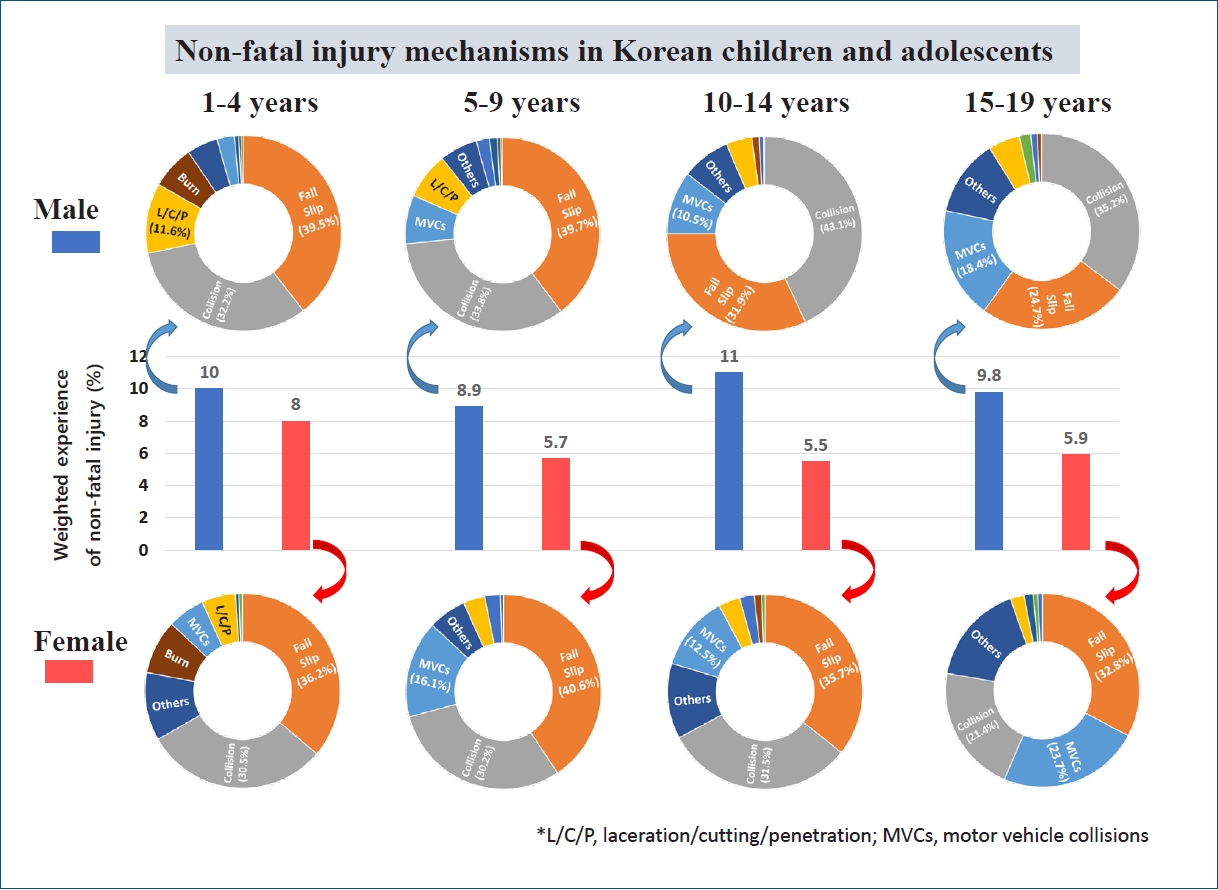
Question: How many children and adolescents have experienced nonfatal injuries in the previous year?
Finding: Among Korean children and adolescents, 8.1% experienced at least one injury per year. We found no significant change in the incidence of injuries over the previous 12 years.
Meaning: The incidence of injuries is higher than this estimation; therefore, more attention and effort are needed to prevent injuries among children and adolescents.
- Clinical note
- General Pediatrics
- Diabetic ketoacidosis in children induced by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) diabetic ketoacidosis post-COVID-19 in children (10 times)
- Neha Thakur, Narendra Rai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):209-210. Published online November 30, 2021
-
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Low bone mineral density can occur in children after shortterm systemic glucocorticoid treatment (10 times)
- Moon Bae Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):300-301. Published online April 27, 2022
-
Osteoporosis diagnosed in children with chronic diseases is a major endocrine complication triggered by the disease itself or its treatment. Although age upon starting osteotoxic agents and the their duration of use are vital contributors, spontaneous recovery of bone mass following treatment completion is a privilege of this specific age group. For any patients short-term glucocorticoid therapy, bone health screening is the next step.
- Letter to the Editor
- Cardiology
- Early prophylaxis of cardiomyopathy with beta-blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (10 times)
- Heirim Lee, Jinyoung Song, I-Seok Kang, June Huh, Jin A Yoon, Yong Beom Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):507-509. Published online August 22, 2022
-
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Is there a link between social media usage and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children? (10 times)
- Hae Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):169-170. Published online March 23, 2023
-
Social media use has potential benefits and risks, including links to adverse health problems in children such as functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). Screen time control, emotional support, and parental guidance can help children navigate social media safely and reduce the risk of developing FGIDs.
- Clinical Note
- Other
- Novel PTRH2 gene variant causing IMNEPD (infantile-onset multisystem neurologic, endocrine, and pancreatic disease) in 2 Saudi siblings (10 times)
- Dalal K. Bubshait
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):223-225. Published online March 23, 2023
-

- Editorial
- Other
- Advancing pediatric health: the multifaceted scope of Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics (10 times)
- Jin Hee Oh, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):171-172. Published online March 29, 2023
-
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics (CEP) is a journal that specializes in pediatric research topics. It covers a wide range of research areas, including basic research, translational research, and research related to improving pediatric health and diseases. CEP also focuses on the coordination of societal structures and processes that orchestrate pediatric health and disease throughout society, and the parallel relationship between regional characteristics and globalization. The journal intends to continue promoting pediatric health through relentless efforts and the discovery of new research areas.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Echocardiographic reference z scores of right ventricular dimension and systolic function of children aged 5–12 years (10 times)
- Alaba Busola Oladimeji, Moriam Omolola Lamina, Peter Odion Ubuane, Motunrayo Oluwabukola Adekunle, Omolara Adeolu Kehinde, Barakat Adeola Animasahun, Olisamedua FidelisNjokanma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):215-222. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Question: Z score reference values for right ventricular size and systolic function in children using echocardiography are available in several countries. Despite the high burden of diseases involving the right ventricle in Nigeria, these reference values have limited applicability.
Finding: The right ventricular sizes of Nigerian children differed from those published elsewhere.
Meaning: These reference values will aid the treatment, monitoring, and pre- and postintervention for Nigerian children.
- Correspondence
- General Pediatrics
- Letter to the editor: Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6-18 years, Iran (9 times)
- Amar Taksande
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):412-413. Published online October 27, 2021
-
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Clinical and diagnostic importance of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (9 times)
- Eun Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):129-130. Published online January 14, 2022
-
∙ Because childhood lipid concentrations continue into adulthood, early evaluation and treatment are needed, but dyslipidemia awareness is low.
∙ For the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in childhood and adolescence, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease in adulthood, lifestyle modifications, appropriate exercise, and drug treatment are required.
∙ A large-scale study of the prevalence and therapeutic effects of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents in Korea is needed.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Changes in epidemiology of parainfluenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus infection during coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea (9 times)
- Kyung-Ran Kim, Hwanhee Park, Doo Ri Kim, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):320-321. Published online March 10, 2022
-
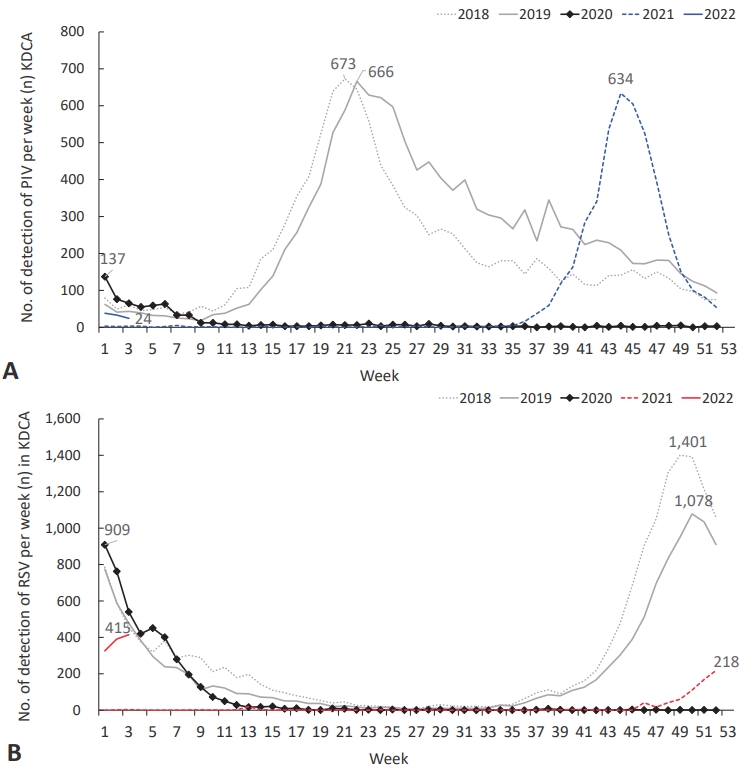
Question: How the epidemiology of other childhood respiratory viruses has changed during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea?
Finding: Parainfluenza virus (PIV) typically circulated in the spring, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) epidemic started in autumn in Korea before COVID-19 pandemic. PIV and RSV seasons disappeared in 2020 and came back in 2021 with atypical seasonality. PIV season was changed from spring to autumn, and the beginning of RSV season was slightly delayed from autumn to early winter in 2021.
Meaning: Circulation of PIV and RSV was changed to unusual seasons and patterns during COVID-19 pandemic period.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Coronavirus disease 2019 and mRNA vaccines: what’s next – miRNA? (9 times)
- Joon Kee Lee, Heon-Seok Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):302-303. Published online March 28, 2022
-
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small single-stranded noncoding RNA molecules that function in RNA silencing and the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. The potential role of miRNAs as biomarkers of myocarditis is promising, and miRNAs are expected to be utilized in various clinical fields in the future.
- Endocrinology
- Is type 1 diabetes related to coronavirus disease 2019 in children? (9 times)
- Minsun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):252-253. Published online March 29, 2022
-
· Evidence shows that patients with type 1 diabetes have been severely affected by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in various ways.
· Although there is no reliable evidence that COVID-19 worsens or induces diabetes, it can impair β-cell insulin secretion and glucose control by inducing inflammation and cytokine production.
· A study is needed of the short- and long-term relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 in the Korean pediatric population.
- Nutrition
- Human milk oligosaccharides as immunonutrition key in early life (9 times)
- Jung Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):344-345. Published online May 3, 2022
-
· Human milk is a major source of immunonutrients for neonates and infants. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) act as prebiotics and promote the growth of commensal bacteria.
· HMOs inhibit microorganism adhesion to the gut mucosa through interactions with the commensal microbiome and improve gut barrier function by increasing short-chain fatty acid mediated by bifidobacteria and immunomodulation.
· Several randomized controlled trials recently reported on HMOs.
- Perspective
- Infection
- Statement on healthcare system preparedness in response to COVID-19 Omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5 surge in Korea from the Korean Pediatric Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases (9 times)
- Eun Young Cho, Dong Hyun Kim, Soo-Han Choi, Ki Wook Yun, Jong Gyun Ahn, Hye-Kyung Cho, Hyunju Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Yae-Jean Kim; Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):510-511. Published online September 23, 2022
-
In order to respond to the recent surge in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases and the continuously changing epidemiology of COVID-19, a sustainable and flexible pediatric healthcare system must be prepared considering the specificity of pediatric care. We demand a more proactive response from the health authorities to check the current state of pediatric COVID-19 patient care and to ensure that pediatric patients receive appropriate and timely management.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







