Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six month.
- Review Article
- Neurobehavior
- Jeopardized mental health of children and adolescents in coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (1,906 times)
- Bohyun Jin, Sohee Lee, Un Sun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):322-329. Published online June 3, 2022
-
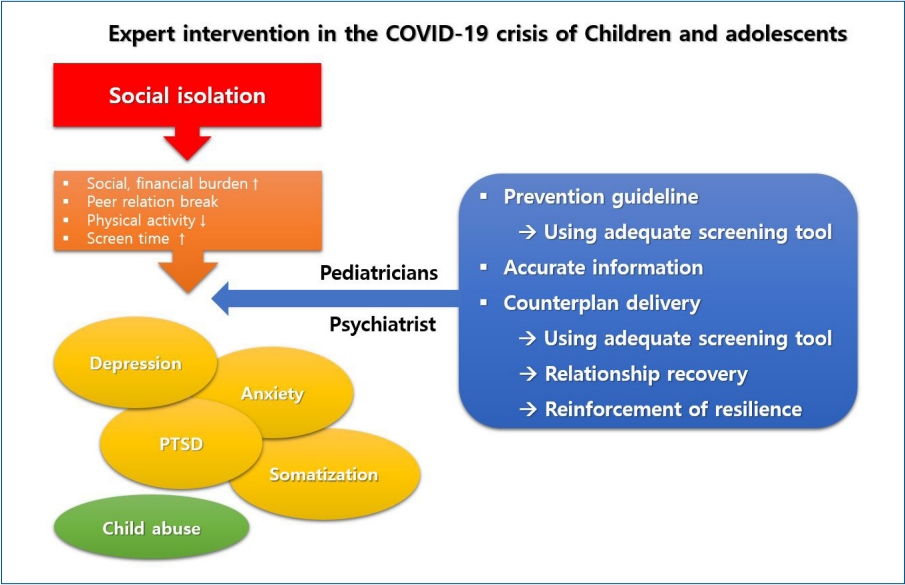
∙ The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has required preventive measures like self-quarantine, school closures, and lockdown, which ultimately make youth directly and indirectly vulnerable to depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and somatization.
∙ Child abuse is more common in the COVID-19 era than previously.
∙ Pediatricians should carefully examine parental and child mental health to directly and indirectly aid their physical and mental health.
- Pulmonology
- Long COVID in children and adolescents: prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management strategies (1,882 times)
- Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):465-474. Published online June 19, 2023
-
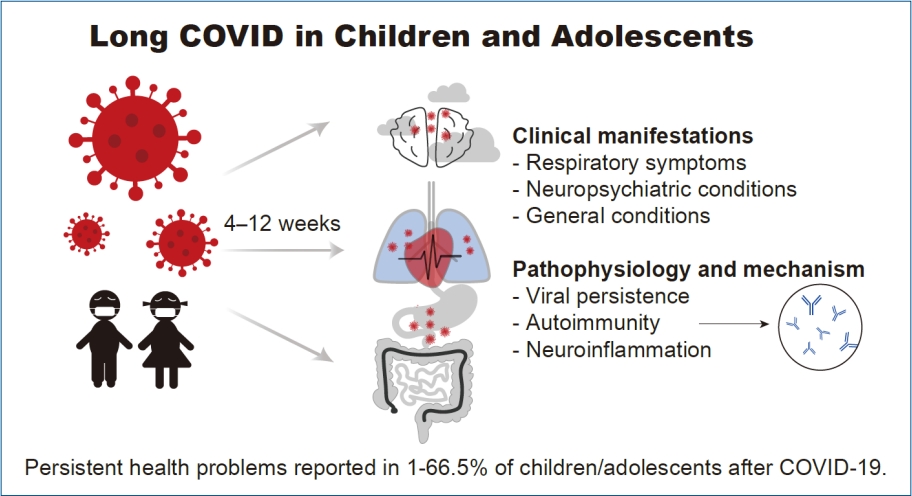
· Current definitions of long coronavirus disease (COVID) in children and adolescents vary in duration, ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
· The clinical spectrum of long COVID in children and adolescents comprises a wide range of symptoms and might be a multisystem disorder.
· Persistent health problems with a prevalence of 1%–66.5% were reported in children and adolescents after COVID-19, with a higher incidence of persistent single or multiple symptoms.
- Other
- Epidemiology of pediatric fractures before versus during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (1,865 times)
- Chi Hoon Oh, Siyeong Yoon, Kyung Rae Ko, Young Woo Kwon, Kyeong Mi Kim, Hyun Seo Park, Hogyeong Kang, Inseok Jang, Soonchul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):330-336. Published online June 3, 2022
-

∙ The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was first reported in December 2019 as a cluster outbreak in Wuhan, since then, national lockdowns have included school closures, stay-at-home orders.
∙ The characteristics of adolescent fractures were often related to physical activity such as sports-related injury.
∙ During the COVID-19 pandemic, both in the East and the West, the incidence of fractures in children and adolescents is showing a decreasing trend worldwide.
∙ Fractures in children and adolescents were significantly reduced in the proportion of relatively low-energy damage, and the incidence of fractures in adolescents with greater activity compared to children was reduced.
∙ If COVID-19 pandemic ends, normal academic and sports activities increase due to the easing of lockdown policies, the number of trauma patients related to increased activity may increase rapidly, and clinics should prepare for this change.
- Infection
- Therapeutics for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and adolescents (1,797 times)
- Soo-Han Choi, Jae Hong Choi, Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):377-386. Published online June 27, 2022
-
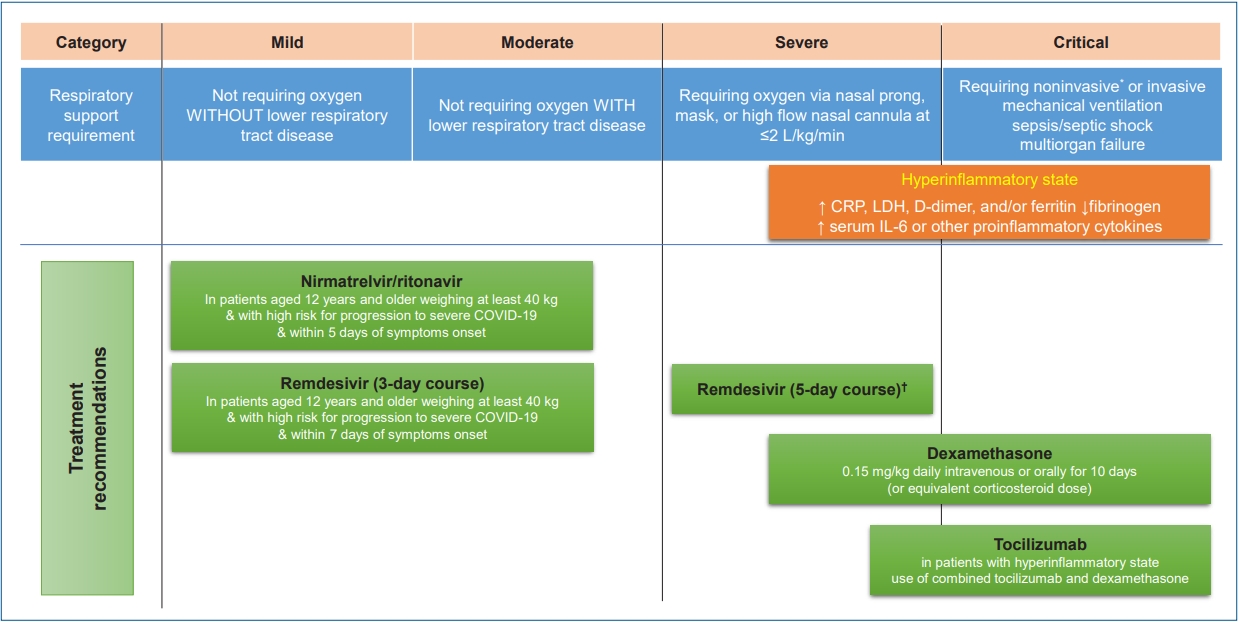
· Children and adolescents with high risks for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be identified and proper treatment should be provided promptly according to the patient’s condition.
· Remdesivir can be considered for pediatric patients of all ages with COVID-19 who have an emergent or increase in supplemental oxygen.
· The use of corticosteroids is not recommended for patients with nonsevere COVID-19. Corticosteroids are recommended in children and adolescents with severe and critical COVID-19.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Survey of Korean pediatrician’s perceptions of barriers to and improvements in breastfeeding (1,789 times)
- Seong Phil Bae, Woo Ryoung Lee, Won-Ho Hahn, Hye-Jung Shin, Young Min Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Yong Joo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Youn Jeong Shin, Dae Yong Yi, Soon Min Lee, Juyoung Lee, Jin A Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Euiseok Jung, Eui Kyung Choi, Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):540-546. Published online July 29, 2022
-
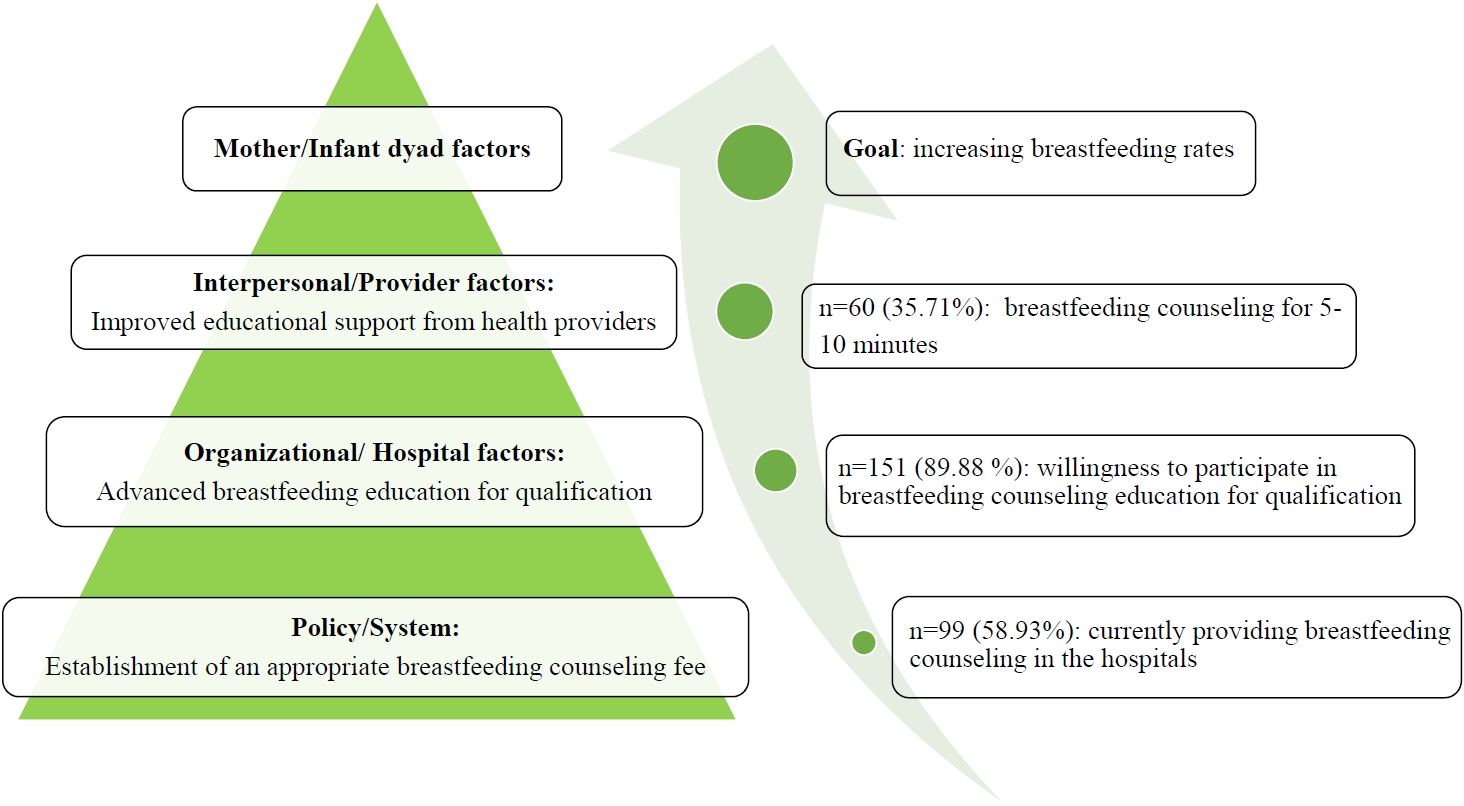
Question: What barriers to breastfeeding do Korean pediatricians perceive?
Finding: Regardless of medical institution, breastfeeding counseling for parents is currently limited, and breastfeeding is commonly discontinued due to various maternal and neonatal factors.
Meaning: To promote breastfeeding, increasing pediatrician participation in breastfeeding counseling with the establishment of appropriate breastfeeding counseling fees and the expansion of practical and high-quality breastfeeding education for medical staff should be considered.
- Review Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Ferritin in pediatric critical illness: a scoping review (1,762 times)
- Ivy Cerelia Valerie, Anak Agung Sagung Mirah Prabandari, Dyah Kanya Wati
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):98-109. Published online September 16, 2022
-
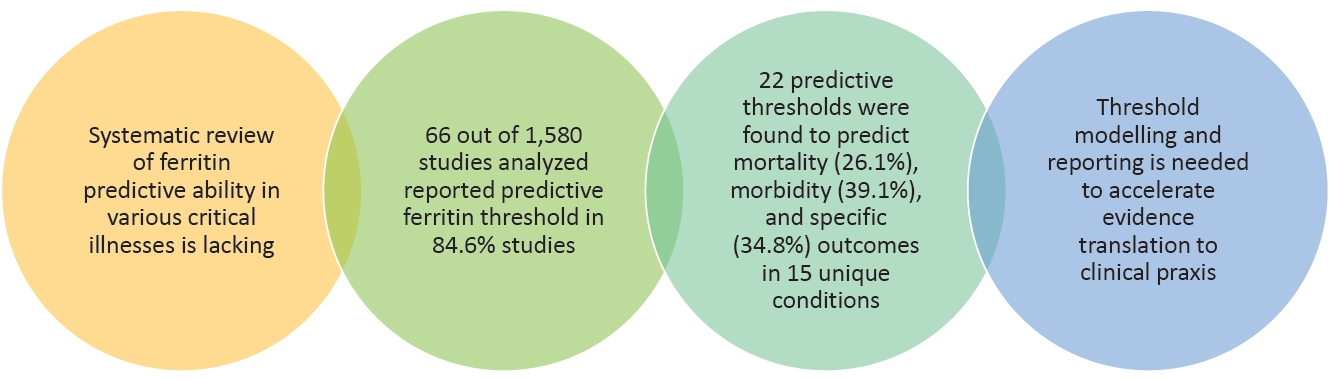
The number of studies on ferritin predictive ability in pediatric critical illness has grown exponentially over the past 2 decades. However, among the 66 of 1,580 studies analyzed here, summary statistics for overall and condition-specific studies were only reported in 45.4% and 71.2%, respectively. In contrast, ferritin as a categorical variable with a preset threshold was a significant predictor in 84.6% of studies.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Clinical practice guidelines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: recent updates (1,760 times)
- Tae Hoon Eom, Young-Hoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):26-34. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Primary pediatricians should play a key role in the diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
· The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition, has lowered the diagnostic threshold for older teens and adults and a comorbid diagnosis with autism is now allowed.
· The American Academy of Pediatrics had added recommendation-related comorbid conditions in its guideline and the Society of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics recently developed a complex ADHD guideline.
· The European ADHD Guideline Group recently developed a guideline for managing ADHD during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis (1,747 times)
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
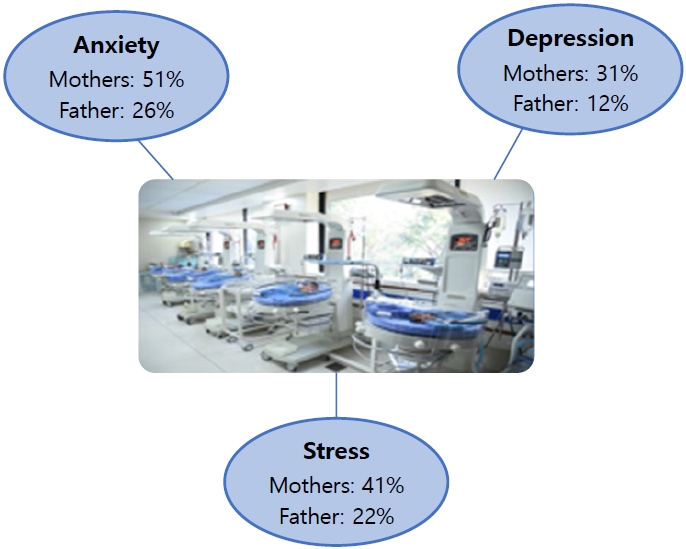
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
- Review Article
- Infection
- COVID-19 among infants: key clinical features and remaining controversies (1,733 times)
- Nevio Cimolai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):1-16. Published online November 27, 2023
-
· Clinical studies of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in infants should be supported by rigorous laboratory diagnostic criteria.
· Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spreads to infants similarly to other viral respiratory infections.
· Among infants ≤1 year of age beyond the immediate postpartum period, COVID-19 is relatively mild, but even the low risk of severe disease requires prevention.
· Comorbidities increase infection vulnerability and complications in infants.
· Clinical and laboratory data do not sufficiently distinguish COVID-19 from other respiratory viral infections.
· Coinfection with SARS-CoV-2 is uncommon among infants.
· Unique infection sequelae, including multi-inflammatory syndrome in children and neonates and long COVID require further study and refinement of diagnostic criteria.
· Infection control standards applied to mother-infant dyads should be tempered by standard preventive strategies, maternal input, accommodation potential, and overall safety.
· Maternal vaccination prevents disease in early infancy.
- COVID-19 in immunocompromised children and adolescents (1,702 times)
- Byung Ok Kwak, Byung Wook Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):182-189. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Most immunocompromised children and adolescents are not at increased risk of developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). COVID-19 outcomes for low- or medium-risk immunocompromised children are favorable, while more serious illness reportedly occurs in high-risk immunocompromised children by underlying disease, its treatments, and other factors. Therefore, the early detection and timely management of severe COVID-19 and treatment of underlying disease are important. Hospitalization and COVID-19 vaccination should be carefully considered.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal sepsis-causing bacterial pathogens and outcome of trends of their antimicrobial susceptibility a 20-year period at a neonatal intensive care unit (1,676 times)
- Woo Sun Song, Hye Won Park, Moon Youn Oh, Jae Young Jo, Chae Young Kim, Jung Ju Lee, Euiseok Jung, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):350-357. Published online December 9, 2021
-
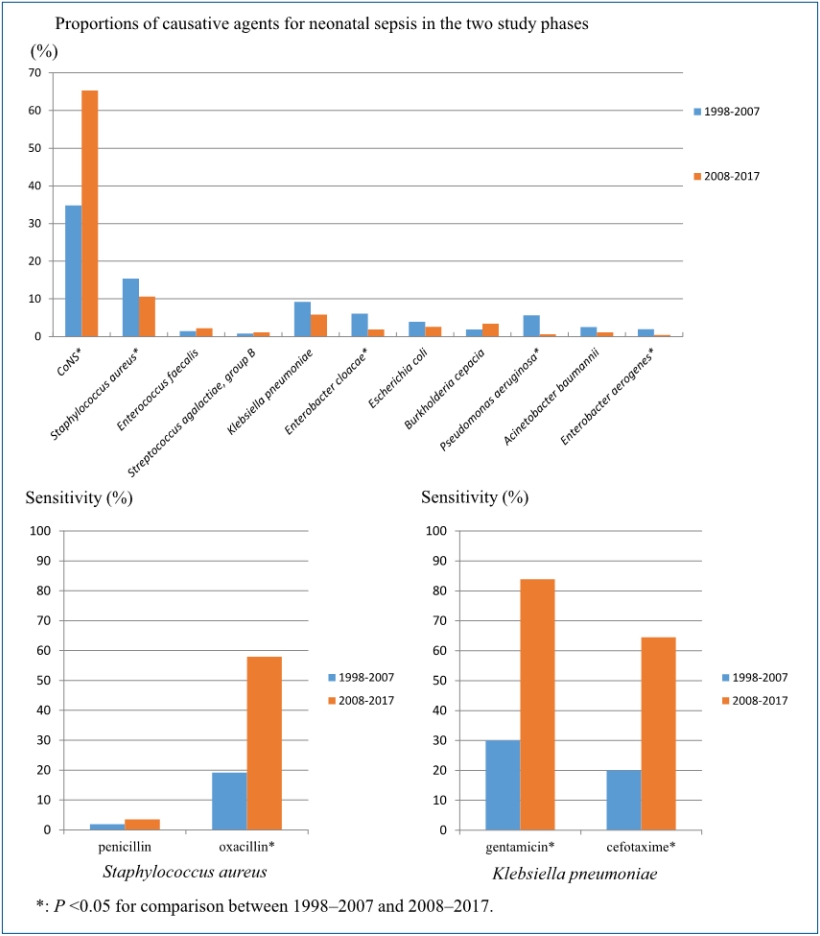
Question: What is prevalence of bacterial pathogens causing sepsis and their antimicrobial susceptibility over 20 years?
Finding: Coagulase-negative remains most common causative organism. The most common gram-negative organism was Klebsiella pneumonia. The susceptibility of staphylococcus aureus and K. pneumonia showed increased susceptability to oxacillin, cefotaxime and amikacin, gentamicin, respectively.
Meaning: Answers to the question asked is important in choosing antimicrobials and to monitor emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution anorectal manometry in children (1,656 times)
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):57-63. Published online June 14, 2023
-
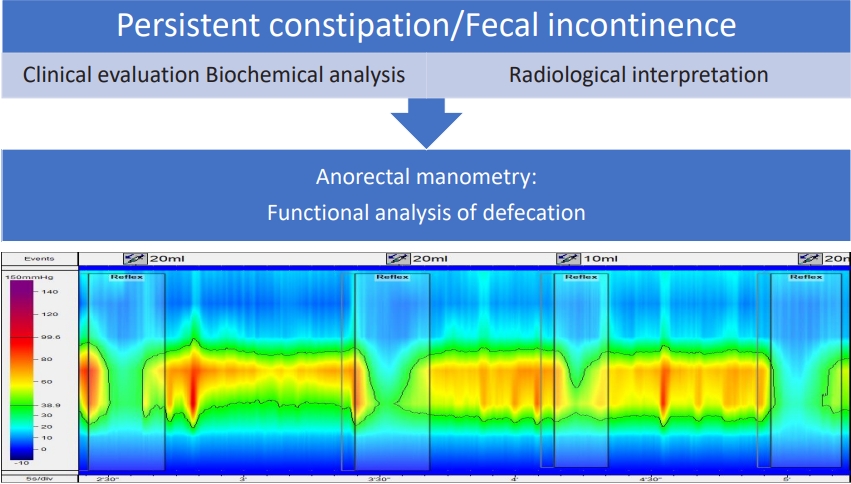
· Anorectal manometry is safe in children.
· Defecation Dyssynergia is one of the commonest cause of chronic constipation.
· Positive Rectoanal inhibiory reflex rules out Hirschsprung's Disease
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Impact of short and intensive art-based intervention on symptomatology and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (1,656 times)
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Bayar Mohammed Omar Abdulla, Pranee Liamputtong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):447-454. Published online September 14, 2023
-

Question: Does a short and intensive art-based intervention affect symptoms and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Finding: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not affect symptoms in children with ASD level 2 or 3, including social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and autistic mannerisms.
Meaning: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not improve the symptoms of patients with ASD.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- A thickened formula reduces feeding-associated oxygen desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants (1,648 times)
- Gayoung Lee, Juyoung Lee, Ga Won Jeon, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):32-37. Published online December 15, 2022
-
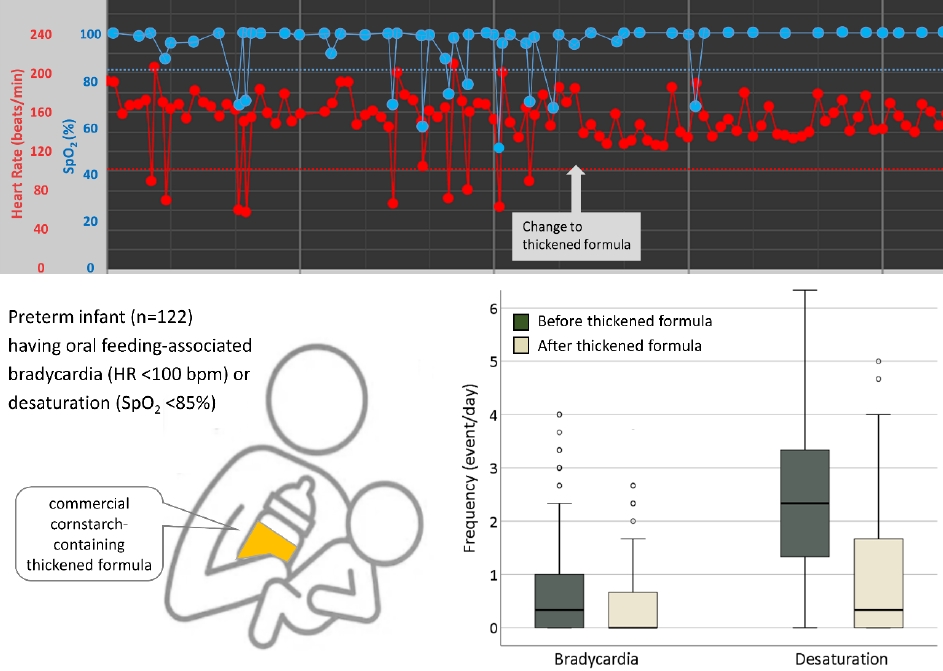
Question: Is a commercial thickened formula able to alleviate oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants?
Finding: Thickened formula feeding significantly reduced oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants.
Meaning: Thickened formula feeding stabilizes oxygen saturation and heart rate during oral feeding among preterm infants with feeding difficulties.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants (1,637 times)
- In Gyu Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):281-287. Published online December 30, 2022
-
· Among survivors, 60.9% of infants born at 22 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments, whereas 50.3% born at 23 weeks’ and 42.2% at 24 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments.
· Moderate and late preterm infants reportedly have less severe disease than very preterm infants, but they still experience adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.
· The careful follow-up and early detection of developmental problems in these patients are required.
- Letter to the Editor
- Other
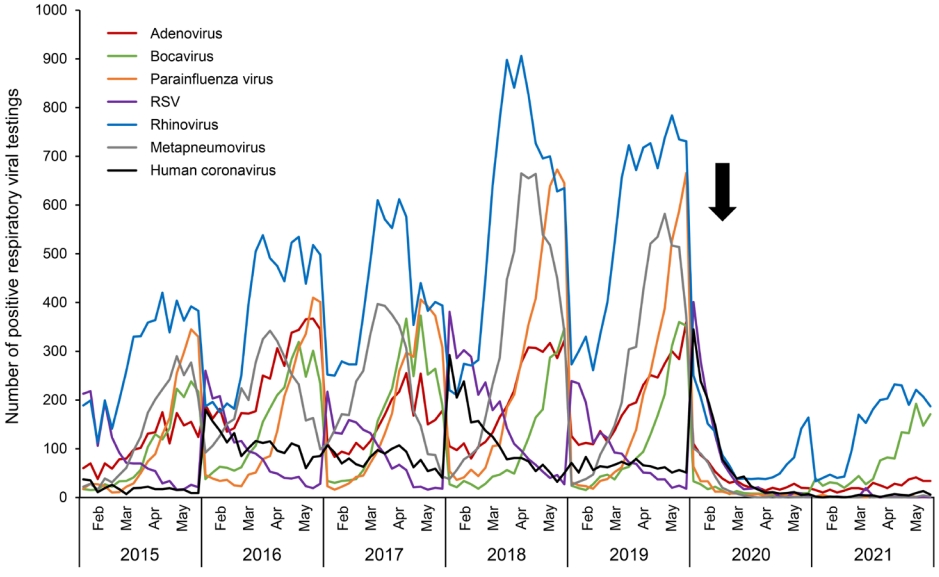
- Changes in air pollution and childhood respiratory viral infections in Korea post-COVID-19 outbreak (1,630 times)
- Hyung Kyu Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):211-213. Published online February 17, 2022
-
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Liver fibrosis in children: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapy (1,620 times)
- Elif Ozdogan, Cigdem Arikan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):110-124. Published online December 19, 2022
-
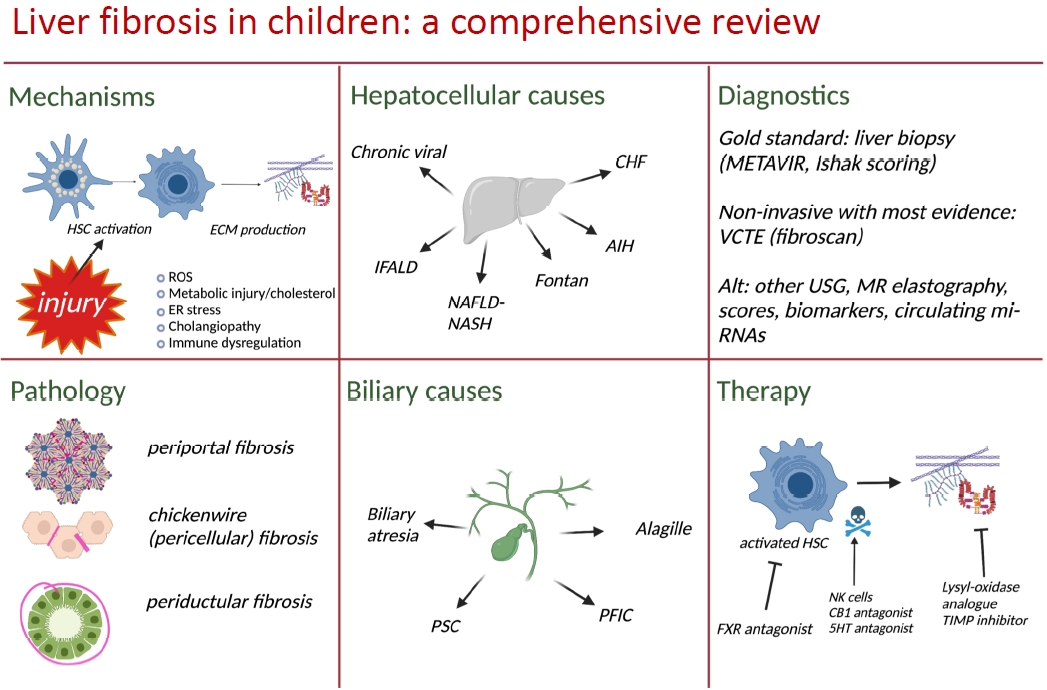
· Chronic liver diseases in children are heterogenous but converge in the common pathway of fibrosis.
· Much of the literature on mechanisms of fibrogenesis focus on adults but pediatric physiology has documented differences.
· Understanding of these distinctions are necessary to define, treat, and prevent fibrosis.
· Current management of liver fibrosis relies heavily on liver biopsy. Multiple tools have shown high diagnostic performance in pediatric and adult populations. Large, multicenter studies are needed for validation.
- Update on eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease beyond eosinophilic esophagitis in children (1,619 times)
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):233-239. Published online January 3, 2023
-

· Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease (EGID) is uncommon, with a prevalence of 1–30/100,000 in the general population; however, it is increasing worldwide.
· The diagnosis of EGID is based on histopathological findings of endoscopic mucosal biopsy in which tissue eosinophils are counted in each gastrointestinal tract segment of patients with chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms.
· Individualized treatment strategies, including adequate dietary and pharmacological therapy, may help improve outcomes of children with EGID.
- Allergy
- Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children: focus on systemic Th2 cytokine receptor antagonists and Janus kinase inhibitors (1,606 times)
- Jeong Hee Kim, Mona Salem Samra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):64-79. Published online June 14, 2023
-
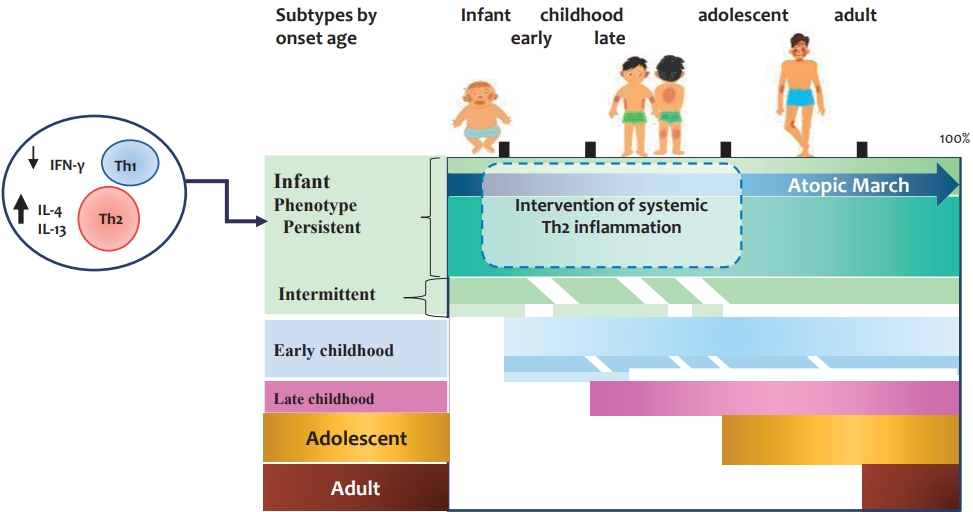
· Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by a strong T helper (Th)2 response, although the extents of Th22, Th17/ interleukin (IL)-23, and Th1 responses vary among disease subtypes.
· Children with moderate to severe AD may require early systemic therapy to reduce the systemic inflammation caused by increased Th2 cytokine levels.
· Dupilumab, which blocks IL-4/IL-13 receptor, has equivalent efficacy for extrinsic and intrinsic AD and a favorable safety profile in infants and children aged 6 months and older.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: from diagnosis to management (1,585 times)
- Eujin Park, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):17-25. Published online June 14, 2023
-
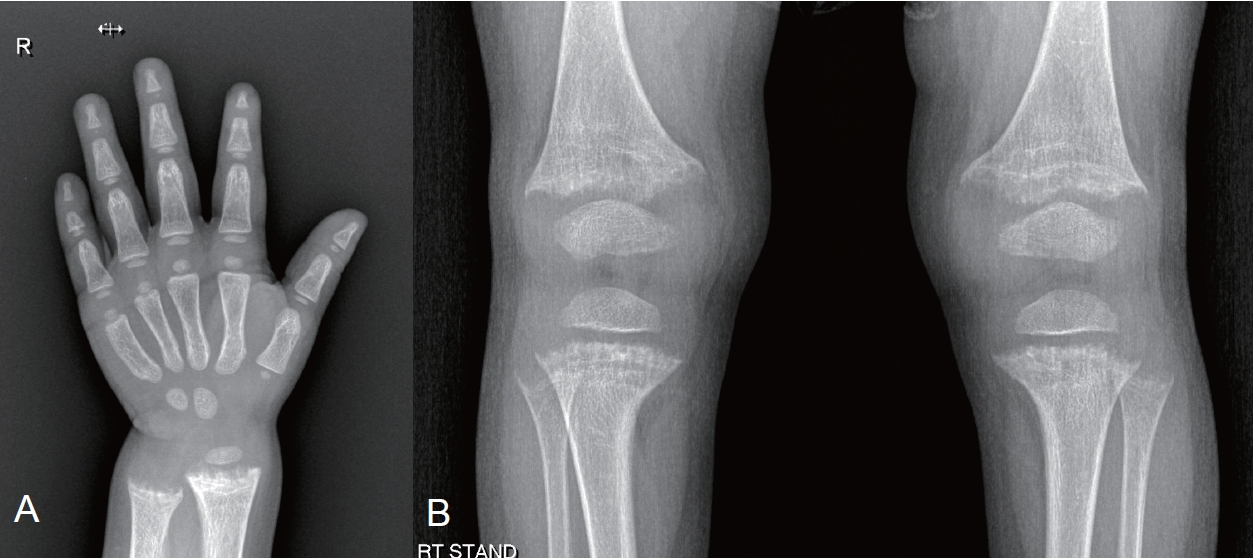
· X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), the most common cause of hypophosphatemic rickets, affects 1/20,000 people.
· XLH is caused by a loss-of-function mutation of the PHEX gene.
· Its main pathogenesis is elevated fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) level.
· Burosumab, an FGF23 inhibitor, was developed in the early 2000s.
· Burosumab was approved in Korea in 2020 for XLH patients aged 1+ years with radiographic evidence of bone disease.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review (1,565 times)
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
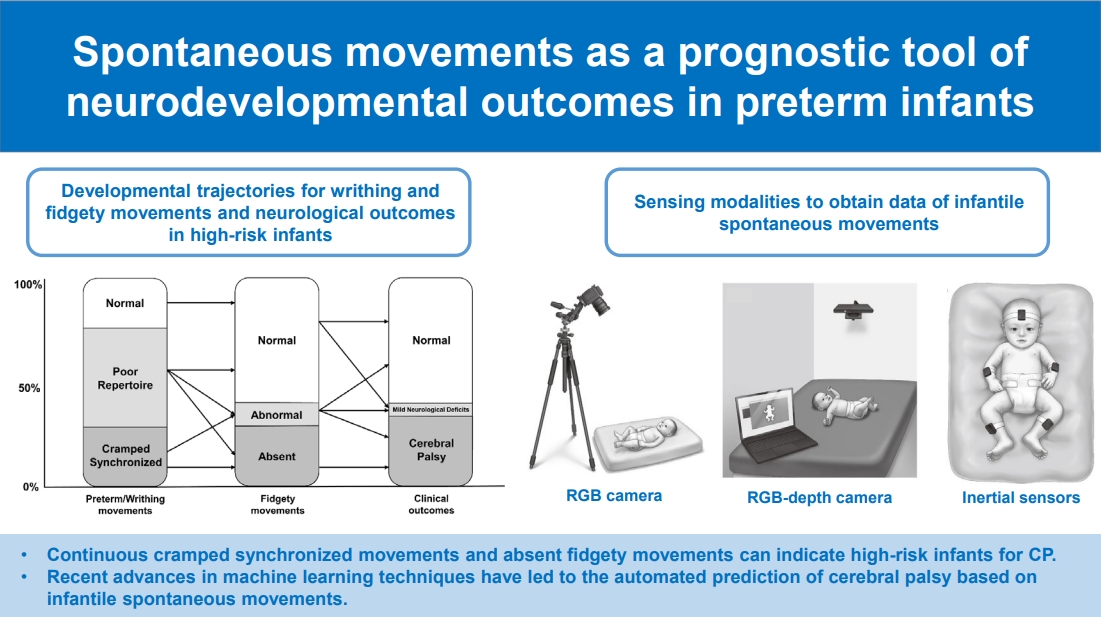
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Allergy
- Practical issues of oral immunotherapy for egg or milk allergy (1,555 times)
- Sukyung Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):140-148. Published online June 19, 2023
-
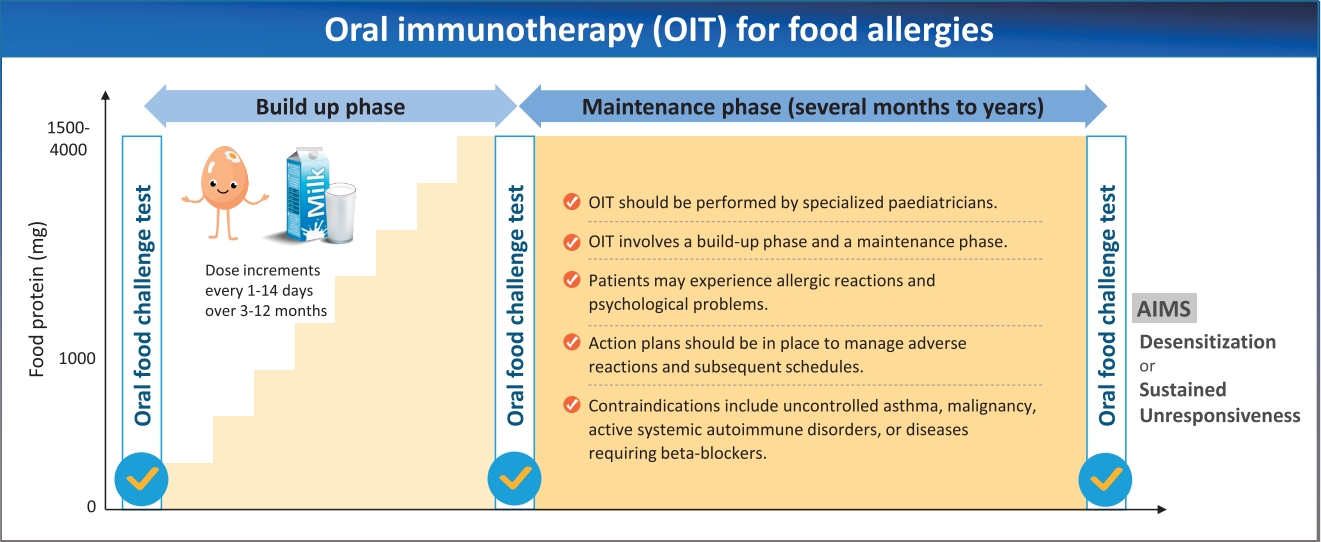
· Oral immunotherapy should be supervised by pediatricians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing allergic reactions.
· Food allergen intake is gradually increased and maintained for years.
· Patients may experience allergic reactions and psychological problems.
· Adjunctive therapies (biologics, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists) may improve efficacy and safety.
· Contraindications include uncontrolled asthma, malignancy, active autoimmune disorders, and beta-blocker usage.
- Infection
- Epidemiological changes in infectious diseases during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea: a systematic review (1,539 times)
- Jong Gyun Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):167-171. Published online November 30, 2021
-
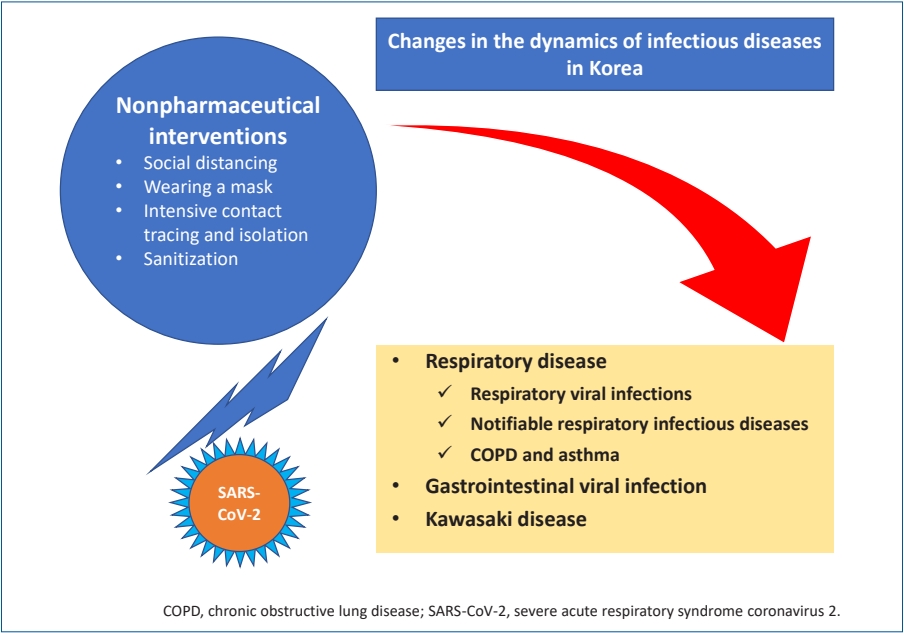
· Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have had a major impact on the epidemiology of various infectious diseases in Korea.
· Respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal viral diseases were significantly reduced during the NPI period.
· The decrease in Kawasaki disease after the introduction of NPI is an unintended result.
· Infectious diseases that decreased during NPI use may re-emerge.
· We must continuously monitor the epidemiology of various infectious diseases during the coronavirus era
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Effectiveness of Helmet therapy for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly (1,527 times)
- Jeongho Kim, Jina Kim, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):46-53. Published online December 5, 2023
-
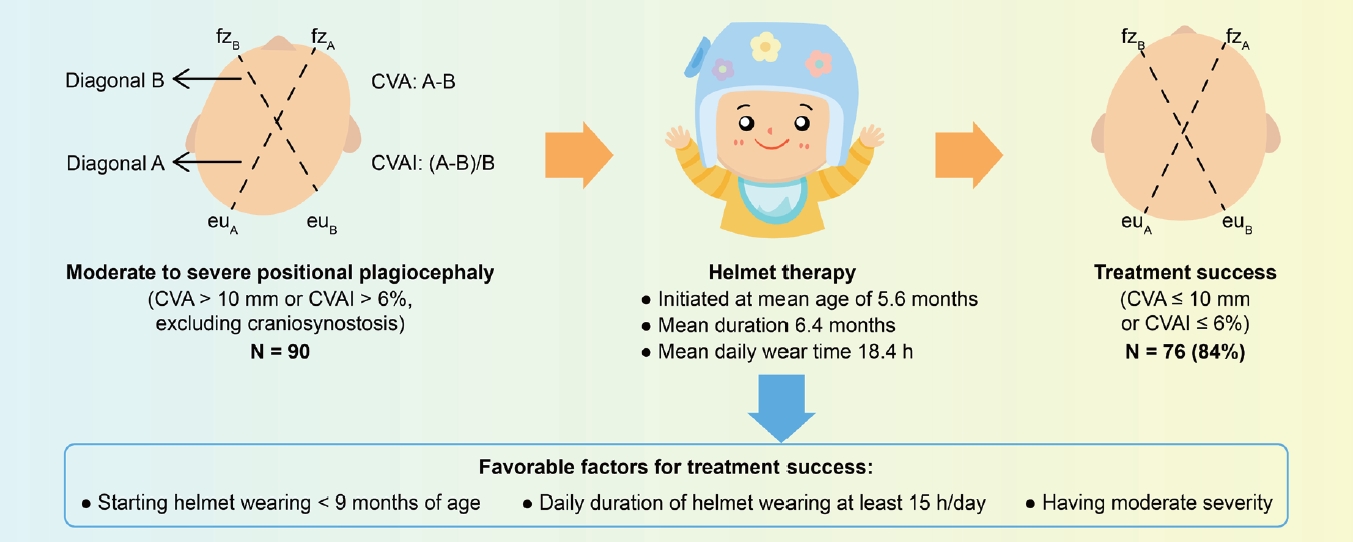
Question: Is helmet therapy effective for positional plagiocephaly? What factors influence helmet therapy efficacy for positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Helmet therapy is effective for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly, and its effectiveness is influenced by age at treatment initiation, severity of head asymmetry, and daily duration of helmet wear.
Meaning: Pediatricians should initiate helmet therapy for positional plagiocephaly sooner, ideally before 9 months of age, to maximize treatment efficacy.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmia and COVID-19 in children (1,478 times)
- Mi Kyoung Song, Bryan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):190-200. Published online April 18, 2023
-
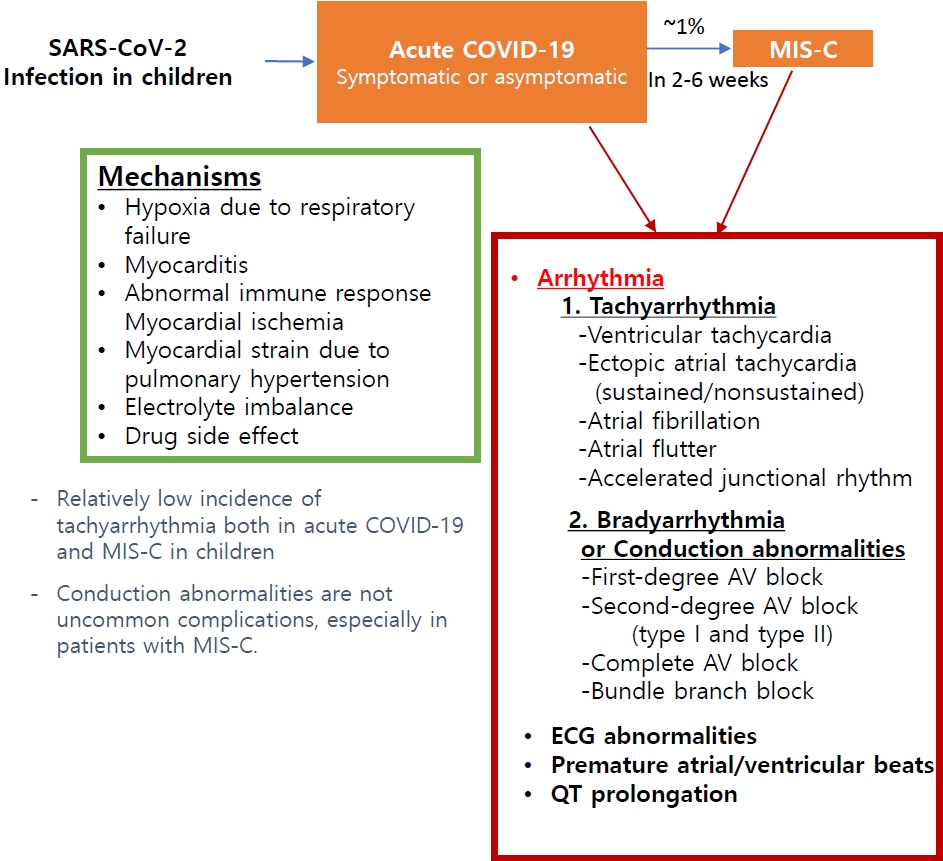
· Pediatric patients have a relatively low incidence of tachyarrhythmia both in acute coronavirus disease 2019 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), but it was associated with an increased risk of poor outcomes.
· Conduction abnormalities were not uncommon, especially in those with MIS-C. Most patients recovered to normal sinus rhythm; however, some progressed to advanced atrioventricular block and rarely required permanent pacemaker implantation.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models (1,433 times)
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents (1,421 times)
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
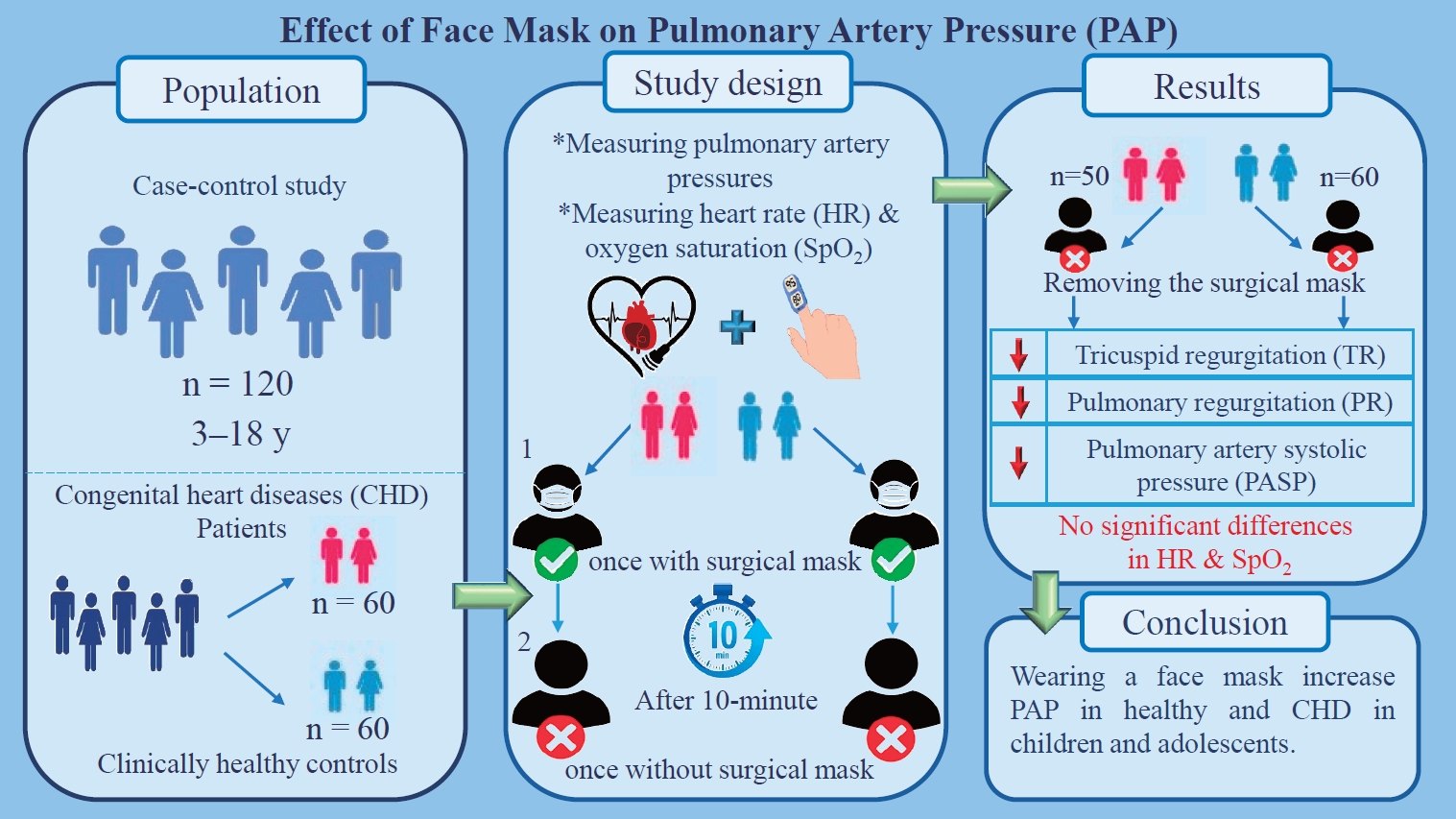
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Efficacy of body position on gastric residual in preterm infant: a systematic review and meta-analysis (1,405 times)
- Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Prabhaker Mishra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):262-270. Published online November 30, 2022
-
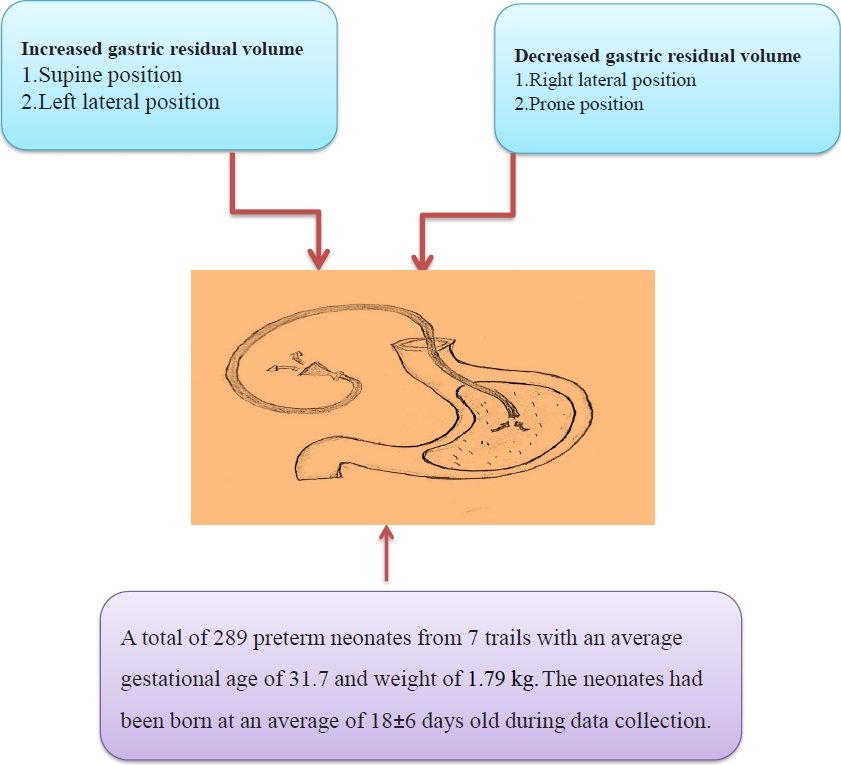
Breastfeeding and it's tolerance are the positive indicators for preterm babies. Placing the preterm infant in the right lateral or prone position after feed had lesser gastric residual volume compared to placing them in left lateral or supine positions. The post-feed position is a vital element in enhancing feeding tolerance, mechanical functions of the gastrointestinal tract and the overall development of preterm infants.
- Gastroenterology
- Inferior vena cava to aorta ratio in dehydrated pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis (1,403 times)
- Gilbert Sterling Octavius, Michelle Imanuelly, Johan Wibowo, Nadia Khoirunnisa Heryadi, Melanie Widjaja
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):477-484. Published online June 14, 2023
-
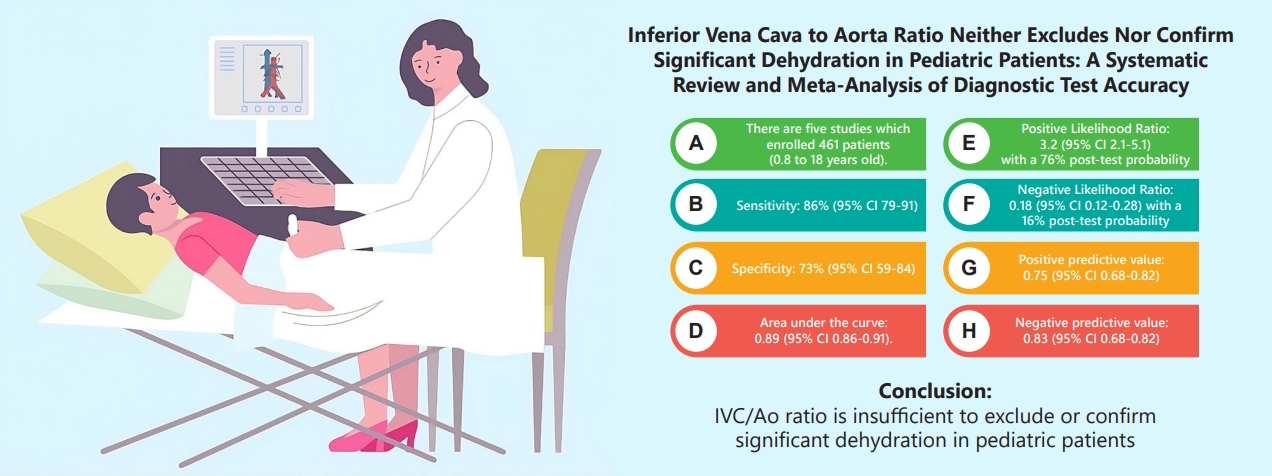
Question: The inferior vena cava to aorta (IVC/Ao) ratio measured via ultrasound has been touted as a promising noninvasive technique to assess clinically significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
Finding: Our meta-analysis found that IVC/Ao ratio had a positive likelihood ratio of 3.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–5.1) and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12–0.28).
Meaning: Hence, IVC/Ao ratio is insufficient to exclude or confirm significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
- Review Article
- Other
- Knowledge-guided artificial intelligence technologies for decoding complex multiomics interactions in cells (1,395 times)
- Dohoon Lee, Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):239-249. Published online November 26, 2021
-
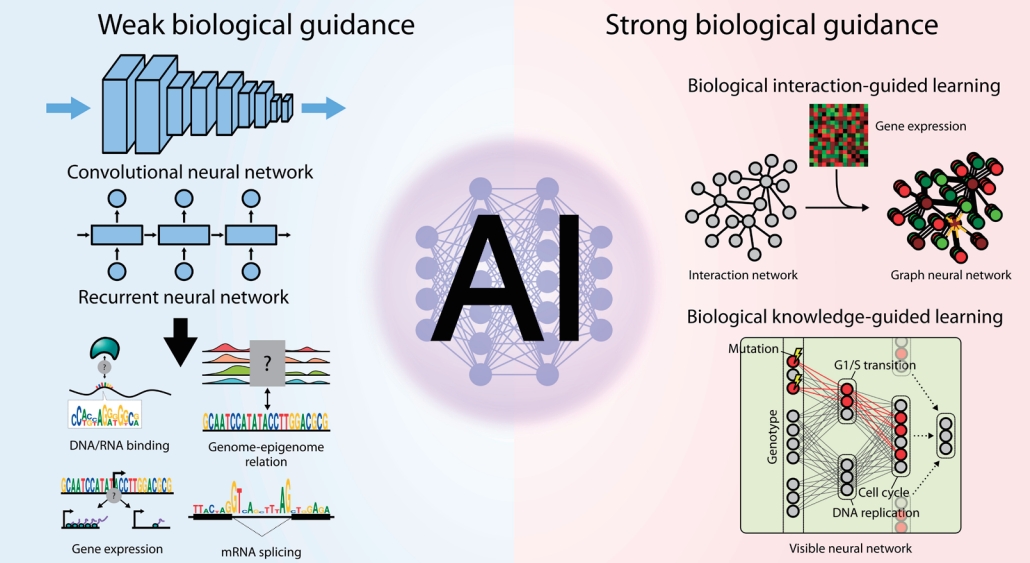
· The need for data-driven modeling of multiomics interactions was recently highlighted.
· Many artificial intelligence-driven models have been developed, but only a few have incorporated biological domain knowledge within model architectures or training procedures.
· Here we provide a comprehensive review of deep learning models to decipher complex multiomics interactions regarding the biological guidance imposed upon them to facilitate further development of biological knowledge-guided deep learning models.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







