Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review
- Sani Soleman, Muhammad Adnan, Hilmi Sudiarto, Satria Mahathma, Alya Tazkia, Hana Firdaus, Alfreda Khotijah, Miranti Pramaningtyas, Emi Choironi
-
Unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) in children owing to diethylene glycol (DEG) contamination during drug production has gained attention in recent years. This qualitative study investigated the effects of DEG exposure on the incidence of unknown AKI in children. A systematic review following the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis) guidelines was proposed to search for studies... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.01039 [Accepted]
- Nutrition
- Protein substitutions as new-generation pharmanutrition approach to managing phenylketonuria
- Fatma Nur Keskin, Teslime Özge Şahin, Raffaele Capasso, Duygu Ağagündüz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):320-331. Published online November 1, 2022
-
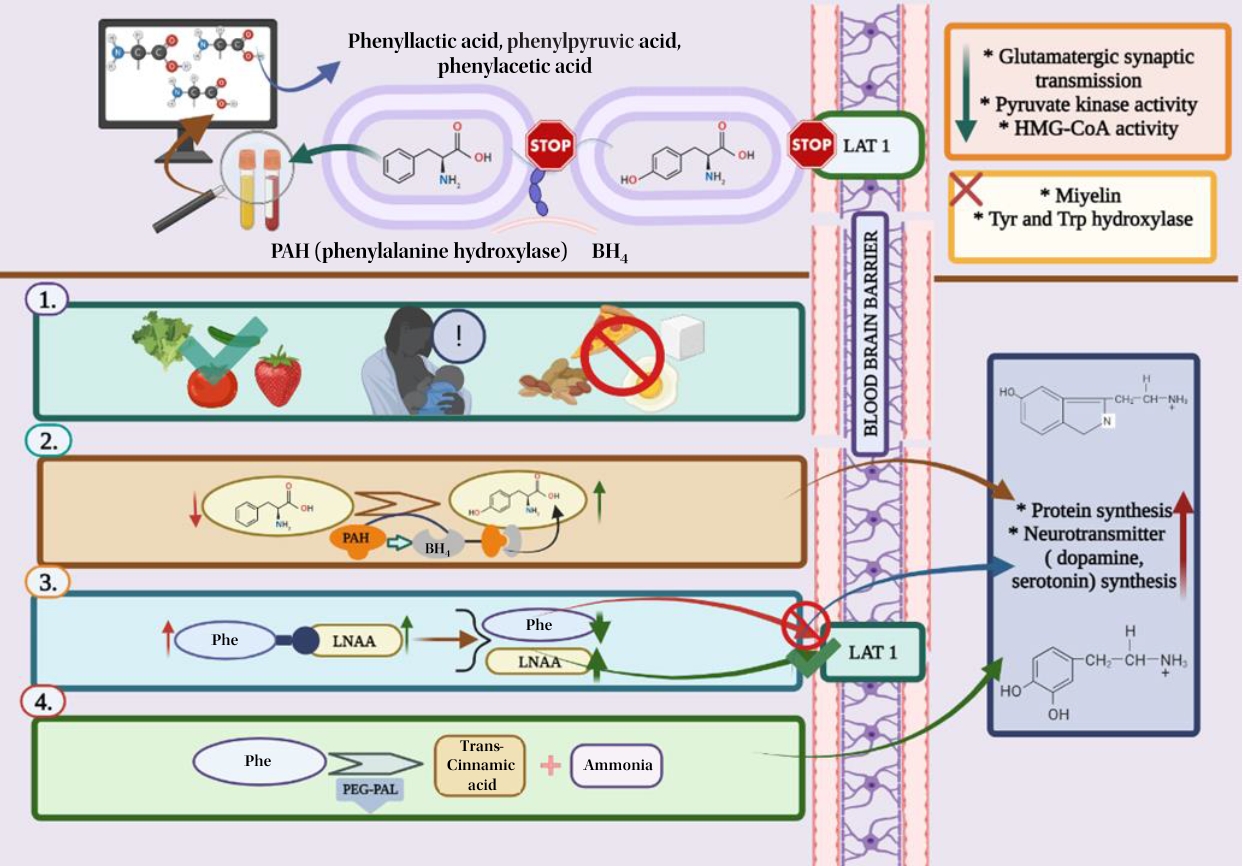
Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disease that results from the inability to metabolize phenylalanine, is currently treated with medical nutrition therapy. New treatment approaches such as tetrahydrobiopterin, glycomacropeptide, large neutral amino acids, pegvaliase, and gene therapy significantly impact disease management and dietary enrichment. This article also reviews animal and human studies that have evaluated the efficacy and safety of these new protein substitutes.
- Dietary intake and nutritional status of Korean children and adolescents: a review of national survey data
- Minji Kang, So Yoon Choi, Minyoung Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):443-458. Published online December 28, 2020
-
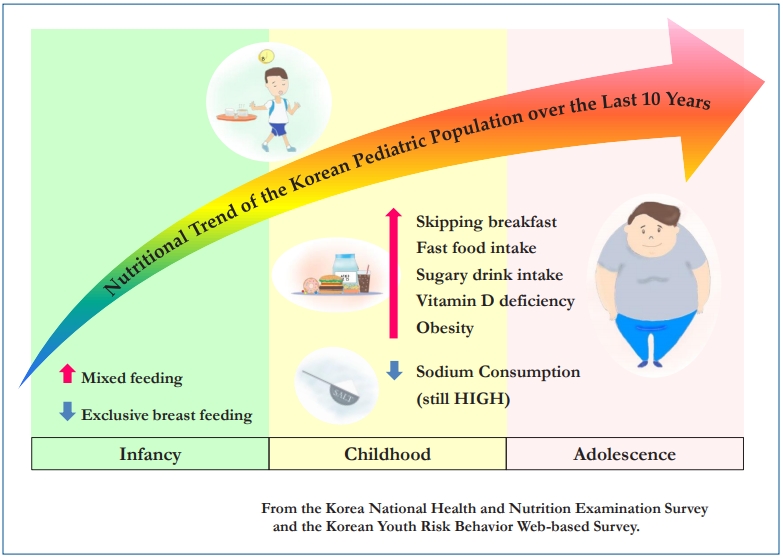
In Korea, several national cross-sectional surveys monitor the diet, nutritional status, and health status of children. This continual dedicated national surveillance system contributes to the identification of nutritional and health issues, establishment of public health policies, and development of nutrition recommendations. This paper provides recent information about the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and the Korean Youth Risk...
- Infection
- The COVID-19 pandemic: an unprecedented tragedy in the battle against childhood obesity
- Maximilian Andreas Storz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):477-482. Published online November 5, 2020
-

Large-scale quarantine and home confinement during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic will impose new and unfamiliar stressors on children, thereby worsening the childhood obesity epidemic. Physical, nutritional, and psychosocial factors that promote obesity in children during this special situation complementarily contribute to an unprecedented obesogenic environment. Involved stakeholders, including governments, schools, and families, must make all efforts to minimize the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on childhood obesity.
- Gastroenterology
- Increasing incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents: significance of environmental factors
- Sowon Park, Yunkoo Kang, Hong Koh, Seung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):337-344. Published online December 6, 2019
-
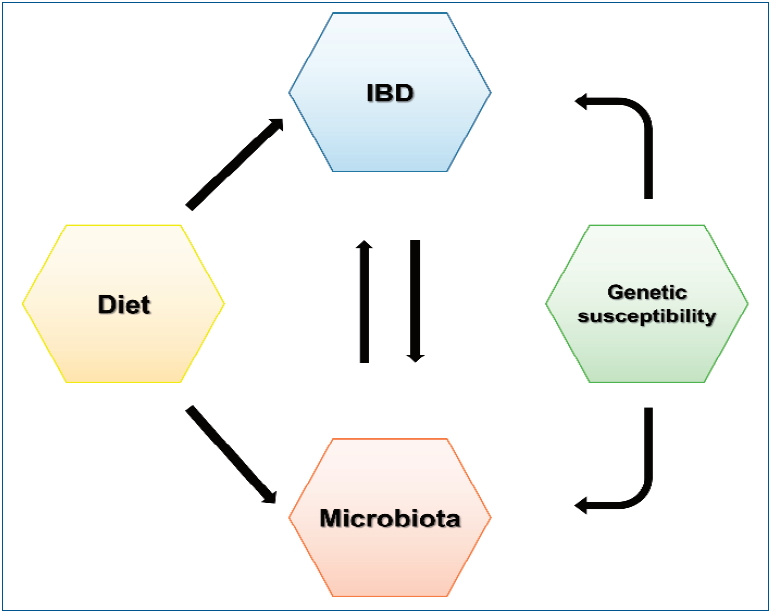
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic relapsing immune-mediated disease of the intestinal tract. Although its prevalence is reportedly lower in Asia than in Western countries, the rapid increase in the incidence of IBD has drawn attention to its etiology, including genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. Specifically, recent studies concerning dietary treatments and intestinal microbiota suggest that these factors may...
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- The effect of high fat dietary modification and nutritional status on the outcome of critically ill ventilated children: single-center study
- Nehal Mohamed El Koofy, Hanaa Ibrahim Rady, Shrouk Moataz Abdallah, Hafez Mahmoud Bazaraa, Walaa Ahmed Rabie, Ahmed Ali El-Ayadi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):344-352. Published online April 2, 2019
-
Background: Ventilator dependency constitutes a major problem in the intensive care setting. Malnutrition is considered a major determinant of extubation failure, however, attention has been attracted to modulating carbon dioxide production through decreasing carbohydrate loading and increasing the percent of fat in enteral feeds. The detected interrelation between substrate oxidation and ventilation outcome became the base of several research to...
- Gastroenterology
- Dietary habits and gastroesophageal reflux disease in preschool children
- You Jin Choi, Eun Kyo Ha, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(7):303-307. Published online July 31, 2016
-
Purpose To identify the relationship between dietary habits and childhood gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in preschool children.
Methods We performed a questionnaire study to analyze the relationship between dietary habits and GERD in 85 preschool children with GERD and 117 healthy children of the same age.
Results Irregular and picky eating were more p–revalent in the GERD group than in the control group (odds ratio...
- Review Article
- Food protein-induced proctocolitis: Is this allergic disorder a reality or a phantom in neonates?
- Jin-Bok Hwang, Jeana Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(12):514-518. Published online December 20, 2013
-
The etiology of small and fresh rectal bleeding in neonates who are not sick is usually unknown; the only known cause is food protein-induced proctocolitis (FPIPC). It has been recently reported that FPIPC is a rare cause of rectal bleeding in newborns, and most cases have been proved to be due to idiopathic neonatal transient colitis. A recommended strategy for...
- Lower fat and better quality diet therapy for children with pharmacoresistant epilepsy
- Jung-Rim Yoon, Heung Dong Kim, Hoon-Chul Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(8):327-331. Published online August 27, 2013
-
The ketogenic diet (KD) is an established, effective, nonpharmacologic treatment for children with pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Although the KD is the most well-established dietary therapy for epilepsy, it is too restrictive and is associated with serious complications; therefore, alternative lower-fat diets, including a modified Atkins diet and low-glycemic index diet, have been developed. Recent ongoing clinical evidence suggests that other dietary...
- The use of ketogenic diet in special situations: expanding use in intractable epilepsy and other neurologic disorders
- Munhyang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(9):316-321. Published online September 14, 2012
-
The ketogenic diet has been widely used and proved to be effective for intractable epilepsy. Although the mechanisms underlying its anti-epileptic effects remain to be proven, there are increasing experimental evidences for its neuroprotective effects along with many researches about expanding use of the diet in other neurologic disorders. The first success was reported in glucose transporter type 1 deficiency...
- Original Article
- Dietary patterns and metabolic syndrome risk factors among adolescents
- Hyojee Joung, Soyoung Hong, Yoonju Song, Byung Chul Ahn, Mi Jung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(4):128-135. Published online April 30, 2012
-
Purpose Unbalanced diets and decreased physical activity have contributed to increased prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome in adolescents. We have performed a systematic review and data analysis to examine the association between dietary pattern and metabolic syndrome risk factors in adolescents.
Methods We searched the PubMed and BioMedLib databases for appropriate articles published during the past 10 years and selected 6 articles....
- Review Article
- Treatment and management of patients with inherited metabolic diseases
- Jin-Sung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(11):1152-1157. Published online November 15, 2006
-
Inherited metabolic disease is rare disorders that show symptoms mainly in pediatric age and early treatment is important for preventing complications of the disease. Recent development in molecular and biochemical techniques help clinicians with proper diagnosis of patients, however, many of the disease still remain lack of effective therapeutic strategies. Better understanding on biochemical and molecular basis of pathogenesis of... -
- Original Article
- The efficacy of ketogenic diet in childhood intractable epilepsy with malformation of cortical development
- Young-Mock Lee, Du Cheol Kang, Da Eun Chung, Hoon Chul Kang, Heung Dong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(2):192-197. Published online February 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Malformation of cortical development(MCD) constitutes an important etiology of intractable epilepsy and is considered an indication for surgical treatments, though their efficacy is limited and variable depending on MCD's location or distribution. Ketogenic diets are widely known to be effective, but as little study has been made concerning their efficacy on epilepsy with MCD, we evaluated the efficacy... -
- Case Report
- Two Cases of Renal Stone Associated with Ketogenic Diet
- Ju-Young Chung, Ja-Wook Koo, Hoon-Churl Kang, Sang-Woo Kim, Heung-Dong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(2):204-207. Published online February 15, 2005
-
Ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, low-protein diet used in the treatment of epilepsy since 1920's. Recently, it's use for intractable epilepsy in childhood has increased. Complications of ketogenic diet are known to include dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea, renal stones, metabolic derangement, hypercholesterolemia and refusal to eat. We experienced two cases of renal stones in children with intractable epilepsy during ketogenic... -
- A Case of Infantile Spasm Associated with Acute Renal Failure and Kwashiorkor after Ketogenic Diet
- Young-Myoung Kim, Tae-Hong Kim, Jin-A Jung, Kyu-Geun Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(11):1131-1134. Published online November 15, 2003
-
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-protein, low-carbohydrate diet developed in the 1920s for the treatment of difficult-to-control seizures. Despite advances in both the pharmacotherapy and the surgery of epilepsy, many children continue to have difficult-to-control seizures. In this situation, a ketogenic diet should be considered as an alternative therapy. However, less attention has been paid to associated adverse events... -
- Original Article
- Nutritional Assessment and the Effectiveness of Dietary Counseling in Infants and Young Children with Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Ja Kyoung Kim, Eun Young Ko, Yu Jin Lee, Yong Hun Jun, Soon Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(1):11-16. Published online January 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Iron deficiency is still the most common nutrient deficient disorder despite the improvement in general health and nutrition. This study is designed to evaluate the dietary history of infants and young children with iron deficiency anemia(IDA) and the effects of nutritional counseling. Methods : This study was conducted on 120 children from 6 to 36 months of age with... -
- Case Report
- Three Cases of Urine Abnormalities Associated with Ketogenic Diet
- Hye Won Hahn, Ki Jung Kim, Il Soo Ha, Hae Il Jung, Yong Seung Hwang, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(6):709-713. Published online June 15, 2001
-
Ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low carbohydrate, low protein diet used in treatment of pediatric epilepsy since the 1920s. Currently it is used primarily to treat refractory childhood epilepsy. Few serious complications caused by ketogenic diet have been reported. Short-term complications include dehydration, hypoglycemia, vomiting, diarrhea, and refusal to eat. Long-term complications include kidney stones, recurrent infections, metabolic derangement, hypercholesterolemia,... -
- A Case of Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency Successfully Treated with Protein Restriction and Living Related Liver Transplantation
- Bong Seong Kim, Kyung Mo Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Sung Gyu Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(6):868-873. Published online June 15, 1999
-
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency(OTCD), the most common inborn error of the urea cycle, is inherited in X-linked manner. In affected hemizygote males, OTCD manifests hyperammonemic coma that often leads to death during the newborn period. Our patient was at high risk for inborn error of urea cycle metabolism, since his two elder brothers died a few days after birth due to... -
- Erratum
- Reference Values of Hematologic and Biochemical Parameters of Nutrition around Weaning Period
- Seung Joo Lee, Jeong Wan Seo, Jae Ock Park, Jae Hoon Shin, Hae Ran Lee, Ji Tae Chung, Hae Il Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(1):6-14. Published online January 15, 1999
-
Purpose : To determine the reference values of hematologic and biochemical parameters of nutrition around the weaning period. Methods : From February 1996 to March 1997, several nutritional laboratory values were evaluated in 130 healthy babies and 120 inpatients in the recovery stage of acute illness at six general hospitals. Results : Reference values in 9-month-old healthy babies(range : 6-12 months) were... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Dietary Treatment of Vitamin B12 Non-responsive Methylmalonic Acidemia
- Won Young Song, Ki Soo Kim, Han Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(4):549-554. Published online April 15, 1997
-
Methylmalonic acidemia is a metabolic disorder of amino acid and fatty acid metabolism. A Female infant, who was diagnosed as methylmalonic acidemia based on findings; methylmalonic aciduria, metabolic acidosis with increased anion gap, hyperammonemia, has been followed up for 9 months. She has been placed on the planned diet according to Ross metabolic formula nutrition support protocol. The diet is... -
- Original Article
- Body Composition of Children and Adolescents with Insulin-dependetn Diabetes Mellitus
- Hye Young Kang, Mi Jung Park, Duk Hi Kim, You Kyung Park, Jong Ho Lee, Ho Seong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(12):1709-1716. Published online December 15, 1994
-
Bodycomposition measurement is useful in the diagnosis of pathoogy, assessment of disease process and response to treatment in many endoclonologic and metabolic diseases. The Techniques used currently are mostly indirect, often expensive, difficult and time-consuming. A new method for estimation of body composition, infrared interactance, is rapid, safe, noninvasive, and may be useful in research ad clinical studies. Body composition was... -
- The effect of dietary fats of immune response in sublethally irradiated rats.
- Soon Hwan Oh, Dong Soo Kim, Hae Won Nam, Juhn Kyu Loh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(11):1494-1504. Published online November 30, 1991
-
To investigate the effect of dietary fats on cellular immune response in the immunosuppressed rats, different compositions in the quality and quantity of dietary fats were fed to sublethally irradiated male rats. The results are as follows; 1) After 2 weeks of irradiation, the mean body weight of the fat free dietary group was significant- ly lower than the com oil group. The organ weight, especially... -
- Effect of dietary fats on immune response in rats.
- Soon Hwan Oh, Dong Soo Kim, Hae Won Nam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(10):1334-1345. Published online October 31, 1991
-
To investigate the effect of dietary fats on the humoral and cellular immune response, different compositions in the quality and quantity of dietary fats were fed to male rats. The results are as follows; 1) The mean body weights of the rats which were fed the various dietary fats were not significant during the experimental period. The weights of the organs measured were the spleen,... -
- Case Report
- Dietary Hypocalcemic Tetany.
- Kyu Hyung Lee, Chang Bin Im, Yoon Taik Kim, Keun Chan Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(5):483-487. Published online May 31, 1984
-
Hypocalcemic tetany is important cause of convulsion during perinatal or infantile period. We have experienced three cases of dietary hypocalcemic tetany, which was induced by non-fortified commerical weaning food or breast-fed without vitamine supplement. So we report the cases with review of the related literature. -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







