Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Development of orphan drugs for rare disease
- Han-Wook Yoo
-
Most rare diseases(orphan diseases) still lack approved treatments despite major advances in research providing the tools to understand their molecular basis, as well as legislation providing regulatory and economic incentives to expedite the development of specific therapies. Addressing this translational gap is a multifaceted challenge, for which a key aspect is the selection of the optimal therapeutic modality for translating... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.00535 [Accepted]
- Allergy
- Drug Allergy in Children: What Should We Know?
- Ji Soo Park, Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):203-210. Published online November 12, 2019
-

The drug allergy “label” may have a lifetime of consequences for a child. Many children with alleged drug allergies are proven to be tolerant to the culprit medication when challenged. The field of drug hypersensitivity is a recently evolving field of research, but studies on its epidemiology and diagnostic tools are lacking in children. Clinical history is significant in the...
- Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neurobehavior
- Evaluation of drug interventions for the treatment of sleep disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Sara Ataei, Saeid Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):405-409. Published online October 2, 2019
-
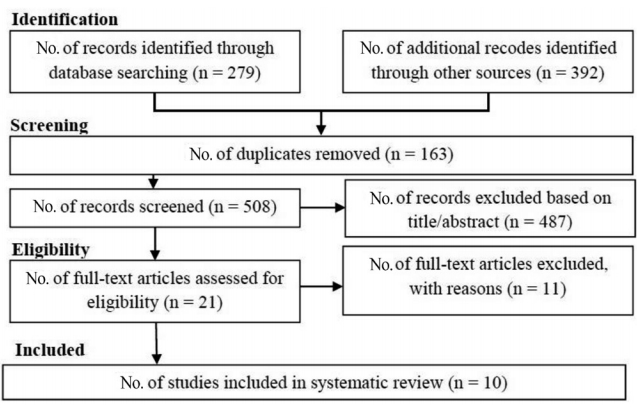
A structured review study of drug interventions on sleep disorders in patients with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) has not been published to date. This systematic review aimed to investigate drug interventions for the treatment of sleep disorders in children with ASD. The Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus databases were searched until March 2019. Study quality was assessed using the...
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Benefits and risks of therapeutic alternatives for macrolide resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):199-205. Published online March 15, 2019
-
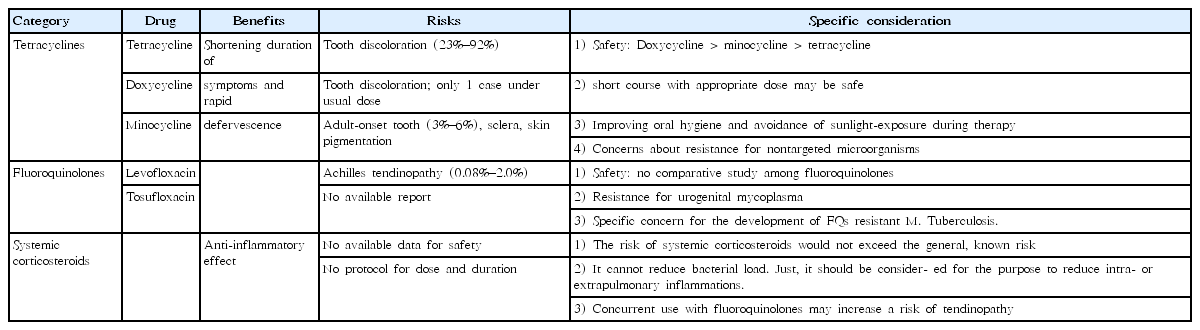
Although Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) has been generally susceptible to macrolides, the emergence of macrolide-resistant MPP (MRMP) has made its treatment challenging. MRMP rapidly spread after the 2000s, especially in East Asia. MRMP is more common in children and adolescents than in adults, which is likely related to the frequent use of macrolides for treating M. pneumoniae infections in children....
- Case Report
- Allergy
- Drug eruption by antihistamine mistaken for chronic urticaria in a child
- Gun Moo Lee, Shou-Yu Chu, Sung Yeon Kang, Hyo-Bin Kim, Jin-Sung Park, Ja Kyoung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(2):75-78. Published online October 30, 2018
-
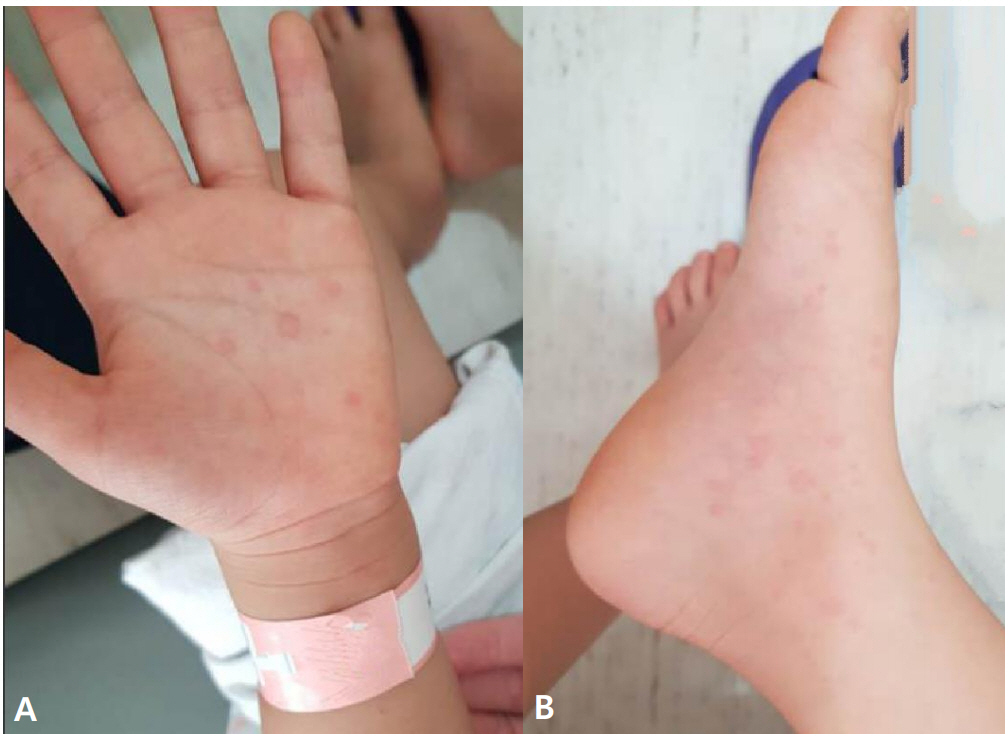
Although rare, antihistamines can cause adverse effects, including drug-induced eruptions or anaphylaxis. A 4-year-old child visited the pediatric department of a hospital for skin eruptions after administration of antihistamines, (e.g., ucerax [hydroxyzine] or leptizine [levocetirizine]), for cholinergic rashes; he did not have pruritus. Skin prick, intradermal, and drug provocation tests were performed to determine the relationship between the antihistamines and...
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Increased procalcitonin level is a risk factor for prolonged fever in children with Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Ji Eun Jeong, Ji Eun Soh, Ji Hee Kwak, Hye Lim Jung, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Moon Soo Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):258-263. Published online August 15, 2018
-
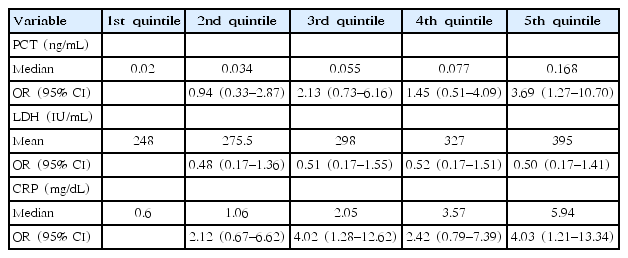
Purpose: Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is characterized by prolonged fever and radiological progression despite macrolide treatment. Few studies have examined serum procalcitonin (PCT) level in children with MPP. We aimed to investigate the association of acute inflammation markers including PCT with clinical parameters in children with MPP. Methods: A total of 147 children were recruited. The diagnosis of MPP...
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Mechanism of resistance acquisition and treatment of macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children - Hyeon-Jong Yang, Dae Jin Song, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(6):167-174. Published online June 22, 2017
-
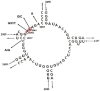
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is one of the most common forms of community-acquired pneumonia in children and adolescents. Outbreaks of MPP occur in 3- to 7-year cycles worldwide; recent epidemics in Korea occurred in 2006–2007, 2011, and 2015–2016. Although MPP is known to be a mild, self-limiting disease with a good response to macrolides, it can also progress into a...
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Prevalence and clinical manifestations of macrolide resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children - Eun Lee, Hyun-Ju Cho, Soo-Jong Hong, Jina Lee, Heungsup Sung, Jinho Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(5):151-157. Published online May 31, 2017
-
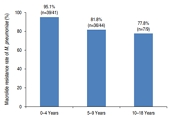
Purpose Macrolide resistance rate of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae has rapidly increased in children. Studies on the clinical features between macrolide susceptible-M. pneumoniae (MSMP) and macrolide resistant-M. pneumoniae (MRMP) are lacking. The aim of this study was to identify the macrolide resistance rate ofM. pneumoniae in Korean children withM. pneumoniae penupmonia in 2015 and compare manifestations between MSMP and MRMP.Methods Among 122...
- Case Report
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by lamotrigine treatment in a child
- Youngsuk Yi, Jeong Ho Lee, Eun Sook Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(3):153-156. Published online March 31, 2014
-
Toxic epidermal necrolysis is an unpredictable and severe adverse drug reaction. In toxic epidermal necrolysis, epidermal damage appears to result from keratinocyte apoptosis. This condition is triggered by many factors, principally drugs such as antiepileptic medications, antibiotics (particularly sulfonamide), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, allopurinol, and nevirapine. Lamotrigine has been reported potentially cause serious cutaneous reactions, and concomitant use of valproic acid...
- Review Article
- Antibiotics resistance of
Helicobacter pylori and treatment modalities in children withH. pylori infection - Ji-Hyun Seo, Hyang-Ok Woo, Hee-Shang Youn, Kwang-Ho Rhee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(2):67-71. Published online February 24, 2014
-
Pediatric infection with
Helicobacter pylori may occur early in childhood and persist lifelong. Global pediatric clinical studies have reported a decreasing tendency in the overall rate ofH. pylori eradication. In pediatric patients withH. pylori infection, pediatric patients with peptic ulcer, and the first-degree relatives of patients with a history of gastric cancer, it is commonly recommended thatH....
- Original Article
- Early-onset sepsis in a neonatal intensive care unit in Beni Suef, Egypt: bacterial isolates and antibiotic resistance pattern
- Sameh Samir Fahmey
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(8):332-337. Published online August 27, 2013
-
Purpose To identify the frequency of bacterial isolates in early-onset neonatal sepsis (EONS) and their antimicrobial resistance pattern.
Methods A retrospective study of EONS was conducted at the Beni Suef University Hospital from September 2008 to September 2012. A case of EONS was defined as an infant who had clinical signs of infection or who was born to a mother with risk factors...
- Review Article
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children- You-Sook Youn, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(2):42-47. Published online February 14, 2012
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP), the smallest self-replicating biological system, is a common cause of upper and lower respiratory tract infections, leading to a wide range of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary manifestations. MP pneumonia has been reported in 10 to 40% of cases of community-acquired pneumonia and shows an even higher proportion during epidemics. MP infection is endemic in larger communities of the...
- Case Report
- An adverse event following 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccination: a case of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
- Sang Teak Lee, Young June Choe, Won Jin Moon, Jin Woo Choi, Ran Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(10):422-424. Published online October 31, 2011
-
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system that typically follows an infection or vaccination and has a favorable long-term prognosis. We describe the first reported case of ADEM after vaccination against novel influenza A (H1N1). A previously healthy 34-month-old boy who developed ADEM presented with a seizure and left-sided weakness 5 days after...
- Original Article
- Usefulness of drug provocation tests in children with a history of adverse drug reaction
- Hye Ran Na, Jeong Min Lee, Jo Won Jung, Soo-Young Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(7):304-309. Published online July 31, 2011
-
Purpose There are very few reports of adverse drug reactions (ADR) and almost no study of drug provocation test (DPT) in Korean children. We aimed to assess the role of DPT in children with unpredictable ADRs, and compare the causative drugs and clinical characteristics between detailed history of ADRs and result of DPTs.
Methods We included 16 children who were experienced ADRs referred...
- Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin according to initial dosing regimen in pediatric patients
- Dae Il Kim, Mi Sun Im, Jin Hyoung Choi, Jina Lee, Eun Hwa Choi, Hoan Jong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(12):1000-1005. Published online December 31, 2010
-
Purpose This study aimed to determine the optimal initial vancomycin dose to achieve appropriate trough levels in pediatric patients.
Methods We analyzed clinical data for 309 children treated with intravenous vancomycin between 2004 and 2009 at 2 different hospitals in South Korea. The patients were 1-16 years old and exhibited normal renal function. Patient data, including reason for treatment and initial dosing regimen,...
- Review Article
- Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Kwang Nam Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(11):936-941. Published online November 30, 2010
-
The systematic approach to pharmacologic treatment is typically to begin with the safest, simplest, and most conservative measures. It has been realized that the more rapidly inflammation is under control, the less likely it is that there will be permanent sequelae. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the mainstay of initial treatment for inflammation. In addition, the slow-acting antirheumatic drugs (SAARDs)...
- Original Article
- Change of interictal epileptiform discharges after antiepiletic drug treatment in childhood epilepsy
- Mun Ju Kim, Sang Ook Nam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):560-564. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Electroencephalography (EEG) findings can play a critical role in a variety of decisions, including initiation and withdrawal of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) therapy. Interictal epileptiform discharges (IEDs) are predictor of recurrent seizures. We investigated IEDs in EEG after AED therapy and related factors in epileptic children. Methods : The subjects were 257 children [151 males and 106 females; age,... -
- Review Article
- Pediatric tuberculosis and drug resistance
- Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(5):529-537. Published online May 15, 2009
-
Drug-resistant tuberculosis in children has important implications for both the patients and tuberculosis control programs. In Korea, among all new patients, the isoniazid resistance rate was 9.9% and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis rate was 2.7% in 2004 (in patients aged 10-19 yr, the multidrug-resistant tuberculosis rate reached 2.1%). Tuberculosis in pediatric patients is difficult to diagnose because many children have nonspecific clinical... -
- Treatment of latent tuberculous infection in children and adolescent
- Jong-Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(5):519-528. Published online May 15, 2009
-
Tuberculosis continues to cause an unacceptably high toll of disease and death among children worldwide. Whereas intense scientific and clinical research efforts into novel diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive interventions have focused on tuberculosis in adults, childhood tuberculosis has been relatively neglected. However, children are particularly vulnerable to severe disease and death following infection, and those with latent infection become the... -
- Original Article
- Drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in children
- Soo Jin Lee, Young Min Ahn, Hee Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(1):61-67. Published online January 15, 2009
-
Purpose : The rate of drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) in children is an indicator of the effectiveness of TB control programs in the community. This study aimed to assess the prevalence of DR-TB in children and evaluate TB management. Methods : Between January 1999 and July 2007, drug susceptibility tests for anti-TB drugs were employed for patients aged less than 19... -
- Case Report
- A case of vancomycin-induced drug hypersensitivity syndrome
- Kyung Sun Min, Woo Yeon Choi, Eun Song Song, Dong Kyun Han, Young Kuk Cho, Jae Sook Ma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1228-1231. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Drug hypersensitivity syndrome (DHS) has rarely been reported in association with vancomycin treatment. Here, we describe an 11-year-old girl who developed fever and a maculopapular rash on day 18 of intravenous vancomycin for treatment of infective endocarditis. The patient presented with fever, a maculopapular skin rash, hepatitis, and acute renal failure caused by vancomycin-induced DHS. The symptoms resolved in less... -
- Original Article
- Health and risk taking behaviors of freshmen in college
- Hong Ki Ko, Jae Joon Han, Yoon Lee, Young Yoo, Kee Hyoung Lee, Ji Tae Choung, Sang Hee Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1042-1049. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : This study was conducted to survey the preliminary data on risk behaviors and to identify the factors that prevent risk-behaviors in late adolescence. Methods : Freshmen(n=1,297) beginning the first semester in Korea University, Seoul, Korea completed self-administered risk behavior questionnaires, comprising 5 domains : demographics, smoking, drinking, drug abuse and sexual behavior. Results : The rate of smoking experience was... -
- The effect of local rifampicin instillation on the treatment of suppurative BCG lymphadenitis
- Min Son Kim, Dae Sun Jo, Kang Mi Kyung, Sang Jae Kim, Jung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(1):40-45. Published online January 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to evaluate the types of lymphadenitis after BCG vaccination and the effect of local rifampicin instillation on the treatment of suppurative BCG lymphadenitis. Methods : A total of 32 otherwise healthy infants with suppurative BCG lymphadenitis, who visited the Department of Pediatrics of Chonbuk National University Hospital, from March 2002 through June 2004,... -
- Clinical Lecture
- The Pharmacotherapy of Childhood Epilepsy
- Sang Ook Nam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(8):821-826. Published online August 15, 2004
-
Epilepsy is one of the most common and disabling neurologic disorders in childhood. The primary goal of epilepsy treatment is to choose the treatment modality that provides the best chance of improving the patient's quality of life. In addition to classic antiepileptic drugs, newly developed antiepileptic drugs ketogenic diet, epilepsy surgery, and vagal nerve stimulation have improved the ability to... -
- Original Article
- Outcome after Discontinuation of Antiepileptic Drugs in Well Controlled Epileptic Children - Recurrence and Related Risk Factors
- Hyo-Bin Kim, Su Jeong You, Tae-Sung Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):66-75. Published online January 15, 2004
-
Purpose : There has been no exact criteria established for when to discontinue antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in epileptic children who had been well controlled for a long period. This study was undertaken to evaluate the recurrence rate and predictive risk factors of relapse after discontinuation of AEDs in epileptic children who had been seizure-free. Methods : We retrospectively studied 294 children... -
- Efficacy of Antiepileptic Drug on the Benign Childhood Epilepsy with Centro-Temporal Spikes
- Mee Hye Oh, Soo Young Kim, Won Hee Seo, Dae Hun Pee, Byung Min Choi, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(9):893-897. Published online September 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes(BECT) is characterized by an excellent prognosis. Therefore, the necessity for the use of antiepileptic drugs is controversial. The object of this study is to know about the long-term follow-up of BECT, comparing daily treatment with antiepileptic drug(AED) versus no medication. Methods : We retrospectively studied 56 cases of BECTs, examined at Pediatric Neurology... -
- A Follow-Up Study after Discontinuation of Antiepileptic Drug Therapy in Children with Well-Controlled Epilepsy : The Factors that Influence Recurrence
- Sa Jun Chung, Hye Jeon Chung, Young Mi Choi, Eu Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(12):1559-1570. Published online December 15, 2002
-
Purpose : There has been no exact answer to the question of when to discontinue antiepileptic drugs(AEDs) in children with well-controlled epilepsy for a long period. This study is about the risk factors of relapse after withdrawal of AEDs in seizure(Sz)-free patients to show a guideline for discontinuation of AEDs. Methods : One hundred and sixty-nine children were diagnosed as epileptic... -
- A Study on the Disease Course and Prognosis of Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
- Hye Ran Yang, Jae Sung Ko, Jeong Kee Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(10):1141-1156. Published online October 15, 2001
-
Purpose : To describe clinical features of cyclic vomiting syndrome(CVS), managements during episodes, prophylactic drugs as long term therapy and to investigate the disease course and prognostic factors of CVS. Methods : Thirty two children who fulfilled the diagnostic criteria of CVS and who presented to Seoul National University Children's Hospital from March 1989 to December 2000, were included. Data were... -
- Treatment Outcome of Penicillin-resistant S. Pneumoniae Infection
- Min Sook Choi, Young Won Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Kyung Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(2):149-153. Published online February 15, 2001
-
Purpose : Streptococcus pneumoniae is a normal flora and common pathogen of the upper respiratory tract. S. pneumoniae infections are estimated to cause not only localized infection such as pneumonia, and otitis media, but also systemic infections, for example meningitis, sepsis, and so on. Recently, the resistance of S. pneumoniae to penicillin and multidrug has been rapidly increasing in many... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Fixed Drug Eruption Due to Acetaminophen
- Eui Jeong Min, Dae Hyun Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Seung Won Choi, Byong Kwan Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(8):1149-1152. Published online August 15, 2000
-
Fixed drug eruption normally presents as single or multiple sharply demarcated erythematous lesions that recur at the same location upon re-exposure to the offending agent. When the acute inflammation subsides, it often leaves residual hyperpigmentation. Commonly implicated substances are phenolphthalein, barbiturates, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, salicylates, gold and pyrazolone derivatives. Despite frequent use of acetaminophen, drug eruptions, especially fixed drug eruptions, due... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







