Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review article
- Evidence-based management guidelines for noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in children and adolescents
- Eun Lee, Kyunghoon Kim, You Hoon Jeon, In Suk Sol, Jong Deok Kim, Taek Ki Min, Yoon Ha Hwang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Dong In Suh, Hwan Soo Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Sung-Il Woo, Yong Ju Lee, Sungsu Jung, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Gwang Cheon Jang
-
Noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis is a chronic respiratory disease that carries high socioeconomic and medical burdens and is caused by diverse respiratory illnesses. To improve clinical outcomes, early recognition, active treatment of exacerbations, and prevention of further exacerbations are essential. However, evidence for the treatment and prevention of acute exacerbation of noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis, especially in children, is lacking. Therefore, the... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.00871 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Liver fibrosis in children: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapy
- Elif Ozdogan, Cigdem Arikan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):110-124. Published online December 19, 2022
-
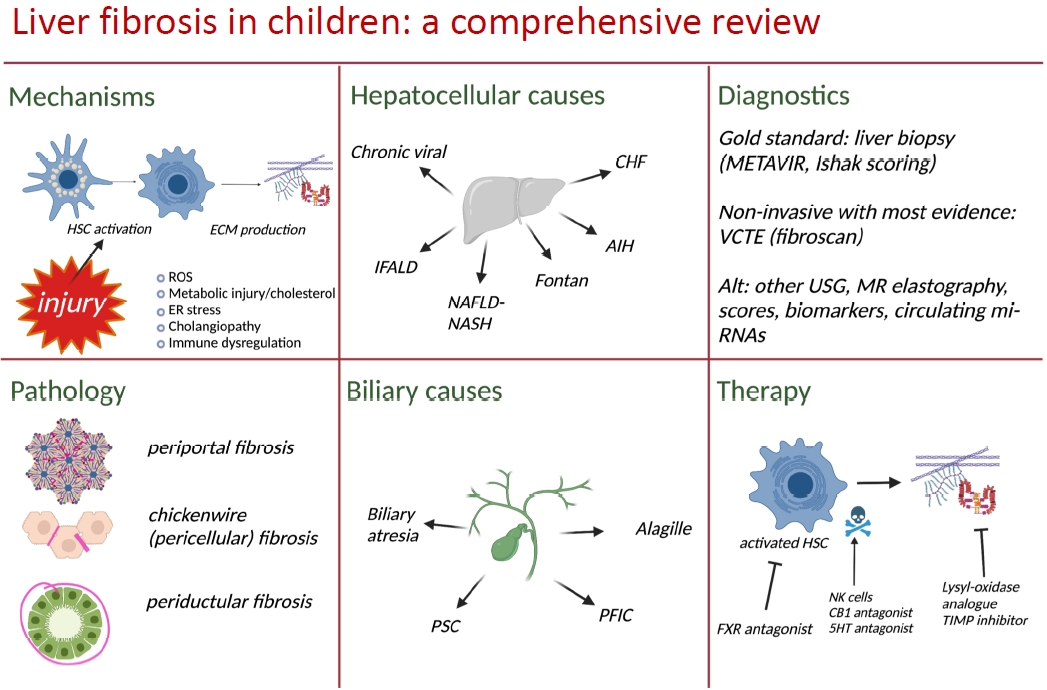
· Chronic liver diseases in children are heterogenous but converge in the common pathway of fibrosis.
· Much of the literature on mechanisms of fibrogenesis focus on adults but pediatric physiology has documented differences.
· Understanding of these distinctions are necessary to define, treat, and prevent fibrosis.
· Current management of liver fibrosis relies heavily on liver biopsy. Multiple tools have shown high diagnostic performance in pediatric and adult populations. Large, multicenter studies are needed for validation.
- Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans in children: lessons from bronchiolitis obliterans after lung transplantation and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Jinho Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(12):459-465. Published online December 22, 2015
-
Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans (PIBO) is an irreversible obstructive lung disease characterized by subepithelial inflammation and fibrotic narrowing of the bronchioles after lower respiratory tract infection during childhood, especially early childhood. Although diagnosis of PIBO should be confirmed by histopathology, it is generally based on history and clinical findings. Irreversible airway obstruction is demonstrated by decreased forced expiratory volume in 1...
- Case Report
- Cystic fibrosis of pancreas and nephrotic syndrome: a rare association
- Selvi Kelekçi, Müsemma Karabel, Aydın Ece, Velat Şen, Ali Güneş, İlyas Yolbaş, Cahit Şahin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(10):456-458. Published online October 31, 2013
-
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disease with autosomal recessive inheritance and is common in Caucasian people. The prevalence of this disease is between 1/2,000 and 1/3,500 live births, and the incidence varies between populations. Although the CF transmembrane conductance regulator gene is expressed in the kidneys, renal involvement is rare. With advances in the treatment of CF, life expectancy...
- Review Article
- Noninvasive diagnosis of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(2):45-51. Published online February 25, 2013
-
Because nonalcoholic steatohepatitis can progress towards cirrhosis even in children, early detection of hepatic fibrosis and accurate diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are important. Although liver biopsy is regarded as the gold standard of diagnosis, its clinical application is somewhat limited in children due to its invasiveness. Noninvasive diagnostic methods, including imaging studies, biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress,...
- Original Article
- The efficacy of aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for assessing hepatic fibrosis in childhood nonalcoholic steatohepatitis for medical practice
- Earl Kim, Yunkoo Kang, Seungmin Hahn, Mi Jung Lee, Young Nyun Park, Hong Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(1):19-25. Published online January 29, 2013
-
Purpose Childhood obesity is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and it has become one of the most common causes of childhood chronic liver diseases which significant as a cause of liver related mortality and morbidity in children in the United States. The development of simpler and easier clinical indices for medical practice is needed to identify advanced hepatic fibrosis...
- Review Article
- Renal fibrosis
- Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(7):735-740. Published online July 31, 2010
-
Renal fibrosis, characterized by tubulointerstitial fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis, is the final manifestation of chronic kidney disease. Renal fibrosis is characterized by an excessive accumulation and deposition of extracellular matrix components. This pathologic result usually originates from both underlying complicated cellular activities such as epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, fibroblast activation, monocyte/macrophage infiltration, and cellular apoptosis and the activation of signaling molecules such as...
- Original Article
- A case of cystic fibrosis presented with meconium ileus in a female neonate
- In-Ok Hwang, Eun-Sil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1252-1256. Published online December 15, 2007
-
Meconium ileus (MI) is the earliest clinical manifestation of cystic fibrosis (CF) in infants. It arises from the intraluminal accumulation of highly viscid, protein-rich meconium, typically present in the terminal ileum as a neonatal intestinal obstruction. Therefore, the clinical symptoms include abdominal distension, bilious vomiting and delayed passage of meconium. CF is caused by mutations in the transmembrane conductance regulator... -
- The Preventive Effect of Dexrazoxane and Pentoxifylline on Adriamycin Induced Cardiomyopathy
- Ling Zhu, Eun-Jung Bae, Il-Soo Ha, Jung-Wook Seo, Chung-Il Noh, Jung-Yun Choi, Yong-Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(12):1378-1384. Published online December 15, 2005
-
Purpose : We hypothesized dexrazoxane(DXR) and pentoxifylline(PTX) may prevent myocardial damage in adriamycin(ADR)-induced cardiomyopathic rat model. We also investigated their effects on the myocardial apoptosis and fibrosis in ADR induced cardiomyopathy. Methods : The six-week old female Spregue-Dawley rats were divided into control group(CNT, n= 4), ADR group(n=6), ADR+DXR group(DXR, n=5), ADR+PTX group(PTX, n=6), ADR+DXR+PTX group(DXPT, n=5). ADR(5 mg/week, twice) was... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis Accompanied by Renal Tubular Ectasia, Caroli Syndrome and Choledochal Cyst
- Bong Seok Choi, Sang Nam Bae, Yong Tak Im, Jae Hong Park, Chang Hoon Lee, Jun Woo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(7):923-927. Published online July 15, 2002
-
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is a relatively rare disease, characterized by bile ductular proliferation and prominent fibrosis in the portal area of liver resulting in portal hypertension. It is frequently associated with other abnormalities such as polycystic kidney, Caroli syndrome, cystic dysplasia of pancreas, intestinal lymphangiectasia, pulmonary emphysema, hemangioma, and cleft palate. We report here a case of congenital hepatic fibrosis... -
- Original Article
- A Catalogue of Gene Expression Difference in Biliary Cirrhosis due to Biliary Atresia Using Differential Expressed Sequence Tags(EST) Screening
- Byung-Ho Choe, Hyun-Mi Lee, Moon-Kyu Kim, Jung-Chul Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(1):60-69. Published online January 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Extrahepatic biliary atresia is the most common indication for liver transplantation in children, but the etiology of this disorders remains unknown. It would be very signficant to identify genes that are specifically expressed in pathologic liver tissue of biliary atresia and analyze the pattern of expression in those genes. Methods : We made dot blot panels consisting of 1,730 different EST(expressed sequence... -
- Longterm Follow-up of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
- June Huh, Il Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Jeong Kee Seo, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(12):1693-1699. Published online December 15, 1998
-
Purpose : This study was aimed to assess the clinical manifestations and courses of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease(ARPKD). Methods : The medical records of 10 children diagnosed as infantile or juvenile ARPKD at Seoul National University Children's Hospital between January, 1984 and December, 1996, were reviewed, retrospectively. Results : The average age at diagnosis was 3 8/12 years(4months-7 3/12 years)... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Secondary Hemosiderosis and Hepatic Fibrosis in a Pateint with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
- Hyoung No Kim, Jae Won Huh, Jae Sun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(3):420-424. Published online March 15, 1998
-
Chronic iron overload is associated with life-threatening complications, such as cardiomyopathy, liver cirrhosis, diabetes, hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism and hypogonadism. We experienced a case of secondary hemosiderosis with hepatic fibrosis in a 8-year-old boy who had been transfused 56 pints of packed red blood cells for a supportive therapy of acute myelogenous leukemia for a 27-month period. Intramuscular injection of Desferroxamine(40mg/kg/day) was... -
- Original Article
- The Effect of Alfacalcidol in the Treatment of Idiopathic Myelofibrosis in Children
- Soon Ki Kim, Jeong Hee Kim, Dae Hyun Lim, Jong Woon Choi, Byong Kwan Son, Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(3):339-346. Published online March 15, 1994
-
Idiopathic myelofibrosis (IMF), which is characterized by marrow fibrosis, leukoerythroblastic anemia, teardrop poikilocytosis and splenomegaly due to extramedullary hematopoiesis, has known to have no form of therapy. On the ground of the possibility of reversing collagen deposition in IMF using 1, 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol [1, 25(OH)2D3], we report here our observations of 5 patients (M:F = 1:4) with IMF before and after treatment... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Agnogenic Myeloid Metaplasia
- Byung Jin Kim, Byung Yeon Kim, Jung Sik Min, Ho Seong, Chang Hee Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(8):1178-1182. Published online August 15, 1993
-
Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia (AMM) is a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by leukoerythroblastosis, tear-drop erythrocytes, extramedullary hematopoiesis with hepatosplenomegaly, and varying degrees of myelofibrosis. The mean age at presentation is about 60 years, and pediatric cases are rare. We experienced a case of AMM in 9 months old female who was presented with pallor, huge splenomegaly and intermittent fever. Peripheral blood showed leukoerythroblastosis... -
- Two Cases of Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis
- Cue Jung Hwang, Young Hun Kim, Dae Kyun Koh, Byung Churl Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(4):569-574. Published online April 15, 1992
-
The congenital hepatic fibrosis is a rare condition defined pathologically by the presence within the line of bands of fibrous tissue which after contain linear or circular spaces lined by bile duct cells, It is commonly associated with intrahepatic portal hypertension but hepatocellular function is almost always preserved. The prinicipal clinical features of this disease are abdominal distension, firm hepatomegaly,... -
- Two Cases of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Young Gyun Oh, Seoung Hwan Kim, Mi Reong Kim, Byung Kiu Park, Hee-Shang Youn, Myung Kul Yum
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(1):122-128. Published online January 15, 1992
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a heterogeneous group of disorder which predominantly affects the lung parenchyma and spares the airway. We report two cases of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in a 2 year 11 month-old female and a 1 year 1 month-old male patients who were treated with steroid. These patients presented with dyspnea and showed fine crepitant rales in both lung... -
- Original Article
- A case of myelofibrosis with juvenile xanthogranuloma.
- Jong Chan Kim, Hae Yong Lee, Hwang Min Kim, Baek Keun Lim, Jong Soo Kim, Young Hyuk Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(6):869-876. Published online June 30, 1991
-
Myelofibrrosis is characterized by anemia, leukoerythroblastosis, extramedullary hematopoiesis, hepatosplenomegaly, osteosclerosis and fibrosis of bone marrow. Idiopathc myelofibrosis is usually a disease of the adult and is rare in the pediatric age group. Juvenile xanthogranuloma is characterized by multiple papules on forehead and scalp. Lipid laden histiocytes and Touton giant cell are found in skin biopsy. We experienced a case of myelofibrosis with juvenile xanthogranuloma.... -
- A case of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis.
- Hak Won Kim, Ho Joon Im, In Joon Seol, Ha Baik Lee, Hahng Lee, Seok Chol Jeon, Moon Hyang Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(1):107-114. Published online January 31, 1991
-
Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis is a rare, diffuse lug disease which has a tendency to destroy the lung architectures by consequent healing with progressively severe fibrosis. We report with a brief review of literature, one case of a 7-year old female with the typical pictures of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, histologically on open lung biopsy, and clinically presenting with chronic respiratory difficulty but without definite symptoms... -
- A Case of Agnogenic Myeloid Metaplasia.
- Min Sook Um, Jo Sam koo, Jae Sun Park, Sook Ja Park, Hae Kyung Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(11):1486-1493. Published online November 30, 1988
-
Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia characterized by marrow fibrosis, leukoerythroblastic anemia, extramedullary hematopoiesis with varying degree of hepatosplenomgaly, is very rare disorder in children. We experienced a case of agnogenic myeloid metaplasia 34 months old male patient who was presented with pallor, generalized petechiae, marked hepatosplenomegaly and intermittent fever. Peripheral blood smear showed leukoerythroblastosis, poikilocytosis and tear drop cells. Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy showed fibrosis with no... -
- A Case of Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis with Hypersplenism.
- Hye Suk Hong, Yang Won Lee, Keon su Rhee, Young Hun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1987;30(12):1456-1460. Published online December 31, 1987
-
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is a relatively rare disease of liver in children and young adults, manifesting a heredofamilial tendency, that is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly, protal hypertension and frequent renal involvement. A generalized portal and interlobular fibrosis of liver are characteristic finding on microscopy, with relative preservation of hepatocyte and liver function. Recently, we have experienced a case of congenital hepatic fibrosis in a... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Myelofibrosis.
- Ho Seong Yoo, Jin Heon Kim, Keun Chul Myung, Chang Soo Ra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(8):829-834. Published online August 31, 1983
-
Myelofibrosis is characterized by fibrosis of bone marrow, leukoerythrobla stotic anemia and extramedullary hematopoesis with varying degree of hepatosplenomegaly. Idiopathic myelofibrosis is primarily a disease of the adult and is rare in the pediatric age group. We experienced a case of idiopathic myelofibrosis in a 2 year 5 month old male who showed severe anemia with abnormal forms of red blood cell (teardrops, ovalocytes),... -
- A case of myelofibrosis.
- Hae Jung Cho, Keun Chull Choi, Chul Lee, Myong Ho Lee, Sook Ja Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1982;25(9):945-953. Published online September 30, 1982
-
The so called “Myelofibrosis” within the category of myeloproliferative disorders consists of various degrees of leukoerythroblatosis, bone marrow fibrosis, and extramedullary hema- topoiesis with hepatosplenomegaly. Primary myelofibrosis occurs predominantly in adults and few in childhood. We experie- nced one case of myelofibrosis, at 17 month old male patient. He was admitted due to intermittent fever, pallor and abdominal distension. On admission, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia and generalized petechia... -
- A Case of Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis.
- Son Moon Shin, Sang Il Lee, Joong Gon Kim, Hyo Seop Ahn, Hyung Ro Moon, Kwang Wook Ko, Je Geun Chi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(6):577-583. Published online June 15, 1981
-
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is a relatively rare liver disease in children and young adults,that is characterized by stony hard hepatomegaly and portal hypertension with relative preservation of liver function and underlying architecture. Since this Condition was first delineated by Kerr et al in 1961, approximately over 150 cases have been reported in the literature. However, congenital hepatic fibrosis was not... -
- Caroli's Disease.
- Jong Hoon Park, In Hyun Cho, Sun Ja Lee, Dong Hyuk Kum, Soo Dong Pai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(4):401-406. Published online April 15, 1981
-
Caroli*s disease, a rare syndrome characterized by congenital, segmental saccular dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts, is first described by Caroli & associaties in 1958. It is though by many to be part of spectrum of congenital hepatic fibrosis. The disease usually presents with bile stasis and stone formation with further complication arising from recurrent cholangitis and liver abscess. The preoperative diagnosis... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







