Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neonatal hypertension: concerns within and beyond the neonatal intensive care unit
- Kathleen Altemose, Janis M. Dionne
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):367-376. Published online May 30, 2022
-
Some neonates, especially those who are premature, may experience hypertension while in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The most common causes are prematurity-related and the hypertension usually resolves over the first 1–2 years of life. Unfortunately, the increasing population of NICU graduates is at risk for later cardiovascular and kidney disease in childhood and adulthood. This population requires careful attention to blood pressure and weight throughout their life course.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short- and long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Korea: Korean Neonatal Network update in 2019
- Jang Hoon Lee, YoungAh Youn, Yun Sil Chang; Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):284-290. Published online February 5, 2020
-

The Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) has collected population-based data for very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) born in Korea since 2013. The survival rate of all VLBWIs was 86% in Korea. The overall prevalence of cerebral palsy was 6.2%–6.6%. Bilateral blindness and hearing loss were reported in 0.2%–0.3%, 0.8%–1.9%, respectively. The KNN has published annual reports and papers for facilitating the improvement of VLBWIs outcome in Korea.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Transient intubation for surfactant administration in the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in extremely premature infants
- Ji Won Koh, Jong-Wan Kim, Young Pyo Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):315-321. Published online September 16, 2018
-
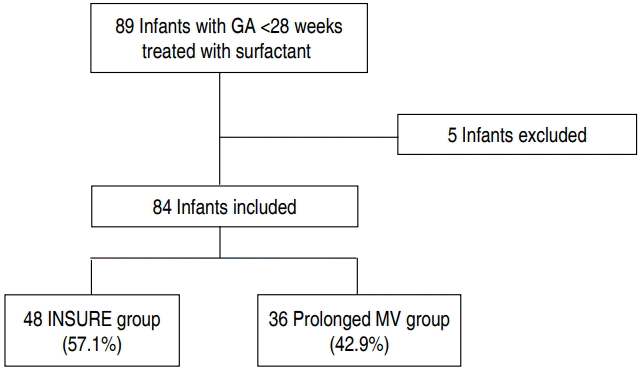
Purpose: To investigate the effectiveness of transient intubation for surfactant administration and extubated to nasal continuous positive pressure (INSURE) for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and to identify the factors associated with INSURE failure in extremely premature infants. Methods: Eighty-four infants with gestational age less than 28 weeks treated with surfactant administration for RDS for 8 years were included. Perinatal...
- Low levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 at birth may be associated with subsequent development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
- Choae Lee, Jaewoo An, Ji Hee Kim, Eun Sun Kim, Soo Hyun Kim, Yeon Kyung Cho, Dong Hyun Cha, Man Yong Han, Kyu Hyung Lee, Youn Ho Sheen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):415-420. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Purpose Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is characterized by inflammation with proteolytic damage to the lung extracellular matrix. The results from previous studies are inconsistent regarding the role of proteinases and antiproteinases in the development of BPD. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8, MMP-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2, and TIMP-1 levels in the serum of...
- Review Article
- Necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns: update in pathophysiology and newly emerging therapeutic strategies
- Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):505-513. Published online December 31, 2014
-
While the survival of extremely premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome has increased due to advanced respiratory care in recent years, necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) remains the leading cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity. NEC is more prevalent in lower gestational age and lower birth weight groups. It is characterized by various degrees of mucosal or transmural necrosis of the intestine....
- Original Article
- The relationship between eosinophilia and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants at less than 34 weeks' gestation
- Joo Yun Yang, Jihei Cha, So-Yeon Shim, Su Jin Cho, Eun Ae Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):171-177. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Purpose Eosinophilia is common in premature infants, and its incidence increases with a shorter gestation period. We investigated the clinical significance of eosinophilia in premature infants born at <34 weeks gestation.
Methods We analyzed the medical records of premature infants born at <34 weeks gestation who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital between January 2003...
- Case Report
- PHACE association with intracranial, oropharyngeal hemangiomas, and an atypical patent ductus arteriosus arising from the tortuous left subclavian artery in a premature infant
- Do-Hyun Kim, Jang Hwan Choi, Jung Ha Lee, Hee Sup Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(1):29-33. Published online January 31, 2012
-
PHACE association is a rare neurocutaneous condition in which facial hemangiomas associate with a spectrum of posterior fossa malformations, arterial cerebrovascular anomalies, cardiovascular anomalies, and eye anomalies. We reported a case of PHACE association in a premature infant showing facial, intracranial, and oropharyngeal hemangiomas with evidence of the Dandy-Walker variant and complicated cardiovascular anomalies, including a right-sided aortic arch and...
- Original Article
- A study on the measurement of the nucleated red blood cell (nRBC) count based on birth weight and its correlation with perinatal prognosis in infants with very low birth weights
- Tae Hwan Kil, Ji Yeon Han, Jun Bum Kim, Gyeong Ok Ko, Young Hyeok Lee, Kil Young Kim, Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(2):69-78. Published online February 28, 2011
-
Purpose The aim of this study was conducted to investigate the mean nRBC count in very low births weight infants (VLBWIs) and to determine the usefulness of the nRBC as an independent prognostic factors of perinatal complications in VLBWIs.
Methods This study was conducted on 112 VLBWIs who were hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) of the author's hospital within the...
- Review Article
- Changes in birth rates of low birth weight and premature infants in Korea over the past 7 years
- Min Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(3):233-236. Published online March 15, 2008
-
In recent years, Korea has experienced a steadily declining birth rate, which is a serious social problem in the country. Although living conditions have improved, the birth rates for low birth weight infants and preterm babies has increased because more and more women choose to give birth later in life and the social environment has changed. The rise in low... -
- Original Article
- Factors influencing birth weight premature infants
- Ji A Aum, Hee Jin Jung, Jae Won Huh, Su Young Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(10):954-958. Published online October 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing premature infants who are small for their gestational ago. Methods : The medical records of 1,010 premature infants of 26 to 35 weeks of gestational age born at Il-Sin Christian Hospital, Busan from January 2000 to August 2006 were reviewed. We collected data on gestational age, birth weight, infant... -
- Antithrombin III in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Premature Infants
- Su Jin Cho, Hye Ryung Choi, Young Mi Hong, Kyung Hee Kim, Keun Lee, Eun Ae Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(7):740-745. Published online July 15, 2004
-
Purpose : We evaluated the diagnostic implications and therapeutic efficacy of antithrombin III(AT III) in the disseminated intravascular coagulation(DIC) of premature infants. Methods : Ninety-two premature infants diagnosed with DIC and treated with AT III from March, 2000 to May, 2003 were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical manifestations, complete blood counts, coagulation tests, and AT III levels were compared between the two groups... -
- Changes of Neutrophil Count in Peripheral Blood of the Neonate with Periventricular Leukomalacia
- Hwan Seok Lee, Kyung Pil Park, Heng Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(10):966-971. Published online October 15, 2003
-
Purpose : It is now well established that infection and inflammation play an important role in the pathogenesis of ischemic brain damage. The loss of neutrophils from systemic circulation is an associated finding in injury mediated by granulocyte. Periventricular leukomalacia(PVL) caused by ischemia is the principal form of brain injury in premature infants. This study was conducted to evaluate whether... -
- Total Parenteral Nutrition-associated Cholestasis in Premature Infants
- Kyung Pil Park, Se Young Kim, Heng Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(1):17-23. Published online January 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Cholestasis is a major complication in prolonged use of TPN, especially in the neonatal period, but there are few long-term reviews examining the clinical course in premature infants. Thus, in this study, we reviewed premature infants with TPN-associated cholestasis(TPNAC) to determine the incidence, clinical courses and possible risk factors. Methods : Retrospective review of 66 premature infants less than... -
- Usefulness of Serum Prealbumin Concentration as a Marker for Nutritional Adequacy in Premature Infants
- Soo Jin Lee, Eun Ae Park, Jeong Wan Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(8):867-874. Published online August 15, 2001
-
Purpose : Serum prealbumin concentration has been proposed as a useful nutritional marker that responds rapidly and sensitively to calory and protein intake. But the reports of prealbumin in premature infants are not sufficient and variable. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of serum prealbumin concentration as a marker for nutritional adequacy in premature infants. Methods... -
- Thyroid Hormone Concentrations in Preterm Infants
- Sung Keun Moon, Jeong Nyun Kim, Mi Jung Park, Myung Jae Choi, Chrul Young Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(10):1324-1328. Published online October 15, 1998
-
Purpose : To establish reference ranges for thyroid hormone concentrations in premature infants, we measured T4 and thyroid stimulating hormone(TSH) concentrations and analyzed the relation to gestational age and birth weight. Methods : Serum T4 and TSH concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay for 391 premature infants born in Sanggye Paik Hospital for two years and eight months. Results : Gestational age of... -
- The Study of Transplacental Transfer of Immunoglobulin G in Premature Infants
- Sung Soo Moon, Yoon Ki Kang, Soo Chul Cho, Jung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(6):747-753. Published online June 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Premature infants have low serum immunoglobulin G(IgG) levels because IgG is transplacentally acquired, primarily after 32-34 weeks of gestational age. We studied the transplacental transfer of serum IgG in preterm infants. Methods : The IgG levels in the sera were measured by radial immunodiffusion method(Behring nephelometer, Germany). Results : There was a significant difference between IgG concentration and gestational age; the IgG concentration increased... -
- Effects of Patent Ductus Arteriosus on Right Ventricle in Premature Infants : by M-mode and Doppler Echocardiography
- Eun Jeung Kim, Eun Sil Lee, Young Hwan Lee, Son Moon Shin, Jeong Ok Hah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(6):734-740. Published online June 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Patent ductus arteriosus, derived left to right shunt flows, elevate the pulmonary artery pressure in infants and children and may alter right ventricular afterload thereby right ventricular function. Therefore, we examined the effects of patent ductus arteriosus on the right ventricular systolic time interval in premature infants by non-invasive Doppler echocardiography. Methods : Tweleve premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus were studied... -
- Case Report
- Two Cases of Systemic Candidiasis in Premature Infants
- Dae Kyun Kim, Woo Chul Suh, Eun Gyeoung Jung, Eun Seok Yang, Sang-Kee Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(11):1558-1564. Published online November 15, 1995
-
Reports of systemic candidiasis in neonates have been noted recently with its major advances in neonatal care permitting the frequent survival of low birth weight infant. Factors influencing the development of systemic candidiasis include prematurity, very low birth weight, the presence of intravascular catheter, the use of hyperalimentation, prolonged broad spectrum antimicrobial therapy and prolonged endotracheal intubation. We experienced two cases... -
- Transfusion-Acquired Cytomegalovirus Infections in Two Premature Infants
- Dong Wook Kim, Kyung Un No, Mi Jung Kim, Soon Mee Park, Hee Sup Kim, Young Pyo Chang, Hoan Jong Lee, Jung-Hwan Choi, Chong Ku Yun, Je Geun Chi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(8):1141-1147. Published online August 15, 1992
-
Transfusion-acquired perinatal cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection can cause significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in premature infants with a birth wight of less than 1,500 gm. This recognizable syndrome consisted of deterioration of respiratory function, hepatosplenogaly, unusual gray pallor with disturbing septic appearance, lymphocytosis, thrombocytopenia and hemolytic anemia. We experienced transfusion-acquired CMV infections in 2 premature infants with a birth weight of... -
- Original Article
- Indomethacin therapy in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus.
- Dug Ha Kim, Jung Hwan Choi, Chong Ku Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(10):1381-1390. Published online October 31, 1991
-
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a common disease that occurred in 20 〜 40 percent of premature infants. The incidence of PDA is inversely related to the gestational age and birth weight. Hemodynamically significant PDA increases the morbidity and mortality of premature infants. So, the management of PDA is one of the major problems in neonatal intensive care unit. Based on experimental animal studies,... -
- A case of neonatal systemic candidiasis.
- Eun Ae Park, Gyoung Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(9):1286-1293. Published online September 30, 1991
-
Systemic infection with Candida albicans in very premature infants is frequently fatal or associated with significant morbidity in survivors. Several common practices in newborn intensive care units, such as insertion of indwelling catheters, provision of parenteral nutrition, and prolonged administra- tion of broad-spectrum antibiotics or aminophylline, are associated with an increased risk of systemic disease. We have experienced a case of systemic candidiasis in 1/365... -
- Changein Regional Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Premature Infant.
- Young Kyoo Shin, Chang Sung Son, Joo Won Lee, Young Chang Tockgo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(10):1333-1340. Published online October 31, 1990
-
In order to estimate the influence of systemic hemodynamic change in cerebral blood flow before and after closure of ductus arteriosus in premature mewborn infants, blood flow velocities of internal carotid artery (ICA), anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA) were measured in 17 premature newborn infants by pulsed Doppler ultrasonography. The data was compared with those of normal full-term infants by... -
- Exogenous Surfactant Replacement Therapy of Hyaline Membrane Disease: A controlled clinical trial.
- Ran Namgung, Chul Lee, Kook In Park, Dong Gwan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(1):22-34. Published online January 31, 1990
-
We conducted a clinical controlled trial of exogenous surfactant replacement therapy in premature infants with hyaline membrane disease at the neonatal intensive care unit of Yonsei University Medical Center form Nov. 1987 to May 1988. Sixteen premature infants with severe HMD were randomly assigned to control group or surfactant-treated group. Eight infants (mean gestational age 29.9±2.8 week, mean birth weight 1, 425±308.9 gm) were given... -
- Blood Glucose Values in Healthy Premature Infants.
- Heung Kyu Kim, Chul Seung Son, Eun Hee Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(4):319-325. Published online April 30, 1984
-
Serial blood glucose values were measured over the first twenty-four hours of life on 202 healthy permature infants. Whose weights were less than 2,300 grams. The 76 infants who were evaluated over a period of four weeks divided into two groups; 22 premature infants weighing less than 1,700 grams at birth, and 54 premature infants weighing over 1,700 grams. Eight... -
- Hyperglycemia in Stressed Premature Infants.
- Heung Kyu Kim, Kyung Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(2):124-129. Published online February 28, 1983
-
The blood glucose response to a constant glucose infusion were measured in 62 premature infants weighing 1,000 to 2,200 gm. The study includes 32 stressed premature infants who had respiratory distress, Necrotizing enterocolitis, premature rupture of membranes, sepsis and 30 control premature infants. During the first three hours of life, the glucose values were similar in both stressed and the control groups. During the four... -
- Result of a Mixture with Vegimil A(50%) and a known Local Infant Formular (50%) to Premature Infants.
- Keun Soo Lee, Soo Jee Moon, Gwi Jong Choi, Sang Yoon Lee, Kyu Youp Kim, Kee Young Youn, Jin Woo Hahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 1983
-
A prospective observation for growth (by weight) of 100 premature infants (some low birthweight infants were included) were conducted at the premature baby ward of Hanyang University Hospital during the one year period from May, 1981 to April, 1982. 100 subjects of the observation were devided in to 2 groups (A and B). Group A was consisted of 50 premature... -
- Platelet Counts in Healthy Premature Infants.
- Heung Kyu Kim, You Nam Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(9):805-811. Published online September 15, 1981
-
Serial platelet counts performed at four day intervals on forty two healthy premature infants whose birth weights were less than 2200 grams. The forty two infants were divided into two groups: twelve premature infants weighing less than 1700 grams, and thirty prematures infants weighing over 1700 grams at birth. We evaluated the length of time for the platetet counts of... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







