Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants in the Neonatal Research Network of Japan: importance of neonatal intensive care unit graduate follow-up
- Yumi Kono; on behalf of the Neonatal Research Network of Japan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(7):313-321. Published online November 9, 2020
-

· Very low birth weight infants remain at high risk of developing neurodevelopmental impairments in early childhood.
· It is important to establish a network follow-up protocol and complete assessments with fewer dropouts to enable clarification of the outcomes of registered infants.
· All possible strategies should be employed to maintain good compliance after neonatal intensive care unit discharge.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Fluconazole prophylaxis against invasive candidiasis in very low and extremely low birth weight preterm neonates: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mahmoud Robati Anaraki, Masoud Nouri-Vaskeh, Shahram Abdoli Oskoei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(4):172-179. Published online May 14, 2020
-
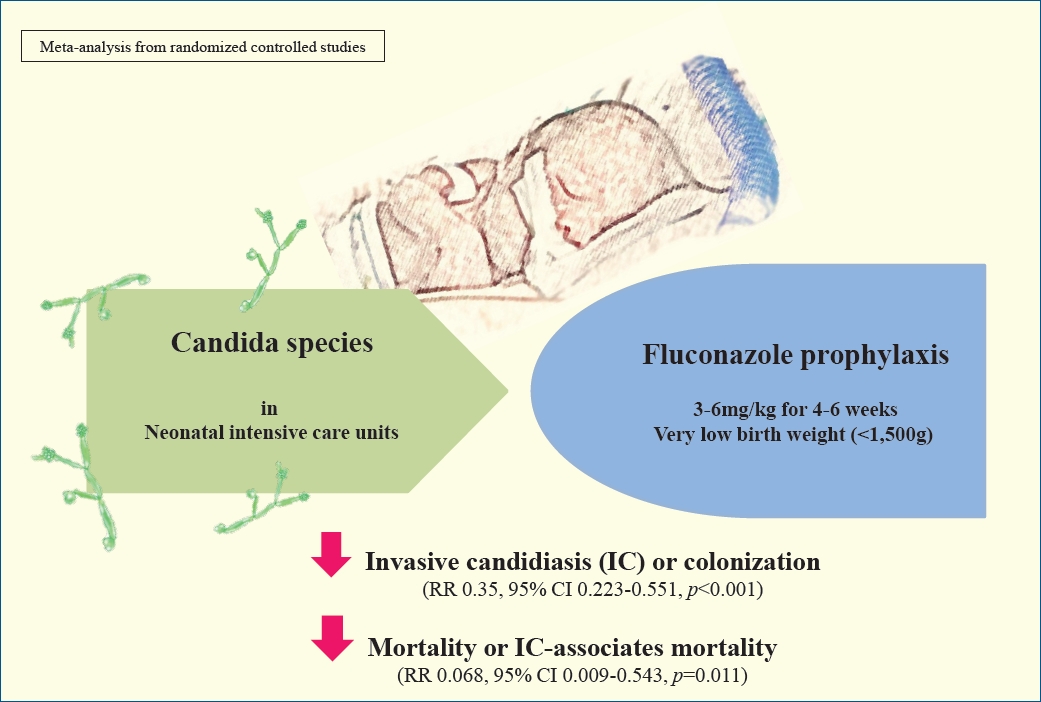
· Mortality is decreased significantly in meta-analysis of studies in different regimen of fluconazole prophylaxis.
· Significant decrease was seen in incidence of invasive candidiasis-associated mortality in extremely low birth weight infants in same schedules of prophylaxis.
· More studies required to relief the concerns.
- Effect of red blood cell transfusion on short-term outcomes in very low birth weight infants
- Eui Young Lee, Sung Shin Kim, Ga Young Park, Sun Hyang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):56-62. Published online February 6, 2020
-
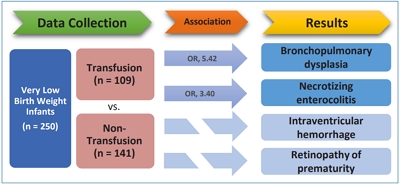
Question: Does RBC transfusion affect the short-term outcomes of VLBW infants?
Finding: The results showed that RBC transfusion was significantly related to the incidence of BPD (OR, 5.42; P<0.001) and NEC (OR, 3.40; P=0.009).
Meaning: Careful consideration of the patient’s clinical condition and appropriate guidelines is required before administering RBC transfusions.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short- and long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Korea: Korean Neonatal Network update in 2019
- Jang Hoon Lee, YoungAh Youn, Yun Sil Chang; Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):284-290. Published online February 5, 2020
-

The Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) has collected population-based data for very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) born in Korea since 2013. The survival rate of all VLBWIs was 86% in Korea. The overall prevalence of cerebral palsy was 6.2%–6.6%. Bilateral blindness and hearing loss were reported in 0.2%–0.3%, 0.8%–1.9%, respectively. The KNN has published annual reports and papers for facilitating the improvement of VLBWIs outcome in Korea.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Synbiotics use for preventing sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight neonates: a randomized controlled trial
- Ozge Serce Pehlevan, Derya Benzer, Tugba Gursoy, Guner Karatekin, Fahri Ovali
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):226-231. Published online February 5, 2020
-
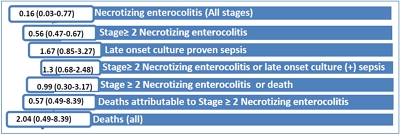
Background: Probiotics and prebiotics have strain-specific effects on the host. Synbiotics, a mixture of probiotics and prebiotics, are proposed to have more beneficial effects on the host than either agent has alone.
Purpose: We performed a randomized controlled trial to investigate the effect of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium together with oligosaccharides and lactoferrin on the development of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) or sepsis...
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Validity of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for very-low-birth-weight infants
- Chae Young Kim, Euiseok Jung, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):187-192. Published online March 20, 2019
-
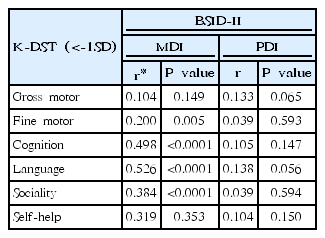
Purpose: The importance of the neurodevelopmental outcomes of very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants has been emphasized as their mortality rate has markedly improved. This study aimed to assess the validity of the Korean Developmental Screening Test (K-DST), a developmental screening tool approved by the Korean Society of Pediatrics, for the timely diagnosis of neurodevelopmental delay in VLBW infants. Methods: Subjects included VLBW infants...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Association between vitamin D level at birth and respiratory morbidities in very-low-birth-weight infants
- Ian Kim, Sung Shin Kim, Jee In Song, Seock Hwa Yoon, Ga Young Park, Yong-Wha Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):166-172. Published online October 24, 2018
-
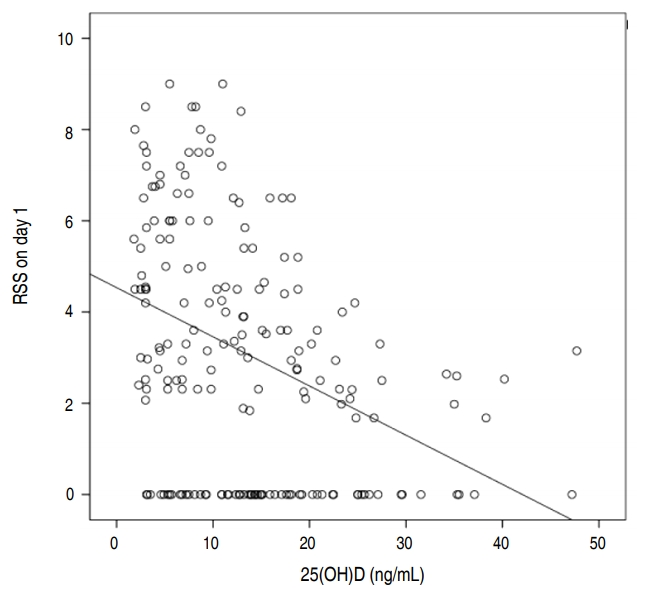
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate vitamin D status at birth in very-low-birth-weight infants (VLBWIs: <1,500 g) and to determine the association between vitamin D level and respiratory morbidity. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted at Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital between November 2013 and November 2017. We collected blood samples and data on respiratory morbidity from 230 VLBWIs on the first...
- The impact of a quality improvement effort in reducing admission hypothermia in preterm infants following delivery
- Han Saem Choi, Soon Min Lee, Hoseon Eun, Minsoo Park, Kook-In Park, Ran Namgung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):239-244. Published online August 15, 2018
-
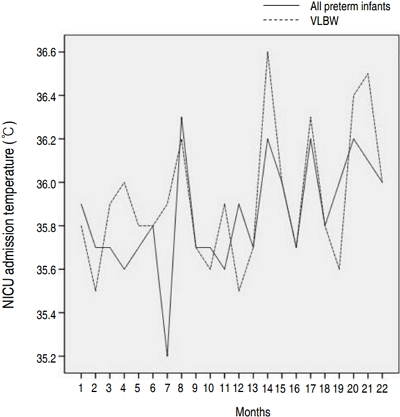
Purpose: Hypothermia at admission is associated with increased mortality and morbidity in preterm infants. We performed a quality improvement (QI) effort to determine the impact of a decrease in admission hypothermia in preterm infants. Methods: The study enrolled very low birth weight (VLBW) infants born at Gangnam Severance Hospital between January 2013 and December 2016. This multidisciplinary QI effort included the...
- Postdischarge growth assessment in very low birth weight infants
- Joon-Sik Park, Jungho Han, Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Ho Seon Eun, Min-Soo Park, Kook-In Park, Ran Namgung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):64-69. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose The goal of nutritional support for very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants from birth to term is to match the
in utero growth rates; however, this is rarely achieved.Methods We evaluated postdischarge growth patterns and growth failure in 81 Korean VLBW infants through a retrospective study. Weight and height were measured and calculated based on age percentile distribution every 3 months until age 24...
- Modification of nutrition strategy for improvement of postnatal growth in very low birth weight infants
- Ah Young Choi, Yong Wook Lee, Mea-young Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):165-173. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose To identify the effects of modified parenteral nutrition (PN) and enteral nutrition (EN) regimens on the growth of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants.
Methods The study included VLBW infants weighing <1,500 g, admitted to Chungnam National University Hospital between October 2010 and April 2014, who were alive at the time of discharge. Subjects were divided according to 3 periods: period 1...
- Thyroid dysfunction in very low birth weight preterm infants
- Ji Hoon Lee, Sung Woo Kim, Ga Won Jeon, Jong Beom Sin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):224-229. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose Thyroid dysfunction is common in preterm infants. Congenital hypothyroidism causes neurodevelopmental impairment, which is preventable if properly treated. This study was conducted to describe the characteristics of thyroid dysfunction in very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs), evaluate risk factors of hypothyroidism, and suggest the reassessment of thyroid function with an initially normal thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as part of a newborn...
- Analysis of the association between necrotizing enterocolitis and transfusion of red blood cell in very low birth weight preterm infants
- Seon-Yeong Bak, Sihyoung Lee, Jae-Hong Park, Kyu-Hee Park, Ji-Hyun Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(3):112-115. Published online March 18, 2013
-
Purpose To investigate the association between necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) and red blood cell transfusions in very low birth weight (VLBW) preterm infants.
Methods We studied were 180 VLBW preterm infants who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of CHA Gangnam Hospital from January of 2006 to December of 2009. The subjects were divided into 2 groups: an NEC group (greater than...
- The control of invasive
Candida infection in very low birth weight infants by reduction in the use of 3rd generation cephalosporin - Yu Jin Chang, Il Rak Choi, Won Sub Shin, Jang Hoon Lee, Yun Kyung Kim, Moon Sung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(2):68-74. Published online February 25, 2013
-
Purpose To evaluate the effectiveness of new management policies on the incidence of invasive Candida infections
Methods This observational study involved a retrospective analysis of the patients' medical records. In total, 99 very low birth weight infants, who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit at Ajou University Hospital from January 2010 to December 2011, were enrolled for the study. Period I,...
- Effect of early postnatal neutropenia in very low birth weight infants born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypertension
- Yang Hee Park, Gyung Min Lee, Jung Min Yoon, Enn Jung Cheon, Kyung Ok Ko, Yung Hyuk Lee, Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(12):462-469. Published online December 20, 2012
-
Purpose In this study, we aimed to investigate the perinatal clinical conditions of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) focusing on the effects of early postnatal neutropenia.
Methods We reviewed the medical records of 191 VLBW infants who were born at Konyang University Hospital, between March 2003 and May 2011. We retrospectively analyzed the clinical characteristics...
- A study on the measurement of the nucleated red blood cell (nRBC) count based on birth weight and its correlation with perinatal prognosis in infants with very low birth weights
- Tae Hwan Kil, Ji Yeon Han, Jun Bum Kim, Gyeong Ok Ko, Young Hyeok Lee, Kil Young Kim, Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(2):69-78. Published online February 28, 2011
-
Purpose The aim of this study was conducted to investigate the mean nRBC count in very low births weight infants (VLBWIs) and to determine the usefulness of the nRBC as an independent prognostic factors of perinatal complications in VLBWIs.
Methods This study was conducted on 112 VLBWIs who were hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) of the author's hospital within the...
- Effect of SynagisⓇ (palivizumab) prophylaxis on readmission due to respiratory syncytial virus in very low birth weight infants
- Soo Kyoung Park, Yu Jin Jung, Hye Soo Yoo, So Yoon Ahn, Hyun Joo Seo, Seo Heui Choi, Myo Jing Kim, Ga Won Jeon, Soo Hyun Koo, Kyung-Hoon Lee, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(3):358-363. Published online March 15, 2010
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to determine the efficacy of SynagisⓇ (palivizumab) in reducing the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) readmission rate in very low birth weight infants (VLBWI ) and the subgroup that showed the most effective vaccination. Methods : We enrolled 350 VLBWI who had been discharged alive from the neonatal intensive care unit of Samsung Medical... -
- Case Report
- High-dose caspofungin salvage in a very-low-birth-weight infant with refractory candidemia
- Eun Sun Seo, Geun Hwa Park, Sung Mi Kim, Hye An Jung, Byoung Kuk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):239-243. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Candidiasis is one of the most common causes of late-onset infection among very-low-birth-weight infants (VLBW) in most neonatal intensive care units and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Standard therapy consists of the administration of amphotericin B, amphotericin B complex, and fluconazole. In many cases, candidiasis is not easily eradicated, despite the administration of these drugs. We report our... -
- Original Article
- Magnetic resonance imagining findings of the white matter abnormalities in the brain of very-low-birth-weight infants
- Jae Hyuk Choi, Young Pyo Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(10):1127-1135. Published online October 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To observe the abnormal white matter findings on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of very-low- birth-weight (VLBW) infant brains at term-equivalent age and to determine the clinical risk factors for the development of periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). Methods : In all, MRI was performed in 98 VLBW infants and the white matter abnormalities were observed. Clinical risk factors... -
- Case Report
- Postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in an extremely premature infant transmitted via breast milk: A case report
- Ji Hye Kim, Eun-Jin Chung, Hyun Kyung Park, Soo Ji Moon, Su-Mi Choi, Sung Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(9):1053-1058. Published online September 15, 2009
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is one of the most commonly encountered viral pathogens in newborn infants and is found in 0.3-2.4% of all live births. It has been demonstrated that 40-96% of seropositive mothers shed the virus via their breast milk. Breast milk containing CMV can cause almost one-third of CMV infections occurring in infants. A case of postnatal CMV infection in... -
- Original Article
- Changes in the outcomes of neonatal intensive care unit at a single center over 12 years
- Hyun-Hee Lee, Tae-Yeon Kim, Seon-Hee Shin, Tae-Jung Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(8):881-887. Published online August 15, 2009
-
Purpose:The survival rate of very low birth weight infant (VLBWI) had increased as a result of advances in neonatal intensive care. We evaluated the changes in outcomes of VLBWI who admitted to the neonatal care unit of Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital. Methods:Retrospective review of 339 VLBWI who were born from 1st January 1997 to 31th December 2008 were performed. Outcomes including survival... -
- Clinical course and prognosis of hemodynamically significant congenital heart defects in very low birth weight infants
- Hye Soo Yoo, Ji Eun Kim, Soo Kyoung Park, Hyun Ju Seo, Yoo Jin Jeong, Seo Heui Chio, Soo In Jeong, Sung Hoon Kim, Ji Hyuk Yang, June Huh, Yun Sil Chang, Tae Gook Jun, I Seok Kang, Won Soon Park, Pyo Won Park, Heung Jae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(4):481-487. Published online April 15, 2009
-
Purpose : This study investigated the clinical course and prognostic factor of very low birth weight infants (VLBWI) with hemodynamically significant congenital heart defects (CHDs). Methods : Medical records of 1,098 VLBWI with birth weight <1,500 g who had been admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of Samsung Medical Center from October 1994 to December 2007 were reviewed retrospectively. The... -
- Gastrointestinal surgery in very low birth weight infants : Clinical characteristics
- Ji Eun Kim, Hye Soo Yoo, Hea Eun Kim, Soo Kyoung Park, Yoo Jin Jeong, Seo Heui Choi,, Hyun Joo Seo, Yun Sil Chang, Jeong Meen Seo, Won Soon Park, Suk Koo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):295-302. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To report our experience of gastrointestinal (GI) operations (OP) performed in very low birth weight infants (VLBWI) and to evaluate their clinical characteristics. Methods : Among the 1,117 VLBWI admitted to the SMC neonatal intensive care unit from November 1994 to February 2007, the medical records of 37 infants who underwent GI OP (except inguinal hernia OP) and 1,080... -
- Review Article
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants and extremely low birth weight infants in Korea, 1984-2008
- In Kyung Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(1):14-21. Published online January 15, 2009
-
Neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants (VLBWI) and extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWI) in Korea on 14 reports from 1984 to 2008 were analyzed. Follow-up rates were varied from 42.9% to 90.2%. Duration of follow-up ranged from 4 months to 5 years. The prevalence of cerebral palsy (CP) of VLBWI was as follows: 4.3-5.3% in 1980s, 7.1-9.1... -
- Original Article
- Growth and clinical efficacy of fortified human milk and premature formula on very low birth weight infants
- Heewon Chueh, Myo Jing Kim, Young-A Lee, Jin-A Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(7):704-712. Published online July 15, 2008
-
Purpose : A prospective, controlled trial was conducted to evaluate growth, efficacy, safety and nutritional status for very low birth weight infants fed with human milk fortified with Maeil human milk fortifier (Maeil HMF ; Maeil Dairies Co., Ltd.). Methods : We enrolled 45 premature infants with a birth weight <1,500 g and gestational age <33 weeks, who were born at... -
- Review Article
- Trends in survival rate for very low birth weight infants and extremely low birth weight infants in Korea, 1967-2007
- Ki-Soo Kim, Chung-Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(3):237-242. Published online March 15, 2008
-
To investigate the trends in the survival rate (SR) for very low birth weight infants (VLBW) and extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWI) in Korea, a total of 43 articles pertaining to SR were analyzed, covering the years from 1967 to 2007. The changes in SR were compared using 5 year periods. The SR for VLBWI has increased remarkably, from... -
- Original Article
- Effect of women's first childbearing age on the risk of low birth weight
- Jung Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1206-1211. Published online December 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the risk of low birth weight associated with delayed first childbearing in Korea. Methods : The national birth certificate data of the singletons and first babies in Korea from January 2001 to December 2003 (n=736,167) was used. Outcome measures were rates of low birth weight infant, very low birth weight... -
- Fluconazole prophylaxis in high-risk, very low birth weight infants
- Soo Young Kim, Soon Joo Lee, Mi Jeong Kim, Eun Song Song, Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(7):636-642. Published online July 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Fluconazole prophylaxis for very low birth weight (VLBW) infants has been shown to reduce invasive fungal infection and its mortality. This study aims to evaluate the effect of fluconazole prophylaxis in VLBW infants on the incidence and mortality of fungal infection. Methods : VLBW infants with endotracheal intubation and central vascular access admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care... -
- The effect of restricted fluid intakes in the first week of life on the risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth weight infants
- Hoe Kyoung Koo, Eun Na Choi, Ran Namgung, Min Soo Park, Kook In Park, Chul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(6):536-542. Published online June 15, 2007
-
Purpose : We investigated the effects of restricted fluid in the first 7 days of life on the risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) or patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants. Methods : Eighty three VLBW infants who lived more than 28 days were selected. The amount of daily maintenance fluid was determined by calculation of insensible... -
- High-resolution computed tomography findings of lung parenchyme changes in very low birth weight infants treated with oxygen
- Young Man Jin, David Chanwook Chung, Young Pyo Chang, Yung Suk Lee, En Sun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(3):255-261. Published online March 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The objective of this study is to observe high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings of lung parenchyme in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants between the corrected age of 38-42 weeks who were treated with oxygen after birth, and to compare them to the clinical severity of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). Methods : The lungs of fourty-four VLBW infants with gestational... -
- Changes of neurodevelopmental outcomes and risk factors of very low birth weight infants below 1,500 g, in the last 10 years
- Se Kyu Lee, Ji Hyun Lee, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1050-1055. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : As a result of advances in neonatal intensive care and perinatal care, neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infant(VLBWIS) is expected to lead to improvement. The aim of this study was to report neurodevelopmental outcomes and risk factors of neurologic impairment of very low birth weight infants during the past 10 years. Method : We performed a retrospective... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







