Topics
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Topics
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (3)
- Allergy (52)
- Cardiology (76)
- Critical Care Medicine (8)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (17)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (51)
- Gastroenterology (57)
- General Pediatrics (37)
- Genetics and Metabolism (20)
- Hematology (11)
- Immunology (12)
- Infection (66)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (103)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (49)
- Neurology (88)
- Nutrition (25)
- Oncology (15)
- Neurobehavior (11)
- Pulmonology (25)
- Rheumatology (2)
- Other (28)
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Is it time to add point-of-care ultrasound education to pediatric residency curriculum?
- Shin Ae Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):33-34. Published online October 12, 2021
-
Growing point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) use in pediatric patients has led to the need for POCUS education for pediatric residents. Recent experimental studies have suggested that POCUS education improves self-rated POCUS confidence and comfort in pediatric resident training. Considering the effective and sustainable POCUS education curriculum in pediatric resident training, simulation-based education would be a solution.
- Endocrinology
- Pediatricians must consider familial environment when diagnosing and managing childhood obesity
- Young Suk Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):31-32. Published online April 19, 2021
-
•The prevalence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide, including in the Republic of Korea, creating a major public healthissue.
•Accumulated evidence indicates a strong relationship between parentalandchildobesity.
•A family-based approach is indicated to prevent and manage childhoodandadultobesity.
- Pediatric obesity: life cycle approach of pediatrician and society
- Yong Hee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):29-30. Published online December 28, 2021
-
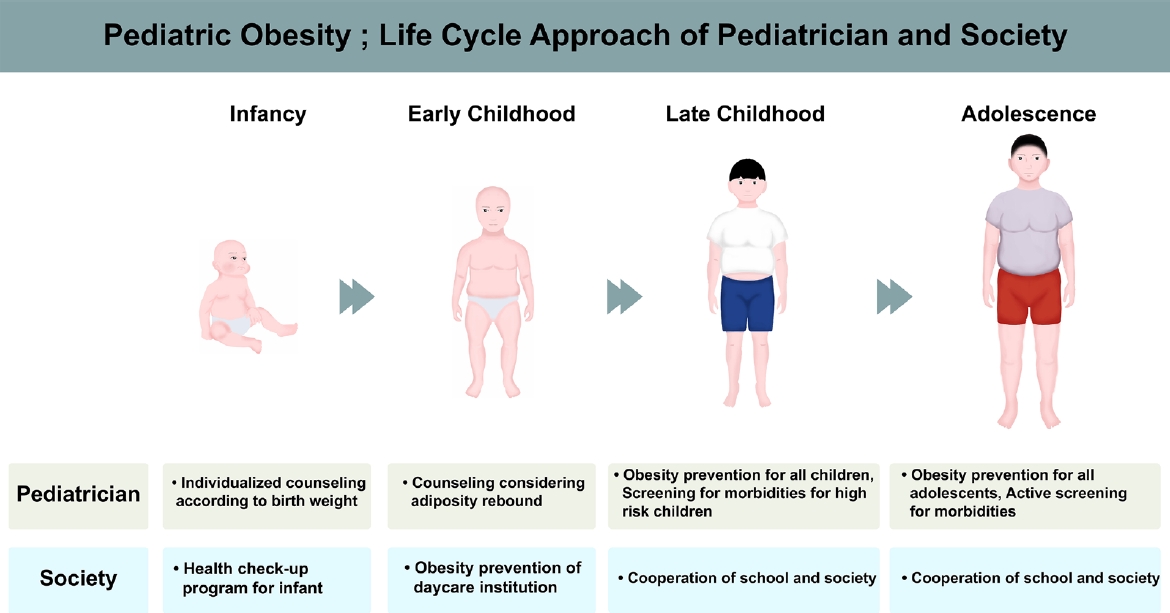
• With the emerging epidemic of pediatric obesity, many endocrine comorbidities classically seen in adulthood are surfacing much earlier in life.
• Appropriate obesity counseling and education should be provided from infancy to adolescence.
• Managing pediatric obesity may require school and society involvement.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Upper gastrointestinal tract involvement of Crohn disease: clinical implications in children and adolescents
- Eun Sil Kim, Mi Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):21-28. Published online September 10, 2021
-
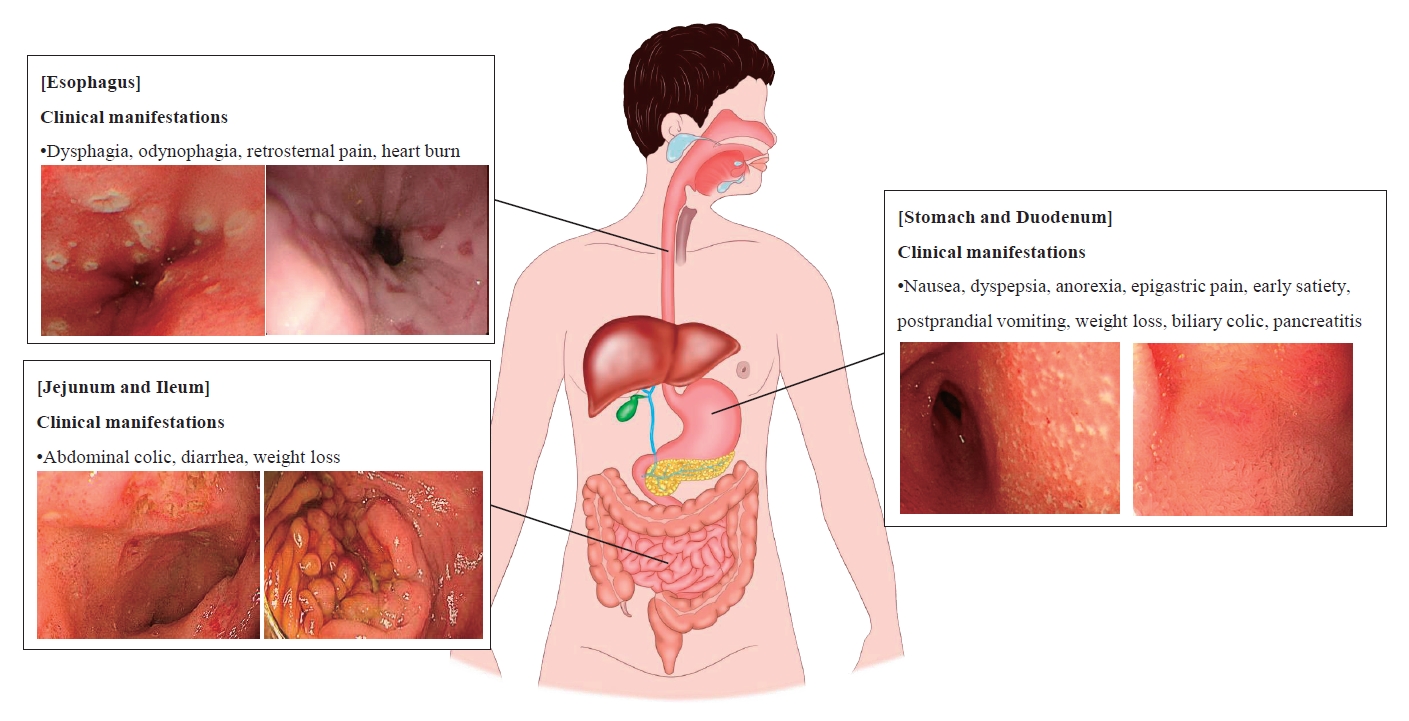
· Clinical manifestations of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) tract involvement in Crohn's disease (CD) are common but often clinically underestimated.
· Diagnosing CD by confirming inflammation of the UGI tract histologically is challenging because macroscopic and microscopic findings overlap with those of other diseases.
· Ongoing efforts are needed to enable a standardized assessment of UGI CD in the future.
- Neurology
- Worldwide national intervention of developmental screening programs in infant and early childhood
- Seunghyo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):10-20. Published online September 30, 2021
-

∙ Prevalence rate of developmental disabilities has been reported from 8% to 15% and its rate is increasing worldwide.
∙ The critical period of intervention for developmental delay is before the child reaches 3 years of age.
∙ All primary care pediatricians should conduct developmental surveillance and screening tests to infants and children at scheduled visits. Through this, they are liable for providing early identification and timely intervention.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Growth patterns of preterm infants in Korea
- Joohee Lim, So Jin Yoon, Soon Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):1-9. Published online July 8, 2021
-
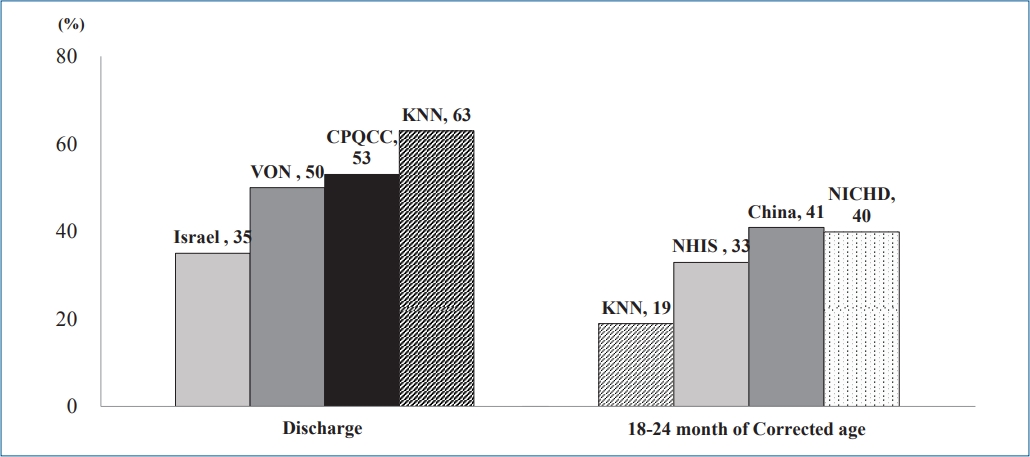
∙ The growth of preterm infants is a main focus of neonatology.
∙ Preterm infants in Korea, especially those with a very low birth weight, achieve retarded growth.
∙ Careful growth monitoring and early intervention will contribute to better development outcomes and quality of life for preterm infants and improve public health.
- Letter to the Editor
- Allergy
- Environmental and dietary factors to be checked for treatment of atopic dermatitis in rural children
- Sanghwa Youm, Eunjoo Lee, Jeongmin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):661-663. Published online October 1, 2021
-

Question: What are the distinctive features of rural children with atopic dermatitis?
Finding: Birch and dog dander were the second most sensitized aeroallergens (32.6%), followed by house dust mites. Doctors and guardians reported food allergy comorbidities differently (19.9% and 43.5%, respectively). Dietary restrictions without medical evaluation were observed in 39.7% of patients.
Meaning: Effects of pollen distribution and indirect animal exposure should be evaluated. Evidence-based dietary restrictions must be implemented.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Viral load and rebound in children with coronavirus disease 2019 during the first outbreak in Daegu city
- Mi Ae Chu, Yoon Young Jang, Dong Won Lee, Sung Hoon Kim, Namhee Ryoo, Sunggyun Park, Jae Hee Lee, Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):652-660. Published online October 12, 2021
-
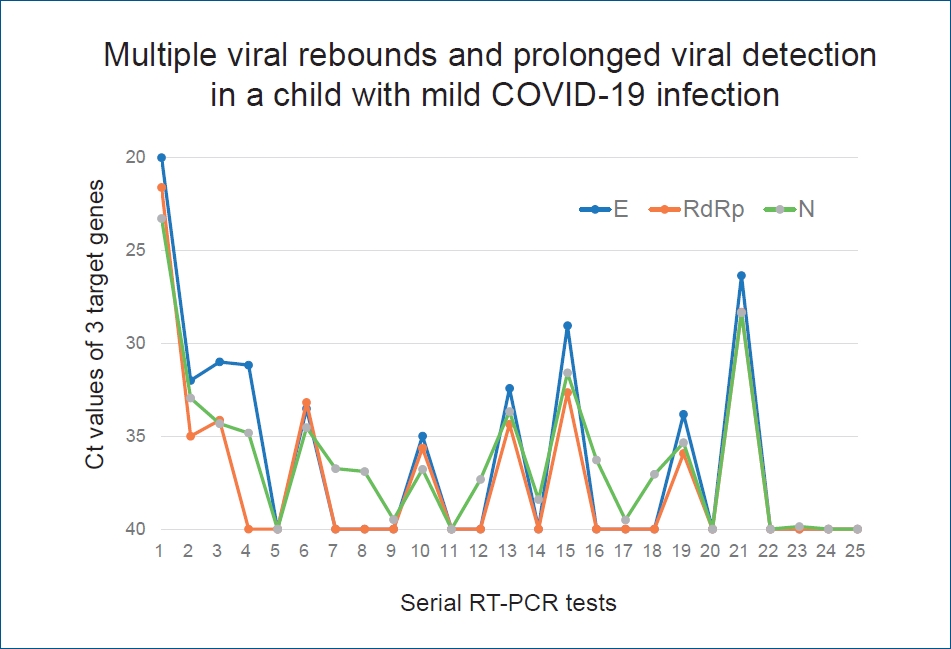
Question: What is the natural course of viral load in children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?
Finding: A significant number of patients still had a relatively high viral load once clinically asymptomatic. Nearly half of the patients experienced viral rebound, which contributed to prolonged viral detection in their respiratory specimens.
Meaning: Further studies are needed to determine the clinical significance of viral rebound in asymptomatic or mild pediatric cases of COVID-19.
- General Pediatrics
- Efficacy of probiotics for managing infantile colic due to their anti-inflammatory properties: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- Reza Shirazinia, Ali Akbar Golabchifar, Mohammad Reza Fazeli
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):642-651. Published online April 12, 2021
-
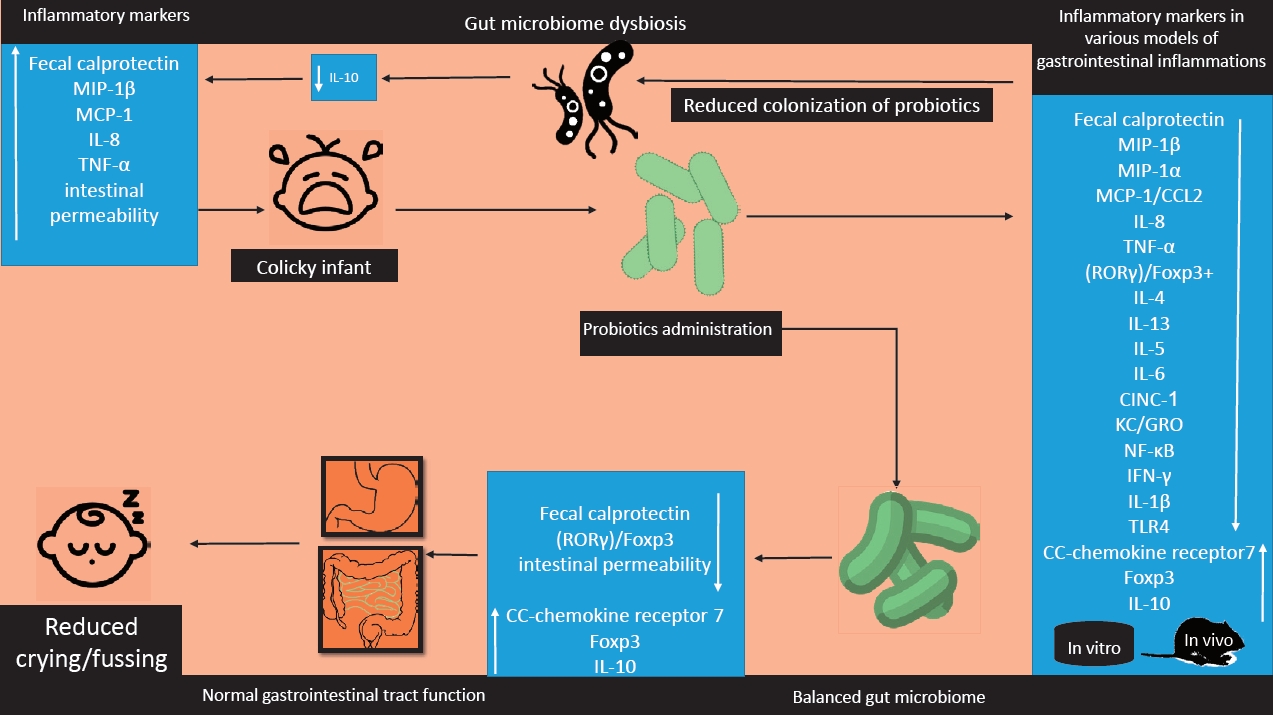
Question: Do probiotics reduce colic symptoms?
Finding: Probiotics reduced colic symptoms in colicky infants probably due to the anti-inflammatory properties.
Meaning: Probiotics may be an effective and less noxious way to manage infantile colic.
- Other
- Spatial modeling of mortality from acute lower respiratory infections in children under 5 years of age in 2000–2017: a global study
- Ali Almasi, Sohyla Reshadat, Alireza Zangeneh, Mehdi Khezeli, Raziyeh Teimouri, Samira Rahimi Naderi, Shahram Saeidi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):632-641. Published online March 19, 2021
-

Question: We assessed the spatial modeling of mortality from acute lower respiratory infections in children under 5 years old during 2000–2017 using a global data.
Finding: The total number of child deaths during the study period decreased, while the number of hot spots increased among countries.
Meaning: Hot spots were concentrated in Asia in 2000 but shifted toward African countries by 2017. A cold spot formed in Europe over the study period.
- Editorial
- Other
- Global trend and disparity of acute lower respiratory infection as cause of mortality in children under 5 years of age
- Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):630-631. Published online June 11, 2021
-
Acute lower respiratory infection (ALRI) is the leading cause of death among children under 5 years of age worldwide, especially in low- and middle-income countries. A spatial analysis explains the trends and severity based on the conditions of each country. Countries in Asia and Africa experience many cases of mortality caused by ALRI.
- Neurology
- Recent studies are focus on the new treatments for hypoxicischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and long-term outcomes in later childhood and adolescence in children with a history on HIE
- Eun Sook Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):628-629. Published online September 30, 2021
-
Neonatal encephalopathy is the most important reason for morbidity and mortality. The early detection of neonate with high risk for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and treatment are important for prevent long term complication. Hypothermia is currently standard treatment option for HIE. Several clinical studies have been performed due to improve the long term outcome. New therapeutic options including xenon, allopurinol, erythropoietin, topiramate will help to reduce neuropsychiatric disability.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Endocrine comorbidities of pediatric obesity
- Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):619-627. Published online August 26, 2021
-

∙ Pediatric obesity can involve endocrine comorbidities such as prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome, and central precocious puberty.
∙ Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in youth aged 10–19 years had a prevalence of 25.9% and 0.6% in 2013–2014, respectively.
∙ Dyslipidemia in Korean adolescents aged 10–18 years had a prevalence of 7.64% (total cholesterol ≥200 mg/dL), 6.09% (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL), 8.69% (triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL), and 12.52% (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL) in 2007–2018.
∙ Metabolic syndrome in Korean youth has a prevalence of 1.9%–14.7% in males and 1.7%–12.6% in females with wide variation in definitions.
∙ Appropriate comorbidity screening and management and/or specialist referral are necessary for obese children and adolescents.
- Neurology
- Cognitive outcomes in late childhood and adolescence of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Bo Lyun Lee, Hannah C. Glass
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):608-618. Published online May 24, 2021
-
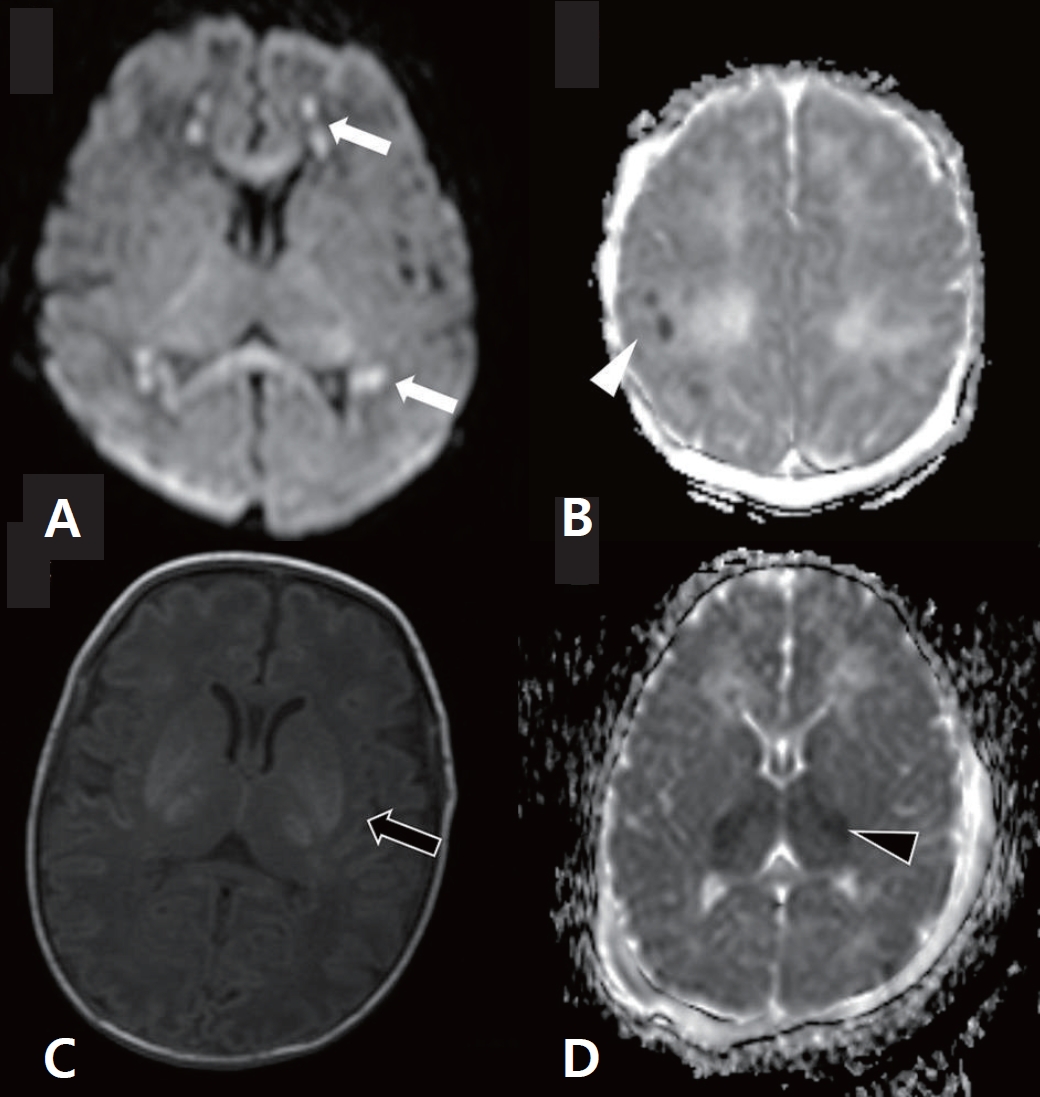
∙ Cognitive impairments occur in children with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) even without neuromotor deficits.
∙ Therapeutic hypothermia has improved neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with HIE; however, 40% of children remain at risk of death/disability or cognitive impairments necessitating the development of adjunctive neuroprotective therapies.
∙ Long-term follow-up until adolescence is required to identify cognitive dysfunction.
∙ A pattern of watershed injury on brain imaging is associated with poor cognitive outcomes.
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis, inactivated poliovirus, Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate, and hepatitis B vaccine in infants
- Hye-Kyung Cho, Su Eun Park, Yae-Jean Kim, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Byung-Wook Eun, Taek-Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Hyunju Lee, Ki Hwan Kim, Eun Young Cho, Jong Gyun Ahn, Eun Hwa Choi; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):602-607. Published online June 8, 2021
-
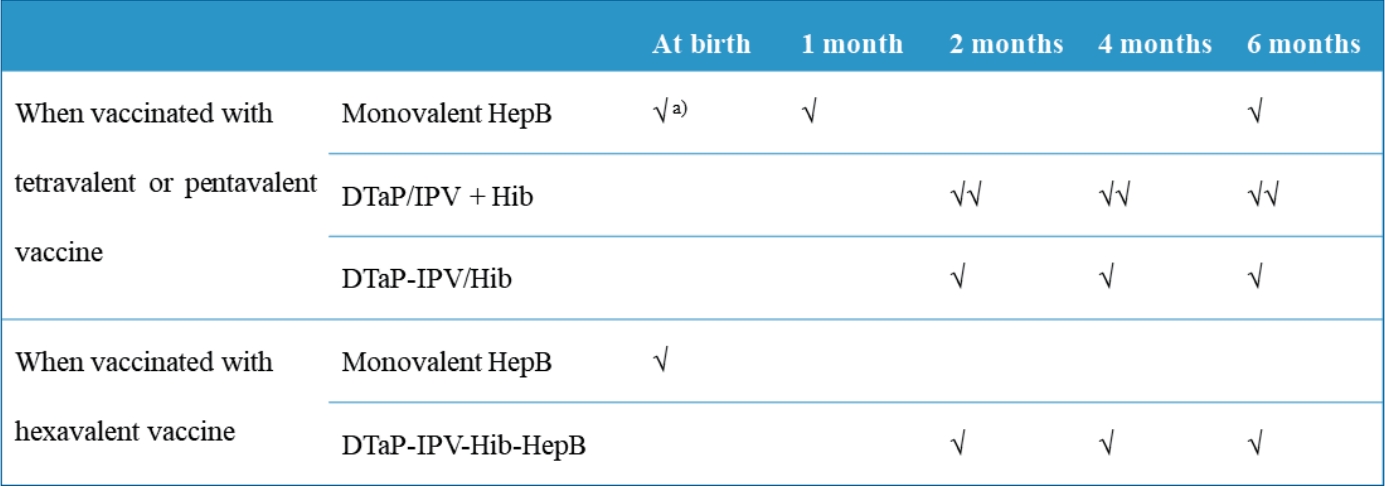
∙ Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis-inactivated poliovirus-Haemophilus influenzae type b-hepatitis B (DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB) was licensed in Korea in April 2020.
∙ DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB is indicated as a 3-dose primary series for infants aged 2, 4, and 6 months who received the standalone HepB vaccine at birth.
∙ Infants born to HepB surface antigen-positive mothers are currently recommended to be immunized with HepB immunoglobulin at birth and then monovalent HepB vaccine at 0, 1, and 6 months.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and Kawasaki disease in infants: 2 sides of the same coin?
- Hing Cheong Kok, Dinesh Nair, Ke Juin Wong, Siew Moy Fong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):599-601. Published online October 7, 2021
-
Question: Are multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and Kawasaki disease (KD) in infants, 2 sides of the same coin?
Finding: Here we report on a 4-month-old girl with MIS-C and signs of KD with shock. Most (83%) infants with MIS-C had features of KD, especially KD shock syndrome.
Meaning: MIS-C is similar to KD, and likely is a consequence of dysregulated immune responses secondary to sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.
- Clinical Note
- Infection
- A neonate infected with coronavirus disease 2019 with severe symptoms suggestive of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood
- Fatemeh Eghbalian, Ghazal Sami, Saeid Bashirian, Ensiyeh Jenabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):596-598. Published online September 10, 2021
-
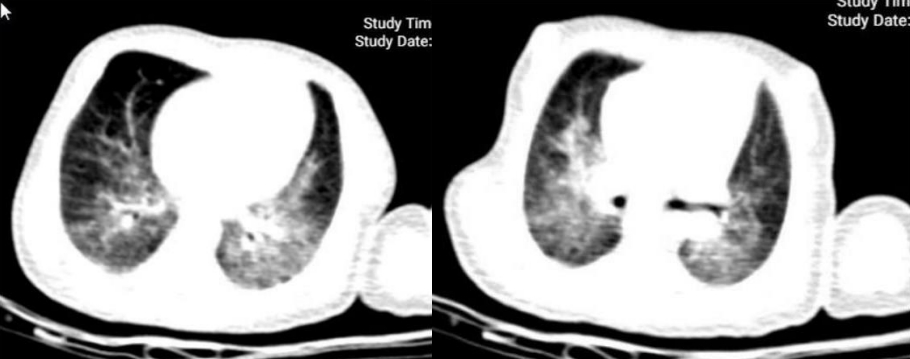
Question: Can multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood (MIS-C) occur in the neonate associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?
Finding: A 9-day-old neonate infected with COVID-19 had fever, respiratory distress, and gastrointestinal symptoms suggestive of MIS-C. This neonate recovered after treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG).
Meaning: IVIG successfully treated a rare case of a 9-day-old neonate with COVID-19 and severe symptoms suggestive of MIS-C.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Risk factors for childhood pneumonia: a case-control study in a high prevalence area in Indonesia
- Vivi Ninda Sutriana, Mei Neni Sitaresmi, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):588-595. Published online March 15, 2021
-

Question: Is the incidence of childhood pneumonia influenced by breastfeeding and basic immunization status?
Finding: Exclusive breastfeeding and complete basic immunization status have an effect in limiting the incidence of childhood pneumonia.
Meaning: While exclusive breastfeeding and complete basic immunization the Expanded Program on Immunization status are important factors for reducing the incidence of childhood pneumonia, indoor air pollution was also a significant risk factor.
- Cardiology
- Assessment of cardiac function in syncopal children without organic causes
- Heoungjin Kim, Lucy Youngmin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):582-587. Published online March 10, 2021
-

Question: Does a subtle deterioration in cardiac function affect the severity of syncope in patients without underlying disease?
Finding: For syncope patients with reasonable cardiac function but without underlying disease, tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) measurements helped reveal subtle differences in cardiac function with syncope and predicted the severity of syncope or a potential recurrent event.
Meaning: TDI measurements might be a useful indicator for predicting the severity of syncope.
- Original article
- Infection
- The global prevalence of Toxocara spp. in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Behnam Abedi, Mehran Akbari, Sahar KhodaShenas, Alireza Tabibzadeh, Ali Abedi, Reza Ghasemikhah, Marzieh Soheili, Shnoo Bayazidi, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):575-581. Published online February 5, 2021
-
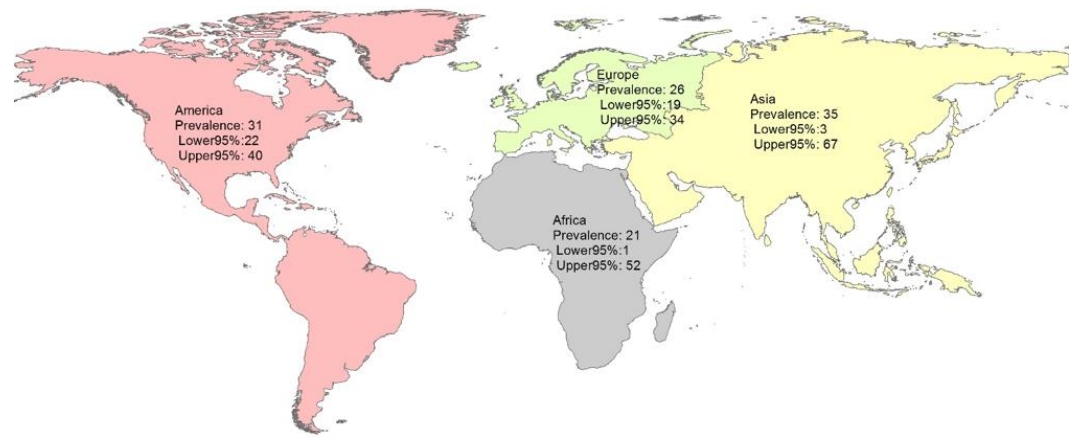
Is the global prevalence of toxocariasis high among children? The prevalence of toxocariasis is high in pediatric patients. Asian children are more susceptible to the disease than other children. Its virulence varies among different socioeconomic classes in various countries. Hand washing after soil contact, routine pet deworming, and appropriate disposal of pet feces in households with Asian pediatrics are needed to prevent toxocariasis.
- Editorial
- Oncology
- Infantile hemangioma: timely diagnosis and treatment
- Meerim Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):573-574. Published online July 22, 2021
-

While the majority of infantile hemangiomas (IHs) do not require therapy and regress spontaneously, about 10%–15% develop complications such as ulceration, obstruction, or disfigurement. Early intervention is recommended for infants with potentially problematic IHs. Oral propranolol 2–3 mg/kg/day is currently the treatment of choice.
- Review Article
- Oncology
- Update on infantile hemangioma
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):559-572. Published online May 26, 2021
-

· Infantile hemangiomas (IHs) are the most common benign vascular tumors, occurring in 5%–10% of infants.
· IHs are characteristically not present at birth but are usually diagnosed at 1–4 weeks of age, rapidly proliferate until 5 months of age, and then spontaneously involute.
· High-risk IHs (10%) require early treatment from 1 month of age.
· Oral propranolol, a nonselective beta-blocker, is the first-line treatment for IHs.
- Nutrition
- Changes in health status of North Korean children and emerging health challenges of North Korean refugee children
- Seong-Woo Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):552-558. Published online May 17, 2021
-

· Among North Korean refugee (NKR) children under 5 years, 61% and 9.3% were underweight in 1998 and 2017, respectively.
· The immunization rate of NKR children exceeded 90% since 2006.
· For NKR children, protein-energy malnutrition was the #1 cause of death in 2009 versus #17 in 2019.
· In 2020, stunting affected 5.4% and 0.9% and obesity affected 10.7% and 2.7% of NKR versus South Korean children, respectively.
- Infection
- Effects of nasopharyngeal microbiota in respiratory infections and allergies
- Hyun Mi Kang, Jin Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):543-551. Published online April 15, 2021
-

· The nasal microbiota varies with age and is shaped by various factors in healthy individuals.
· The pathological condition of the respiratory tract appears to be associated with reduced nasal microbiota biodiversity, while dysbiosis is involved in the pathophysiology of many respiratory diseases, including otitis, sinusitis, allergic diseases, and lower respiratory infections.
- Original Article
- Neurobehavior
- Association between small for gestational age and risk of autism spectrum disorders: a meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Zahra Asali, Mahdieh Seyedi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):538-542. Published online January 28, 2021
-
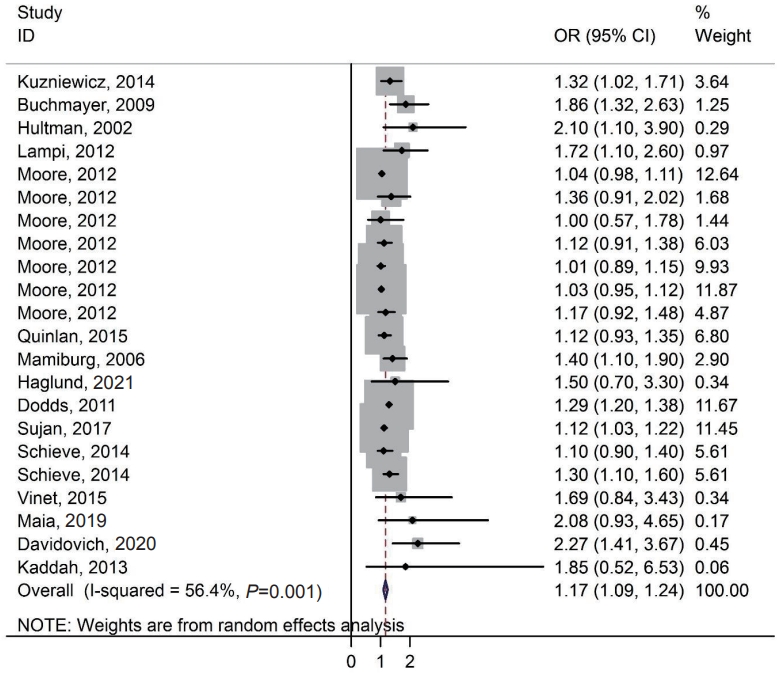
• The relationship between small for gestational age (SGA) and autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and remains conflicting.
• We showed based on odds ratio reports in epidemiological studies that SGA can increase the risk of ASD and SGA is a risk factor for ASD.
• The association between SGA and the risk of ASD has further momentum to the current public health emphasis on appropriate prepregnancy weight and weight gain during pregnancy
- Other
- Clinical spectrum and short-term outcomes of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in a south Indian hospital
- Muruganantham Balagurunathan, Thrilok Natarajan, Jothilakshmi Karthikeyan, Venkateshwaran Palanisamy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):531-537. Published online August 4, 2021
-

Question: What are the clinical spectrum, course, and short-term outcomes of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C)?
Finding: MIS-C can have variable clinical manifestations. Fever is most common, followed by gastrointestinal and cardiovascular symptoms. Early identification and appropriate management lead to favorable outcomes.
Meaning: MIS-C can present in a myriad of ways and severities. High suspicion is necessary to ensure its early identification and appropriate management and favorable patient outcomes.
- Endocrinology
- Correlation between total air pollutant emissions and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the Russian Federation
- Hoon Sung Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Ji-Young Seo, Faina Linkov, Evgeniy Shubnikov, Hong Kyu Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):525-530. Published online January 18, 2021
-
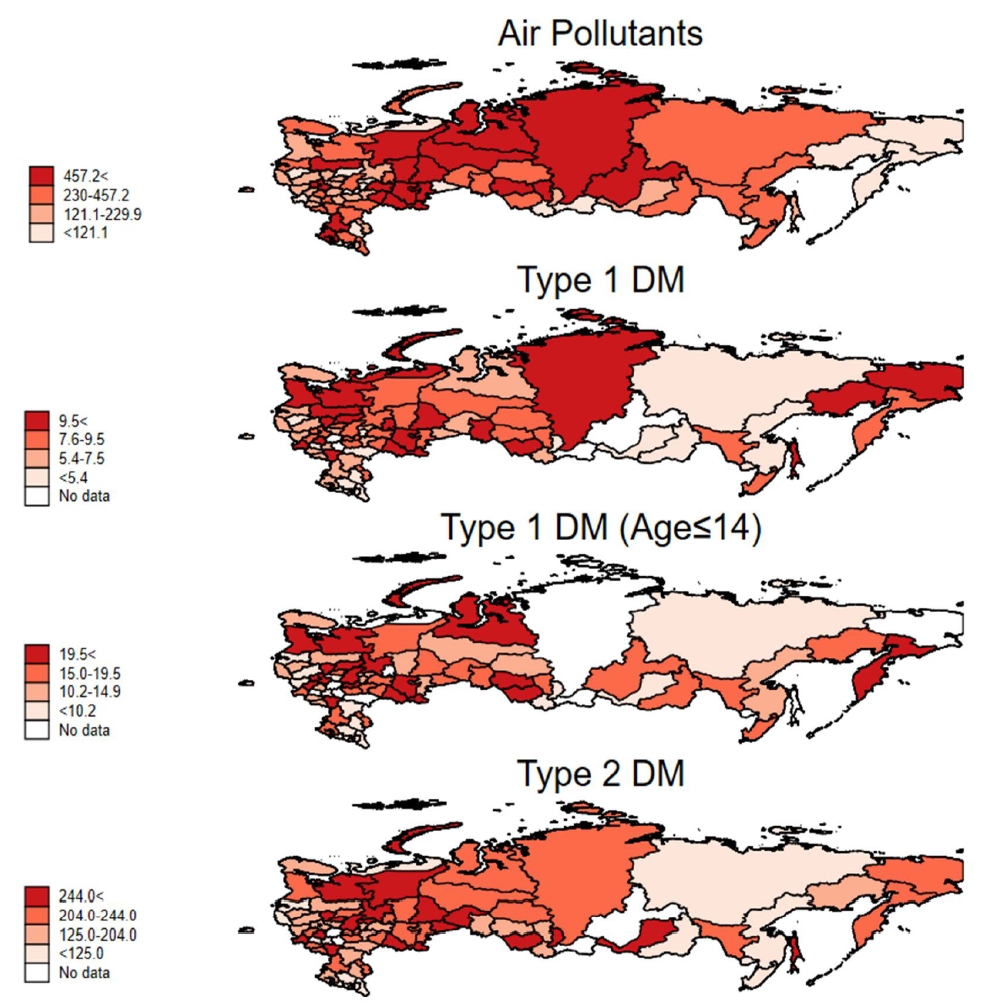
Question: Is there a quantitative relationship between air pollutant emissions and the incidence of type 1 diabetes (T1D)?
Finding: The incidence of T1D in each region of the Russian Federation correlated with the total air pollutants emitted each year.
Meaning: These findings suggest that air pollution contributes to the development of T1D.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Ambient air pollution and pediatric diabetes
- Jae Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):523-534. Published online March 12, 2021
-
· Epidemiological studies have shown that ambient air pollution is associated with diabetes mellitus in children and adults.
· The mechanism of ambient air pollution causing diabetes mellitus is unclear.
· A study of the association between diabetes and air pollution in Korean pediatric populations is required.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Obesity and chronic kidney disease: what should pediatric nephrologists know?
- Jung Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):521-522. Published online June 1, 2021
-
• Obesity is not only a comorbidity of hypertension, it may be a riskfactorfor chronickidneydisease.
• Renal impairment associated with obesity is believed to start early in childhood and continue into adulthood, implying a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
• The identification of kidney injury, implementation of preventive strategies, and prompt treatment are essential to improving clinical outcomes in obese children with early kidney disease.
- Immunology
- Importance of neonatal screening for primary immunodeficiencies
- Jung Woo Rhim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):519-520. Published online May 4, 2021
-
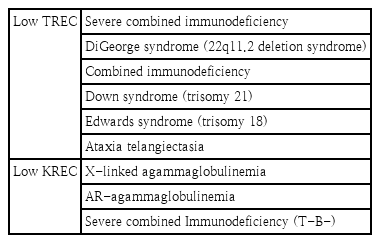
· Early detection of asymptomatic infants with primary immunodeficiencies before the onset of infections enables effective treatment and intervention to prevent serious sequelae.
· T-cell receptor excision circles and kappa-deleting recombination excision circles have recently been used to detect T- or B-cell lymphopenia in neonates.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







