Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six months.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Long COVID in children and adolescents: prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management strategies (58 times)
- Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):465-474. Published online June 19, 2023
-
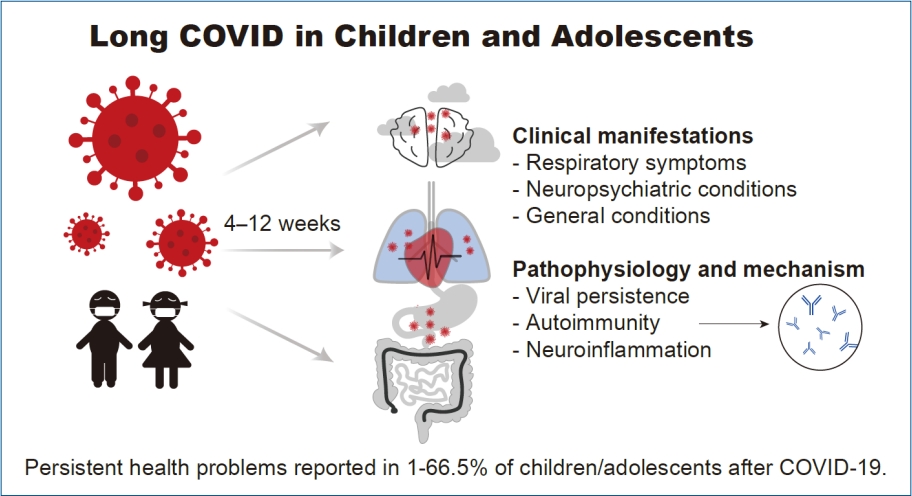
· Current definitions of long coronavirus disease (COVID) in children and adolescents vary in duration, ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
· The clinical spectrum of long COVID in children and adolescents comprises a wide range of symptoms and might be a multisystem disorder.
· Persistent health problems with a prevalence of 1%–66.5% were reported in children and adolescents after COVID-19, with a higher incidence of persistent single or multiple symptoms.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Virtual reality for pain reduction during intravenous injection in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials (57 times)
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Masoud Rafiee, Mozhdeh Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):533-537. Published online June 14, 2023
-
Question: This is the first meta-analysis to examine published evidence of the effectiveness of virtual reality at reducing pain during pediatric intravenous injections.
Finding: Our results suggest that virtual reality effectively reduces pain associated with intravenous injections in pediatric patients.
Meaning: These findings suggest the importance of virtual reality in decreasing the pain of intravenous injections among children.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review (55 times)
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
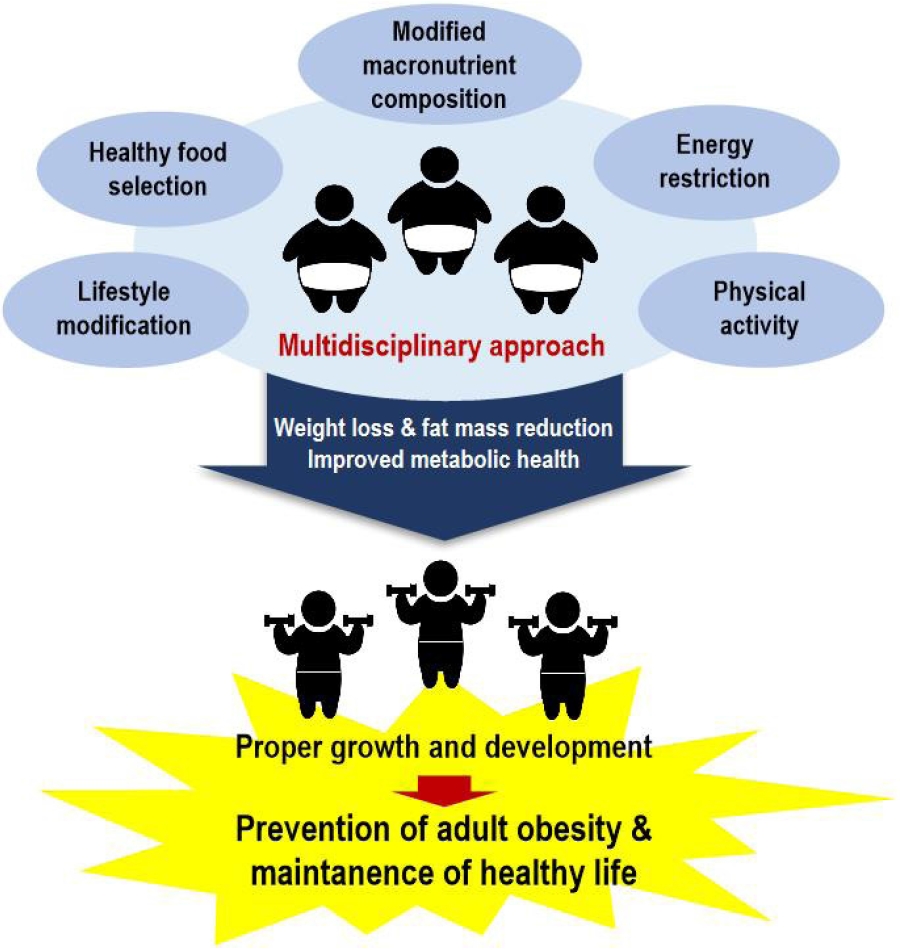
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review (53 times)
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
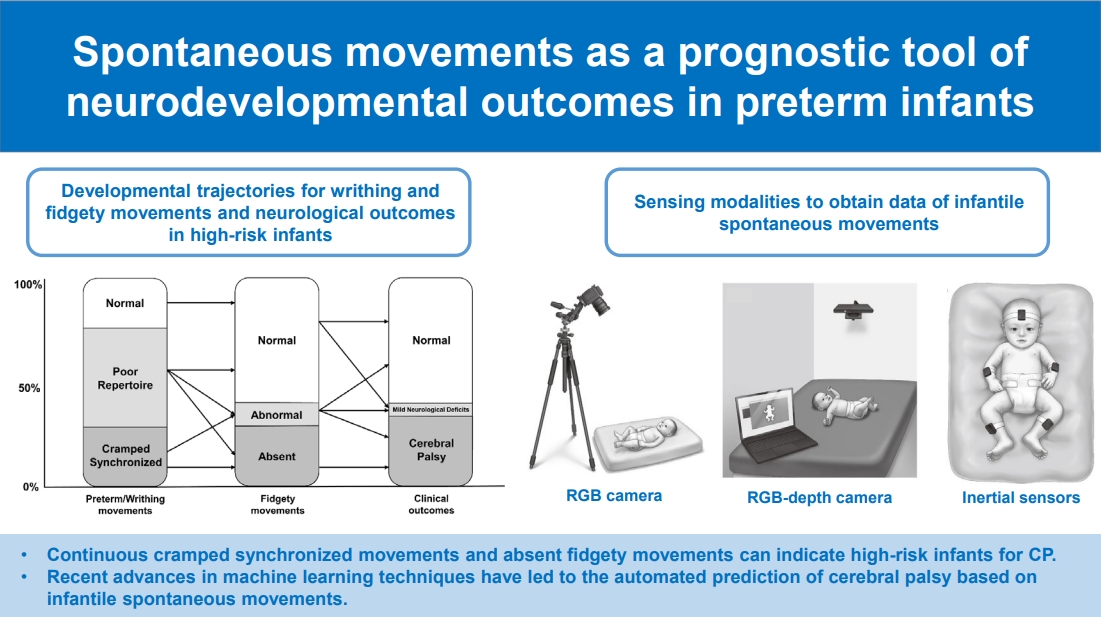
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Clinical Note
- Neurology
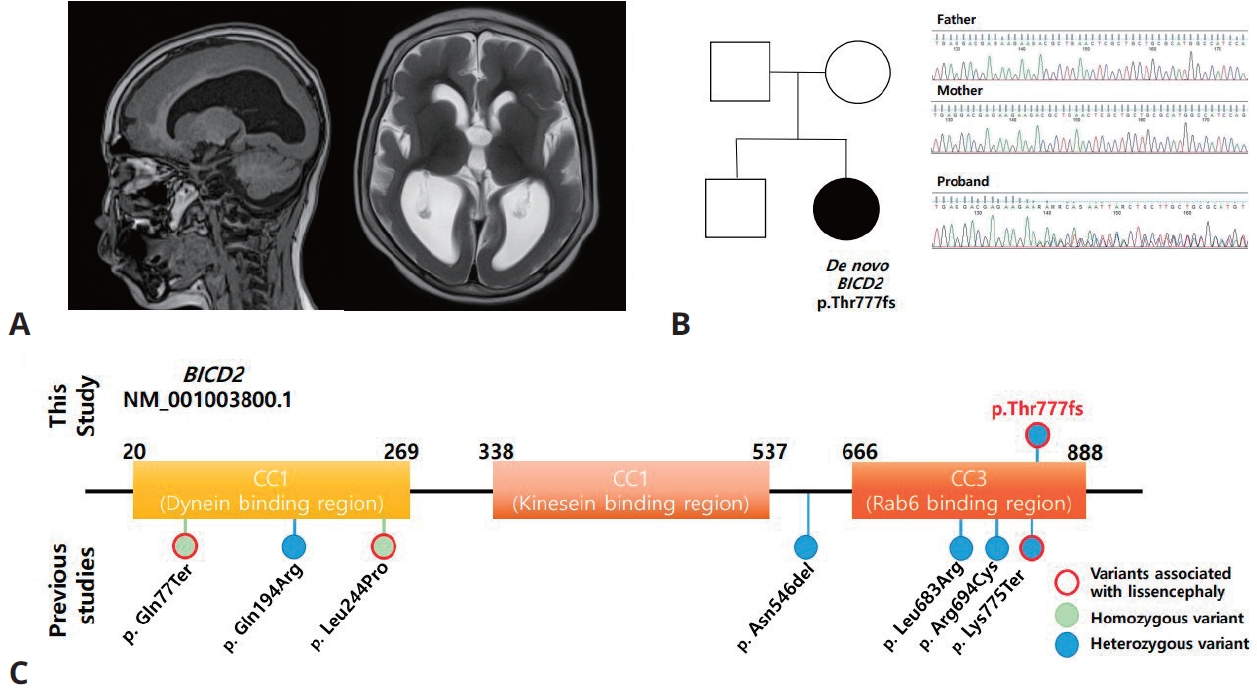
- Expanding association between BICD2 variants and brain malformations and associated lissencephaly (53 times)
- Jaeso Cho, Haeryung Kim, Seoungbok Lee, Jihoon G Yoon, HyeJin Kim, Minhye Kim, Seoyun Jang, Woojoong Kim, Soo Yeon Kim, Jong Hee Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):54-56. Published online December 21, 2023
-
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Gross motor dysfunction and balance impairments in children and adolescents with Down syndrome: a systematic review (52 times)
- Preyal D. Jain, Akshatha Nayak, Shreekanth D. Karnad, Kaiorisa N. Doctor
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):142-149. Published online June 11, 2021
-
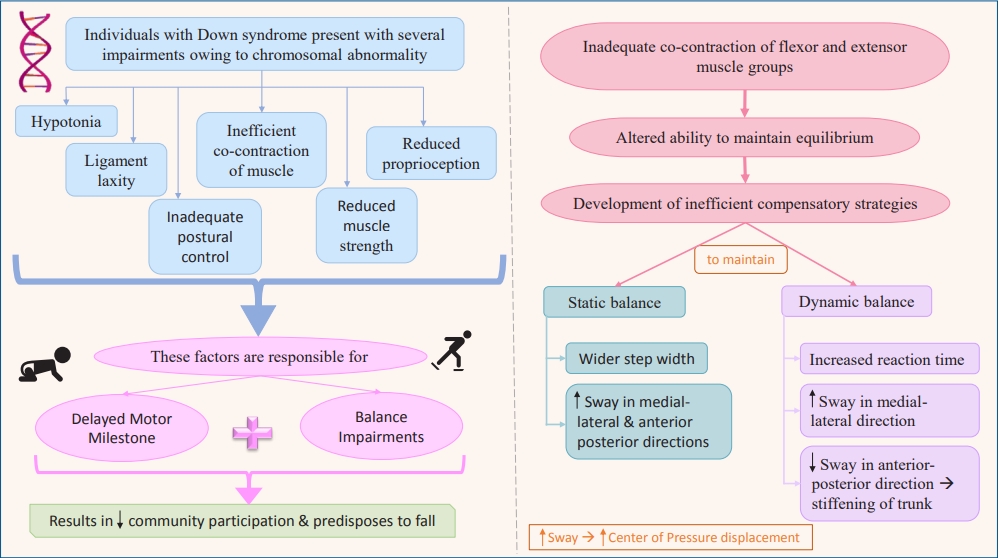
Question: What are the primary motor and balance dysfunctions in children with Down syndrome?
Finding: These individuals have gross delays, altered balance, and inefficient compensatory mechanisms.
Meaning: Neuromuscular and musculoskeletal impairments due to the chromosomal abnormality lead to developmental delay. These children also exhibit poor balance with greater instability and inefficient compensatory mechanisms including altered center of pressure displacement and trunk stiffening that predisposes them to falls.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Global varicella vaccination programs (52 times)
- Young Hwa Lee, Young June Choe, Jia Lee, Eunseong Kim, Jae Young Lee, Kwan Hong, Yoonsun Yoon, Yun-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):555-562. Published online November 2, 2022
-
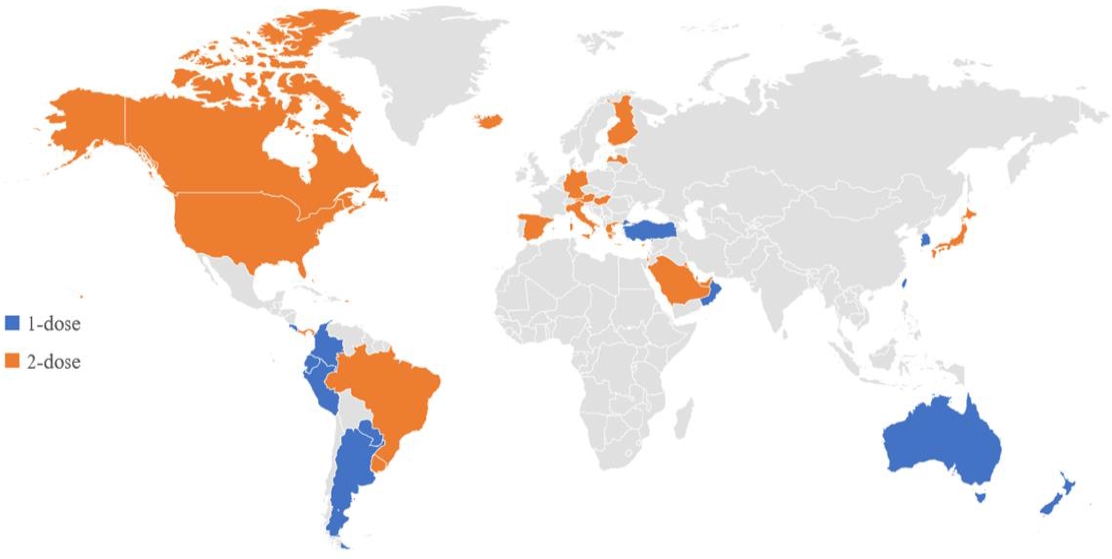
It is important to evaluate its effectiveness at the national level and to determine the varicella vaccine schedule based on the evidence generated through the studies.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants (52 times)
- In Gyu Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):281-287. Published online December 30, 2022
-
· Among survivors, 60.9% of infants born at 22 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments, whereas 50.3% born at 23 weeks’ and 42.2% at 24 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments.
· Moderate and late preterm infants reportedly have less severe disease than very preterm infants, but they still experience adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.
· The careful follow-up and early detection of developmental problems in these patients are required.
- Neurology
- Update on benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (51 times)
- Yeong Seok Lee, Ga Hee Lee, Young Se Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):469-475. Published online December 27, 2021
-
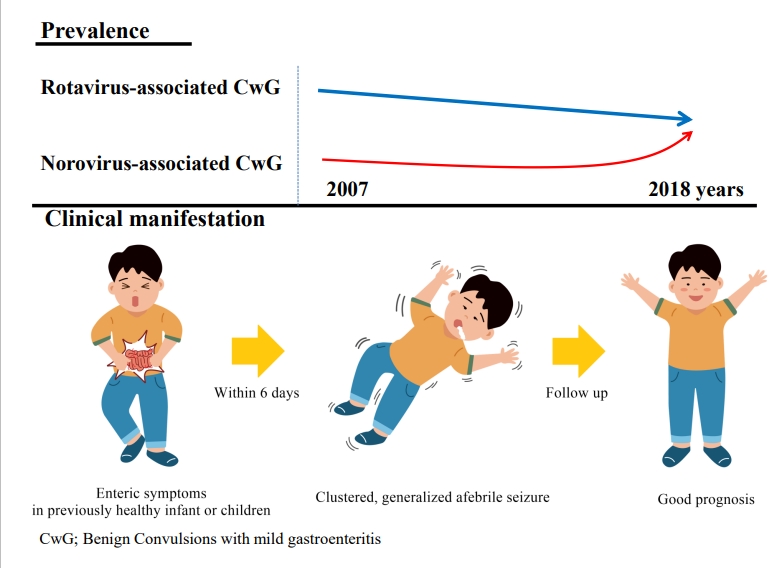
∙ The main pathogen for benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG) was previously rotavirus; however, cases associated with norovirus are increasing.
∙ CwG is characterized by clustered generalized seizures. Electroencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging show transiently abnormal findings in the acute phase that eventually normalize with progression. Its prognosis is good, and long-term treatment is unnecessary.
∙ There are many reports on the pathophysiological mechanism of CwG, which remains unclear.
- Gastroenterology
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children (51 times)
- Jisun Hwang, Hee Mang Yoon, Pyeong Hwa Kim, Ah Young Jung, Jin Seong Lee, Young Ah Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):12-21. Published online July 4, 2022
-
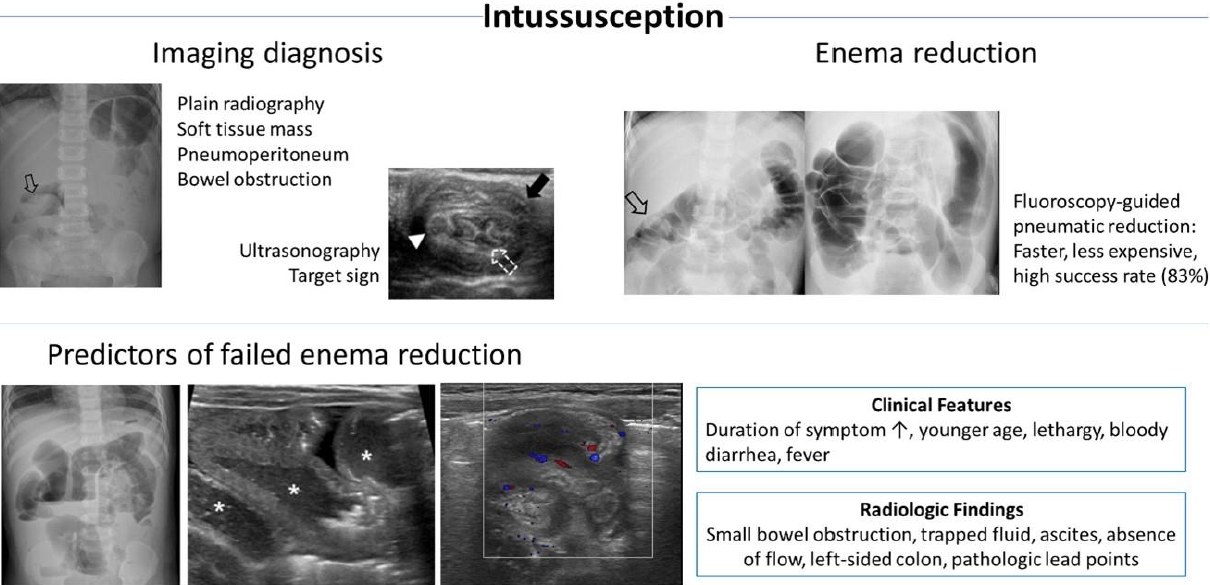
· Intussusception, the most common cause of small bowel obstruction in young children, has an overall incidence in Korea of 28.3 cases per 100,000 person-years.
· Its cause is idiopathic inmost cases, although viral or bacterial gastroenteritis has beenpostulated as a cause. Approximately 4% of children have pathological lead points for intussusception, and Meckel’s diverticulum is the most common cause.
· Intussusception in preterm infants is extremely rare. Older children (>5 years of age) are at increased risk of pathological lead points.
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (51 times)
- Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):432-438. Published online June 14, 2023
-
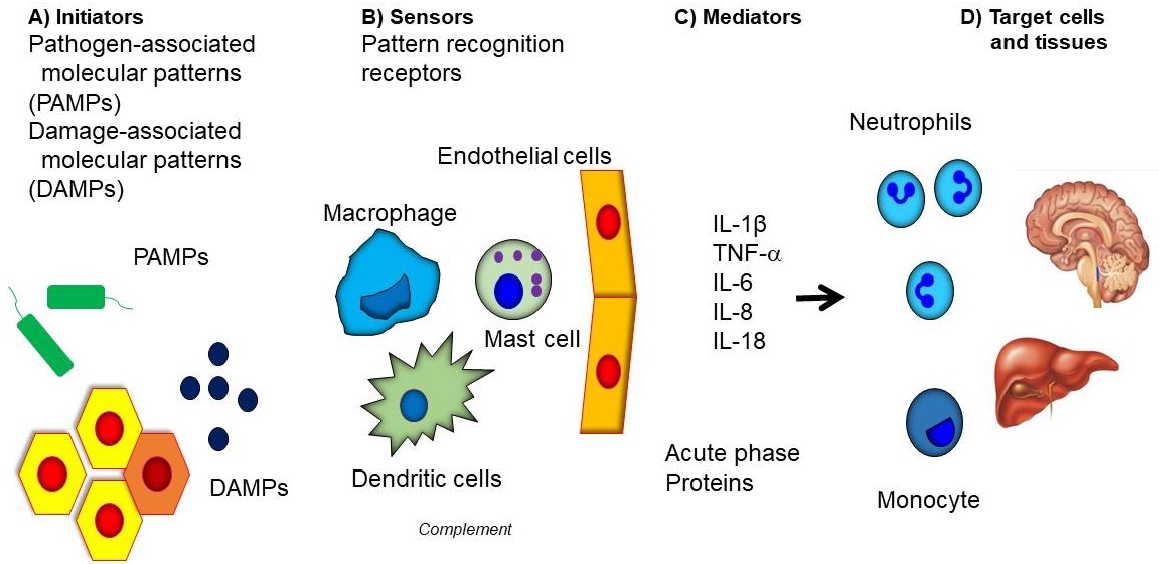
· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAID) are disorders caused by dysregulation of the innate immunity with genetic background, leading to recurrent episodes of systemic inflammation.
· SAID is characterized by recurrent acute inflammatory responses including fever or skin manifestations, unrelated with infection or malignancy.
· Diagnosis is based on family and long-term history with detailed clinical and laboratory manifestations during febrile periods.
- Endocrinology
- Applications of genomic research in pediatric endocrine diseases (51 times)
- Ja Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):520-530. Published online June 14, 2023
-
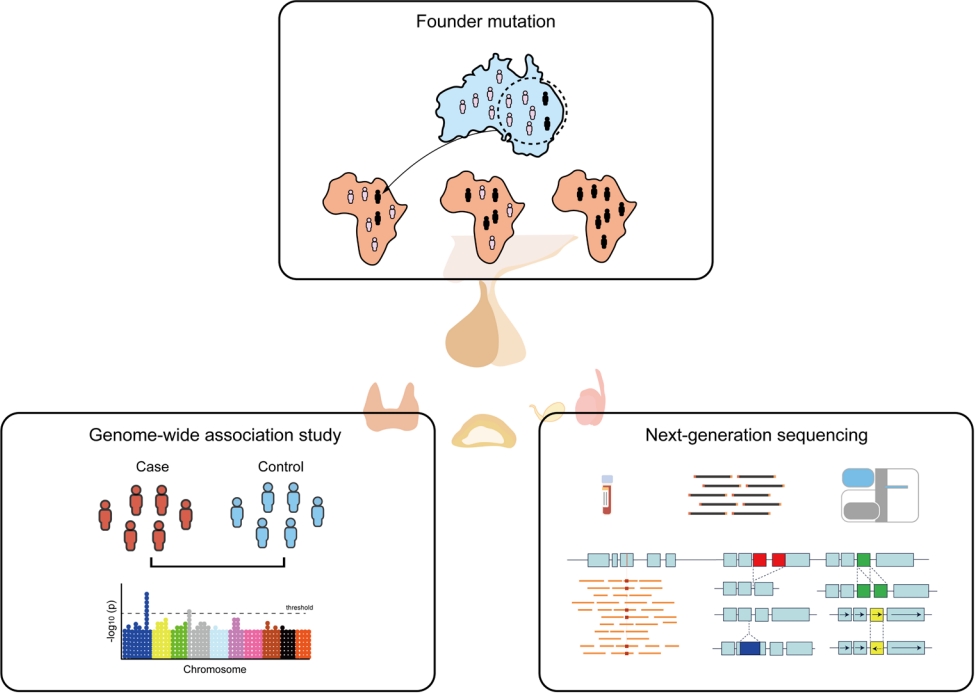
· Recent advances in molecular genetics have improved our understanding of pediatric endocrine disorders and are now used in mainstream medical practice.
· Genome-wide association studies can increase our understanding of the biological mechanisms of disease and inform new therapeutic options.
· The identification of founder mutations leads to the efficient localization of the genes underlying Mendelian disorders.
· Next-generation sequencing technologies benefit clinical practice and research of pediatric endocrinology.
- Neurology
- Gut microbiota affects brain development and behavior (48 times)
- Gun-Ha Kim, Jung-Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):274-280. Published online November 8, 2022
-

· The gut microbiota can alter a host’s brain development and behavior.
· Gut bacteria communicate with the brain via the microbiota-gut-brain axis.
· Fecal microbial transplantation is a promising treatment strategy for autism spectrum disorder.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates intestinal injury in necrotizing enterocolitis (48 times)
- Yeong Seok Lee, Yong Hoon Jun, Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):152-160. Published online February 19, 2024
-
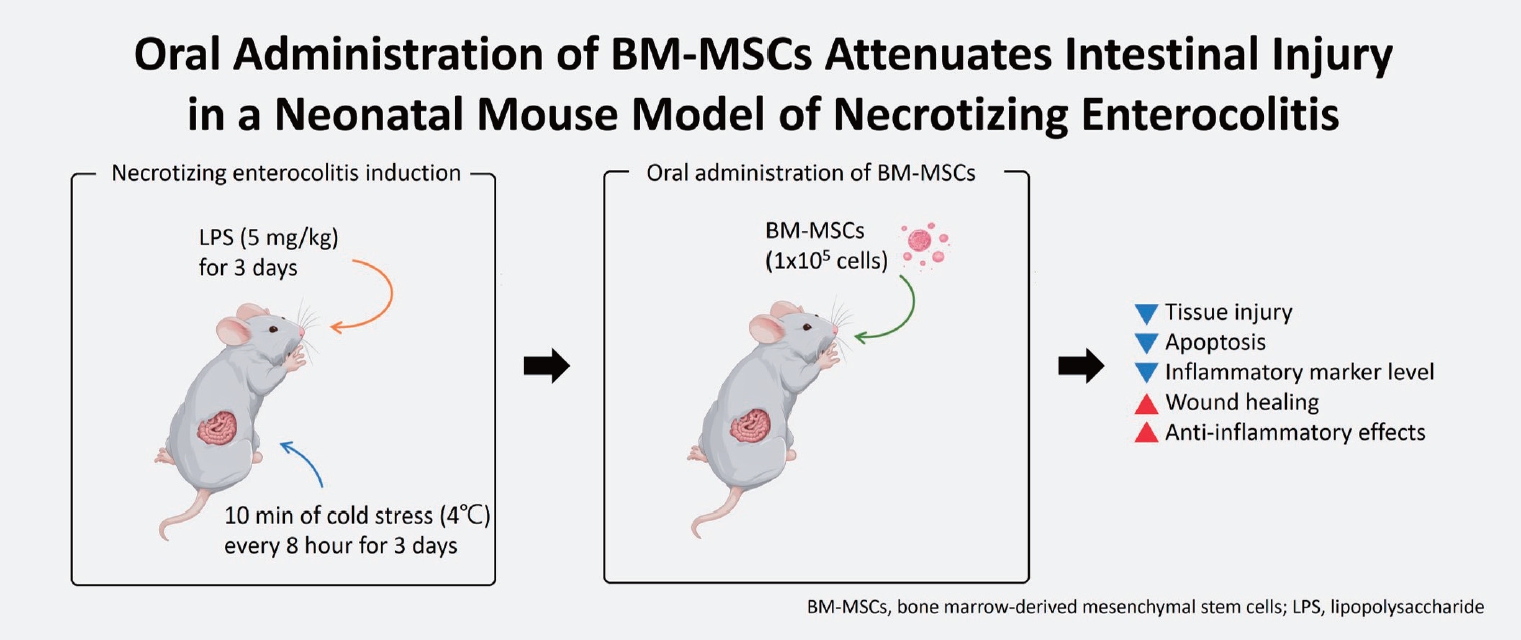
Question: What is the optimal dose of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for treating necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and is orally administered BM-MSC effective?
Findings: High (1×106 cells) or multiple BM-MSC doses showed similar effects as low (1×105 cells) doses of intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs. Furthermore, orally administered BM-MSCs were as effective as intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs.
Meaning: Orally administered low-dose BM-MSCs are a potential treatment for NEC.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Bisphenol A leaching from polycarbonate baby bottles into baby food causes potential health issues (46 times)
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):450-452. Published online July 25, 2022
-

Can bisphenol A (BPA) leach out from polycarbonate baby bottles into baby food? BPA and other toxic materials can leach out from baby bottles and increase the risk of various health problems, including endocrine disturbances. Although the use of BPA in baby bottles has been banned, many developing countries still use it, which can cause health issues. Thus, public awareness of this issue is required.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Genetic factors in precocious puberty (44 times)
- Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):172-181. Published online October 18, 2021
-
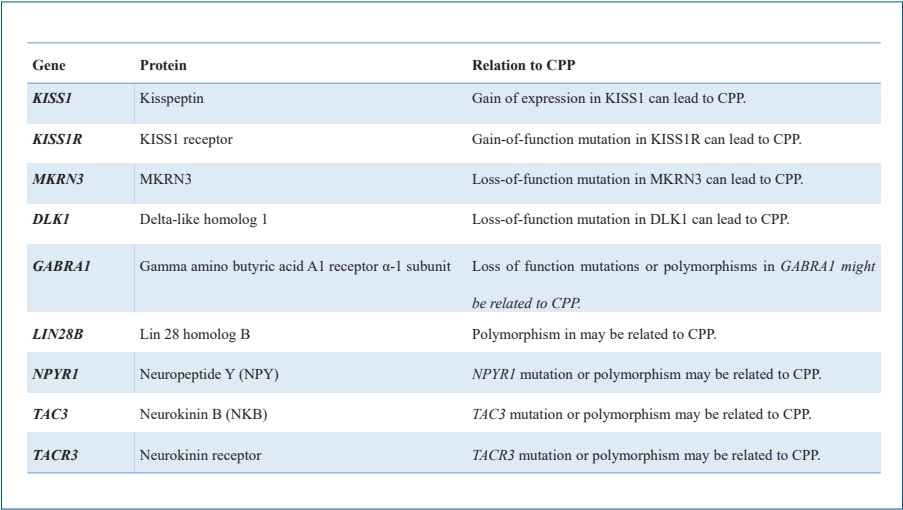
· Mutations in the kisspeptin (KISS1), kisspeptin receptor (KISS1R), makorin ring finger protein 3 (MKRN3), and delta-like homolog 1 (DLK1) genes are associated with idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP).
· A few genes related to pubertal onset have been implicated in ICPP.
· Epigenetic factors such as DNA methylation, histone posttranslational modifications, and noncoding ribonucleic acids may be related to ICPP
- Nutrition
- Association of gut microbiota with obesity in children and adolescents (44 times)
- Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):148-154. Published online November 16, 2022
-

The gut microbiota is an emerging factor in the development of pediatric obesity, which is affected by renowned risk factors such as diet, lifestyle, and socioeconomic status. This review aimed to describe the association between the gut microbiota and childhood obesity.
- Original Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children (44 times)
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
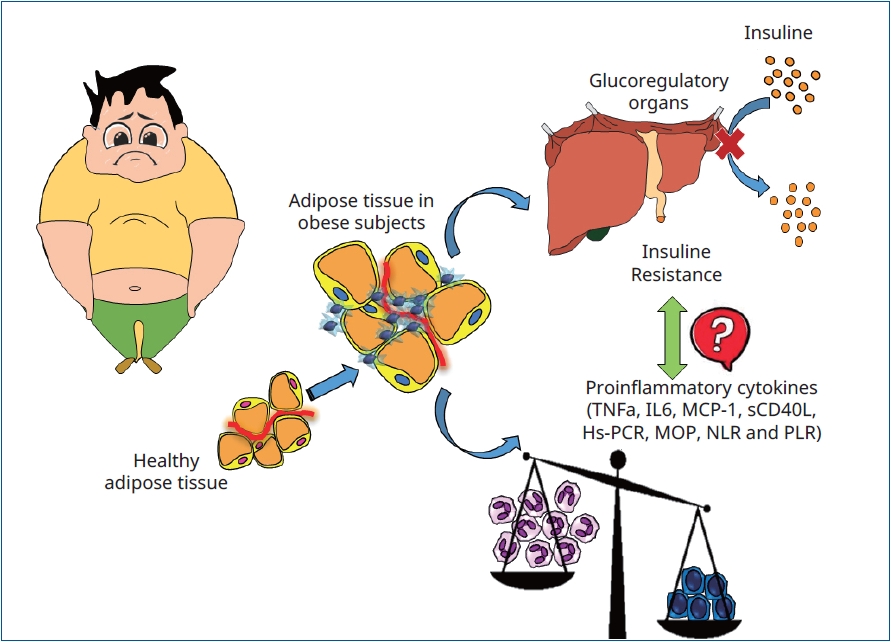
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- General Pediatrics
- Global relationship between parent and child obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis (42 times)
- Ju Suk Lee, Mi Hyeon Jin, Hae Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):35-46. Published online March 29, 2021
-

Question: Are parent and child obesity correlated worldwide?
Finding: Overweight and obese status of parents and children were significantly associated worldwide. The association between parent and child obesity was stronger in Asia than in Europe and the Middle East, and in high-income than in middle- and low-income countries.
Meaning: Childhood obesity is highly influenced by parental weight status, indicating that parents could play an important role in its prevention.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Influence of infant microbiome on health and development (42 times)
- Noelle Younge
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):224-231. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· The infant gut microbiome is highly dynamic and individualized.
· Microbes are vertically transmitted from mother to infant during delivery and throughout infancy.
· Delivery mode, gestational age, diet, and antibiotic use influence infant microbiome composition and function.
· In animal studies, the microbiome played critical roles in the structural and functional development of the infant gastrointestinal and immune systems.
· Microbiome-targeted therapies have great potential to reduce infant morbidity and mortality.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents (42 times)
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
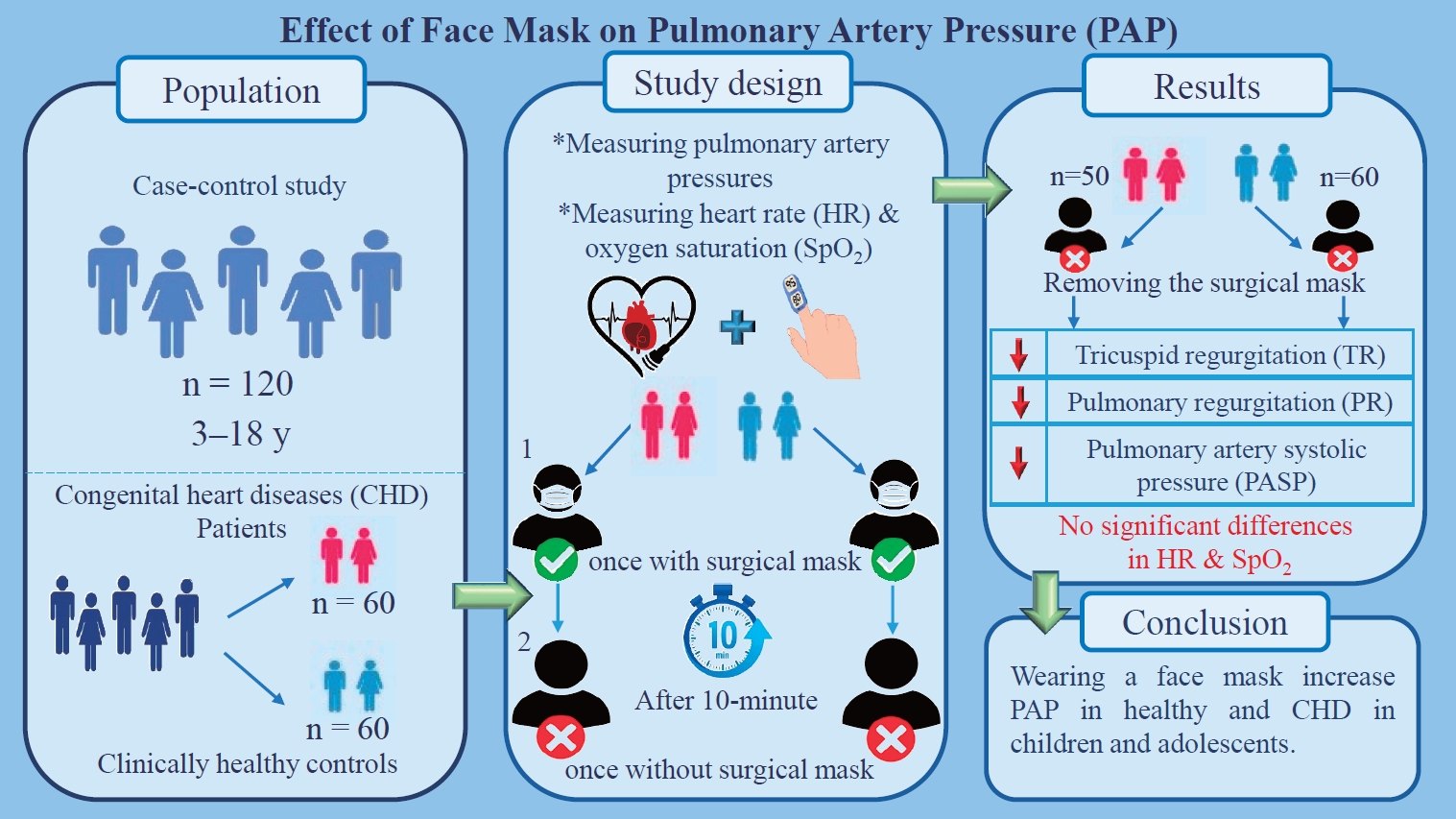
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system complications: clinicoradiological features and potential mechanisms (39 times)
- Kyung Yeon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):483-493. Published online February 7, 2022
-

∙ Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system (CNS) complications are fairly common in children.
∙ Common clinicoradiological features include benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis, acute encephalopathies/encephalitis, cerebellitis, and neonatal rotavirus-associated leukoencephalopathy.
∙ Possible mechanisms for CNS complications include direct viral invasion into the brain via several potential routes such as the blood-brain barrier and vagus nerve, and entry of various brain-damaging mediators and activated immune cells into the brain.
- Allergy
- Diagnosis and management of asthma in infants and preschoolers (39 times)
- Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):574-584. Published online April 19, 2022
-
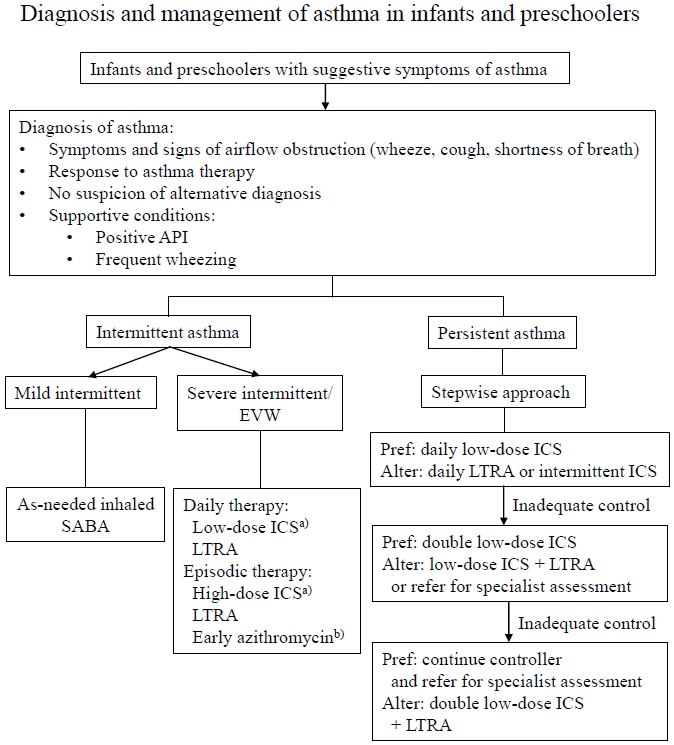
· Asthma in infants and preschoolers involves heterogeneous phenotypes.
· Asthma diagnosis is based on symptom patterns, therapeutic responses, and the presence of risk factors with careful consideration of differential diagnosis.
· Daily inhaled corticosteroid therapy remains the most effective strategy for managing persistent asthma symptoms irrespective of phenotype.
· Future research, including genetic and molecular studies, is needed to develop a clear definition of asthma and personalized therapeutic approaches.
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy (39 times)
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
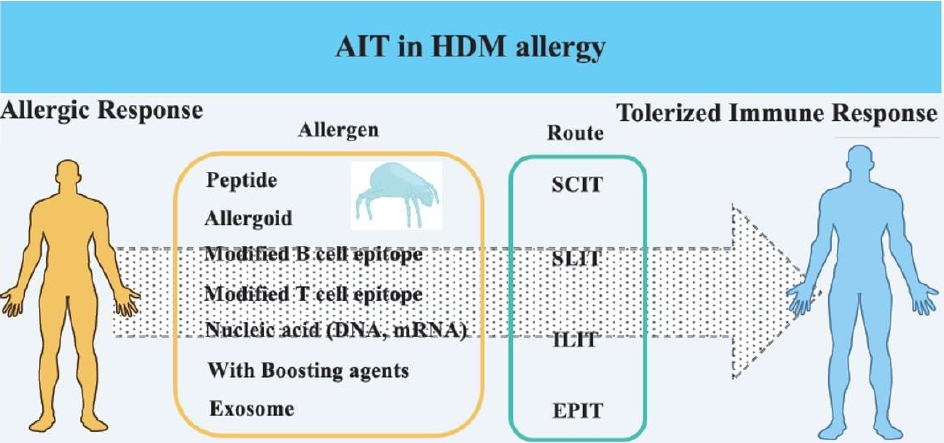
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Other
- MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases (39 times)
- Hwal Rim Jeong, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):119-125. Published online May 24, 2023
-

MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post transcriptionally, and MiRNA expression levels vary with developmental stages. MiRNAs play an important role in several biological processes in children, including growth, neuro-development, inflammation, and tumor formation. Research on miRNAs may uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying various pediatric diseases, leading to the development of novel biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of these diseases.
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review (39 times)
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
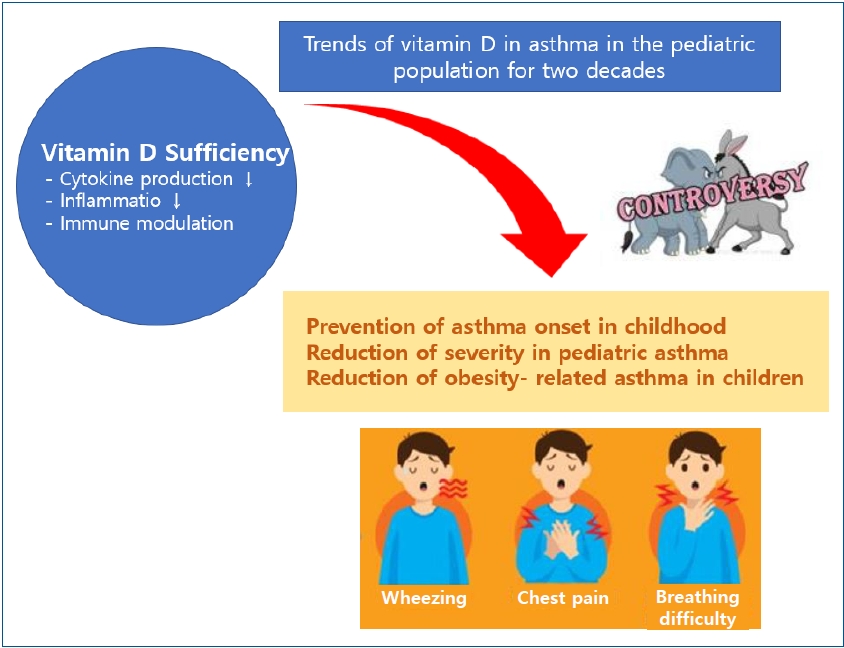
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of maternal and child factors on stunting: partial least squares structural equation modeling (38 times)
- Agus Santosa, Essa Novanda Arif, Dinal Abdul Ghoni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):90-97. Published online May 4, 2021
-
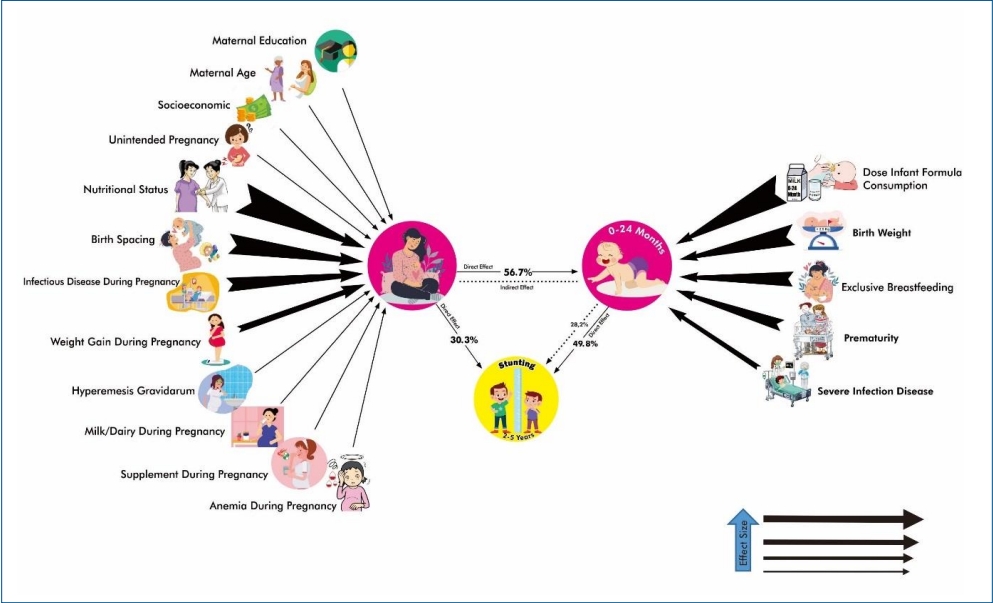
Question: What effects do maternal and child factors have on stunting? Are there significant indicators of stunting?
Finding: Child and maternal factors had 49.8% and 30.3% effects on stunting, respectively. The primary child factor was infant formula dose, while the primary maternal factor was nutritional status.
Meaning: More attention to nutritional status during pregnancy and ensuring the appropriate dose of infant formula at ages 6–24 months can prevent stunting.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Big data analysis and artificial intelligence in epilepsy – common data model analysis and machine learning-based seizure detection and forecasting (36 times)
- Yoon Gi Chung, Yonghoon Jeon, Sooyoung Yoo, Hunmin Kim, Hee Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):272-282. Published online November 26, 2021
-
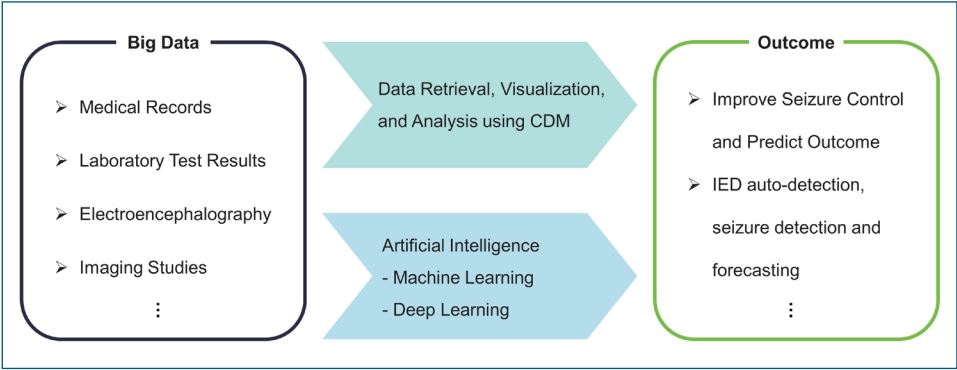
· Big data analysis, such as common data model and artificial intelligence, can solve relevant questions and improve clinical care.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 0.887–0.996 areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve for automated interictal epileptiform discharge detection.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 62.3%–99.0% accuracy for interictal-ictal classification in seizure detection and 75.0%– 87.8% sensitivity with a 0.06–0.21/hr false positive rate in seizure forecasting.
- Gastroenterology
- Factors influencing development of the infant microbiota: from prenatal period to early infancy (36 times)
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):439-447. Published online December 23, 2021
-
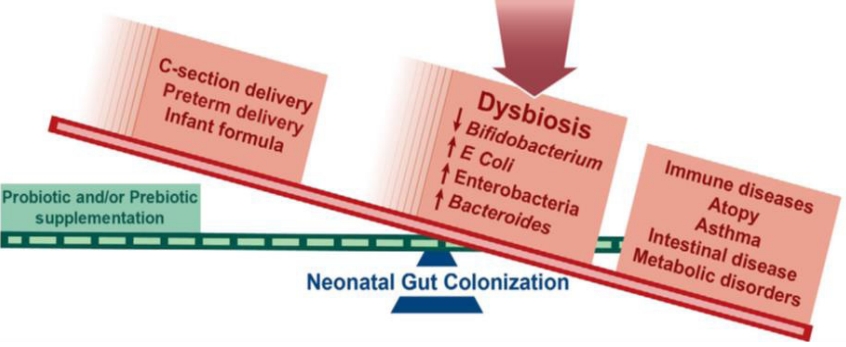
∙ Microbial colonization primarily occurs after birth but there may be some colonization in utero, although this remains highly controversial.
∙ Maternal factors during pregnancy affect the infant microbiota: diet, weight, gestational weight gain, and antibiotic usage.
∙ Microbes are passed from mother-to-infant during and after birth. Delivery mode, breastfeeding, early life antibiotic, and proton pump inhibitor treatment have the largest effects on microbial composition in early life.
∙ The early life gut microbiome plays an important role in the development of the immune system and metabolism.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Impact of short and intensive art-based intervention on symptomatology and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (36 times)
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Bayar Mohammed Omar Abdulla, Pranee Liamputtong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):447-454. Published online September 14, 2023
-

Question: Does a short and intensive art-based intervention affect symptoms and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Finding: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not affect symptoms in children with ASD level 2 or 3, including social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and autistic mannerisms.
Meaning: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not improve the symptoms of patients with ASD.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







