- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: how can we improve its outcomes?
- Tae-Jung Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):367-373. Published online May 17, 2019
-
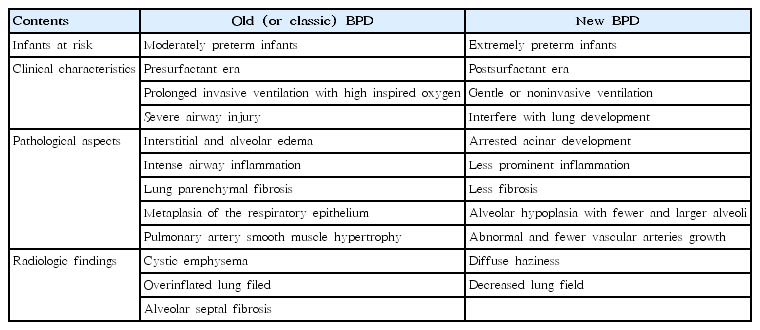
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung disease of preterm infants with multiple factors affected from prenatal to postnatal periods. Despite significant advances in neonatal care over almost 50 years, BPD rates have not decreased; in fact, they may have even increased. Since more preterm infants, even at periviable gestational age, survive today, different stages of lung development affect the...
- Systematic review and meta-analysis
- General Pediatrics
- The maternal prepregnancy body mass index and the risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder among children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saied Bashirian, Salman Khazaei, Zohreh Basiri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):374-379. Published online June 14, 2019
-
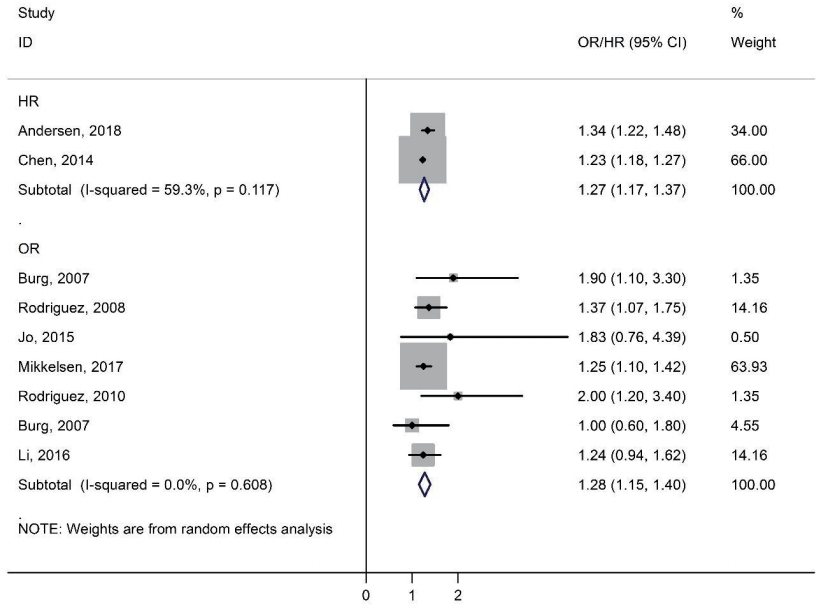
Background: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms have a major impact on individuals, families, and society. Therefore identification risk factors of ADHD are a public health priority.
Purpose: This is meta-analysis evaluated the association between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and the risk of ADHD among the resulting offspring. Methods: The search identified studies published through December 2018 in the PubMed, Web...
- Editorials
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Strategies to improve outcomes of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Young Hwa Jung, Chang Won Choi, Beyong Il Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):380-381. Published online September 11, 2019
-
- Central line-associated bloodstream infections in the neonatal intensive care unit
- Woo Ryoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):382-383. Published online July 17, 2019
-
- Gastroenterology
- Can proton pump inhibitors cause intestinal inflammation in children?
- Ben Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):384-385. Published online October 2, 2019
-
- Original Articles
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Clinical impact of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight infants: results from Korean Neonatal Network
- Na Hyun Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, Juyoung Lee, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):386-394. Published online May 22, 2019
-
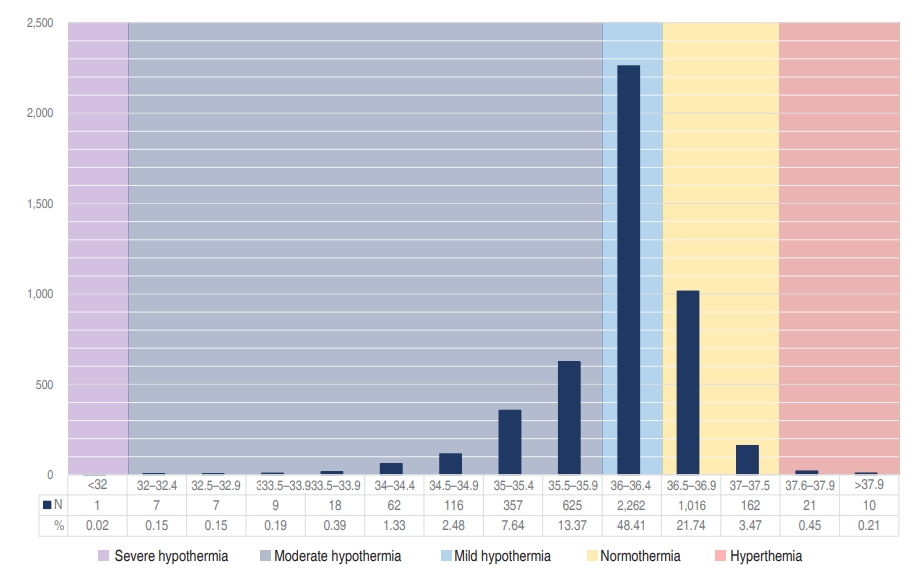
Background: Preterm infants have difficulty maintaining body temperature after birth. However, clinical guidelines advocate that neonatal body temperature should be maintained at 36.5°C–37.5°C.
Purpose: We aimed to investigate the incidence of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants and to determine the association of admission temperature with in-hospital mortality and morbidities. Methods: A cohort study using prospectively collected data involving...
- Gastroenterology
- Endoscopic postdilatation application of Mitomycin C in children with resistant esophageal strictures
- Yasser K. Rashed, Mohamed El-Guindi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):395-399. Published online June 24, 2019
-
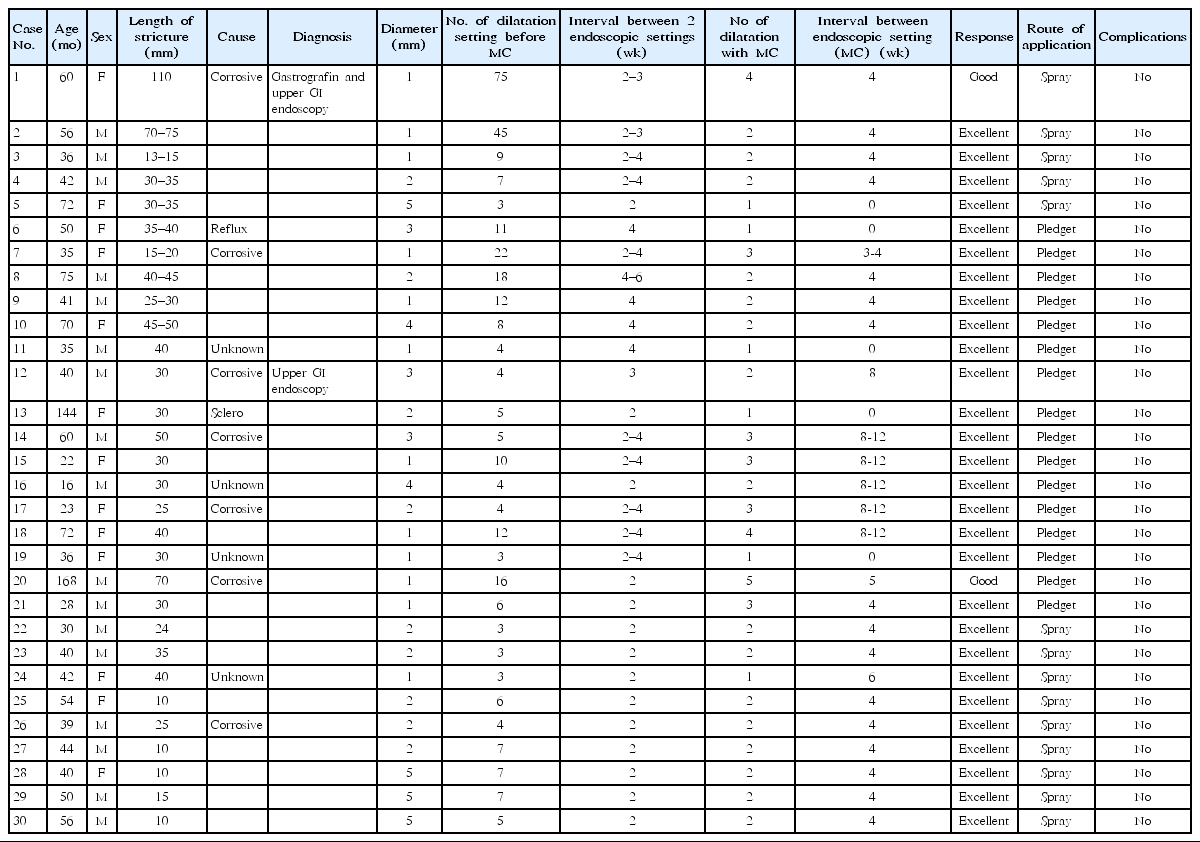
Background: The esophagus is the most common part of gastrointestinal (GI) tract at the risk of stricture. Benign disorders are the leading causes of narrowing. Caustic ingestion is the most common cause of esophageal stricture in children, especially in developing countries. Clinical responses to the topical application of Mitomycin C in various medical procedures have been reported.
Purpose: The study aimed...
- Influence of proton pump inhibitor therapy on intestinal inflammation assessed by fecal calprotectin in pediatric patients
- Su Yeong Kim, Na Mi Lee, Sin Weon Yun, Soo Ahn Chae, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi, Dae Yong Yi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):400-404. Published online July 3, 2019
-
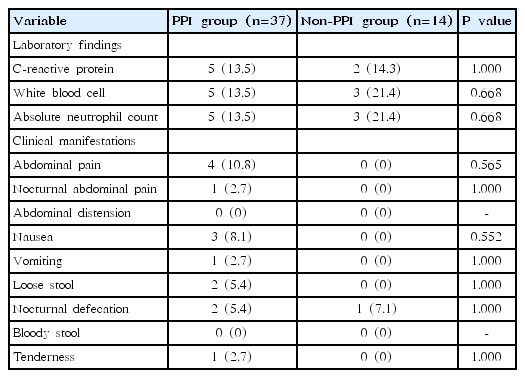
Background: An increase in the numbers of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms has recently been observed.
Purpose: To investigate the effects of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy on intestinal inflammation in children and adolescents as confirmed by clinical manifestations and objectively assessed by fecal calprotectin (FC) level measurement. Methods: Consecutive children (aged 3–18 years) who presented with gastrointestinal symptoms and were treated with...