- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Genetics of hereditary nephrotic syndrome: a clinical review
- Tae-Sun Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):55-63. Published online March 27, 2017
-
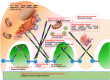
Advances in podocytology and genetic techniques have expanded our understanding of the pathogenesis of hereditary steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). In the past 20 years, over 45 genetic mutations have been identified in patients with hereditary SRNS. Genetic mutations on structural and functional molecules in podocytes can lead to serious injury in the podocytes themselves and in adjacent structures, causing sclerotic...
- Original Articles
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Postdischarge growth assessment in very low birth weight infants
- Joon-Sik Park, Jungho Han, Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Ho Seon Eun, Min-Soo Park, Kook-In Park, Ran Namgung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):64-69. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose The goal of nutritional support for very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants from birth to term is to match the
in utero growth rates; however, this is rarely achieved.Methods We evaluated postdischarge growth patterns and growth failure in 81 Korean VLBW infants through a retrospective study. Weight and height were measured and calculated based on age percentile distribution every 3 months until age 24...
- Nutrition
- Maternal food restrictions during breastfeeding
- Goun Jeong, Sung Won Park, Yeon Kyung Lee, Sun Young Ko, Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):70-76. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose This study investigated self-food restriction during breastfeeding, reviewed the literature showing the effect of maternal diet on the health of breast-fed infants, and explored the validity of dietary restrictions.
Methods Questionnaire data were collected from breastfeeding Korean mothers who visited the pediatric clinic of Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center from July 2015 through August 2015. The survey included items assessing...
- Infection
- Etiology and clinical characteristics of fever of unknown origin in children: a 15-year experience in a single center
- Yi-Seul Kim, Kyung-Ran Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Jong-Min Kim, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):77-85. Published online March 27, 2017
-
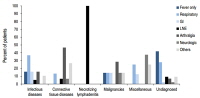
Purpose Fever is one of the most common symptoms in children. In previous studies, infectious disease was the most common cause of pediatric fever of unknown origin (FUO). The aim of this study is to investigate the etiology, clinical characteristics and prognosis of pediatric FUO in 21 century with more diagnostics available and to analyze the factors for certain disease categories.
Methods Among...
- Oncology
- Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder after pediatric solid organ transplantation: experiences of 20 years in a single center
- Hyung Joo Jeong, Yo Han Ahn, Eujin Park, Youngrok Choi, Nam-Joon Yi, Jae Sung Ko, Sang Il Min, Jong Won Ha, Il-Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):86-93. Published online March 27, 2017
-
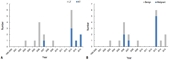
Purpose To evaluate the clinical spectrum of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) after solid organ transplantation (SOT) in children.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 18 patients with PTLD who underwent liver (LT) or kidney transplantation (KT) between January 1995 and December 2014 in Seoul National University Children's Hospital.
Results Eighteen patients (3.9% of pediatric SOTs; LT:KT, 11:7; male to female, 9:9) were diagnosed...
- Case Report
- Genetics and Metabolism
- A compound heterozygous mutation in the
FMO3 gene: the first pediatric case causes fish odor syndrome in Korea - Ji Hyun Kim, Sung Min Cho, Jong-Hee Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):94-97. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Trimethylaminuria (TMAuria), known as “fish odor syndrome,” is a congenital metabolic disorder characterized by an odor resembling that of rotting fish. This odor is caused by the secretion of trimethylamine (TMA) in the breath, sweat, and body secretions and the excretion of TMA along with urine. TMAuria is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (
FMO3 )....