2017 Clinical practice guidelines for dyslipidemia of Korean children and adolescents
Article information
Abstract
The Committee on Dyslipidemia of Korean Pediatric and Adolescents of the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology has newly developed evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for dyslipidemia in Korean children and adolescents. These guidelines were formulated with the Grading of Recommendations, which include both the strength of recommendations and the quality of evidence. In the absence of sufficient evidence, conclusions were based on expert opinion. These guidelines are based on the 2011 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Guidelines, which focus on the prevention of cardiovascular disease in children and draw from a comprehensive review of evidence. These guidelines contain the definition of and screening process for dyslipidemia and introduce new dietary methods: the Cardiovascular Health Integrated Lifestyle Diet (CHILD)-1, the CHILD-2-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and the CHILD-2-triglyceride. Potential drug therapies for dyslipidemia along with their main effects and doses were also included.
Key message
Question: How are children and adolescents with dyslipidemia treated and managed in Korea?
Finding: 2017 guidelines recommend to measure nonfasting non-HDL-C as a screening test and introduce new diet methods: Cardiovascular Health Integrated Lifestyle Diet (CHILD)-1, CHILD-2-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and CHILD-2-triglyceride. Statin is the only drug approved in children older than 10 years.
Meaning: New clinical practice guidelines for treating and managing dyslipidemia of Korean children and adolescents are provided.
Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, including in Korea [1,2]. The prevalence of CVD in Korea has historically been much lower than the rate reported in Western countries. Recently, however, the CVD-associated mortality rate in Korea has increased to 27.6%, which is comparable to that in the United States (US) [2].
Increased total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG), and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) are well-known risk factors associated with CVD [3-6]. The Korean Heart Study, a 10-year prospective study of 430,920 adult men and women, also concluded that high TC and low HDL-C levels increased the risk of CVD [7].
Dyslipidemia is closely related to other CVD risk factors, such as hypertension, obesity, and smoking status, not only in adults but also in children and adolescents [3,8]. Furthermore, the prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome, which are other risk factors for CVD, has steadily increased in Korea and is now comparable to the rate reported in the US [6,9]. This trend likely resulted from recent changes in dietary habits among Korean people that are commonly associated with a western lifestyle [9,10].
Although CVD does not usually develop until the fourth decade of life, it is well known that atherosclerosis begins in childhood [8,11,12]. The initial stages of atherosclerosis and its progression are associated with dyslipidemia [13]. Autopsy data from the Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth Study showed a strong correlation between high cholesterol and the development of fatty streaks and fibrous plaques in coronary vasculature at an early age [14]. In the Bogalusa Heart Study, the extent of fatty streaks and fibrous plaques increased with age and was correlated with antecedent serum TG, very-high LDL-C, and obesity [3].
Among Korean children and adolescents aged 10–19 years, 20% had at least one type of dyslipidemia [15]. The prevalence of hypercholesterolemia, high LDL-C, high TG, and low HDL-C concentrations among Korean children and adolescents was 6.5%, 4.7%, 10.1%, and 11.9%, respectively [16]. The rate of dyslipidemia in Korean obese adolescents has been reported as 56.1% [15].
Early recognition of and intervention for dyslipidemia in Korean children and adolescents is important for preventing CVD later in life. In this context, the Committee on Pediatric Dyslipidemia of the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology (KSPE) has recently developed evidence-based clinical practice guidelines to treat dyslipidemia in Korean children and adolescents.
Definition of dyslipidemia
Several studies, such as the Lipid Research Clinics Prevalence Study and the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, have shown that there are sexual, racial, and ethnic differences in lipid profiles and also in the overall prevalence of dyslipidemia [17,18]. The mean and 50th percentiles for TC, LDL-C, non-HDL-C, TG, and HDL-C were similar between Koreans and Caucasians from the US [17,18]. According to the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV (2007–2009), the 95th percentiles for TC and LDL-C and the 10th percentile for HDL-C in Korean children and adolescents aged 10–18.9 years were 203 mg/dL, 129 mg/dL, and 38 mg/dL, respectively. The 90th and 95th percentiles for TG concentrations were 150 and 185 mg/dL, respectively. In addition, a non-HDL-C of 145 mg/dL corresponds to approximately the 90th to 95th percentiles [15,19].
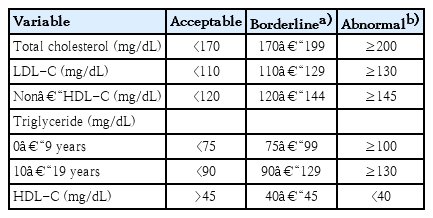
The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the KSPE decided to adopt the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHBLI) 2011 guidelines for dyslipidemia to prevent adulthood CVD by lifestyle modification or medical intervention [20]. The cutoff levels for serum lipid levels to diagnose dyslipidemia in Korean children and adolescents are listed and defined in Table 1.
There have been controversies in the optimum TG cutoff level. Because carbohydrates make up a major part of the Korean traditional diet, some researchers have insisted that a higher TG concentration of 150 mg/dL, which corresponds to the 90th percentile of Korean adolescents, is more appropriate in defining dyslipidemia [15]. However, recent studies have shown that the consumption of simple sugars, fructose, and alcohol is a main factor that increases TG levels [21,22]. Furthermore, because TG is the main target of lifestyle modification in dyslipidemia, we decided to define hypertriglyceridemia as a TG concentration > 130 mg/dL. For Korean children younger than 10 years of age, further studies will be required to determine more appropriate reference and cutoff points for dyslipidemia.
According to the cutoff points of the NHBLI guidelines, 19.7% of Korean children and adolescents from 10–18 years of age had at least one abnormal lipid concentration [15]. The prevalence of hypercholesterolemia, high LDL-C, high TG, and low HDL-C (<40 mg/dL) was 6.5% (5.8% in males, 7.4% in females), 4.7% (4.1% in males, 5.5% in females), 10.1% (9.8% in males, 10.3% in females), and 11.9% (14.5% in males, 9.5% in females), respectively [15,16]. The prevalence of dyslipidemia was 20.7%, 39.6%, and 56.1% for boys (and 24.5%, 36.6%, and 53.1% for girls) who were normal weight, overweight, and obese, respectively [16].
Screening recommendations
Screening for lipids in children is based on the rationale that early identification and control of pediatric dyslipidemia will reduce the risk and severity of CVD in adulthood. Therefore, the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of KSPE recommends “universal screening.” Universal screening in this guideline might be performed to detect those with undiagnosed heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia who would require more intensive treatment, possibly including pharmacological therapy [20,23]. In contrast, targeted screening based on family history of CVD or hypercholesterolemia fails to detect a substantial number (from 30%–60%) of children with elevated lipid levels [24]. Almost 51% of untreated children with dyslipidemia will go on to develop clinical CVD by 50 years of age, and 5% do so by 30 years of age [25].
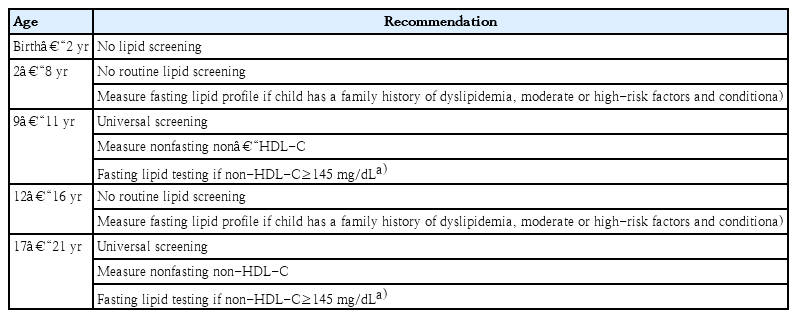
Universal lipid screening should be performed with the measurement of nonfasting non-HDL-C in all children aged 9–11 and 17–21 years. Non-HDL-C is calculated as follows: non-HDL-C=TC–HDL-C. Non-HDL-C includes all cholesterol types present in lipoprotein particles (LDL-C, lipoprotein(a), intermediate density lipoprotein, and very-low-density lipoprotein) that are considered atherogenic. Therefore, non-HDL-C is a better independent predictor of CVD than LDL-C and is also as good a predictor of future adulthood dyslipidemia that can replace LDL-C [26-28]. If non-HDL-C is >145 mg/dL, 2 additional fasting lipid panels (at least 2 weeks but no more than 12 weeks apart) should be obtained and the average values are used.
Screening for dyslipidemia is not recommended until 2 years of age. For children aged 2–8 and 12–16 years, routine lipid screening is also not recommended. Targeted screening is only encouraged if there is a family history of high cardiovascular risk or other risk factors and conditions. The risk factors and conditions to consider for the screening and treatment decisions in children with dyslipidemia are included in Tables 2 and 3 [20].
Management
Rising rates of dyslipidemia in Korean children and adolescents might be due to increases in adoption of the western lifestyle, especially the westernized diet and decrease in physical activity [29,30]. Therefore, lifestyle modifications, such as promoting a healthy diet and regular physical activity, are thought to be essential in treating dyslipidemia. The algorithm used for dyslipidemia management is shown in Fig 1.
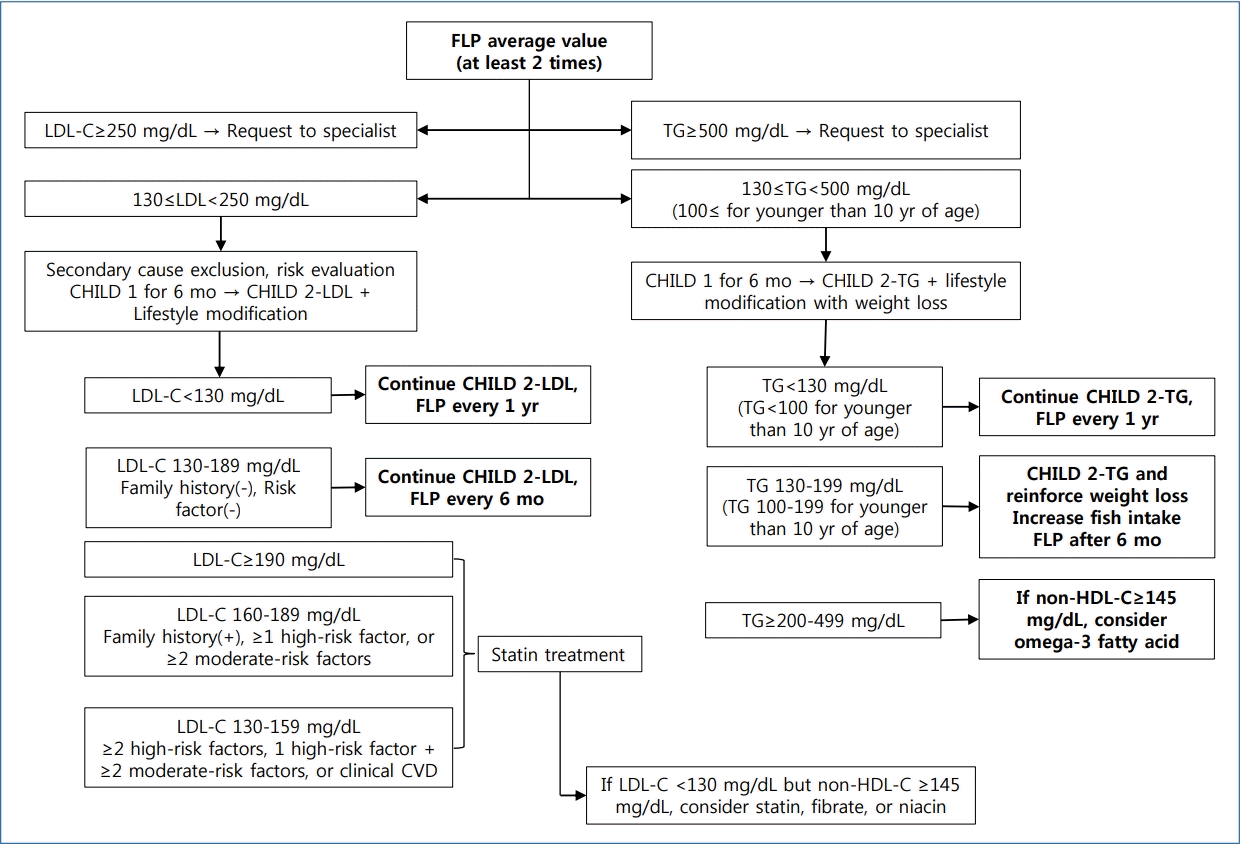
Algorithm for dyslipidemia treatment. FLP, fasting lipid profile; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CHILD 1, Cardiovascular Health Integrated Lifestyle Diet 1; CHILD 2-LDL, Cardiovascular Health Integrated Lifestyle Diet 2; non-HDL-C, non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; CVD, cardiovascular disease.
1. Lifestyle change and diets
The KSPE guidelines recommend that all children and adolescents engage in moderate-to-vigorous physical activity for at least one hour a day and limit sedentary activity, including television, internet, and video games, to <2 hours a day. Cigarette exposure also should be strongly discouraged. In addition, all children and adolescents should try to attain an ideal body weight (body mass index ≤85th percentile for age and sex).
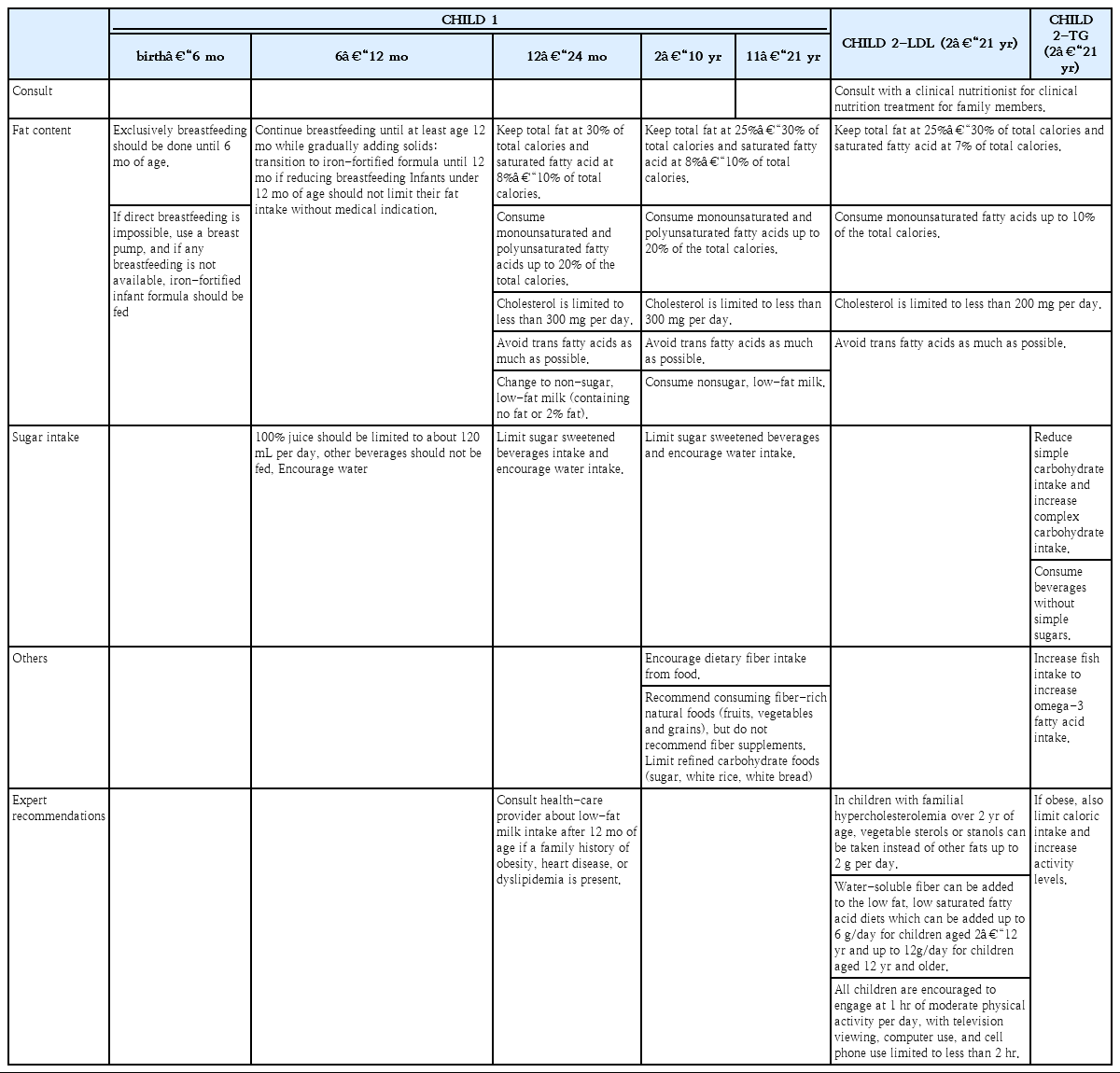
Any diet change must provide optimal nutrition for growth and development. The 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend the Cardiovascular Health Integrated Lifestyle Diet (CHILD-1) be used in children and adolescents 2 years of age or older who are at risk for CVD [31].
Exclusively breastfeeding should be done until 6 months of age. If direct breastfeeding is impossible, use a breast pump, and if any breastfeeding is not available, iron-fortified infant formula should be fed. Breastfeeding should continue for at least 12 months while gradually adding solids. If breast milk decreases, feed iron-fortified formula until 12months. Infants under 12 months of age should not limit their fat intake without medical indication and limit 100% juice to about 120 mL per day, drink water without any other beverages.
Consult health-care provider about low-fat milk intake after 12 months of age if a family history of obesity, heart disease, or dyslipidemia is present [20].
If the fasting lipid profile findings exceed the therapeutic goals after a 3-month trial of the CHILD-1 diet, then the CHILD-2-LDL, or CHILD-2-TG diet should be recommended based on specific abnormal lipid parameters.
The detailed contents of each diet are listed in Table 4. The CHILD-1 urges specific protocols: drink fat-free unflavored milk primarily, limit/avoid sugar-sweetened beverages, encourage water consumption, limited total fat content (25%–30% of the daily kcal/estimated energy requirements [EER] per day for age/gender), limit saturated fat 8%–10% of the daily kcal/EER, avoid transfat as much as possible, and recommend monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat up to 20% of the daily kcal/EER, and limit cholesterol intake to <300 mg/day [20]. In addition, these recommendations advocate the intake of dietary fiber (14 g/1,000 kcal), limiting naturally sweetened juice (no added sugar) to 120 mL/day, limiting sodium intake, and encouraging healthy eating habits overall. The CHILD-2 is divided into CHILD-2-LDL and CHILD-2-TG guidelines depending on the dyslipidemia target. Above all, it is important to refer these children and adolescents to a registered dietitian for family-based medical nutrition therapy and to decrease their total sugar intake. The CHILD-2 diet recommends the following: avoiding transfats, consuming <200 mg/day of cholesterol, and sustaining total, saturated, and monounsaturated fat at 25%–30%, 7%, and <10% of total calories, respectively. Supportive dietary plans are different between the CHILD-2-LDL and the CHILD-2-TG. The CHILD-2-LDL diet recommends phytosterols up to 2 g per day as substitutes for dietary fats in children with familial hypercholesterolemia who are older than 2 years. Water-soluble fiber, such as psyllium, can be added to a low-fat, low-saturated fatty acid diet (6 g/day for children from 2–12 years and 12 g/day for children >12 years). With the CHILD-2-TG, an increase in fish intake is critical in improving the levels of omega-3 fatty acids. TG levels are very responsive to weight loss, diet composition, and exercise [32].
2. Drug therapy
Decisions regarding the need for drug therapy should be based on the average values from at least 2 fasting lipid tests obtained at least 2 weeks but no more than 3 months apart.
Drug therapy is recommended in children ≥10 years with a poor response to diet and lifestyle therapy for at least 6–12 months [20]. The choice of medication depends on the lipid profile, age, sex, family history, and the pediatricians’ experience [33]. In Korea, at least 0.41% of Korean children and adolescents are candidates for pharmacological treatment [16].
Children with average LDL-C levels ≥250 mg/dL or TG≥ 500 mg/dL should be referred directly to a lipid specialist. If the TG concentration is >500 mg/dL, there is a risk of pancreatitis, and specialist consultation is therefore necessary [34].
Statin treatment is generally not started in children under the age of 10, and it is limited to patients homozygous for familial hypercholesterolemia or with LDL-C≥400 mg/dL, primary hypertriglyceridemia≥500 mg/dL, CVD, or cardiac transplantation.
If the LDL-C remains ≥190 mg/dL after a 6-month trial of lifestyle management (CHILD-1 → CHILD-2-LDL) for children aged 10 years and older, statin therapy should be considered [20,35]. For patients with an LDL-C concentration between 160–189 mg/dL, statin treatment should be considered if there is a positive family history of premature CVD in first-degree relatives, at least one high-level risk factor or risk condition, or at least 2 moderate-level risk factors or risk conditions. If the LDL-C concentration is between 130–159 after 6 months of lifestyle modification, and if the children have at least 2 high-risk factors or conditions or at least one high-level risk factor and two or more moderate-risk factors or conditions or clinical CVD, statin therapy should be considered.
In children who are at least 10 years of age, the administration of statins, fibrates, or niacin may be considered if the LDL-C has reached its target but the non-HDL-C remains ≥145 mg/dL [20,36].
When TG improves with weight control and lifestyle changes in children with hypertriglyceridemia, medication therapy is unnecessary. As a supportive medical therapy, the use of omega-3 fatty acids is suggested along with lifestyle modification via the CHILD-2-TG, especially in children with hypertriglyceridemia. When the affected child has TG levels from 200–499 mg/dL and a non-HDL-C result ≥ 145 mg/dL, omega-3 fatty acid treatment may be considered [36].
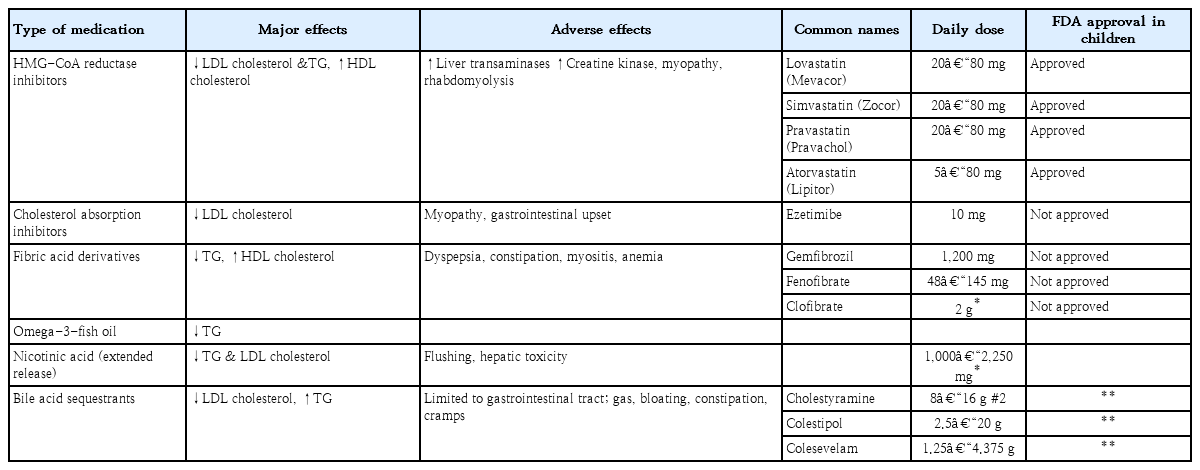
However, safety issues remain unclear due to the limited experience with omega-3 fatty acids in children, which have only been used in a small number of cases [37]. (Table 5)
Statins and bile acid-binding resins are the two main classes of medications currently used to treat this condition in pediatric patients. Commonly used medications are listed in Table 6. Statins that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in children older than 10 years include pravastatin, simvastatin, lovastatin, and atorvastatin. Cholesterol-absorption inhibitors, such as niacin and fibrates, are not yet approved by the US FDA.
A statin is recommended as the initial medication of choice for children with elevated LDL-C or non-HDL-C levels. Statins inhibit the rate-limiting enzyme β-hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase and induce endogenous synthesis of cholesterol. Statins are effective at lowering cholesterol levels by 20%–50% below the baseline. They are also known to have minimal side effects and do not affect growth [31,38,39]. The treatment regime should begin at the lowest dose given once daily at bedtime. Atorvastatin can be taken either in the morning or evening because of its long half-life. Before beginning statin treatment, baseline measurements of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and creatinine kinase should be obtained. Liver function tests, creatinine kinase, and a fasting lipid profile should be repeated at 4 and 8 weeks after the initiation of therapy and then again every 3 to 6 months. If liver enzymes are more than 3 times the upper limit or the creatinine kinase is >10 times the upper limit of the reference range, the statin medication should be stopped [40,41].
The target LDL-C value is typically <130 mg/dL, but if the patient is at high risk, such as with familial hypercholesterolemia or diabetes mellitus, the target LDL-C level should be maintained below 100 mg/dL. If target levels are not achieved within three months, the statin dose can be gradually increased to the maximum amount.
Since statins are potentially teratogenic, it is essential for physicians to confirm that adolescent girls are not pregnant before initiating statin therapy.
Bile acid sequestrants are the first line of therapy for children with dyslipidemia as these compounds are not absorbed systemically [42]. They work by preventing cholesterol reuptake in the enterohepatic circulation. However, cholestyramine and colestipol are unpalatable and are associated with gastrointestinal side effects, including bloating, nausea, diarrhea, and constipation. Therefore, compliance with this type of therapy is generally poor.
Ezetimibe (a cholesterol-absorption inhibitor) enters the enterohepatic circulation and reduces bile acid reuptake as well as cholesterol absorption. Ezetimibe is approved in children older than 10 years of age at a dosage of 10 mg/day as an adjuvant to statin therapy. In adults, ezetimibe has been shown to reduce the LDL-C by 20% [43]. No studies have investigated the treatment of ezetimibe alone in children, but data regarding children’s experience with niacin and fibrates are also limited.
Therefore, niacin, fibrates, and ezetimibe should only be initiated after consulting with a lipid specialist. When these drugs are used in combination in children, they exert an increased combined effect, but the occurrence of side effects is not increased.
Conclusions
Atherosclerosis begins in childhood and can lead to CVD in adulthood. Early detection and proper management of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents are urgently needed to reduce adult CV morbidity. The 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Dyslipidemia of Korean Children and Adolescents are intended to help identify children who are at increased risk of CVD and may benefit from the early screening and intervention of dyslipidemia. These guidelines provide a schematic approach that will help pediatricians make timely decisions regarding the screening and management of Korean children and adolescents with risks and conditions associated with accelerated atherosclerosis.
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the members of Committee on Dyslipidemia of Korean Pediatric and Adolescents and the Korean Society for Pediatric Endocrinology for their support in developing and publishing these guidelines. This guideline is being simultaneously published in Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism and Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.