Complete trisomy 14 mosaicism: first live-born case in Korea
Article information
Abstract
Trisomy 14 mosaicism is a rare chromosome disorder characterized by delayed development, failure to thrive, and facial dysmorphism. Only approximately 30 trisomy 14 mosaicism cases have been reported in the literature because trisomy 14 is associated with early spontaneous abortion. We report a case of a 17-month-old girl with abnormal skin pigmentation, delayed development, facial dysmorphism, and failure to thrive with the 47,XX,+14/46,XX chromosome complement.
Introduction
Trisomy for D group chromosomes is common through nondisjunction in meiosis and anaphase lagging1,2). However, trisomy 14 mosaicism is a rare chromosomal defect with approximately 30 cases reported in the literature. Unlike other acrocentric chromosomes, lethality of complete trisomy 14 or less susceptibility to errors of disjunction of chromosome 14 may result in spontaneous abortion of embryos and fetuses1,3,4). Mosaic trisomy 14 involves complete trisomy with an extra chromosome 14 in 58% of cases and partial trisomy. We describe the first live born case with complete trisomy 14 mosaicism (47,XX,+14[15]/46,XX[17]) in Korea and compare the characteristic phenotypes between complete and partial trisomy mosaicism based on the reported cases to date.
Case report
A 17-month-old female was referred for evaluation of delayed development and abnormal skin pigmentation on the trunk and both extremities. The patient was born at 40 weeks gestational age to a 37-year-old gravida 1 para 1 healthy mother with no drug history during pregnancy. The patient had no genetic and cerebrovascular disease in family history. The delivery was by cesarean section due to a uterine myoma in the mother, and uncomplicated. At birth, the body weight was 1,800 g (small for gestational age, <3rd percentile). The mother could not remember the height, and head and chest circumferences of her newborn. At 4 months of age, the patient underwent a cleft lip repair and a ventricular septal defect was noted on echocardiography at that time.
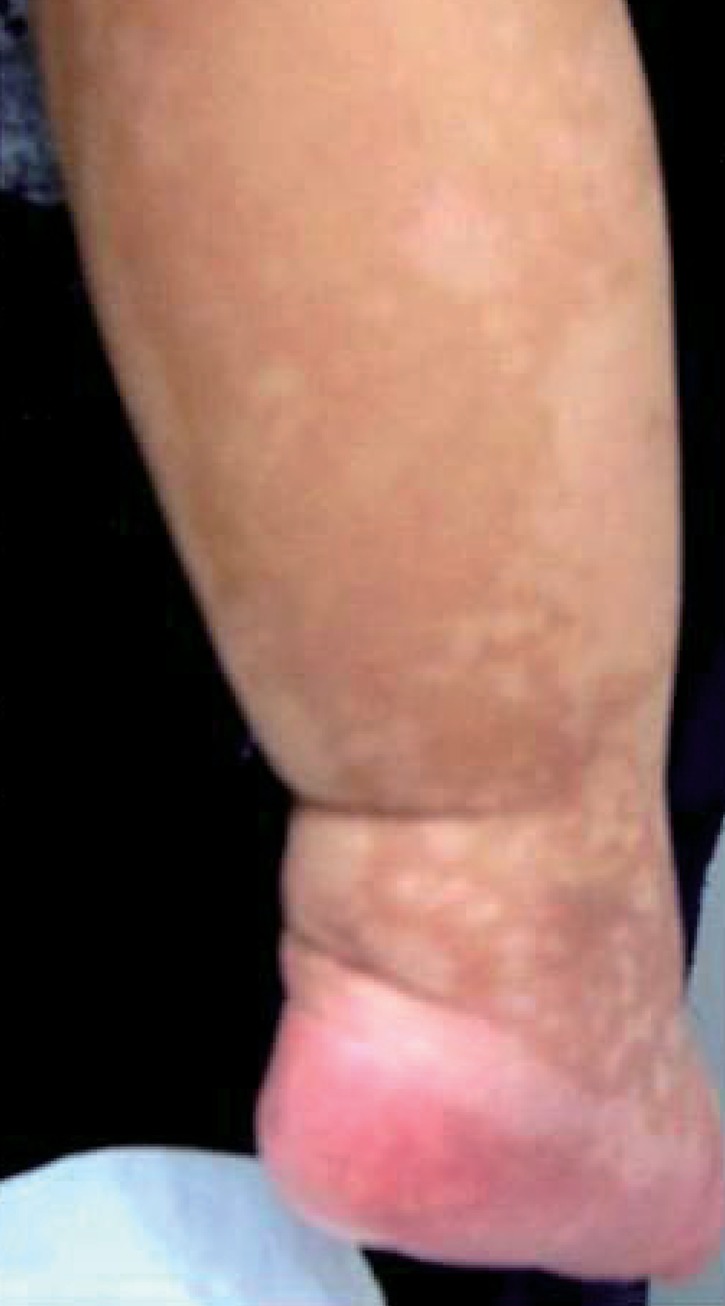
At the age of 17 months, weight was 7.3 kg (<3rd percentile), height was 70.5 cm (<3rd percentile), and head circumference was 46.5 cm (50th percentile). The patient had a dysmorphic face (frontal bossing, micrognathia, deep-set eyes, broad nasal bridge, anteverted nose, high arch palate, cleft lip, and triangular and wide lip) and simian crease on both hands. No other gross anomalies of the extremities and genitourinary tract were noted. A cardiac murmur was not auscultated and echocardiography showed a closed ventricular septal defect. The skin was hyperpigmented with a reticular pattern on the trunk and limbs (Fig. 1). The patient had hypotonic muscle tone and normal deep tendon reflexes. Development was globally delayed by about 10 months, corresponding to same-aged Korean infant and child developmental testing. The patient could not stand or walk without support. A brain magnetic resonance imaging showed no specific abnormal findings. A genitourinary sonogram was normal. The patient underwent bilateral myringotomies at 17 months of age for recurrent otitis media.
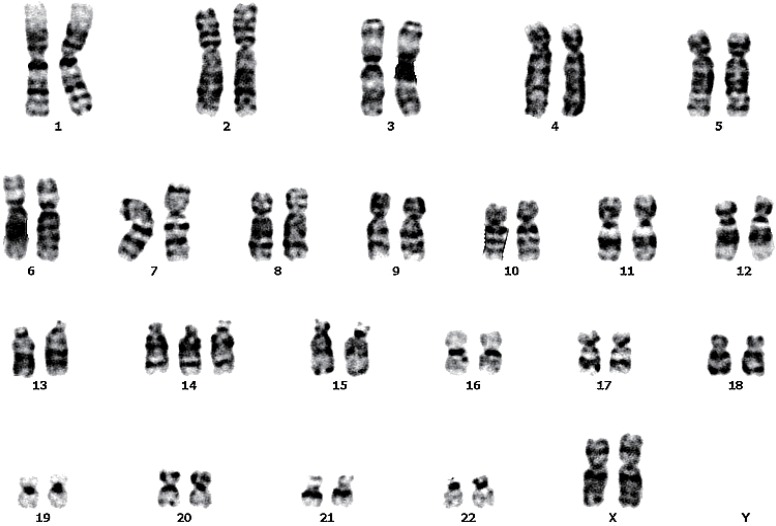
Chromosome analysis of the patient was performed from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures with GTW-banding. A total of 32 metaphases were analyzed. Fifteen cells (44%) had trisomy for chromosome 14(47,XX,+14) (Fig. 2). Cytogenetic studies of the parents were not carried out.
Discussion
This is the first report of a live born female with complete trisomy 14 mosaicism in Korea. Trisomy 14 mosaicism is characterized by a clinical distinct phenotype, such as delayed development, failure to thrive, facial dysmorphism, congenital heart disease, skin pigmentation, and genitourinary anomalies, although trisomy 14 mosaicism and other chromosomal abnormalities are difficult to distinguish4-6). Our patient was suspected not specific trisomy 14 but certain chromosomal anomaly due to nonspecific morphologic characteristics. But skin pigmentation let us consider trisomy 14 as well as other chromosomal abnormalities including hypomelanosis of Ito, incontinentia pigmenti, Pallister-Killian syndrome, and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis7,8).
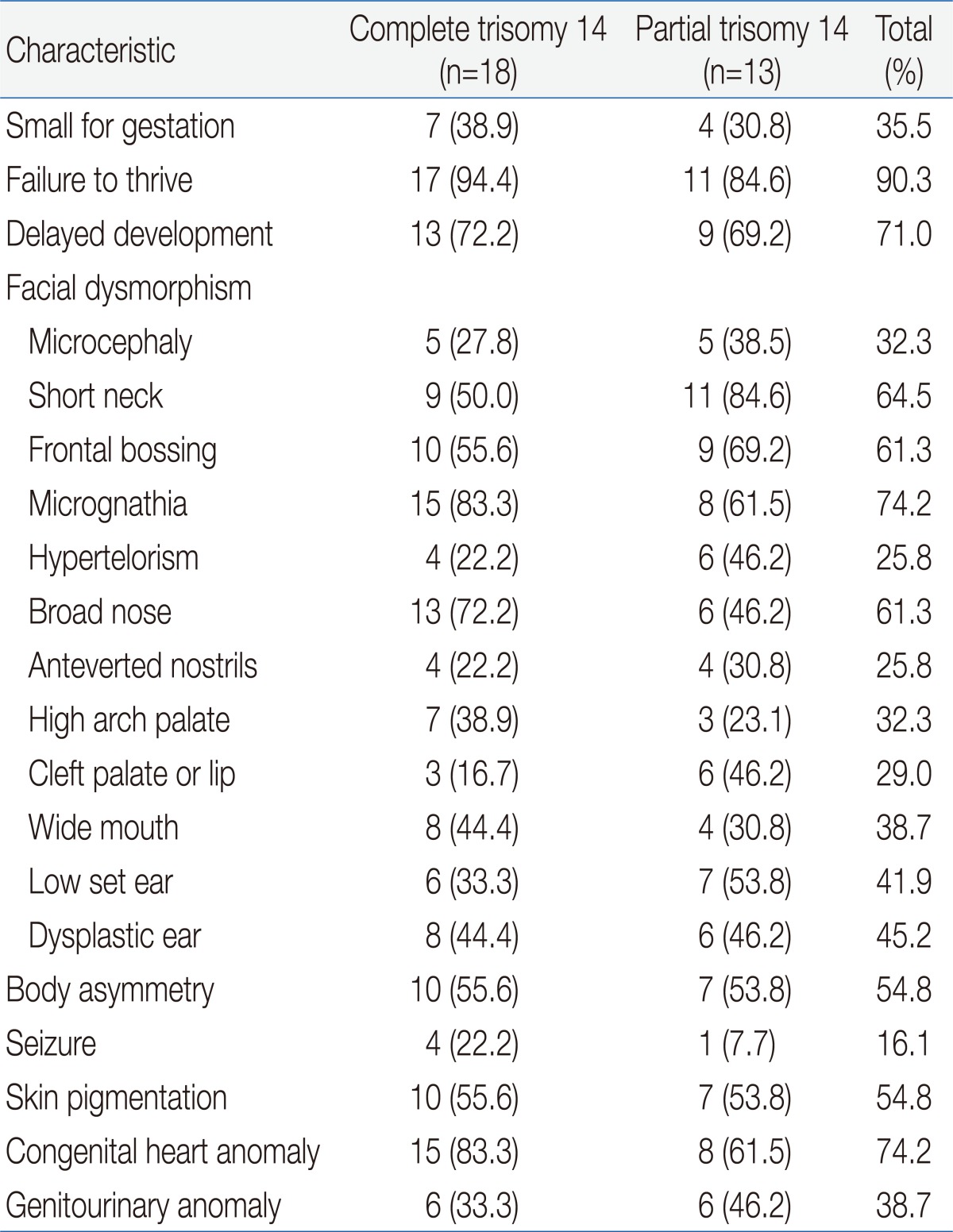
To summarize the clinical distinct phenotype for trisomy 14, we compared clinical phenotype for complete and partial trisomy based on previously reported cases (Table 1). The phenotype between the two groups was similar although the incidence of seizures is more in patients with complete than partial trisomy 14 mosaicism9-14). The similarity between the two groups could suggest that the 14q abnormality might result in a clinically-recognizable phenotype1). The phenotype of our patient was also similar to previous reported Korean cases for partial trisomy 14 mosaicism, except for abnormal skin pigmentation15,16). The phenotype in trisomy 14 mosaicism is not related to trisomic type such as complete and partial patterns9), as well as the percentage of trisomic cells in reported cases14). Trisomy 13 also has no relationship between the percentage of trisomic cells and the level of cognition17). However, the differing percentage or tissue distribution of trisomic cells in case of trisomy 21 mosaicism reflects the variability of clinical phenotype18).
Life expectancy of patients with trisomy 14 has not been studied, but about two-thirds of patients with trisomy14 mosaicism survive relatively free of serious medical problems after infancy9). Because of the variability of involved 14q segment and the possibilities of low grade mosaicism in trisomy 14 mosaicism, the frequency of trisomy 14 mosaicism might be underestimated. Low-level mosaicism can be masked by high percentage of normal cell line and may be difficult to diagnose only by cytogenetic method. Array-CGH could be helpful in detecting of low-level mosaicism which was not detected by conventional karyotyping14). Hence, we should consider array-CGH as well as cytogenetic study if the patient is clinically suspected trisomy 14.