Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 65(5); 2022 |
|
Abstract
Cells survive and proliferate through complex interactions among diverse molecules across multiomics layers. Conventional experimental approaches for identifying these interactions have built a firm foundation for molecular biology, but their scalability is gradually becoming inadequate compared to the rapid accumulation of multiomics data measured by high-throughput technologies. Therefore, the need for data-driven computational modeling of interactions within cells has been highlighted in recent years. The complexity of multiomics interactions is primarily due to their nonlinearity. That is, their accurate modeling requires intricate conditional dependencies, synergies, or antagonisms between considered genes or proteins, which retard experimental validations. Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, including deep learning models, are optimal choices for handling complex nonlinear relationships between features that are scalable and produce large amounts of data. Thus, they have great potential for modeling multiomics interactions. Although there exist many AI-driven models for computational biology applications, relatively few explicitly incorporate the prior knowledge within model architectures or training procedures. Such guidance of models by domain knowledge will greatly reduce the amount of data needed to train models and constrain their vast expressive powers to focus on the biologically relevant space. Therefore, it can enhance a model’s interpretability, reduce spurious interactions, and prove its validity and utility. Thus, to facilitate further development of knowledge-guided AI technologies for the modeling of multiomics interactions, here we review representative bioinformatics applications of deep learning models for multiomics interactions developed to date by categorizing them by guidance mode.
Graphical abstract.
To date, the mechanistic principles of cellular processes have been primarily characterized as a series of interactions between various intracellular molecules including DNA, RNA, proteins, and metabolites. The identification of such interactions using carefully designed experimental approaches has increased our understanding of molecular biology over decades [1,2]. Meanwhile, the development of high-throughput measurement technologies has led to the rapid accumulation of a vast number of omics profiles that offer great opportunities for the comprehensive identification of multiomics interactions. However, it is difficult to fully leverage these valuable resources using experimental approaches and conventional bioinformatic approaches owing to the limitations of cost and computational expressive powers, respectively. On the other hand, modern artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, mainly deep neural network models and deep learning, are inherently suitable for processing large amounts of data and, thus, have great potential for the modeling of complex multiomics interactions in this era of big biodata [3].
The interaction between entities from different omics layers can be conceived as an evolutionarily principled way to propagate biological information within cells, or even across a cell population [4,5]. The precise and efficient transmission of such information is crucial for a cell to survive diverse environmental perturbations by eliciting appropriate responses. Indeed, these interactions are extremely complex. For example, some interactions are condition-dependent [6], in which they only take place upon a certain level of upstream stimuli above the threshold, while other interactions are competitive against each other as the number of common participants is limited [7]. Therefore, the dynamics of multiomics interactions are nonlinear, which means that their dynamics cannot be modeled simply based on the number of immediate participants. This complexity makes the extensive characterization of multiomics interactions with handcrafted features that are almost intractable. In this regard, a neural network model is one of the most plausible model architecture choices because it can automatically extract important features from data while being trained.
There have been many approaches utilizing AI technologies in the field of computational biology, but it is crucial to note that the performance of AI-driven modeling substantially varies depending on deep neural network model architecture. The most recent and prominent example emphasizing the power of a well-designed neural network architecture is AlphaFold [2,8] which predicts the structure of a protein with near-experimental accuracy. In fact, deep learning-based approaches have already been employed to solve protein structure prediction 2 years before the development of AlphaFold [2,9,10] but one of the reasons that AlphaFold2 far outperformed the other deep learning models stems from its well-designed model architecture. It nudges the model to attend to the most relevant biological information, namely the evolutionary context of amino acids and the interaction between amino acid pairs, while allowing the mutual exchange of information between the 2 factors. Therefore, embedding biological knowledge into the structures of neural network models can dramatically improve model performance.
Deep neural networks consist of numerous neurons. Each neuron is connected to other neurons, and a scalar value called weight is assigned to each connection. Given the numeric representation of input data, a neural network, defined as a set of directed connections of neurons, produces output through the forward propagation of information. During forward propagation, the information contained in a set of neurons is linearly combined according to the weight assigned to the corresponding connection toward a descendent neuron. As a result, the following neuron receives the information and decides how much information it will keep and propagate through its descendent neurons by a nonlinear activation function. This nonlinearity allows each neuron to decide whether it should be activated based on the input values received. Therefore, deep learning models can manage the conditionality and competitiveness occurring in typical multiomics interactions. The goal of training a deep learning model is to identify the optimal configuration of weights that achieves the best result based on predefined criteria.
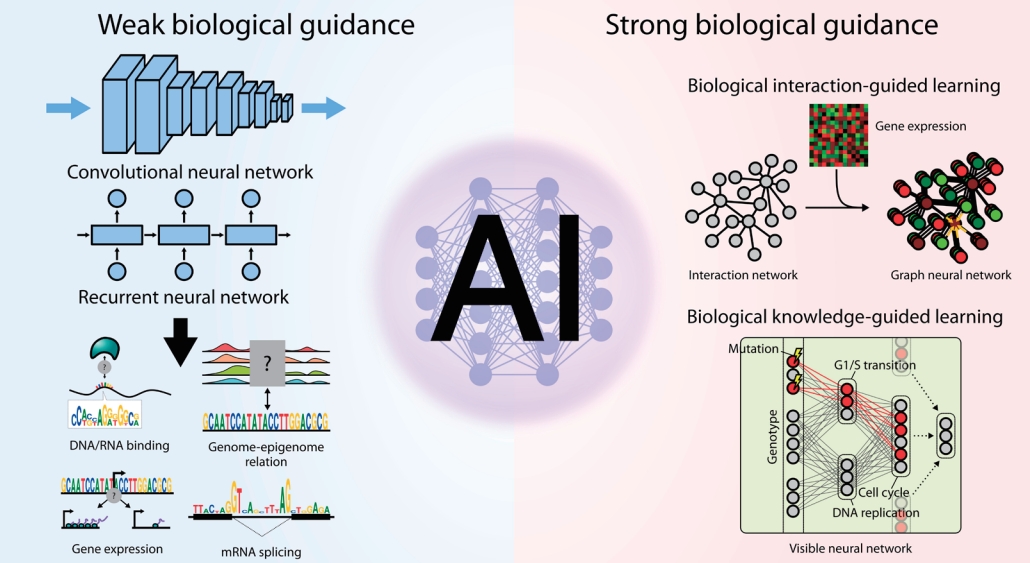
Given the importance of neural network architecture integrated with biological prior knowledge, here we comprehensively review neural network models developed to date to decipher complex multiomics interactions by classifying them into 2 categories based on the characteristics of the biological guidance imposed on them: (1) weak guidance, in which little to no biological knowledge is used; and (2) strong guidance, in which prior knowledge is explicitly utilized for model architecture or training.
Early applications of deep learning to biological problems tended to simply adopt the existing prominent neural network architectures from general AI studies. Because such general-purpose neural network architectures are not specifically designed to address biological challenges, the models are passively guided to learn the core principles of multiomics interactions from scratch. Nevertheless, training models with passive or minimal guidance are still important since they can reveal many exciting patterns of multiomics interactions in an unbiased manner. In this section, we review how the fundamentals of molecular biology can be derived only from the compilation of omics profiles by deep learning (Fig. 1).
The efficiency of the interaction between proteins and DNA is often determined by the compatibility between protein structure and DNA sequence [11]. In particular, many DNA-binding proteins, including transcription factors (TFs), have an intrinsic preference for short stretches of DNA with unique ordering of nucleotides, or sequence motifs [12]. Sequence motifs bound by TFs, namely TF-binding sites (TFBSs), are conventionally determined by high-throughput experiments such as chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with DNA sequencing (ChIP-seq) [13] or SELEX-seq [14] followed by motif-finding algorithms including MEME [15] and HOMER [16]. The resulting TFBSs are often represented as position weight matrices (PWMs) that encode the relative base preference for each position within the motif.
DeepBind [17] pioneered the application of deep learning for binding prediction of TF or RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) using high-throughput experimental data. For each TF or RBP, individual DeepBind models were trained to classify whether the corresponding protein would bind to the given nucleotide sequence in a supervised manner. More specifically, a number of short nucleotide sequences that were experimentally validated to be bound by the protein were prepared along with random negative sequences. The model weights were optimized to make the model produce correct predictions for either of the 2 classes.
Although no explicit prior knowledge was incorporated in DeepBind training, it is worth noting that the choice of model architecture provides minimal guidance or inductive bias for the model to successfully detect motifs. DeepBind adopts a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture [18], which was originally developed for computer vision applications such as image recognition. Key operators at the CNN core are convolutional filters, which iteratively slide throughout the image and produce a scalar for each of its patches. The scalar value is computed as a dot product between the weight of the filter and the pixel intensity of the image patch, thus producing high values at the patch that are preferred by the filter. A simple but powerful analogy can be derived from this formulation when we consider a convolutional filter as a learnable PWM that slides through the sequence and detects the short substring that is compatible with the PWM. The PWM denoting TF-binding motifs can be learned by optimizing the model to respond positively to TF-binding sequences.
DeepBind models showed improved accuracy of TF-binding specificity prediction compared to conventional models. Furthermore, it could predict mutations that would disrupt TF binding, and many have already been reported as disease-associated mutations. Since the successful introduction of deep learning models for the task of revealing protein-DNA/RNA interactions, many variants of DeepBind models have been developed. DeeperBind [19] appended recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture [20] after convolutional layers to capture dependencies between motifs as well as positional bias in probes used for high-throughput screens such as protein-binding microarrays. DanQ [21] is another model that uses the hybrid structure of CNN and RNN, but it differs from the aforementioned models in that it is trained by multitask learning [22]. In other words, it is a single unified model that predicts the binding specificity of about 1,000 TFs. The utility of multitask learning is especially highlighted in biological applications because the most fundamental dogmas are shared across every cell. More recently, a CNN-based model without pooling, called BPNet [23], along with a motif discovery method TF-MoDISco [24], further captured the detailed syntaxes of TF-binding motifs, such as helical periodicity of motifs and multiple motifs repeatedly occurring at a fixed distance because of the cooperative DNA binding of interacting proteins. The fine resolution of the analysis could be achieved using high-resolution TF-binding signals from ChIP-nexus [25] experiments, underscoring the importance of training data quality.
As discussed above, TFBSs mark hotspots of protein-DNA interactions and potentiate the activation of downstream genes upon binding to the corresponding TFs. In other words, TFBSs can serve as major sequence determinants of gene expression. If a deep learning model is powerful enough, by training the model to predict whether a gene is highly or lowly expressed solely based on the nearby DNA sequence (especially promoters), the model may learn the sequence motifs of TFBSs and localize them. At first glance, this seems infeasible because the model is trained without any information on TFs, but surprisingly, deep learning models can successfully fill the missing links of TF binding between DNA sequences and gene expression.
Basenji [26] is one of the first CNN-based attempts to predict gene expression levels from DNA sequences. It adopts a multitask learning scheme that predicts read coverage representing various modalities in 128-bp genomic bins using genomic sequence information. Gene expression measurements were obtained by cap analysis of gene expression followed by sequencing (CAGE-seq [27]), which allows the precise quantification of gene expression specifically in the vicinity of the transcription start sites. Moreover, the models were trained to predict chromatin features measured by DNase-seq and ChIP-seq. Interestingly, Basenji was able to predict expression quantitative trait loci and disease-associated variants without any prior knowledge of them. Similarly, a multitask CNN-based model named Expecto [28] allows tissue-specific stratification of variants in terms of their transcriptional effect; using the genomic information of other species, especially mice, it boosts the accuracy of gene expression prediction based on deep learning models [29]. Another CNN-based model, Xpresso [30], trained solely based on promoter sequences, can explain about 60% of the variation in human gene expression and clearly reveals general sequencebased features dictating gene expression, such as promoter CpG contents. More recently, modern deep learning architectures, apart from CNNs, have started being applied to genomic tasks. Enformer [31] is one of the forefront applications of transformer architecture [32] for gene expression prediction. Transformer layers allow the model to capture the long-range interactions of distal elements at most 100 kb away from the gene, whereas Basenji only captures a 20-kb window.
Meanwhile, mRNA splicing is a complex biological process that confers the functional diversity and plasticity of cells. Since the process involves sequential binding of RBPs to pre-mRNAs, it is conceivable that the signals governing the efficiency of splicing lie within DNA sequences. Several well-known grammars of mRNA splicing have been firmly established, including the consensus sequence of donor and acceptor sites [33] and the existence of branch points [34]. However, there are numerous combinations of donor and acceptor sites within a gene, only a subset of which is actually spliced out. In other words, the current knowledge on the grammars of mRNA splicing is insufficient to specifically determine the splice site. SpliceAI [35] filled this gap by training a deep learning model with reference genome sequence and exon annotations, and it almost perfectly predicted whether a base is a splice donor or acceptor. One interesting observation drawn from SpliceAI training is that the performance steadily increased as the model was allowed to see larger genomic windows (up to 10 kbp), implying the long-range sequence determinant of mRNA splicing.
The intimate relationship between genomic sequence and epigenomic features has been of great research interest because it enabled the high-throughput measurement of epigenomes. Revealing the dependency of the epigenome on genomic sequences is especially important in clinical applications since it may reveal uncharted pathologic roles of noncoding variants. However, characterizing their quantitative relationship is challenging because there are many complex types of nonlinear interactions across different epigenomic features involving diverse protein machineries. Accordingly, there are great opportunities for the application of deep learning approaches.
DeepSEA [36] is a CNN-based model that predicts allele-specific chromatin profiles from a 1,000-bp sequence window. Models were trained to simultaneously predict 125 DNase I-hypersensitive site profiles and 104 histone mark profiles along with 690 TF-binding profiles. The training data were compiled from ENCODE (Encyclopedia of DNA Elements) [37] and Roadmap Epigenomics projects [38]. The model not only accurately predicted chromatin features based on DNA sequences, it also showed the capability to functionally prioritize single nucleotide variants. The functional impact of each variant was determined by mutating a single base from the original input and propagating the mutated input through the model to obtain the perturbed prediction. The discrepancy between the perturbed and original predictions represents the functional impact of the variant. The power of DeepSEA for functional prioritization of variants implies that deep learning models can capture the general rules of sequence-based regulation of the epigenome while not being overfitted to the training data.
Similarly, Basset [39] is another CNN-based model trained to predict sequence-level grammars by controlling genome accessibility. As mentioned above, its modified version, Basenji [26], accepts a much larger genomic window as an input and predicts more diverse profiles, including ChIP-seq and CAGE profiles. Strikingly, Basenji successfully captured the importance of distal regulatory elements. By computing the gradient of the model prediction with respect to each of the input base positions, one can obtain the effect of small perturbation or mutation in each position in the sequence on the model prediction. Accordingly, a base is considered important when the magnitude of the corresponding effect size, or saliency, is large. Peaks in the saliency map derived from Basenji revealed that the model focuses on distal regulatory elements, especially enhancers, in addition to promoters. This observation underscores the importance of using sufficiently large genomic windows as inputs to allow the model to capture as many unbiased sequence features as possible.
DNA methylation is another major epigenetic feature that regulates gene expression. It is defined as the covalent attachment of a methyl group at the fifth carbon of cytosine bases, and it commonly refers to the methylation of cytosine bases within CG dinucleotides. Since DNA methylation is tightly associated with the regulation of nearby chromatin states, the link between aberrant patterning of DNA methylation and diseases has long been studied. However, systematic characterization of the role of genomic sequences in the regulation of DNA methylation patterns remains challenging.
DeepCpG [40] predicts a single-cell-level DNA methylation state based on the DNA sequence context and nearby methylation states of multiple cells observed by single-cell bisulfite sequencing. It consists of 2 modules, in which the CpG module summarizes the neighboring methylation states of cells with bidirectional RNN and the DNA module summarizes the genomic sequence with the CNN. The outputs of the 2 modules were combined in a joint module. Investigating the filters of the first convolutional layer revealed de novo sequence motifs associated with cell-to-cell methylation variability as well as average methylation levels. While DeepCpG conducts binary classification of DNA methylation states at the single-cell level, MRCNN [41] is a CNN-based model that aims to regress cell population–level methylation.
Finally, deeply learned correlative relationships between genomic and epigenomic features allow us to predict or impute the missing observations for certain epigenomic features from the other present features. The correct imputation of missing epigenomic profiles is important because it may significantly reduce experimental costs and thus facilitate the large-scale measurement of epigenomic features. Avocado [42] is a clever deep factorization-based approach that decomposes the signal value into multiscale genomic position factors, assay factors, and cell-type factors. By jointly learning the 3-factor embeddings and weights for their nonlinear combinations to produce accurate signals, the model could correctly predict epigenomic signals that were not observed during training. As the learned latent embedding enhanced the performance of downstream predictive tasks, such as the prediction of gene expression, promoter-enhancer interaction, and replication timing, Avocado successfully encoded the underlying correlative relationship between epigenetic features.
The methods discussed so far mainly focus on binary interactions between the 2 omics layers. However, the actual landscape of intracellular multiomics interactions is far more complex because it involves multiple interactions among several omics modalities.
Although we still have a long way to go to achieve clear deep learning model understanding and explaining of the multiomics interaction landscape, there have been several initial attempts to show the potential of deep learning-based multiomics integration. One approach utilized a bottlenecked autoencoder to integrate mRNA expression, DNA methylation, and miRNA expression levels and showed that deeply integrated features perform well as a biomarker for predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma [43]. Here, a bottlenecked autoencoder is defined as a model that is trained to emit an output that is identical to the input, where the dimension of the bottleneck layer is far smaller than that of the input. The expression and methylation levels were concatenated into a single vector and fed into the model. The rationale behind this study is that the model should learn a compact representation that captures the interactions involving 2 or more omics layers. On the other hand, MOLI [44] adopts the late integration of mutation, copy number, and gene expression profiles with deep learning. Each omics feature was separately encoded by an individual neural network called encoding subnetwork, and the representations were concatenated and fed into the fully connected layers to predict the drug response of the corresponding sample.
While many fundamental scientific findings for multiomics interactions can be made through training models with minimal guidance, such approaches have several limitations. First, since the weights in general-purpose deep learning models are usually difficult to interpret by themselves, the interpretation of a trained model requires post-hoc interpretation methods such as guided backpropagation [45], DeepLIFT [46], integrated gradients [47], or in silico mutagenesis [36]. These model interpretation methods are useful, but their interpretation often largely depends on the method of choice, which is undesirable for drawing firm conclusions. Next, the findings from passively guided models are prone to false positives because the model cannot discern the causative relationships from spurious or confounded correlations. Finally, these drawbacks result in poor model performance and generalizability.
The active integration of domain knowledge into the deep learning model is a promising way to address these challenges. When the design of a model constrains its weight to have conceptual biological meaning, the interpretation of the trained model will be straightforward and unique since it does not depend on external interpretability methods. Moreover, our prior knowledge of the basic principles of multiomics interactions can be used to prevent the model from being deceived by many false-positive relationships and guide it to be more focused on potentially causal relationships.
With the establishment of large-scale knowledge bases of biological concepts and interactions, there has been increasing interest in the development of methods that actively utilize them as practical guidance imposed on the model. The knowledge bases can be coarsely classified into 3 groups: (1) databases for biological interactions, (2) databases for biological concepts, and (3) databases for other experimental observations. In this section, we discuss how these databases have been incorporated into deep learning models to model multiomics interactions and briefly show how the models can be applied to address various biomedical challenges.
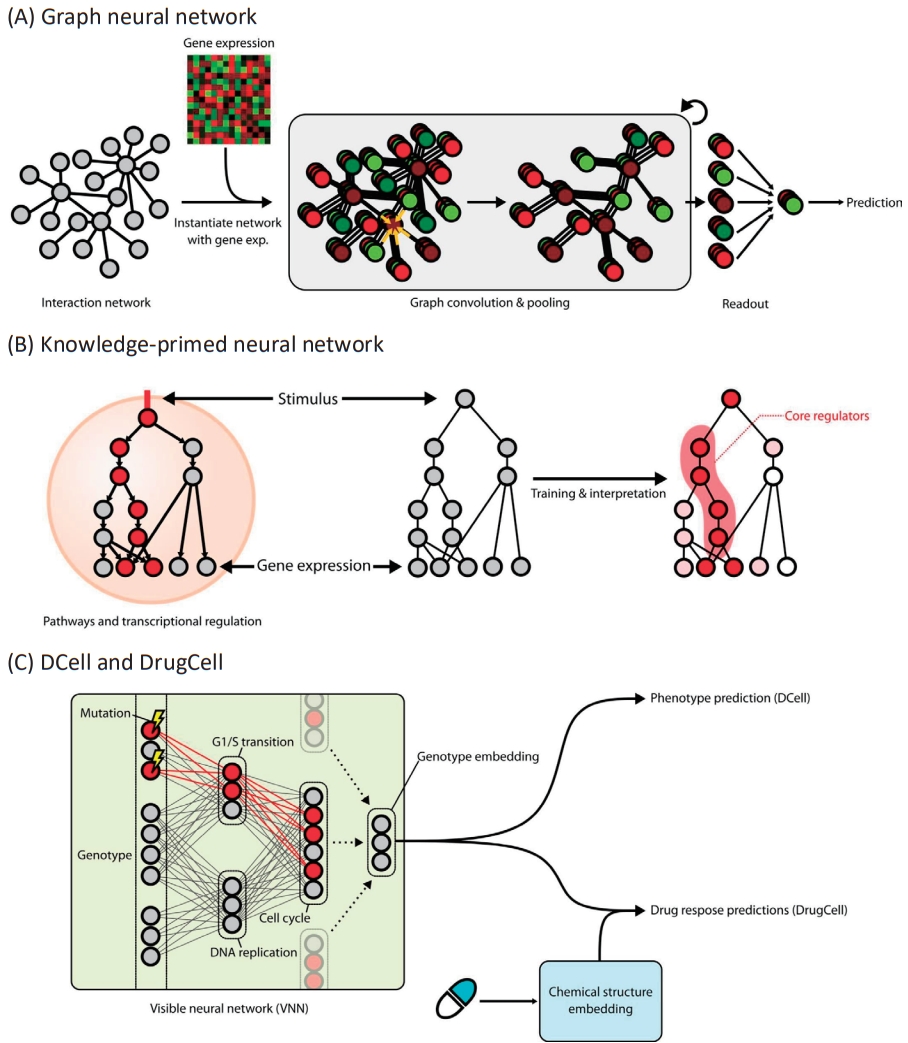
Large-scale networks for functional interactions between proteins and genes include BioGRID [48], STRING [49], HumanNet [50], and Reactome [51]. Because edges in such networks represent paths through which biological information flows, its modeling will be straightforward if we locally propagate information only through the neighboring nodes. To this end, graph neural networks (GNNs) [52] have been widely applied for networkguided modeling of multiomics interactions (Fig. 2A). An early study [53] utilizing graph convolutional filtering on GNNs to capture localized patterns of gene expressions showed promising increase in performance of predicting subtypes of breast cancer samples, and another work using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways [54] along with attention-based interpretation revealed subtype-specific aberrations in the biological pathways [55].
On the other hand, networks can also be indirectly used as a regularizer for the latent features learned by the model. The multiview factorization autoencoder [56] adopts a general scheme called graph Laplacian regularizer [57] to incorporate network information in the training of autoencoders. The graph Laplacian regularizer measures the overall discrepancy of the learned features between neighboring nodes (e.g., genes) in terms of Euclidean distance, and its value is added to the loss term. Thus, a pair of genes connected by an edge in the network is forced to have similar latent representations.
Knowledge-primed neural networks (KPNNs) [58] are examples of biologically transparent and interpretable model architectures that use biological networks (Fig. 2B). Each node in the KPNN represents a gene or a protein, and the edges between nodes denote the known interactions between them. Given that the model achieves the desired performance for modeling a biological phenomenon, the model itself can be interpreted as a quantitative hypothesis for the phenomenon. The weight of a connection between 2neurons in the network represents the importance of the regulatory connection between them, thus allowing the prioritization of genes or proteins in the biological process. Notably, a KPNN trained for single-cell experimental results of T-ell receptor (TCR) stimulation showed prediction accuracy comparable to that of a generic deep neural network. Understandably, the topology of KPNN resembles that of a biological network in terms of 4 properties: (1) shortcuts between layers, (2) scale-freeness, (3) modularity, and (4) restricted reachability of hidden neurons to input neurons. As a result, the key mediators of TCR signaling could be identified by analyzing the activation of the edge weights connected to each gene upon stimulation compared to control inputs. Since the model could be clearly explained in terms of genes and proteins while accurately predicting the system-level outcome, it would be a good starting point for system-level characterization and simulation of a cell. Recent work on estimating transcriptomic age using KPNN supports this as known associations between the core pathways and aging were captured, but virtual knockdown of genes accurately recapitulated the effects on aging that were experimentally validated.
Many biomedical concepts can be represented hierarchically. Therefore, these concepts are naturally organized as tree-like data structures. For example, the concept “cell cycle” encompasses more specific concepts such as “mitotic cell cycle” and “meiotic cell cycle,” and “mitotic cell cycle” includes concepts like “G1/S transition” and “DNA replication.” The most prominent example of the hierarchical compilation of biomedical concepts is the gene ontology (GO) terms [59], where the concepts are organized into 3 trees rooted in 3 categories: biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components. MeSH (medical subject headings) [60] is another exemplary database that uses a conceptual hierarchy to organize biomedical terms.
DCell [61] was the first approach to constructing a deep learning architecture that inherits the topology of the GO hierarchy (Fig. 2C). Its model, the visible neural network (VNN), consists of thousands of subsystems corresponding to each term in the GO hierarchy. Multiple neurons constitute a subsystem, and the connections between neurons are only allowed for the 2 neurons belonging to a pair of subsystems with hierarchical relationships. Since the leaf nodes of the GO hierarchy are genes, each node at the input layer of the VNN corresponds to a gene and its state represents the mutation status of the corresponding gene. Therefore, the input as a vector collectively denotes the cell’s genotype. The model was trained to predict the growth phenotype of yeast cells based on their genotypes. DCell could be used for mechanistic interpretation of perturbed biological processes due to mutations. Because the information flow originating from the mutations at the input layer is visible and interpretable throughout the network, a mechanistic explanation of genotype-phenotype association and their simulation is possible.
DrugCell [62] extends DCell to predict the drug responses of human cancer cells based on their genotype. The genotypes are embedded with VNN as in DCell, and the latent representation of drugs is computed using generic deep neural networks. The resulting 2 representations, genotypes and drugs, are concatenated and fed to a fully connected layer with nonlinearities to predict the cell’s response to the drug. The authors expressed this procedure as an in silico treatment of a cell with a drug. Similar to DCell, DrugCell was able to prioritize subsystems according to their predictive strength for the drug response of the cell. In other words, DrugCell revealed specific mechanisms that convey the effects of drug treatment. Since the model could identify the most crucial intracellular subsystem for each drug, strikingly, the principled design of synergistic drug combinations that maximizes the drug efficacy was demonstrated as possible.
Although much biological knowledge can be structured in the form of networks as discussed so far, much knowledge cannot be simply organized as networks. Therefore, it is becoming an active area for researchers to apply their own ideas to transform rich information into an organized form that can explicitly guide models.
As discussed in the previous section, the binding motif preference of TFs can be learned de novo through supervised learning. However, it would be desirable to utilize the precompiled TF-binding motif preference data such as JASPAR [63], TRANSFAC [64], or GTRD [65]. This idea was initially examined by Ploenzke and Irizarry [66], where the weights of the convolutional filters were initialized with PWMs of JASPAR motifs. Because not all TFs are important for a specific prediction task, the filters are discarded if their contribution to the model performance is negligible. New randomly initialized filters were added to the model to allow de novo motif learning. On the other hand, because the PWMs allow us to compute the putative binding sites and binding affinities of each subsequence, we can incorporate the precomputed TFBSs into the deep learning model. Kang et al. [67] realized this idea by adding the binding site information and the expression levels of corresponding TFs as extra information for the gene expression prediction task. Interestingly, guiding the model with putative TFBSs resulted in slightly improved model performance. Combined with attention weights, the model enabled the mechanistic interpretation of the interaction between TF binding and methylation level on gene expression.
Analysis of the 3-dimentional (3D) organization of chromatin has recently been of great interest. Accordingly, there are still many unexplored possibilities when the traditional 1-dimensional view of genomic sequences is modified to a 3D view. In particular, the prediction of gene expression levels may benefit from such new modeling of genomes because it allows the efficient incorporation of distal regulatory relationships. The 3D chromatin contacts are usually measured by Hi-C and are represented as a pairwise contact map representing the likelihood of contact between genomic fragments. Thus, utilizing the contact map in deep learning may increase its performance. ChromeGCN [68] was the first model to use 3D chromatin contacts to predict chromatin profiles. Using the 500,000 most likely Hi-C contacts between 1,000-bp fragments per chromosome, ChromeGCN views each chromosome as a graph in which the nodes and edges represent genomic fragments and contacts between them, respectively. As a result, the study showed that exchanging the information of genomic sequences through graph edges based on 3D contact using a graph convolutional network outperformed the state-of-the-art model that uses only a local sequence context.
In this review, we discussed the diverse applications of AI methodologies for deciphering complex multiomics interactions. Despite their extreme complexity, the simple adoption of general-purpose deep learning to model interactions worked surprisingly well. This is presumably due to the vast expressibility of deep learning models for nonlinear relationships between variables. However, these generic deep learning models are often referred to as black-box models because their interpretation is not straightforward and often nonrobust. Moreover, the dimension of multiomics profiles is usually far larger than the number of samples and the modeling powers of deep models are usually too powerful, so they become overconfident with spurious interactions that are not actually present in living cells. Therefore, sensible ways to guide models with prior knowledge are especially desirable for the biological application of deep learning.
Designing new methods for the biological guidance of deep learning models is still a largely unexplored area of research, although there exist a few useful modular approaches such as GNNs or transformers to incorporate knowledge in the form of networks. GNN allows restricted information transfer between multiomics entities that are known to interact. This approach resembles the way cells specifically propagate biological information; therefore, it has the potential to accurately model multiomics interactions. The transformer seems to be a more versatile choice at the cost of computational burden because it can naturally learn the optimal all-pairwise affinities between any input features, while the prior pairwise relevance measures can be incorporated as a bias term.
Meanwhile, although deep learning models that reflect prior biological knowledge offer great opportunities for systematic and interpretable cellular modeling, their performances are often worse than or comparable to those of black-box models. This is a typical example of the trade-off between interpretability and performance, which has recently become a major research interest in the field of AI. Based on the recent rapid development of explainable AI technologies, we expect that a highly explainable AI model for biological modeling that outperforms conventional black-box models will be developed in the near future. Another drawback of strongly guided AI methods is that they cannot be applied to complex nonmodel organisms, for which comprehensive knowledge of their cellular characteristics has yet to be established. One appealing approach to addressing this challenge until the accumulation of a sufficient amount of relevant knowledge is to utilize and transfer existing knowledge from well-known model organisms. It can be done in the form of transfer learning or meta-learning, in which the knowledge is directly transferred or the model is guided to learn how to learn the relationship between biological entities. It should be noted that since all species are evolutionarily related, knowledge transfer or meta-training would be better done by incorporating evolutionary relationships between species.
A single groundbreaking AI-driven approach can greatly accelerate the forward movement of the entire field. It may also give rise to numerous additional discoveries derived from it. AlphaFold2 is obviously a good example since studies using its results are already rapidly accumulating. In the near future, it is almost certain that the field of biological science will enter a cycle in which AI-powered hypotheses on multiomics interactions facilitate experimental validation and accumulating biological evidence accelerates the identification of plausible targets by deep learning models. The key to this path is the creative and effective idea to incorporate accumulated biological knowledge into the architecture or training process of deep learning models.
In particular, complete modeling of cell biology through deep modeling of cells will revolutionize therapeutic strategies for diseases. Given the genetic background of a patient and tissuespecific reference model, perhaps in the form of knowledge-guided deep learning models, it will become possible to model the response of cells to a certain stimulus, including drug treatment. Elucidating the precise molecular mechanisms of a drug response will optimize the combination of synergy between drugs, as in DrugCell, and dramatically reduce side effects. Furthermore, the accumulation of high-resolution molecular profiles will allow the temporal modeling of cellular responses to establish drug treatment schedules that are optimized for each patient. The modeling of multiomics interactions and, therefore, of cell biology, will be a pivotal milestone that must be achieved to finally realize AI-driven precision medicine.
Footnotes
Funding
This research was supported by the Collaborative Genome Program for Fostering New Post-Genome Industry of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (NRF-2014M3C9A3063541), a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI15C3224), and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF (NRF-2019M3E5D4065965).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Collaborative Genome Program for Fostering New PostGenome Industry of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (NRF-2014M3C9A3063541); a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI15C3224) and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF (NRF-2019M3E5D4065965); and a grant from the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) funded by the Korean government(MSIT) (no. 2021-0-01343, Artificial Intelligence Graduate School Program, Seoul National University).
Fig. 1.
Interactions between omics layers that are modeled by weakly guided deep learning models. The schematic diagram shows 6 types of interactions that are formulated as tasks for deep learning models: (1) DNA/RNA binding specificity prediction, (2) mRNA splicing prediction, (3) gene expression prediction based on genomic sequences, (4) prediction of DNA methylation states and levels based on genomic sequences, (5) capturing relationship between genome and epigenome, and (6) simultaneous integration of multiple omics features. The black lines denote DNA, purple lines denote mRNA, and green lines denote miRNA. The black and white circles denote the methylation states of CpG sites, while the other colored circles represent proteins.
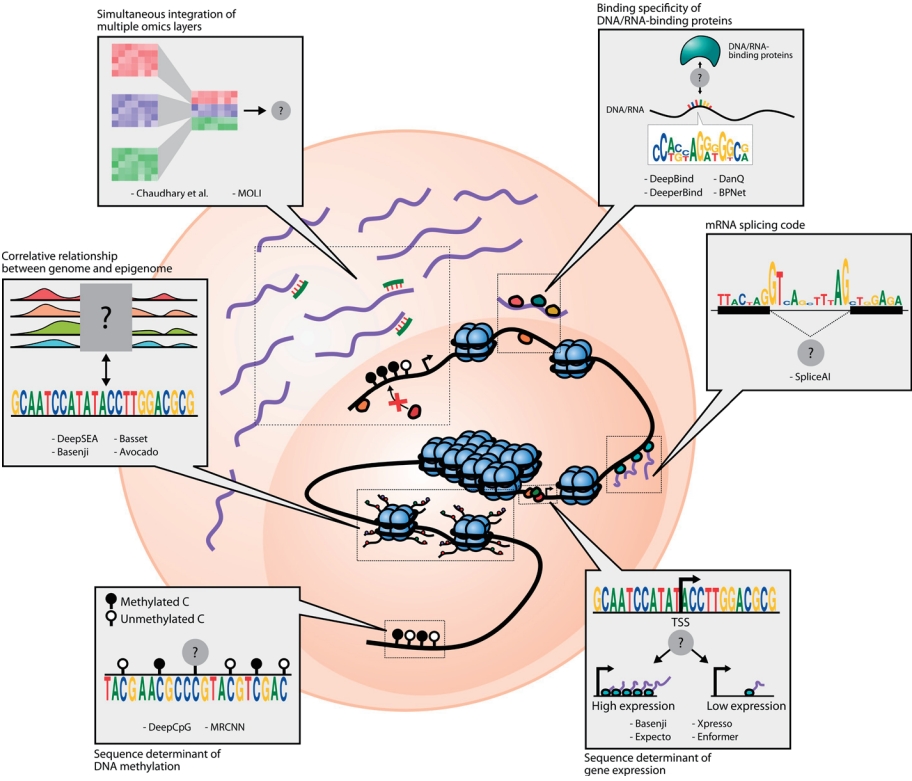
Fig. 2.
Strong biological guidance of deep learning models. (A) Graph neural networks (GNNs) are suitable for the modeling of interaction networks. Gene expression values for each sample are assigned to the corresponding nodes in the network to instantiate the network as an input for GNNs. Information of each gene is propagated to its neighbors by graph convolution. After a few iterations of graph convolution and pooling, information of the whole node is aggregated through readout function. Aggregated information is used to predict output values. (B) Knowledge-primed neural network. Nodes in a knowledge-primed neural network directly correspond to genes or proteins, and edges represent the interaction and transcriptional regulation between them. After training the network to predict the observed biological outcome upon certain stimuli, the model is clearly interpretable by edge weights and, thus, the core regulators of the process can be identified. (C) DCell and DrugCell incorporate hierarchical representations of biological knowledge to their network structure called a visible neural network (VNN). While input nodes denote the mutational states of genes, the nodes in hidden layers correspond to the biological concepts. Note that the nodes close to the output layer represent the broader concept. The VNN output, an embedding of the genotype, is subsequently used for phenotype prediction in DCell and drug response prediction in DrugCell.
References
1. Fields S, Song OK. A novel genetic system to detect protein–protein interactions. Nature 1989;340:245–6.


2. Joung JK, Ramm EI, Pabo CO. A bacterial two-hybrid selection system for studying protein-DNA and protein-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97:7382–7.



4. Pawson T, Nash P. Protein-protein interactions define specificity in signal transduction. Genes Dev 2000;14:1027–47.


5. Lemos B, Meiklejohn CD, Hartl DL. Regulatory evolution across the protein interaction network. Nat Genet 2004;36:1059–60.


6. Gavin AC, Bosche M, Krause R, Grandi P, Marzioch M, Bauer A, et al. Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature 2002;415:141–7.


7. Munoz Descalzo S, Rue P, Faunes F, Hayward P, Jakt LM, Balayo T, et al. A competitive protein interaction network buffers Oct4-mediated differentiation to promote pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Mol Syst Biol 2013;9:694.



8. Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, Green T, Figurnov M, Ronneberger O, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021;596:583–9.



9. Senior AW, Evans R, Jumper J, Kirkpatrick J, Sifre L, Green T, et al. Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning. Nature 2020;577:706–10.


10. Mardt A, Pasquali L, Wu H, Noe F. VAMPnets for deep learning of molecular kinetics. Nat Commun 2018;9:5.



11. Luscombe NM, Austin SE, Berman HM, Thornton JM. An overview of the structures of protein-DNA complexes. Genome Biol 2000;1:REVIEWS001.


12. Wang J, Zhuang J, Iyer S, Lin X, Whitfield TW, Greven MC, et al. Sequence features and chromatin structure around the genomic regions bound by 119 human transcription factors. Genome Res 2012;22:1798–812.



13. Park PJ. ChIP-seq: advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat Rev Genet 2009;10:669–80.



14. Riley TR, Slattery M, Abe N, Rastogi C, Liu D, Mann RS, et al. SELEX-seq: a method for characterizing the complete repertoire of binding site preferences for transcription factor complexes. In: Graba Y, Rezsohazy R, editors. Hox genes. New York: Humana Press, 2014:255–78.
15. Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW. MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34:W369–73.



16. Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E, Lin YC, Laslo P, et al. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cisregulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell 2010;38:576–89.



17. Alipanahi B, Delong A, Weirauch MT, Frey BJ. Predicting the sequence specificities of DNA-and RNA-binding proteins by deep learning. Nat Biotechnol 2015;33:831–8.


18. LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 1998;86:2278–324.

19. Hassanzadeh HR, Wang MD. DeeperBind: enhancing prediction of sequence specificities of DNA binding proteins. PProceedings (IEEE Int Conf Bioinformatics Biomed) 2016;2016:178–83.

20. Lipton ZC, Berkowitz J, Elkan C. A critical review of recurrent neural networks for sequence learning. arXiv:1611.05777 [Preprint] 2016;[cited 2021 Sep 2]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1611.05777.

21. Quang D, Xie X. DanQ: a hybrid convolutional and recurrent deep neural network for quantifying the function of DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 2016;44:e107.



22. Ruder S. An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks. arXiv:1706.05098 [Preprint] 2017;[cited 2021 Sep 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.05098.

23. Avsec Ž, Weilert M, Shrikumar A, Krueger S, Alexandari A, Dalal K, et al. Base-resolution models of transcription-factor binding reveal soft motif syntax. Nat Genet 2021;53:354–66.



24. Shrikumar A, Tian K, Avsec Ž, Shcherbina A, Banerjee A, Sharmin M, et al. Technical note on transcription factor motif discovery from importance scores (TF-MoDISco) version 0.5. 6.5. arXiv:1811.00416 [Preprint] 2018 [cited 2021 Sep 5]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1811.00416.

25. He Q, Johnston J, Zeitlinger J. ChIP-nexus enables improved detection of in vivo transcription factor binding footprints. Nat Biotechnol 2015;33:395–401.



26. Kelley DR, Reshef YA, Bileschi M, Belanger D, McLean CY, Snoek J. Sequential regulatory activity prediction across chromosomes with convolutional neural networks. Genome Res 2018;28:739–50.



27. Shiraki T, Kondo S, Katayama S, Waki K, Kasukawa T, Kawaji H, et al. Cap analysis gene expression for high-throughput analysis of transcriptional starting point and identification of promoter usage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003;100:15776–81.



28. Zhou J, Theesfeld CL, Yao K, Chen KM, Wong AK, Troyanskaya OG. Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk. Nat Genet 2018;50:1171–9.



29. Kelley DR. Cross-species regulatory sequence activity prediction. PLoS Comput Biol 2020;16:e1008050.



30. Agarwal V, Shendure J. Predicting mRNA abundance directly from genomic sequence using deep convolutional neural networks. Cell Rep 2020;31:107663.


31. Avsec Ž, Agarwal V, Visentin D, Ledsam JR, Grabska-Barwinska A, Talyer KR, et al. Effective gene expression prediction from sequence by integrating long-range interactions. Nat Methods 2021;18:1196–203.



32. Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, et al. Attention is all you need. In: 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017); Long Beach (CA), USA.
34. Reed R, Maniatis T. The role of the mammalian branchpoint sequence in pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev 1988;2:1268–76.


35. Jaganathan K, Panagiotopoulou SK, McRae JF, Darbandi SF, Knowles D, Li YI, et al. Predicting splicing from primary sequence with deep learning. Cell 2019;176:535–48.


36. Zhou J, Troyanskaya OG. Predicting effects of noncoding variants with deep learning-based sequence model. Nat Methods 2015;12:931–4.



37. ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012;489:57.



38. Kundaje A, Meuleman W, Ernst J, Bilenky M, Yen A, Heravi-Moussavi A, et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 2015;518:317–30.


39. Kelley DR, Snoek J, Rinn JL. Basset: learning the regulatory code of the accessible genome with deep convolutional neural networks. Genome Res 2016;26:990–9.



40. Angermueller C, Lee HJ, Reik W, Stegle O. DeepCpG: accurate prediction of single-cell DNA methylation states using deep learning. Genome Biol 2017;18:67.



41. Tian Q, Zou J, Tang J, Fang Y, Yu Z, Fan S. MRCNN: a deep learning model for regression of genome-wide DNA methylation. BMC Genomics 2019;20:1–10.



42. Schreiber J, Durham T, Bilmes J, Noble WS. Avocado: a multi-scale deep tensor factorization method learns a latent representation of the human epigenome. Genome Biol 2020;21:81.



43. Chaudhary K, Poirion OB, Lu L, Garmire LX. Deep learning–based multi-omics integration robustly predicts survival in liver cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2018;24:1248–59.


44. Sharifi-Noghabi H, Zolotareva O, Collins CC, Ester M. MOLI: multiomics late integration with deep neural networks for drug response prediction. Bioinformatics 2019;35:i501–9.



45. Springenberg JT, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T, Riedmiller M. Striving for simplicity: the all convolutional net. arXiv:1412.6806 2014; [cited 2021 Sep 10]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.6806.

46. Shrikumar A, Greenside P, Kundaje A. Learning important features through propagating activation differences. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning; Sydney, Australia. PMLR 2017;70:3145–53.
47. Sundararajan M, Taly A, Yan Q. Axiomatic attribution for deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning; Sydney, Australia. PMLR. 2017;70:3319–28.
48. Stark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Reguly T, Boucher L, Breitkreutz A, Tyers M. BioGRID: a general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34(Database issue): D535–9.


49. Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D, Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, et al. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res 2021;49(D1): D605–12.


50. Hwang S, Kim CY, Yang S, Kim E, Hart T, Marcotte EM, et al. HumanNet v2: human gene networks for disease research. Nucleic Acids Res 2019;47:D573–80.


51. Fabregat A, Jupe S, Matthews L, Sidiropoulos K, Gillespie M, Garapati P, et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 2020;48:D498–503.


52. Scarselli F, Gori M, Tsoi AC, Hagenbuchner M, Monfardini G. The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 2008;20:61–80.


53. Rhee S, Seo S, Kim S. Hybrid approach of relation network and localized graph convolutional filtering for breast cancer subtype classification. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-18); Stockholm (Sweden). 2018 Jul 13–19; IJCAI 2018;3527-34.

54. Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2000;28:27–30.



55. Lee S, Lim S, Lee T, Sung I, Kim S. Cancer subtype classification and modeling by pathway attention and propagation. Bioinformatics 2020;36:3818–24.


56. Ma T, Zhang A. Multi-view factorization autoencoder with network constraints for multi-omic integrative analysis. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine; 2018 Dec 3-6; IEEE BIBM 2018;702-7.

57. Ando RK, Zhang T. Learning on graph with Laplacian regularization. In: Schölkopf B, Platt J, Hofmann T, , editors. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference. 200719::25.
58. Fortelny N, Bock C. Knowledge-primed neural networks enable biologically interpretable deep learning on single-cell sequencing data. Genome Biol 2020;21:190.



59. Gene Ontology Consortium. The gene ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res 2019;47:D330–8.


60. Lipscomb CE. Medical subject headings (MeSH). Bull Med Library Assoc 2000;88:265–6.
61. Ma J, Yu MK, Fong S, Ono K, Sage E, Demchak B, et al. Using deep learning to model the hierarchical structure and function of a cell. Nat Methods 2018;15:290–8.



62. Kuenzi BM, Park J, Fong SH, Sanchez KS, Lee J, Kreisberg JF, et al. Predicting drug response and synergy using a deep learning model of human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2020;38:672–84.



63. Khan A, Fornes O, Stigliani A, Gheorghe M, Castro-Mondragon JA, Van Der Lee R, et al. JASPAR 2018: update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles and its web framework. Nucleic Acids Res 2018;46:D260–6.


64. Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, et al. TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34:D108–10.

65. Kolmykov S, Yevshin I, Kulyashov M, Sharipov R, Kondrakhin Y, Makeev VJ, et al. GTRD: an integrated view of transcription regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 2021;49:D104–11.


66. Irizarry RA. Interpretable convolution methods for learning genomic sequence motifs. bioRxiv [Preprint] 2018;[cited 2021 Sep 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/411934.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


