Pulmonology
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Pulmonology
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (62)
- Cardiology (81)
- Critical Care Medicine (13)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (64)
- Gastroenterology (73)
- General Pediatrics (57)
- Genetics and Metabolism (26)
- Hematology (19)
- Immunology (16)
- Infection (78)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (125)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (54)
- Neurology (96)
- Nutrition (32)
- Oncology (17)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (34)
- Rheumatology (3)
- Other (43)
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Effect of vitamin C supplement in treatment of childhood pneumonia requiring hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial
- Chutima Phuaksaman, Katechan Jampachaisri, Klaita Srisingh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):690-699. Published online April 1, 2025
-

This study assessed the effects of vitamin C on children with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Vitamin C supplementation improved clinical symptoms within 48–72 hours compared to placebo but did not reduce the length of hospital stay (LOS). These findings suggest that vitamin C is beneficial for managing CAP severity, but does not affect LOS.
- Association of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor gene and growth differentiation factor 15 gene polymorphisms and their circulating levels with respiratory distress syndrome among preterm neonates
- Ali Helmi Bakri, Mohammed H. Hassan, Khaled Abdalla Abd-Elbaseer, Mahmoud Abo-Alhassan Sayed, Ahmed Alamir Mahmoud Abdallah, Eman Ahmed Abd-Elmawgood
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):680-689. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Do macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) levels and their gene polymorphisms affect RDS among preterm babies?
Finding: Significantly higher serum MIF and GDF-15 levels were observed in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The mutant G- and C-alleles of GDF-15 rs4808793 C>G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and MIF rs755622 G>C SNP were present at significantly higher frequencies in preterm neonates with RDS.
Meaning: MIF and GDF-15 play a significant role in neonatal RDS and its severity.
- Clinical course of children with postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans with versus without comorbid bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Lamia Medghoul, Julien Grosjean, Christophe Marguet, Hortense Petat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):497-502. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans (PIBO) is a chronic respiratory disease that typically develops in children after a severe respiratory infection. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is often comorbid in patients with PIBO.
Finding: Corticosteroid pulse therapy effectively manages PIBO with or without comorbid BPD, significantly reducing exacerbations and decreasing the daily requirement for inhaled corticosteroids.
Meaning: Therapeutic effects of corticosteroid pulses are rapid and sustained over time, in both groups.
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):489-496. Published online March 11, 2025
-

Question: Is there a nonlinear relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and asthma in children and adolescents?
Finding: NLR showed a nonlinear association with asthma, with an NLR threshold of 2.23 identifying individuals at higher risk.
Meaning: An NLR<2.23 may serve as a potential biomarker for asthma risk assessment and management in pediatric populations, thereby offering a simple tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals.
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Polysomnographic features of children with obesity: body mass index predict severe obstructive sleep apnea in obese children?
- Rungrat Sukharom, Prakarn Tovichien, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Pinyapach Tiamduangtawan, Wattanachai Chotinaiwattarakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):80-90. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: How Common is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in obese children? OSA is common in obese children, even without habitual snoring.
Finding: Among the subjects, 60.6% had positional OSA, 40.2% had rapid eye movement-related OSA, 59.8% had desaturation, 20.5% had sleep-related hypoventilation, and 5.0% had obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Body mass index (BMI) and neck and waist circumferences were significantly associated with severe OSA.
Meaning: We recommend screening obese children (BMI > 29.2 kg/m2) for OSA.
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis
- Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Evidence-based management guidelines for noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in children and adolescents
- Eun Lee, Kyunghoon Kim, You Hoon Jeon, In Suk Sol, Jong Deok Kim, Taek Ki Min, Yoon Ha Hwang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Dong In Suh, Hwan Soo Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Sung-Il Woo, Yong Ju Lee, Sungsu Jung, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Gwang Cheon Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):418-426. Published online January 23, 2024
-

· We suggest offering long-term macrolides to children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis with frequent exacerbations (conditional recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
· We do not recommend the routine use of mucolytic agents, inhaled corticosteroids, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent exacerbation of bronchiectasis in children (inconclusive, very low quality of evidence).
· We recommend the use of nebulized hypertonic saline to prevent exacerbations and improve the lung function of children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (weak recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Oligohydramnios affects pulmonary functional/structural abnormalities in school-aged children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Mi-Jung Lee, Jungho Han, Joohee Lim, Haerin Jang, Ho Seon Eun, Min Soo Park, Soo Yeon Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Ji Ye Jung, Kyung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):257-266. Published online April 16, 2024
-

Question: Is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) associated with functional/structural abnormalities later in life?
Finding: School-aged children with severe BPD had abnormalities on pulmonary function tests and lung computed tomography despite no subjective respiratory symptoms; however, only prenatal oligohydramnios and prolonged ventilator use were associated with abnormal lung function.
Meaning: Long-term monitoring of preterm infants’ lung health is essential, especially for those with prenatal oligohydramnios or prolonged ventilator use.
- Letter to the Editor
- Pulmonology
- Metabolic syndrome and pulmonary dysfunction in asthmatic children during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Jue Seong Lee, Sang Hyun Park, Yoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):168-170. Published online February 19, 2024
-
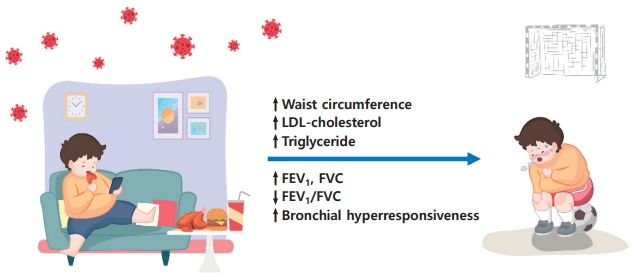
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Long COVID in children and adolescents: prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management strategies
- Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):465-474. Published online June 19, 2023
-
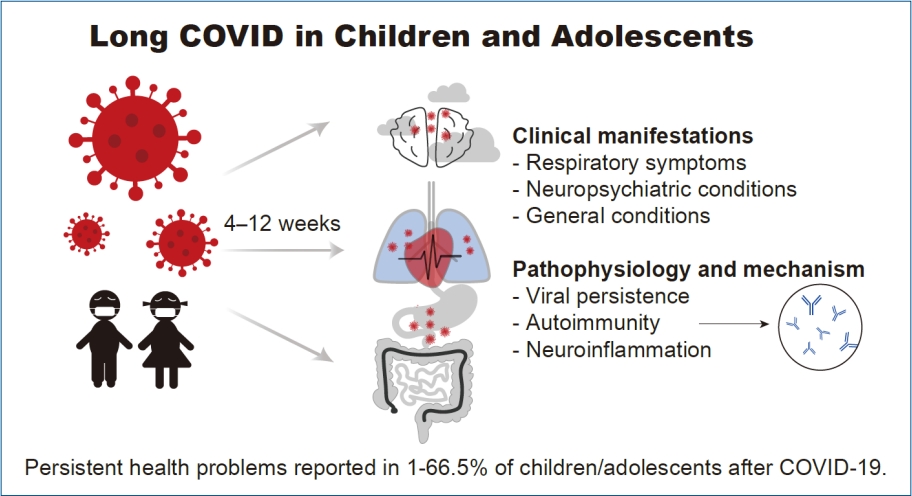
· Current definitions of long coronavirus disease (COVID) in children and adolescents vary in duration, ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
· The clinical spectrum of long COVID in children and adolescents comprises a wide range of symptoms and might be a multisystem disorder.
· Persistent health problems with a prevalence of 1%–66.5% were reported in children and adolescents after COVID-19, with a higher incidence of persistent single or multiple symptoms.
- Editorial
- Pulmonology
- Wheezing in infants and preschoolers: phenotypes and treatment options
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):26-27. Published online December 6, 2022
-
· Knowing who will develop into asthma or who will not is important to impose proper treatment and early intervention in a child with the first episode of wheezing.
· Phenotypes of severe bronchiolitis in less than 2-year-old children with first episode of wheezing were suggested for different treatment options
· RV-induced and/or atopy-associated severe wheezing in preschool children may benefit from early intervention of asthma treatment.
- Community-acquired pneumonia in Korean children: time to read between the lines
- Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):22-23. Published online November 10, 2022
-
· Various studies have reported the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in Korean children
· Factors other than etiology are equally important to a compre hensive understanding of CAP
· Knowledge from archived reports is no longer directly applicable to the current CAP and requires careful modification
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Predictors of high-flow nasal cannula failure in pediatric patients with acute respiratory distress
- Kantara Saelim, Busawan Thirapaleka, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Pharsai Prasertsan, Wanaporn Anuntaseree
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):595-601. Published online November 1, 2022
-

SpO2/FiO2 ratio ≤166, pediatric respiratory rate-oxygenation index <132, and clinical respiratory score ≥6 at 12 hours after high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) initiation were useful bedside predictors for HFNC failure in pediatric patients.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Epidemiology and surveillance implications of community-acquired pneumonia in children
- Eui Jeong Roh, Jung Yeon Shim, Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):563-573. Published online October 17, 2022
-
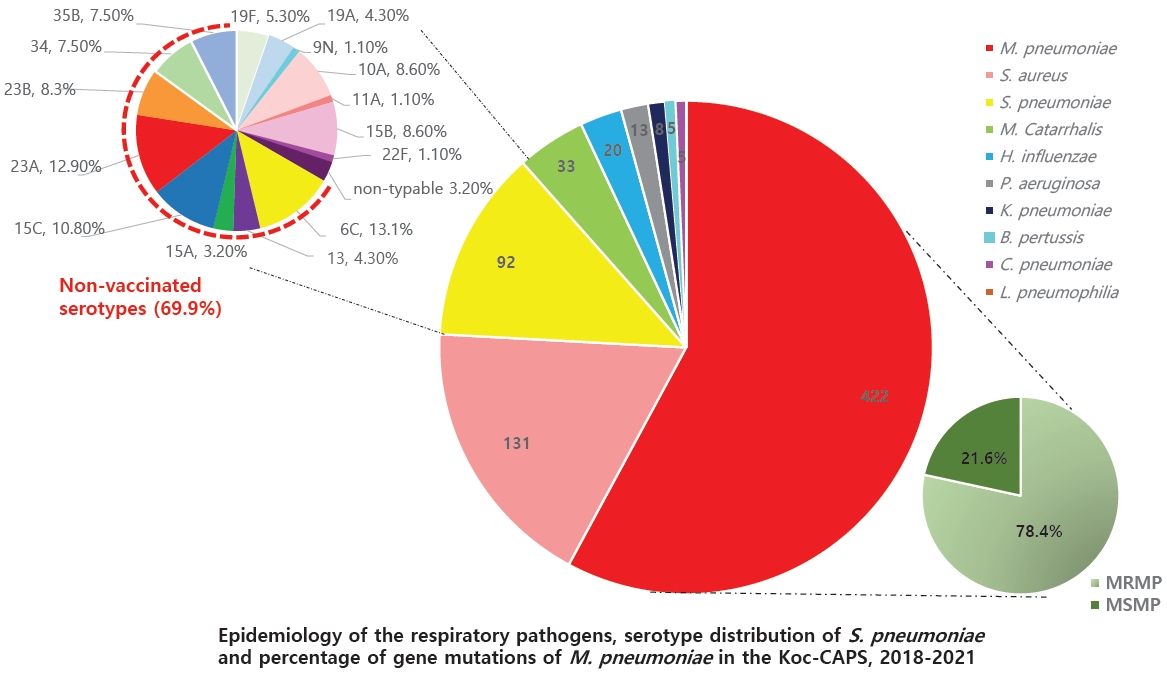
The identification of the causative pathogens of community-acquired pneumonia and appropriate treatment and prevention can reduce mortality and the socioeconomic burden by reducing the medical expenses. The world has been in the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic since 2020, and there is always a risk of continuous emergence and epidemic of new respiratory infectious diseases. Therefore, it is important to sustain a monitoring system for respiratory infectious diseases including pneumonia.
- Editorial
- Pulmonology
- Now lung ultrasound has been established as a fundamental examination in pediatric respiratory diseases
- Kyunghoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):401-402. Published online July 13, 2022
-
· Several studies demonstrated the usefulness of lung ultrasound in pediatric respiratory diseases including coronavirus disease 2019.
· Knowledge of lung ultrasound is increasing, and lung ultrasound has been established as a fundamental diagnostic examination for pediatric respiratory diseases.
- Influence of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on respiratory health in children
- Hyo-Bin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):348-349. Published online May 3, 2022
-
· Practicing hand hygiene, wearing a mask, maintaining social distancing, and other lockdown measures were implemented to reduce the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a worldwide disaster that started in 2019.
· The advent of the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic resulted in positive secondary effects, such as reduced respiratory viral infections in children and decreased degrees of air pollution.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Modified high-flow nasal cannula for children with respiratory distress
- Sarocha Itdhiamornkulchai, Aroonwan Preutthipan, Jarin Vaewpanich, Nattachai Anantasit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):136-141. Published online May 24, 2021
-
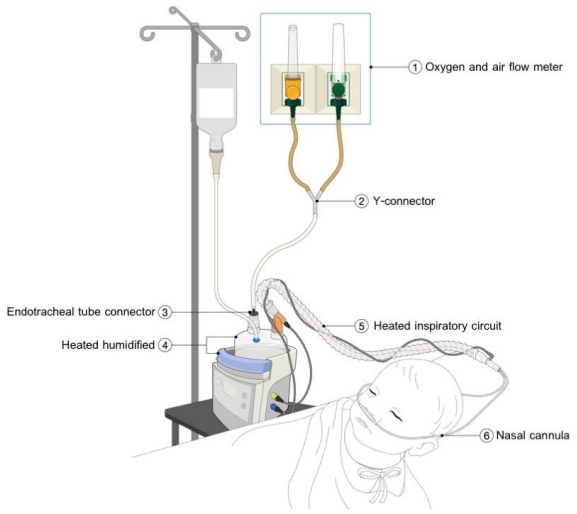
Question: Can the modified high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) provide alternative respiratory support for children with acute respiratory distress?
Finding: A total of 74 patients were assigned to the modified or commercial HFNC groups. The intubation rate, length of hospital stay, and adverse events did not differ between the 2 groups.
Meaning: The modified HFNC can provide alternative respiratory support for pediatric respiratory distress.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Current perspectives on atypical pneumonia in children
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):469-476. Published online June 10, 2020
-
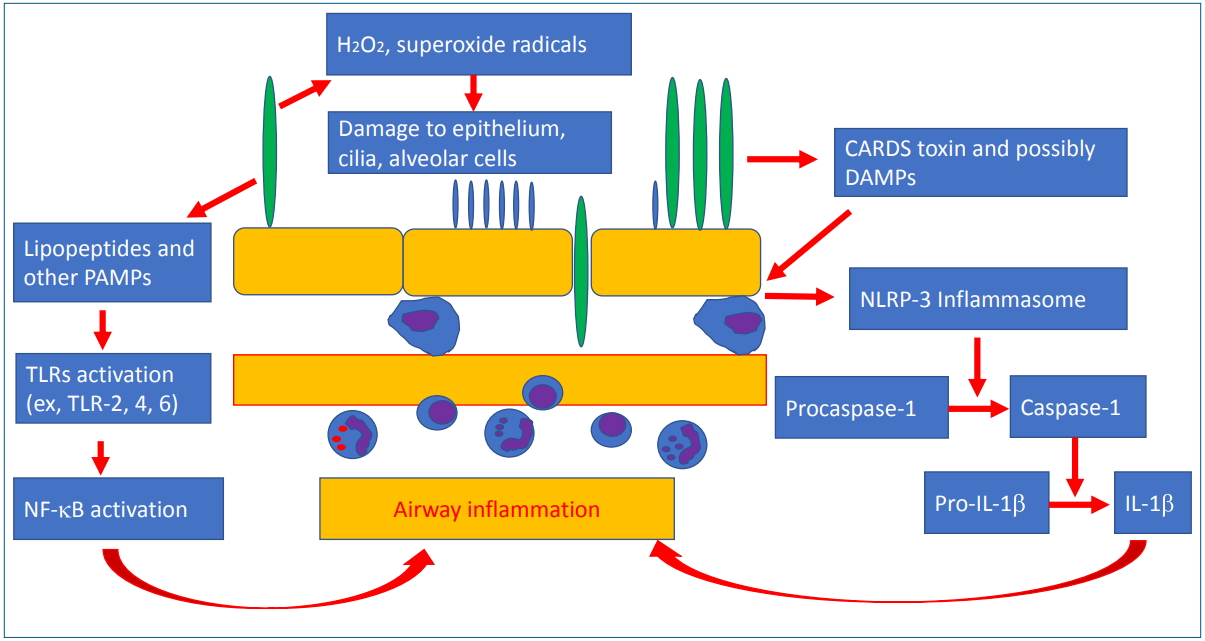
Macrolides are the first line treatment in atypical pneumonia caused by M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, and L. pneumophila. Macrolide-resistant mycoplasma pneumonia (MRMP) is emerging worldwide, especially in East Asia. Immune modulators such as corticosteroids or second line antibiotics are treatment options for MRMP. Pediatricians should be careful with empirical therapy of macrolides in children with mild to moderate community-acquired pneumonia not to increase the risk of MRMP.
- Overview of management of children with COVID-19
- Dyah Kanya Wati, Arya Krisna Manggala
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):345-354. Published online July 17, 2020
-
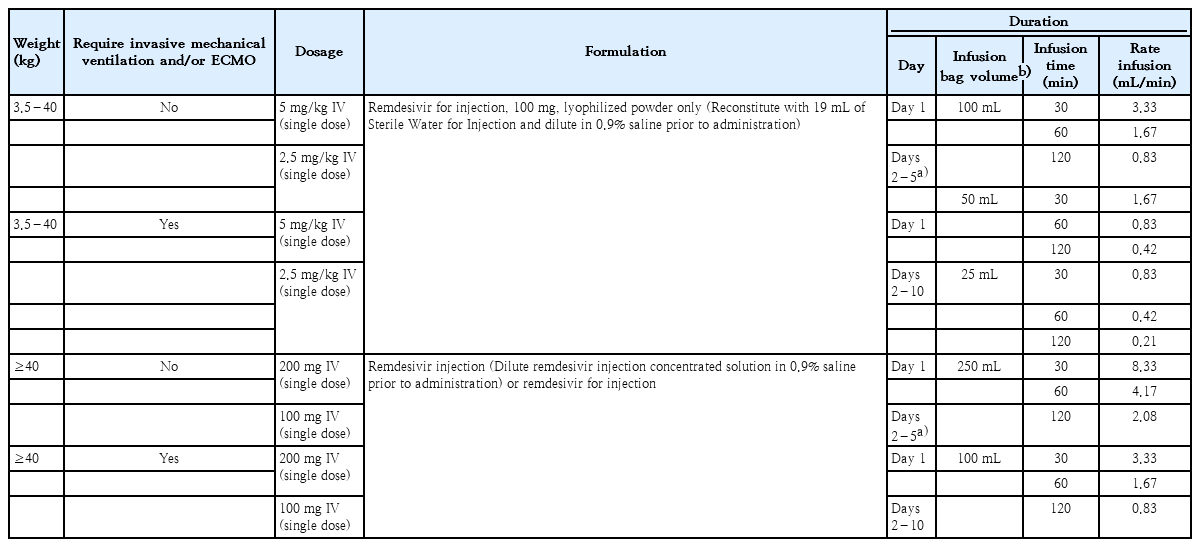
The specific treatments for COVID-19 in children remain inconclusive and debatable despite effectively decreasing its signs and symptoms.
The need for clinical trials and reports should be investigated.
- The past, present, and future of humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung diseases in children
- Eun Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):251-258. Published online December 9, 2019
-
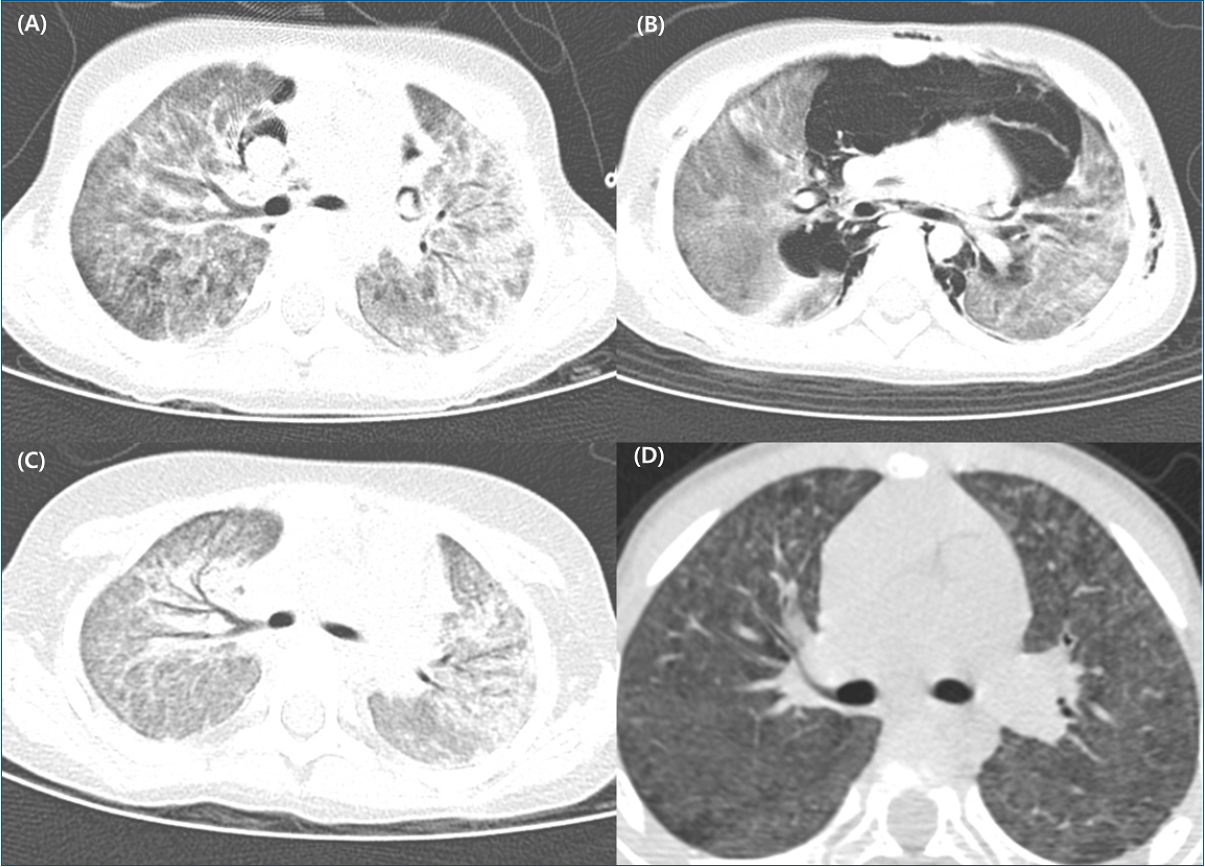
Exposure to environmental factors can cause interstitial lung diseases (ILDs); however, such types of ILDs are rare. From 2007 to 2011, an ILD epidemic occurred in South Korea owing to inhalational exposure to toxic chemicals in humidifier disinfectants (HDs). HD-associated ILDs (HD-ILDs) are characterized by rapidly progressing respiratory failure with pulmonary fibrosis and a high mortality rate of 43.8%−58.0%. Although...
- Perspective
- Pulmonology
- Early preemptive immunomodulators (corticosteroids) for severe pneumonia patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):117-118. Published online April 8, 2020
-
- Editorial
- Pulmonology
- Are alternative antibiotics needed for antibiotic-nonresponsive Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia?
- Eun-Ae Yang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):44-45. Published online February 15, 2020
-
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in children: a clinical review
- Ji-Won Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):3-7. Published online October 28, 2019
-
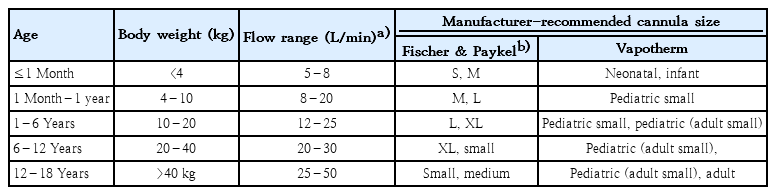
High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) is a relatively safe and effective noninvasive ventilation method that was recently accepted as a treatment option for acute respiratory support before endotracheal intubation or invasive ventilation. The action mechanism of HFNC includes a decrease in nasopharyngeal resistance, washout of dead space, reduction in inflow of ambient air, and an increase in airway pressure. In preterm...
- Benefits and risks of therapeutic alternatives for macrolide resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):199-205. Published online March 15, 2019
-
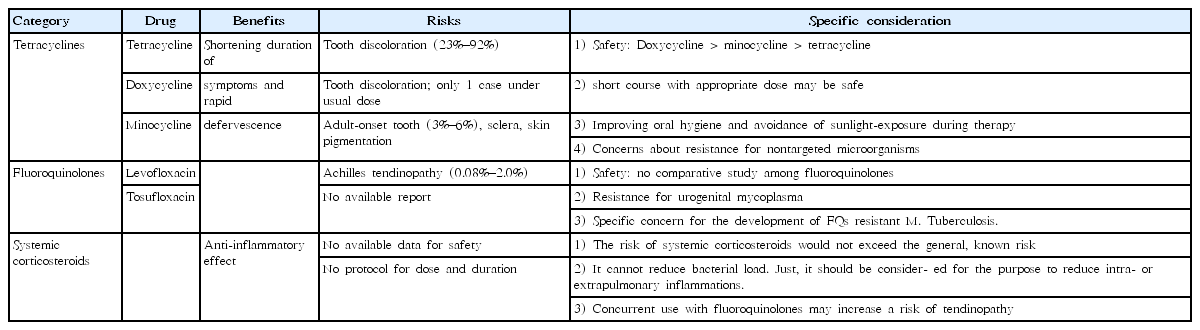
Although Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) has been generally susceptible to macrolides, the emergence of macrolide-resistant MPP (MRMP) has made its treatment challenging. MRMP rapidly spread after the 2000s, especially in East Asia. MRMP is more common in children and adolescents than in adults, which is likely related to the frequent use of macrolides for treating M. pneumoniae infections in children....
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- The changes of prevalence and etiology of pediatric pneumonia from National Emergency Department Information System in Korea, between 2007 and 2014
- Eun Ju Shin, Yunsun Kim, Jin-Young Jeong, Yu Mi Jung, Mi-Hee Lee, Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):291-300. Published online September 15, 2018
-
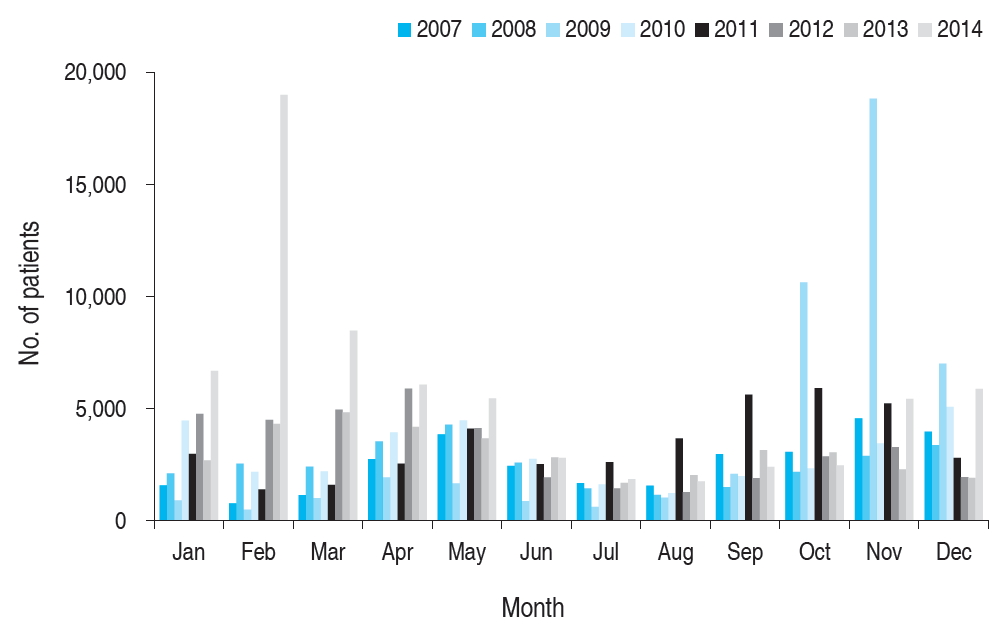
Purpose: Understanding changes in pathogen and pneumonia prevalence among pediatric pneumonia patients is important for the prevention of infectious diseases. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data of children younger than 18 years diagnosed with pneumonia at 117 Emergency Departments in Korea between 2007 and 2014. Results: Over the study period, 329,380 pediatric cases of pneumonia were identified. The most frequent age group was...
- Increased procalcitonin level is a risk factor for prolonged fever in children with Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Ji Eun Jeong, Ji Eun Soh, Ji Hee Kwak, Hye Lim Jung, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Moon Soo Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):258-263. Published online August 15, 2018
-
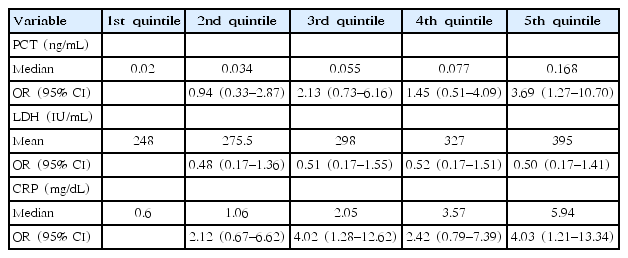
Purpose: Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is characterized by prolonged fever and radiological progression despite macrolide treatment. Few studies have examined serum procalcitonin (PCT) level in children with MPP. We aimed to investigate the association of acute inflammation markers including PCT with clinical parameters in children with MPP. Methods: A total of 147 children were recruited. The diagnosis of MPP...
- Comparison of cytokine expression profiles in infants with a rhinovirus induced lower respiratory tract infection with or without wheezing: a comparison with respiratory syncytial virus
- Da Eun Roh, Sook-Hyun Park, Hee Joung Choi, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(9):296-301. Published online September 21, 2017
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate whether infants with rhinovirus (RV) infection-induced wheezing and those with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection-induced wheezing have different cytokine profiles in the acute stage.
Methods Of the infants with lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) between September 2011 and May 2012, 88 were confirmed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and hospitalized. Systemic interferon-gamma (IFN-γ),...
- Case Report
- Pulmonology
- A pediatric case of relapsed pulmonary alveolar proteinosis despite successful whole lung lavage
- Seung Young Jin, Hye Ri Yun, Yun Jung Choi, Jun Dong Park, Jin Tae Kim, Chang Hyun Kang, Young Sik Park, Young Hun Choi, Woo Sun Kim, Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(7):232-236. Published online July 31, 2017
-
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare disease in children characterized by intra-alveolar accumulation of surfactant proteins, which severely reduces gaseous exchange. Whole lung lavage (WLL) is the preferred technique for the treatment of severe PAP. Herein, we present a pediatric case of PAP treated with WLL. An 11-year-old boy was admitted with the chief complaint of a dry cough...
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Mechanism of resistance acquisition and treatment of macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children - Hyeon-Jong Yang, Dae Jin Song, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(6):167-174. Published online June 22, 2017
-
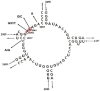
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is one of the most common forms of community-acquired pneumonia in children and adolescents. Outbreaks of MPP occur in 3- to 7-year cycles worldwide; recent epidemics in Korea occurred in 2006–2007, 2011, and 2015–2016. Although MPP is known to be a mild, self-limiting disease with a good response to macrolides, it can also progress into a...
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











