Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with intermittent sigh breaths on carbon dioxide levels in neonates (508 times)
- Kulthida Baingam, Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):178-184. Published online November 13, 2024
-
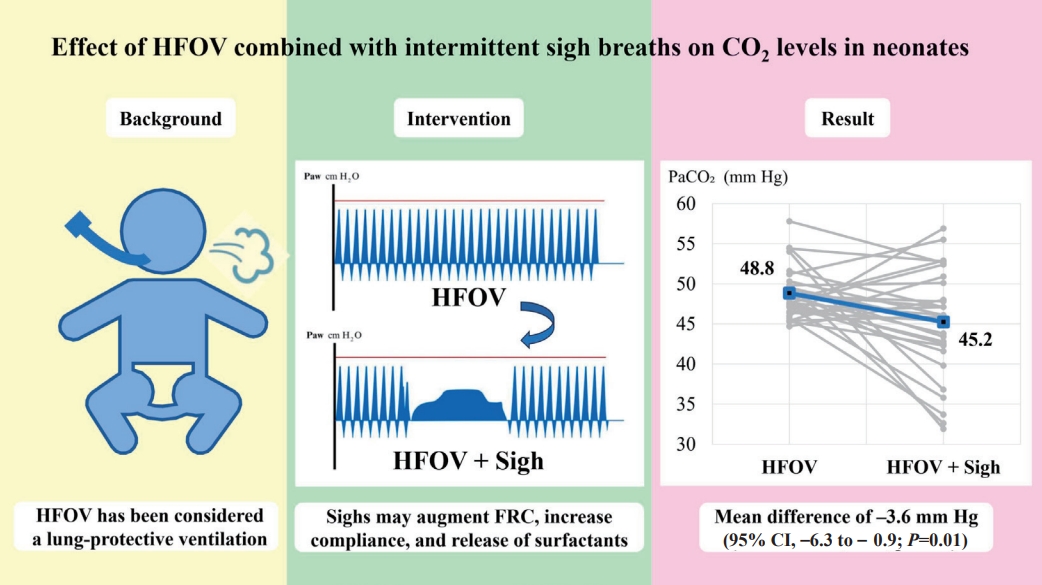
Question: Can sigh breaths (Sighs) application during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) decrease partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels?
Finding: The mean PaCO2 level after Sighs during HFOV was significantly decreased compared to that after HFOV alone (mean difference, -3.6 mmHg).
Meaning: HFOV plus Sighs functionality can reduce PaCO2 levels. However, further studies are required to conclusively determine the effects of Sighs.
- Characterization of gut microbiota in very low birth weight infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (469 times)
- Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate, Kamonnut Singkhamanan, Komwit Surachat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):503-511. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Does the gut microbiota differ between very low birth weight (VLBW) infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)?
Finding: Common respiratory pathogens were notably elevated in the BPD group, whereas anaerobic and butyrate-producing taxa, key components of postbiotics, were dominant in the non-BPD group.
Meaning: In gut-lung communication, the interplay between the intestinal and respiratory systems may implicate pro- and postbiotics in VLBW infants with BPD.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Community-acquired pneumonia in children: updated perspectives on its etiology, diagnosis, and treatment (436 times)
- Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):80-89. Published online June 14, 2023
-
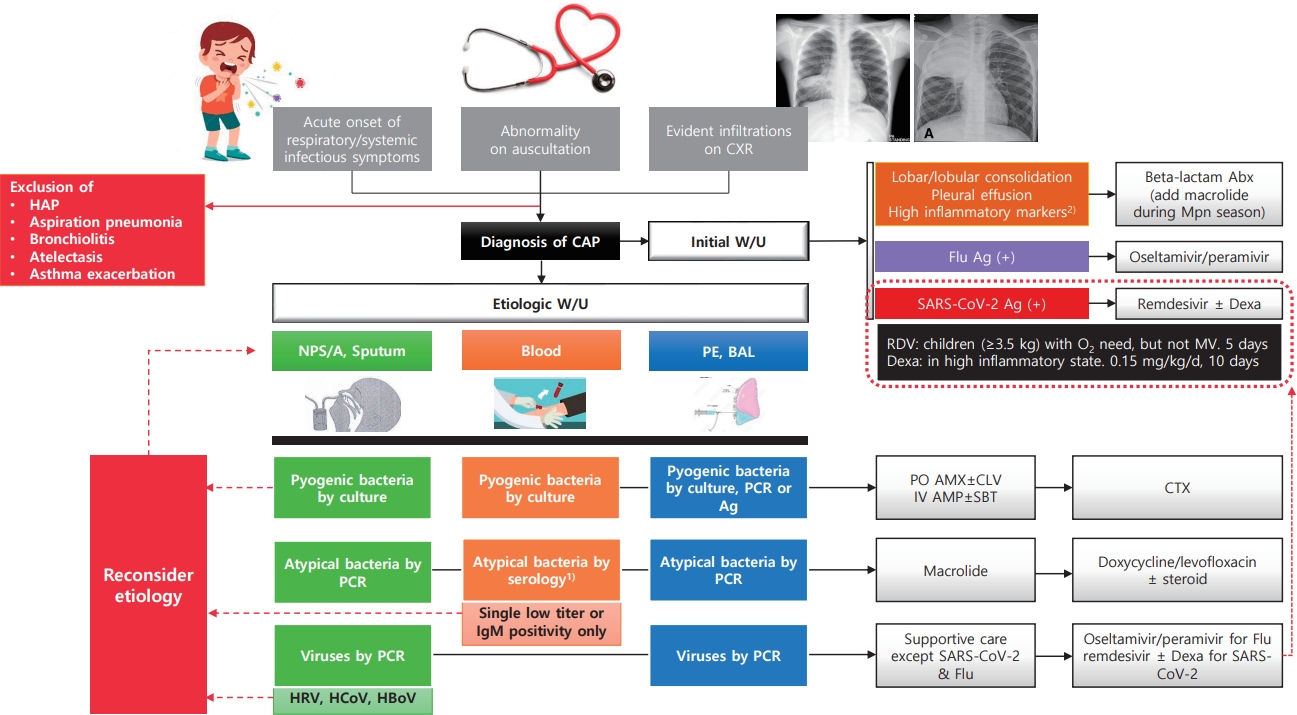
· Most commonly confirmed causes of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae (8%–40%) and respiratory syncytial virus (15%–20%).
· Pyogenic bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus pneumoniae (40%–50%) and Streptococcus pyogenes (10%–25%), are detected in 2%–5% of children hospitalized with CAP.
· CAP should be diagnosed conservatively according to clinical and radiological criteria.
· The etiology should be identified via appropriate test result interpretation.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Characteristics of temper tantrums in 1–6-year-old children and impact on caregivers (377 times)
- Warangkana Prutipaisan, Issarapa Chunsuwan, Tippawan Hansakunachai, Paskorn Sritipsukho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):170-177. Published online November 13, 2024
-
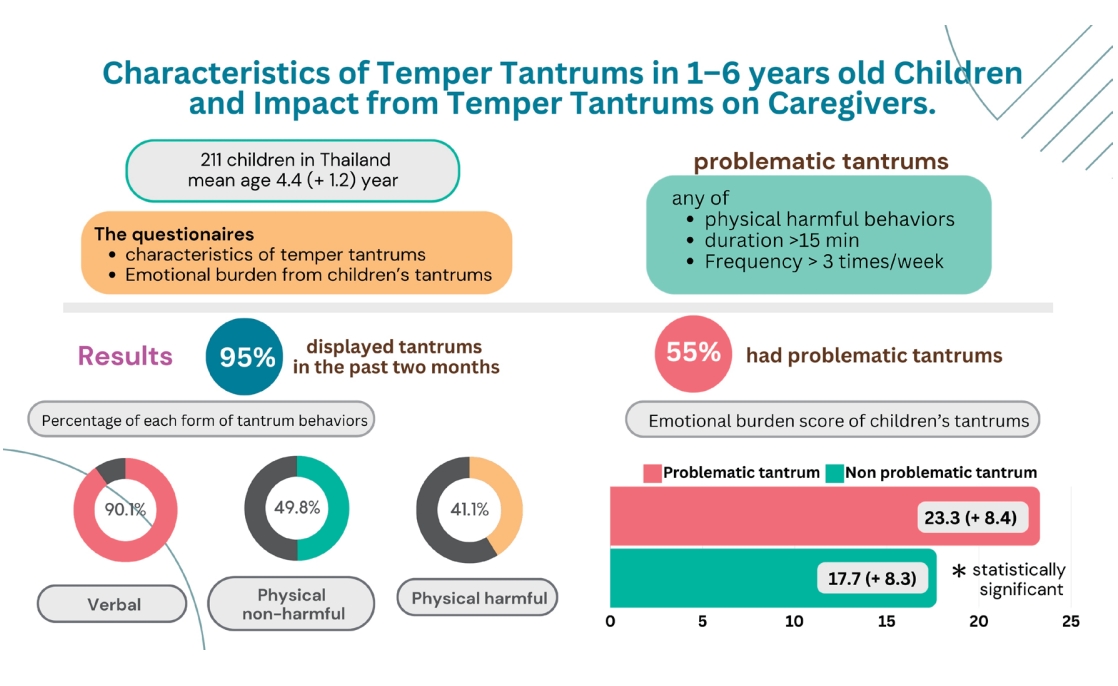
Question: What are common tantrum behaviors in preschool children, and how frequently are problematic behaviors observed? Do problematic tantrums have a different emotional impact on caregivers compared to typical tantrums?
Finding: Temper tantrums are common in preschool children, and verbal tantrums are the most common type.
Meaning: Problematic tantrums, defined as tantrums exhibiting aggressive physical behavior, long duration (>15 minutes), or frequent occurrence (>3 days/wk), significantly affected caregivers’ emotions.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Comprehensive evaluation of the child with global developmental delays or intellectual disability (286 times)
- Abdullah Nasser Aldosari, T. Saeed Aldosari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):435-446. Published online May 29, 2024
-

· A detailed history and comprehensive physical examination remain the cornerstones for establishing a diagnosis of global developmental delay/intellectual disability (GDD/ID).
· Comprehensive surveillance and screening programs play a significant role in the early detection of GDD.
· Whole-exome sequencing is highly recommended as first- or second-line testing for individuals with idiopathic GDD/ID.
· Early intervention by a well-versed multidisciplinary team can significantly improve the outcomes and prognosis of GDD/ID.
- Endocrinology
- Growth plate closure and therapeutic interventions (258 times)
- Ja Hyang Cho, Hae Woon Jung, Kye Shik Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):553-559. Published online October 28, 2024
-

Height gains result from longitudinal bone growth. Upon adequate growth, growth plate closure limits longitudinal bone growth. To date, gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs, aromatase inhibitors, C-type natriuretic peptide analogs, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 inhibitors have been studied or used as therapeutic interventions to delay growth plate closure and increase human height. The development of more effective therapeutic modalities for short stature, precocious puberty, and skeletal dysplasia is anticipated.
- Other
- Myopia: a review of current concepts, association with nonophthalmological conditions, and treatment strategy in children and adolescents (247 times)
- Yeon Woong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):554-565. Published online April 1, 2025
-
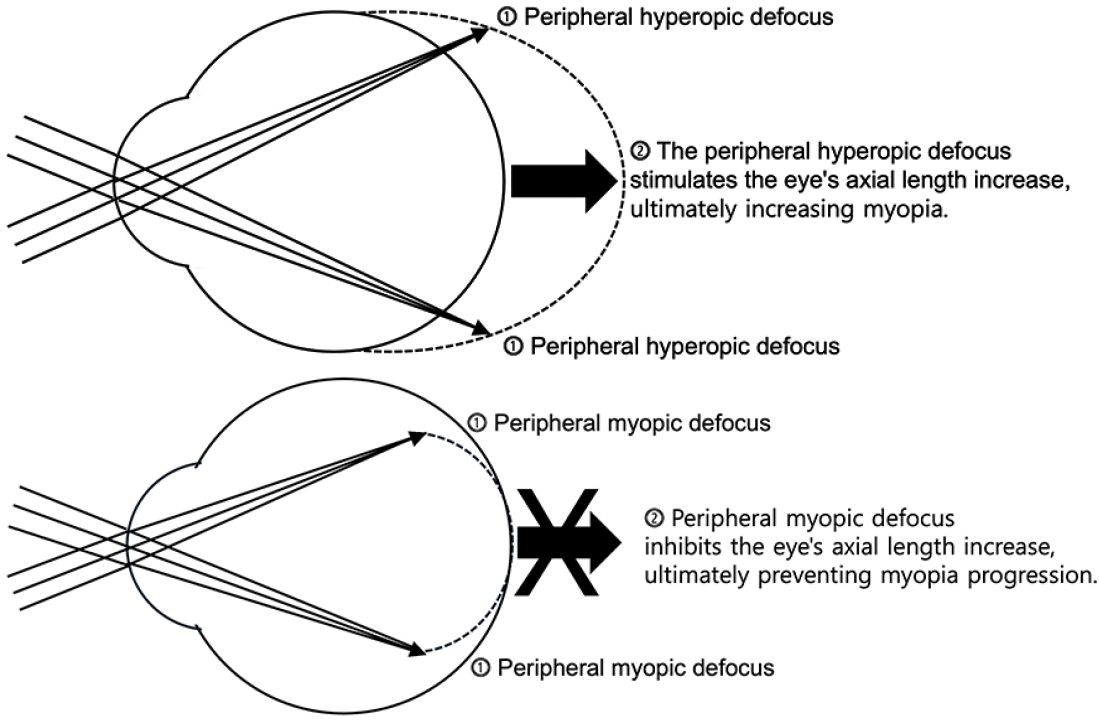
Myopia is a major ophthalmological disorder with increasing prevalence worldwide, particularly in East Asia. Evidence indicates that its development involves complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Body stature, sleep patterns, and nutritional status significantly influence the progression of myopia during childhood and adolescence. Its treatment and prevention strategies include optical correction, atropine therapy, increased outdoor activity, decreased near work, and regular retinal monitoring.
- Perspective
- Gastroenterology
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in children: a practical update based on Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ISPGHAN) 2024 guidelines (244 times)
- Ankit Agrawal, Arghya Samanta
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):546-550. Published online May 12, 2025
-

- Review Article
- Other
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: current applications, potential, and implementation considerations (223 times)
- Taejin Park, In-Hee Lee, Seung Wook Lee, Sek Won Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):641-651. Published online June 25, 2025
-

Artificial intelligence (AI) offers potential benefits in pediatric care, but its real-world adoption requires clinician literacy, ethical and legal safeguards, and cautious implementation. Large language models are emerging across healthcare, but their use in pediatric clinical practice remains premature. Thus, the cautious and accountable implementation of AI is crucial to preventing unintended harm and realizing its potential.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Liposomal SunActive versus conventional iron for treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in children aged 2–12 years: a prospective randomized controlled trial (219 times)
- Wael A. Bahbah, Yasmin A.H.S. Younis, Hanan Salama Elbelouny, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):608-615. Published online July 18, 2025
-
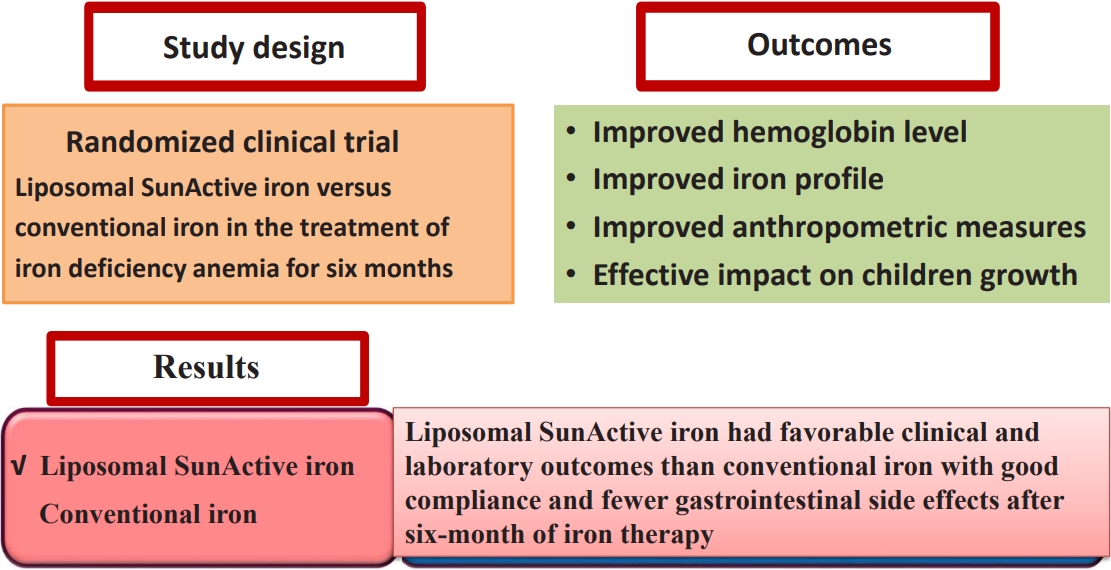
Background: Liposomal iron, a novel oral formulation of ferric pyrophosphate that demonstrates improved gastrointestinal absorption and bioavailability with fewer side effects than conventional iron, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia (IDA).
Purpose: To conduct an in-depth comparative study of liposomal SunActive and conventional iron supplements (iron polymaltose complex) for treating IDA in children aged 2–12 years Methods: This...
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial (192 times)
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-
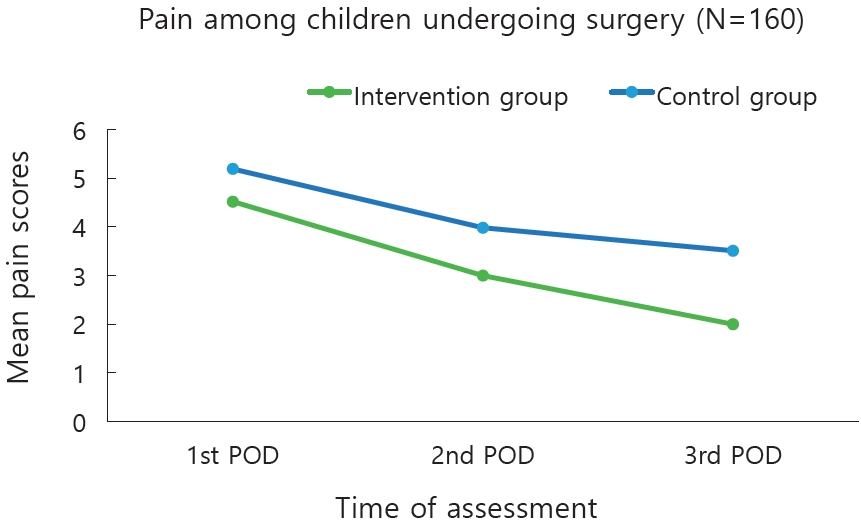
Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Global burden of asthma among children and adolescents with projections to 2050: a comprehensive review and forecasted modeling study (182 times)
- Tae Hyeon Kim, Hyunjee Kim, Jiyeon Oh, Soeun Kim, Michael Miligkos, Dong Keon Yon, Nikolaos G Papadopoulos
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):329-343. Published online April 22, 2025
-

Pediatric asthma can persist to adulthood and must be effectively managed. This review examined the prevalence of asthma among individuals younger than 20 years and revealed a decline from 1990 to 2021, higher rates in males, and a peak in children aged 5–9 years. Despite a projected continued decrease in prevalence by 2050, asthma will remain a significant health concern for children and adolescents.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Demographic transition in South Korea: implications of falling birth rates (180 times)
- Chae Young Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):498-509. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· Since 1960, South Korea's TFR decreased from 6.33 to 0.78 in 2022, below the 2.1 replacement level since 1983, with women's average age at first marriage rising to 31.3 in 2022.
· Policies needed: financial incentives, longer parental leave, better childcare.
· The U.S. (15.3% immigrants) and Germany (18.8%) use immigration to maintain demographic stability, a strategy South Korea is considering.
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of a long-acting monoclonal antibody to prevent respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants and young children (180 times)
- Soo-Han Choi, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Ki Wook Yun, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):742-750. Published online September 3, 2025
-
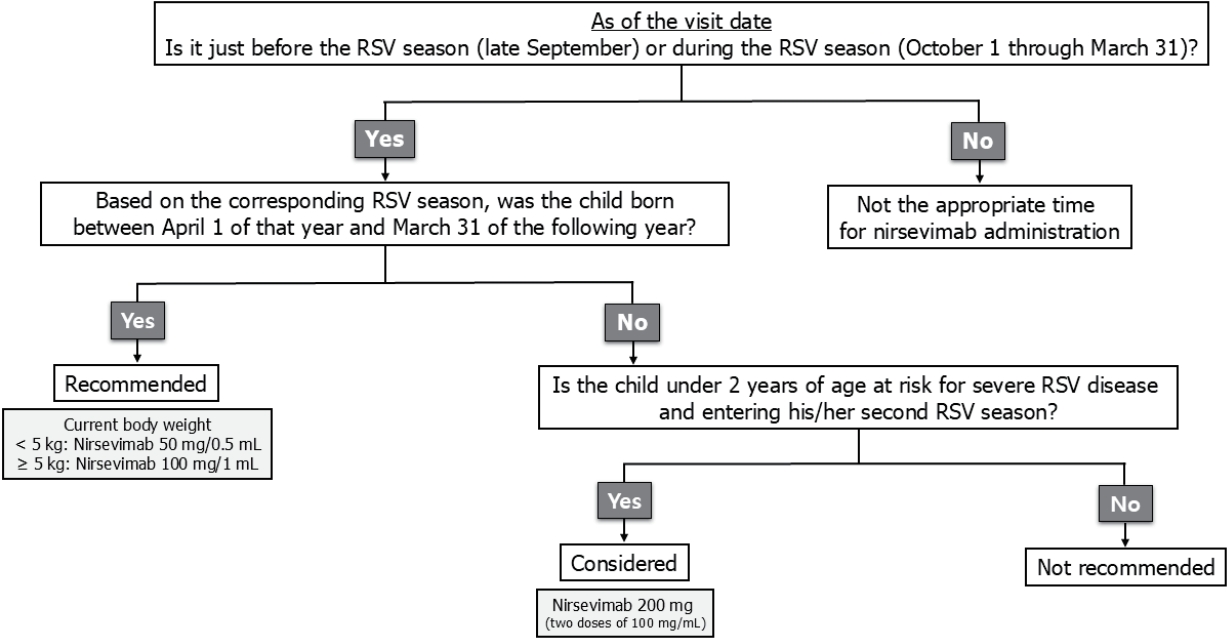
To prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-associated lower respiratory tract infections, a single dose of nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, is recommended for all neonates born during the RSV season (October to March) and all infants younger than 6 months old at the start of the RSV season. Nirsevimab should be administered shortly after birth to neonates and just before or early in the season to infants entering their first RSV season.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: bridging potential, clinical practice, and ethical considerations (179 times)
- Yoon Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):652-655. Published online August 28, 2025
-

· Artificial intelligence (AI) holds transformative potential for pediatric healthcare, with applications spanning prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up across diverse subspecialties; however, ethical concerns, scarcity of pediatric- specific data, and limited funding remain significant challenges.
· International consensus on pediatric AI guidelines, expanding child-specific datasets, and incorporating explainable AI are essential to ensure safety and trust.
· Multicenter collaboration and increased investment can address these gaps, enabling equitable, reliable, and pediatric- centered AI solutions.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Clinical practice guidelines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: recent updates (178 times)
- Tae Hoon Eom, Young-Hoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):26-34. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Primary pediatricians should play a key role in the diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
· The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition, has lowered the diagnostic threshold for older teens and adults and a comorbid diagnosis with autism is now allowed.
· The American Academy of Pediatrics had added recommendation-related comorbid conditions in its guideline and the Society of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics recently developed a complex ADHD guideline.
· The European ADHD Guideline Group recently developed a guideline for managing ADHD during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis (169 times)
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
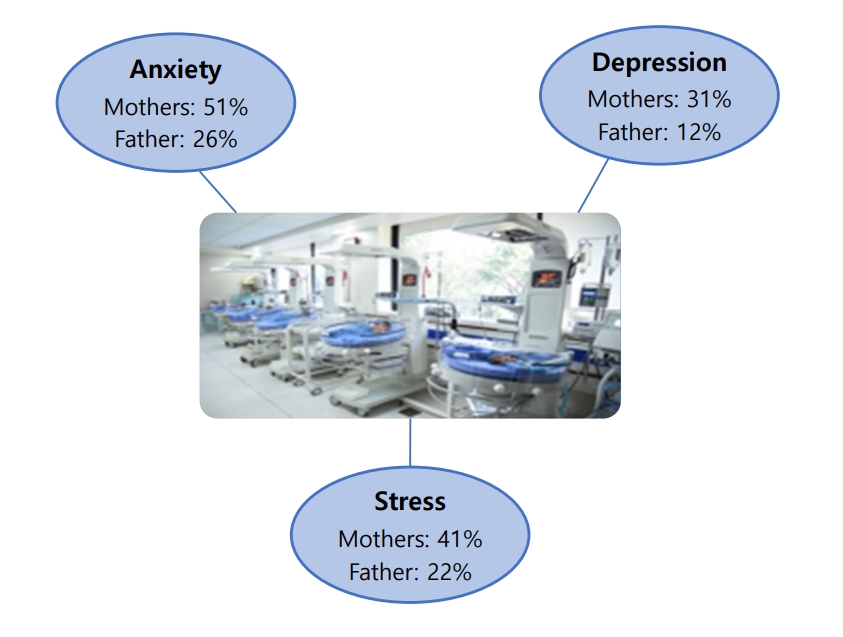
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: from diagnosis to management (169 times)
- Eujin Park, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):17-25. Published online June 14, 2023
-
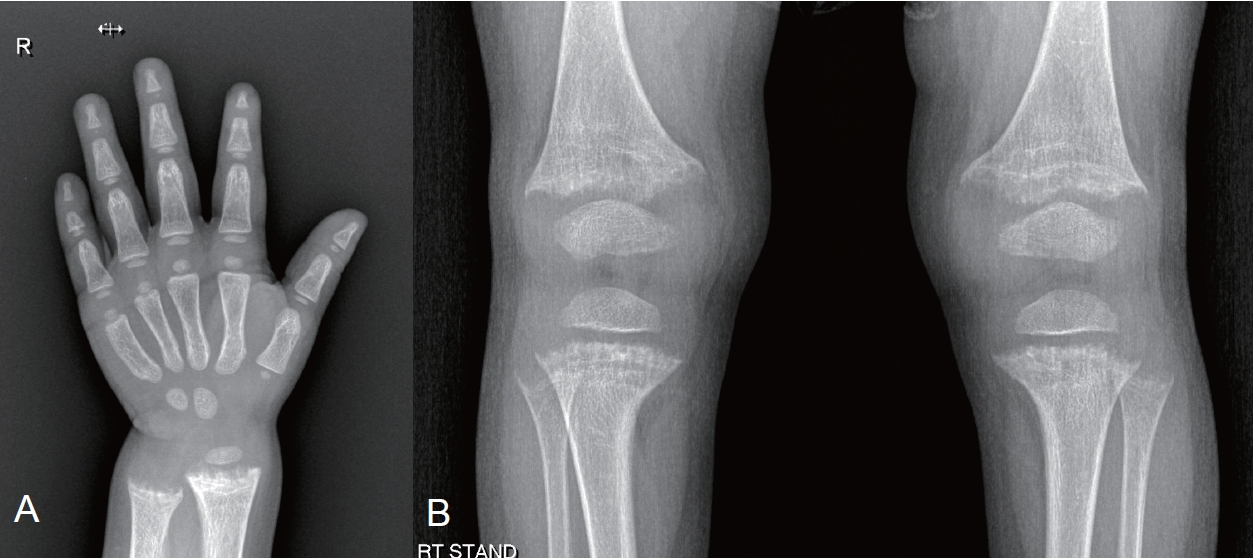
· X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), the most common cause of hypophosphatemic rickets, affects 1/20,000 people.
· XLH is caused by a loss-of-function mutation of the PHEX gene.
· Its main pathogenesis is elevated fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) level.
· Burosumab, an FGF23 inhibitor, was developed in the early 2000s.
· Burosumab was approved in Korea in 2020 for XLH patients aged 1+ years with radiographic evidence of bone disease.
- Other
- Acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children: no valid rationale for controversy (167 times)
- Lisa Zhao, John P. Jones, Lauren G. Anderson, Zacharoula Konsoula, Cynthia D. Nevison, Kathryn J. Reissner, William Parker
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):126-139. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Despite worldwide acceptance of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in pediatric medicine, careful examination reveals no valid objections to the conclusion that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children. Nevertheless, debate that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury has centered around the prenatal period, evidence of which is relatively limited compared to that in the postnatal period, which is the time of greatest absolute and relative risk.
- Cardiology
- Heart failure in children and adolescents: an update on diagnostic approaches and management (166 times)
- Amit Agrawal, Dalwinder Janjua, Abdulrahman Ahmed Alsayed Ali Zeyada, Ahmed Taher Elsheikh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):178-190. Published online June 19, 2023
-
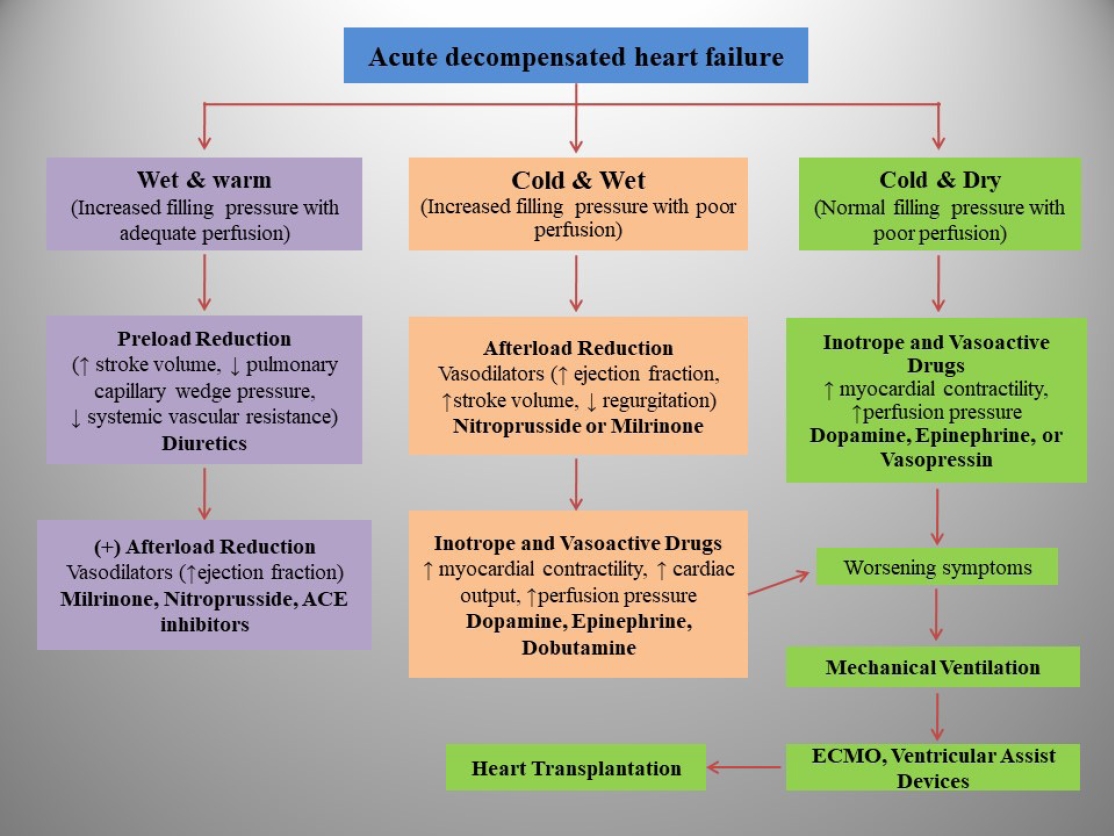
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Effect of vitamin C supplement in treatment of childhood pneumonia requiring hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial (158 times)
- Chutima Phuaksaman, Katechan Jampachaisri, Klaita Srisingh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):690-699. Published online April 1, 2025
-

This study assessed the effects of vitamin C on children with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Vitamin C supplementation improved clinical symptoms within 48–72 hours compared to placebo but did not reduce the length of hospital stay (LOS). These findings suggest that vitamin C is beneficial for managing CAP severity, but does not affect LOS.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Malaysia: a systematic review and meta-analysis (155 times)
- Ker Yang Chua, Ker Yung Chua, Karuthan Chinna, Chooi Ling Lim, Maheeka Seneviwickrama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):115-126. Published online November 13, 2024
-
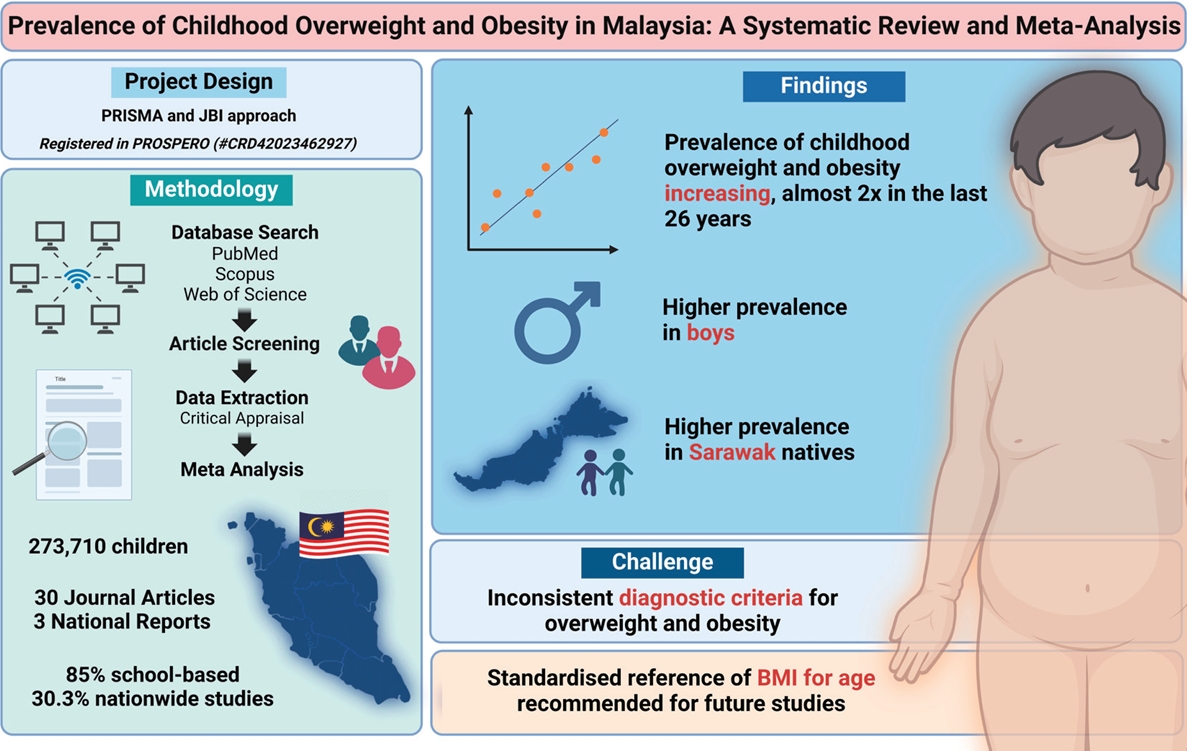
The incidence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide. National surveys in Malaysia have shown similar trends. This review aimed to increase our understanding of the prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight, obesity, and excess weight in Malaysia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted of studies reporting the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Malaysian children aged <18 years....
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial (151 times)
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Pulmonology
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis (148 times)
- Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age.
- Critical Care Medicine
- High-dose methylprednisolone and tocilizumab improve survival of patients with high-risk pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy (147 times)
- Chaonan Fan, Fei Li, Kechun Li, Zheng Li, Yiyang Mao, Lijuan Wang, Gang Liu, Yingchao Liu, Quan Wang, Suyun Qian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):56-64. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Which immunomodulatory strategies can reduce mortality in children with acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE)?
Finding: High-dose methylprednisolone (30 mg/kg/day) significantly improved the survival of high-risk patients, particularly when combined with tocilizumab.
Meaning: These findings support the use of a severity-based immunotherapy approach to optimize the outcomes of pediatric ANE.
- Review Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases (141 times)
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):315-327. Published online June 28, 2023
-
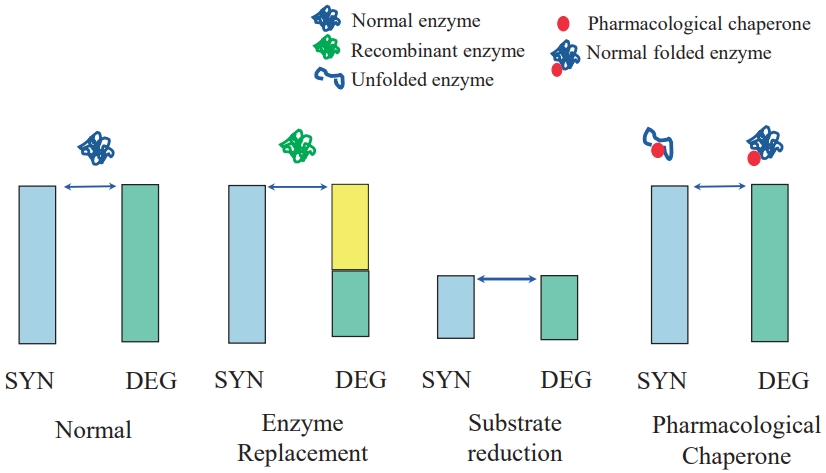
· Orphan disease is a rare disease, primarily affecting newborn and children. Vast majority of orphan diseases has genetic background.
· Orphan disease is individually rare. But as a whole, it is not rare, becoming a great socioeconomic burden.
· The diagnosis of rare genetic disease has been problematic, but recent progress of genome analysis technologies makes it faster and more precise.
· There are many unmet needs as to the curative treatment. However, the number of treatable rare diseases is growingly increasing owing to the development of biotechnology.
· Most orphan drugs are extremely expensive because of numer ous hurdles during the process of drug development as well as small number of patients.
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- C3 glomerulopathy in children: experience at a resource-limited center (130 times)
- Soumya Reddy, Abhishek Ghante, Mahesha Vankalakunti, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):311-318. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Question: What are the clinicopathological features and outcomes of pediatric C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) in resource-limited settings?
Finding: Children with C3G in resource-limited settings have significant morbidities, and most experience kidney sequelae despite treatment. Electron microscopy was performed in only 50% of our patients, while none received complement assays or genetic testing.
Meaning: Pediatric C3G presentation, management, and kidney outcomes vary. Its thorough evaluation and management are challenging in resource-limited settings.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Respiratory severity score-guided postnatal systemic corticosteroid therapy for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely preterm infants (126 times)
- Gyeong Eun Yeom, Ju Sun Heo, Baek Sup Shin, Seh Hyun Kim, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):656-665. Published online July 8, 2025
-

Question: Does a respiratory severity score (RSS)-guided postnatal corticosteroid protocol improve respiratory outcomes of extremely preterm (EP) infants without worsening neurodevelopmental outcomes?
Finding: The protocol enabled targeted and early steroid use, thereby reducing severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia without affecting mortality or causing neurodevelopmental impairments.
Meaning: The RSS-guided protocol may offer a more precise and individualized postnatal corticosteroid therapy for EP infants.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Bridging the gap: autism spectrum disorder in children in the United States and worldwide: a narrative review (120 times)
- Sandhya J. Kadam, Malika Goel
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):852-857. Published online October 2, 2025
-

The prevalence of autism is increasing worldwide. The United States has the highest numbers, likely due to the availability of better treatment options. However, global disparities exist, especially in low-resource settings in which stigma, underdiagnosis, and limited services hinder care. A coordinated international approach emphasizing early screening, inclusive policies, and culturally sensitive support systems can bridge this gap and improve the outcomes for children with autism and their families worldwide.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Updates in neonatal resuscitation: routine use of laryngeal masks as an alternative to face masks (117 times)
- Eun Song Song, Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):240-246. Published online July 11, 2023
-

In neonatal resuscitation:
· Laryngeal masks are recommended when endotracheal intubation or positive-pressure ventilation fails.
· Laryngeal masks are useful even during chest compressions.
· Laryngeal masks aid neonates >34 weeks’ gestation and/or with a birth weight >2 kg.
· Main usage barriers include limited experience (81%), preference for endotracheal tubes (57%), and lack of awareness (56%).
· Second-generation laryngeal masks have a built-in esophageal drainage tube that prevents regurgitation into the glottis, and an orogastric tube can be inserted within the esophageal drainage tube to protect against gastric inflation.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











