Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 66(3); 2023 |
|
Abstract
Syncope is a heterogeneous syndrome with complex underlying mechanisms, hence, the spectrum of patients presenting with syncope is broad. The diagnosis of syncope begins with history taking, and an accurate diagnosis can be established through correct history taking and interpretation. Building and interpreting patient history are the main factors that cause a diagnostic yield gap between experts and nonexperts. The most frequent source of error is a clinician’s misconception rather than an inaccurate account of patient symptoms. Clinicians can have several diagnostic pitfalls while evaluating patient history, which can be avoided by in-depth understanding of the link between syncope pathophysiology and clinical clues. Furthermore, clinicians need to understand the clinical features of diseases that require differentiation from syncope, such as seizures. The use of confusing terms is one of the barriers that prevents accurate diagnosis and communication between doctors and patients. In this review, we address the terms of syncope and its essential history-taking components in connection with the mechanism of syncope.
Graphical abstract. Pearls and pitfalls in history taking of pediatrc syncope.
Syncope is categorized as a nontraumatic transient loss of consciousness (TLOC), which includes seizures (epileptic or non-epileptic) and a miscellaneous group of rare causes (Fig. 1) [1]. It is a heterogeneous syndrome that is classified into three subgroups (reflex, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension [OH] syncope) according to the underlying pathophysiology and risk [1]. Distinguishing between syncopal and nonsyncopal TLOC (particularly seizures) and elucidating their pathophysiology is crucial for managing syncope.
History taking is crucial to an accurate diagnosis and should begin by answering the question “Is it a syncopal episode or not?” [1] If a TLOC with rapid onset and short duration occurs and the patient recovers completely without sequelae that are accompanied by loss of postural tone, the episode is likely syncope [2]. However, a detailed history-taking is necessary to diagnose syncope and determine its possible etiology. The initial evaluation of suspected syncope consists of a careful history taking, physical examination, and electrocardiography (ECG) [2]. A diagnosis using initial examination differs between expert (~85%) and nonexpert (60%–70%) physicians owing to history taking as a main factor [3-5]. Agreement between clinicians regarding the interpretation of the written history of patients with TLOC is surprisingly low [6]. The misconceptions held by clinicians might be the most frequent source of error rather than symptom reporting inaccuracy by patients or their caregivers [6]. On the other hand, a study that analyzed the diagnostic value of a comprehensive questionnaire revealed that systematic interpretation of patient-reported symptoms alone could be used to classify seizures and syncope at 91% accuracy [7]. Confused terms related to syncope and different criteria also significantly affect the diagnosis [8]. Hence, to properly diagnose syncope, it is essential to understand it in detail by linking its symptoms with circuitry physiology and considering the clinical presentation of other causes of TLOC while using accurate terminology.
This review addresses TLOC classification and terminologies specifically associated with syncope. The present authors discuss the essential questions that clinical history must answer and list the pitfalls and pearls of the awareness of history-taking.
Reflex syncope is defined as syncope due to a reflex that causes vasodilatation and/or bradycardia [9]. A normal reflex for hypotension increases peripheral resistance and cardiac output by mediating an increase in sympathetic tone and the withdrawal of parasympathetic outflow. However, an inappropriate reflex may be triggered under certain conditions, including an increase in the parasympathetic tone and the inhibition of sympathetic outflow. This results in sudden hypotension and bradycardia, ultimately reducing cerebral perfusion [10]. Consequently, reflex syncope occurs when a reflex temporarily responds inappropriately. Stimulation of the medullary vasodepressor region of the brain stem might be related to the mechanisms of bradycardia and/or vasodilatation in reflex syncope [11]. This brain region can be stimulated by various receptors, including cardiac C fibers, cardiopulmonary baroreceptors, cranial nerves, cerebral cortex, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary mechanoreceptors [11]. Therefore, they can occur in various situations in which such receptors are stimulated. Neurally mediated syncope is synonymous with reflex syncope because the reflex arc is composed of afferent, central, and efferent pathways of the autonomic nervous system. The function of each reflex arc component is typically normal during reflex syncope. The term “neurocardiogenic syncope” is also frequently used to describe reflex syncope; however, its use is currently discouraged because the origin of this reflex rarely occurs in the heart [12].
Reflex syncope can be further classified into vasovagal syncope (VVS), situational syncope, and carotid sinus syndrome [9]. VVS is the most common form of reflex syncope; therefore, these 2 terms are often used interchangeably. Reflex syncope mediated by the vasovagal reflex is called VVS [9]. Various definitions or diagnostic criteria exist for VVS, preventing the diagnosis. The 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society Guideline defines “a syncope syndrome as: (1) that which may occur in an upright posture (standing or seated) or due to exposure to emotional stress, pain, or medical settings; (2) typically characterized by diaphoresis, warmth, nausea, and pallor; (3) being associated with vasodepressor hypotension and inappropriate bradycardia; and (4) being often followed by fatigue.” [9] Identifiable triggers and a characteristic prodrome are important for the diagnosis, often preceding VVS [9]. Orthostatic stress, as well as emotions (fear, pain, instrumentation, or blood phobia), often unidentifiable or underestimated, can trigger VVS and are usually combined with central hypovolemia (from upright posture or dehydration) in vasovagal syncopal episodes [13]. Situational syncope is defined as syncope that occurs only in specific and usually memorable circumstances, including coughing, laughing, swallowing, micturition, defecation, singing, and weightlifting [9].
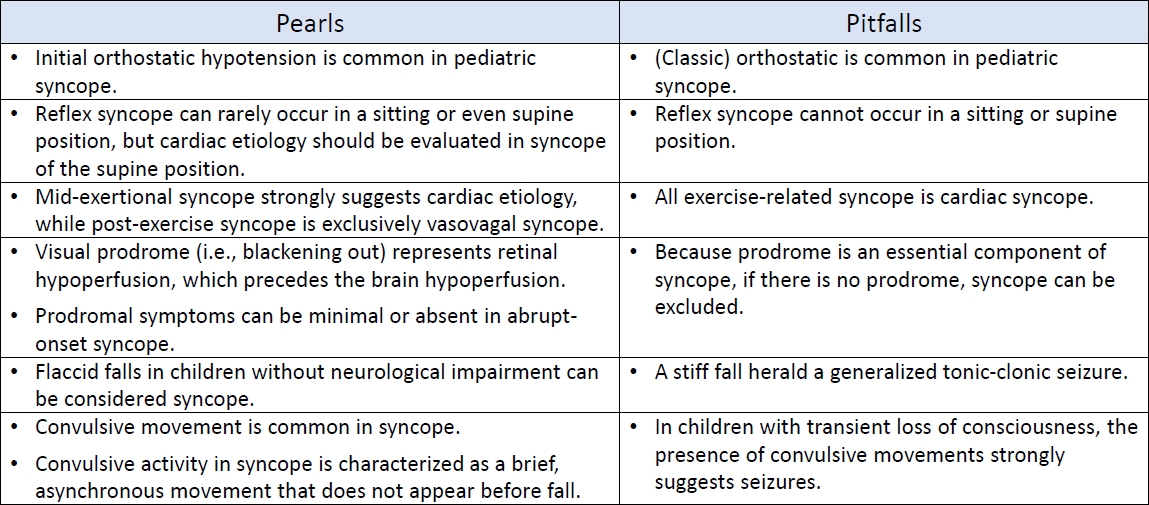
OH has long been called the “rule of thumb” without a clear consensus [14]. Pediatricians and adolescents are familiar with transient hypotension with symptoms of lightheadedness within a few seconds of standing up quickly [14]. It is often referred to as OH but differs distinctly from classical OH. Transient hypotension upon rising is categorized as a variant of initial OH, which is defined as a decrease in transient blood pressure [BP] (>40 mmHg systolic BP and >20 mmHg diastolic BP) within 15 seconds of standing up [12]. Initial OH is not a disorder but rather a temporal mismatch of the physiological response to a rapid postural change [15]. Initial OH may be a common unrecognized cause of syncope in children and adolescents [12]. Autonomic nervous system dysfunction is a leading cause of classical OH. Classical OH is rare in pediatric patients and accounts for approximately 1% of total TLOC cases [16]. It is defined as a fall of >20 mmHg in systolic BP or >10 mmHg in diastolic BP within 3 minutes of assuming an upright position [12]. Another variant, delayed OH, is defined as symptomatic hypotension beyond 3 minutes of arising [12]. Delayed OH may be a mild or early form of autonomic dysfunction [12]. This demonstrates that the underlying mechanisms differ according to hypotension timing and duration associated with an upright position. Furthermore, it is necessary to use a clear term to describe the condition depending on the onset of hypotension upon standing. Initial OH should be considered if syncope or presyncope is observed in teens and adolescents within a few seconds of standing up [15].
Cardiac syncope is fatal but rare in children. TLOC accounts for 4% of pediatric TLOC cases [16]. If TLOC is diagnosed as syncope, the next step should be to determine whether it is cardiac. Syncope caused by bradycardia, tachycardia, hypotension due to a low cardiac index, blood flow obstruction, vasodilatation, or acute vascular dissection is defined as cardiac syncope [9].
Owing to the gravitational effects on blood, reflex syncope, particularly VVS, occurs most often in the standing position. Cardiac syncope is primarily caused by arrhythmia and structural cardiac disease, with arrhythmia being the most common cause in children [16]. Arrhythmia generally occurs regardless of posture [17]. Furthermore, syncope can occur irrespective of posture if the circulation stops [17]. Therefore, syncope in the supine position is a strong warning sign of cardiac syncope, while increased orthostatic stress is predictive of reflex syncope, namely VVS [18].
However, orthostatic stress increases while standing up and sitting down. Sitting intolerance occurred in approximately 10% of children with sitting-induced hemodynamic changes [19]. A study of 111 adult patients with syncope, excluding those of cardiac origin, reported that syncope developed in standing (n=67), sitting (n=16), standing and sitting (n=23), sitting and supine (n=1), and all three positions (n=4) [20]. That is, 40% and 4.5% of patients reported syncope in the sitting and supine positions, respectively [20]. Prodromal symptoms and circumstances were similar irrespective of position; however, emotional triggers were commonly observed in patients with syncope in the sitting and supine positions [20]. This study showed that reflex syncope, although rare, may occur in sitting and supine positions. If syncope is suspected in body positions other than standing, a specific situation and activity (swallowing, coughing, or urination) or emotional trigger (pain or fear) should be carefully investigated. However, this study emphasized that no patients had syncope in the supine position alone [20]. Furthermore, no VVS occurred in the supine position in 268 syncopal children [21]. Reflex syncope is possible in the supine position; however, cardiac syncope should be considered initially.
Activity immediately before an attack is important to the differential diagnosis of syncope. However, the association between exercise and syncope remains unclear. In most cases, exerciserelated syncope is not an indicator of underlying severe cardiac disease [22]. However, midexertional syncope (i.e., before the child can stop exercising) suggests a cardiac etiology [22]. An epidemiological study of 7,568 young athletes a mean age of 16 years of age showed that exercise-related syncope occurs infrequently [22]. Among athletes diagnosed with syncope (n=474), postexertional syncope was observed in 57 athletes (12%), while exertional syncope was present in only 6 (1.3%) [22]. All episodes of postexertional syncope had the typical features of VVS, whereas 2 midexertional syncope episodes had cardiac etiologies [22]. A study of 60 midexertional syncopes in children demonstrated that 32 (53%) had a cardiac origin [23]. Neither exertional activity type nor all symptoms occurring during syncopal events (before, immediately preceding, and after the syncopal event) could be differentiated based on the presence or absence of a cardiac diagnosis [23]. These studies suggest that midexertional syncope is a rare but crucial historical aspect of cardiac syncope, even at a young age.
Postexercise syncopal events typically occur when an individual suddenly stops exercising and stands motionless for the first 5–10 minutes after exercise [24]. Postexercise syncope shares the same mechanism as VVS. Venous return is dramatically decreased due to reduced muscle pumping of the lower extremities, while cardiac contractility remains high, and blood vessel dilation occurs during syncope [24]. That is, the Bezold-Jarisch reflex may involve postexercise syncope.
On the other hand, electrical myopathy and mechanical outflow obstruction are the primary underlying etiologies of cardiac syncope in children [23]. In both cases, a decrease in cardiac output was responsible for the syncope. A brief review of the physiology of syncope during exercise in patients diagnosed with long QT syndrome (LQTS) is warranted, as it is the most common cause of cardiac syncope in children [23]. Decreased function of the delayed rectifier potassium current, either rapid (IKr) or slow (IKs), normally controls cardiac repolarization and causes LQTS [25]. Adrenergic stimulation causes quantitatively similar enhancement of both L type calcium current, an inward current tending to a prolonged cardiac action potential, and IKs, shortening the action potential [25]. The balance between them allows for cardiac contractility enhancement during exercise without excessive action potential prolongation [25]. When IKs is dysfunctional, as in LQTS 1, sustained increases in adrenergic tone develop intense action potential prolongation and subsequently predispose patients to lethal ventricular arrhythmia [25].
Prodromal symptoms are caused by 2 main mechanisms. The first is symptoms related to “autonomic activation” of sympathetic and parasympathetic activity, while the second consists of the consequences of retinal and cerebral hypoperfusion [26]. Symptoms of autonomic activation include sweating, facial pallor, nausea, pupillary dilatation, and palpitations [26]. The symptoms of hypoperfusion include lightheadedness, unclear thinking, blurred or darkened vision, and tinnitus [26]. A prodromal sensation of vision is caused by retinal hypoperfusion [27]. Unlike the brain and brainstem, the eye is not protected by the pressure-equalizing effects of cerebrospinal fluid [27]. Because retinal hypoperfusion precedes brain hypoperfusion, visual prodromes (i.e., blackening out) can occur before a TLOC [27].
Prodrome is an essential symptom of syncope, providing a clue in differentiating it from other TLOC, particularly seizures [28]. However, clinicians must recognize that prodromal symptoms can be reported only when the fall in BP is detectable and the patient’s sensations are listed for later recall [26]. Therefore, prodromal symptoms and signs are minimal or absent in abruptonset syncope caused by provoked (i.e., fainting lark) or cardiac standstill [26]. Consequently, sudden onset and lack of prodromal symptoms provide clinical clues for cardiac causes, typically like a stroke-Adams attack (i.e., complete atrioventricular block) [26]. Meanwhile, the clinical features of syncope in ventricular tachycardia differ from those in a typical stroke-Adams attack, possibly depending on differences in the BP fall rate. Loss of consciousness (LOC) usually occurs later after the onset of ventricular tachyarrhythmias (20–120 seconds)29) than after asystole (4–15 seconds) [30].
Prodrome is more commonly reported in children with VVS than in those with cardiac syncope [31]. Zhang et al. [31] reported that 48 of 55 children (87.3%) with VVS had overall prodromal symptoms versus 16 of 31 (51.6%) with cardiac syncope. These symptoms include dizziness, headaches, chest discomfort, palpitations, sweating, paleness, nausea/vomiting, blurred vision, and fatigue [31]. Among these, dizziness, headache, and chest discomfort were significantly more common in the VVS group. Meanwhile, other symptoms, including palpitations and blurred vision, did not differ between groups [31]. On multivariate analysis, a history of abnormal electrocardiogram findings and midexertional syncope remained independent predictors of cardiac syncope but not the presence of prodromal symptoms [31]. Hurst et al. [32] analyzed 3,445 pediatric patients who visited the emergency department with syncope and reported that only 3 had a previously undiagnosed cardiac cause. They determined the sensitivity and specificity of historical features to identify cardiac syncope [32]. Among the three children with cardiac syncope, 1 did not have prodromal symptoms [32]. Thus, the sensitivity and specificity of syncope without prodrome in identifying cardiac syncope were 67% and 70%, respectively [31]. Unlike Zhang et al. [31], Hurst et al. [32] analyzed palpitations as an independent clinical feature rather than a prodrome. They reported that the sensitivity and specificity of palpitations were 100% and 98%, respectively [32]. These inconsistent results suggest that the presence or absence of prodromal symptoms alone should not be used to discriminate between cardiac and noncardiac syncope. Importantly, approximately 50% of children diagnosed with cardiac syncope also report prodromal symptoms [31].
Symptoms of VVS have the following temporal sequence: the first symptoms are feeling uncomfortable, epigastric discomfort, nausea, and abdominal cramps [26]. If patients ignore these warning signs, signs and symptoms of cerebral and retinal dysfunction develop [26]. The first sign of impending vasovagal fainting is often facial pallor, which results from reduced skin blood flow due to sympathetic and vasopressin-induced vasoconstriction [26]. During this phase, palpitations are a common complaint due to an adrenergic surge preceding the vagal response. Symptoms of palpitations often present as cardiac syncope and VVS [32]. Meanwhile, Hurst et al. [32] reported that the presence of at least 2 of the following features yielded 100% sensitivity and specificity for cardiac syncope in children: absence of prodromal symptoms, a midexertional event, and chest pain or palpitations.
Interviewing individuals with witnessed syncope may be helpful. Details including fall type, LOC duration, movements during attack, and tongue biting should be asked whenever possible.
Fall type provides valuable information for the differential diagnosis of epilepsy and syncope [33]. As a rule, during an epileptic attack, a fall to the ground is tonic, whereas during syncope, it is generally flaccid [34]. Flaccidity during LOC contradicts seizures. The only exception is “atonic seizure,” [34] which occur rarely, primarily in children diagnosed with epileptic encephalopathy [35]. Therefore, if a child without neurological impairment collapses with flaccidity (kneeling over), it is reasonable to diagnose syncope rather than seizures. However, due to this common knowledge, syncope is mistaken for seizure. Stiff falls during syncope have been commonly described in laboratory-observed syncope [36]. Lempert et al. [36] reported that only half of healthy volunteers collapsed flaccidly during fainting, while the others fell with their knees and hips extended. Clinicians must understand that a stiff fall does not necessarily herald a generalized tonic-clonic seizure [37]. A stiff fall is part of the continuum of tonic posturing and shares the same mechanism as tonic posturing, which is described in the next section.
Convulsive movements, including tonic or myoclonic muscle activity, eye deviations, automatisms, and vocalizations, often accompany syncope. The reported frequencies of convulsive movements in syncope vary widely (5%–90%) depending on study design [36,38]. A video study of adolescents documented myoclonus in 91%, facial grimacing in 78%, vocalization in 65%, and head deviation in 34% of the patients during tilting [39]. Owing to these convulsive features, syncope is misdiagnosed as epilepsy. Approximately 20% of patients referred to epilepsy clinics suffer from recurrent syncope [40]. Furthermore, 35% of patients diagnosed with reflex syncope are treated with antiepileptic drugs [41]. In recent studies of children who were referred to new-onset seizure clinics, nonepileptic events were reported in 24%–45% of cases [42,43], and syncope was the most or second most common cause. Convulsions are an integral component of the cerebral response to hypoxia. Therefore, the presence of convulsive movements depends on brain hypoperfusion degree [44]. Specific features should be based on distinguishing convulsive syncope from seizures, not by the mere presence or absence of motor phenomena [44].
The most common movement in syncope is myoclonic activity [36]. Syncopal myoclonus is often multifocal with asynchronous muscle jerks and occasionally generalized with bilateral synchronous muscle activation [36]. However, unlike epileptic myoclonus, syncopal myoclonus has arrhythmic features and is sustained for several seconds [36,45]. A study that analyzed video electroencephalography (EEG) records of 65 cases of syncope and 50 cases of convulsive seizures reported myoclonic jerks in 33 (51%) and 50 cases (100%), respectively [45]. This study clearly showed different intergroup features of myoclonic jerks: the synchrony rate and jerk frequency were lower in the syncope versus seizure group [45]. More than 20 jerks were noted in all convulsive group patients [45]. Meanwhile, all but one patient in the syncope group exhibited fewer than 10 jerks [45]. These findings suggest that fewer than 10 jerks indicates syncope and more than 20 jerks indicates convulsive seizures [45].
Lateral head turns with an ipsilateral gaze have been reported; however, they never reached the forced tonic quality of epileptic head turns [36]. Syncope may also produce complex motor activity resembling epileptic automatisms, including lip-smacking, chewing, fumbling, reaching the head, turning or raising the head, and sitting up [36,39,46]. In contrast to epileptic automatisms, these movements are primarily brief and solitary rather than repetitive [44]. This convulsive activity in syncope occurs after rather than before the loss of postural tone, which may provide an essential clue for differentiating syncope from seizures [36]. As a rule, eyes are open during syncope, a feature shared by seizures but not psychogenic TLOC [47]. The most consistent ocular sign is upward turning of the eyes early in syncope, after which lateral deviation may follow [47]. In contrast to sustained or forceful epileptic eye deviation, syncopal eye turns are typically brief [45].
Studies measuring EEG changes during syncope have demonstrated the nature of convulsive movements in syncope. Slow background activity appears first [48], followed by high-amplitude delta activity associated with LOC, eye-opening, myoclonic jerks, and general stiffening [49,50]. If hypoperfusion persists, EEG flattening is accompanied by tonic posturing, vocalization, slow horizontal eye movement, and stertorous breathing [50]. Tonic posturing is “probably universal” when syncope lasts long enough to produce a flat EEG [46]. A breath-holding spell is a good example, often accompanied by intense opisthotonic stiffening caused by profound but brief cerebral hypoxia [46,51]. The “slow-flat-slow” pattern sequence is independent of syncopal mechanisms. However, mild forms of syncope may present as isolated background slowing without EEG flattening. Myoclonic jerks predominantly occur during the slow EEG phase, whereas tonic posturing occurs during the flat phase [45]. These EEG correlates suggest that jerks in syncope are likely of cortical origin, whereas tonic posturing results from brainstem disinhibition due to complete jerks [45]. Therefore, the degree of cerebral hypoperfusion during syncope determines whether convulsive activity will occur [37].
Prospective clinical observations and laboratory-induced syncope studies reported that LOC usually lasts for approximately <30 seconds [36,52]. Although eyewitnesses often report long periods of unconsciousness, the reliability of such estimates of syncope duration is debatable [26]. Body position may play a role in the duration of LOC in syncope. If a person collapses and falls to the floor during syncope, the LOC period is brief because cerebral perfusion causes immediate recovery. By contrast, cerebral perfusion may remain inadequate for longer durations in those who remain upright or slump during syncope [26].
A meta-analysis showed that tongue biting has excellent value in the differential diagnosis of syncope and seizures [53]. Tongue biting increases the probability of epileptic seizures [53]. In a prospective study of an epilepsy monitoring unit, 8 of 34 patients with epileptic seizures displayed tongue biting on the lateral side [54]. Moreover, only 1 of the 45 patients with syncope had tongue lacerations at the tip [54]. This study suggested an extremely high (99%) specificity for tongue biting in general and 100% specificity when the injury was due to seizures versus syncope [54].
Urinary incontinence may occur during both syncope and epileptic seizures, and meta-analysis demonstrated that urinary incontinence has no value in the differential diagnosis between them [55]. Incontinence rate variations have been reported to be up to 25% of syncopal events [52]. Urinary incontinence was twice as common in patients with syncope versus seizures [56]; thus, it is more likely associated with syncope than seizures [57]. However, these findings were derived from adult studies. A pediatric study revealed that urinary incontinence occurred in approximately 56% of cardiac syncope cases versus 2.6% of noncardiac syncope cases [58]. The urinary sphincter releases tone upon asystole lasting longer than 20 seconds [30]. Unlike adults, cardiac syncope is rare in children. Therefore, further studies are needed to estimate the value of incontinence in pediatric age groups to differentiate syncope from seizures.
Reorientation is usually immediate in syncope and does not exceed 30 seconds even after an extended attack [29]. Any postictal disorientation lasting longer than 30 seconds suggests an epileptic seizure [28,37]. The interval from the LOC start back to the oriented state is only approximately 20–30 seconds in abruptonset laboratory-induced syncope [36,46]. Immediate complete reorientation is also observed in cardiac syncope if the cardiac standstill is brief [30]. Additional importance in the clinical picture of VVS is the postsyncopal symptoms characterized by persistent pallor, nausea, weakness, and sweating. Overactive autonomic nerve function takes time to return to baseline after a severe VVS attack. Thus, the syncope recurs if an individual reassumes an upright posture too soon [59]. Table 2 summarizes the pearls and pitfalls in history taking for the differential diagnosis of syncope.
As discussed earlier, no definitive symptoms or history can be used to identify the etiology of TLOC [60]; however, quantitative histories and diagnostic scores improve the diagnostic accuracy. Syncope diagnostic scores based on historical features designed or applied to the pediatric population are introduced and summarized in Table 3.
To the best of our knowledge, a diagnostic score based on a quantitative history taking to differentiate between seizures and syncope in children has not yet been established. The most frequently used diagnostic score for differentiating between syncope and seizure in adults is the Calgary Syncope Seizure Score (CSSS) from the Calgary Syncope Symptom Study, which was investigated by Sheldon et al. [28]. A 118-item historical questionnaire was used to analyze 539 adult patients, including those with seizures (n=102) and syncope (n=437) [28]. Among the 118 historical items, 9 were selected for differentiating seizures from syncope [28]. Six questions are predictive of seizures, including preceding emotional stress, déjà vu or jamais vu, head turning and unusual posturing or motor activity during an event, confusion upon awakening, and tongue laceration [28]. The other 3 questions were predictive of syncope and included separate episodes of presyncope, preceding diaphoresis, or events precipitated by prolonged standing or sitting that were suggestive of syncope [28]. The sensitivity and a specificity of this CSSS were 94% and 94%, respectively, when the point score was ≥1 [28]. Although emotional stress is commonly observed in patients with syncope [61], it is difficult to evaluate preceding emotional stress in children. Therefore, the modified version was applied to children [62]. In the modified version, the question “Loss of consciousness with emotional stress?” has been replaced by “Loss of consciousness during sleep?” [62] Zou et al. [62] applied CSSS and modified CSSS in the differential diagnosis of VVS and epilepsy in children. When the cutoff score was ≥1, the sensitivity and specificity for seizure diagnosis were 91% and 95% for the CSSS and 92% and 96% for the modified CSSS [62]. The authors reported that the CSSS and modified CSSS were useful for the differential diagnosis of syncope and epilepsy in children [62].
Although no quantitative diagnostic score is available for children, a score from the Evaluation of Guidelines in Syncope Study (EGSYS), which was designed to differentiate between cardiac and noncardiac causes of syncope in adult patients (Table 3), has been applied [63]. This study included 216 patients with noncardiac syncope and 44 with cardiac syncope who visited the emergency department [63]. Abnormal ECG and/or heart disease, palpitations before syncope, syncope during effort or in the supine position, absence of precipitating or predisposing factors, and absence of autonomic prodromes were predictors of cardiac syncope [63]. They suggested that cardiac syncope is likely if the EGSYS score is ≥3 (sensitivity, 95%; specificity, 61%) and is very likely if the score is ≥4 (sensitivity, 32%; specificity, 99%) in adults [63]. Környei et al. [64] applied this score to children with channelopathy. Among 48 affected children, 13 presented with syncope [64]. Seven of 8 children (87%) with witnessed syncope events had a score of ≥3 [64]. The striking finding of this study was that a half of the patients presenting with syncope were initially misdiagnosed as having epilepsy and were followed up for 2–14 years for “therapy-resistant” or “atypical” epilepsy [64]. This study underscores the need for caution in diagnosing recurrent syncope-like events [64]. The multivariable EGSYS score seems to identify syncope of arrhythmic origin, even in children who were previously misdiagnosed with epilepsy [64].
A few studies reported the diagnostic value of history-taking in patients with cardiac syncope. As previously mentioned, the high risk of cardiac syncope in children includes syncope during exercise, preceding palpitations, and syncope without prodromal symptoms [31,32]. The Canadian Cardiovascular Society and Canadian Pediatric Cardiology Association created clinical guidelines for the evaluation and management of pediatric patients based on a literature review of 231 studies [65]. They documented mid-exertional syncope, a family history of unexplained death, and the absence of prodromal symptoms as being suggestive of cardiac syncope [65]. Meanwhile, motor activity preceding TLOC, prolonged LOC over 5 minutes, and LOC in the supine position were classified as symptoms suggestive of seizures [65]. However, these guidelines have not yet been validated. The New-Onset Syncope Study evaluated the clinical value of predefined specific historical features of cardiac syncope, including past cardiac history, chest pain, palpitations, syncope with exercise, and absence of prodromal symptoms with syncope [66]. Of the 2,293 patients with syncope who were included in the study, only 9 were ultimately diagnosed with cardiac syncope, while the rest were diagnosed with VVS [66]. All 9 patients with cardiac syncope had at least one positive specific history factor. Of the 1,972 patients with no specific findings, none had a cardiac etiology [66].
A recent systematic review reported that psychogenic pseudosyncope is rarer than cardiac syncope, with an average of 1.7% of all TLOC cases [16]. Here we briefly introduce a diagnostic score designed to differentiate between pseudosyncope and VVS in children rather than examining the clinical symptoms of pseudosyncope in detail.
Zhang et al. [67] analyzed the clinical features of 150 children with VVS and 26 with pseudosyncope and established a scoring model that could differentiate between the 2 groups. This study evaluated clinical symptoms and ECG data and vital signs [67]. They showed that QT dispersion (QTd), syncope duration, and upright posture at inducement were independent factors for differentiating VVS from pseudosyncope [67]. A total score of ≥3 predicted the likelihood of pseudosyncope versus VVS [67]. This scoring system showed a sensitivity of 91% and specificity of 76.9% [67]. The QTd is the difference between the longest and shortest QT distances on a 12-lead surface ECG. However, its results cannot be determined quickly; therefore, the usefulness of this scoring system may be limited in the clinical setting. Therefore, the same research group has developed an easier scoring system. Li et al. [68] analyzed 183 children with VVS and 50 with pseudosyncope. They assigned the following four independent variables: no upright posture, LOC duration ≥ 9 minutes, daily frequency of attacks ≥ 2, and body mass index ≥ 20.5 kg/m2. When a total score ≥ 5 points was used as the cutoff value for the initial differentiation between VVS and pseudosyncope, the sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of pseudosyncope were 92.0% and 90.7%, respectively [68]. Although a lower body mass index has been observed in children with VVS versus healthy controls [68], the relationship between body mass index and pseudosyncope is unclear. The authors suggested that the clinical symptom–based scoring model is a simple and efficient measure to distinguish between VVS and pseudosyncope [67,68]. However, further validation of these scoring systems is required.
Understanding the mechanisms of syncopal symptoms and their underlying physiology is the first step toward diagnostic accuracy that can avoid the pitfalls during history taking. Specific clinical features and accompanying situations should be considered in the syncope diagnosis in addition to the presence or absence of symptoms or signs.
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of TLOC. TLOC, transient loss of consciousness; TIA, transient ischemic attac.
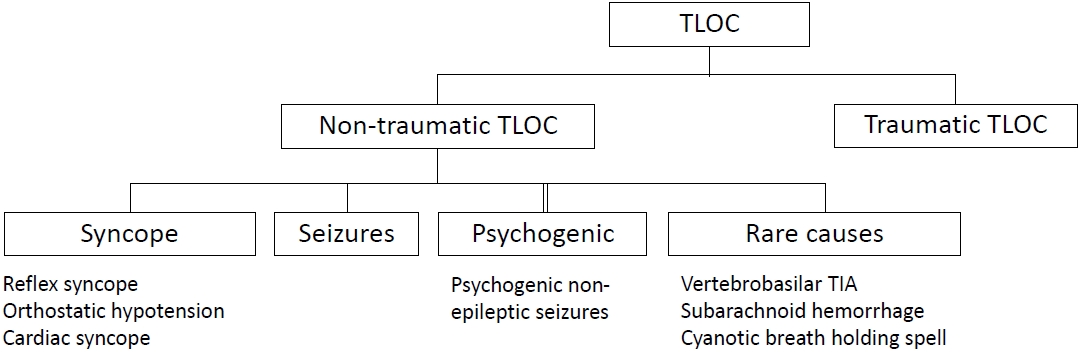
Table 1.
Relevant terms and definitions
| Term | Definition* | |
|---|---|---|
| Syncope | A symptom that presents with an abrupt, transient, complete loss of consciousness, associated with an inability to maintain postural tone, with rapid and spontaneous recovery. [9] | |
| Reflex syncope | Syncope due to a reflex that causes vasodilation, bradycardia, or both. [9] | |
| Vasovagal syncope | The most common form of reflex syncope mediated by the vasovagal reflex. VVS: (1) may occur with upright posture (standing or seated or with exposure to emotional stress, pain, or medical settings; (2) typically is characterized by diaphoresis, warmth, nausea, and pallor; (3) is associated with vasodepressor hypotension and/or inappropriate bradycardia; and (4) is often followed by fatigue. [9] | |
| Situational syncope | Reflex syncope associated with a specific action, such as coughing, laughing, swallowing, micturition, or defecation. These syncope events are closely associated with specific physical functions. [9] | |
| Orthostatic hypotension | A drop in systolic BP of ≥20 mmHg or diastolic BP of ≥10 mmHg with assumption of an upright posture. [12] | |
| Initial OH | A transient BP decrease within 15 seconds after standing, with presyncope or syncope. [12] | |
| Classic OH | A sustained reduction of systolic BP of ≥20 mmHg or diastolic BP of ≥10 mmHg within 3 minutes of assuming upright posture. [12] | |
| Delayed OH | A sustained reduction of systolic BP of ≥20 mmHg (or 30 mmHg in patients with supine hypertension) or diastolic BP of ≥10 mmHg that takes >3 minutes of upright posture to develop. [12] | |
| Cardiac syncope | Syncope caused by bradycardia, tachycardia, or hypotension due to low cardiac index, blood flow obstruction, vasodilatation, or acute vascular dissection | |
Table 2.
Summary of pitfalls and pearls in history taking in cases of suspected syncope
Table 3.
Summary of syncope diagnostic score studies based on symptoms in children
| Study | Diagnostic score/original study or from adult study | Aims | Study disease and number of patients/age range | Items (score) | Application in the study population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zou et al. [62] (2017) | The (modified) Calgary Syncope Symptom Score (CSSS)/from adult study of Sheldon et al. [28] | Differential diagnosis between syncope and seizures | Neutrally mediated syncope (N=119) vs. epilepsy (N=82) / –18 years old | Suggestive of seizures: preceding emotional stress (LOC during sleep in modified score) (+1), déjà vu or jamais vu (+1), head turning or motor activity during an event (+1), confusion upon awakening (+1), tongue laceration (+2) | Cutoff score ≥1 is predictive of seizure, sensitivity, and specificity of the (modified) CSSS/: 91.4% (92.6 %), 95.8% (96.6%) |
| Suggestive of syncope: presyncope (-2), diaphoresis before a spell (-2), and LOC with prolong sitting or standing (-2) | |||||
| Környei et al. [64] (2021) | Evaluation of Guideline in Syncope Study (EGSYS)/adopted from an adult study by Del Rosso et al. [63] | Usefulness of EGSYS in raising suspicion of cardiac syncope | Children with channelopathy (N=48)/median age 10.4 years old | Suggestive of cardiac syncope: palpitation (+4), abnormal ECG (+3), effort syncope (+3), syncope in supine position (+2) | Cutoff score ≥1 is suggestive of a cardiac origin in 7 out of 8 (88 %) children who present with syncope |
| Suggestive of vasovagal syncope: prodromes (-1), precipitating or predisposing factor (-1) | |||||
| Zhang et al. [67] (2020) | No specific name of the score/original study in pediatric patients | Differential diagnosis between VVS and psychogenic pseudosyncope | VVS (N=150) vs. pseudosyncope (N=26)/ 5–17 years old | Suggestive of pseudosyncope: syncope duration> 30 min (+3), upright posture as inducement (+2), QTd ≥1 (+1) | ≥3 is predictive of pseudosyncope/sensitivity (91%) and specificity (76%) |
| Li et al. [68] (2022) | No specific name of the score/original study in pediatric patients | Differential diagnosis between VVS and psychogenic pseudosyncope | VVS (N=183) vs. psychogenic pseudosyncope (N=50)/5–17 years old | Suggestive of pseudosyncope: syncope duration ≥9 minutes (+4), daily frequency of attacks ≥2 times (+8), body mass index ≥20.5 kg/m2 (+1), events in postures other than the upright posture (+4) | ≥5 is predictive of pseudosyncope/sensitivity (92.0%) and specificity (90.7%) |
References
1. Brignole M, Moya A, de Lange FJ, Deharo JC, Elliott PM, Fedorowski A, et al. 2018 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Eur Heart J 2018;39:1883-948.


2. Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Syncope; European Society of Cardiology (ESC); European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA); Heart Failure Association (HFA); Heart Rhythm Society (HRS); Moya A, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope (version 2009). Eur Heart J 2009;30:2631-71.


3. van Dijk N, Boer KR, Colman N, Bakker A, Stam J, van Grieken JJ, et al. High diagnostic yield and accuracy of history, physical examination, and ECG in patients with transient loss of consciousness in FAST: the fainting assessment study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2008;19:48-55.


4. Brignole M, Ungar A, Casagranda I, Gulizia M, Lunati M, Ammirati F, et al. Prospective multicentre systematic guideline-based management of patients referred to the syncope units of general hospitals. Europace 2010;12:109-18.


5. Wieling W, de Lange FJ, Olde Nordkamp LR, Thijs RD, van Dijk JG, Linzer M, et al. History taking as a diagnostic test in patients with syncope: Developing expertise in syncope. Eur Heart J 2015;36:277-80.


6. Hoefnagels WA, Padberg GW, Overweg J, Roos RA. Syncope or seizure? A matter of opinion. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1992;94:153-6.


7. van Wijnen VK, Gans ROB, Wieling W, ter Maaten JC, Harms MPM. Diagnostic accuracy of evaluation of suspected syncope in the emergency department: usual practice vs. ESC guidelines. BMC Emerg Med 2020;20:59.




8. Thijs RD, Benditt DG, Mathias CJ, Schondorf R, Sutton R, Wieling W, et al. Unconscious confusion--a literature search for definitions of syncope and related disorders. Clin Auton Res 2005;15:35-9.



9. Writing Committee Members, Shen WK, Sheldon RS, Benditt DG, Cohen MI, Forman DE, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the evaluation and management of patients with syncope: a report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines and the heart rhythm society. Heart Rhythm 2017;14:e155-217.

10. Deharo J. Reflex syncope. In: Camm AJ, Lüscher TF, Maurer G, Serruys PW, editors. ESC CardioMed. 3rd ed. Oxford (UK): Oxford University Press, 2018.
12. Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, Benditt DG, Benarroch E, Biaggioni I, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res 2011;21:69-72.



13. Jeanmonod R, Sahni D, Silberman M. Vasovagal episode. In: StatPearls [internet],Treasure island (FL): StatPearls publishing, 2022jan-.
14. Stewart JM. Transient orthostatic hypotension is common in adolescents. J Pediatr 2002;140:418-24.


15. Wieling W, Krediet CT, van Dijk N, Linzer M, Tschakovsky ME. Initial orthostatic hypotension: review of a forgotten condition. Clin Sci (Lond) 2007;112:157-65.



16. Zavala R, Metais B, Tuckfield L, DelVecchio M, Aronoff S. Pediatric syncope: a systematic review. Pediatr Emerg Care 2020;36:442-5.



17. van Dijk JG, van Rossum IA, Thijs RD. Timing of circulatory and neurological events in syncope. Front Cardiovasc Med 2020;7:36.


18. Colman N, Nahm K, van Dijk JG, Reitsma JB, Wieling W, Kaufmann H. Diagnostic value of history taking in reflex syncope. Clin Auton Res 2004;14 Suppl 1:37-44.



19. Tao C, Han Z, Yan Y, Pan Z, Zhu H, Li X, et al. Sitting-induced hemodynamic changes and association with sitting intolerance in children and adolescents: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep 2020;10:13921.




20. Khadilkar SV, Yadav RS, Jagiasi KA. Are syncopes in sitting and supine positions different? body positions and syncope: a study of 111 patients. Neurol India 2013;61:239-43.


21. Ikiz MA, Cetin II, Ekici F, Guven A, Degerliyurt A, Kose G. Pediatric syncope: is detailed medical history the key point for differential diagnosis? Pediatr Emerg Care 2014;30:331-4.

22. Colivicchi F, Ammirati F, Santini M. Epidemiology and prognostic implications of syncope in young competing athletes. Eur Heart J 2004;25:1749-53.


23. Miyake CY, Motonaga KS, Fischer-Colbrie ME, Chen L, Hanisch DG, Balise RR, et al. Risk of cardiac disease and observations on lack of potential predictors by clinical history among children presenting for cardiac evaluation of mid-exertional syncope. Cardiol Young 2016;26:894-900.


24. Krediet CT, Wilde AA, Wieling W, Halliwill JR. Exercise related syncope, when it's not the heart. Clin Auton Res 2004;14 Suppl 1:25-36.



25. Wu CT, Nattel S. Triggering of cardiac arrhythmic events in long QT syndrome: lessons from funny bunnies. J Physiol 2012;590:1311-2.



26. Wieling W, Thijs RD, van Dijk N, Wilde AA, Benditt DG, van Dijk JG. Symptoms and signs of syncope: a review of the link between physiology and clinical clues. Brain 2009;132:2630-42.


27. Wieling W, van Dijk JG, van Lieshout JJ, Benditt DG. Pathophysiology and clinical presentation. In: Benditt DG, Blanc JJ, Brignole M, Sutton R, editors. The evaluation and treatment of syncope: a handbook for clinical practice. 2nd ed. Malden (MA): Blckwell Publishing, 2006:16-28.
28. Sheldon R, Rose S, Ritchie D, Connolly SJ, Koshman ML, Lee MA, et al. Historical criteria that distinguish syncope from seizures. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;40:142-8.


29. Aminoff MJ, Scheinman MM, Griffin JC, Herre JM. Electrocerebral accompaniments of syncope associated with malignant ventricular arrhythmias. Ann Intern Med 1988;108:791-6.


31. Zhang Q, Zhu L, Wang C, Du Z, Hu X, Tian H, et al. Value of history taking in children and adolescents with cardiac syncope. Cardiol Young 2013;23:54-60.


32. Hurst D, Hirsh DA, Oster ME, Ehrlich A, Campbell R, Mahle WT, et al. Syncope in the pediatric emergency department - can we predict cardiac disease based on history alone? J Emerg Med 2015;49:1-7.


33. Calkins H, Shyr Y, Frumin H, Schork A, Morady F. The value of the clinical history in the differentiation of syncope due to ventricular tachycardia, atrioventricular block, and neurocardiogenic syncope. Am J Med 1995;98:365-73.


34. Alboni P, Dipaola F, Stucci N, Furian R. Initial evaluation of the patients with transient loss of consciousness. In: Alboni P, editor. Vasovagal syncope. 2nd ed. Cham (Switzerland): Springer, 2015:105-22.
35. Baraldi S, Farrell F, Benson J, Diehl B, Wehner T, Kovac S. Drop attacks, falls and atonic seizures in the video-EEG monitoring unit. Seizure 2015;32:4-8.


36. Lempert T, Bauer M, Schmidt D. Syncope: a videometric analysis of 56 episodes of transient cerebral hypoxia. Ann Neurol 1994;36:233-7.


38. Song PS, Kim JS, Park J, Yim HR, Huh J, Kim JH, et al. Seizure-like activities during head-up tilt test-induced syncope. Yonsei Med J 2010;51:77-81.



39. Heyer GL, Schmittauer C, Islam MP. The clinical and electroencephalographic spectrum of tilt-induced syncope and "near syncope" in youth. Pediatr Neurol 2016;62:27-33.


40. Petkar S, Hamid T, Iddon P, Clifford A, Rice N, Claire R, et al. Prolonged implantable electrocardiographic monitoring indicates a high rate of misdiagnosis of epilepsy--REVISE study. Europace 2012;14:1653-60.


41. Josephson CB, Rahey S, Sadler RM. Neurocardiogenic syncope: Frequency and consequences of its misdiagnosis as epilepsy. Can J Neurol Sci 2007;34:221-4.


42. Kim S, DeGrauw T, Berg AT, Hass KB, Koh S. Evaluation of pediatric patients in new-onset seizure clinic (NOSc). Epilepsy Behav 2020;112:107428.


43. Shah S, Nagarajan L, Palumbo L, Walsh P, Silberstein J, Cannell P, et al. Paediatric new-onset seizure clinic in Australia: experience and lessons learnt. J Paediatr Child Health 2019;55:789-94.



44. Lempert T. Convulsive syncope [Internet]. San Diego: Medlink Neurol; c2022 [cited 2023 Feb 1]. Available from: https://www.medlink.com/articles/convulsive-syncope.
45. Shmuely S, Bauer PR, van Zwet EW, van Dijk JG, Thijs RD. Differentiating motor phenomena in tilt-induced syncope and convulsive seizures. Neurology 2018;90:e1339-46.


46. Stephenson JBP. Fits and faints. London: Mac Keith Press, 1990.
48. Gastaut H, Fischer-Williams M. Electro-encephalographic study of syncope; its differentiation from epilepsy. Lancet 1957;273:1018-25.

50. van Dijk JG, Thijs RD, van Zwet E, Tannemaat MR, van Niekerk J, Benditt DG, et al. The semiology of tilt-induced reflex syncope in relation to electroencephalographic changes. Brain 2014;137:576-85.


51. Brna P, Camfield P, Camfield C, Messenger M, Finley J. When are episodes of loss of consciousness life-threatening? Paediatr Child Health 2006;11:359-61.



52. Lin JT, Ziegler DK, Lai CW, Bayer W. Convulsive syncope in blood donors. Ann Neurol 1982;11:525-8.


53. Brigo F, Nardone R, Bongiovanni LG. Value of tongue biting in the differential diagnosis between epileptic seizures and syncope. Seizure 2012;21:568-72.


54. Benba dis SR, Wolgamuth BR, Goren H, Brener S, Fouad-Tarazi F. Value of tongue biting in the diagnosis of seizures. Arch Intern Med 1995;155:2346-9.


55. Brigo F, Nardone R, Ausserer H, Storti M, Tezzon F, Manganotti P, et al. The diagnostic value of urinary incontinence in the differential diagnosis of seizures. Seizure 2013;22:85-90.


56. Hoefnagels WA, Padberg GW, Overweg J, van der Velde EA. Transient loss of consciousness: the value of the history for distinguishing seizure from syncope. J Neurol 1991;238:39-43.



57. Roberts JR. Clinically differentiating seizure from syncope. Emerg Med News 2017;39:8-9.
58. Zhang Q, Jin H, Qi J, Yan H, Du J. Diagnostic value of serum brain natriuretic peptide in syncope in children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr 2013;102:e210-4.


59. Benditt DG, Van Dijk JG, Krishnappa D, Adkisson WO, Sakaguchi S. Neurohormones in the pathophysiology of vasovagal syncope in adults. Front Cardiovasc Med 2020;7:76.



61. France CR, France JL, Himawan LK, Lux P, McCullough J. Donation related fears predict vasovagal reactions and donor attrition among high school donors. Transfusion 2021;61:102-7.



62. Zou R, Wang S, Zhu L, Wu L, Lin P, Li F, et al. Calgary score and modified Calgary score in the differential diagnosis between neurally mediated syncope and epilepsy in children. Neurol Sci 2017;38:143-9.



63. Del Rosso A, Ungar A, Maggi R, Giada F, Petix NR, De Santo T, et al. Clinical predictors of cardiac syncope at initial evaluation in patients referred urgently to a general hospital: the EGSYS score. Heart 2008;94:1620-6.


64. Környei L, Szabó A, Róth G, Kardos A, Fogarasi A. Frequency of syncope as a presenting symptom in channelopathies diagnosed in childhood. Can the multivariable EGSYS score unmask these children? Eur J Pediatr 2021;180:1553-9.



65. Sanatani S, Chau V, Fournier A, Dixon A, Blondin R, Sheldon RS. Canadian Cardiovascular Society and Canadian Pediatric Cardiology Association Position Statement on the approach to syncope in the pediatric patient. Can J Cardiol 2017;33:189-98.


66. Gupta A, Menoch M, Levasseur K, Gonzalez IE. Screening pediatric patients in new-onset syncope (SPINS) study. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2020;59:127-33.








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


