Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six month.
- Review Article
- Other
- Acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children: no valid rationale for controversy (101,725 times)
- Lisa Zhao, John P. Jones, Lauren G. Anderson, Zacharoula Konsoula, Cynthia D. Nevison, Kathryn J. Reissner, William Parker
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):126-139. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Despite worldwide acceptance of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in pediatric medicine, careful examination reveals no valid objections to the conclusion that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children. Nevertheless, debate that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury has centered around the prenatal period, evidence of which is relatively limited compared to that in the postnatal period, which is the time of greatest absolute and relative risk.
- Original Article
- Basic Research
- Linezolid mitigates tissue injury in experimental model of pediatric testicular torsion: TLR-4/MAPK/NF-κB involvement (74,011 times)
- Moein Ghasemi, Abolfazl Basiri, Houman Kazemzadeh, Mohammad Amin Manavi, Seyed Mohammad Tavangar, Ahmad Reza Dehpour, Hamed Shafaroodi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):700-711. Published online August 26, 2025
-

Question: What pharmacological strategies can limit ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric patients with testicular torsion?
Finding: In a rat model of testicular torsion, linezolid reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue injury via the Toll-like receptor 4/mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappa beta pathway.
Meaning: Linezolid may offer a pharmacological approach to attenuate testicular damage in pediatric patients with testicular torsion, warranting further clinical investigation.
- Other
- Impact of thyroid hormones and serum endothelin levels on pediatric asthma control: a case-control study of an Indian population (67,582 times)
- Murugaiyan Sathishbabu, Sathiya Ramasamy, Niranjjan Ramachandran, Soundararajan Palanisamy, Arulvijayavani Subramaniam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):831-837. Published online September 22, 2025
-
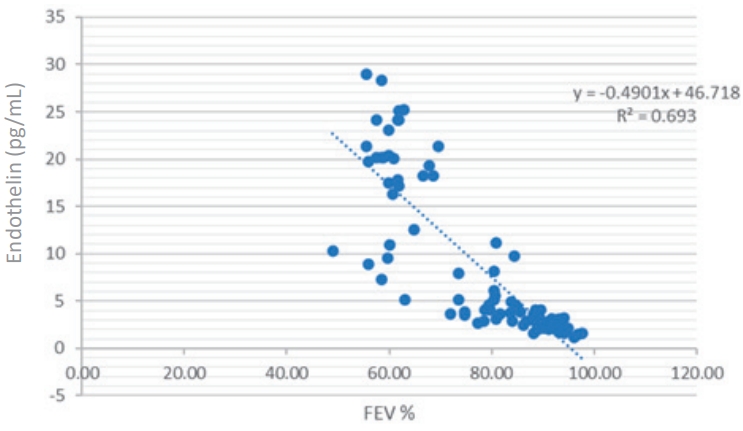
Question: What are the roles of thyroid hormones and endothelin in South Indian children with asthma?
Finding: Thyroid hormone and endothelin levels were significantly elevated in South Indian children with asthma; poorly controlled cases exhibited the highest levels. Elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone and endothelin levels were correlated with asthma severity.
Meaning: Serum endothelin is a potential surrogate marker for asthma severity that could aid the assessment and management of childhood asthma.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with intermittent sigh breaths on carbon dioxide levels in neonates (64,975 times)
- Kulthida Baingam, Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):178-184. Published online November 13, 2024
-
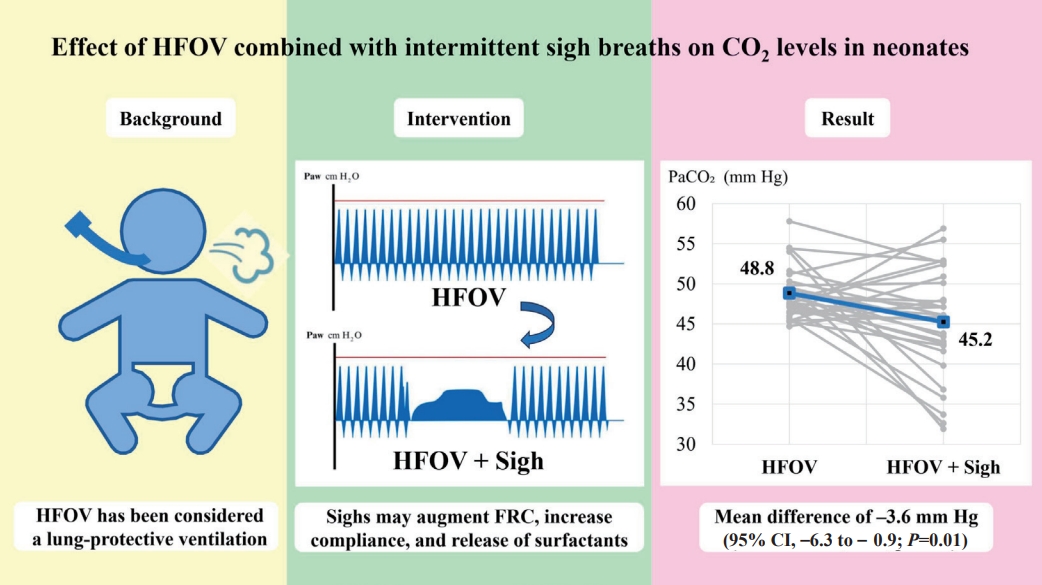
Question: Can sigh breaths (Sighs) application during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) decrease partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels?
Finding: The mean PaCO2 level after Sighs during HFOV was significantly decreased compared to that after HFOV alone (mean difference, -3.6 mmHg).
Meaning: HFOV plus Sighs functionality can reduce PaCO2 levels. However, further studies are required to conclusively determine the effects of Sighs.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Clinical practice guidelines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: recent updates (54,203 times)
- Tae Hoon Eom, Young-Hoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):26-34. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Primary pediatricians should play a key role in the diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
· The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition, has lowered the diagnostic threshold for older teens and adults and a comorbid diagnosis with autism is now allowed.
· The American Academy of Pediatrics had added recommendation-related comorbid conditions in its guideline and the Society of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics recently developed a complex ADHD guideline.
· The European ADHD Guideline Group recently developed a guideline for managing ADHD during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis (45,135 times)
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
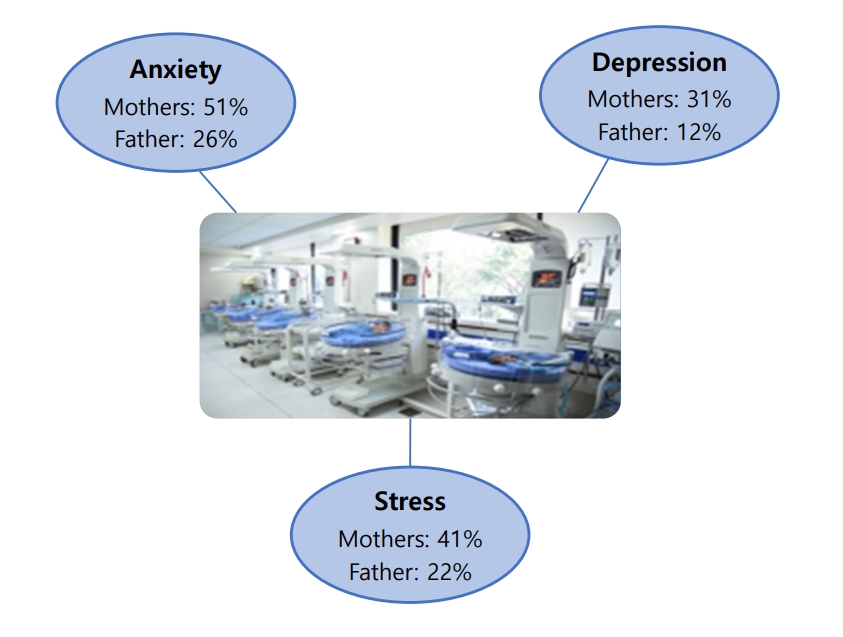
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of a long-acting monoclonal antibody to prevent respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants and young children (43,575 times)
- Soo-Han Choi, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Ki Wook Yun, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):742-750. Published online September 3, 2025
-
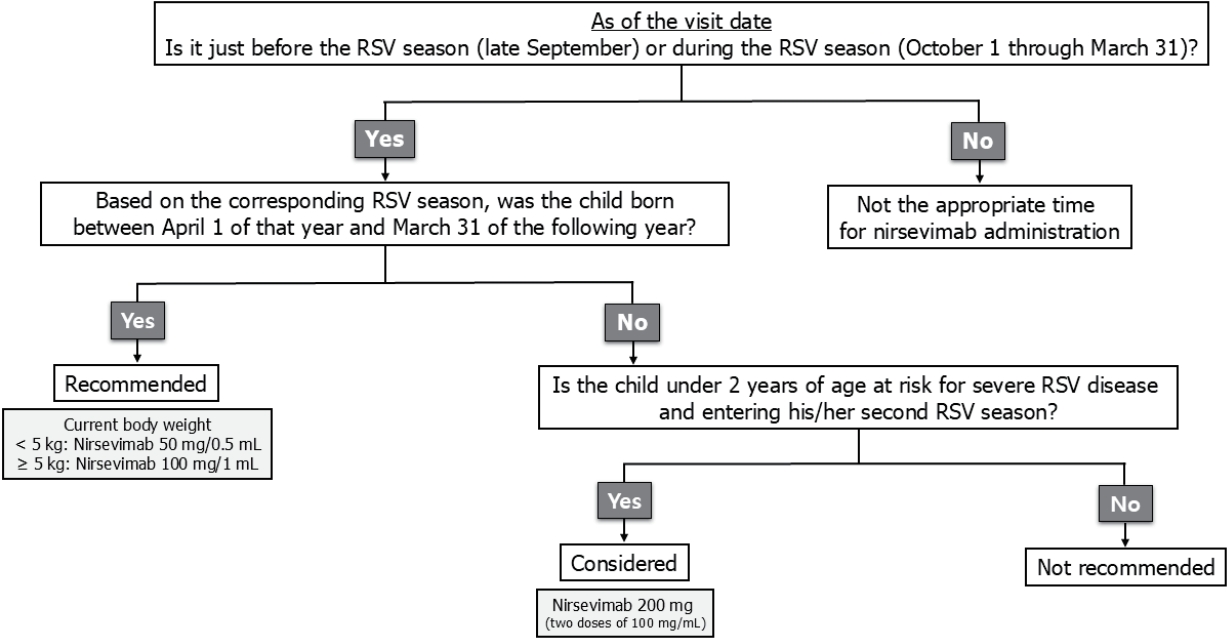
To prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-associated lower respiratory tract infections, a single dose of nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, is recommended for all neonates born during the RSV season (October to March) and all infants younger than 6 months old at the start of the RSV season. Nirsevimab should be administered shortly after birth to neonates and just before or early in the season to infants entering their first RSV season.
- Endocrinology
- Growth plate closure and therapeutic interventions (42,994 times)
- Ja Hyang Cho, Hae Woon Jung, Kye Shik Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):553-559. Published online October 28, 2024
-

Height gains result from longitudinal bone growth. Upon adequate growth, growth plate closure limits longitudinal bone growth. To date, gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs, aromatase inhibitors, C-type natriuretic peptide analogs, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 inhibitors have been studied or used as therapeutic interventions to delay growth plate closure and increase human height. The development of more effective therapeutic modalities for short stature, precocious puberty, and skeletal dysplasia is anticipated.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Demographic transition in South Korea: implications of falling birth rates (37,390 times)
- Chae Young Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):498-509. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· Since 1960, South Korea's TFR decreased from 6.33 to 0.78 in 2022, below the 2.1 replacement level since 1983, with women's average age at first marriage rising to 31.3 in 2022.
· Policies needed: financial incentives, longer parental leave, better childcare.
· The U.S. (15.3% immigrants) and Germany (18.8%) use immigration to maintain demographic stability, a strategy South Korea is considering.
- Other
- Myopia: a review of current concepts, association with nonophthalmological conditions, and treatment strategy in children and adolescents (35,944 times)
- Yeon Woong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):554-565. Published online April 1, 2025
-
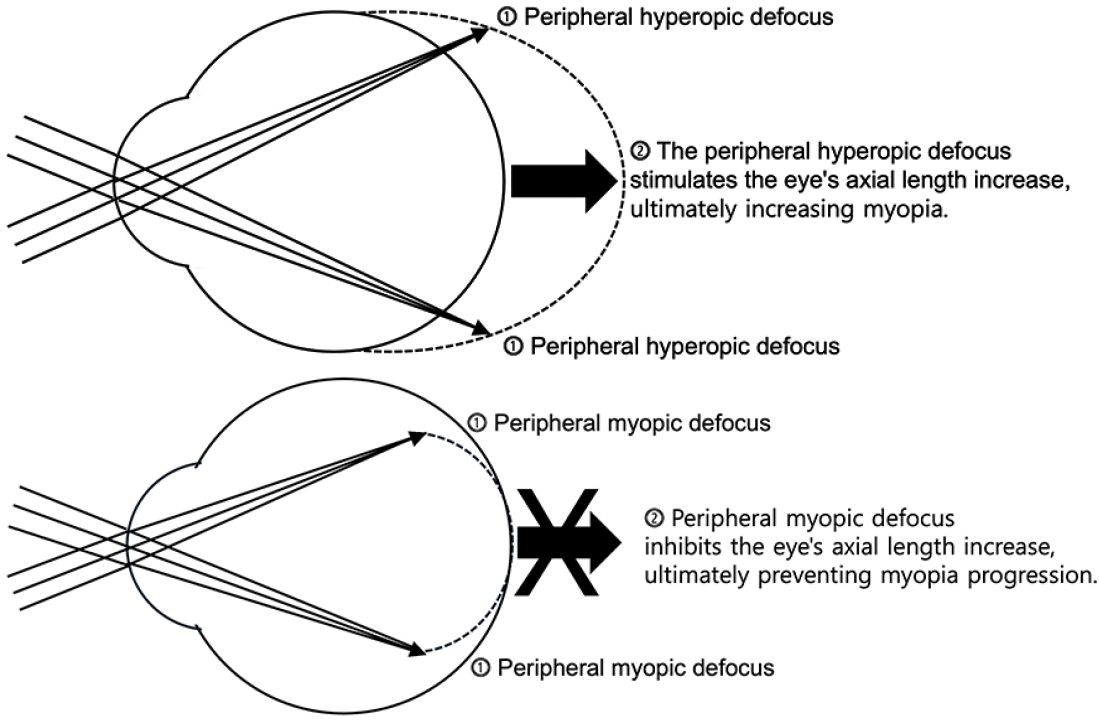
Myopia is a major ophthalmological disorder with increasing prevalence worldwide, particularly in East Asia. Evidence indicates that its development involves complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Body stature, sleep patterns, and nutritional status significantly influence the progression of myopia during childhood and adolescence. Its treatment and prevention strategies include optical correction, atropine therapy, increased outdoor activity, decreased near work, and regular retinal monitoring.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Liposomal SunActive versus conventional iron for treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in children aged 2–12 years: a prospective randomized controlled trial (32,593 times)
- Wael A. Bahbah, Yasmin A.H.S. Younis, Hanan Salama Elbelouny, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):608-615. Published online July 18, 2025
-
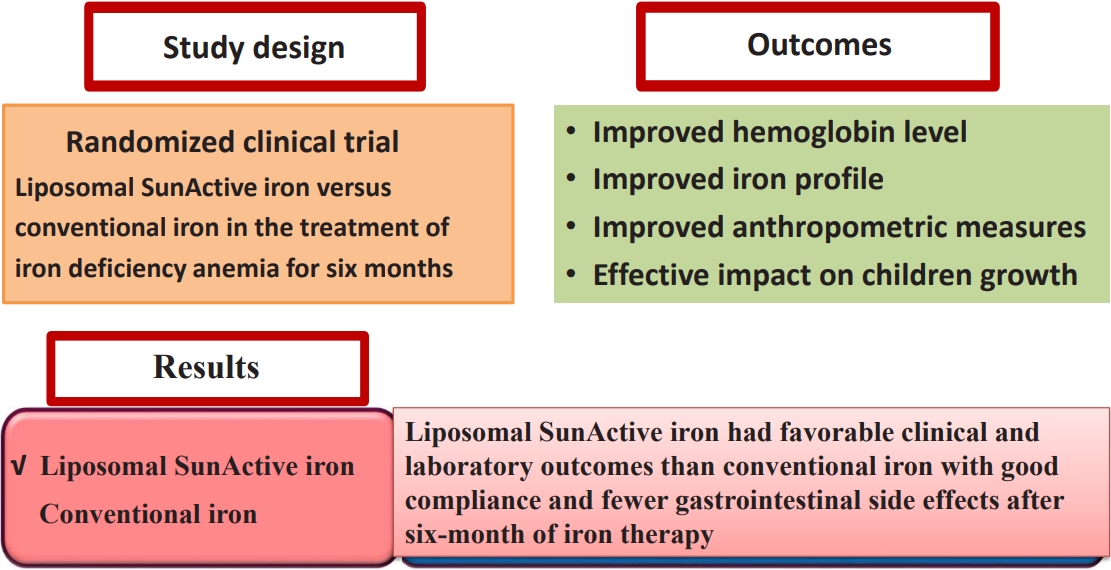
Background: Liposomal iron, a novel oral formulation of ferric pyrophosphate that demonstrates improved gastrointestinal absorption and bioavailability with fewer side effects than conventional iron, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia (IDA).
Purpose: To conduct an in-depth comparative study of liposomal SunActive and conventional iron supplements (iron polymaltose complex) for treating IDA in children aged 2–12 years Methods: This...
- Review Article
- Infection
- Community-acquired pneumonia in children: updated perspectives on its etiology, diagnosis, and treatment (32,265 times)
- Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):80-89. Published online June 14, 2023
-
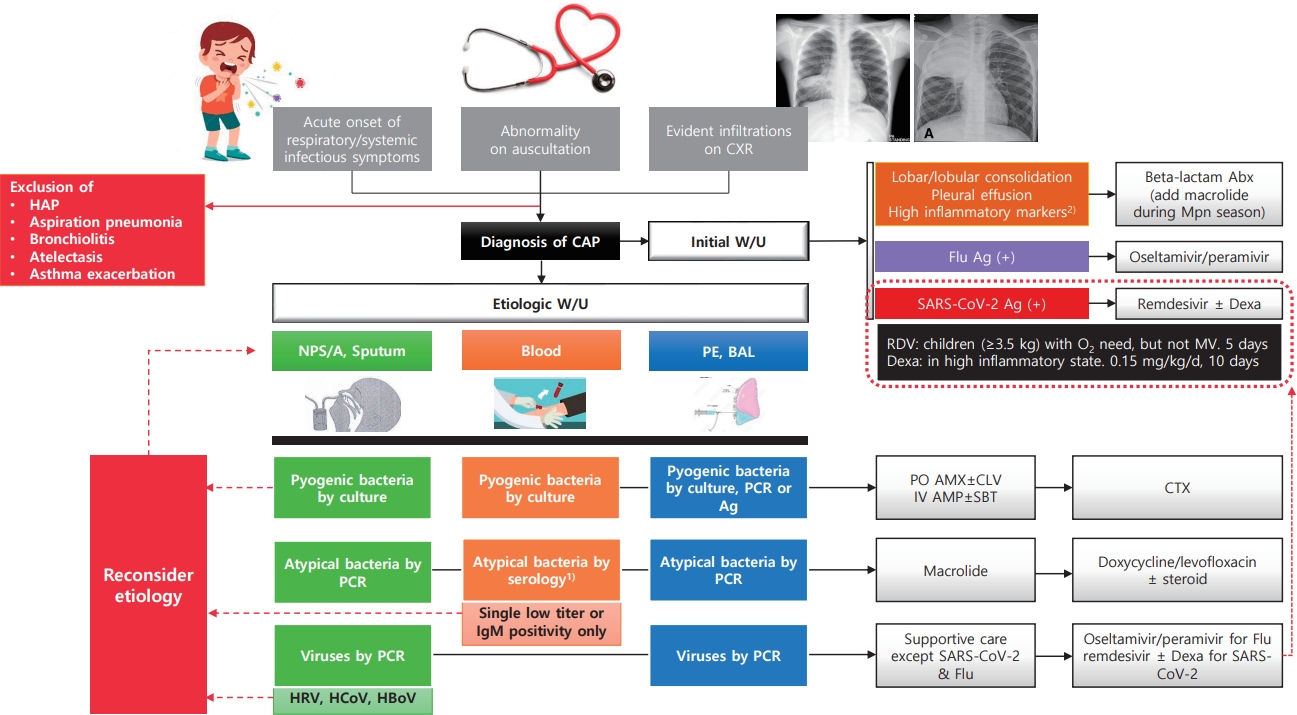
· Most commonly confirmed causes of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae (8%–40%) and respiratory syncytial virus (15%–20%).
· Pyogenic bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus pneumoniae (40%–50%) and Streptococcus pyogenes (10%–25%), are detected in 2%–5% of children hospitalized with CAP.
· CAP should be diagnosed conservatively according to clinical and radiological criteria.
· The etiology should be identified via appropriate test result interpretation.
- Original Article
- Other
- Role of neutrophil elastase in predicting infection among children with chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia (31,307 times)
- Mahmoud A. El-Hawy, Doaa M. Elian, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid, Esraa T. Allam, Mariam S. Kandeel, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):801-807. Published online June 10, 2025
-
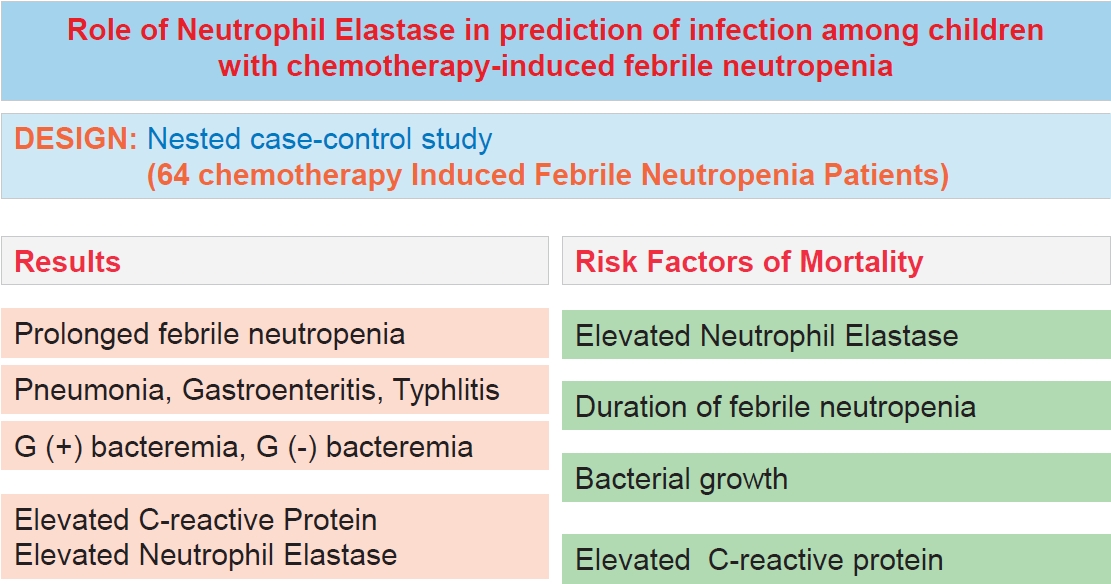
Question: Can neutrophil elastase (NE) levels predict infection— the primary cause of mortality—among children with hematological malignancies and febrile neutropenia (FN)?
Finding: Elevated levels of NE were found in children with chemotherapy-induced FN and a bacterial infection.
Meaning: Increased NE levels and prolonged FN are important factors associated with mortality risk.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Comprehensive evaluation of the child with global developmental delays or intellectual disability (30,141 times)
- Abdullah Nasser Aldosari, T. Saeed Aldosari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):435-446. Published online May 29, 2024
-

· A detailed history and comprehensive physical examination remain the cornerstones for establishing a diagnosis of global developmental delay/intellectual disability (GDD/ID).
· Comprehensive surveillance and screening programs play a significant role in the early detection of GDD.
· Whole-exome sequencing is highly recommended as first- or second-line testing for individuals with idiopathic GDD/ID.
· Early intervention by a well-versed multidisciplinary team can significantly improve the outcomes and prognosis of GDD/ID.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effectiveness of Kinder Lebensqualität Fragebogen (KINDL) and Children’s Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) for measuring postacute sequelae of COVID-19 in children: a diagnostic validation study (30,003 times)
- Lawrence Shih-Hsin Wu, Pei-Chi Chen, Xiao-Ling Liu, Shu-Tsen Liu, Chi-Hung Wei, Yu-Lung Hsu, Kai-Sheng Hsieh, Huan-Cheng Lai, Chien-Heng Lin, Chieh-Ho Chen, An-Chyi Chen, I-Ching Chou, Wen-Jue Soong, Hui-Ju Tsai, Chung-Ying Lin, Jiu-Yao Wang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):944-951. Published online September 12, 2025
-

Question: Although children with postacute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 (PASC) may experience persistent symptoms that affect their quality of life (QoL), a screening tool for identifying high-risk children is lacking.
Finding: Kinder Lebensqualität fragebogen (KINDL) and Children's Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) were significantly correlated. An optimal KINDL cutoff score (74.75) detected those at high risk of a reduced QoL.
Meaning: Integrating KINDL and CSSI-24 into routine pediatric outpatient care may enable timely identification and interventions for children at risk of PASC-related impairments.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis (29,852 times)
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Assessment of natural killer cell subpopulations in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major (27,958 times)
- Fathia Ibrahim Elbassal, Mohamed Abdel Rehim Soliman, Nourhan Hossam Eldin Mohamed, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid, Hanan Hassan El-Sheity
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):981-990. Published online September 12, 2025
-
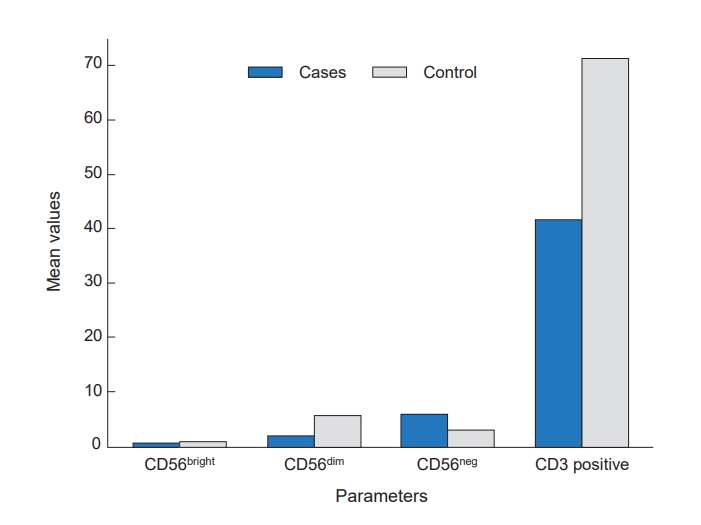
Question: How does iron overload affect immunity in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major?
Finding: Iron overload in these patients is associated with disrupted natural killer (NK) cell subpopulations, reflecting impaired innate immunity.
Meaning: This highlights the need to monitor immune profile alongside iron status during thalassemia management.
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial (27,049 times)
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cytokine profile of Post–cardiopulmonary bypass in children (26,576 times)
- Kantara Saelim, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Jirayut Jarutach, Pongsanae Duangpakdee, Smonrapat Surasombatpattana, Pharsai prasertsan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1015-1022. Published online September 19, 2025
-

Question: Can cytokine levels predict low cardiac output syndrome (LCOS) in children post–cardiopulmonary bypass?
Finding: Elevated interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were associated with LCOS, with an increase in IL-8 of >56 pg/mL from baseline to immediately postoperative being the strongest predictor.
Meaning: Monitoring immediately postoperative IL-8 levels may help identify pediatric patients at risk of LCOS, enabling timely interventions to improve outcomes.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Global burden of asthma among children and adolescents with projections to 2050: a comprehensive review and forecasted modeling study (26,096 times)
- Tae Hyeon Kim, Hyunjee Kim, Jiyeon Oh, Soeun Kim, Michael Miligkos, Dong Keon Yon, Nikolaos G Papadopoulos
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):329-343. Published online April 22, 2025
-

Pediatric asthma can persist to adulthood and must be effectively managed. This review examined the prevalence of asthma among individuals younger than 20 years and revealed a decline from 1990 to 2021, higher rates in males, and a peak in children aged 5–9 years. Despite a projected continued decrease in prevalence by 2050, asthma will remain a significant health concern for children and adolescents.
- Comparison and review of international guidelines for treating asthma in children (24,148 times)
- Eui Jeong Roh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):447-455. Published online August 20, 2024
-

Asthma is the most common chronic disease among children. Although asthma in children may spontaneously improve, it continues into adulthood in many cases. Therefore, appropriate disease management and medication are essential. Consistent and objective guidelines are needed to manage pediatric asthma and related adverse reactions.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Effect of vitamin C supplement in treatment of childhood pneumonia requiring hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial (23,416 times)
- Chutima Phuaksaman, Katechan Jampachaisri, Klaita Srisingh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):690-699. Published online April 1, 2025
-

This study assessed the effects of vitamin C on children with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Vitamin C supplementation improved clinical symptoms within 48–72 hours compared to placebo but did not reduce the length of hospital stay (LOS). These findings suggest that vitamin C is beneficial for managing CAP severity, but does not affect LOS.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Screen time among preschoolers: exploring individual, familial, and environmental factors (22,614 times)
- Sangha Lee, Donghee Kim, Yunmi Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):641-650. Published online September 12, 2024
-
This systematic review examined the correlation between screen time and various factors in preschoolers. Findings suggest that media parenting, including setting appropriate media limits, is crucial in protecting against excessive screen exposure. However, limited research has been done on the impact of family and personal factors, particularly with the increasing use of portable devices among young children.
- Other
- Microplastic and human health with focus on pediatric well-being: a comprehensive review and call for future studies (22,362 times)
- Rogers Wainkwa Chia, Ntegang Venant Atem, Jin-Yong Lee, Jihye Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):1-15. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· Milk and formula are common sources of microplastic in infants.
· Water and air are the most common sources of microplastic pollution from infancy to adolescence.
· Microplastic use by children of all ages can cause cell damage and affect their health.
· Microplastics present in children can be quantified using a stereomicroscope and characterized using micro- Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Characteristics of temper tantrums in 1–6-year-old children and impact on caregivers (21,293 times)
- Warangkana Prutipaisan, Issarapa Chunsuwan, Tippawan Hansakunachai, Paskorn Sritipsukho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):170-177. Published online November 13, 2024
-
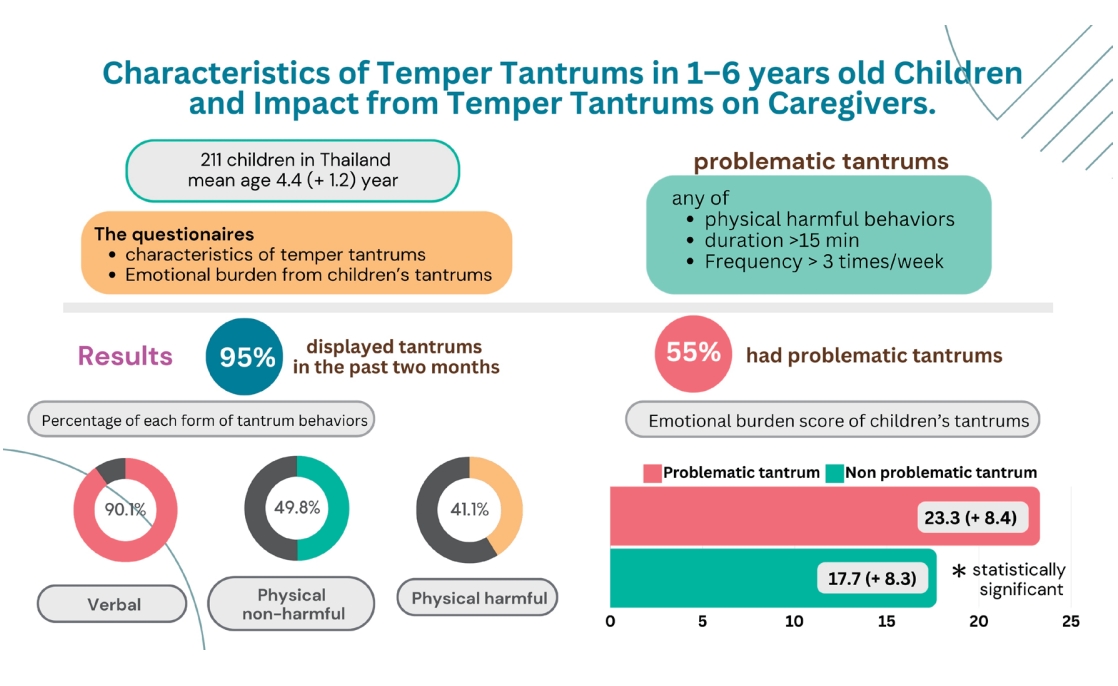
Question: What are common tantrum behaviors in preschool children, and how frequently are problematic behaviors observed? Do problematic tantrums have a different emotional impact on caregivers compared to typical tantrums?
Finding: Temper tantrums are common in preschool children, and verbal tantrums are the most common type.
Meaning: Problematic tantrums, defined as tantrums exhibiting aggressive physical behavior, long duration (>15 minutes), or frequent occurrence (>3 days/wk), significantly affected caregivers’ emotions.
- Review Article
- Other
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: current applications, potential, and implementation considerations (21,160 times)
- Taejin Park, In-Hee Lee, Seung Wook Lee, Sek Won Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):641-651. Published online June 25, 2025
-

Artificial intelligence (AI) offers potential benefits in pediatric care, but its real-world adoption requires clinician literacy, ethical and legal safeguards, and cautious implementation. Large language models are emerging across healthcare, but their use in pediatric clinical practice remains premature. Thus, the cautious and accountable implementation of AI is crucial to preventing unintended harm and realizing its potential.
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Malaysia: a systematic review and meta-analysis (18,585 times)
- Ker Yang Chua, Ker Yung Chua, Karuthan Chinna, Chooi Ling Lim, Maheeka Seneviwickrama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):115-126. Published online November 13, 2024
-
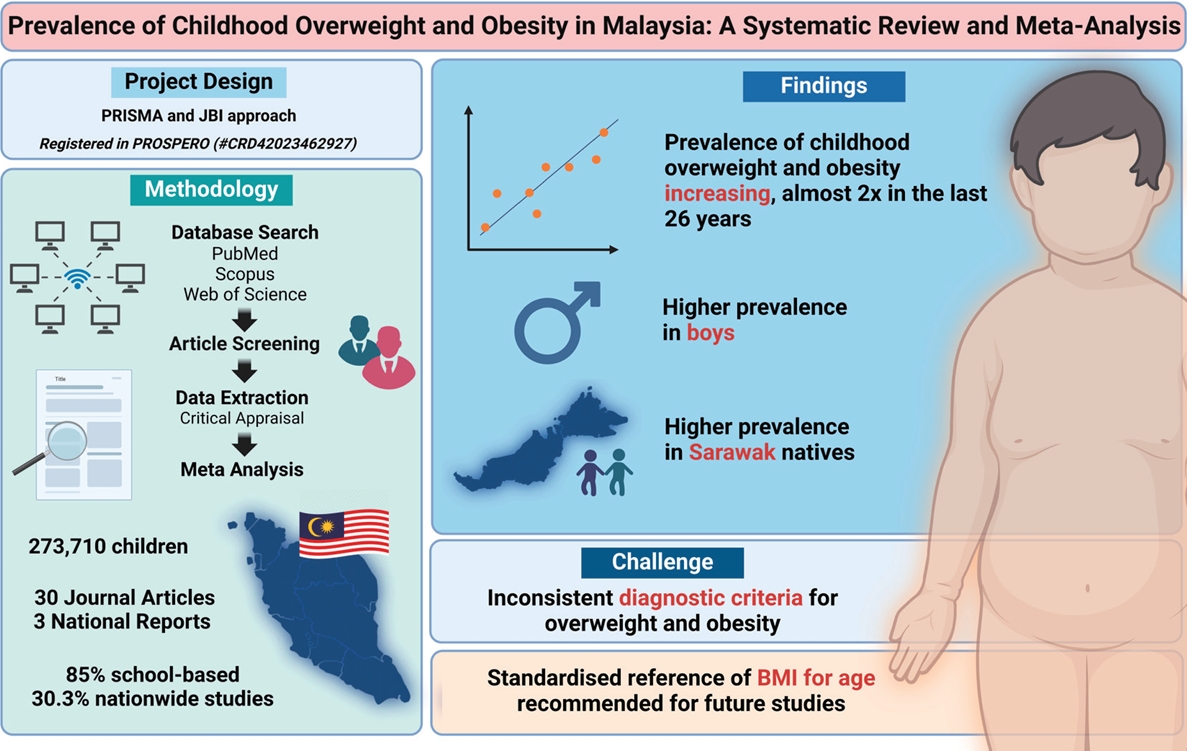
The incidence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide. National surveys in Malaysia have shown similar trends. This review aimed to increase our understanding of the prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight, obesity, and excess weight in Malaysia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted of studies reporting the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Malaysian children aged <18 years....
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Effectiveness of Helmet therapy for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly (18,335 times)
- Jeongho Kim, Jina Kim, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):46-53. Published online December 5, 2023
-
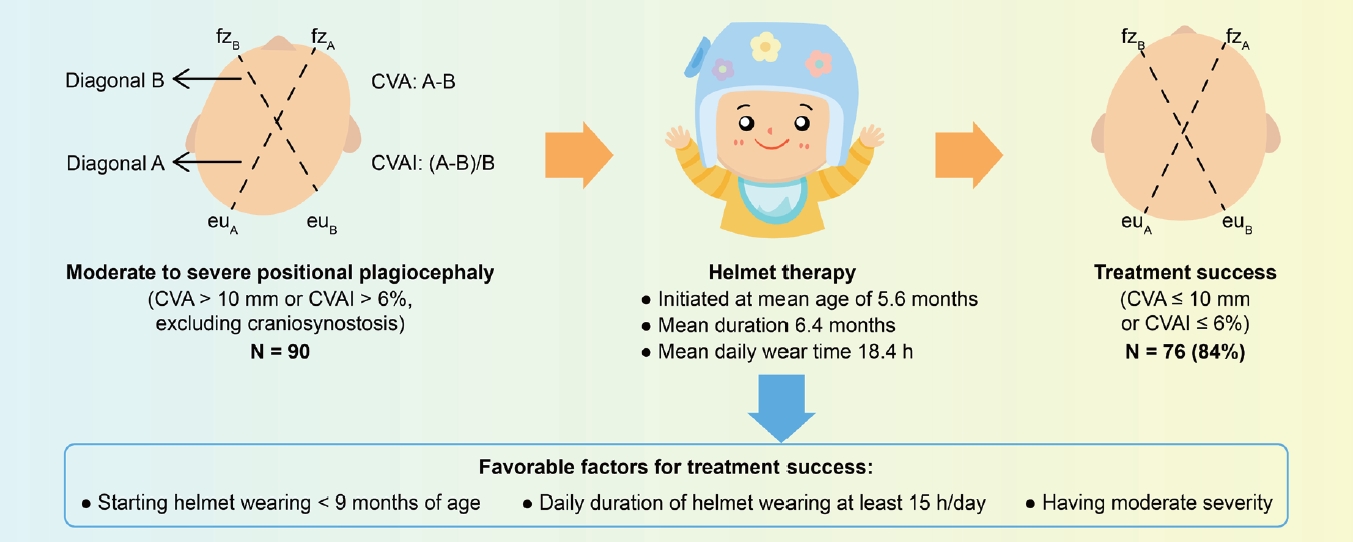
Question: Is helmet therapy effective for positional plagiocephaly? What factors influence helmet therapy efficacy for positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Helmet therapy is effective for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly, and its effectiveness is influenced by age at treatment initiation, severity of head asymmetry, and daily duration of helmet wear.
Meaning: Pediatricians should initiate helmet therapy for positional plagiocephaly sooner, ideally before 9 months of age, to maximize treatment efficacy.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Need for national guidance regarding proactive care of infants born at 22–23 weeks' gestation (18,265 times)
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):53-61. Published online November 13, 2024
-

With advancements in neonatal intensive care, the limit of viability has shifted to 22–23 weeks' gestation, whose survival rates vary across countries and institutions. These rates are not static and can be improved through the proactive and centralized care guided by national protocols, including maternal transfer to high-activity regions with better neonatal intensive care practices before delivery.
- Pulmonology
- Evidence-based management guidelines for noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in children and adolescents (16,123 times)
- Eun Lee, Kyunghoon Kim, You Hoon Jeon, In Suk Sol, Jong Deok Kim, Taek Ki Min, Yoon Ha Hwang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Dong In Suh, Hwan Soo Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Sung-Il Woo, Yong Ju Lee, Sungsu Jung, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Gwang Cheon Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):418-426. Published online January 23, 2024
-

· We suggest offering long-term macrolides to children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis with frequent exacerbations (conditional recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
· We do not recommend the routine use of mucolytic agents, inhaled corticosteroids, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent exacerbation of bronchiectasis in children (inconclusive, very low quality of evidence).
· We recommend the use of nebulized hypertonic saline to prevent exacerbations and improve the lung function of children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (weak recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











