Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 67(3); 2024 |
|
Abstract
Despite the worldwide acceptance of acetaminophen (APAP) as a necessary medicine in pediatrics, evidence that early exposure to APAP causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children has been mounting for over a decade. The evidence is diverse and includes extensive work with laboratory animals, otherwise unexplained associations, factors associated with APAP metabolism, and limited studies in humans. Although the evidence has reached an overwhelming level and was recently reviewed in detail, controversy persists. This narrative review evaluates some of that controversy. Evidence from the pre- and postpartum periods was considered to avoid controversy raised by consideration of only limited evidence of risks during the prepartum period. Among other issues, the association between APAP use and the prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders was considered. A systematic review revealed that the use of APAP in the pediatric population was never tracked carefully; however, historical events that affected its use were documented and are sufficient to establish apparent correlations with changes in the prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders. Moreover, problems with the exclusive reliance on results of meta-analyses of large datasets with limited time frames of drug exposure were reviewed. Furthermore, the evidence of why some children are susceptible to APAPinduced neurodevelopmental injuries was examined. We concluded that available evidence demonstrates that early exposure to APAP causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and small children.
Graphical abstract. ASD, autism spectrum disorder.
Acetaminophen (APAP; N-acetyl-p-aminophenol; paracetamol) as well as an antidote for its overdose (N-acetylcysteine) are listed by the World Health Organization as essential medicines for children [1]. Despite the worldwide acceptance of APAP in pediatric medicine, evidence that exposure to the drug during early development is a primary inducer of neurodevelopmental injury has been mounting for more than a decade. Although evidence is largely circumstantial or based on animal model studies, the preponderance of evidence weighs so heavily that a causal relationship can be inferred without remaining reasonable doubt [2]. This evidence is summarized in Fig. 1 and Table 1. Evidence demonstrates that, while most babies and children are relatively unharmed by APAP exposure, some are at risk due to the presence of oxidative stress [2,3]. Evidence points conclusively to the induction of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) with possible connections to both developmental delay and attention deficits [2]. Furthermore, evidence points toward exposure between birth and approximately 5 years of age as the period of highest risk, with the risk during prenatal exposure being significant in numerous studies [4] albeit less consequential [2,3]. Much of this evidence has recently been reviewed in detail elsewhere [2,3].
A recent exhaustive review of the literature complete with citation tracking demonstrated that, within the medical profession, APAP is widely considered safe when used as directed in the pediatric population [5]. Unfortunately, the widely held belief that it is safe for pediatric use is based on numerous clinical studies that assume that the liver is the target of drug toxicity [5]. In adults, the liver was identified as the target of APAP toxicity in the 1960s [6-8]. At that time, however, the view that babies metabolize drugs identically to adults was already known to be an unreliable and potentially dangerous assumption [9]; this knowledge had yet to be applied to the toxicity of APAP in children [5]. More than a decade later, a study using laboratory animals demonstrated that this assumption probably did not apply to APAP metabolism [10]. Although the target organ of APAP toxicity in newborn rats was not identified in that study, it was not the liver [10], a finding that was recently verified [11]. Within the last decade, the brain was identified as a target organ for APAP toxicity in newborn laboratory mice based on profound, long-term loss of cognitive function observed following exposure to relatively low drug doses [12]. Supporting the view that APAP is neurotoxic, a 2010 study of adult rats demonstrated that APAP induces the death of cortical neurons at concentrations lower than those required to induce acute liver failure [13].
A recent summary statement by Bauer et al. [14] examined the potential role of APAP exposure in utero in the induction of neurodevelopmental problems. This summary statement called for increased awareness of the potential role of APAP in this phenomenon, but it was criticized heavily by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). In its response [15], the ACOG concluded that available studies “show no clear evidence that proves a direct relationship between the prudent use of APAP during any trimester and fetal developmental issues.” The ACOG further concluded that “physicians should not change clinical practice until definitive prospective research is done.” Considering the ACOG response, it is important to note that evidence of APAP inducing neurodevelopmental problems during the prenatal period is concerning but limited [2,16,17]. As shown in Table 1, only one of 20 lines of evidence was related only to the prenatal period. The other 19 lines of evidence were consistent with the involvement of the postnatal period and, in some cases, indicated that the postnatal period is the time of the greatest sensitivity to APAP induced neurodevelopmental injury. The relative safety of the prenatal versus postnatal period is perhaps not surprising given the particularly efficient metabolism of APAP by the mother during pregnancy [18] and the limited capacity of neonates to metabolize pharmaceuticals [19]. Unfortunately, considerable public debate concerning APAP-inuced neurodevelopmental problems has focused on the Bauer consensus statement involving the prenatal period [14] and is fueled by ongoing lawsuits involving its prenatal use [20]. Thus, despite substantial controversy surrounding the view that APAP causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible individuals, this debate and its surrounding controversy are primarily focused on the relatively limited evidence pointing specifically toward the prenatal period. Tragically, the public debate has not yet moved toward its postnatal use, for which relative and absolute risks are greater and evidence of neurodevelopmental injury is conclusive [2].
As shown inTable 1, evidence that early exposure toAPAP causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children is much more robust than that limited to prenatal exposure only (Table 1). The body of extensive evidence pointing to APAP-induced neurodevelopmental injury in the postnatal period has not been directly challenged. However, objections have been voiced to particular lines of evidence. Here, we review several issues that may be considered controversial in the field, considering each line of evidence independently and in the light of all other lines of evidence. In particular, issues associated with studies in humans and animal models and factors associated with APAP metabolism were considered.
To establish any association between the use of APAP in the pediatric population and the incidence of neurodevelopmental disorders, it is most convenient to establish the prevalence of both factors over time with some degree of certainty. A systematic review was conducted to evaluate what is known about the prevalence of APAP use in the pediatric population at different times and locations (Fig. 2A). Although 48 studies were identified that evaluated the extent of APAP use in babies and children under 6 years of age, it is difficult to establish exactly how much APAP was used historically and when or where practice changed. Data were obtained from 38 countries, and those of 14 were limited to the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) [21] in 2000–2003. Furthermore, in four countries in which the ISAAC study was not the lone study, its results deviated by a mean of 26.5% from those of other studies. In Hungary and Portugal, the ISAAC study found higher APAP use than other sources, whereas in New Zealand and Spain, the study found lower APAP use. In addition, results from the Danish National Birth Cohort (DNBC) [22] were also in disagreement with independently conducted work, with approximately 10% using APAP during the first 18 months of life [23] versus 65% using it within a 3-month period in an independent study evaluating a subset of the population assessed by the DNBC [24]. Furthermore, data from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children study in England [25] were not consistently reported, with the use of APAP in babies 0–6 months of age during 1991–1992 reportedly 6% [26] and 84% [27].
Moreover, data from more than one independent study were found for only 11 of the 38 countries while three or more studies were found for only five countries. Fig. 2B shows the results from those five countries (the United States [US], Italy, New Zealand, Norway, and Spain), for which at least 3 independent studies evaluated the use of APAP in babies and children under 6 years of age. Although numerous studies have been conducted in various countries since the late 1990s, trends over time are not evident, and the results vary considerably. This makes it difficult to correlate changes in the prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders with changes in medical practice. However, as discussed in the next section, key historical events affecting APAP use in the pediatric population have been documented that can be useful in estimating APAP use through time.
At least three of the 20 lines of evidence summarized in Table 1 and in Fig. 1 involve the association through time between factors affecting pediatric use of APAP and the prevalence of ASD (Fig. 3). One such temporal relationship (Fig. 3) entails an increase in the ratio of regressive versus infantile ASD beginning in children born after 1980 [28], which coincides with the time that aspirin use in babies and children was being replaced by APAP use due to increasing awareness of the connection between aspirin and Reye syndrome [29-31]. This shifting ratio indicates that some factor was introduced into the population that could induce ASD even after brain development had proceeded for years on a relatively normal trajectory.
A second distinct temporal relationship (Fig. 3) involves the beginning of the rise in the prevalence of ASD in the early 1980s, coinciding again with the replacement of aspirin in babies and children with APAP due to concerns over Reye syndrome. Although it has been argued that aspirin was replaced by ibuprofen rather than APAP in the US in the early 1980s [32], this is contradicted by available data demonstrating that APAP was the drug of choice in the US when the pediatric use of aspirin was dramatically reduced [29,30], Furthermore, as pointed out by Saugstad [33], ibuprofen was not approved as a prescription drug for children in the US until 1989, more than 30 years after a formulation of APAP was first marketed for children. Finally, ibuprofen was not approved for over-the-counter use in children until 1995 [34], long after the measured prevalence of ASD began to increase (Fig. 3).
A third temporal correlation is shown in Fig. 3 in which the rate of ASD continued to climb as direct-to-consumer advertising in the US increased dramatically and then became a part of US culture. However, the actual use of APAP in the pediatric population has been poorly tracked as discussed above. Trends in use over time are complicated by multiple means of acquiring the drug: through administration by physicians in clinics and hospitals and by caregivers using over-the-counter formulations at home. Thus, while changes in the quantity and qualitative nature of ASD coincide with major events affecting pediatric APAP use (Fig. 3), the exact pattern of change over time cannot be accurately ascertained from the literature. Nevertheless, the use of APAP in babies and young children, which was a relatively uncommon occurrence half a century ago, is now extremely common.
One potential argument that APAP cannot cause ASD is that the rising rates of ASD over time are, at least in part, a consequence of changing diagnostic criteria, increased awareness, and other factors (discussed by co-author CDN and colleagues [35]). Based on this argument, it was concluded that no chemical can account for the increased rate of ASD [36,37]. However, careful analysis of epidemiological evidence strongly suggests that the perceived increase in ASD since 1980 is real, at least in part, and not entirely due to artificial inflation [35]. Furthermore, the view that increases in the incidence of ASD are not real cannot readily account for the changing ratio of regressive to infantile ASD observed in the early 1980s (Fig. 3). Perhaps more importantly, disparities in the prevalence of ASD measured in side-by-side cohorts [38,39] demonstrate that some environmental factor or factors, at least under certain circumstances, play a pivotal role in the induction of ASD [2]. Finally, a number of factors independent of epidemiological evidence point toward a causal role of early exposure to APAP in the induction of neurodevelopmental disorders, particularly ASD [2,3].
Other objections to the conclusion that early exposure to APAP causes ASD in susceptible children include the fact that an association does not prove causation [40]. On the other hand, causation cannot exist without association, and multiple independent associations coupled with other lines of independent evidence support causation. However, temporal associations in this case were complicated by several factors. For example, as pointed out above, the actual use of APAP in the pediatric population was not tracked well over time. In addition, factors affecting oxidative stress, the necessary co-factor in APAP-induced neurological injury (discussed in detail below), may change over time [41]. Furthermore, the idea that medical establishments and society in general might need to recalibrate diagnostics and the awareness of a rapidly increasing incidence of cognitive dysfunction seems reasonable. Such a recalibration could account for short-term shifts in data concerning the incidence of ASD. Nevertheless, it seems implausible to attribute the dramatic and steady 40-year increase in prevalence to such factors. Indeed, ASD, although known by other labels over time [42], has consistently been distinguished by a deficit in social awareness [43] and was viewed as rare by knowledgeable individuals in the US and independently in Europe at the time of its discovery 80 years ago [44,45].
Limited studies have attempted to ascertain the association between postnatal exposure to APAP and ASD in humans. Notably, Alemany et al. [26] recently observed an increase in ASD associated with the postnatal use of APAP in the DNBC. The analysis showed an unacceptably large odds ratio (1.30) for a common occurrence (postnatal APAP exposure), indicating that the postnatal exposure to APAP reported in this study accounts for a substantial number of cases of ASD. However, despite the inclusion of more than 60,000 children, the degree of uncertainty ranged from an odds ratio of 1.02 (clinically insignificant) to 1.66 (intolerable by any standard). Thus, it is not possible to draw firm conclusions from the study of Alemany et al. [26] on the importance of postnatal exposure to APAP in the pathogenesis of ASD. We have previously demonstrated that the common use of the drug in babies and children without oxidative stress (and thus not at risk for APAP-associated neurodevelopmental problems) interferes with multivariate analyses, such as the one performed by Alemany et al. [26], resulting in (1) underestimation of the impact of APAP on the incidence ofASD and (2) a lack of statistical power leading to confidence intervals that are too large to draw conclusions [2]. Since the lack of reliability of the multivariate analysis in this context was examined previously [2], it will not be discussed here. An additional problem with the analysis of data obtained from databases, such as the DNBC, is evident in the systematic review described above. This review casts doubt on the reliability of information pertaining to APAP use in large databases, which could adversely affect the reliability of the results obtained from the data analysis. Thus, results from multivariate analyses of large datasets do not provide a valid basis for asserting that early exposure to APAP might be safe for neurodevelopment.
The first study to indicate that pediatric use of APAP is associated with ASD was a survey-based, case-controlled study published by Schultz et al. [46], a physician who saw his son develop regressive ASD following a vaccination [47]. Schultz et al. [46] noted that APAP use with vaccination was associated with ASD. In cases in which APAP was not administered, no significant association with ASD was found. The odds ratios for ASD diagnosis following APAP exposure were striking, depending on the comparisons made, exceeding 20-fold in some cases [46]. Although the study by Schultz et al. [46] was small, the results were persuasive and comprised one piece of evidence of early exposure to APAP as a cause of ASD [2].
Several criticisms of the study of Schultz et al. [46] have been published, some of which can be readily dismissed. For example, one objection was that Schultz et al. [46] did not “estimate a sample size required for a study of this nature (a survey study).” [48] In response, Schultz [49] stated that, given that calculating a study’s appropriate sample size requires some foreknowledge of the size of the expected effect, the appropriate sample size could not have been calculated prior to initiation of the study. The fact that the comparisons were statistically significant does, in fact, demonstrate that the sample size was adequate.
The most common objection to the study of Schultz et al. [46] is that the selection of subjects from internet groups produced a “biased sample.” [40,48] The supposition that the study of Schultz et al. [46] was undermined by bias among the participants may explain why the study never affected clinical practice, did not stimulate follow-up studies, and was omitted more than once during critical considerations of the role of APAP exposure in neurodevelopmental outcomes [32,50]. Given the potential importance of the study of Schultz et al. [46], it is worth examining the potential bias of the cohort studied. The cohort was recruited from 2 internet-based groups in 2005 and 2006 after both Wakefield et al. [51] and Rimland [28] suggested that vaccines might cause ASD. Furthermore, the bias that vaccines cause ASD has persisted in parents of children with ASD [52,53], so it seems highly likely that the parents in the study of Schultz et al. [46] were biased in favor of the view that vaccines can induce ASD.
In contrast to biases related to vaccines, a review of the literature published at the time suggests that bias probably did not exist favoring the view that early exposure to APAP causes ASD in susceptible children. A PubMed search using the terms “paracetamol” or “acetaminophen” and “autism” revealed only four papers prior to 2006. None of the four studies suggested that APAP might cause ASD. The initial study, by Alberti et al. [54] in Italy, showed profound impairment of APAP metabolism in children with ASD and was published in 1999, several years prior to the study of Schultz et al. [46] However, Alberti et al. [54] did not suggest that exposure to APAP causes ASD. Furthermore, the study of Alberti et al. [54] was cited in PubMed-indexed journals only 3 times prior to 2006 [55-57], all within the context of understanding the physiology of ASD, not the cause. The study of Alberti et al. [54] was cited in the Alternative Medicine Review (not PubMed indexed) in 2002 [58], and APAP was listed by the author as a potentially neurotoxic compound in children with oxidative stress. However, concerns regarding APAP occupied only one line of a 25-page report that included a page-long discussion on the potential role of vaccines and vaccine components in the induction of ASD. In 2003, Torres at the Utah State University suggested that the use of antipyretics in general may lead to ASD [59]; however, the hypothesis was that the absence of fever, rather than the presence of APAP, might be a problem. This paper was not cited in the literature until 2009, and was, interestingly, cited in the context of the potential importance of vaccines, not APAP, in the etiology of ASD [60]. Furthermore, coauthor WP has been actively engaged with the community of parents of children with ASD and has observed that few parents, even in the past 5 years, have been aware of the view that early exposure to APAP can cause ASD in susceptible babies and children.
Thus, it seems highly likely that the parents surveyed in the study of Schultz et al. [46] were indeed biased in favor of the idea that vaccines cause ASD; however, it seems unlikely that they had a similar bias against APAP. Indeed, as Schultz explained, “The hypothesis that APAP causes ASD was completely unknown to the parents being surveyed. In fact, my study conducted in 2005 and 2006 was the first to explore this hypothesis.” (personal communication with coauthor WP, used with written permission.) It has been suggested that parents with ASD might try harder to recall information while searching for answers [40]; however, studies probing this issue have not found that parents of children with adverse outcomes have better recall [61]. Perhaps more importantly, the data provided by Schultz et al. [46] do not suggest that parents of children with ASD have better recall than parents of neurotypical children. The study of Schultz et al. [46] used yes or no questions, and the response rate to particular questions could be taken, at least in part, as a surrogate indicator of recall. Using the response rate as a metric, the data of Schultz et al. [46] revealed no evidence that parents of children with ASD had better recall than parents of neurotypical controls. For example, the answer rate was 100.0% for cases and controls when asked about their child’s APAP use in conjunction with vaccines, 83.1% and 85% for cases and controls, respectively, when asked about their child’s APAP use between 12 and 18 months of age, and 59.0% and 72.5% for cases and controls, respectively, when asked about their child’s exposure to ibuprofen between 12 and 18 months of age. Furthermore, Schultz specifically addressed the issue of recall by independently analyzing surveys with a greater time lapse since the events in question. As pointed out by Schultz [49], the results were robust and did not indicate that time had affected the outcome.
With the above discussion in mind, the conclusions of the study of Schultz et al. [46] can be amended. In cases in which the parents are likely biased toward the view that vaccines cause ASD, exposure to APAP rather than vaccines was likely a factor in the induction of ASD in their child. Furthermore, it is apparent that the dismissal of the study due to bias is unwarranted and not supported by any available information. Thus, the study of Schultz et al. [46] contributed evidence pointing to APAP use as a cause of neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children [2].
The metabolism of APAP is well characterized and provides considerable insight into how APAP can cause neurodevelopmental injury [41,62]. The human body processes APAP via three primary pathways (Fig. 4). Two of these pathways involve the addition of highly water-soluble structures: glucuronate via the glucuronide pathway or sulfate via the sulfation pathway. In adults, the addition of glucuronate predominates over the addition of sulfate [63], whereas in babies and children under the age of 9 years, the addition of sulfate predominates over the addition of glucuronate [63,64]. The third pathway also involves the addition of a highly water-soluble molecule (glutathione). The first step of this pathway involves the production of a highly toxic substance, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI). Fortunately, in healthy individuals, NAPQI is rapidly neutralized by glutathione (Fig. 4). Unfortunately, children with ASD tend to have an impaired ability to utilize the sulfate pathway [54,65,66]. Additionally, children with ASD tend to experience oxidative stress [3,67], which depletes glutathione [65]. Furthermore, APAP exposure significantly depletes glutathione [68], suggesting that repeated exposure to the drug is potentially more hazardous than a single exposure.
Although APAP metabolism is well characterized, a high degree of variability in APAP metabolism within the pediatric population has been observed, and the factors affecting this variability are poorly understood [69]. One factor affecting the metabolism of APAP is the presence of autoantibodies that impair folate transport to the brain, which is found in almost 3 quarters of children with ASD [70]. Since folate is necessary for the synthesis of glutathione, an impaired ability to detoxify NAPQI is expected in these children. Thus, many children with ASD have impaired sulfation and glutathione-dependent pathways for the clearance of APAP. A third pathway, glucuronidation, has been speculated to compensate for this problem [40]. However, the glucuronidation pathway is not upregulated by repeated exposure to APAP [71] and is a minor pathway in babies and children, as discussed above [63,64]. Furthermore, because some NAPQI is created regardless of the function of the other 2 pathways, failure in the glutathione-dependent pathway is expected to result in the accumulation of NAPQI and subsequent toxicity, even if the other 2 pathways are functional.
It is not surprising that both sulfation- and glutathione-dependent pathways are aberrant in the same population because they are metabolically connected [41,72,73]. Alterations in both pathways enhance oxidative stress and increase APAP toxicity. Unfortunately, even at levels of APAP that are currently considered acceptable, this situation will result in the exposure of some babies and children to levels of APAP toxicity that are much greater than those seen in typical, nonsusceptible individuals or in laboratory animals exposed to the same doses of APAP (Fig. 5).
In this narrative review and our previous narrative reviews on the safety of pediatric APAP use, we addressed several lines of evidence that might be considered controversial. We believe that considering multiple lives of evidence is necessary given the complexities particular to this topic. For example, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis by Tan et al. [74] at the University of Auckland considering almost 20 studies and a quarter of a million children less than 2 years of age raised no substantial flags concerning the safety of early exposure to APAP. Unfortunately, based on the approach used in the study by Tan et al. [74], the results obtained were expected regardless of whether early exposure to APAP was responsible for most cases of ASD. Tan et al. [74] noted that exposure rates to APAP in the pediatric population now approach 95%, a factor that precludes the identification of APAP as a causative agent in neurodevelopmental disorders using a multivariate analysis of large data sets [2]. Consistent with our recent results [5], Tan et al. [74] noted that the measures of adverse outcomes were limited to acute events rather than neurodevelopmental outcomes. As previously discussed, other factors impede the usefulness of such analyses, including the need for long-term monitoring of exposure from the time of conception, the inability to separate confounding factors from oxidative stress-inducing cofactors, and the use of intravenous formulations of APAP containing an antidote for toxicity in some studies. Indeed, an evaluation of the effect of early exposure to APAP on neurodevelopmental outcomes would require substantial effort that is unlikely to occur in the near future as previously discussed [5].
Studies in animal models are currently sufficient to conclude that early exposure to APAP causes neurodevelopmental problems [5]. The observation of APAP-induced neurodevelopmental problems in laboratory animals is robust, encompassing both laboratory rats and mice and a variety of study designs (see Patel et al. [2] and recent studies from the University of New Orleans [75,76]). However, studies have yet to recapitulate the symptoms of ASD, which remains a highly laudable goal of research in the field. Although it has been argued that “clinically relevant” doses of APAP should be used in such studies, it is expected that recapitulating conditions in susceptible humans using healthy laboratory animals will require higher drug doses than those commonly encountered by humans (Fig. 5). In summary, laboratory rats under ideal laboratory conditions will be more resistant to APAP-induced neurodevelopmental injury than humans that have significant problems metabolizing the drug. Not only are laboratory rats bred to be healthy under standard laboratory conditions, potentially reducing the genetic factors making them susceptible to disease, they are also fed an exceedingly healthy diet [2] and are often largely free of infections, environmental toxins, and other oxidative stress factors associated with ASD in humans. Taking this into account, current regulations stipulate that preclinical testing should include higher drug doses than those expected to be encountered by patients [77].
The failure of the medical community to accurately track APAP use in the pediatric population over time as well as its almost ubiquitous use identified in some studies (Fig. 2) reflects a high degree of acceptance of the drug. The incorrect assumption that babies react to APAP similarly to adults is a key factor in its current level of acceptance [5]. However, other factors undoubtedly contribute to this. For example, (1) critical studies in laboratory animals were conducted only recently; (2) most babies and children suffer no apparent serious adverse neurodevelopmental effects from APAP use; (3) severe adverse neurodevelopmental effects may not be diagnosed until long after drug exposure; (4) the diverse array of oxidative stress-inducing cofactors in APAP-induced neurodevelopmental injury creates a large and potentially confusing number of associations with neurodevelopmental injury; and (5) any severe adverse neurodevelopmental effects might be attributed to the indication for the drug.
Most clinicians and caregivers are not currently aware of the available knowledge concerning apparent adverse reactions to early APAP exposure in susceptible children. Conducting large long-term studies in human children may not be feasible as discussed above. However, this point may be irrelevant given that the preponderance of available evidence renders such a study unnecessarily risky and thus unethical. With this in mind, regulatory agencies and professional medical societies should move forward with the currently available information. The immediate goals are to first acknowledge and then promote awareness of the problem. Changes in medical practice should be implemented that effectively weigh the risks and benefits of neonatal and pediatric APAP use. Failure to implement change in medical practice currently constitutes disregard for the ample evidence of harm despite the absence of any valid rationale for the view that APAP might be safe for neurodevelopment. Finally, the ability of antidotes for APAP toxicity, such as N-acetylcysteine, to prevent APAP-induced neurodevelopmental injury could be probed.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the kind support provided by John Poulton, Susan Poulton, and Tabitha J. Parker. The authors also thank Susanne Meza-Keuthen for carefully reviewing the manuscript.
Fig. 1.
Summary of evidence pointing toward the induction of neurodevelopmental disorders by early exposure to acetaminophen (APAP). The numbering of individual lines of evidence is as in Table 1. References and more detailed descriptions of each line of evidence are listed in Table 1. The 20 lines of evidence are separated into 5 miscellaneous lines of evidence, with the remaining 15 lines of evidence divided evenly into 5 categories: Studies in animal models, associations with human activities, associations in time, postnatal observations, and molecular mechanism of action. Lines of evidence numbers 10 and 11 were derived from the same data, while lines of evidence numbers 14 and 16 were derived from the same study. These lines of evidence are therefore not independent, which is indicated by the connecting lines in the diagram. DNBC, Danish National Birth Cohort; CF, cystic fibrosis.
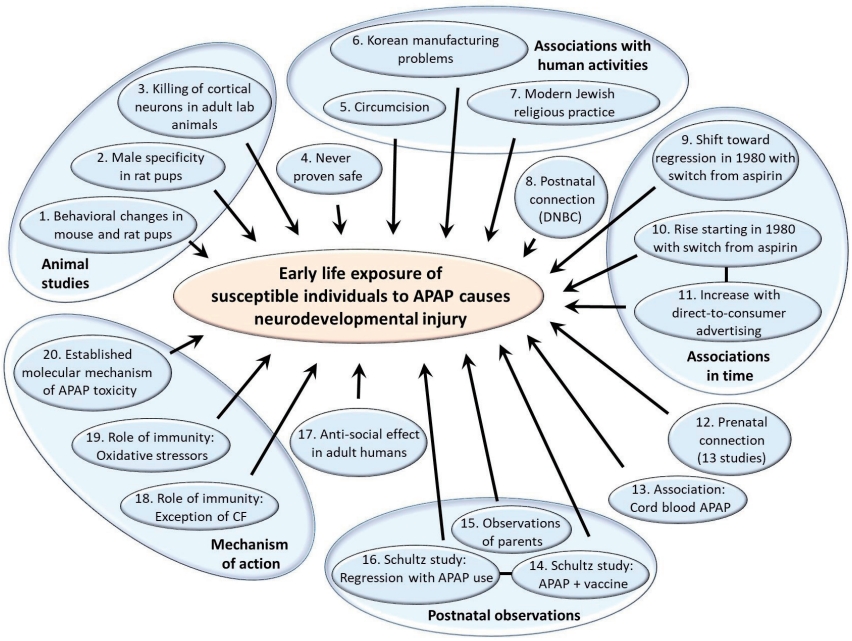
Fig. 2.
Studies tracking acetaminophen (APAP) use in the general population ≤5 years of age. In diagram A, the systematic search strategy is shown. The initial search was conducted of PubMed on August 25, 2022 without any restrictions on time frame. The search terms used were (acetaminophen or paracetamol)+(use or administration)+(infant or child or postnatal or pediatric or neonate or newborn or baby)-(review or mouse or mice or rat). The initial title review was conducted by co-author WP. The initial full-text review was conducted by co-author LZ, while the second and final full-text review was conducted by co-authors LZ and WP. In diagram B, variations in studies probing the use of APAP in babies and children younger than 6 years of age is illustrated. Results are shown for all 5 countries in which at least 3 studies using independent data sets have evaluated the use of APAP in babies and children under 6 years of age. In cases in which 2 studies used the same data set, the results are presented together. The number of babies/children in the study, their ages at the time of the study, and the years in which APAP use was measured are shown in the box attached to each data point. The lowest value shown for the country of Spain is the average of 3 similar values (49.1%, 51.4%, and 52.0%) from three studies using the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood in Spain data, 2 evaluating data from 2000–2003 [116,117] and one evaluating data from 2006–2007 [118].
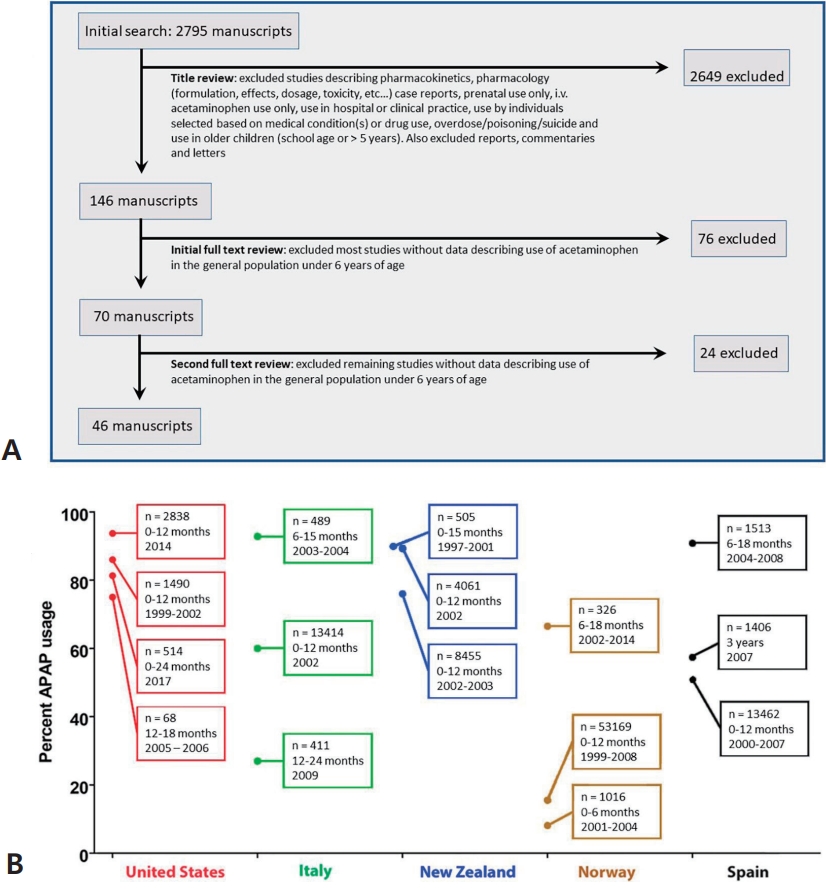
Fig. 3.
Temporal associations between the reported incidence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in California and factors affecting the use of acetaminophen (APAP). The prevalence of ASD in California as compiled by Nevison et al [35] is shown in the graph. The data are a composite of “snapshot” data (information collected at one point in time) from the California Department of Developmental Services (covering birth years 1970–2011) [35]. From 1982 to 1986, government warnings on using aspirin due to the association with Reye syndrome were issued from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration [119]. From 1990 to 2007, total spending on direct-to-consumer pharmaceutical advertising underwent great increases from $47 million to $5 billion [120]. In the inset, previously published survey data [28] from the Autism Research Institute and the Autism Society of America are shown [28]. The number of surveys that were collected within a given time frame are shown, and reports are separated into reports describing infantile (nonregressive or early-onset) ASD (solid line) and those describing regressive ASD (dashed line). The information in this diagram does not consider increases in use of glutathione-depleting compounds such as pesticides and plastic-associated chemicals that have occurred during the time frame shown. Given that oxidative stress is a co-factor in the induction of APAP-induced neurodevelopmental issues [2,3,41], such factors are expected to influence the incidence of ASD [41].
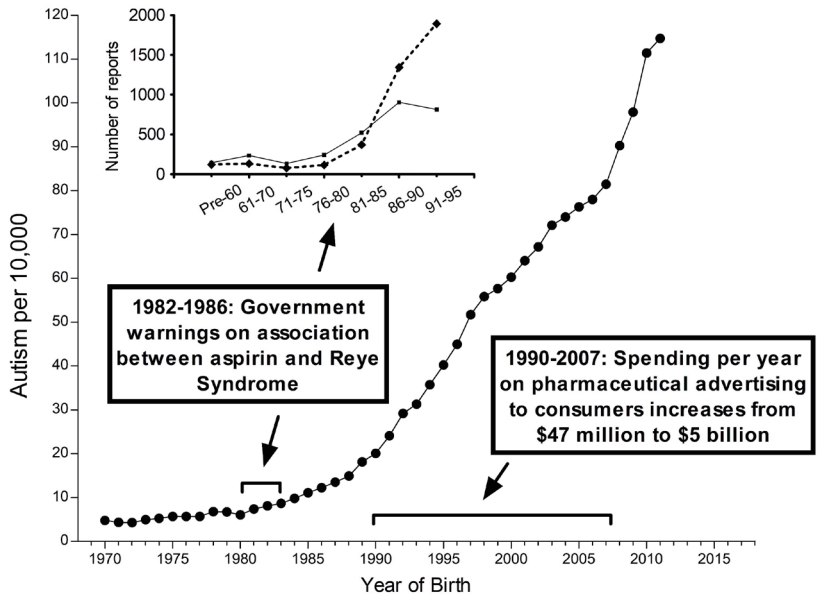
Fig. 4.
Metabolism of acetaminophen (APAP) in humans. The 3 pathways—glucuronidation, sulfation, and oxidation—followed by a reaction with glutathione are shown. The major pathway in babies and in children, sulfation, tends to be impaired in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This is expected to shunt more of the drug through the oxidative pathway, resulting in the production of excess N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), the toxic compound shown in the diagram. Unfortunately, children with ASD also tend to have a reduced ability to detoxify NAPQI, resulting in increased toxicity of APAP due to excess NAPQI.
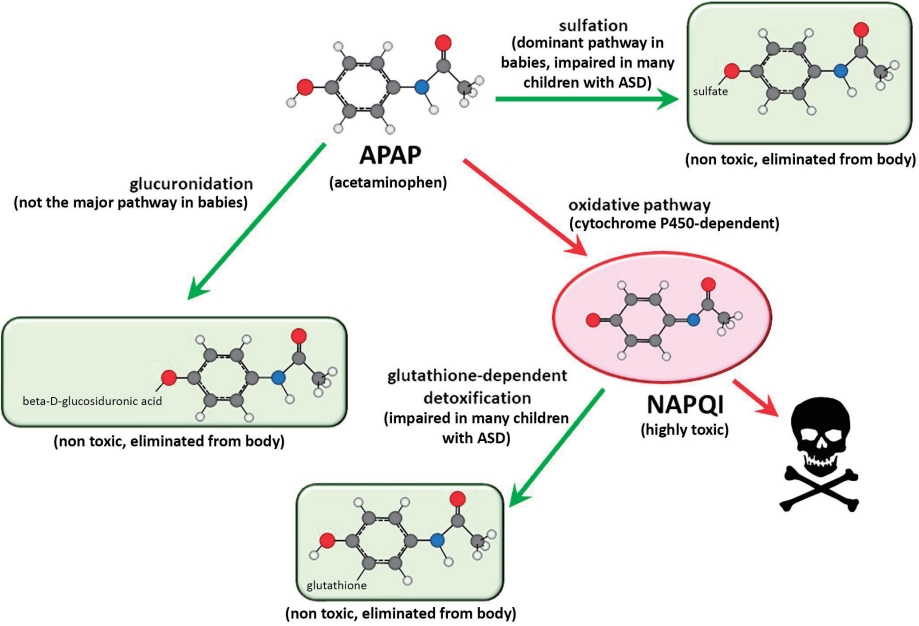
Fig. 5.
Schematic diagram illustrating relative sensitivities of laboratory animal pups and of human infants and children to acetaminophen (APAP)-induced neurodevelopmental injury. The diagram illustrates how laboratory conditions can be modified to enhance oxidative stress, thus increasing the sensitivity of the animals to APAP-induced neurodevelopmental injury. The schematic diagram illustrates that the sensitivity of healthy laboratory pups to APAP-induced neurodevelopmental injury is relatively homogenous and less broadly distributed than that of human babies and children. Further, the diagram illustrates that the sensitivity of healthy laboratory animal pups to APAP-induced neurodevelopmental injury is of lesser magnitude than that of at-risk human babies and children. In this model, exposures of laboratory animals can be made comparable to exposures in at-risk human babies and children by either increasing the dose of APAP in the laboratory pups, or increasing oxidative stress in the laboratory pups. Quantitative estimates of the difference in the risks between laboratory animal pups and human babies and children have not been made, and the schematic diagram is not meant to indicate quantitative values.
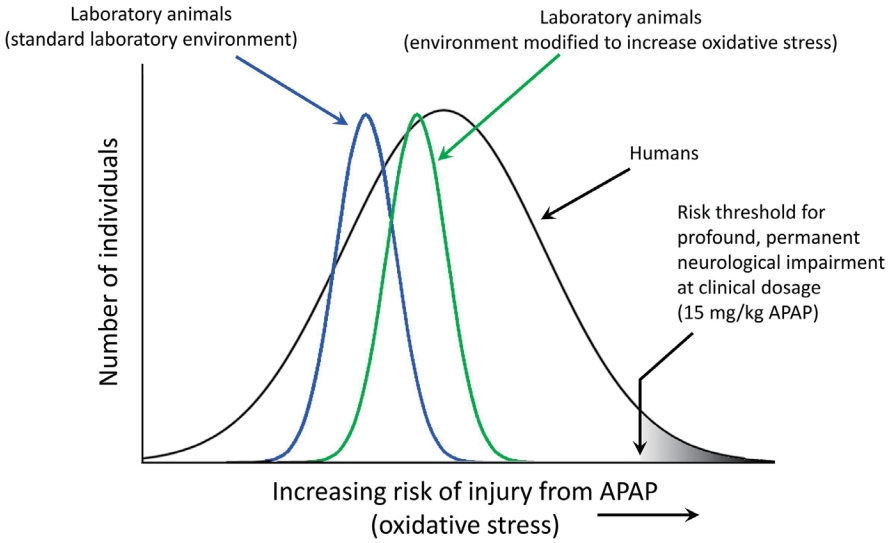
Table 1.
Current evidence indicating that early exposure of individuals to APAP causes long-term neurodevelopmental problems
| Summary of evidence leading to the conclusion that early life exposure to APAP in susceptible children causes neurodevelopmental injury | Relevance to prenatal versus postnatal exposure: nature of evidence |
| 1. Laboratory mice and rats develop long-term brain damage and exhibit behavioral changes following early life APAP exposure at doses that are similar to or even less than doses received by human babies and children.1 [2,78-81] | Points toward the postnatal period more so than the prenatal period: laboratory animal studies |
| 2. In laboratory rats, APAP affects the developing male brain more than the female brain. [80] ASD also affects males more than females. [82] | Postnatal: laboratory animal studies |
| 3. APAP causes death of cortical neurons in adult laboratory rats at concentrations lower than it causes liver failure. [13] Affected cortical neurons are implicated in ASD. [83,84] | Postnatal: laboratory animal studies |
| 4. Despite the fact that APAP targets the brain, APAP use in babies and children was only proven safe for acute side effects, not for neurodevelopment. [5] | Postnatal: systematic review of the literature |
| 5. Male circumcision, often performed using APAP as an analgesic, is associated with a dramatic increase in the risk for early-onset (infantile) ASD. [39] | Postnatal: association with human behavior |
| 6. An unexpectedly high prevalence of ASD was identified in South Korea. [85,86] where APAP-containing products for children were repeatedly found to contain amounts of drug exceeding the package label. [87] | Postnatal: association with human behavior |
| 7. Ultra-Orthodox Jews [88] and Arabs [88,89] in Israel have a reported prevalence of ASD less than half of that of other Israelis. Israelis have high rates of circumcision concomitant with ritual use of alcohol. Alcohol use depletes glutathione, particularly in the brain, [90] thereby increasing susceptibility to APAP-induced injury. Thus, use of traditional circumcision practices without APAP by some communities in Israel could account in part for their lower rates of ASD compared to other Israelis. | Postnatal: association with human behavior |
| 8. Analysis of 61,430 babies in the Danish National Birth Cohort found an odds ratio of 1.3 (confidence interval, 1.02–1.66) for ASD associated with postnatal APAP exposure. [26] This result is especially concerning since heav y use of the drug among nonsusceptible children will cause dramatic underestimation of the actual risk. [2] | Postnatal use: epidemiologic study with some control for indication |
| 9. The ratio of regressive to infantile ASD rose at the same time as pediatric APAP use rose, [28] after aspirin was associated with Reye syndrome. [3] | Postnatal: temporal association |
| 10. The incidence of ASD began to increase in the early 1980s, coinciding with the increase in APAP use after aspirin was associated with Reye syndrome. [3] | Postnatal: temporal association |
| 11. The incidence of ASD has steadily increased3 as direct-to-consumer advertising [91] and perhaps other factors have driven up use of pharmaceutical products. | Prenatal and postnatal: temporal association |
| 12. Use of APAP in pregnant women is associated with long-term effects that include lower IQ, increased ASD, and increased ADHD. [26,92-104] | Prenatal use: epidemiologic studies, some with controls for indication |
| 13. Levels of APAP in cord blood are associated with ASD. [96] | Prenatal and postnatal: association |
| 14. APAP given alongside vaccine administration but not vaccination alone is associated with ASD. [46] | Postnatal: observation made in a small case-controlled study |
| 15. Many parents believe that their children’s ASD was induced by a vaccine based on their own observations or the observations of trusted social networks. [52,53] APAP is frequently used with vaccinations, although vaccinations alone do not cause ASD. | Postnatal: parent’s observations |
| 16. APAP use during early childhood is associated with a dramatic increase in regressive ASD. [46] | Postnatal: observation made in a small case-controlled study |
| 17. APAP use in adults temporarily blunts social trust [105] and awareness, [106] emotional responses to external stimuli, [107] and the ability to identify errors, [108] indicating that the drug targets regions of the brain affected in patients with ASD. | Postnatal: observation in adult humans |
| 18. Cystic fibrosis is associated with unusually efficient (effective) metabolism of APAP, [109,110] and some evidence suggests that the prevalence of ASD may be very low in patients with cystic fibrosis. [3] | Prenatal and postnatal: evaluation of molecular mechanism |
| 19. Genetic and immune factors associated with an increased risk of ASD have a detrimental effect on the body’s ability to metabolize APAP. [3,54,70] | Prenatal and postnatal: evaluation of molecular mechanism |
| 20. APAP is known to be highly toxic in the presence of oxidative stress. The mechanism by which this toxicity occurs has been established for decades, [111] and involves the formation of the potent toxin, NAPQI. [112-114] More recent studies indicate that concomitant mitochondrial damage [115] is important in the process. | Prenatal and postnatal: evaluation of molecular mechanism |
References
1. World Health Organization. World Health Organization model list of essential medicines for children – 8th list. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization, 2021.
2. Patel E, Jones Iii JP 3rd, Bono-Lunn D, Kuchibhatla M, Palkar A, Cendejas Hernandez J, et al. The safety of pediatric use of paracetamol (acetaminophen): a narrative review of direct and indirect evidence. Minerva Pediatr 2022;74:774–88.

3. Parker W, Hornik CD, Bilbo S, Holzknecht ZE, Gentry L, Rao R, et al. The role of oxidative stress, inflammation and acetaminophen exposure from birth to early childhood in the induction of autism. J Int Med Res 2017;45:407–38.




4. Patel R, Sushko K, van den Anker J, Samiee-Zafarghandy S. Long-term safety of prenatal and neonatal exposure to paracetamol: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Pub Health 2022;19:2128.



5. Cendejas-Hernandez J, Sarafian J, Lawton V, Palkar A, Anderson L, Lariviere V, et al. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) use in infants and children was never shown to be safe for neurodevelopment: a systematic review with citation tracking. Eur J Pediatr 2022;181:1835–57.




6. Maclean D, Peters TJ, Brown RA, McCathie M, Baines GF, Robertson PG. Treatment of acute paracetamol poisoning. Lancet 1968;2:849–52.


8. Davidson DG, Eastham WN. Acute liver necrosis following overdose of paracetamol. Br Med J 1966;2:497–9.



9. Yaffe SJ, Avery ME, Gold AP, Kenny FM, Riley HD Jr, Schafer IA, et al. Drug testing in children: FDA regulations. Pediatrics 1969;43:463–5.



10. Green MD, Shires TK, Fischer LJ. Hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen in neonatal and young rats. I. Age-related changes in susceptibility. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1984;74:116–24.

11. Bao Y, Wang P, Shao X, Zhu J, Xiao J, Shi J, et al. Acetaminophen-induced liver injury alters expression and activities of cytochrome P450 enzymes in an age-dependent manner in mouse liver. Drug Metab Dispos 2020;48:326–36.



12. Viberg H, Eriksson P, Gordh T, Fredriksson A. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) administration during neonatal brain development affects cognitive function and alters its analgesic and anxiolytic response in adult male mice. Toxicol Sci 2014;138:139–47.


13. Posadas I, Santos P, Blanco A, Muñoz-Fernández M, Ceña V. Acetaminophen induces apoptosis in rat cortical neurons. PLoS One 2010;5:e15360.



14. Bauer AZ, Swan SH, Kriebel D, Liew Z, Taylor HS, Bornehag CG, et al. Paracetamol use during pregnancy — a call for precautionary action. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2021;17:757–66.




15. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). ACOG response to consensus statement on paracetamol use during pregnancy Washington, DC. ACOG, 2021.
16. Khan FY, Kabiraj G, Ahmed MA, Adam M, Mannuru SP, Ramesh V, et al. A systematic review of the link between autism spectrum disorder and acetaminophen: a mystery to resolve. Cureus 2022;14:e26995.



17. Bührer C, Endesfelder S, Scheuer T, Schmitz T. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and the developing brain. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:11156.



18. Miners JO, Robson RA, Birkett DJ. Paracetamol metabolism in pregnancy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1986;22:359–62.



19. Cresteil T. Onset of xenobiotic metabolism in children: toxicological implications. Food Addit Contam 1998;15 Suppl:45–51.


20. Buckfire LJ. Tylenol and autism and ADHD lawsuits. National Law Rev 2022;XIII(277). Available from: https://www.natlawreview.com/article/tylenol-and-autism-and-adhd-lawsuits.
21. Asher MI, Keil U, Anderson HR, Beasley R, Crane J, Martinez F, et al. International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC): rationale and methods. Eur Respir J 1995;8:483–91.


22. Olsen J, Melbye M, Olsen SF, Sørensen TI, Aaby P, Andersen AM, et al. The Danish National Birth Cohort--its background, structure and aim. Scand J Pub Health 2001;29:300–7.

23. Inoue K, Ritz B, Ernst A, Tseng WL, Yuan Y, Meng Q, et al. Behavioral problems at age 11 years after prenatal and postnatal exposure to acetaminophen: parent-reported and self-reported outcomes. Am J Epidemiol 2021;190:1009–20.




24. Ertmann RK, Møller JJ, Waldorff FB, Siersma V, Reventlow S, Söderström M. The majority of sick children receive paracetamol during the winter. Danish Med J 2012;59:A4555.
25. Boyd A, Thomas R, Hansell AL, Gulliver J, Hicks LM, Griggs R, et al. Data resource profile: the ALSPAC birth cohort as a platform to study the relationship of environment and health and social factors. Int J Epidemiol 2019;48:1038–9k.




26. Alemany S, Avella-García C, Liew Z, García-Esteban R, Inoue K, Cadman T, et al. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to acetaminophen in relation to autism spectrum and attentiondeficit and hyperactivity symptoms in childhood: meta-analysis in six European population-based cohorts. Eur J Epidemiol 2021;36:993–1004.




27. Hawkins N, Golding J. A survey of the administration of drugs to young infants. The Alspac Survey Team. Avon Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1995;40:79–82.



28. Rimland B. The autism increase: research needed on the vaccine connection. Autism Res Rev Intl 2000;14:3.
29. Rahwan GL, Rahwan RG. Aspirin and Reye’s syndrome: the change in prescribing habits of health professionals. Drug Intell Clin Pharmacol 1986;20:143–5.


30. Arrowsmith JB, Kennedy DL, Kuritsky JN, Faich GA. National patterns of aspirin use and Reye syndrome reporting, United States, 1980 to 1985. Pediatrics 1987;79:858–63.



31. Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Surgeon General's advisory on the use of salicylates and Reye syndrome. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1982;31:289–90.

32. van den Anker JN, Allegaert K. Acetaminophen use in pregnant women and their neonates: safe or unsafe till proven otherwise? Neonatology 2020;117:249–51.



33. Saugstad OD. Acetaminophen and the developing brain: reason for concern? Neonatology 2020;117:245–8.



34. Motrin [Internet]. New Brunswick (NJ): Johnson & Johnson Consumer Inc.; c2022 [cited 2022 Aug 30]. Available from: https://www.motrin.com/safety-dosing/faq.
35. Nevison C, Blaxill M, Zahorodny W. California autism prevalence trends from 1931 to 2014 and comparison to national ASD data from IDEA and ADDM. J Autism Dev Disord 2018;48:4103–17.




36. Luterman S. Contentious study prompts backlash from autism researchers [Internet]. Spectrum; 2021 August 11 [cited 2022 Aug 30]. Available from: https://www.spectrumnews.org/news/contentious-study-prompts-backlash-from-autism-researchers/.
37. Grinker RR. Offit Paul: autism’s false prophets: bad science, risky medicine, and the search for a cure. J Autism Dev Disord 2009;39:544–6.


38. Hoang VM, Le TV, Chu TTQ, Le BN, Duong MD, Thanh NM, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders and their relation to selected socio-demographic factors among children aged 18–30 months in northern Vietnam, 2017. Int J Mental Health Syst 2019;13:29.




39. Frisch M, Simonsen J. Ritual circumcision and risk of autism spectrum disorder in 0- to 9-year-old boys: national cohort study in Denmark. J R Soc Med 2015;108:266–79.




40. Kennon-McGill S, McGill MR. Extrahepatic toxicity of acetaminophen: critical evaluation of the evidence and proposed mechanisms. J Clin Transl Res 2018;3:297–310.

41. Good P. Evidence the U.S. autism epidemic initiated by acetaminophen (Tylenol)is aggravated by oral antibiotic amoxicillin/ clavulanate (Augmentin) and now exponentially by herbicide glyphosate (Roundup). Clin Nutr ESPEN 2018;23:171–83.


42. Barahona-Corrêa JB, Filipe CN. A concise history of Asperger syndrome: the short reign of a troublesome diagnosis. Front Psychol 2015;6:2024.

43. Hodges H, Fealko C, Soares N. Autism spectrum disorder: definition, epidemiology, causes, and clinical evaluation. Transl Pediatr 2020;9(Suppl 1): S55–65.



44. Asperger H. Die “autistischen psychopathen” im kindesalter. Archiv Psychiatr Nervenkrankheit 1944;117:76–136.


45. Kanner L. Autistic disturbances of affective contact. Nervous Child 1943;2:217–50.
46. Schultz ST, Klonoff-Cohen HS, Wingard DL, Akshoomoff NA, Macera CA, Ji M. Acetaminophen (paracetamol) use, measlesmumps-rubella vaccination, and autistic disorder. The results of a parent survey. Autism 2008;12:293–307.



47. Schultz S. Understanding autism: my quest for Nathan. Austin (TX): Schultz Publishing LLC, 2013.
48. Cox AR, McDowell S. A response to the article on the association between paracetamol/acetaminophen: use and autism by Stephen T. Schultz. Autism 2009;13:123. –4. author reply, 124-5.



49. Schultz ST. Response to the letter by Cox and McDowell: association of paracetamol/acetaminophen use and autism. Autism 2009;13:124–5.


50. Di Pietrantonj C, Rivetti A, Marchione P, Debalini MG, Demicheli V. Vaccines for measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2021;4:CD004407.
51. Wakefield AJ, Murch SH, Anthony A, Linnell J, Casson DM, Malik M, et al. Ileal-lymphoid-nodular hyperplasia, non-specific colitis, and pervasive developmental disorder in children. Lancet 1998;351:637–41.

52. Freed GL, Clark SJ, Butchart AT, Singer DC, Davis MM. Parental vaccine safety concerns in 2009. Pediatrics 2010;125:654–9.



53. Bazzano A, Zeldin A, Schuster E, Barrett C, Lehrer D. Vaccinerelated beliefs and practices of parents of children with autism spectrum disorders. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil 2012;117:233–42.



54. Alberti A, Pirrone P, Elia M, Waring RH, Romano C. Sulphation deficit in “low-functioning” autistic children: a pilot study. Biol Psychiatr 1999;46:420–4.

55. Posey DJ, McDougle CJ. The pathophysiology and treatment of autism. Curr Psychiatr Rep 2001;3:101–8.


56. Horvath K, Perman JA. Autism and gastrointestinal symptoms. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2002;4:251–8.



57. Erickson CA, Stigler KA, Corkins MR, Posey DJ, Fitzgerald JF, McDougle CJ. Gastrointestinal factors in autistic disorder: a critical review. J Autism Dev Disord 2005;35:713–27.



58. Kidd PM. Autism, an extreme challenge to integrative medicine. Part 1: the knowledge base. Altern Med Rev 2002;7:292–316.

59. Torres AR. Is fever suppression involved in the etiology of autism and neurodevelopmental disorders? BMC Pediatr 2003;3:9.




60. Ewing GE. What is regressive autism and why does it occur? Is it the consequence of multi-systemic dysfunction affecting the elimination of heavy metals and the ability to regulate neural temperature? North Am J Med Sci 2009;1:28–47.
61. Infante-Rivard C, Jacques L. Empirical study of parental recall bias. Am J Epidemiol 2000;152:480–6.


62. Shaw W. Evidence that increased acetaminophen use in genetically vulnerable children appears to be a major cause of the epidemics of autism, attention deficit with hyperactivity, and asthma. J Restor Med 2013;2:1–16.

63. Miller RP, Roberts RJ, Fischer LJ. Acetaminophen elimination kinetics in neonates, children, and adults. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1976;19:284–94.



64. Cook SF, Stockmann C, Samiee-Zafarghandy S, King AD, Deutsch N, Williams EF, et al. Neonatal maturation of paracetamol (acetaminophen) glucuronidation, sulfation, and oxidation based on a parent-metabolite population pharmacokinetic model. Clin Pharmacokinet 2016;55:1395–411.




65. Geier DA, Kern JK, Garver CR, Adams JB, Audhya T, Geier MR. A prospective study of transsulfuration biomarkers in autistic disorders. Neurochem Res 2009;34:386–93.



66. Pagan C, Benabou M, Leblond C, Cliquet F, Mathieu A, Lemière N, et al. Decreased phenol sulfotransferase activities associated with hyperserotonemia in autism spectrum disorders. Transl Psychiatr 2021;11:23.


67. Bilbo SD, Nevison CD, Parker W. A model for the induction of autism in the ecosystem of the human body: the anatomy of a modern pandemic? Microb Ecol Health Dis 2015;26:26253.



68. Nuttall SL, Khan JN, Thorpe GH, Langford N, Kendall MJ. The impact of therapeutic doses of paracetamol on serum total antioxidant capacity. J Clin Pharm Ther 2003;28:289–94.



69. Krasniak AE, Knipp GT, Svensson CK, Liu W. Pharmacogenomics of acetaminophen in pediatric populations: a moving target. Front Genet 2014;5:314.



70. Frye RE, Sequeira JM, Quadros EV, James SJ, Rossignol DA. Cerebral folate receptor autoantibodies in autism spectrum disorder. Mol Psychiatr 2013;18:369–81.


71. Krekels EH, van Ham S, Allegaert K, de Hoon J, Tibboel D, Danhof M, et al. Developmental changes rather than repeated administration drive paracetamol glucuronidation in neonates and infants. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2015;71:1075–82.




72. Price VF, Jollow DJ. Effects of sulfur-amino acid-deficient diets on acetaminophen metabolism and hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1989;101:356–69.


73. Glazenburg EJ, Jekel-Halsema IM, Scholtens E, Baars AJ, Mulder GJ. Effects of variation in the dietary supply of cysteine and methionine on liver concentration of glutathione and “active sulfate” (PAPS) and serum levels of sulfate, cystine, methionine and taurine: relation to the metabolism of acetaminophen. J Nutr 1983;113:1363–73.


74. Tan E, Braithwaite I, McKinlay CJD, Dalziel SR. Comparison of acetaminophen (paracetamol) with ibuprofen for treatment of fever or pain in children younger than 2 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2020;3:e2022398.



75. Herrington JA, Guss Darwich J, Harshaw C, Brigande AM, Leif EB, Currie PJ. Elevated ghrelin alters the behavioral effects of perinatal acetaminophen exposure in rats. Dev Psychobiol 2022;64:e22252.



76. Harshaw C, Warner AG. Interleukin-1β-induced inflammation and acetaminophen during infancy: distinct and interactive effects on social-emotional and repetitive behavior in C57BL/6J mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2022;220:173463.


77. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Estimating the maximum safe starting dose in initial clinical trials for therapeutics in adult healthy volunteers. . Rockville (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2005.
78. Suda N, Cendejas Hernandez J, Poulton J, Jones JP, Konsoula Z, Smith C, et al. Therapeutic doses of acetaminophen with co-administration of cysteine and mannitol during early development result in long term behavioral changes in laboratory rats. PLoS One 2021;16:e0253543.



79. Philippot G, Gordh T, Fredriksson A, Viberg H. Adult neurobehavioral alterations in male and female mice following developmental exposure to paracetamol (acetaminophen): characterization of a critical period. J Appl Toxicol 2017;37:1174–81.



80. Dean SL, Knutson JF, Krebs-Kraft DL, McCarthy MM. Prostaglandin E2 is an endogenous modulator of cerebellar development and complex behavior during a sensitive postnatal period. Eur J Neurosci 2012;35:1218–29.



81. Philippot G, Hosseini K, Yakub A, Mhajar Y, Hamid M, Buratovic S, et al. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and its effect on the developing mouse brain. Front Toxicol 2022;4:867748.



82. McCarthy MM, Wright CL. Convergence of sex differences and the neuroimmune system in autism spectrum disorder. Biol Psychiatr 2017;81:402–10.



83. Donovan AP, Basson MA. The neuroanatomy of autism - a developmental perspective. J Anat 2017;230:4–15.




84. Casanova MF, Sokhadze EM, Casanova EL, Opris I, Abujadi C, Marcolin MA, et al. Translational neuroscience in autism: from neuropathology to transcranial magnetic stimulation therapies. Psychiatr Clin North Am 2020;43:229–48.


85. Kim YS, Leventhal BL, Koh YJ, Fombonne E, Laska E, Lim EC, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders in a total population sample. Am J Psychiatr 2011;168:904–12.


86. Baird G. 2.64% of South Korean children aged 7 to 12 have autism spectrum disorders. Evid Based Mental Health 2012;15:11.

87. Hall C, Smith M. Increased cGMP enforcement has gone international: South Korean action against Johnson & Johnson serves as warning. Philadelphia (PA): Saul Ewing LLP, 2013.
88. Raz R, Weisskopf MG, Davidovitch M, Pinto O, Levine H. Differences in autism spectrum disorders incidence by subpopulations in Israel 1992-2009: a total population study. J Autism Dev Disord 2015;45:1062–9.




89. Levaot Y, Meiri G, Dinstein I, Menashe I, Shoham-Vardi I. Autism prevalence and severity in Bedouin-Arab and Jewish communities in Southern Israel. Comm Meantal Health J 2019;55:156–60.


90. Guerri C, Grisolía S. Changes in glutathione in acute and chronic alcohol intoxication. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1980;13 Suppl 1:53–61.


91. Donohue J. A history of drug advertising: the evolving roles of consumers and consumer protection. Milbank Q 2006;84:659–99.



92. Tovo-Rodrigues L, Schneider BC, Martins-Silva T, Del-Ponte B, Loret de Mola C, Schuler-Faccini L, et al. Is intrauterine exposure to acetaminophen associated with emotional and hyperactivity problems during childhood? Findings from the 2004 Pelotas birth cohort. BMC Psychiatr 2018;18:368.




93. Vlenterie R, Wood ME, Brandlistuen RE, Roeleveld N, van Gelder MM, Nordeng H. Neurodevelopmental problems at 18 months among children exposed to paracetamol in utero: a propensity score matched cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 2016;45:1998–2008.



94. Liew Z, Ritz B, Virk J, Arah OA, Olsen J. Prenatal use of acetaminophen and child IQ: a Danish cohort study. Epidemiology 2016;27:912–8.


95. Liew Z, Bach CC, Asarnow RF, Ritz B, Olsen J. Paracetamol use during pregnancy and attention and executive function in offspring at age 5 years. Int J Epidemiol 2016;45:2009–17.


96. Ji Y, Azuine RE, Zhang Y, Hou W, Hong X, Wang G, et al. Association of cord plasma biomarkers of in utero acetaminophen exposure with risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder in childhood. JAMA Psychiatr 2020;77:180–9.



97. Avella-Garcia CB, Julvez J, Fortuny J, Rebordosa C, Garcia-Esteban R, Galan IR, et al. Acetaminophen use in pregnancy and neurodevelopment: attention function and autism spectrum symptoms. Int J Epidemiol 2016;45:1987–96.


98. Skovlund E, Handal M, Selmer R, Brandlistuen RE, Skurtveit S. Language competence and communication skills in 3-yearold children after prenatal exposure to analgesic opioids. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2017;26:625–34.



99. Liew Z, Ritz B, Rebordosa C, Lee PC, Olsen J. Acetaminophen use during pregnancy, behavioral problems, and hyperkinetic disorders. JAMA Pediatr 2014;168:313–20.


100. Liew Z, Ritz B, Virk J, Olsen J. Maternal use of acetaminophen during pregnancy and risk of autism spectrum disorders in childhood: a Danish national birth cohort study. Autism Res 2016;9:951–8.

101. Ystrom E, Gustavson K, Brandlistuen RE, Knudsen GP, Magnus P, Susser E, et al. Prenatal exposure to acetaminophen and risk of ADHD. Pediatrics 2017;140:e20163840.




102. Thompson JM, Waldie KE, Wall CR, Murphy R, Mitchell EA. Associations between acetaminophen use during pregnancy and ADHD symptoms measured at ages 7 and 11 years. PLoS One 2014;9:e108210.



103. Stergiakouli E, Thapar A, Davey Smith G. Association of acetaminophen use during pregnancy with behavioral problems in childhood: evidence against confounding. JAMA Pediatr 2016;170:964–70.



104. Brandlistuen RE, Ystrom E, Nulman I, Koren G, Nordeng H. Prenatal paracetamol exposure and child neurodevelopment: a sibling-controlled cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 2013;42:1702–13.



105. Roberts ID, Krajbich I, Way BM. Acetaminophen influences social and economic trust. Sci Rep 2019;9:4060.




106. Dewall CN, Macdonald G, Webster GD, Masten CL, Baumeister RF, Powell C, et al. Acetaminophen reduces social pain: behavioral and neural evidence. Psychol Sci 2010;21:931–7.



107. Durso GRO, Luttrell A, Way BM. Over-the-counter relief from pains and pleasures alike: acetaminophen blunts evaluation sensitivity to both negative and positive stimuli. Psychol Sci 2015;26:750–8.




108. Randles D, Kam JWY, Heine SJ, Inzlicht M, Handy TC. Acetaminophen attenuates error evaluation in cortex. Social Cognit Affective Neurosci 2016;11:899–906.



109. Hutabarat RM, Unadkat JD, Kushmerick P, Aitken ML, Slattery JT, Smith AL. Disposition of drugs in cystic fibrosis. III. Acetaminophen. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1991;50:695–701.


110. Kearns GL. Hepatic drug metabolism in cystic fibrosis: recent developments and future directions. Ann Pharmacother 1993;27:74–9.



111. Guengerich FP. A history of the roles of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the toxicity of drugs. Toxicol Res 2021;37:1–23.




112. Albano E, Rundgren M, Harvison PJ, Nelson SD, Moldéus P. Mechanisms of N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine cytotoxicity. Mol Pharmacol 1985;28:306–11.


113. Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Potter WZ, Davis DC, Gillette JR, Brodie BB. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. I. Role of drug metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1973;187:185–94.


114. Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Potter WZ, Gillette JR, Brodie BB. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis.IV. Protective role of glutathione. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1973;187:211–7.


115. Du K, Farhood A, Jaeschke H. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant Mito-Tempo protects against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 2017;91:761–73.




116. Garcia-Marcos L, González-Díaz C, Garvajal-Urueña I, PacSa MR, Busquets-Monge RM, Suárez-Varela MM, et al. Early exposure to paracetamol or to antibiotics and eczema at school age: modification by asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2010;21:1036–42.


117. Murphy R, Stewart AW, Braithwaite I, Beasley R, Hancox RJ, Mitchell EA. Association between paracetamol use in infancy or childhood with body mass index. Obesity 2015;23:1030–8.



118. Gonzalez-Barcala FJ, Pertega S, Perez Castro T, Sampedro M, Sanchez Lastres J, San Jose Gonzalez MA, et al. Exposure to paracetamol and asthma symptoms. Eur J Pub Health 2013;23:706–10.

119. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21. Rockville (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2017.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


