1. Fitzgerald RK, Davis AT, Hanson SJ. Multicenter analysis of the factors associated with unplanned extubation in the PICU. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2015;16:e217-23.


3. Smith HAB, Besunder JB, Betters KA, Johnson PN, Srinivasan V, Stormorken A, et al. 2022 Society of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines on prevention and management of pain, agitation, neuromuscular blockade, and delirium in critically Ill pediatric patients with consideration of the ICU environment and early mobility. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2022;23:e74-110.


6. Long D, Gibbons K, Le Brocque R, Schults JA, Kenardy J, Dow B. Midazolam exposure in the paediatric intensive care unit predicts acute post-traumatic stress symptoms in children. Australian Critical Care 2022;35:408-14.


7. Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, Ely EW, Gélinas C, Dasta JF, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 2013;41:263-306.

11. EndNote. 20 ed. Philadelphia (PA): Clarivate, 2013.
13. Sterne JAC, Savovic J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019;366:l4898.


15. Iorio A, Spencer FA, Falavigna M, Alba C, Lang E, Burnand B, et al. Use of GRADE for assessment of evidence about prognosis: rating confidence in estimates of event rates in broad categories of patients. BMJ 2015;350:h870.


17. R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 4.2.1 ed. Vienna (Austria): R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2022.
18. Schwarzer G. meta: General Package for Meta-Analysis 2022. v6.0.0 [Internet]. GitHub, Inc.; [cited 2022 May 24]. Available from:
https://github.com/guido-s/meta.
19. Sean Mcgrath XZ, Steele R, Benetti A. metamedian: Meta-analysis of Medians 2022. v0.1.6 [Internet]. GitHub, Inc.; [cited 2023 May 1]. Available from:
https://github.com/stmcg/metamedian.
20. Cooper H, Hedges LV, Valentine JC. The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis, 2nd ed. New York (NY): Russell Sage Foundation, 2009;xvi, 615-xvi, p.
23. Knapp G, Hartung J. Improved tests for a random effects meta-regression with a single covariate. Stat Med 2003;22:2693-710.


24. Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002;21:1539-58.


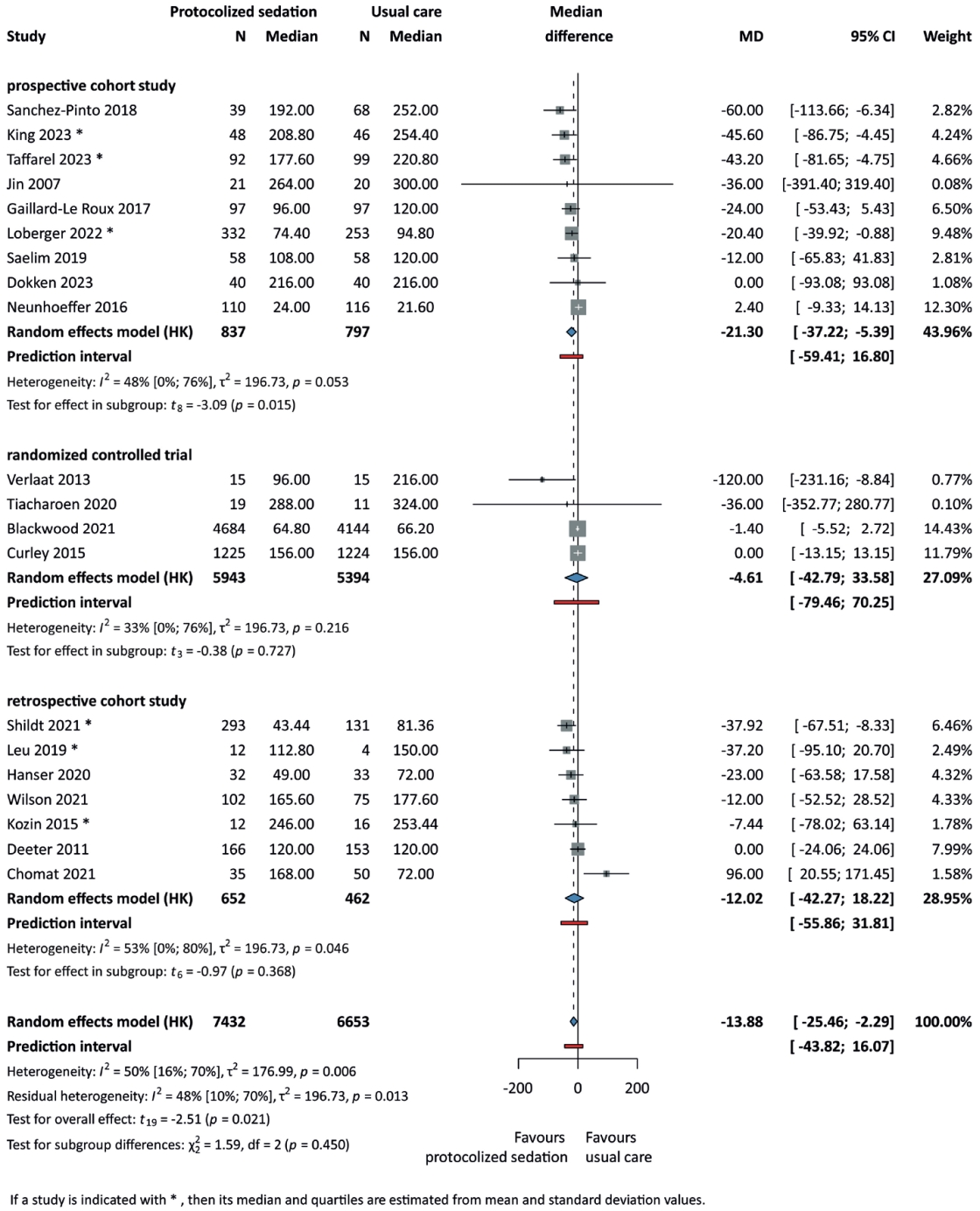
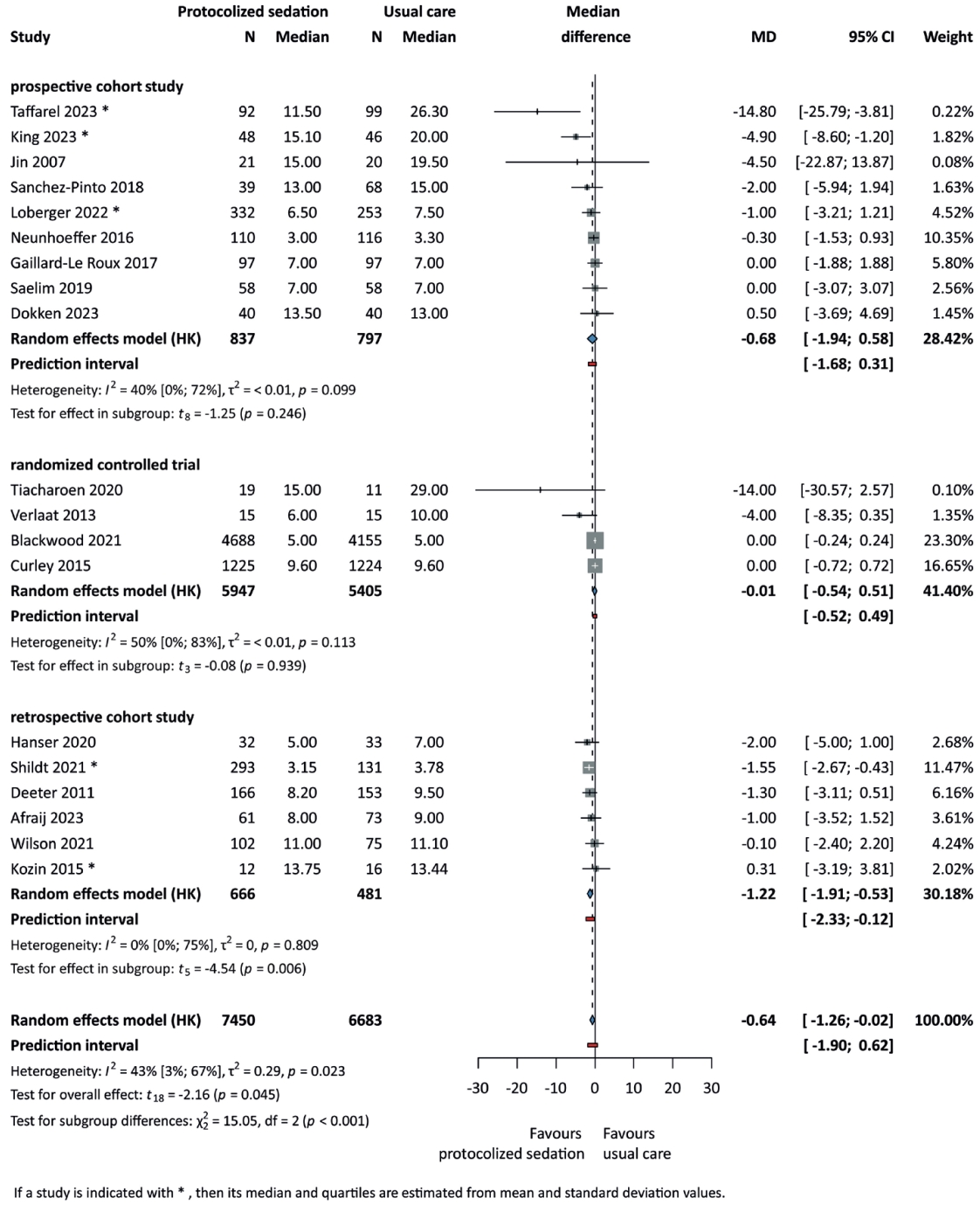
26. Blackwood B, Tume LN, Morris KP, Clarke M, McDowell C, Hemming K, et al. Effect of a sedation and ventilator liberation protocol vs usual care on duration of invasive mechanical ventilation in pediatric intensive care units: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2021;326:401-10.


29. Deeter KH, King MA, Ridling D, Irby GL, Lynn AM, Zimmerman JJ. Successful implementation of a pediatric sedation protocol for mechanically ventilated patients. Crit Care Med 2011;39:683-8.


30. Gaillard-Le Roux B, Liet JM, Bourgoin P, Legrand A, Roze JC, Joram N. Implementation of a Nurse-Driven Sedation Protocol in a PICU Decreases Daily Doses of Midazolam. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2017;18:e9-17.


32. Kleiber N, de Wildt SN, Cortina G, Clifford M, van Rosmalen J, van Dijk M, et al. A comparative analysis of preemptive versus targeted sedation on cardiovascular stability after high-risk cardiac surgery in infants. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2016;17:321-31.


37. Neunhoeffer F, Seitz G, Schmidt A, Renk H, Kumpf M, Fideler F, et al. Analgesia and sedation protocol for mechanically ventilated postsurgical children reduces benzodiazepines and withdrawal symptoms-but not in all patients. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2017;27:255-62.


39. Sanchez-Pinto LN, Nelson LP, Lieu P, Koh JY, Rodgers JW, Larson KA, et al. Implementation of a risk-stratified opioid weaning protocol in a pediatric intensive care unit. J Crit Care 2018;43:214-9.


40. Solodiuk JC, Greco CD, O'Donnell KA, Morrill DR, Curley MAQ. Effect of a sedation weaning protocol on safety and medication use among hospitalized children post critical illness. J Pediatr Nurs 2019;49:18-23.


42. Verlaat CW, Heesen GP, Vet NJ, de Hoog M, van der Hoeven JG, Kox M, et al. Randomized controlled trial of daily interruption of sedatives in critically ill children. Paediatr Anaesth 2014;24:151-6.


44. Achuff BJ, Lemming K, Causey JC, Sembera KA, Checchia PA, Heinle JS, et al. Opioid weaning protocol using morphine compared with nonprotocolized methadone associated with decreased dose and duration of opioid after norwood procedure. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2022;23:361-70.


45. Alfraij A, Abdelmoniem A, Surour M, Basuni M, Elseadawy M. Effect of target-driven sedation protocol to ventilator liberation in pediatric intensive care unit: pre- and postimplementation single-center study. J Pediatr Intensive Care 2023;
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1774306.

46. Dokken M, Rustøen T, Diep LM, Fagermoen FE, Huse RI, Egerod I, et al. Implementation of an algorithm for tapering analgosedation reduces iatrogenic withdrawal syndrome in pediatric intensive care. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2023;67:1229-38.


47. King CE, Wood DN, Koo J, Cutler AB, Vesel TP. Sedation weaning initiative targeting methadone exposure: single center improvements in withdrawal symptoms and hospital length of stay for pediatric cardiac critical care. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2023;24:E332-41.


51. Taffarel P, Widmer J, Fiore Á, Rodríguez AP, Meregalli C, Jorro Barón F. Impact of the implementation of a sedation and analgesia protocol in a pediatric intensive care unit. Arch Argent Pediatr 2023;121:e202202806.

59. van Dijk M, Peters JWB, van Deventer P, Tibboel D. The COMFORT Behavior Scale: a tool for assessing pain and sedation in infants. Am J Nurs 2005;105:33-6.
60. Curley MA, Harris SK, Fraser KA, Johnson RA, Arnold JH. State Behavioral Scale: a sedation assessment instrument for infants and young children supported on mechanical ventilation. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2006;7:107-14.


61. Traube C, Silver G, Kearney J, Patel A, Atkinson TM, Yoon MJ, et al. Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium: a valid, rapid, observational tool for screening delirium in the PICU*. Crit Care Med 2014;42:656-63.










 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


