Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 67(10); 2024 |
|
Abstract
As an endocrine disruptor chemical, pesticide exposure may affect the regulation of growth hormones such as insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). A few current studies to date have noted that long-term pesticide exposure disrupted IGF-1, a potential risk of stunting in children. This study aims to evaluate studies to date of the effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence. This systematic review and meta-analysis adhered to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis) guidelines. The PubMed and EBSCO databases were searched for relevant articles without publication restrictions. This review aimed to include reviews, randomized controlled trials (RCT), and cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies, which provide actual exposure types of pesticides with stunting measurement by height-age z score. A screening, extraction, and synthesis were conducted, leading to a consensus for reaching mutual agreement. The analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel 2017 for the screening and extraction, Revman version 5.4 software for the meta-analysis, and OpenMEE software for the meta-regression. Of the 13 studies subjected to the qualitative analysis, 6 were eligible for inclusion in the meta-analysis: 2 reviews, 2 RCTs, 2 cohorts, 2 case-control, and 5 cross-sectional studies. Exposure to organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticides was not associated with stunting (P=0.78; odds ratio [OR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.65–1.88). Heterogeneity existed for 79% of the meta-analysis (P≤0.000; z=-5.37; 95% CI, -0.034 to -0.016), and the meta-regression identified age as the causative covariate. Pesticide exposure, regardless of type, is not associated with stunting in children.
Graphical abstract
Over the past few decades, stunting has become a significant public health concern. The growth of many children is being stunted globally due to a complex interaction of household, environment, culture, and socioeconomic-political factors as reported by the World Health Organization's conceptual framework of childhood stunting [1]. Although the prevalence of stunting has decreased over the past 3 decades, an estimated 21.3% (144 million children) under 5 years of age are stunted globally [2]. The largest proportion of these children live in Africa, followed by a few parts of the Asian region and Latin America [2]. Like other causes of malnutrition in children, stunting affects a child's physical endurance and causes neurodevelopmental deficits and cognitive dysfunction [3]. Moreover, a stunted child is prone to contracting infectious diseases [4] and developing chronic diseases with long-term effects, such as obesity and hypertension [5].
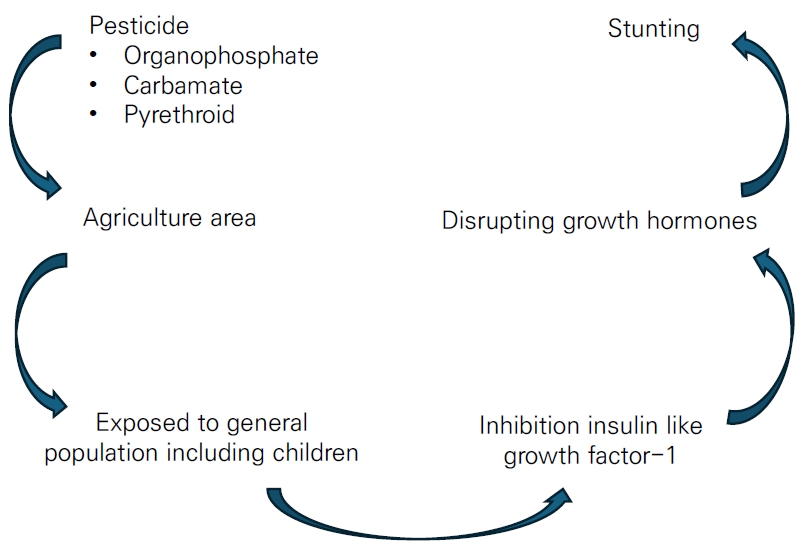
In addition to the aforementioned interactions, stunting may be influenced by the ingestion of food contaminated by pesticides. An estimated 3 billion kilograms of pesticides are used across the globe annually [6], a figure that is expected to increase over the forthcoming year. Thus, the health effects of long-term exposure to pesticides require analysis. Long-term pesticide exposure plays a role in dysregulating hormone interactions, such as acetylcholinesterase [7] (interrupting neurobehavioral disorders) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1; disrupting growth hormone), in children [8]. As a vulnerable population, children in the agriculture sector are at high risk of pesticide poisoning. The analysis of urine samples from children exposed to pesticides showed that levels of dimethyl thiophosphate were proportionately higher than those of other dialkyl phosphate metabolites [9]. A similar study also reported that the mean urinary dimethyl organophosphate metabolite level was higher for children who lived <61 m from an orchard (0.1 µg/mL)than for those who lived >61 m away (0.04 µg/mL) [10].
The long-term effect of chemicals, particularly pesticide exposure, has been reported on behalf of stunted children [11,12]. IGF-1 dysregulation is evidence of this mechanism through the inhibition binding-site receptors. [13] Zumbado et al. [14] reported IGF-1 concentrations in children and young adults exposed to organochlorine DDT pesticide. Among those participants, mean IGF-1 concentrations were higher in females than males (298 µg/L vs. 249 µg/L for young adults and 312 µg/L vs. 293 µg/L for children, respectively). Among the DDT metabolites, p,p'-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (p,p'-DDE) was the higher than p,p'-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (p,p'-DDT) and p,p'-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane (p,p'-DDD) (80.6 ng/g-fat in boys and 60.40 ng/g-fatin young men). Thus, organochlorine metabolites, DDE, DDD, and total DDT were significantly associated with IGF-1 concentrations in young male, but not female, subjects. The authors concluded that organochlorine pesticides modulated IGF-1 differently by age and sex. Another survey by Kartin et al. [12] strengthened the previous finding by Zumbado et al. [14] that the mean IGF-1 level decreased twofold among children exposed to pesticides used for onion farming versus unexposed groups (66.74 ng/mL vs. 112.57 ng/mL, respectively).
Considering the impact of IGF-1 inhibition, pesticide contamination in children likely causes stunting. Among the pesticide classes, organochlorine pesticide toxicity has most often been reported for children, adolescents [14], and pregnant women [15,16]. Conversely, despite limited data on the related mechanisms, exposure to the organophosphate and pyrethroid classes have also been associated with stunting [17,18]. The massive use of the organophosphate class replaced organochlorine for agriculture and its applications are enormous; thus, studies examining the effect of exposure to organophosphate and other insecticides on children's development have become more common. A systematic review by Bliznashka et al. [19] examined the effects of pesticide exposure on birth weight, birth length, low birth weight, and preterm birth. The study summarized that organochlorine and its metabolite were the most commonly used in agriculture-rich areas, followed by organophosphate, carbamate, and pyrethroid. The study found no association between prenatal exposure to pesticide, regardless of type, with outcomes including birth length [19]. Thus, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to strengthen the previous evidence that exposure to pesticides, regardless of class, contribute to stunting among children. This study may provide essential insight and feedback to control pesticide-induced growth and development effects in children.
This systematic review and meta-analysis was based on PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis) guidelines [20], and its protocol number was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023462432).
Eligible studies published in English through April 2023 were retrieved from the PubMed and EBSCO databases. The reference lists of the retrieved articles were manually searched for additional applicable sources. We used predefined search terms to identify relevant articles (Table 1). After the removal of duplicates, the titles and abstracts were screened by the authors (MF, MK, VW, KW, NAD, MR, and ESH). Articles that met the inclusion criteria were then subjected to full-text screening. Cases of discrepancy were settled by consulting other authors (SRS and YAJ). Consensus was reached upon mutual agreement of all authors. A paper's corresponding author was contacted for clarification if needed. The data collection and extraction processes were conducted using Microsoft Excel 2017 and Mendeley software, and the data were stored in the cloud using a service provided by Universitas Islam Indonesia.
The inclusion criteria were the analysis of the influence of pesticide exposure, regardless of class, on stunting incidence. Pesticide exposure was defined for every child who lived on or near an agricultural facility. We broadened the exposure criteria based on laboratory examinations and observational criteria to capture exposed and nonexposed children. Additionally, stunting in an article must be quantified by a height-age z score (HAZ) measurement, while self-reported information or other measurements were omitted from the analysis. Observational studies (cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional), randomized controlled trials (RCTs), interventional studies, reviews, and proceedings were eligible for inclusion and analysis. However, opinion, perspective, and descriptive data, including case reports, case series, and case studies, that did not examine the association between pesticide exposure and stunting were excluded. A certainty analysis of every included study was performed using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) summary [21].
A quality assessment was performed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for non-RCTs, observational studies, cohort, and case-control studies [22]. This method offers a risk of bias (RoB) assessment in 3 domains: selection, comparability, and outcome or exposure. Given the limitation of poor agreement and lack of a comprehensive manual [23], the NOS method is the most applicable RoB tool for nonrandomized studies and meta-analyses. Cross-sectional studies were examined using the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality guidelines [24]. RCT studies were examined using the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool [25]. Two authors (YAJ and MK) performed the RoB analysis.
Seven authors (MF, MK, VW, KW, NAD, MR, and ESH) extracted each study's author name, research design, population, pesticide type, stunting outcome, and finding. In cases of uncertainty, other authors were consulted (SRS and YAJ) until consensus was reached. The data were analyzed similarly. The data analysis focused on the endpoint estimation effects, including relative risk (RR), odds ratio (OR), mean difference, correlation coefficient, P value, and confidence interval (CI). Studies for which statistical data were missing were removed from the quantitative analysis. A study's corresponding author was contacted as necessary for further information. If no OR or RR values were reported by a study, the calculation of a 2×2 table was warranted. Since this study analysis was also quantitative, heterogeneity was used to assess the diversity of the included studies. A random effects model was used, and a forest plot was created to display effect estimates and CIs for the individual studies. The source of any heterogeneity was identified by meta-regression using OpenMEE software. A sensitivity and validity analysis was conducted using a funnel plot in Revman version 5.4 software (Cochrane, Fredericksburg, VA, USA).
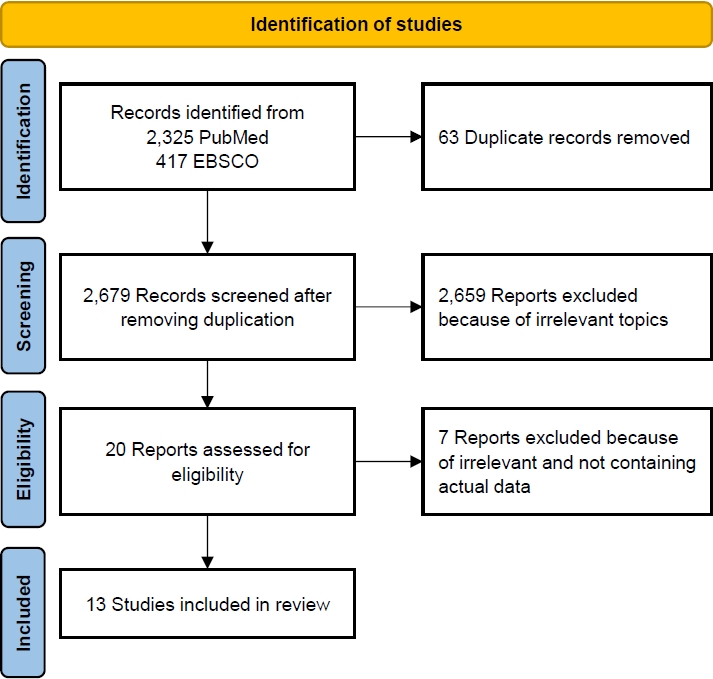
The database search retrieved 3,178 papers related to the effects of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence. After the elimination of duplicates, 2,753 papers remained. The elimination of studies with irrelevant topics resulted in 20 eligible papers. Of them, 13 were included in the systematic review and meta-analysis. A detailed flowchart of the study retrieval and selection process is presented in Fig. 1.
A total of 13 studies were included in the analysis: 2 reviews [26,27], 2 RCT [17,28], 2 cohort studies [18,29], 2 case-control studies [12,30], and 5 cross-sectional studies [11,31-34]. Four studies elucidated the effects of pesticides on stunting [11,12,27,30], 3 focused on organophosphate and carbamate [29,31,32], 5 focused on permethrin, a pyrethroid class [17,18,33,34], and one simultaneously analyzed metabolite herbicide, organophosphate, and pyrethroid [29]. Most studies analyzed stunting using HAZ; only one used the ponderal index [35] and, thus, was omitted from the further analysis. Among the 13 retrieved studies, 6 included a meta-analysis. The detailed baseline characteristics of the included studies are presented in Table 2 and Supplementary Table 1.
Kartini et al. [12] examined high-exposure pesticide-induced stunting among school-aged children who lived near onion farming (adjusted OR [aOR], 3.9; 95% CI, 1.15–13.26). Evidence of stunting was proven by HAZ and low IGF-1 levels (aOR, 8.35; 95% CI, 3.65–19.14). Kartini et al. [12] thoroughly evaluated risk factors for stunting, including nutritional status, low birth weight, infection history, and parents’ education and occupation. Protein and energy intake as well as high exposure to pesticides were associated with stunting. However, the sample size was inadequate, which limited the study's power. The study of Paudel et al. [30] corroborated the findings of Kartini et al. [12] in their adjusted multivariate analysis (aOR, 3.51; 95% CI, 1.33–9.23). The strength association of the results was proven by its adequate sample size, but the study was limited by its use of poor methods of detecting pesticide exposure. A review by Vilcins et al. [30] summarized a similar result to that of Paudel et al. [27] of pesticide-induced stunting (aOR, 3.51; 95% CI, 1.33–9.23). Apart from the previous findings, Grandjean et al. [11] found that a low score on the Stanford-Binet Copying Test, a neurodevelopment test, was associated with pesticide exposure (β=-1.01; standard error [SE]=0.37; P<0.00) and stunting in children (β=-0.74; SE=0.35; P<0.05). Of 37 exposed groups (-1.84±0.83; range, -3.65 to 0.35), 15 stunted children had median dimethyl metabolite and diethyl metabolite levels of 0.2 nmol/kg/day and 0.27 nmol/kg/day, respectively [11].
In general, pesticide exposure was associated with stunting. However, the limited sample sizes and inadequate pesticide exposure assessments prevented acceptance of the stated hypothesis.
Low use of organophosphate and carbamate was correlated with HAZ in children compared to their high and intermediate use (-1.95±1.86, -1.05±1.5, -1.25±1.27, F=4.06, P=0.0194, respectively) [31]. This finding seems different because the low carbamate and organophosphate use levels were 0.65±0.93 kg and 0.64±0.74 kg, respectively, compared with the high (0.28±0.27 and 0.60±0.47) and intermediate (0.45±0.33 and 0.91±0.79) levels [31]. Additionally, significantly more carbamate was used than organophosphate (P=0.04 vs. P=0.12). Overall, stunting was noted in 11 of 41 children in the low use group versus 2 of 40 in the intermediate use group and 4 of 54 children in the high use group. Unfortunately, this study did not examine the correlation between urinary pesticide exposure and HAZ in children [31]. Handal et al. [32] also reported that organophosphate and carbamate pesticide exposure was not correlated with stunting incidence in children (OR, 0.04; P=0.84). Stunting, however, affects a child's gross motor function, making it a moderate variable or independent factor in an individual's neurodevelopment. The prevalence of stunting was increased after high or low pesticide exposure, and children in both regions replace with in both exposure level resided in rural areas with lower education and income levels [32]. Another study reported on the effects of exposure to 4 organophosphate metabolites on stunting [29], including 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCPy; chlorpyrifos metabolite), 4-nitrophenol (parathion and methyl parathion metabolite), malathion dicarboxylic acid (malathion metabolite), and 2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-hydroxypirimidine (IMPY; diazinon metabolite). This study found that organophosphate exposure was not correlated with stunting, even after 2 years of follow-up (RR at Q4: TCPy, 1.16 [0.8–1.68]; 4-nitrophenol, 0.85 [0.61–1.19]; IMPY, 1.04 [0.73–1.49]) [29]. Exposure to organophosphate, regardless of class, was not associated with stunting. However, this study was limited by its small sample size, exposure assessments used, and poor design. Jaacks et al. [29] used the most applicable research method that seemingly required a larger sample size and long-term cohort evaluation to prove the relationship between exposure and outcomes.
Permethrin, a class of pyrethroid, was the most commonly used pesticide for treating malaria, namely insecticide-treated nets (ITN), according to some retrieved studies [17,18,29,33,34]. Stunting cases increased parallelly with high exposure to malaria among children with HIV (RR, 1.24 [1.06–1.48]) [18], malaria treatment with ITN caused malnutrition, including stunting (-0.20±0.09) [33], and ITN coverage was less effective at preventing stunting (OR, 0.02 or mean difference, 0.19; range, 0.18–0.19) [34]. An RCT by Friedman et al. [28] found that use of the ITN intervention did not correlate with stunting (mean pooled data, -0.95; 95% CI, -1.07 to -0.86). A similar RCT by Ter Kuile et al. [17] indicated that use of the ITN intervention versus control was correlated with HAZ (mean ITN, -1.40 vs. control, -1.76; mean difference, 0.36; range, 0.10–0.62; P=0.001). Another study of the more specific metabolite pyrethroid 3-PBA found no correlation with stunting incidence at the first or second follow-up (mean difference, 1.01; range, 0.83–1.24; and mean difference, 0.95; range, 0.69–1.32, respectively) [29].
Although an RCT design and large sample size were proposed in the ITN study on stunting, the result regarding the relationship between exposure and outcome was debatable. No suitable pyrethroid assessment was performed in either of the studies, so a questionnaire was used to collect the information. The robust method used in the Jaacks et al. cohort study inadequately proved an association between pesticide contamination and stunting. Thus, pyrethroid exposure was not associated with stunting incidence.
Six studies were included in the quantitative analysis, as presented in Figs. 2 and 3 [11,12,28,30-32]. Of 445 subjects who used ITN treatment to eradicate malaria in the study of Friedman et al. [28], 79 (16.7 %) denoted stunting, and 76 of 393 controls were positive for stunting. The study of Grandjean et al. [11] reported that 15 of 37 children with prenatal pesticide exposure versus 16 of 35 unexposed children were stunted. A history of pesticide applications was stratified as high, moderate, low, and unexposed; of them, 13, 14, 13, and 8 were stunted, respectively. On the other hand, similar results were seen among control subjects (14, 31, 39, and 28, respectively). Thus, 40 of 124 exposed versus eight of 36 controls were stunted [12]. Orozco et al. [31] stratified pesticide use intensity into more, intermediate, and less levels. We defined high pesticide exposure as high and moderate intensity and low exposure as less intensity. The authors reported that 28 of 94 children with high exposure versus 21 of 41 children with low exposure were stunted [31]. In a flower plantation area in the study of Handal et al. [32], greater pesticide exposure led to stunting in 83 of 154 children, while lesser exposure led to stunting in 68 of 129 children. Paudel et al. [30] also clarified the presence of 58 of 85 stunted children in pesticide-exposed groups versus 60 of 151 stunted children in nonexposed groups.
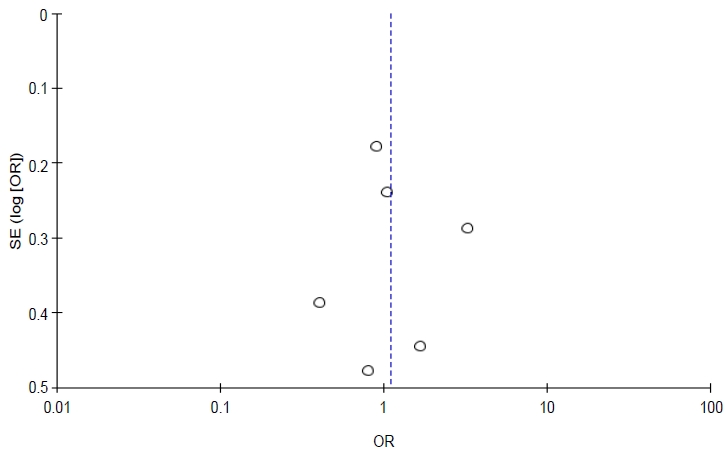
Total events were 278 of 845 population in the exposed group versus 228 of 774 in the unexposed group. Although the funnel plot to verify sensitivity confirmed symmetrical data, heterogeneity existed (I2=75%, P=0.003). Additionally, a meta-regression determined that age was a significant (P≤0.001) source of heterogeneity. Therefore, pesticide exposure was not associated with stunting in children (P= 0.28).
General exposure to pesticides was associated with stunting incidence. There are several points related to this result. First, the exposure assessment was more community-based than the individual assessment, and the community data could not provide actual concentrations compared to the individual data. Second, regarding baseline characteristics among the retrieved papers, particularly occupational status, most respondents worked as merchants [12] and housewives [27], which likely creates a risk of selection bias. Assessments of community exposure should focus on farmers, who work more frequently in the field.Second, the data were collected by interview or general assessment exposure [12,27,30] and included limited sample sizes [11], which likely created selection bias. Although one study evaluated pesticide concentrations [11], the results were significant only for the reaction time test. Nevertheless, other tests had limited significance due to including a small size sample size. Regarding the meta-analysis results, exposure to pesticides was not associated with stunting. Therefore, the meta-analysis proved the potential bias in the retrieved papers that supports the null hypothesis.
Due to concerns about specific pesticides, namely organophosphate and carbamate, the retrieved studies agreed that neither is associated with stunting. The study by Jaacks et al. verified the presence of specific pesticide metabolites and found insufficient evidence of an association between exposure and stunting. We argue that the detection method used in that study lacked sensitivity (only a 60% detection rate for all metabolite pesticides). Stunting is an independent variable of neurodevelopment delay [36,37] that is not correlated with exposure status, even with higher exposure to pesticides and higher socioeconomic status and maternal education [32]. The study of Orozco et al. [31] corroborated that, in the areas with the most extensive pesticide use, the average HAZ score was in the normal range. However,this study included a limited sample size.
Permethrin usage for malaria eradication is not correlated with stunting. A cohort study by Arinaitwe et al. [18] of respondents treated with ITN evaluated the association between stunting and malaria. Beyond the strength of the research method, stunting versus non-stunting was correlated with the incidence of malaria. However, whether ITN was associated with stunting was doubtful due to a lack of information about insecticide dose and detection method. Thus, the correlation of ITN with stunting requires further investigation. Similarly, the study of Friedman et al. [33] examined the impact of ITN on malnutrition, including stunting. However,the study was also prone to the causation of ITN coverage with stunting. Here, pyrethroid used for malaria eradication contributed to stunting. However, actual data to prove stunting is limited and unable to prove the causal relationship. It would be useful to determine whether malnutrition predicts infection in children or an infected child is prone to malnutrition and delayed development [37-39]. Further assessments are warranted to observe the causal relationship.
This study has several limitations. The retrieved studies do not holistically verify multifactorial stunting, including protein intake, parental knowledge of stunting, educational background, and economic status. Most studies did not perform individual assessments of pesticide exposure; thus, it is difficult to verify the dose-response relationship. Community exposure by questionnaire or self-reporting is susceptible to selection bias. A robust study of pesticide exposure is limited, and the remaining included studies were Prone to bias (Table 3), especially in terms of allocation concealment and blinding in RCT studies as well as low-quality reporting on the GRADE summary (Table 4). Additionally, 75% heterogeneity and P<0.000 existed in the meta-regression analysis due to the age covariate (Table 5). Therefore,the effect of pesticide exposure on the incidence of stunting is uncertain and requires a completed assessment in a forthcoming study. A future study must focus on multiple pesticide exposures, particularly ofthe organochlorine class, to evaluate the dose-response relationship of individual exposure with a large sample and using a robust method. IGF-1 testing should also be assessed to obtain accurate parameters of exposed groups.
In conclusion, beyond the agreement about the mechanism by which pesticides, especially organochlorine, influence stunting by inhibiting IGF-1, this study's findings do not suggest that pesticide exposure is correlated with stunting. Several studies denoted that pesticide exposure was correlated with stunting, but each was limited by a small sample size, lack of exposure assessment method, and poor design. Most published studies examined organochlorine pesticide-induced stunting in animal models; thus, the mechanisms by which organophosphate, pyrethroid, and carbamate affect stunting remain to be elucidated. The different toxicological properties of these pesticides will likely result in different mechanisms of action on growth hormone. Although determining the relationship between exposure and stunting is challenging, pesticides have negative effects on human health. This study provides evidence needed for a recommendation to control pesticide use in farming. Protecting vulnerable populations, including children in agricultural areas, is still urgently needed to prevent harmful events in forthcoming years.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table 1 and Fig. 1 can be found via https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.01522.
Supplementary Table 1. Included studies of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence (2 review, 2 RCT, 2 cohort, 2 case-control, and 5 cross sectional studies)
cep-2023-01522-Supplementary-Table-1.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 1. Risk of bias in randomized controlled trial study.
cep-2023-01522-Supplementary-Fig-1.pdf
Acknowledgments
We thank to Faculty of Medicine Universitas Islam Indonesia which provides funding this study.
Fig. 2.
Forest plot of association between pesticide exposure with stunting. IV, inverse variance; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom.
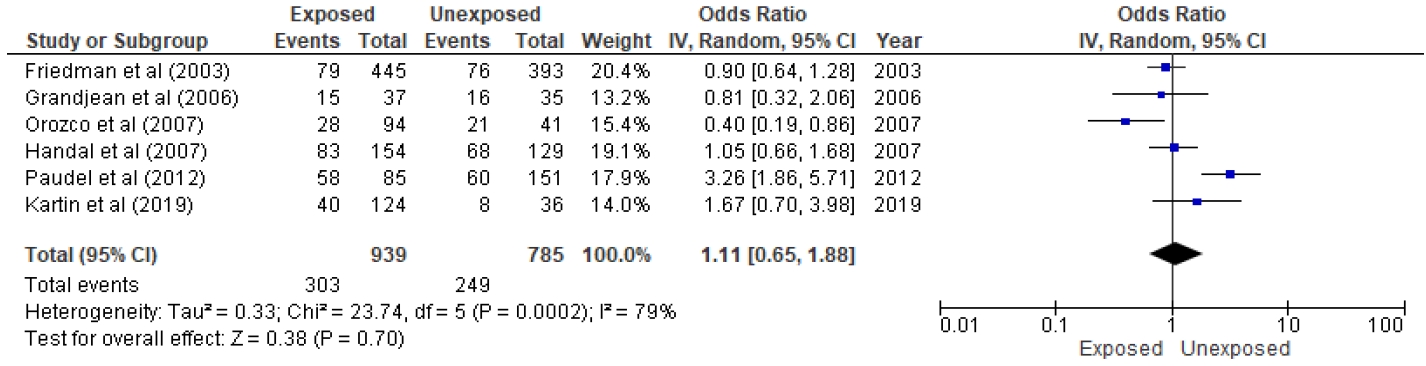
Table 1.
Predefined search terms
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of retrieved studies
| Study | Study design | Participants | Exposure |
Outcome |
Summary | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stunting | Total sample | Estimation effect | |||||
| Salam et al. [26] | Scoping review | 1 Study included (411 children with ITN and 420 control) | ITN (permethrin) | NI | NI | OR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.86–1.42 | There was no association between ITN used with stunting |
| Vilcin et al. [27] | Systematic review | 1 Study included consist of 354 children | Pesticide | NI | NI | NI | Pesticide was associated with stunting |
| Friedman et al. [28] | RCT | 455 Children in ITN village and control 421 children. | ITN (permethrin) | 155 | 876 | Mean, -0.96; 95% CI, -1.0 to -0.86 | Pesticide was not associated with stunting |
| Ter Kuile et al. [17], a) | RCT | 411 Children in ITN intervention and 420 control | ITN (permethrin) | NI | 831 | MD, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.10–0.62; P=0.01 | ITN was associated with stunting 0 to 23 months old children |
| Jaacks et al. [29], b) | Cohort | 289 Pregnant women followed for one-year exposed pesticide on stunting in her children | Herbicide, organophosphate, pyrethroid | 197 | 289 | RR, 0.99, 95% CI, 0.77–1.27 (TCPy) | Metabolite organophosphate, TCPy, did not correlate with stunting during 1-year follow-up |
| Arinaitwe et al. [18] | Cohort | 99 HIV-unexposed | ITN (permethrin) among children with HIV | 252 | 358 | RR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.03–1.48; P=0.008 | ITN exposure was associated with moderate severe stunting |
| 202 HIV-exposed | |||||||
| 57 HIV-infected | |||||||
| Kartini et al. [12] | Case-control | 160 Children 8-12 yr (48 case and 112 control) | Pesticide | 48 | 160 | OR, 3.9, 95% CI, 1.15–13.26 | History high-exposed pesticide associated with stunting |
| Paudel et al. [30] | Case-control | 236 Children 6 to 59 months | Pesticide | 118 | 236 | aOR, 3.51. 95% CI, 1.33–9.23 | Pesticide exposure was associated with stunting. |
| Grandjean et al. [11] | Cross-sectional | 72 Children primary school | Pesticide | 31 | 72 | Β=-0.74, SE=0.35, P=0.03 | Stunting was independent predictor of neurobehavior in exposure pesticide. |
| Friedman et al. [33] | Cross-sectional | 1862 Children | ITN (permethrin) | 466 | 1396 | Mean=-0.29, P=0.003 | ITN used in high density parasitemia was associated with stunting |
| Amoako Johnson [34] | Cross sectional | NI (using DHS data) | ITN (permethrin) | NI | NI | OR, 0.192; 95% CI, 0.18–0.199 (pooled data) | ITN coverage was associated with stunting in DHS data |
| Orozco et al. [31] | Cross sectional | 54 = more intensive | Organophosphate and carbamate | 49 | 135 | P=0.019 | There was association between intensity used pesticide with stunting in children |
| 40 = intermediate | |||||||
| 41 = less intensive | |||||||
| Handal et al. [32] | Cross sectional | 283 children aged 3-61 mo | OP and carbamate | 151 | 283 | OR, 0.04; P=0.87 | Pesticide exposure did not correlate with stunting |
DHS, demographic health survey; ITN, insecticide treatment net; NI, no information; MD, mean difference; TCPy, 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol; OR, odds ratio; aOR, adjusted OR; RR, relative risk; CI, confidence interval.
Table 3.
Risk of bias (RoB) of included studies
| NOS | Selection | Comparability | Exposure/outcome | Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaacks et al. [29] | *** | ** | *** | 8 | ||||||||
| Arinaitwe et al. [18] | *** | ** | *** | 8 | ||||||||
| Kartini et al. [12] | **** | ** | ** | 8 | ||||||||
| Paudel et al. [30] | **** | ** | ** | 8 | ||||||||
| AHRQ | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Q11 | Total |
| Grandjean et al. [11] | + | ? | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 8 |
| Friedman et al [33] | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | - | + | - | 8 |
| Amoako Johnson [34] | + | - | ? | + | ? | + | ? | + | NA | + | - | 5 |
| Orozco et al. [31] | + | ? | + | - | ? | + | - | + | - | - | - | 3 |
| Handal et al. [32] | + | + | ? | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | 7 |
| Cochrane RoB | Selection | Selection | Performance | Detection | Attrition | Reporting | Others | |||||
| Friedman et al. [28] | + | ? | - | + | + | + | + | |||||
| Ter Kuile et al. [17] | ? | - | ? | ? | + | + | + | |||||
Table 4.
GRADE summary for certainty
Table 5.
Meta-regression result of potential effect modifiers in meta-analysis
References
1. World Health Organization. Context, causes, and consequences. Stunted growth and development. Geneva (Switzerland), World Health Organization: 2018.
2. Montenegro CR, Gomez G, Hincapie O, Dvoretskiy S, DeWitt T, Gracia D, et al. The pediatric global burden of stunting: focus on Latin America. Lifestyle Med 2022;3:e67.


3. de Onis M, Branca F. Childhood stunting: a global perspective. Matern Child Nutr 2016;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1): 12–26.

4. Mutasa K, Tome J, Rukobo S, Govha M, Mushayanembwa P, Matimba FS, et al. Stunting status and exposure to infection and inflammation in early life shape antibacterial immune cell function among Zimbabwean children. Front Immunol 2022;13:899296.



5. De Sanctis V, Soliman A, Alaaraj N, Ahmed S, Alyafei F, Hamed N. Early and Long-term consequences of nutritional stunting: from childhood to adulthood. Acta Biomed 2021;92:e2021168.


6. Tudi M, Daniel Ruan H, Wang L, Lyu J, Sadler R, Connell D, et al. Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18:1112.



7. Strelitz J, Engel LS, Keifer MC. Blood acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase as biomarkers of cholinesterase depression among pesticide handlers. Occup Environ Med 2014;71:842–7.



8. Boada LD, Lara PC, Alvarez-León EE, Losada A, Zumbado ML, Limiñana-Cañal JM, et al. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I in relation to organochlorine pesticides exposure. Growth Horm IGF Res 2007;17:506–11.


9. Curl CL, Fenske RA, Kissel JC, Shirai JH, Moate TF, Griffith W, et al. Evaluation of take-home organophosphorus pesticide exposure among agricultural workers and their children. Environ Health Perspect 2002;110:A787–92.



10. Lu C, Fenske RA, Simcox NJ, Kalman D. Pesticide exposure of children in an agricultural community: evidence of household proximity to farmland and take home exposure pathways. Environ Res 2000;84:290–302.


11. Grandjean P, Harari R, Barr DB, Debes F. Pesticide exposure and stunting as independent predictors of neurobehavioral deficits in Ecuadorian school children. Pediatrics 2006;117:e546–56.



12. Kartini A, Subagio HW, Hadisaputro S, Kartasurya MI, Suhartono S, Budiyono B. Pesticide exposure and stunting among children in agricultural areas. Int J Occup Environ Med 2019;10:17–29.




13. Talia C, Connolly L, Fowler PA. The insulin-like growth factor system: a target for endocrine disruptors? Environ Int 2021;147:106311.


14. Zumbado M, Luzardo OP, Lara PC, Alvarez-León EE, Losada A, Apolinario R, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) serum concentrations in healthy children and adolescents: relationship to level of contamination by DDT-derivative pesticides. Growth Horm IGF Res 2010;20:63–7.


15. Anand M, Taneja A. Organochlorine pesticides residue in placenta and their influence on anthropometric measures of infants. Environ Res 2020;182:109106.


16. Arrebola JP, Cuellar M, Bonde JP, González-Alzaga B, Mercado LA. Associations of maternal o,p'-DDT and p,p'-DDE levels with birth outcomes in a Bolivian cohort. Environ Res 2016;151:469–77.


17. Ter Kuile FO, Terlouw DJ, Kariuki SK, Phillips-Howard PA, Mirel LB, Hawley WA, et al. Impact of permethrin-treated bed nets on malaria, anemia, and growth in infants in an area of intense perennial malaria transmission in western Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;68(4 Suppl): 68–77.


18. Arinaitwe E, Gasasira A, Verret W, Homsy J, Wanzira H, Kakuru A, et al. The association between malnutrition and the incidence of malaria among young HIV-infected and -uninfected Ugandan children: a prospective study. Malar J 2012;11:90.




19. Bliznashka L, Roy A, Jaacks LM. Pesticide exposure and child growth in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Environ Res 2022;215(Pt 1): 114230.



20. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71.



21. Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:383–94.


22. Lo CK, Mertz D, Loeb M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers' to authors' assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014;14:45.




23. Luchini C, Stubbs B, Solmi M, Veronese N. Assessing the quality of studies in meta-analyses: advantages and limitations of the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. World J Metaanal 2017;5:80.

24. Mamikutty R, Aly AS, Marhazlinda J. Selecting risk of bias tools for observational studies for a systematic review of anthropometric measurements and dental caries among children. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18:8623.



25. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343:d5928.



26. Salam RA, Das JK, Lassi ZS, Bhutta ZA. Impact of community-based interventions for the prevention and control of malaria on intervention coverage and health outcomes for the prevention and control of malaria. Infect Dis Poverty 2014;3:25.




27. Vilcins D, Sly PD, Jagals P. Environmental risk factors associated with child stunting: a systematic review of the literature. Ann Glob Health 2018;84:551–62.



28. Friedman JF, Phillips-Howard PA, Hawley WA, Terlouw DJ, Kolczak MS, Barber M, et al. Impact of permethrin-treated bed nets on growth, nutritional status, and body composition of primary school children in western Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;68(4 Suppl): 78–85.


29. Jaacks LM, Diao N, Calafat AM, Ospina M, Mazumdar M, Ibne Hasan MOS, et al. Association of prenatal pesticide exposures with adverse pregnancy outcomes and stunting in rural Bangladesh. Environ Int 2019;133(Pt B): 105243.



30. Paudel R, Pradhan B, Wagle RR, Pahari DP, Onta SR. Risk factors for stunting among children: a community based case control study in Nepal. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ) 2012;10:18–24.


31. Orozco F, Cole DC, Muñoz V, Altamirano A, Wanigaratne S, Espinosa P, et al. Relationships among production systems, preschool nutritional status, and pesticide-related toxicity in seven ecuadorian communities: a multi-case study approach. Food Nutr Bull 2007;28(2 Suppl): S247–57.



32. Handal AJ, Lozoff B, Breilh J, Harlow SD. Effect of community of residence on neurobehavioral development in infants and young children in a flower-growing region of Ecuador. Environ Health Perspect 2007;115:128–33.



33. Friedman JF, Kwena AM, Mirel LB, Kariuki SK, Terlouw DJ, Phillips-Howard PA, et al. Malaria and nutritional status among pre-school children: results from cross-sectional surveys in western Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2005;73:698–704.


34. Amoako Johnson F. Spatiotemporal clustering and correlates of childhood stunting in Ghana: analysis of the fixed and nonlinear associative effects of socio-demographic and socio-ecological factors. PLoS One 2022;17:e0263726.



35. Steinholt M, Ha SO, Houy C, Odland JØ, Odland ML. An increased risk of stunting among newborns in poorer rural settings: a cross-sectional pilot study among pregnant women at selected sites in rural Cambodia. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019;16:4170.



36. Wondemagegn AT, Mulu A. Effects of nutritional status on neurodevelopment of children aged under five years in East Gojjam, Northwest Ethiopia, 2021: a community-based study. Int J Gen Med 2022;15:5533–45.




37. Oumer A, Fikre Z, Girum T, Bedewi J, Nuriye K, Assefa K. Stunting and underweight, but not wasting are associated with delay in child development in Southwest Ethiopia. Pediatric Health Med Ther 2022;13:1–12.









 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


