Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 63(7); 2020 |
|
Abstract
Exposure to environmental factors can cause interstitial lung diseases (ILDs); however, such types of ILDs are rare. From 2007 to 2011, an ILD epidemic occurred in South Korea owing to inhalational exposure to toxic chemicals in humidifier disinfectants (HDs). HD-associated ILDs (HD-ILDs) are characterized by rapidly progressing respiratory failure with pulmonary fibrosis and a high mortality rate of 43.8%−58.0%. Although 18.1%−31.1% of the general population used HDs, only a small proportion of HD users were diagnosed with HD-ILDs. This finding suggests that investigation of the pathophysiologies underlying HD-ILDs is needed in addition to the identification of susceptibility to HD-ILDs. Further, there have been several concerns regarding the diverse health effects of exposure to toxic chemicals in HDs, including those that have not been identified, and long-term prognoses in terms of pulmonary function and residual pulmonary lesions observed on follow-up chest images. In this review, we summarize the clinical features, pathologic findings, and changes in radiologic findings over time in patients with HD-ILDs and the results of previous experimental research on the mechanisms underlying the effects of toxic chemicals in HDs. Studies are currently underway to identify the pathophysiologies of HD-ILDs and possible health effects of exposure to HDs along with the development of targeted therapeutic strategies. The experience of identification of HD-ILDs has encouraged stricter control of safe chemicals in everyday life.

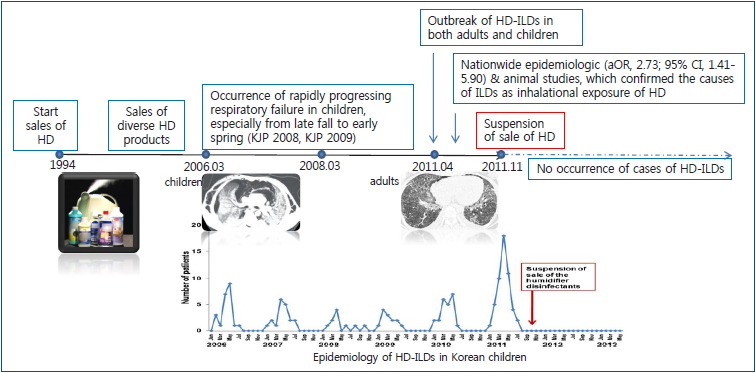
Graphical abstract. Identification history of HD-ILDs in Korean children. HD, humidifier disinfectants; KJP, Korean Journal of Pediatrics; HD-ILDs, humidifier disinfectants-associated interstitial lung diseases; aOR, adjusted odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) in children are rare and encompass a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying degrees of inflammatory and fibrotic changes in the lung parenchyma and alveolar walls [1]. The most common causes of ILDs in infants and children are developmental disorders, growth abnormalities, and genetic diseases [2]. Children with ILDs usually complain of dyspnea, and show diffuse infiltrates on chest radiography and abnormal lung functions with/without impaired gas exchange. However, the clinical manifestations can be diverse, from nonspecific to severe respiratory failure, according to the underlying diseases and their pathophysiologies, which need to be carefully considered for diagnosing patients with atypical symptoms.
Exposure to environmental factors can cause ILDs; however, there have been few reports of such ILDs [3]. An epidemic of ILDs occurred after inhalational exposure to toxic chemicals in humidifier disinfectants (HDs) contained in water tanks of humidifier to reduce microbial growth in South Korea from 2007 to 2011. At that time, no information was available on the harmful health effects of HDs, and therefore, HDs had been widely used. A study conducted among Korean children born in 2008 showed that 75.6% of the study population had used a humidifier and 31.1% of the children had been exposed to HDs until the age of 7 years [4]. In another cross-sectional study, 37.2% of the adults from the general population had used a humidifier and 18.1% had been exposed to HDs [5]. Although the majority of the population had been exposed to HDs, only a small proportion of the exposed population was diagnosed with HD-associated ILDs (HD-ILDs). Until early 2019, 255 children had been diagnosed with HD-ILDs and 110 children had died because of HD-ILDs [6]. An investigation on the causal relationship between HD exposure and development of HD-ILDs is currently underway.
Typically, patients with HD-ILDs complain of subacute respiratory symptoms, such as cough and mild tachypnea, with rapid progression to respiratory failure. Patients with atypical respiratory symptoms, which differ from those identified as ILD symptoms in terms of clinical manifestations, radiologic features, and pathologic findings, are diagnosed with HD-ILDs after multidisciplinary investigations. In this review, we summarize the identification history, clinical characteristics, and radiologic and pathologic features of HD-ILDs. In addition, we describe the current concerns about unidentified but possible health effects of toxic chemicals in HDs, investigations of the mechanisms underlying HD-ILDs, and unresolved problems associated with HD-ILDs.
In 2006, there was an epidemic of unidentified ILDs in children, which were characterized by rapid progression of respiratory failure with diffuse alveolar damage, poor response to any treatment, and a predominant occurrence in spring [7,8]. In March 2009, we identified 2 series of familial cases showing rapidly progressing respiratory failure almost simultaneously with high mortality, especially during the spring season [9]. Lung histopathology of these patients showed bronchiolar destruction and obliteration due to fibroblastic proliferation, which suggested that inhalational injury caused by unknown toxic mate rials might be associated with the rapidly progressing respi ratory disease accompanied by lung fibrosis, when combin ed with simultaneous occurrence in some family members in the similar timing [9].
After an outbreak of severe respiratory failure in pregnant women in April 2011 [10,11], the Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (KCDC) was involved with pediatric pulmonary specialists, adult pulmonary specialists, radiologists, pathologists, epidemiology specialists, and toxicology specialists for the identification of the disease. Although diverse respiratory viruses were identified in some patients (20.2%−31.0%) [3,7,8,12], the clinical manifestations could not be explained by respiratory virus infections. Through nationwide epidemiologic studies on this type of ILDs [3,13-15] and subsequent experimental studies [16,17], this type of ILDs was identified to be associated with HD use. A case-control study showed that the use of HD significantly increased the risk of this type of ILDs with an odds ratio of 2.73 (95% confidence interval, 1.41−5.90) [13]. The retrospective and prospective studies, performed by the Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease, were the first to provide strong evidence for the association between HD use and development of ILDs in children [3]. Research is currently underway, over several rounds, to identify the association between the development of HD-ILDs and HD use in subjects who had used HD. At the same time, close monitoring for health effects related to HD exposure in patients with HD-ILDs is underway.
Toxic chemicals in HDs include polyhexamethylene guanidine (PHMG), oligo (2-(2-ethoxy)ethoxyethyl) guanidine chloride) (PGH), chloromethylisothiazolinone (CMIT), and methylisothi azolinone (MIT) [18]. The most commonly used HDs contained PHMG, followed by PGH and CMIT/MIT (Table 1) in 447 child ren with information on HD brands [18,19]. A nationwide survey on the characteristics of HD usage showed that 57%−67% of patients with HD-ILDs had used HDs for less than 1 year [18,19]. Exposure to the highest quartile concentrations of estimated airborne HDs (range, 135 to 1,443 μg/m3) increased the risk of HD-ILDs in a dose-dependent manner compared to exposure to the lowest quartile concentration of HDs (≤33 μg/m3) [20]. Exposure to higher concentrations during a short period, especially in early life, was significantly associated with the development of HD-ILDs [20]. In addition, the use of more than 2 brands of HDs was associated with an increased risk of HD-ILDs, although the underlying mechanisms remain to be identified [20].
Previous in vitro and animal studies have identified the health effects of toxic chemicals in HDs and their mechanisms (Table 2). In the early era of the identification of HD-ILDs, toxicology studies showed that exposure to PHMG and PGH resulted in severe inflammation, atherogenesis, hepatic toxicity, and aging [16]. Subsequent experimental studies identified that inhalational exposure to PHMG contributed to pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, and thymic atrophy with decreased T-cell development [21,22]. In consecutive studies, researchers tried to identify the pathophysiologies underlying the development of HD-ILDs in animal and cellular studies. PHMG has been reported to cause cytotoxicity through the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species through alterations in gene expression [17,23-25].
Although most published studies have identified the health effects of PHMG and PGH, studies on health effects of inhalational exposure to CMIT and MIT are lacking. In real clinical situations in humans, HD-ILDs had been occurred after exposure to CMIT and MIT, which showed similar patterns of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis as those associated with exposure to PHMG and PGH [26-28].
Children with HD-ILDs complain of rapidly progressing respiratory distress after the initial mild respiratory symptoms of cough and tachypnea with chest retraction [3,12]. Table 3 describes the clinical features of HD-ILDs in children in the representative nationwide epidemiologic study of HD-ILDs in children [3]. The clinical course of HD-ILDs was different from those of typical ILDs, in that, the former type was characterized by relatively rapid progression of respiratory distress and was commonly accompanied by air leak syndrome (30%−44% cases) and a lack of response to all possible treatments of ILDs, including steroid pulse therapy, intravenous immunoglobulins, and antifibrotic agents [9,12]. Diverse respiratory viruses, including rhinovirus and parainfluenza virus, were identified in some cases (20.2%−31.0%), which resulted in confusion with regard to the identification of the disease [3,12]. Ventilator care was needed in 31.0-56.5% of cases and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) was needed in 18.1% of cases [3]. A child with an HD-ILD successfully underwent heart-lung transplantation after application of ECMO for more than 100 days [29]. The mortality rate associated with HD-ILDs has been reported to be as high as 43.8%−58.0% despite active treatment [3,8].
During follow-up among children with HD-ILDs, diverse pulmonary function parameters, including forced vital capacity, showed a decreasing pattern followed by a constant state (Fig. 1), which might be attributed to the restriction on the development of lung function [30]. This finding is different from those in adults with HD-ILDs, in that, adult patients showed decreased pulmonary function followed by stabilization of pulmonary function over time, although changes in pulmonary function were affected by exposure intensity [31]. When considering the developmental patterns of lung function, which increases until an individual’s early twenties [32], lifetime follow-up of pulmonary function with other respiratory health problems is warranted in children with HD-ILDs.
Radiologic findings in children with HD-ILDs differ according to the stage (early vs. late stage) and severity of HD-ILDs [12,33]. Fig. 2 shows the representative chest computed tomography (CT) scan in a child with HD-ILDs according to the chronologic changes. In the early phase (mean, 13 days; range, 4 to 33 days after the initial symptom presentation), patchy consolidation was predominant followed by centrilobular opacity in the advanced stage, the mean time interval for which was 33 days after the initial symptom presentation [12,33]. The patchy con solidation was present mainly in the lower lung, whereas there was no zonal predominance of centrilobular opacity [33]. In the resolving phase in survivors, faint centrilobular nodules were observed after a mean period of 113 days after the initial symptom presentation [33,34]. Spontaneous air leak was most commonly observed in the advanced stage followed by the early and resolving stages [33]. In survivors, the air leak had improved in the end stage. In addition, centrilobular opacities disappeared with the remaining faint centrilobular nodules in the survivors.
Spontaneous air leaks, consolidation, and diffuse groundglass opacities were associated with poor prognoses, whereas a large area of centrilobular opacity was associated with a good prognosis [33]. Compared with radiologic findings in survivors, the time interval from the symptom onset to the first chest CT was shorter in nonsurvivors [33]. This finding might suggest that the clinical course in nonsurvivors is more rapid compared to that in survivors.
The differential diagnosis of HD-ILD is complex (Table 4). The radiologic features of HD-ILDs are somewhat different from those of other types of diffuse lung diseases. Multifocal patchy consolidation, commonly observed in acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute interstitial pneumonia, hypersensitivity pneumonia, and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia, is not associated with centrilobular opacities. Although diffuse centrilobular ground-glass opacities, usually present in the late phase of HD-ILD, can be observed even in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis, there was no response to treatment, including avoidance of causative allergens and administration of corticosteroids, in patients with HD-ILDs. Moreover, the characteristic distribution of lesions showing centrilobular distribution with subpleural sparing was observed only in patients with HD-ILDs. Mosaic attenuation patterns, observed in hypersensitivity pneumonitis or bronchiolitis obliterans, were not observed in patients with HD-ILDs [35].
The pathologic examinations showed chronologic changes according to the timings of lung biopsies. In the early phase, bronchiolar destruction was observed with alveolar destruction due to inflammatory cell infiltration and fibroblastic proliferation, which showed centrilobular distribution (Fig. 3A, B) [13,34]. The central characteristic of HD-ILDs was broncho centric distribution of fibro-inflammatory lung injuries [3,8], which suggested the possible cause of this disease to be inhalation of toxic chemicals. In alveolar spaces, accumulation of multifocal foamy histiocytes was observed with interstitial fibrosis. In the late phase, the parenchymal architecture was displaced because of inflammation and fibrosis, especially in the centrilobular area (Fig. 3C, D) [12]. Granulomatous lesions, which are a charac teristic of hypersensitivity pneumonitis, were not observed in patients with HD-ILDs [36].
Inhalational exposure to HD can cause airway inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis. Exposure period and timing and individual susceptibility might differently affect respiratory health [18,20]. Exposure to HDs in early life was associated with an increased risk of development and persistence of asthma in young children in the 2 general population-based birth cohort studies [37]. When considering diverse phenotypes of asthma, long-term follow-up studies are needed to determine the characteristics and prognosis of asthma associated with exposure to toxic chemicals in HDs in children [38].
In addition, some HD-ILD patients suggested the possibilities of development or aggravation of diverse subtypes of rhinitis, including allergic rhinitis, after inhalational exposure to HD. Some complained of exacerbation and persistence of dermatitis, of which is possible in that methylisothiazolinone, one of the toxic components of HDs, can cause contact dermatitis [39,40]. However, further research is needed to determine whether the toxic chemicals in HDs are related to the development of atopic dermatitis or other types of dermatitis. In addition to respiratory and skin-related health effects directly related to HD exposure, there have been concerns about the possible health effects in other organs, such as liver [41]. When rats were made to inhale PHMG labeled with indium-111 (111In) for 7 days, 74% of PHMG was distributed to the lungs and 5.3% to the liver after 168 hours [41]. Although it is unclear whether HD exposure affects liver health in humans, it is suggested that exposure to HD can cause toxic hepatitis. Studies on the investigation of diverse health effects, which have not been considered, in exposure to toxic chemicals in HDs are underway. In the near future, multiple health effects of exposure to toxic chemicals in HDs and their pathophysiologies would be revealed.
The most common psychological symptoms in patients with HD-ILDs as well as their family members are anxiety, followed by fear and depression [42]. The bereaved of the patients with HD-ILDs showed higher rates of alcohol and smoking abuse and insomnia than those of other psychologic responses [42]. Therefore, support for psychologic health is urgently needed along with monitoring of the health of patients with HD-ILDs and their family.
Identification of the underlying mechanisms of HD-ILDs is necessary. Most of the pathophysiologies underlying HD-ILDs have been identified in animal or in vivo studies, and studies in humans are lacking. In the future, studies on the pathophysiologies of and susceptibility to HD-ILDs in humans are needed along with the discovery of genetic or molecular biomarkers, which can predict the prognoses and facilitate the development of therapy of HD-ILDs and distinguish whether a person was exposed to toxic chemicals in HDs or not, even if the exposure occurred long ago. Multiomics studies could be helpful in identifying biomarkers for the prediction and diagnosis of HD-ILDs and could facilitate the development of therapeutics for HD-ILDs.
In addition, exposure to toxic chemicals could exacerbate the underlying diseases in patients with diverse diseases. The identification of differential points that can distinguish the exacer bation of the underlying diseases due to exposure to HD is needed. Until now, little has been learnt about the association between HD-ILDs and the health effects of toxic chemicals in HDs. In the near future, results of health monitoring including pulmonary function trajectories in affected patients would be available in addition to information on the diverse health effects of inhalational exposure to HDs. Lifetime follow-ups for health monitoring are urgently needed in children with HD-ILDs. Nationwide concerns are needed to prevent additional health disasters resulting from unknown health effects of exposure to environmental toxic chemicals.
Since the clinical, radiologic, and pathologic features of HD-ILDs are different from those in the previously known ILDs, multidisciplinary experts have devoted their efforts toward identifying the HD-ILDs with an aim to prevent the additional occurrence of this fatal lung disease. From our experience with the epidemic of HD-ILDs, we have learned that stricter supervision of chemicals in everyday life is needed and a cautious approach is required in patients with atypical presentations to identify the related causes.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Environmental Health Center for Hazardous Chemical Exposure funded by the Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea (2019).
Fig. 1.
Chronologic changes in pulmonary function parameters in a child with humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung diseases. FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC, forced vital capacity.
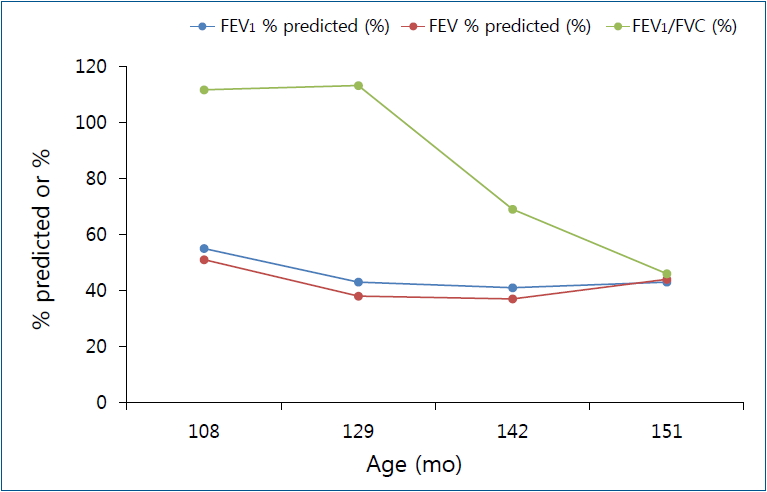
Fig. 2.
Radiologic features in a girl diagnosed with humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung diseases at 37 months of age. (A) Initial chest computed tomography (CT) after 3 weeks of development of symptoms including mild cough, decreased oral intake, and dyspnea. (B) Chest CT after 2 weeks of hospital administration. Combined air leak syndromes, patchy consolidation, and ground-glass opacities are observed. (C) After 3 weeks of hospitalization, the air leak syndrome was improved; however, diffuse centrilobular ground-glass opacities were observed with relative subpleural sparing. (D) In the resolving period, the centrilobular opacities disappeared with the remnant faint centrilobular nodules.

Fig. 3.
Pathologic findings of lung biopsy in a humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung disease case. (A) In the early phase, centrilobular distribution of interstitial thickening and fibrosis was observed (H&E, ×40). (B) Disrupted bronchioles infiltrated by lymphocytes and histiocytes were observed in the early phase (H&E, ×200). (C) In the advanced phase, interstitial thickening with fibrosis was observed with centrilobular distribution and relative sparing of the subpleural parenchyma (H&E, ×40). (D) Extensive interstitial fibroblast proliferation was seen in the pale myxoid stroma (arrows) and collapsed alveolar spaces were lined by activated pneumocytes (arrowhead). Intra-alveolar collection of foamy histiocytes (asterisk) was observed (H&E, ×200).
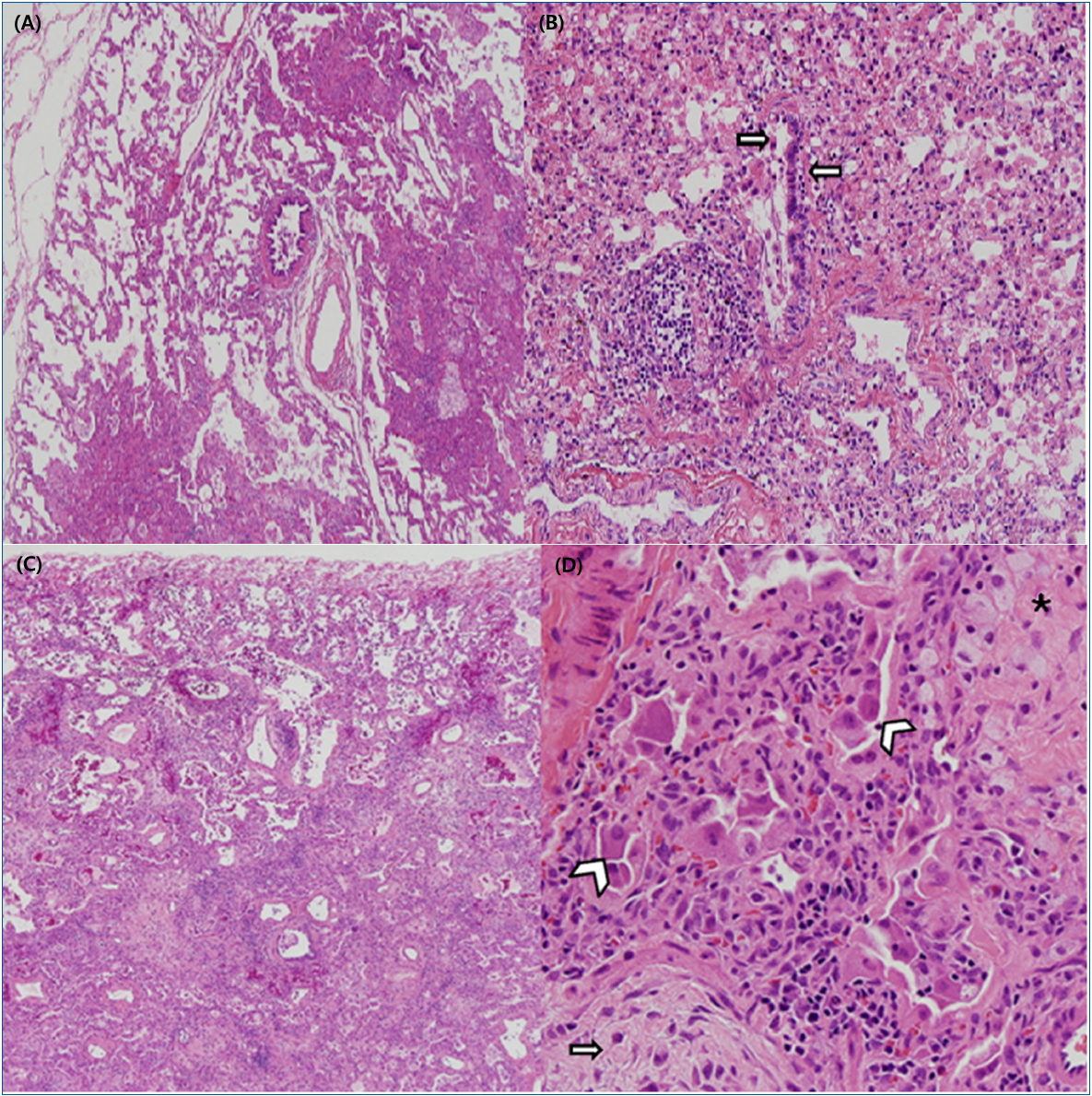
Table 1.
Main chemical components in various humidifier disinfectants in 447 children with HD-ILDs (listed by brand name)
| Brand names of the humidifier disinfectant | Main chemical component | Number of HD-ILDs (%) [18] |
|---|---|---|
| Oxy Saksak | PHMG phosphate | 176 (39.4) |
| Cefu | PGH | 27 (6.0) |
| Aekyung Home Clinic | CMIT/MIT | 22 (4.9) |
| E-mart Eplus | CMIT/MIT | 2 (0.4) |
| Lotte Mart Wiselect | PHMG phosphate | 13 (2.9) |
| Homeplus | PHMG phosphate | 3 (0.7) |
| Vegetable clean-up | PHMG phosphate | 0 (0.0) |
| Mixed brands | 204 (45.6) | |
| Brands with PHMG-P | PHMG-P | 42 (9.4) |
| Brands with a mixture of CMIT/MIT | CMIT/MIT | 2 (0.4) |
| Brands with a mixture of ingredients | 160 (35.8) | |
| Total | 447 (100) |
Patients with HD-ILDs included those in whom more than a possible degree of associationa) was found between HD usage and development of HD-ILDs.
HD-ILDs, humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung diseases; PHMG, polyhexamethylene guanidine; PGH, [oligo(2-(2-ethoxy)ethoxyethyl guanidinium chloride]; CMIT, chloromethylisothiazolinone; MIT, methylisothiazolinone.
Table 2.
Summary of studies on the mechanisms underlying the health effects of toxic chemicals in humidifier disinfectants
| Year | Title | Method | Main finding |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 [16] | Acute cardiovascular toxicity of sterilizers, PHMG, and PGH: severe inflammation in human cells and heart failure in zebrafish | Human lipoproteins, macrophages, dermal fibroblasts | Exposure to PHMG and PGH caused acute toxicity in the blood circulation system, including severe inflammation, atherogenesis, and aging, as well as embryotoxicity. |
| 2014 [17] | Cytotoxicity and gene expression profiling of PHMG hydrochloride in human alveolar A549 cells | A549 cells | PHMG induces cytotoxicity through the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species and alteration of gene expression. |
| 2015 [43] | The role of the NF-κB signaling pathway in PHMG phosphate-induced inflammatory response in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells | Murine RAW264.7 macrophages | PHMG phosphate induces inflammatory responses via the NF-κB signaling pathway. |
| 2016 [22] | Aerosol particles of PHMG phosphate induce pulmonary inflammatory and fibrotic responses | Rats | PHMG phosphate infiltrating the lungs in the form of aerosol particles would induce an airway barrier injury via the generation of reactive oxygen species ROS and release of fibrotic inflammatory cytokines, and trigger a wound-healing response, leading to pulmonary fibrosis. |
| 2017 [23] | Analysis of genomic responses in a rat lung model treated with a humidifier sterilizer containing PHMG phosphate | Rats | Twenty-one genes were upregulated and 4 genes were downregulated in response to PHMG phosphate in a time-dependent manner. These findings suggest that changes in genomic responses could be a significant molecular mechanism underlying PHMG phosphate toxicity. |
| 2018 [24] | MicroRNA regulatory networks reflective of PHMGinduced fibrosis in A549 human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells | A549 cells | Thirteen putative EMT-related targets that may play a role in PHMG phosphate-induced fibrosis. |
| 2019 [44] | PHMG phosphate-induced ROS-mediated DNA damage caused cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in lung epithelial cells | A549 cells | PHMG-p triggered G1/S arrest and apoptosis through the ROS/ATM/p53 pathway in lung epithelial cells. |
Table 3.
Clinical characteristics of HD-ILDs in children
Table 4.
Differential diagnosis of HD-ILDs
| Variable | HD-ILD | Acute interstitial pneumonitis | Hypersensitivity pneumonitis [45] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause | Toxic chemicals in HD | No identified causes | Recurrent exposure to causative environmental |
| Clinical feature | Subacute cough and dyspnea followed by rapidly progressing respiratory difficulty | Rapid onset with a prodromal illness for 7− 14 days before presentation | Fever, dry cough, and dyspnea after exposure to causative agents |
| Radiologic feature | Early: patchy consolidation, mainly in the lower lung | Diffuse, bilateral, air-space opacification | Upper- and middle-lobe predominant groundglass opacities, poorly defined centrilobular nodules; mosaic attenuation, air trapping, or rarely, consolidation |
| Late: centrilobular opacity | |||
| Resolving phase: faint centrilobular nodules | |||
| Commonly combined air leak syndrome | |||
| Pathologic feature | Early: bronchiolar destruction, with alveolar destruction | Diffuse alveolar damage | Lymphoplasmocytic/mononuclear (macrophage) infiltrates, airway-centric lymphocytic infiltrates |
| Late: displaced parenchymal architecture due to inflammation and fibrosis, especially in the centrilobular area | |||
| Treatment | No identified treatment strategies | Supportive care | Exposure avoidance |
| Prognosis | High mortality rate (43.8%–58%) | High mortality (more than 50 %) | Variable depends on causal antigen, duration of antigen exposure, and host response |
References
1. Clement A, Eber E. Interstitial lung diseases in infants and children. Eur Respir J 2008;31:658–66.


2. Kurland G, Deterding RR, Hagood JS, Young LR, Brody AS, Castile RG, et al. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: classification, evaluation, and management of childhood interstitial lung disease in infancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013;188:376–94.



3. Kim KW, Ahn K, Yang HJ, Lee S, Park JD, Kim WK, et al. Humidifier disinfectant-associated children's interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014;189:48–56.


4. Yoon J, Cho HJ, Lee E, Choi YJ, Kim YH, Lee JL, et al. Rate of humidifier and humidifier disinfectant usage in Korean children: a nationwide epidemiologic study. Environ Res 2017;155:60–3.


5. Jeon BH, Park YJ. Frequency of humidifier and humidifier disinfectant usage in Gyeonggi provine. Environ Health Toxicol 2012;27:e2012002.




6. Quiros-Alcala L, Hansel NN, McCormack MC, Matsui EC. Paraben exposures and asthma-related outcomes among children from the US general population. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2019;143:948–56. e4.


7. Cheon CK, Jin HS, Kang EK, Kim HB, Kim BJ, Yu J, et al. Epidemic acute interstitial pneumonia in children occurred during the early 2006s. Korean J Pediatr 2008;51:383–90.

8. Kim BJ, Kim HA, Song YH, Yu J, Kim S, Park SJ, et al. Nationwide surveillance of acute interstitial pneumonia in Korea. Korean J Pediatr 2009;52:324–9.

9. Lee E, Seo JH, Kim HY, Yu J, Song JW, Park YS, et al. Two series of familial cases with unclassified interstitial pneumonia with fibrosis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 2012;4:240–4.



10. Koh Y. What have we learnt from the tragic events related to humidifier disinfectant inhalation in 2011? J Korean Med Sci 2016;31:1855–6.



11. Huh JW, Hong SB, Do KH, Koo HJ, Jang SJ, Lee MS, et al. Inhalation lung injury associated with humidifier disinfectants in adults. J Korean Med Sci 2016;31:1857–62.



12. Lee E, Seo JH, Kim HY, Yu J, Jhang WK, Park SJ, et al. Toxic inhalational injury-associated interstitial lung disease in children. J Korean Med Sci 2013;28:915–23.



13. Yang HJ, Kim HJ, Yu J, Lee E, Jung YH, Kim HY, et al. Inhalation toxicity of humidifier disinfectants as a risk factor of children's interstitial lung disease in Korea: a case-control study. PLoS One 2013;8:e64430.



14. Kim HJ, Lee MS, Hong SB, Huh JW, Do KH, Jang SJ, et al. A cluster of lung injury cases associated with home humidifier use: an epidemiological investigation. Thorax 2014;69:703–8.


15. Hong SB, Kim HJ, Huh JW, Do KH, Jang SJ, Song JS, et al. A cluster of lung injury associated with home humidifier use: clinical, radiological and pathological description of a new syndrome. Thorax 2014;69:694–702.


16. Kim JY, Kim HH, Cho KH. Acute cardiovascular toxicity of sterilizers, PHMG, and PGH: severe inflammation in human cells and heart failure in zebrafish. Cardiovasc Toxicol 2013;13:148–60.



17. Jung HN, Zerin T, Podder B, Song HY, Kim YS. Cytotoxicity and gene expression profiling of polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride in human alveolar A549 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2014;28:684–92.


18. Ryu SH, Park DU, Lee E, Park S, Lee SY, Jung S, et al. Humidifier disinfectant and use characteristics associated with lung injury in Korea. Indoor Air 2019;29:735–47.


19. Park DU, Ryu SH, Lim HK, Kim SK, Choi YY, Ahn JJ, et al. Types of household humidifier disinfectant and associated risk of lung injury (HDLI) in South Korea. Sci Total Environ 2017;596-597:53–60.


20. Park DU, Ryu SH, Roh HS, Lee E, Cho HJ, Yoon J, et al. Association of high-level humidifier disinfectant exposure with lung injury in preschool children. Sci Total Environ 2018;616-617:855–62.


21. Song JA, Park HJ, Yang MJ, Jung KJ, Yang HS, Song CW, et al. Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate induces severe lung inflammation, fibrosis, and thymic atrophy. Food Chem Toxicol 2014;69:267–75.


22. Kim HR, Lee K, Park CW, Song JA, Shin DY, Park YJ, et al. Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate aerosol particles induce pulmonary inflammatory and fibrotic responses. Arch Toxicol 2016;90:617–32.



23. Kim MS, Jeong SW, Choi SJ, Han JY, Kim SH, Yoon S, et al. Analysis of genomic responses in a rat lung model treated with a humidifier sterilizer containing polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate. Toxicol Lett 2017;268:36–43.


24. Shin DY, Jeong MH, Bang IJ, Kim HR, Chung KH. MicroRNA regulatory networks reflective of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate-induced fibrosis in A549 human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol Lett 2018;287:49–58.


25. Chang HY, Suh DI, Yang SI, Kang MJ, Lee SY, Lee E, et al. Prenatal maternal distress affects atopic dermatitis in offspring mediated by oxidative stress. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016;138:468–75. e5.


26. Lee E, Son SK, Yoon J, Cho HJ, Yang SI, Jung S, et al. Two cases of chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone-associated toxic lung injury. J Korean Med Sci 2018;33:e119.



27. Cho HJ, Park DU, Yoon J, Lee E, Yang SI, Kim YH, et al. Effects of a mixture of chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone on peripheral airway dysfunction in children. PLoS One 2017;12:e0176083.



28. Lee SY, Park DU, Do KH, Jang SJ, Hong SJ. The pathological findings of chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone-associated lung injury. J Korean Med Sci 2019;34:e102.



29. Jhang WK, Park SJ, Lee E, Yang SI, Hong SJ, Seo JH, et al. The first successful heart-lung transplant in a korean child with humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung disease. J Korean Med Sci 2016;31:817–21.



30. Cho HJ, Lee SY, Park D, Ryu SH, Yoon J, Jung S, et al. Early-life exposure to humidifier disinfectant determines the prognosis of lung function in children. BMC Pulm Med 2019;19:261




31. Lee E, Lee SH, Kwon JW, Kim YH, Yoon J, Cho HJ, et al. Persistent asthma phenotype related with late-onset, high atopy, and low socioeconomic status in school-aged Korean children. BMC Pulm Med 2017;17:45




32. McGeachie MJ, Yates KP, Zhou X, Guo F, Sternberg AL, Van Natta ML, et al. Patterns of growth and decline in lung function in persistent childhood asthma. N Engl J Med 2016;374:1842–52.



33. Yoon HM, Lee E, Lee JS, Do KH, Jung AY, Yoon CH, et al. Humidifier disinfectant-associated children's interstitial lung disease: computed tomographic features, histopathologic correlation and comparison between survivors and non-survivors. Eur Radiol 2016;26:235–43.



34. Dishop MK. Paediatric interstitial lung disease: classification and definitions. Paediatr Respir Rev 2011;12:230–7.


35. Hirschmann JV, Pipavath SN, Godwin JD. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: a historical, clinical, and radiologic review. Radiographics 2009;29:1921–38.


36. Ohshimo S, Guzman J, Costabel U, Bonella F. Differential diagnosis of granulomatous lung disease: clues and pitfalls. Number 4 in the series "pathology for the clinician" edited by Peter Dorfmüller and Alberto Cavazza. Eur Respir Rev 2017;26:170012



37. Yoon J, Lee SY, Lee SH, Kim EM, Jung S, Cho HJ, et al. Exposure to humidifier disinfectants increases the risk of asthma in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2018;12:1583–6.

38. Lee E, Hong SJ. Phenotypes of allergic diseases in children and their application in clinical situations. Korean J Pediatr 2019;62:325–33.




39. Lundov MD, Mosbech H, Thyssen JP, Menné T, Zachariae C. Two cases of airborne allergic contact dermatitis caused by methylisothiazolinone in paint. Contact Dermatitis 2011;65:176–9.


40. Kaae J, Menné T, Thyssen JP. Presumed primary contact sensitization to methylisothiazolinone from paint: a chemical that became airborne. Contact Dermatitis 2012;66:341–2.


41. Shim HE, Lee JY, Lee CH, Mushtaq S, Song HY, Song L, et al. Quantification of inhaled aerosol particles composed of toxic household disinfectant using radioanalytical method. Chemosphere 2018;207:649–54.


42. Yoo S, Sim M, Choi J, Jeon K, Shin J, Chung S, et al. Psychological responses among humidifier disinfectant disaster victims and their families. J Korean Med Sci 2019;34:e29.



43. Kim HR, Shin DY, Chung KH. The role of NF-κB signaling pathway in polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate induced inflammatory response in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Toxicol Lett 2015;233:148–55.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


