Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 60(5); 2017 |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Macrolide resistance rate of Mycoplasma pneumoniae has rapidly increased in children. Studies on the clinical features between macrolide susceptible-M. pneumoniae (MSMP) and macrolide resistant-M. pneumoniae (MRMP) are lacking. The aim of this study was to identify the macrolide resistance rate of M. pneumoniae in Korean children with M. pneumoniae penupmonia in 2015 and compare manifestations between MSMP and MRMP.
Methods
Among 122 children (0–18 years old) diagnosed with M. pneumoniae pneumonia, 95 children with the results of macrolide sensitivity test were included in this study. Clinical manifestations were acquired using retrospective medical records.
Results
The macrolide resistant rate of M. pneumoniae was 87.2% (82 of 94 patients) in children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia. One patient showed a mixed type of wild type and A2063G mutation in 23S rRNA of M. pneumoniae. There were no significant differences in clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings between the MSMP and MRMP groups at the first visit to our hospital. The time interval between initiation of macrolide and defervescence was significantly longer in the MRMP group (4.9±3.3 vs. 2.8±3.1 days, P=0.039).
Conclusion
The macrolide resistant rate of M. pneumoniae is very high in children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia in Korea. The clinical manifestations of MRMP are similar to MSMP except for the defervescence period after administration of macrolide. Continuous monitoring of the occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of MRMP is required to control its spread and establish strategies for treating second-line antibiotic resistant M. pneumoniae infection.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae can cause a variety of respiratory tract diseases, such as upper respiratory infection and atypical pneumonia1). The clinical course of M. pneumoniae infection is diverse and ranges from self-limiting to severe pneumonia with extrapulmonary complications2). Among the diverse clinical presentations, lower respiratory tract infections with pneumonia most commonly require clinical attention.
Macrolide is considered the first-line treatment for M. pneumoniae infection3). Transitional mutations in 23S rRNA of M. pneumoniae were reported in erythromycin-resistant M. pneumoniae in 1995.4) Thereafter, especially since 2000, the prevalence of macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae (MRMP) infection has rapidly increased, with variations according to region and study population5). The macrolide resistance rate of M. pneumoniae is much higher in East Asia than in Europe and North America, with up to 87.1% in Japanese children in 20115,6,7,8). In recent M. pneumoniae epidemics in Korea, the macrolide resistance rate has markedly increased from 2.9% in 2003 to 62.9% in 20115).
In cases of MRMP infection, secondary treatment options are limited due to adverse effects of tetracycline or fluoroquinolones, especially in children9). In addition, resistance to second-line therapy is a concern given the rapid increase in MRMP prevalence. Therefore, continuous survey on the prevalence of MRMP and surveillance on the prescription for M. pneumoniae are inevitably needed in the prevailing state of MRMP.
Previous studies comparing the clinical manifestations of macrolide susceptible M. pneumoniae (MSMP) and MRMP showed inconclusive results10,11,12,13). Although a high macrolide resistance rate of M. pneumoniae has been reported, studies on the treatment patterns of MRMP pneumonia in children are lacking. Further investigation is needed to develop appropriate treatment strategies and monitor the emergence of second-line therapy resistant M. pneumoniae.
The aim of this study was to identify the prevalence of macrolide resistance in children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia in 2015 and compare the clinical features and treatment patterns of MSMP and MRMP in these children.
This study enrolled patients aged between 0–18 years old, who were diagnosed with community-acquired pneumonia due to M. pneumoniae who visited our tertiary hospital in Seoul between April 2015 and November 2015. All of the present study patients underwent chest radiography and either blood tests including specific IgM against M. pneumoniae using a LIAISON Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM kit (DiaSorin, Dublin, Ireland) or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for M. pneumoniae using the AmpliSens Mycoplasma pneumoniae/Chlamydia pneumoniae-FRT PCR kit (InterLabService Ltd., Moscow, Russia) at the initial visit to the hospital.
During the study period, 122 children were diagnosed with M. pneumoniae pneumonia on the basis of either specific IgM positivity in a blood test or positive PCR result combined with chest radiography and physical examination14). Four children received only serologic testing for specific IgM against M. pneumoniae and showed positivity. Eight children underwent only PCR analysis of their sputum for M. pneumoniae and showed a positive result. Ninety-two children showed both specific IgM and PCR positivity for M. pneumoniae. The remaining 18 children were tested for both specific IgM and PCR for M. pneumoniae, but showed a positive result only for PCR. Among the 118 children with positive result by PCR for M. pneumoniae, macrolide resistance tests were performed for 95 children with available samples.
All of the chest radiographs were reviewed by an experienced radiologist. Infiltration on the chest radiography was defined as any poorly defined opacity in the lung field and consolidation was defined as air-space opacification. Information on clinical manifestations and prescribed medicine during the disease course was obtained using a retrospective chart review. Fever was defined as a body temperature above 38℃. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center (approval number: 2015-1400).
During the study period, PCR for M. pneumoniae was performed in children with pneumonia diagnosed on the basis of chest radiography and physical examination. This analysis was done using nasopharyngeal aspirates collected upon visiting to the hospital. For detection of M. pneumoniae, our previously reported procedure was applied15). Evaluations of macrolide resistance were performed in children with a positive PCR result for M. pneumoniae. A total of 95 M. pneumoniae isolates, including one case of a mixed type of MSMP and MRMP, were obtained from sputum samples. Domain V of the 23S rRNA gene was amplified using previously described primer pairs (GenBank accession no. X68422)16). Nested PCR primers and the conditions described by Oh et al.17) were used for the specimens. PCR products were purified using a Power Gel Extraction kit (TaKaRa Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan). The purified templates were sequenced using an ABI Prism BigDye Terminator v3.1 cycle sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and analyzed on an ABI 3730xl DNA analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken by flocked swab and submitted in Universal Transport Medium (Copan Italia S.p.A., Brescia, Italy). Viral RNA was extracted from the swabs with NucliSENS easyMAG (bioMerieux, Marcy I'Etoile, France). cDNA was synthesized using a Revert Aid First Standard cDNA Synthesis kit (Fermentas, York, UK), and each cDNA preparation was subjected to three sets of real-time multiplex PCR with an Anyplex II RV16 Detection kit (Seegene, Seoul, Korea); this kit targets 16 respiratory viruses, including respiratory syncytial viruses A and B, adenovirus, rhinovirus, parainfluenza viruses 1 to 4, influenza viruses A and B, metapneumovirus, bocavirus, corona viruses OC43, 229E, and NL63, and enterovirus. These 16 viruses cause the most common respiratory infections in Korea according to weekly monitoring by the Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention18).
To compare the clinical and radiologic features and treatment regimen between MSMP and MRMP, a t test, Mann-Whitney U test, chi-square test, and Fisher exact test were used, as appropriate. To control for the confounding factors, logistic regression analysis was performed. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 21.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA).
The macrolide resistant rate of M. pneumoniae was 87.2% (82 of 94) in children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia (Table 1). Those with MRMP were significantly younger than those with MSMP (MSMP, 7.6±3.1 years; MRMP, 5.1±2.6 years; P=0.001) in the present study. When stratified according to age, the decreasing pattern of the prevalence of MRMP was observed with a weak trend significance (P=0.052) as follows: 0–4 years, 95.1% (39 of 41); 5–9 years, 81.8% (36 of 44); 10–18 years, 77.8% (7 of 9) (Fig. 1). The macrolide resistance rate of M. pneumoniae was higher in late summer and fall (Fig. 2).
Among the 95 M. pneumoniae-positive samples, 82 cases were diagnosed with A2063G mutation. No other known mutations, such as A2064, in the 23S rRNA gene of M. pneumoniae were identified in the present study. The other 12 samples carried a wild type of 23S rRNA gene. The remaining one case showed a mix of wild type and A2063G mutation.
There were no significant differences in total fever duration and respiratory rate at the initial hospital visit between the MSMP and MRMP groups. The admission rate due to M. pneumoniae pneumonia was 72.6% (69 of 95) in the total population. The hospitalization rate was higher in the MRMP group compared with the MSMP group without statistical significance (75.6% vs. 58.3%; P=0.206) (Table 1). Blood lymphocytes were significantly increased in the MRMP group compared with the MSMP group (P=0.003), although this difference was not significant after controlling for age. Among the children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia, 58.3% showed coinfection with respiratory viruses such as rhinovirus and parainfluenza virus without significant differences between the MSMP (83.3%, 5 of 6) and MRMP (55.6%, 30 of 54) groups.
Chest radiography indicated that consolidation (MSMP, 10 of 12 vs. MRMP, 46 of 82) and effusion (MSMP, 3 of 12 vs. MRMP, 9 of 82) were commonly involved in M. pneumoniae pneumonia regardless of macrolide resistance (Table 2). There were no statistical differences in the prevalence of consolidation or effusion between the MSMP and MRMP groups.
The total duration of antibiotic administration, including non-macrolide antibiotics (beta-lactam and cephalosporin) and macrolide, was slightly longer in the MRMP group than in the MSMP group, without statistical significance. The total number of administered antibiotics was higher in the MRMP group than in the MSMP group (P=0.046) (Table 3). The most commonly prescribed initial antibiotic was macrolide in both the MSMP (80.0%) and MRMP (68.4%) groups, without significant significance. Tetracycline or fluoroquinolone were administered due to unresponsiveness to macrolide in both the MSMP (25.0%, 3 of 12) and MRMP (29.3%, 24 of 82) groups. Changes of antibiotics to other antibiotics among macrolides (azithromycin, clarithromycin, or roxithromycin) were more common in the MRMP group compared with the MSMP group without statistical significance (41.8% vs. 18.2%). The time intervals between the initiation of macrolide and defervescence were significantly longer in the MRMP group compared with the MSMP group (4.9±3.3 vs. 2.8±3.1 days, P=0.039). There was no significant difference in the period between onset of fever and start of macrolide administration (MSMP, 6.6±7.0 days; MRMP, 4.1±3.2 days; P=0.254). Fever was subsided after 1.7 days from the start of administration of tetracycline or fluoroquinolone. There were no side effects of the treatment with tetracycline or fluoroquinolone. None of the variables listed in Table 3 were confounded by age. All patients hospitalized due to M. pneumoniae pneumonia were discharged in a defervescent state with partial or total improvement in chest radiography compared with administration. There was no significant difference in the hospitalization duration between the MSMP (mean±standard deviation, 7.7±5.6 days) and MRMP (6.3±3.4 days) groups. There were also no cases in our current series who needed ventilator care or transfer to an intensive care unit due to the pneumonia.
A mix of wild type and A2363G mutant M. pneumoniae 23S rRNA was detected in a 4-year-old girl, who had presented with fever and cough 4 days earlier. She was prescribed with a 3-day regimen of clarithromycin before sputum sample collection for sequencing of the 23S rRNA gene.
In our current study, we have identified a macrolide resistance rate of 87.2% in children diagnosed with M. pneumoniae in 2015. All cases of this macrolide-resistant strain showed an A2063G point mutation in the 23S rRNA gene. MRMP was detected in younger children with a higher prevalence. There were no significant differences in the clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings between MSMP and MRMP groups. Administration of macrolide led to more rapid defervescence in the MSMP group compared with the MRMP group.
The prevalence of MRMP observed in our present study was higher than that reported for 2000 to 2011 in Korea. This prevalence increased over time and exceeded a peak of 62.9% in 20115), and was similar to that reported in Japanese children in 2011 (87.1%)8) and Chinese children in 2008–2009 (90.0%)13). However, the prevalence of MRMP in Europe has been reported to be less than 26%19,20). Recent studies on the prevalence of MRMP infection are lacking, and our present analysis is significant because it reports on the recent macrolide resistance rate of M. pneumoniae with increasing pattern in Korean children.
We found no significant differences in clinical manifestations or laboratory findings between the MRMP and MSMP groups. Even in the MSMP group, complications of M. pneumoniae infection, such as hepatitis, high C-reactive protein levels, long-term fever, and consolidation and effusion in chest radiography, were similar to those in the MRMP group. In addition, no differences in the clinical manifestations between the 2 groups were found to be associated with the administration of tetracycline or fluoroquinolone before identification of macrolide sensitivity, even in the MSMP group. Previous studies on the comparisons of clinical manifestations between MSMP and MRMP groups also reported no significant differences12,21). However, the mean duration from the start of macrolide treatment to defervescence was longer in the MRMP group compared with the MSMP group in our present study, which is similar to the results of the previous study11). The relatively long-term period of fever in M. pneumoniae infection might be partially attributable to the immune reaction in associated with M. pneumoniae infection regardless of the macrolide resistance22). Large-scale studies on the clinical course of these infections are needed in the future to compare clinical manifestation between MSMP and MRMP infection.
In previous studies, the most common macrolide resistance mutation (up to 97.5%) was the A2063G mutation in the 23s rRNA5,21), which we also observed in our present study. Macrolide inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of 23S RNA at nucleotide positions 2063 and 206421). Mutations at these sites enable protein synthesis that promotes M. pneumoniae survival. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of macrolides differs according to the specific point mutation7,8,21). A2063G and A2064G confer the most resistance to macrolides and also produce resistance to 14-ring macrolides, such as clarithromycin (MIC, 8 to >128) and roxithromycin (MIC, 0.008 to 128), and 15-ring macrolides such as azithromycin (MIC, 1 to 64)5,7,23). Compared to clarithromycin, azithromycin and roxithromycin have lower MIC levels and are preferred as an initial treatment option for M. pneumoniae infection with unidentified macrolide resistance. As widespread macrolide usage is associated with the occurrence of MRMP, continuous monitoring of the MICs for each macrolide and secondary line therapy against M. pneumoniae infection are needed to identify the advent of M. pneumoniae stains that are resistant to other antibiotics and establish treatment strategies for MRMP infection.
We identified one case with mixed A2063G and wild type 23S rRNA. Although most macrolide resistance is detected at the start of the disease course7), a conversion from MSMP to MRMP is also possible during clarithromycin treatment24). Possible underlying mechanisms of mixed type of macrolide resistance in M. pneumoniae include selected outgrowth of MRMP resulting from administration of clarithromycin. The aforementioned case might support the outgrowth of MRMP during M. pneumoniae treatment with macrolide.
In our present study series, 30.2% of the children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia were initially prescribed nonmacrolide antibiotics. Although M. pneumoniae is known to cause pneumonia in older children14), it can also cause lower respiratory tract infections including pneumonia in children as young as 6 months old25). Therefore, M. pneumoniae can be considered as a pathogen for respiratory infections, even in young children, and especially during an epidemic of M. pneumoniae.
Our present study is significant because it has compared the manifestations of MRMP and MSMP in children in a high macrolide resistance period for M. pneumoniae. However, it also had several limitations of note. All of the patients analyzed visited our tertiary hospital, and this population may therefore have included some very severe M. pneumoniae cases. However, we found no significant differences between the clinical, radiologic, and laboratory findings for the MSMP and MRMP groups analyzed. Our sample size was relatively small, and the study duration was relatively short. Therefore, our analysis lacked an evaluation of the full spectrum of M. pneumoniae pneumonia in relation to macrolide resistance. Also, there was a significant difference in age distribution between the 2 groups, which caused a selection bias. However, the prevalence of consolidation and effusion on chest radiography, which might suggest more severe pneumonia, was similar between our 2 study groups even after adjustment for age (data not shown). For the diagnosis of M. pneumoniae infection, serological assays and PCR using sputum samples are widely used. However, these tests have limitations in that false responses can be obtained depending on sample collection time and remote infection in serology tests and colonization in airways in PCR.
In conclusion, there was a high macrolide resistance rate of M. pneumoniae (87.2%) in Korean children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia in 2015. MRMP pneumonia occurred across all ages, including infants. Although there were no significant differences in the clinical, laboratory and radiologic findings between the MSMP and MRMP groups, MRMP is associated with persistence of fever during its clinical course. Further large-scale, nationwide studies are required to control the spread of MRMP and establish strategies for treatment of MRMP infection.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the BioNano Health-Guard Research Center funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea as a Global Frontier Project (grant number: H-GUARD_ERND2-5).
Notes
Conflict of interest:
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Eun BW, Kim NH, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Korean children: the epidemiology of pneumonia over an 18-year period. J Infect 2008;56:326–331.


2. Defilippi A, Silvestri M, Tacchella A, Giacchino R, Melioli G, Di Marco E, et al. Epidemiology and clinical features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children. Respir Med 2008;102:1762–1768.


3. Kwiatkowska B, Maślińska M. Macrolide therapy in chronic inflammatory diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2012;2012:636157


4. Lucier TS, Heitzman K, Liu SK, Hu PC. Transition mutations in the 23S rRNA of erythromycin-resistant isolates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1995;39:2770–2773.



5. Hong KB, Choi EH, Lee HJ, Lee SY, Cho EY, Choi JH, et al. Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, South Korea, 2000–2011. Emerg Infect Dis 2013;19:1281–1284.



6. Dumke R, von Baum H, Lück PC, Jacobs E. Occurrence of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains in Germany. Clin Microbiol Infect 2010;16:613–616.


7. Cao B, Zhao CJ, Yin YD, Zhao F, Song SF, Bai L, et al. High prevalence of macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates from adult and adolescent patients with respiratory tract infection in China. Clin Infect Dis 2010;51:189–194.


8. Okada T, Morozumi M, Tajima T, Hasegawa M, Sakata H, Ohnari S, et al. Rapid effectiveness of minocycline or doxycycline against macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in a 2011 outbreak among Japanese children. Clin Infect Dis 2012;55:1642–1649.


9. Principi N, Esposito S. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: its role in respiratory infection. J Antimicrob Chemother 2013;68:506–511.


10. Miyashita N, Kawai Y, Akaike H, Ouchi K, Hayashi T, Kurihara T, et al. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae in adolescents with community-acquired pneumonia. BMC Infect Dis 2012;12:126



11. Suzuki S, Yamazaki T, Narita M, Okazaki N, Suzuki I, Andoh T, et al. Clinical evaluation of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006;50:709–712.



12. Matsubara K, Morozumi M, Okada T, Matsushima T, Komiyama O, Shoji M, et al. A comparative clinical study of macrolide-sensitive and macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in pediatric patients. J Infect Chemother 2009;15:380–383.


13. Liu Y, Ye X, Zhang H, Xu X, Li W, Zhu D, et al. Characterization of macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolated from children in Shanghai, China. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2010;67:355–358.


15. Yoo SJ, Kim HB, Choi SH, Lee SO, Kim SH, Hong SB, et al. Differences in the frequency of 23S rRNA gene mutations in Mycoplasma pneumoniae between children and adults with community-acquired pneumonia: clinical impact of mutations conferring macrolide resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012;56:6393–6396.



16. Wolff BJ, Thacker WL, Schwartz SB, Winchell JM. Detection of macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae by real-time PCR and high-resolution melt analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2008;52:3542–3549.



17. Oh CE, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Detection of genetic mutations associated with macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Korean J Pediatr 2010;53:178–183.

18. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Acute infectious agents laboratory surveillance reports [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, c2012;cited 2014 Oct 2. Available from: http://www.cdc.go.kr.
19. Chironna M, Sallustio A, Esposito S, Perulli M, Chinellato I, Di Bari C, et al. Emergence of macrolide-resistant strains during an outbreak of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in children. J Antimicrob Chemother 2011;66:734–737.


20. Pereyre S, Charron A, Renaudin H, Bébéar C, Bébéar CM. First report of macrolide-resistant strains and description of a novel nucleotide sequence variation in the P1 adhesin gene in Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical strains isolated in France over 12 years. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:3534–3539.



21. Morozumi M, Takahashi T, Ubukata K. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: characteristics of isolates and clinical aspects of community-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Chemother 2010;16:78–86.


22. Yang J, Hooper WC, Phillips DJ, Talkington DF. Cytokines in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2004;15:157–168.


23. Ye Y, Li S, Yajun L, Li Y, Ren T, Liu K. Mycoplasma pneumoniae 23S rRNA gene mutations and mechanisms of macrolide resistance. Lab Med 2013;44:63–68.

Fig. 1
Rate of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children according to age. P for trend=0.052.
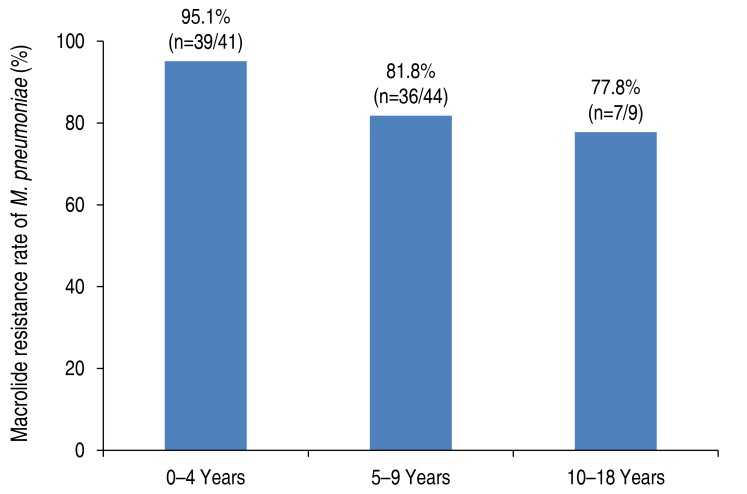
Fig. 2
Monthly distribution of the occurrence of MSMP and MRMP pneumonia in Korean children in 2015. MSMP, macrolide susceptible-Mycoplasma pneumoniae; MRMP, macrolide resistant-M. pneumoniae.
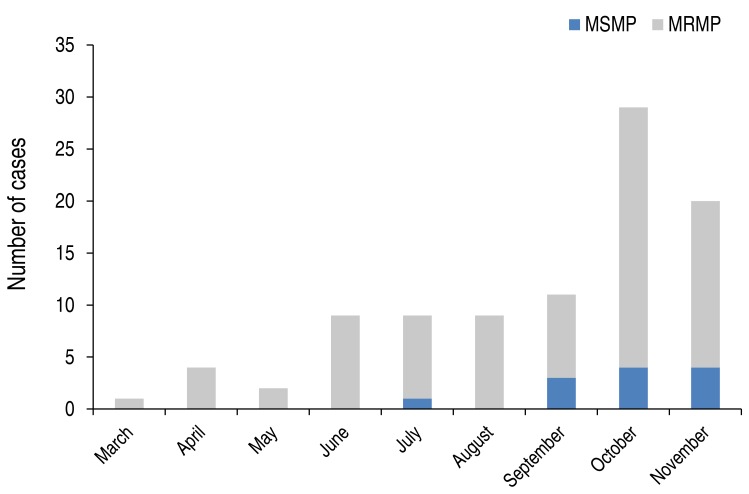
Table 1
Clinical characteristics of study participants with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia according to macrolide susceptibility
Table 2
Comparison of radiologic features between children infected with MSMP and MRMP
| MSMP (n=12) | MRMP (n=82) | Total (n=94) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infiltration | 12 (100) | 82 (100) | 94 (100) | NA |
| Consolidation | 10 (83.3) | 46 (56.1) | 56 (59.6) | 0.073 |
| Effusion | 3 (25.0) | 9 (11.0) | 12 (12.8) | 0.174 |



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


