Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 55(3); 2012 |
Abstract
Several authors suggested that the clinical characteristics of incomplete presentation of Kawasaki disease are similar to those of complete presentation and that the 2 forms of presentation are not separate entities. Based on this suggestion, a diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease in analogy to the findings of complete presentation is reasonable. Currently, the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease might be made in cases with fewer classical diagnostic criteria and with several compatible clinical, laboratory or echocardiographic findings on the exclusion of other febrile illness. Definition of incomplete presentation in which coronary artery abnormalities are included as a necessary condition, is restrictive and specific. The validity of the diagnostic criteria of incomplete presentation by the American Heart Association should be thoroughly tested in the immediate future.
Kawasaki disease is an acute, self-limited systemic type of vasculitis that occurs predominantly in young children. After the 1st report by Tomisaku Kawasaki in Japan1), it is now recognized as the leading cause of acquired heart disease in children in developed countries. The etiology of Kawasaki disease is still unknown and no single pathognomonic clinical or laboratory finding for the diagnosis has been identified. To establish a diagnosis, we inevitably depend on the diagnostic criteria, which are the typical constellation of signs and symptoms, prepared by the Japanese Kawasaki Disease Research Committee2) or the American Heart Association (AHA)3). However, pediatricians sometimes encounter febrile children who do not fulfill the diagnostic criteria but have several findings compatible with those of Kawasaki disease. In this situation, the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease is a clinical challenge, which cannot be avoided by delaying the diagnosis because of the risk of coronary complications pertaining even to the incomplete presentation of the disease4,5). The diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease is reviewed in this paper.
The phrase "atypical Kawasaki disease" was initially used to describe patients with coronary complications who do not fulfill the classical diagnostic criteria6). Recently, the term "atypical Kawasaki disease" has been used to describe patients with incomplete presentation of the disease, regardless of the presence of coronary complications7,8), and is exchangeable for "incomplete Kawasaki disease"2,5). Newburger et al.9) proposed that "atypical Kawasaki disease" should be reserved for patients with complications, e.g., renal impairment, that are generally not seen in Kawasaki disease. This proposition has been supported by other authors4,10,11).
The diagnostic criteria established by the AHA (Table 1)3) are different from the Japanese criteria (Table 2)2) with regard to fever prolongation (≥5 days) as a necessary criterion. In the Japanese criteria, fever prolongation is just an optional criterion and there is no description of the size of cervical lymph nodes (Table 2). In spite of rarely reported cases of Kawasaki disease without fever12), a diagnosis of complete Kawasaki disease is not difficult in typical cases without regard to a selected criteria. Because of a need for early diagnosis and management and alleviation of fever after early infusion of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), the duration of fever was modified in the commentary in both criteria2,3). According to the AHA criteria, experienced clinicians who have treated many Kawasaki disease patients can establish the diagnosis before day 49), and a duration of fever of less than 5 days, which can be achieved by early IVIG treatment, can be considered as a principal symptom according to the Japanese criteria2).
The reported prevalence of incomplete presentation was 15 to 36.2% among patients with Kawasaki disease4,5,7,10,11,13-15). Children with incomplete presentation were more likely to be at the extremes of the age spectrum as compared to those with complete presentation. The prevalence of incomplete presentation was relatively higher in the younger-aged patients16,17). One study reported that patients with incomplete presentation were younger than patients with complete presentation15). In other reports, there was no difference in the mean/median age between the 2 groups5,10,11). However, relatively more children with incomplete presentation were in the extremes of the age spectrum (≤1 year old, or ≥5 to 9 years old)4,11). The risk of delayed diagnosis and management in young infants with incomplete presentation has been pointed out in the past18,19).
No other demographic features (including gender), except the prevalent age, has been reported to be different between patients with incomplete and complete presentation4,11,15). The presence of classical clinical findings in patients with incomplete presentation is properly less frequent than in patients with complete presentation. The frequently reported findings which less frequently observed in incomplete presentation are cervical lymphadenopathy (19 to 38.6%) and extremity changes (21 to 44.3%), and this pattern of order of observed frequencies is equal to that noted in patients with complete presentation4,10,11,20). Comparison of laboratory findings (complete blood count, albumin, hepatic transaminase, acute phase reactants) between these 2 groups also showed no significant differences11,20,21). However, low levels of serum alanine aminotransferase10,11,20), low levels of gamma glutamyl transferase10), low frequency of hyponatremia22), and low frequency of pyuria were reported in children with incomplete presentation20). Several authors who had compared clinical characteristics between the 2 forms of Kawasaki disease suggested that they are not separate entities but are probably located along a continuous spectrum, placing more weight on demographic and laboratory similarities between the 2 groups8,10,11). On the basis of this suggestion, making the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease in analogy to the findings of complete presentation could be reasonable.
Contradicting studies reported incomplete presentation of Kawasaki disease in children to be associated with higher risk4,5,10,15), similar risk11), or lower risk21) of coronary artery abnormalities compared to children with complete presentation. Sudo et al.15) concluded that the higher incidence of coronary artery lesions in patients with incomplete presentation was firstly due to diagnostic bias because of the use of echocardiography in the diagnostic process, and secondly due to delays in the treatment because of difficulties in making the diagnosis. Restricting the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease within children with echocardiographic coronary artery abnormalities will result in above mentioned diagnostic bias. Manlhiot et al.11) elucidated equal incidences of coronary artery abnormalities between both patient groups using their definition of incomplete presentation of Kawasaki disease in which the use of echocardiography is excluded. In children with incomplete Kawasaki disease, the time between onset of symptoms and diagnosis has been reported to be longer5,11,15), and they are less likely to receive IVIG than children with complete presentation11,15). Sudo et al.15) performed multivariate analysis to delineate risk factors of coronary artery lesions and showed that late IVIG treatment (≥7 days of illness) was a significant risk factor of coronary artery lesions in both patient groups.
The presence of coronary artery abnormalities has been used as criterion for the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease2,6). According to the Japanese criteria, this criterion can only be used in cases with 4 principal symptoms2). Many authors believed that this definition is too restrictive and specific7). There are at least 3 problems with this restrictive definition of incomplete presentation. First of all, pediatric clinicians sometimes encounter cases in which Kawasaki disease is suspected with less than 4 principal symptoms. In the diagnostic criteria for incomplete presentation prepared by the AHA, a diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease is possible in cases with fever and 2 principal features (according to Japanese criteria, 3 principal symptoms)9). Secondly, the presence of coronary artery abnormalities is in itself an unfavorable outcome of the disease. The duration of fever has been confirmed as an important risk factor of coronary artery abnormalities23-25). Therefore, it may induce a delay of management to postpone diagnosis of incomplete presentation until confirming of coronary artery abnormality. One study in which the definition of incomplete Kawasaki disease included coronary involvement showed higher coronary complications in the group of infants younger than 6 months of age which had more cases of incomplete disease16). Finally, the Japanese Ministry of Health criteria (Table 3B)26), which have been used as a standard for the diagnosis of coronary complications, are too restrictive. De Zorzi et al.27) showed that the z score of coronary arteries (adjusted for body surface area) was more than 2 in 27% of children with Kawasaki disease whose coronary artery diameters were classified as normal according to the Japanese Ministry of Health criteria. The increase of body surface area-adjusted z score of the coronary diameter was adopted as a standard of coronary artery dilatation in the diagnostic criteria of incomplete Kawasaki disease by the AHA9).
Sudo et al.15) collected data from a total of 23,263 cases with Kawasaki disease in the nationwide survey of Japan from 2007 through 2008. Incomplete Kawasaki disease was defined as the presence of ≤4 principal symptoms of the Japanese criteria, regardless of whether the patient had coronary artery abnormalities15). The prevalence of coronary artery abnormalities was 13.1% in cases with incomplete presentation15). Due to the nature of that study, it was impossible to standardize the diagnostic criteria across all centers; therefore, the clinicians' judgment and local policies may have played a significant role in those cases with few classical diagnostic criteria15). In the incomplete presentation group, 271 children (1.2%) with only 1 or 2 principal symptoms were included15). Currently, a diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease might be made in cases with fewer classical diagnostic criteria and with several compatible clinical, laboratory, or echocardiographic findings, excluding those of other febrile illnesses. This survey15) reflects the current practice of diagnosing incomplete Kawasaki disease.
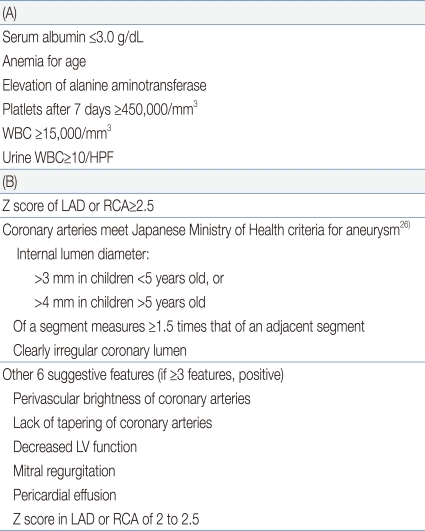
According to the diagnostic criteria of incomplete Kawasaki disease established by the AHA, children ≥6 months of age with incomplete presentation might have unexplained fever for ≥5 days associated with 2 or 3 of the principal clinical features (compatible with 3 or 4 principal symptoms of the Japanese criteria) in the acute phase9). The AHA recommended a diagnostic algorithm of incomplete Kawasaki disease which comprises of 6 supplemental laboratory and echocardiographic criteria (Table 3)9). More than 3 laboratory criteria support the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease (Table 3A). For judging an anemia and an abnormal level of alanine aminotransferase, clinicians should refer to the normal level. Echocardiogram is considered diagnostically positive if any of the following 3 conditions are met: z score of the left anterior descending or right coronary arteries ≥2.5, coronary arteries meet the Japanese Ministry of Health criteria for aneurysms26), or ≥3 other suggestive features exist (Table 3B). Several echocardiographic criteria, except the z score of coronary arteries, are qualitative parameters. Recently, quantitation of the perivascular brightness of coronary arteries was performed in children with Kawasaki disease, but its diagnostic validity could not be demonstrated28). Decreased myocardial contractility caused by myocarditis, which is histologically universal, is common during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease29,30). Thus, evaluation of myocardial contractility is an important step in the initial diagnosis of Kawasaki disease and was adopted as an echocardiographic criterion. Left ventricular dimensions/volumes, shortening fraction or ejection fraction via the M-mode in parasternal view or via a 2-dimensional examination in apical view are recommended parameters, because they are readily measurable and adequate for routine follow-up9). Left ventricular myocardial deformation was analyzed during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease in 1 study31), but the systolic strain rate of the myocardium was not superior to other conventional echocardiographic methods for detecting decreased myocardial contractility. No convincing quantitative threshold values have been proposed for the decision of abnormal pericardial effusion or mitral regurgitation during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. Newburger et al.9) acknowledged the diagnostic criteria for incomplete Kawasaki disease prepared by them to be only an informed opinion of a committee of experts (evidence level C). Yellen et al.20) tested the performance of the diagnostic criteria established by the AHA and reported an applicability of 97%. However, their study subjects were restricted to cases with coronary artery aneurysms. The validity of the diagnostic criteria of incomplete Kawasaki disease established by the AHA should be thoroughly tested in the immediate future because such a systematized guideline is very much needed in pediatric clinical practice.
Additional diagnostically helpful findings are inflammation at the Bacille Calmette-Guérin inoculation site32), anterior uveitis10,18), elevated levels of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)33-36) and N-terminal pro-BNP37), hyponatremia22), elevation of the left ventricular mass38), and diastolic dysfunction of the left ventricle35,39). The diagnostic validities of these clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic findings should also be tested in the future.
Currently, the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease might be made in cases with fewer classical diagnostic criteria and with several compatible clinical, laboratory, or echocardiographic findings, excluding those of other febrile illnesses. In addition, the validity of the diagnostic criteria of incomplete Kawasaki disease prepared by the AHA should be tested in the future.
References
1. Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children. Arerugi 1967;16:178–222.

2. Diagnostic guidelines of Kawasaki disease. Japan Kawasaki Disease Research Center, Japan Kawasaki Disease Research Committee [Internet]. c2012;cited 2001 Jan 9. Tokyo: Japan Kawasaki Disease Research Center, Japan Kawasaki Disease Research Committee, Available from: http://kawasaki-disease.org/diagnostic/.
3. Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease. American Heart Association. Diagnostic guidelines for Kawasaki disease. Circulation 2001;103:335–336.


4. Sonobe T, Kiyosawa N, Tsuchiya K, Aso S, Imada Y, Imai Y, et al. Prevalence of coronary artery abnormality in incomplete Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Int 2007;49:421–426.


5. Witt MT, Minich LL, Bohnsack JF, Young PC. Kawasaki disease: more patients are being diagnosed who do not meet American Heart Association criteria. Pediatrics 1999;104:e10


7. Barone SR, Pontrelli LR, Krilov LR. The differentiation of classic Kawasaki disease, atypical Kawasaki disease, and acute adenoviral infection: use of clinical features and a rapid direct fluorescent antigen test. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000;154:453–456.


8. Forsey J, Mertens L. Atypical Kawasaki disease-a clinical challenge. Eur J Pediatr 2012;2011 Nov 25 [Epub]. DOI:10.1007/s00431-011-1629-9.
9. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 2004;114:1708–1733.


10. Perrin L, Letierce A, Guitton C, Tran TA, Lambert V, Koné-Paut I. Comparative study of complete versus incomplete Kawasaki disease in 59 pediatric patients. Joint Bone Spine 2009;76:481–485.


11. Manlhiot C, Christie E, McCrindle BW, Rosenberg H, Chahal N, Yeung RS. Complete and incomplete Kawasaki disease: two sides of the same coin. Eur J Pediatr 2012;2011 Dec 3 [Epub]. DOI:10.1007/s00431-011-1631-2.
12. Rodriguez-Lozano AL, Rivas-Larrauri FE, Hernandez-Bautista VM, Yamazaki-Nakashimada MA. Fever is not always present in Kawasaki disease. Rheumatol Int 2011;9 01 [Epub]. DOI:10.1007/s00296-011-2123-4.
13. Falcini F, Cimaz R, Calabri GB, Picco P, Martini G, Marazzi MG, et al. Kawasaki's disease in northern Italy: a multicenter retrospective study of 250 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2002;20:421–426.

14. Hsieh YC, Wu MH, Wang JK, Lee PI, Lee CY, Huang LM. Clinical features of atypical Kawasaki disease. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2002;35:57–60.

15. Sudo D, Monobe Y, Yashiro M, Mieno MN, Uehara R, Tsuchiya K, et al. Coronary artery lesions of incomplete Kawasaki disease: a nationwide survey in Japan. Eur J Pediatr 2011;12 10 [Epub]. DOI:10.1007/s00431-011-1630-3.
16. Chang FY, Hwang B, Chen SJ, Lee PC, Meng CC, Lu JH. Characteristics of Kawasaki disease in infants younger than six months of age. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2006;25:241–244.


17. Chuang CH, Hsiao MH, Chiu CH, Huang YC, Lin TY. Kawasaki disease in infants three months of age or younger. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2006;39:387–391.

18. Burns JC, Wiggins JW Jr, Toews WH, Newburger JW, Leung DY, Wilson H, et al. Clinical spectrum of Kawasaki disease in infants younger than 6 months of age. J Pediatr 1986;109:759–763.


19. Rowley AH, Gonzalez-Crussi F, Gidding SS, Duffy CE, Shulman ST. Incomplete Kawasaki disease with coronary artery involvement. J Pediatr 1987;110:409–413.


20. Yellen ES, Gauvreau K, Takahashi M, Burns JC, Shulman S, Baker AL, et al. Performance of 2004 American Heart Association recommendations for treatment of Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 2010;125:e234–e241.



21. Fukushige J, Takahashi N, Ueda Y, Ueda K. Incidence and clinical features of incomplete Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr 1994;83:1057–1060.


22. Muta H, Ishii M, Egami K, Hayasaka S, Nakamura Y, Yanagawa H, et al. Serum sodium levels in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 2005;26:404–407.


23. Koren G, Lavi S, Rose V, Rowe R. Kawasaki disease: review of risk factors for coronary aneurysms. J Pediatr 1986;108:388–392.


24. Ichida F, Fatica NS, Engle MA, O'Loughlin JE, Klein AA, Snyder MS, et al. Coronary artery involvement in Kawasaki syndrome in Manhattan, New York: risk factors and role of aspirin. Pediatrics 1987;80:828–835.



25. Daniels SR, Specker B, Capannari TE, Schwartz DC, Burke MJ, Kaplan S. Correlates of coronary artery aneurysm formation in patients with Kawasaki disease. Am J Dis Child 1987;141:205–207.


26. Japan Kawasaki Disease Research Committee. Report of subcommittee on standardization of diagnostic criteria and reporting of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. 1984;Tokyo: Ministry of Health and Welfare.
27. de Zorzi A, Colan SD, Gauvreau K, Baker AL, Sundel RP, Newburger JW. Coronary artery dimensions may be misclassified as normal in Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 1998;133:254–258.


28. Yu JJ, Jang WS, Ko HK, Han MK, Kim YH, Ko JK, et al. Perivascular brightness of coronary arteries in Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 2011;159:454.e1–457.e1.
29. Hiraishi S, Yashiro K, Oguchi K, Kusano S, Ishii K, Nakazawa K. Clinical course of cardiovascular involvement in the mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. Relation between clinical signs of carditis and development of coronary arterial aneurysm. Am J Cardiol 1981;47:323–330.


30. Newburger JW, Sanders SP, Burns JC, Parness IA, Beiser AS, Colan SD. Left ventricular contractility and function in Kawasaki syndrome. Effect of intravenous gamma-globulin. Circulation 1989;79:1237–1246.


31. Yu JJ, Choi HS, Kim YB, Son JS, Kim YH, Ko JK, et al. Analyses of left ventricular myocardial deformation by speckle-tracking imaging during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 2010;31:807–812.


32. Sinha R, Balakumar T. BCG reactivation: a useful diagnostic tool even for incomplete Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 2005;90:891



33. Kawamura T, Wago M. Brain natriuretic peptide can be a useful biochemical marker for myocarditis in patients with Kawasaki disease. Cardiol Young 2002;12:153–158.


34. Kawamura T, Wago M, Kawaguchi H, Tahara M, Yuge M. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentrations in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Int 2000;42:241–248.


35. Kurotobi S, Kawakami N, Shimizu K, Aoki H, Nasuno S, Takahashi K, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide as a hormonal marker of ventricular diastolic dysfunction in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 2005;26:425–430.


36. Bang S, Yu JJ, Han MK, Ko HK, Chun S, Choi HS, et al. Log-transformed plasma level of brain natriuretic peptide during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease is quantitatively associated with myocardial dysfunction. Korean J Pediatr 2011;54:340–344.



37. Dahdah N, Siles A, Fournier A, Cousineau J, Delvin E, Saint-Cyr C, et al. Natriuretic peptide as an adjunctive diagnostic test in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 2009;30:810–817.


Table 1
Classical Diagnostic Clinical Criteria of Kawasaki Disease Prepared by the American Heart Association3)
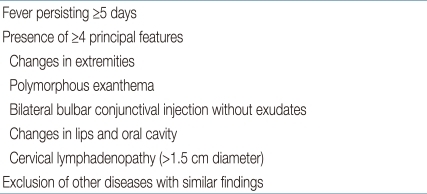
Table 2
Six principal symptoms in the diagnostic guidelines for Kawasaki disease prepared by the Japanese Kawasaki Disease Research Committee2)

Table 3
Supplemental Laboratory Criteria (A) and Echocardiographic Criteria (B) for the Diagnosis of Incomplete Kawasaki Disease Prepared by the American Heart Association9)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


