Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 63(8); 2020 |
|
Abstract
Human breast milk (HBM) is essential for the infant’s growth and development right after birth and is an irreplaceable source of nutrition for early human survival. Various infant formulas have many similarities to HBM in many components, but there is no perfect substitute for HBM. Recently, various breast milk components and their roles have been studied according to the development of various analysis techniques. As is already well known, HBM contains about 87%–88% water, and 124- g/L solid components as macronutrients, including about 7% (60–70 g/L) carbohydrates, 1% (8–10 g/L) protein, and 3.8% (35–40 g/L) fat. The composition may vary depending on the environmental factors, including maternal diet. Colostrum is low in fat but high in protein and relatively rich in immune-protective components. Although HBM contains enough vitamins to ensure normal growth of the infant, vitamins D and K may be insufficient, and the infant may require their supplementation. Growth factors in HBM also serve as various bioactive proteins and peptides on the intestinal tract, vasculature, nervous system, and endocrine system. In the past, HBM of a healthy mother was thought to be sterile. However, several subsequent studies have confirmed the presence of rich and diverse microbial communities in HBM. Some studies suggested that the genera Staphylococcus and Streptococcus may be universally predominant in HBM, but the origin of microbiota still remains controversial. Lastly, milk is the one of most abundant body fluid of microRNAs, which are known to play a role in various functions, such as immunoprotection and developmental programming, through delivering from HBM and absorption by intestinal epithelial cells. In conclusion, HBM is the most important source of nutrition for infants and includes microbiomes and miRNAs for growth, development, and immunity.
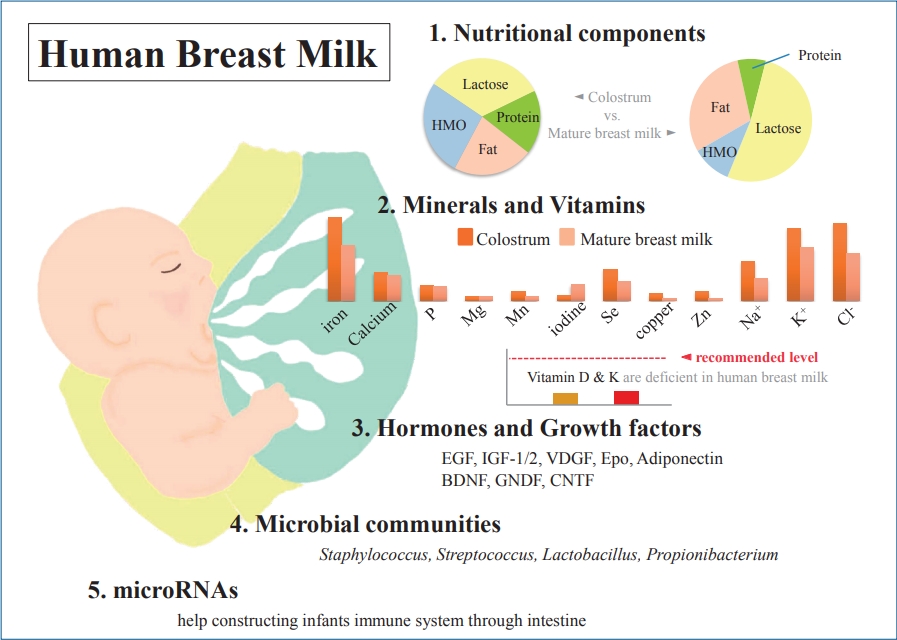
Graphical abstract. Human breast milk (HBM) contains macronutrients and micronutrients, and its composition varies according to environmental factors. Colostrum is low in fat but high in protein and relatively rich in immunoprotective components. Micronutrients, hormones, and growth factors in HBM also play various roles in infant development. Microbial communities and microRNAs help construct the infant immune system.
Human breast milk (HBM) is essential for the infant’s growth and development right after birth and is an irreplaceable source of nutrition for early human survival [1,2]. For this reason, the World Health Organization and United Nations Children’s Fund recommend exclusive HBM feeding for at least 6 months after birth and to continue for up to 2 years of age or beyond [3-5]. In recent years, various infant formulas have been developed for greater similarity to HBM and are being supplemented with breast milk-specific ingredients, such as human milk oligosaccharide (HMO) [6-8]. Although these formulas are similar to HBM in terms of many components, there is no perfect substitute for HBM [9]. This makes it imperative to discuss the components that make HBM more suitable than infant formulas for humans. Many studies to date have revealed nutritional components, such as various macronutrients and micronutrients, in HBM and have studied about its immunologic components. In addition, recently, various HBM components and their roles have been studied with the implementation of various analysis techniques, such as next-generation sequencing. In this article, we will explore the various components of HBM. A better understanding of these HBM components will help in various aspects, such as imparting lactation education and encouraging better feeding habits, as well as in the treatment of high-risk infants, such as those with premature birth, infections, neurological diseases, and gastrointestinal diseases.
As is already well known, HBM contains about 87%–88% water, and it has a specific gravity of 1.030, osmolarity of about 286 mOsm/L, and 124-g/L solid components as macronutrients, including about 7% (60–70 g/L) carbohydrates, 1% (8–10 g/L) protein, and 3.8% (35–40 g/L) fat [10-13] (Table 1). Typically, mature milk contains 65–70 kcal per 100 mL of energy, and about 50% of the total calorie supply is fat and 40% is carbohydrates [14]. However, unlike infant formulas, which have a narrow range of composition guidelines based on strict criteria for health effects on infants, the nutrient composition of HBM is dynamic for various reasons [14-16]. The composition of HBM may vary depending on the maternal diet, mammary gland physiology, maternal health, and many other environmental factors [13,14]. In addition, it may vary depending on prematurity, on whether it is foremilk or hindmilk, and on whether it is colostrum, transitional milk, or mature milk [17]. It may vary depending on the processing conditions, such as storage, pasteurization, and containers [18,19]. In the case of foremilk released by the mammary gland, the fat content is relatively low and increases with feeding, whereas hindmilk has higher fat content. The protein and lactose contents are not significantly different between them. Colostrum is low in fat but high in protein (10%) and is relatively rich in immune-protective components, such as immunoglobulin A (IgA) and lactoferrin, which help prevent neonatal infections.
Carbohydrates are the most prominent macronutrient in HBM and plays an important role in infant’s nutrition, in developing the physiological function of the entire gastrointestinal tract right from birth, and in maintaining the composition of the intestinal microbiota [20,21]. Most humans ingest carbohydrates in the form of glucose, whereas infants, who have not yet developed the gastrointestinal tract, ingest carbohydrates in the form of lactose. Thus, lactose is the major carbohydrate constituent of HBM and is the most abundant nutrient in breast milk. Lactose is digested by lactase-phlorizin hydrolase, also called lactase, which is present on the apical surface of enterocytes in the small intestinal brush border; lactose is readily digested in almost all infants [12]. However, the lack of enzymes can cause various symptoms, such as lactose intolerance or malabsorption. Unlike protein and fat, colostrum contains relatively fairly constant lactose with time [15,22]. A constant level of lactose is important for maintaining a constant osmotic pressure in HBM. In addition, carbohydrate-based bioactive components, such as oligosaccharides, are attached to lactose; this aids in the absorption of minerals and calcium [15]. The levels of free glucose and other glucose metabolites in HBM are low; thus, their nutritional significance is negligible in infants [23].
Highly complex HMOs are the second most abundant carbohydrate in HBM after lactose and the third most abundant solid component [24,25]. HMOs make up about 20% of the total HBM carbohydrates and are present in a concentration of 12–14 g/L in mature milk and >20 g/L in colostrum [24]. Known as “gynolactose” by L'espagnol and Plinowski in the 1930s, more than 150 HMO structures have been described to date [26]. Interest in HMOs has been increasing in recent years not only for the nutrition of infants but also for commercial purposes. HMOsare produced only in lactating mammary glands, which are not found in infant formulas, but recently, various types of oligosaccharides have been added to infant formulas [6,7]. Immediately after birth, the gut is sterile, but to prevent various infections after birth, the infant intestine must adapt to various circumstances and acquire an immune system. While direct ingestion of various bioactive compounds in HBM affects immunity, acquisition of intestinal colonization as an antimicrobial factor is also important [27]. Unlike lactose, which is easily digested, HMOs reache the colon in almost intact form due to their limited digestion; HMOs are known to play an important prebiotic role in the development of gut microbiota in early stages after birth [28]. In various previous studies, HMOs have been shown to reduce the duration of diarrhea and have a positive effect on the growth of bifidobacteria [29-33]. They also play an important role as an energy source for enterocytes and are associated with the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are key signaling molecules for maintaining gut health [28]. These short-chain fatty acids are known to inhibit the growth of potentially harmful gut microbiota by reducing intestinal pH [34]. In addition to this indirect role, some HMOs are thought to be involved in various systemic circulations to regulate direct immune responses [28]. In various studies of human infants, on comparing HMOs and infant formulas, the former also showed positive effects against infections, such as campylobacter. However, various studies are being conducted because much research on infant health is still lacking.
Protein is a major component that functions and organizes all cells in the human body, and sufficient protein supply is essential for growth, development, and function. The protein of HBM comprises a mixture of whey and casein, and various peptides. Casein is micellar and is present in the form of clots or curd in the stomach and is not easily dissolved. Whey is in liquid form and is easy to digest [14]. The whey/casein ratio varies according to the time of breast milk. In colostrum, the whey/casein ratio is absolutely high at almost 90:10, but this gradually changes to 60:40 in mature milk. Nevertheless, the proportion of whey is relatively higher in HBM than in infant formula, wherein it is about 20% [11,35]. Casein exists as alpha, beta, gamma, and kappa casein. Alpha casein is abundant in bovine milk and is rarely present in HBM [13,36]. Casein of HBM is more easily digested in the form of looser micelles and softer curd by carboxypeptidase, which regulates intestinal motility and aids calcium absorption. Lönnerdal et al. [37] reported that low casein proportion in HBM is associated with slower growth in breastfed infants. Representative whey proteins of HBM are alpha-lactalbumin, lactoferrin, and secretory IgA [14]. Among these, alpha-lactalbumin constitutes 40% of the whey protein of HBM, but beta-lactoglobulin is the representative whey protein of bovine milk and is absent in HBM [37]. Alpha-lactalbumin aids in the synthesis of lactose in mammary glands and in the supply of essential amino acids and absorption of minerals and trace elements in infants [38]. It also plays a role in the immune system and antibacterial properties. Lactoferrin and lysozyme inhibit the spread of potentially pathogenic bacteria, and IgA protects intestinal mucosa and destroys bacteria [14].
Protein content in HBM at birth is about 14–16 g/L, but decreases to 8–10 g/L after 3–4 months of birth and further decreases to 7–8 g/L after 6 months [11,15]. The protein concentration of HBM is not significantly affected by maternal diet but increases with maternal body weight for height [14]. In HBM, nonprotein nitrogen is present in about 20%–25% of HBM protein, which is a higher rate than 5% in bovine milk [13,36,39]. Nearly 50% of this is urea nitrogen, which is used to synthesize nonessential amino acids [39].
In HBM, fat is the second largest macronutrient and plays the most important role in the nutrient supply in infants (nearly 50% of the total energy content) and the development of the central nervous system [15]. Colostrum contains 15–20 g/L of fat, but this amount gradually increases, and mature milk contains almost 40 g/L. Its levels are 2–3 times higher in hindmilk than in foremilk [40]. The major component of HBM fatty acid is triglyceride (about 95%–98%), and it also contains 2 essential fatty acids, linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid [11]. Linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid are precursors of arachidonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) respectively, the latter is further converted to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and cannot be synthesized in the human body. In addition, they are important for inflammatory responses, immune function, and growth as components required in the production of in vivo signal transduction and coponents of the nervous system and retina [15]. Fats in HBM are more easily digested and absorbed than those in infant formulas due to the presence of bile salt-stimulated lipases that complement pancreatic lipases and the presence of palmitic acid at the sn-2 position of human milk triglycerides [41]. This positional preference is not well confirmed in infant formulas and affects plasma lipid profile in infants, including cholesterol concentration [25].
Fat content in HBM is closely related to maternal diet and weight gain during pregnancy; in addition, there are regional differences in food intake [15]. The consumption of foods such as breads, snacks, fast foods, and margarines by lactating mothers can cause trans fatty acids to be found in HBM and may account for up to 7.7% of total fatty acids [42]. Trans fatty acid concentrations vary from region to region, and they have adverse effects on infant growth and development and are inversely related to linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acids [42,43]. Arachidonic acid also correlates with arachidonic acid-rich food intake from lactating mothers, and EPA and DHA are also closely related [44,45]. Therefore, vegetarians have very low levels of DHA in their milk because of the lack of fish or other foods in their diet [46]. Therefore, it is recommended to take up to 300 mg of DHA per day to maintain sufficient amount of DHA in breast milk [47].
Although HBM is influenced by the diet in lactating women, in most cases, it contains enough vitamins to ensure normal growth of the infant [15]. However, vitamins D and K may be insufficient in infants who are exclusively breastfeeding and may require supplementation. Vitamin D is influenced by sun exposure as well as the maternal diet, which is related to climate, season, latitude, skin color, and life style. HBM typically contains less than 1 mg or less than 40 IU/L of vitamin D, which is not sufficient to meet the needs of infants. Breastfed infants can receive vitamin D from HBM synthesized by sunlight exposure in lactating mothers or stored during pregnancy. However, the stored vitamin D is rapidly depleted in infants. The Korean Nutritional Society and American Academy of Pediatrics recommend lactating mothers and infants to take vitamin D supplements of 200–400 IU per day in maintenance doses and 2,000 IU/day in deficiency [48,49]. Vitamin K is also transferred from mother to fetus in limited amounts, so newborn infants can be deficient in vitamin K. Therefore, vitamin K supplementation is recommended after birth [15,50]. Water soluble vitamins are also greatly affected by maternal status [51]. In general, mothers who do not have enough diet may be deficient in vitamins B6, B12, and folate but may still have relatively sufficient thiamin and riboflavin content [51]. More than 20 minerals, including iron, copper, and zinc, have been identified in HBM, most of which are abundant in colostrum and decrease as lactation progresses [52]. Unlike vitamins, most minerals are not significantly affected by the maternal status and do not vary greatly with maternal supplements [13-15,53] (Table 2). The mineral content is lower in HBM than in infant formulas, but due to their high bioavailability, no additional supplementation is required during full breastfeeding. In particular, iron content is 0.5–1.0 mg/L in colostrum and 0.3–0.7 mg/L in mature milk, but its bioavailability is 20%–50%, which is more effective than in infant formula (4%–7%). Therefore, in exclusively breastfed infants, it is generally not necessary to supply iron before 4–6 months of age, and then, it is recommended to supply gradually through iron-enriched solid foods.
Premature infants may experience a variety of problems when compared to full-term births. Nutritional attention and sufficient supply are needed because the risk of growth failure, neurodevelopmental delay, sepsis, and gastrointestinal problems, such as necrotizing enterocolitis, is higher [17]. In addition, deficiency-related complications may occur because of the failure to deliver various nutrients that are transferred from the placenta to the fetus during the third trimester [54,55]. Even in this case, HBM plays a primary role as an enteral diet. However, HBM in mothers feeding premature infants differs from HBM in mothers feeding term infants. Protein content and bioactive components tend to be richer, with more fat, free amino acids, and sodium in the preterm [17]. However, these components tend to decrease gradually as lactation progresses. Copper and zinc are also higher in the HBM of mothers feeding preterm infants and decrease gradually with lactation, whereas calcium is lower in preterm cases and gradually increases with lactation [56,57]. Most other minerals have comparable levels at preterm and full term. Lactose, which is present in low amounts in colostrum and increases as lactation progresses, is more pronounced in preterm milk [17]. In addition, lactase in the small intestine is not formed and secreted until 32 weeks of gestation, so it is difficult for premature infants born before 32 weeks of gestation to digest breast milk. HMOs vary in the overall content depending on genetic diversity and the content of fucosylated HMOs [58,59]. Differences in the content of bioactive molecules, such as growth factors and lactoferrin, between colostrum and early mature milk are greater between HBM mothers with preterm birth and HBM mothers with full-term birth [17]. Donor milk or fortification can be used to compensate for the lack of mother's own milk for long-term growth and prognosis of preterm infants [17].
Hormones and growth factors in HBM also serve as various bioactive proteins and peptides [60]. Functions of hormones in HBM, including parathyroid hormone, insulin, leptin, ghrelin, apelin, nesfatin-1, obestatin, and adiponectin, and their effects in infants are not yet well known. Conversely, many growth factors have been studied relatively more and are known to have various effects on the intestinal tract, vasculature, nervous system, and endocrine system [14] (Table 3). Epidermal growth factors play a critical role in intestinal maturation and repair. Their levels in colostrum are 2,000 times higher than in mature milk and decrease with lactation [14,61]. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor act on the enteric nervous system and are necessary for the development of immature intestine in infants [62]. These neuronal growth factors, including ciliary neurotrophic factor, are found in HBM for up to 90 days after birth [63-65]. Among the neuronal growth factors, S100B is higher in mature milk than in colostrum [66]. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and IGF-2 are abundant in colostrum and decrease with lactation; their levels are not significantly different between preterm and term milk, except for IGF-binding protein-2 among in the IGF superfamily [67-69]. IGF is taken up in its bioactive form by the intestine and transported to the blood system [70,71]. IGF-1 plays a role in the survival of enterocytes by protecting them against intestinal damage caused by oxidative stress; furthermore, it stimulates erythropoiesis and helps increase hematocrit [70,72]. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its antagonists are thought to help regulate angiogenesis and reduce damage to the retinopathy of prematurity [14,73]. The concentration of vascular endothelial growth factors is higher in colostrum in both preterm and term and lower in preterm milk than in term milk [74]. Erythropoietin plays a primary role in the increase of red blood cells and is thought to help prevent anemia of prematurity [75,76]. It also plays a role in tightening intestinal junctions and may help reduce the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis [76,77]. Adiponectin is found in large amounts in breast milk, which crosses the intestinal barrier and regulates metabolism and inhibits inflammation [78,79].
Just 20 years ago, HBM of a healthy mother was thought to be sterile according to culture-based studies [80]. The bacteria in the HBM were thought to be contaminants or pathogens, particularly the cause of mastitis. In a culture-based study conducted in 2003, Martin et al. [81] proved for the first time that HBM was a significant source of lactic acid bacteria for the infant gut. They found DNA profiles of lactic acid bacteria from HBM to be different from those in mother’s skin [81]. In the same year, Heikkila and Saris [82] also performed a culture-based study and reported that HBM of healthy mothers contains commensal bacteria. They concluded that an infant consuming about 800 mL of HBM per day ingests 8×104–106 commensal bacteria. Several subsequent studies have confirmed the presence of microbiota in HBM [83-86]. Recently, the development of a nonculture sequencing technique has made way for a changed perception that there are rich and diverse microbial communities in HBM [87] and that they play an important role in the formation of infant gut microbiota [88].
In 2011, Hunt et al. [85] reported in a first study using next-generation sequencing for this examination that there is a core HBM microbiome of 9 bacterial genera. These 9 core bacteria were present in every sample and represented about half of the microbial community. Various subsequent studies have examined the core bacteriome of HBM, but there was a difference in results [85,89,90]. These differences may be due to methodological differences among the studies, but several common bacterial genera, including Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, and Propionibacterium, have been reported. Fitzstevens et al. [87] performed a systematic review of studies using culture-independent methods. They suggested that the genera Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are universally predominant in HBM, regardless of differences in geographic location or analytic methods. A recent systematic review by Togo et al. [91] confirmed a high diversity of human milk microbiota with 820 species. The most of the frequently detected species were facultative anaerobic or strictly aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Cutibacterium acnes, Enterococcus faecalis, Bifidobacterium breve, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus sanguinis, Lactobacillus gasseri, and Salmonella enterica.
The origin of HBM microbiota is still controversial. In an earlier study, Martin et al. [81] suggested that bacteria present in HBM may have an endogenous origin because of the difference between the bacterial DNA profiles of HBM and those of other areas. A recent hypothesis called “enteromammary pathway” states that maternal gut microbiota penetrate the intestinal epithelium, move to the mammary glands, and colonize the infant gut via milk consumption [80,92]. Urbaniak et al. [93] determined that the human breast tissue microbiota and HBM microbiota shared several bacterial genera. Another possible hypothesis is that HBM microbiota comes from mother’s skin or infant’s oral cavity. Ramsay et al. [94] reported using ultrasound imaging that there is a high degree of retrograde flow of milk from the infants’ mouth back into the mammary ducts. This suggests that commensal bacteria from the skin or mouth can enter the mammary duct during breastfeeding.
Several studies have proved the vertical transmission of maternal bacteria to the infant’s gut with HBM feeding [81,88,95-97]. HBM microbiota have been shown to influence the gut colonization and play a role in immunomodulation and endogenous metabolism. A better understanding of HBM microbiota will make it possible to clarify the effect of HBM on short- and longterm human health outcomes and improve them.
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a small noncoding RNA with 18 to 25 nucleotides; it is found in plants, animals, and viruses, among others. It acts as a core regulator at the posttranscriptional level and is known to be involved in the development, differentiation, proliferation, and metabolism of cells and tissues [98-101]. Tens of thousands of these miRNAs are currently known, and many studies are being conducted to understand the pathophysiology of various diseases, including cancer, through miRNAs. Extracellular miRNAs are used as ideal biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of diseases, including cell-cell communication. Milk is the most abundant body fluid of RNAs and miRNAs and is known to play a role in various aspects of the infant's immune system via miRNAs delivered through HBM [102-104]. There are almost 1,400 different species of mature miRNAs in HBM, which vary depending on the test method and research, between colostrum and mature milk, and among milk cell, milk lipid, and milk exosomes [105-107]. MiRNAs in HBM are synthesized in mammary glands and are present in milk as free molecules and packaged in vesicles, such as milk exosomes and fat globules [105,106]. These are thought to be transported to the infant’s intestine through lactation; these remain intact in the degradative conditions of the infant's gastrointestinal system and are absorbed by intestinal epithelial cells [104]. Then, they appear to reach various tissues and organs through the bloodstream and perform various functions, such as immunoprotection and developmental programming [104]. Although miRNAs are also found in high concentrations in animal milk, the infant formula contains few human mature miRNA species which are expressed at much lower levels than in HBM [107]. MiRNAs are also stable in conditions, such as acidic environments, RNase treatment, and freezing compared to HBM fractions; however, they decompose in the presence of detergents or bacterial fermentation [104,105].
With the development of various technologies, humans have been able to replace much of what is available in nature. HBM for infants has also been attempted to be replaced by various artificial milk types. Nevertheless, there is no perfect replacement for HBM yet. Macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins (including immunologic components), fats, various micronutrients, and vitamins, trophic factors, as well as microbiome and miRNA are in the spotlight recently; these are the components of HBM available only in humans and only through lactating mothers, thus making them diverse and irreplaceable. Many of these components and their association with infant growth and development and human health have not been properly elucidated and are being actively studied. However, taken together, as the various components of HBM are best suited for optimal early human growth and development, it remains unchanged that HBM from a lactating mother who is maintaining a balanced diet is the most desirable nutrition for infants.
Acknowledgments
This article was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Science and ICT, No. NRF-2019R1F1A1059569).
Table 1.
Energy and macronutrient composition of human breast milk and proposed composition recommended in cow milk formula
Table 2.
Micronutrient composition of human breast milk and proposed composition recommended in cow milk formula
Table 3.
Growth factors in human breast milk and their functions
References
1. Van Rossum CT, Buchner FL, Hoekstra J. Quantification of health effects of breastfeeding: review of the literature and model simulation. Bilthoven: RIVM, 2006.
2. ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition; Agostoni C, Braegger C, Decsi T, Kolacek S, Koletzko B, et al. Breast-feeding: a commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009;49:112–25.


3. World Health Organization; United Nations Children’s Fund. Global strategy for infant and young child feeding. Geneva: World Health organization, 2003.
4. Ip S, Chung M, Raman G, Chew P, Magula N, DeVine D, et al. Breastfeeding and maternal and infant health outcomes in developed countries. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 2007;153:1–186.
5. Johnston M, Landers S, Noble L, Szucs K, Viehmann L. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012;129:e827–41.


6. Vandenplas Y, Berger B, Carnielli VP, Ksiazyk J, Lagström H, Sanchez Luna M, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides: 2'-fucosyllactose (2'-FL) and lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) in infant formula. Nutrients 2018;10:1161



7. Hegar B, Wibowo Y, Basrowi RW, Ranuh RG, Sudarmo SM, Munasir Z, et al. The role of two human milk oligosaccharides, 2'-fucosyllactose and lacto-N-neotetraose, in infant nutrition. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2019;22:330–40.



8. Koletzko B, Baker S, Cleghorn G, Nete U.F, Gopalan F, Hernall O, et al. Global standard for the composition of infant formula: Recommendations of an ESPGHAN coordinated internation expert group. J Pediatr Gastroenteral Nutr 2005;41:584–99.

10. Riordan J, Wambach K. Breastfeeding and human lactation. 4th ed. Burlington (NJ): Jones & Bartlett Learning, 2016.
11. Guo M. Human milk biochemistry and infant formula manufacturing technology. Cambridge: Elsevier, 2014.
12. Kunz C, Rodriguez-Palmero M, Koletzko B, Jensen R. Nutritional and biochemical properties of human milk, part I: general aspects, proteins, and carbohydrates. Clin Perinatol 1999;26:307–33.


14. Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am 2013;60:49–74.



15. Martin CR, Ling PR, Blackburn GL. Review of infant feeding: key features of breast milk and infant formula. Nutrients 2016;8:279



18. Kim MH, Shim KS, Yi DY, Lim IS, Chae SA, Yun SW, et al. Macronutrient analysis of human milk according to storage and processing in Korean mother. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2019;22:262–9.



19. Chang YC, Chen CH, Lin MC. The macronutrients in human milk change after storage in various containers. Pediatr Neonatol 2012;53:205–9.


21. Brownawell AM, Caers W, Gibson GR, Kendall CW, Lewis KD, Ringel Y, et al. Prebiotics and the health benefits of fiber: current regulatory status, future research, and goals. J Nutr 2012;142:962–74.



22. Hester SN, Hustead DS, Mackey AD, Singhal A, Marriage BJ. Is the macronutrient intake of formula-fed infants greater than breast-fed infants in early infancy? J Nutr Metab 2012;2012:891201




23. Arthur PG, Kent JC, Hartmann PE. Metabolites of lactose synthesis in milk from women during established lactation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1991;13:260–6.


24. Thurl S, Munzert M, Boehm G, Matthews C, Stahl B. Systematic review of the concentrations of oligosaccharides in human milk. Nutr Rev 2017;75:920–33.




25. Andreas NJ, Kampmann B, Mehring Le-Doare K. Human breast milk: a review on its composition and bioactivity. Early Hum Dev 2015;91:629–35.


26. Bode L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama. Glycobiology 2012;22:1147–2.




27. Walker AW, Ince J, Duncan SH, Webster LM, Holtrop G, Ze X, et al. Dominant and diet-responsive groups of bacteria within the human colonic microbiota. ISME J 2011;5:220–30.



28. Plaza-Díaz J, Fontana L, Gil A. Human milk oligosaccharides and immune system development. Nutrients 2018;10(8): 1038



29. Gyorgy P, Norris RF, Rose CS. Bifidus factor. I. A variant of Lactobacillus bifidus requiring a special growth factor. Arch Biochem Biophys 1954;48:193–201.


30. Ward RE, Niñonuevo M, Mills DA, Lebrilla CB, German JB. In vitro fermentation of breast milk oligosaccharides by Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus gasseri. Appl Environ Microbiol 2006;72:4497–9.



31. Ward RE, Niñonuevo M, Mills DA, Lebrilla CB, German JB. In vitro fermentability of human milk oligosaccharides by several strains of bifidobacteria. Mol Nutr Food Res 2007;51:1398–405.


32. Garrido D, Ruiz-Moyano S, Jimenez-Espinoza R, Eom HJ, Block DE, Mills DA. Utilization of galactooligosaccharides by Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis isolates. Food Microbiol 2013;33:262–70.


33. LoCascio RG, Ninonuevo MR, Freeman SL, Sela DA, Grimm R, Lebrilla CB, et al. Glycoprofiling of bifidobacterial consumption of human milk oligosaccharides demonstrates strain specific, preferential consumption of small chain glycans secreted in early human lactation. J Agric Food Chem 2007;55:8914–9.


34. Harmsen HJ, Wildeboer-Veloo AC, Raangs GC, Wagendorp AA, Klijn N, Bindels JG, et al. Analysis of intestinal flora development in breast-fed and formula-fed infants by using molecular identification and detection methods. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2000;30:61–7.


35. Liao Y, Weber D, Xu W, Durbin-Johnson BP, Phinney BS, Lönnerdal B. Absolute Quantification of human milk caseins and the whey/casein ratio during the first year of lactation. J Proteome Res 2017;16:4113–21.


36. Rudloff S, Kunz C. Protein and nonprotein nitrogen components in human milk, bovine milk, and infant formula: quantitative and qualitative aspects in infant nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1997;24:328–44.


37. Lönnerdal B, Woodhouse LR, Glazier C. Compartmentalization and quantitation of protein in human milk. J Nutr 1987;117:1385–95.



38. Lönnerdal B, Lien EL. Nutritional and physiologic significance of alpha-lactalbumin in infants. Nutr Rev 2003;61:295–305.



39. Donovan SM, Lönnerdal B. Non-protein nitrogen and true protein in infant formulas. Acta Paediatr Scand 1989;78:497–504.


40. Saarela T, Kokkonen J, Koivisto M. Macronutrient and energy contents of human milk fractions during the first six months of lactation. Acta Paediatr 2005;94:1176–81.


41. Straarup EM, Lauritzen L, Faerk J, Høy Deceased CE, Michaelsen KF. The stereospecific triacylglycerol structures and Fatty Acid profiles of human milk and infant formulas. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006;42:293–9.


42. Innis SM, King DJ. Trans Fatty acids in human milk are inversely associated with concentrations of essential all-cis n-6 and n-3 fatty acids and determine trans, but not n-6 and n-3, fatty acids in plasma lipids of breast-fed infants. Am J Clin Nutr 1999;70:383–90.



43. Decsi T. Nutritional relevance of trans isomeric fatty acids in human milk. Acta Paediatr 2003;92:1369–71.


44. Del Prado M, Villalpando S, Elizondo A, Rodríguez M, Demmelmair H, Koletzko B. Contribution of dietary and newly formed arachidonic acid to human milk lipids in women eating a low-fat diet. Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74:242–7.



45. Weseler AR, Dirix CE, Bruins MJ, Hornstra G. Dietary arachidonic acid dose-dependency increases with arachidonic acid concetration in human milk. J Nutr 2008;138:2190–7.



46. Jensen CL, Maude M, Anderson RE, Heird WC. Effect of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation of lactating women on the fatty acid composition of breast milk lipids and maternal and infant plasma phospholipids. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;71(1 Suppl): 292S–299S.



47. Fleith M, Clandinin MT. Dietary PUFA for preterm and term infants: review of clinical studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2005;45:205–29.


48. Perrine CG, Sharma AJ, Jefferds ME, Serdula MK, Scanlon KS. Adherence to vitamin D recommendations among US infants. Pediatrics 2010;125:627–32.


49. Ministry of Health and Welfare (KR); The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans 2015. Sejong (Korea): Ministry of Health and Welfare, 2016.
50. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Controversies concerning vitamin K and the newborn. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Pediatrics 2003;112:191–2.


51. Sneed SM, Zane C, Thomas MR. The effects of ascorbic acid, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, and folic acid supplementation on the breast milk and maternal nutritional status of low socioeconomic lactating women. Am J Clin Nutr 1981;34:1338–46.



52. Parr RM, DeMaeyer EM, Iyengar VG, Byrne AR, Kirkbright GF, Schöch G, et al. Minor and trace elements in human milk from Guatemala, Hungary, Nigeria, Philippines, Sweden, and Zaire. Results from a WHO/IAEA joint project. Biol Trace Elem Res 1991;29:51–75.



53. Domellöf M, Lönnerdal B, Dewey KG, Cohen RJ, Hernell O. Iron, zinc, and copper concentrations in breast milk are independent of maternal mineral status. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79:111–5.



54. Innis SM. Impact of maternal diet on human milk composition and neurological development of infants. Am J Clin Nutr 2014;99:734S–741S.



55. Martin CR, Dasilva DA, Cluette-Brown JE, Dimonda C, Hamill A, Bhutta AQ, et al. Decreased postnatal docsahexaenoic and arachidonic acid blood levels in premature infants are associated with neonatal morbidities. J Pediatr 2011;159:743–9.



56. de Figueiredo CS, Palhares DB, Melnikov P, Moura AJ, dos Santos SC. Zinc and copper concentrations in human preterm milk. Biol Trace Elem Res 2010;136:1–7.



57. O'Brien CE, Krebs NF, Westcott JL, Dong F. Relationships among plasma zinc, plasma prolactin, milk transfer, and milk zinc in lactating women. J Hum Lact 2007;23:179–83.


58. Gabrielli O, Zampini L, Galeazzi T, Padella L, Santoro L, Peila C, et al. Preterm milk oligosaccharides during the first month of lactation. Pediatrics 2011;128:e1520. –31.


59. De Leoz ML, Gaerlan SC, Strum JS, Dimapasoc LM, Mirmiran M, Tancredi DJ, et al. Lacto-N-tetraose, fucosylation, and secretor status are highly variable in human milk oligosaccharides from women delivering preterm. J Proteome Res 2012;11:4662–72.



60. Donovan SM. Role of human milk components in gastrointestinal development: current knowledge and future NEEDS. J Pediatr 2006;149(suppl 5): S49–61.

61. Dvorak B, Fituch CC, Williams CS, Hurst NM, Schanler RJ. Increased epidermal growth factor levels in human milk of mothers with extremely premature infants. Pediatr Res 2003;54:15–9.


62. Rodrigues D, Li A, Nair D, Blennerhassett M. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor is a key neurotrophin in the postnatal enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2011;23:e44–56.


63. Li R, Xia W, Zhang Z, Wu K. S100B protein, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and glial cell linederived neurotrophic factor in human milk. PloS One 2011;6:e21663.



64. Fichter M, Klotz M, Hirschberg DL, Waldura B, Schofer O, Ehnert S, et al. Breast milk contains relevant neurotrophic factors and cytokines for enteric nervous system development. Mol Nutr Food Res 2011;55:1592–6.


65. Li R, Xia W, Zhang A, Wu K. S100B protein, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in human milk. PloS One 2011;6:e21663



66. Gazzolo D, Bruschettini M, Lituania M, Serra G, Santini P, Michetti F. Levels of S100B protein are higher in mature human milk than in colostrum and milk-formulae milks. Clin Nutr 2004;23:23–6.


67. Milsom SR, Blum WF, Gunn AJ. Temporal changes in insulin-like growth factors I and II and in insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 1, 2, and 3 in human milk. Horm Res 2008;69:307–1.


68. Prosser CG. Insulin-like growth factors in milk and mammary gland. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 1996;1:297–306.



69. Elmlinger MW, Hochhaus F, Loui A, Frommer KW, Obladen M, Ranke MB. Insulin-like growth factors and binding proteins in early milk from mothers of preterm and term infants. Horm Res 2007;68:124–31.


70. Philipps AF, Kling PJ, Grille JG, Dvorák B. Intestinal transport of insulin-like growth factor-I (igf-I) in the suckling rat. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2002;35:539–44.


71. Philipps AF, Dvorak B, Kling PJ, Grille JG, Koldovsky O. Absorption of milk-borne insulin-like growth factor-I into portal blood of sucklin rats. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2000;31:128–35.


72. Kling PJ, Taing KM, Dvorak B, Woodward SS, Philipps AF. Insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates erythropoiesis when administered enterally. Growth Factors 2006;24:218–23.


73. DiBiasie A. Evidence-based review of retinopathy of prematurity prevenion in VLBW and ELBW Infants. Neonat Network 2006;25:393–403.

74. Loui A, Eilers E, Strauss E, Pohl-Schickinger A, Obladen M, Koehne P. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and soluble VEGF Receptor 1 (Sflt-1) levels in early and mature human milk from mothers of preterm versus term infants. J Hum Lact 2012;28:522–8.


75. Soubasi V, Kremenopoulos G, Diamanti E, Tsantali C, Sarafidis K, Tsakiris D. Follow-up of very low birth weight infants after erythropoietin treatment to prevent anemia of prematurity. J Pediatr 1995;127:291–7.


76. Pasha YZ, Ahmadpour-Kacho M, Hajiahmadi M, Hosseini M. Enteral erythropoietin increases plasma erythropoietin level in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatr 2008;45:25–8.

77. Claud EC, Savidge T, Walker WA. Modulation of human intestinal epithelial cell IL-8 secretion by human milk factors. Pediatr Res 2003;53:419–25.


78. Newburg DS, Woo JG, Morrow AL. Characteristics and potential functions of human milk adiponectin. J Pediatr 2010;156:S41–6.



79. Martin LJ, Woo JG, Geraghty SR, Altaye M, Davidson BS, Banach W, et al. Adiponectin is present in human milk and is associated with maternal factors. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;83:1106–11.



80. Civardi E, Garofoli F, Tzialla C, Paolillo P, Bollani L, Stronati M. Microorganisms in human milk: lights and shadows. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;26 Suppl 2:30–4.


81. Martin R, Langa S, Reviriego C, Jiminez E, Marin ML, Xaus J, et al. Human milk is a source of lactic acid bacteria for the infant gut. J Pediatr 2003;143:754–8.


82. Heikkila MP, Saris PE. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by the commensal bacteria of human milk. J Appl Microbiol 2003;95:471–8.


83. Collado MC, Delgado S, Maldonado A, Rodriguez JM. Assessment of the bacterial diversity of breast milk of healthy women by quantitative real-time PCR. Lett Appl Microbiol 2009;48:523–8.


84. Martin R, Jimenez E, Heilig H, Fernandez L, Marin ML, Zoetendal EG, et al. Isolation of bifidobacteria from breast milk and assessment of the bifidobacterial population by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and quantitative real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009;75:965–9.


85. Hunt KM, Foster JA, Forney LJ, Schutte UM, Beck DL, Abdo Z, et al. Characterization of the diversity and temporal stability of bacterial communities in human milk. PLoS One 2011;6:e21313.



86. Jost T, Lacroix C, Braegger C, Chassard C. Assessment of bacterial diversity in breast milk using culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Br J Nutr 2013;110:1253–62.


87. Fitzstevens JL, Smith KC, Hagadorn JI, Caimano MJ, Matson AP, Brownell EA. Systematic Review of the Human Milk Microbiota. Nutr Clin Pract 2017;32:354–64.


88. Asnicar F, Manara S, Zolfo M, Truong DT, Scholz M, Armanini F, et al. Studying vertical microbiome transmission from mothers to infants by strain-level metagenomic profiling. mSystems 2017;2:e00164–16.



89. Jimenez E, de Andres J, Manrique M, Pareja-Tobes P, Tobes R, Martinez-Blanch JF, et al. Metagenomic analysis of milk of healthy and mastitis-suffering women. J Hum Lact 2015;31:406–15.


90. Urbaniak C, Angelini M, Gloor GB, Reid G. Human milk microbiota profiles in relation to birthing method, gestation and infant gender. Microbiome 2016;4:1



91. Togo A, Dufour JC, Lagier JC, Dubourg G, Raoult D, Million M. Repertoire of human breast and milk microbiota: a systematic review. Future Microbiol 2019;14:623–41.


92. Rodriguez JM. The origin of human milk bacteria: is there a bacterial entero-mammary pathway during late pregnancy and lactation? Adv Nutr 2014;5:779–84.




93. Urbaniak C, Cummins J, Brackstone M, Macklaim JM, Gloor GB, Baban CK, et al. Microbiota of human breast tissue. Appl Environ Microbiol 2014;80:3007–14.



94. Ramsay DT, Kent JC, Owens RA, Hartmann PE. Ultrasound imaging of milk ejection in the breast of lactating women. Pediatrics 2004;113:361–7.


95. Solis G, de Los Reyes-Gavilan CG, Fernandez N, Margolles A, Gueimonde M. Establishment and development of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria microbiota in breast-milk and the infant gut. Anaerobe 2010;16:307–10.


96. Jost T, Lacroix C, Braegger CP, Rochat F, Chassard C. Vertical mother-neonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ Microbiol 2014;16:2891–904.


97. Murphy K, Curley D, O'Callaghan TF, O'Shea CA, Dempsey EM, O'Toole PW, et al. The composition of human milk and infant faecal microbiota over the first three months of life: a pilot study. Sci Rep 2017;7:40597




98. Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998;391:806–11.



99. Grunweller A, Hartmann RK. RNA interference as a gene-specific approach for molecular medicine. Curr Med Chem 2005;12:3143–61.


102. Kosaka N, Izumi H, Sekine K, Ochiya T. microRNA as a new immune-regulatory agent in breast milk. Silence 2010;1:7



103. Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, Huang KH, Lee MJ, et al. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem 2010;56:1733–41.




104. Melnik BC, Schmitz G. MicroRNAs: milk's epigenetic regulators. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017;31:427–42.


105. Zhou Q, Li M, Wang X, Li Q, Wang T, Zhu Q, et al. Immune-related microRNAs are abundant in breast milk exosomes. Int J Biol Sci 2012;8:118–23.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


