Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 65(8); 2022 |
|
Abstract
Neonatal seizures are the most common neurological symptoms caused by various etiologies in the neonatal period, but their diagnosis and treatment are challenging because their pathophysiology and electroclinical manifestations differ from those of patients in older age groups. Many seizures present as electrographic-only events without clinical signs or as obscure clinical manifestations that are difficult to distinguish from other neonatal behaviors. Accordingly, a new definition and classification of neonatal seizures was recently proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy Task Force on neonatal seizures, highlighting the role of electroencephalography in diagnosing and treating neonatal seizures. Neonatal seizures are defined as electrographic events with sudden, paroxysmal, and abnormal alteration of activity and divided into electroclinical seizures and electrographic-only seizures according to their clinical signs, thus excluding clinical events without an electrographic correlation. Seizure types are described by their predominant clinical features and divided into motor (automatisms, clonic, epileptic spasms, myoclonic, tonic, and sequential), nonmotor (autonomic and behavioral arrest), and unclassified. Although many neonatal seizures are acute reactive events caused by hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy or vascular insults, structural, genetic, or metabolic etiologies of neonatal-onset epilepsy should also be thoroughly evaluated to determine their appropriate management.
Graphical abstract
Neonates are most susceptible to seizure development due to their brain immaturity and high risk of injury [1,2]. Neonatal seizures, a most common neurological condition, are associated with high mortality rates of up to 20% [1,2]. Neonatal seizures can lead to long-term outcomes such as epilepsy, cerebral palsy, developmental disabilities, and psychomotor impairments depending on their etiologies and clinical courses [3-5]. The incidence of neonatal seizures is reportedly 1.5–5.5 per 1,000 live births among term infants but tends to be higher in preterm or very low birth weight infants [6,7]. Most neonatal seizures are acute, symptomatic, and provoked by severe brain insults such as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) or intracranial hemorrhages (ICHs), but some may involve neonatal-onset epilepsy related to structural, metabolic, or genetic disorders [2,8,9]. In all cases, the rapid identification and acute management of the seizure and its etiology are imperative, although long-term treatment and prognosis vary widely depending on the underlying etiologies [3,4,10]. However, these goals are not always easy to achieve because of the variable and subtle presentations of neonatal seizures and the need to differentiate epileptic events from nonepileptic movements [11,12]. In addition, the widespread use of continuous electroencephalographic monitoring in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) has led to the recognition that electrographic-only seizures with no clinical correlation are frequent, especially in critically ill neonates [13-15]. The role of electroencephalography (EEG) in the diagnosis of neonatal seizures has been increasingly emphasized, and this recognition has led the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) Task Force on Neonatal Seizures to propose a new definition and classification of neonatal seizures [16]. This review discusses the new definitions and classifications of neonatal seizures based on its pathophysiology, electroclinical relationship, behavioral patterns, and diagnosis through advanced testing of multiple etiologies.
The immature brain in the neonatal period has multiple age-related pathophysiologic mechanisms that increase an individual’s risk of acute seizures [17,18]. The fundamental mechanism is the neurophysiologic condition in which the excitatory neural circuits mature early while the inhibitory circuits mature late in the developing brain [11,19,20]. This amplified excitation is an important physiological condition in many activity or use-dependent developmental processes such as neurogenesis, cell migration and differentiation, synaptogenesis, and circuit development [17-19,21]. Enhanced excitatory neurotransmission and the paucity of inhibitory mechanisms by maturational changes in excitatory glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor function, developmental alterations or modulation of neuronal ion channels and neuropeptides, and age-dependent early microglial activation in early central nervous system (CNS) development increases the risk of seizures during the neonatal period [17,18,22].
In addition, due to the incomplete arborization of axons and dendritic processes and unmyelination of the neonatal brain, electrical activities are less quickly propagated, resulting in fragmented seizures [17]. Because of these neurophysiological conditions, neonatal seizures are usually focal, often short-lasting, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures are rare or absent in neonates [15,23,24].
Other characteristics of the neonatal brain include more advanced development of the limbic system with connections to the midbrain and brainstem than cerebral cortical organization, which leads to a high frequency of mouthing, eye deviation, and apnea as neonatal seizures and uncoupled/dissociated electroclinical seizures for which treatment with antiseizure medication may control clinical events but electrographic seizures persist regardless [15,23,24]. These physiological characteristics are more pronounced in preterm than in term neonates, so the more mmature they are, the shorter the seizures and the higher the proportion of subclinical or electrographic-only seizures. Thus, EEG is essential for diagnosis [10,15,24].
Many etiologies can cause neonatal seizures, although only a few account for most seizures [2,8,25,26]. In contrast to seizures in older age groups, most neonatal seizures are acute symptomatic seizures with suspected specific etiologies that are distinct from neonatal epilepsy [10,12]. Relatively few seizures are idiopathic or neonatal epilepsy syndromes related to structural abnormalities, genetic syndromes, or inborn errors of metabolism, but their identification is important in their management and prognosis. The relative frequency of each etiology differs in term versus preterm infants due to differences in brain maturity and physiologic conditions [2,23]. In term infants, HIE is the most common cause, and HIE-related seizures typically occur–6–8 hours after insult and within the first 24 hours of life [9,23]. On the other hand, cerebrovascular diseases such as infarction or hemorrhage are the most common cause in preterm infants [10,15]. Seizures related to meningitis, inborn errors of metabolism, or brain malformations can occur at any gestational age [8,12,23]. The timelines of occurrence and etiologies of reactive seizures in term versus preterm infants are shown in Fig. 1.
Acute symptomatic seizures in the neonatal period occur as acute reactive events to HIE, stroke, hemorrhage, infection, hypoglycemia, or electrolyte imbalance [9,12]. The most common cause is HIE, which accounts for 35%–45% of all neonatal seizures, typically developing seizures in the first 12–24 hours of life [9,12,27,28]. In HIE patients, seizure semiology varies among brain injury regions, but there is a high prevalence of subclinical or electrographic-only seizures in neonates [14]. The second most common cause of neonatal seizures is cerebrovascular events such as infarction or hemorrhage, which may occur in isolation or be the consequence of a CNS infection [12]. Perinatal arterial ischemic strokes are commonly caused by embolism form the placenta or umbilical cord, carotid artery, or heart, and the most common sign in newborn infants with strokes is seizures, often occurring within the first 24–72 hours of life or later [29-31]. In such cases, perinatal arterial ischemic strokes should be considered the cause of neonatal seizures, especially if the mother has oligohydramnios, chorioamnionitis, premature rupture of the membranes, preeclampsia, diabetes, or a smoking history and the infant has risk factors such as congenital heart disease, systemic infection, coagulopathy, or male sex [8,25,29,31]. Since most perinatal strokes occur in the motor cortex in the middle cerebral artery territory, the seizures often present as focal clonic seizures [29,31]. ICH, which can also cause acute symptomatic seizures, is the second most common etiology of seizures in preterm infants [30]. Hemorrhage size and location determine seizure severity and semiology [29,31,32]. While parenchymal hemorrhages, often caused by underlying vascular malformations, often make an individual prone to seizures, intraventricular hemorrhages rarely progress to seizures unless the amount of bleeding is significant and parenchymal damage occurs [12,32].
Acute metabolic disturbances in calcium, glucose, or sodium can also cause various types of neonatal seizures [9,10,12]. In most cases of metabolic disturbance, acute seizures are resolved by the correction of transient metabolic disturbances without antiseizure medication. However, antiseizure medication can be used in cases of severe and prolonged metabolic disturbances, and it is important to identify and treat their underlying cause to prevent recurrence [33,34]. Acute symptomatic seizures can also be caused by bacterial or viral infection of the CNS [9,10,12]. It is important to recognize and diagnose seizures early to minimize CNS or systemic sequelae of severe infection. Acute seizures caused by infections, such as late group B streptococcal infection or herpes simplex virus infection, can occur at any time during the neonatal period [9,10,12]. Seizure semiology and severity can vary depending on the infection region and severity. In all neonates with a suspected infective etiology, CNS infection should be evaluated through cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests and neuroimaging to ensure accurate and prompt treatment. In addition, as infection-related seizures are often longer than those associated with stroke or hemorrhage, prolonged EEG monitoring is recommended to provide adequate treatment with antiseizure medications [12,35,36].
Although acute symptomatic seizures are more common in the neonatal period, they may be the first presentation of an epilepsy syndrome, with approximately 13% of neonatal seizures [2,23]. It is important to identify epilepsy syndrome and its etiology to determine its treatment and prognosis. Brain malformations, genetic variants, and inborn errors of metabolism can cause neonatal-onset epilepsy syndromes.
Congenital and developmental structural brain abnormalities may cause neonatal seizures and have become more widely recognized with increasing use of head ultrasound (HUS) and high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Malformations of cortical development, including lissencephaly, hemimegalencephaly, focal cortical dysplasia, tuberous sclerosis, and polymicrogyria, may be due to disorders of neuronal and glial proliferation or apoptosis, neuronal migration, or cortical organization and are often related to gene mutation, but they can also be caused by congenital infection, prenatal ischemia, or exogenous or endogenous toxins. Genetic etiologies that cause brain malformations and neonatal-onset epilepsy are pathogenic variants of ARX, TSC1/TSC2, DCX, and DEPDC5, and more genes are being identified by advanced technology. Depending on lesion location and severity, various types of seizures can occur, and many are resistant to treatment.
In some cases, additional congenital anomalies of other organs may be associated; therefore, a thorough clinical evaluation and early consultation for genetic diagnosis and proper treatment are required.
Genetic etiologies are being increasingly recognized in neonatal seizures using advanced genetic evaluation [37-39]. Once strucural abnormalities or reversible metabolic abnormalities are excluded as the etiologies of neonatal seizures, neonatal epilepsy should be considered another etiology as it is important for determining treatment and predicting prognosis and comorbidities [38]. Genetic neonatal epilepsies are largely divided into self-limited and benign epilepsy and severe epilepsy according to clinical course and outcome but display phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity [37,40]. Neonatal epilepsy syndromes include self-limited familial neonatal epilepsy, self-limited neonatal seizures, early-infantile epileptic encephalopathy (EIEE), early myoclonic encephalopathy (EME), and epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures (EIMFS). The clinical characteristics and genetic variants of the representative genetic neonatal epilepsy are summarized in Table 1.
Self-limited familial neonatal seizures are autosomal dominant channelopathies that present as brief seizures within the first few days of life [41,42]. Common types of seizures are frequent, brief, and clustered focal tonic seizures, which are often associated with apnea, vocalizations, or autonomic symptoms. Self-limited neonatal familial epilepsy can be diagnosed if there are no abnormal findings on neurologic examination and laboratory tests, typical clinical manifestations, and a positive family history of neonatal seizures. Seizures are expected to be in remission by 6 months of age but often require treatment with antiseizure medications [41,42].
Self-limited neonatal seizures typically occurring on the fourth or sixth day of life, often having an onset later than that of self-limited familial neonatal seizures [39,40,43]. Self-limited neonatal seizures usually present as unilateral or bilateral clonic seizures that last several minutes, often clustering, migrating, or progressing to status epilepticus, and the background activity of EEG is mostly normal with nonspecific interictal findings. Other acute symptomatic etiologies should be ruled out to ensure an accurate diagnosis, and immediate treatment is typically required, although the seizures tend to decrease spontaneously within 2 days [44].
EIEE, also known as Ohtahara syndrome and EME, consists of severe neonatal epilepsy syndromes with poor prognosis and suppression-burst patterns on EEG [45]. Neonates with EIEE usually present with very frequent tonic seizures and/or rarely as epileptic spasms within the first 3 months but often within the first 2 weeks of life. The EEG of these frequent seizures shows a suppression-burst pattern, with the suppression lasting 35 seconds. EIEE is generally associated with congenital structural brain abnormalities but may be due to multiple single-gene mutations [40,46,47]. In most patients, the prognosis is poor due to severe developmental disabilities and age-specific progression to West syndrome or Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, and early-life mortality rates are high [45].
EME may be seen along with metabolic or genetic disorders such as glycine encephalopathy, pyridoxine/pyridoxal 5′-phosphate dependency, or biotinidase deficiency [45]. Seizures in EME usually begin within the first 3 months, as in EIEE, but typical seizure types are myoclonic, not tonic [45]. Myoclonic seizures may occur irregularly, clustered, or continuously, and they usually appear as generalized seizures, whereas focal myoclonic seizures may initially manifest on the face or extremities. The EEG background for EME is also characterized by a suppression-burst pattern, which is more apparent during sleep and may evolve to hypsarrhythmia by 3–5 months of age in up to 50% of patients with EME [23,45,48]. EME is also associated with pathogenic variants of single genes similar to EIEE, and its prognosis is generally poor with high rates of mortality and severe neurodevelopmental disabilities [39,40].
EIMFS develops within the first 6 months of life and often occurs in the neonatal period [39]. Seizures begin as focal clonic and/or tonic and evolve over time with more prominent autonomic features such as apnea, cyanosis, flushing, or sweating [39,48]. Frequent and multifocal epileptiform discharges in the interictal phase and continuous spike discharges migrating from one cortical area to another in the ictal phase are characteristic of EIMFS [39].
Inborn errors of metabolism are rare causes of neonatal seizures but important causes of intractable neonatal seizures, accounting for 30% of cases [49-51]. Neonatal seizures can occur in a wide variety of inborn errors of metabolism, including various amino acids, disorders of energy metabolism, cofactor-related metabolic diseases, purine and pyrimidine metabolic diseases, congenital disorders of glycosylation, and lysosomal and peroxisomal disorders. It is important to minimize complications by diagnosing treatable inborn errors of metabolism without delay. Pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy is an autosomal recessive disease diagnosed by the intravenous administration of 100 mg of pyridoxine (maximum of 500 mg) while monitoring EEG response or assessing clinical response to a 3-week course of oral pyridoxine [52]. Pyridoxal-phosphate-responsive epilepsy, an autosomal recessive disorder due to a pyridoxal-5′-phosphate oxidase (PNPO) deficiency, responds to oral treatment with pyridoxal phosphate [53]. Partial responsiveness to pyridoxine may be seen in other conditions with neonatal seizures such as neonatal hypophosphatasia, familial hypophosphatasia, nutritional vitamin B6 deficiency, and PNPO deficiency [52,54].
Biotinidase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive inherited disorder that affects the recycling of biotin, an essential B vitamin that presents as intractable neonatal seizures [49]. Folinicacid-responsive epilepsy leads to intractable seizures due to mutations of the ALDH7A1 (antiquitin) gene resulting in alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde (alpha-AASA) dehydrogenase deficiency [55]. Neonates with this condition usually respond to folinic acid within 24–48 hours [55]. Glucose transporter-1 deficiency is an autosomal dominant disorder usually caused by sporadic mutations in the SLC2A1 gene [56]. Glycine encephalopathy (neonatal nonketotic hyperglycinemia) typically presents as seizures on the second or third day of life [50]. Serine deficiency, disorders of creatine biosynthesis, and phenylketonuria should also be considered rare causes of neonatal seizures [49].
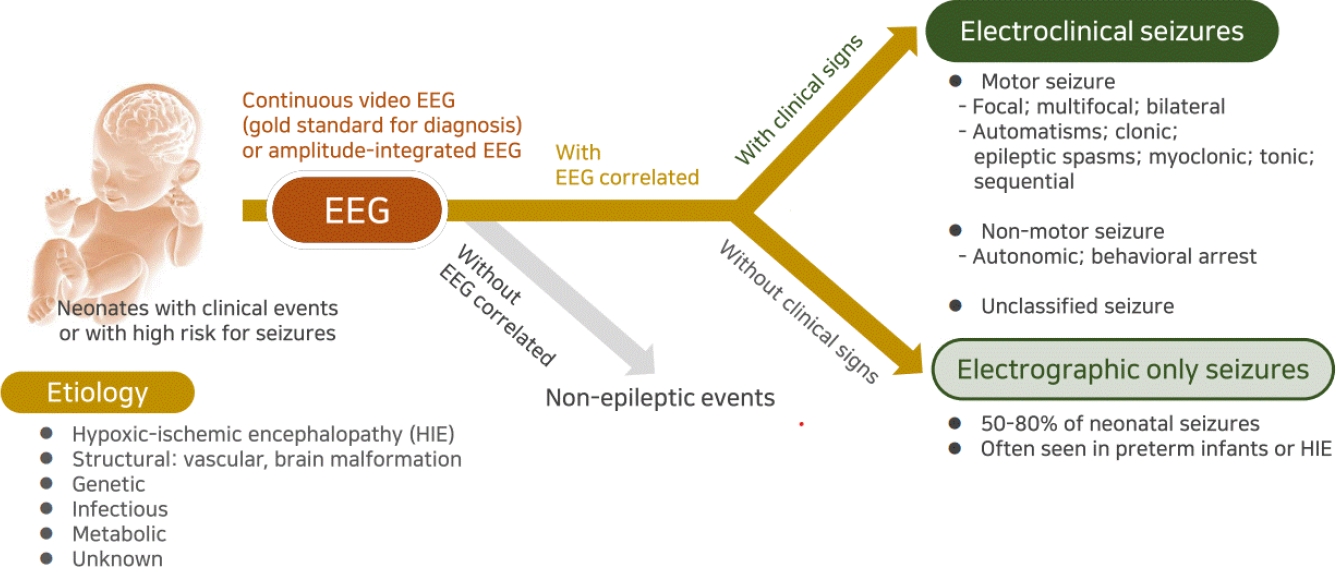
Historically, neonatal seizures have been defined as paroxysmal, repetitive, and stereotypical events with any other type of seizures and categorized according to their motor manifestations, such as focal clonic, multifocal-clonic, generalized tonic, myoclonic, and subtle [57]. It is then further categorized as clinical only, electroclinical, or electrographic-only based on the EEG findings [13,57]. That is, it has been diagnosed based on clinically observed seizures before or regardless of EEG monitoring results. However, neonatal seizures are typically difficult to differentiate them from nonepileptic paroxysmal events, and focal seizures that provoked sensory manifestation cannot be recognized clinically in neonates [24,58,59]. In addition, previous studies have shown that most neonatal seizures are electrographic-only events without clinical symptoms, whereas clinical-only seizures without electrographic seizure activity are not epileptic seizures in nature [35,60]. Therefore, to ensure an accurate neonatal seizure diagnosis, the confirmation of electrographic seizures on EEG monitoring along with bedside clinical observation is essential, and the new definition and classification of neonatal seizures were recently proposed by ILAE Task Force on Neonatal Seizures [16]. The newly proposed definition of neonatal seizures differs from that of infants and children and is based on electrographic events identified by EEG recording rather than clinical events suspicious for seizure [16]. The electrographic criteria for neonatal seizure recently presented by the American Clinical Neurophysiologic Society are a sudden abnormal EEG event defined by sudden and stereotyped repetitive waveforms that evolve in morphology, frequency, and/or location, with a minimum 2 μV peak-to-peak voltage and ≥10-second duration; no evidence of clinical signs is required (Figs. 2, 3A) [61].
These preferentially EEG-defined neonatal seizures are classified into electroclinical seizures and electrographic-only seizures depending on whether clinical signs are accompanied, and their clinical signs are classified as motor, nonmotor, and unclassified according to the movement [16]. The motor seizures are then divided into automatisms, clonic, epileptic spasms, myoclonic, sequential, and tonic seizures by seizure types, and each is divided into foal, multifocal, unilateral, or bilateral (asymmetric or symmetric) depending on the range of symptoms [62]. While the basic principles of the 2017 ILAE classification of seizure types are the initial division of seizures into those of focal and generalized onset, it is unnecessary to distinguish generalized seizures because most neonatal seizures involve exclusively focal or multifocal onset due to their neurophysiologic condition [16,62]. On the other hand, a clinical sign without a specific movement is considered a nonmotor seizure, which is divided into automatism and behavior arrest [16,62]. Seizure semiology can help the physician recognize the underlying cause early because focal clonic seizures are strongly related to acute symptomatic etiology such as stroke and infectious causes, focal tonic seizures with genetic epileptic encephalopathy, autonomic seizures with hemorrhage, and myoclonic seizures with inborn errors of metabolism [36,63]. A description and clinical considerations of each seizure type are listed in Table 2.
Neonatal seizures should also be distinguished from nonepileptic neonatal events. Nonepileptic paroxysmal events include jitteriness, hyperekplexia, benign sleep myoclonus, rapid eye movement sleep behavior, apnea, various motor automatisms, and dystonic or tonic posturing [16,62,64]. Nonepileptic movements can often be provoked with stimulation and are typically suppressed by touching or repositioning during the event. Nonepileptic events occur without any EEG changes [64,65]. However, as with epileptic seizures, nonepileptic events can also appear as symptoms of underlying pathology and should be evaluated systematically [65,66].
Neurophysiological testing is important in the diagnosis and acute treatment of neonatal seizures as emphasized in the new definition and classification [16]. Noninvasive EEG-based diagnostics are easy to set up, portable, practical for bedside testing, and provide a good temporal solution with minimal risk of scalp irritation in the NICU setting [58,59]. Different EEG techniques can be employed, including routine EEG, continuous EEG monitoring (cEEG), video-EEG monitoring, and amplitudeintegrated EEG (aEEG). Continuous video-EEG monitoring is the gold standard for accurate neonatal seizure detection [58,67]. If conventional EEG monitoring is not available, then aEEG can be useful as an initial or complementary tool [58,59]. It is easily available, readily applied, and an easily interpreted method of assessing brain function [68]. However, since aEEG is less sensitive and less specific for seizure detection than conventional EEG, it is not recommended if the latter is available [68].
The relative value of each neurophysiological technique is also dependent upon the availability of hardware and professional staff trained and experienced in interpreting the generated data [69,70]. Polygraphic recordings that concurrently capture ocular, respiratory, and muscle movements in addition to ECG data are preferred [59]. It is usually recommended that neonates with suspicious symptoms be monitored until several typical episodes are detected on EEG. High-risk neonates are typically monitored for 24 hours to screen for seizures [59]. In addition, even if seizures are detected and treated with antiseizure medications, the continuation of cEEG monitoring is generally recommended until at least a 24-hour seizure-free period is confirmed [58]. This is because after the administration of antiseizure medications, electroclinical dissociation often occurs, a period in which clinical seizures are no longer observed despite the EEG-defined events persisting [13,71].
The EEG characteristics of neonatal seizures differ from those of older children and adults. In neonates, interictal epileptiform discharges are rarely present to aid in diagnosis, patterns of electrographic seizure activity vary, and not all electrical seizure activity is accompanied by subclinical signs or evident clinical seizures [24,59,72]. The background activity in infants with suspected seizures may be helpful in the diagnosis. The characteristics of background activity help to estimate the extent and degree of brain injury, possible diagnoses, and prognosis. However, interictal focal sharp waves are not generally considered evidence of focal epileptogenic brain abnormalities in neonatal seizures; thus, they do not provide useful information for the diagnosis of electrical seizures in every infant [58]. As ictal EEG features, electrical seizure activity consists of sustained rhythmic activity with various morphologies, amplitudes, and frequencies. While electrical seizure activity may be present in neonates before 34– 35 weeks after conception (CA), it is less frequent in premature than term infants [24]. Frequency, voltage, and morphology may vary greatly within the same electrical seizure or from one seizure to the next in each infant [24,58]. All electrical seizure activity in neonates begins focally, except for the generalized activity associated with some types of myoclonic jerks or epileptic spasms. Electrical seizure activity in neonates most often arises in the central or temporal region of one hemisphere or the midline central region. Less common sites of onset include the occipital and frontal regions. The region of cortical involvement of the electrical seizure activity determines the motor manifestations of clinical seizures. In general, the onset, morphology, frequency, or propagation patterns of electrical activity are not related to the etiology, but some characteristic patterns on EEG are known to be related to specific etiologies. Focal discharges may be seen in patients with vascular insult or electrolyte imbalance, multifocal discharges in vitamin-related disorders, and suppression-burst with severe epileptic encephalopathies, suggesting specific associations of ictal EEG patterns with underlying etiologies [36].
To identify the risk factors of seizures and clues about the underlying etiology, the birth, maternal, and family histories should be investigated in detail. Risk factors for hypoxic injury, fetal heart rate deceleration, low Apgar scores, abnormal fetal presentation, and the nature of the delivery should be included as gestational and birth history [8,73]. Aspects of maternal history include maternal obesity, gestational diabetes, previous miscarriages, history of illness during pregnancy, placental abnormalities, use of prescription or illegal substances, and coagulopathies [25]. A detailed family history of inborn errors of metabolism or epilepsy, particularly neonatal, has also been identified. Physical examination may also provide clinical clues associated with the underlying etiology and direct further testing. Head size, birthmarks, facial dysmorphism, somatic abnormalities, and signs of infection should be evaluated. In addition, to identify signs suggestive of a structural brain lesion or neonatal encephalopathy, a thorough neurological examination including mental status assessment, cranial nerve examination, and evaluation of muscle tone and primitive reflexes should be performed.
Neuroimaging is essential for detecting structural cerebral pathology, including hemorrhage, infarction, or abnormalities of cortical development [74,75]. HUS remains the first-line tool for assessing neonatal seizures because of its ease of use at the bedside of acutely ill neonates. For locating hemorrhages and defining ventricular size, HUS has high sensitivity and specificity, but it can often miss brain lesions [74]. Lesion yield can be increased by repeating the HUS after several days because some abnormalities are delayed in physical appearance [74]. Brain MRI may be obtained as a complement to HUS once the neonate is stabilized. Brain MRI is the study of choice and, where available, should be performed in all neonates with seizures. Brain MRI is highly sensitive and has good anatomic resolution for identifying cerebral malformations, ICH, stroke, and ischemic changes [74,75]. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) can identify early infarcts. As shown in Fig. 3, the infarct that was not visible on early HUS (Fig. 3B) could be identified by DWI (Fig. 3C); therefore, brain MRI should be performed as early as possible in neonates with seizures. MR angiography and venography should be performed when a vascular etiology is suspected. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy can be valuable for facilitating the diagnosis of inborn metabolic anomalies. Computed tomography is generally avoided in neonates because it involves high exposure to ionizing radiation and has lower resolution than MRI.
Since the presence of multiple causes of seizures is not uncommon, all neonates with seizures should be thoroughly evaluated to rule out potentially treatable or reversible etiologies, and further evaluations should be made to identify specific etiologies according to individual clinical circumstances. Initial laboratory tests for neonatal seizures should include those to evaluate transient metabolic disturbances such as hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, or electrolyte imbalance [11]. Assessments should generally include a complete blood count, blood culture, CSF analysis, urine culture and toxicology, TORCH (toxoplasmosis, rubella cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, and HIV) screening, metabolic screening, and ophthalmologic evaluation. Additional laboratory studies might include determining the levels of serum amino acids (glycine and serine), ammonia, lactate, pyruvate, very long chain fatty acids, urine organic acid, biotinidase, pipecolic acid, CSF lactate, CSF amino acids, CSF chromatogram for folinic acid/pyridoxine-dependent seizures, and CSF pyridoxal-5-phosphate (active form of vitamin B6).
Genetic testing should be strongly considered in neonates with epilepsy for whom an acute provoked seizure cause is not identified on the initial history, examination, and neuroimaging. Genetic testing can reportedly identify the putative etiology of epilepsy in more than 75% of patients with neonatal epilepsy [15,40]. In addition to treatment implications, the identification of a genetic etiology assists in prognostic determinations and genetic counseling and avoids further extensive etiologic testing. When genetic testing is performed using a gene panel for epileptic encephalopathies and brain malformations, whole exome sequencing is suggested because of the phenotypic overlap of various genetic epilepsies [37,40].
Etiologies and electroclinical manifestations of neonatal seizures differ from those of infants and children. In addition, new definitions and classifications of neonatal seizures were recently proposed by the ILAE Task Force on neonatal seizures since the characteristics of neonatal seizures have been more specifically identified by the advanced application of EEG examination and advanced testing for various etiologies. The new definition and classification reflect the importance of EEG testing in the diagnosis and treatment of neonatal seizures. With the active application of continuous EEG monitoring, a more accurate diagnosis will reduce unnecessary treatment and expect better prognosis through more timely treatment.
Fig. 1.
Etiologies of neonatal seizures according to seizure onset timing. The most common causes of seizures occurring within the first 24 hours of life are hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy or vascular etiologies, followed by acute metabolic disturbances such as hypoglycemia or inborn errors of metabolism such as pyridoxine dependency. Within the next 24–72 hours, the main etiologies include infection, cortical malformations, cerebral infarction, inborn errors of metabolism such as glycine encephalopathy, urea cycle disturbances, pyridoxine dependency, and benign familial neonatal seizures. Over the next 72 hours to a week, causes include cortical malformations, cerebral infarction or hemorrhage, or inborn errors of metabolism, such as urea cycle disturbances. In the next 1–4 weeks, the differential includes cortical malformations, viral infections such as herpes simplex, or genetic epilepsy syndromes.
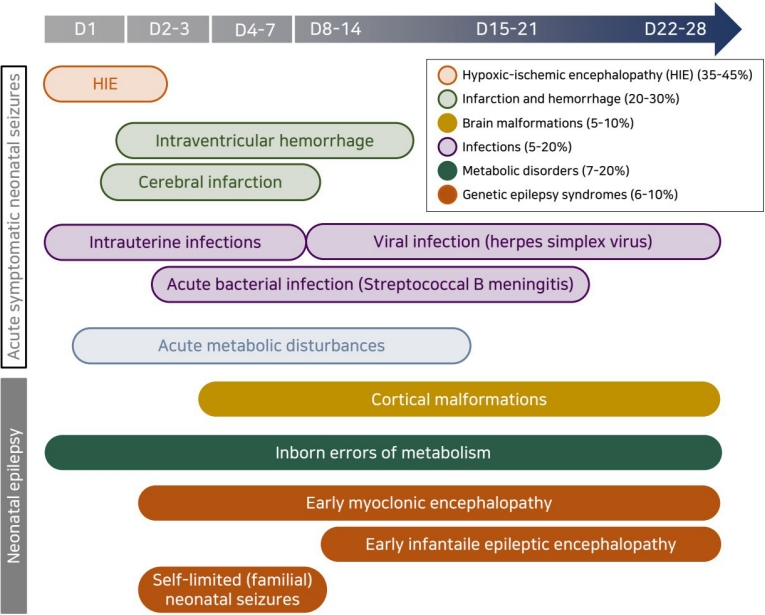
Fig. 2.
Approach to diagnosing neonatal seizures. The new definition and classification by the International League Against Epilepsy Task Force on neonatal seizures diagnoses neonatal seizures as events with an electroencephalography (EEG) correlation that are divided into electroclinical seizures and electrographic-only seizures according to clinical signs. Electroclinical seizures are described by their predominant clinical features and divided into motor (automatisms, clonic, epileptic spasms, myoclonic, tonic, and sequential), nonmotor (autonomic and behavioral arrest), and unclassified. Neonatal seizures are largely divided into acute symptomatic seizures and neonatal-onset epilepsies, and the etiologies can be identified as hypoxicischemic encephalopathy, structural, genetic, infectious, and metabolic by laboratory investigation. CRP, C-reactive protein; CSF, tcerebrospinal fluid; cEEG, continuous EEG; HIE, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
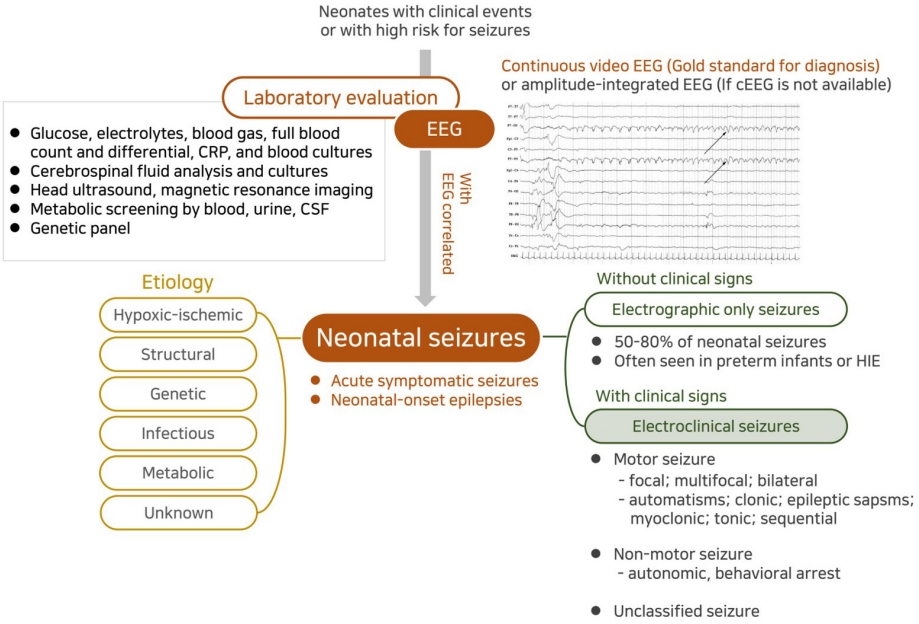
Fig. 3.
Term newborn presenting with apnea and staring on day 1. (A) Electroencephalography on day 2 showed sharply contoured rhythmic activities over the left central region with onset (red arrow) and change of frequency and amplitude. (B) Findings of head ultrasound on day 2 were normal, (C) but diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging on day 2 presented increased signal intensity in the territory of the left middle cerebral artery representing the extension of acute ischemic stroke.
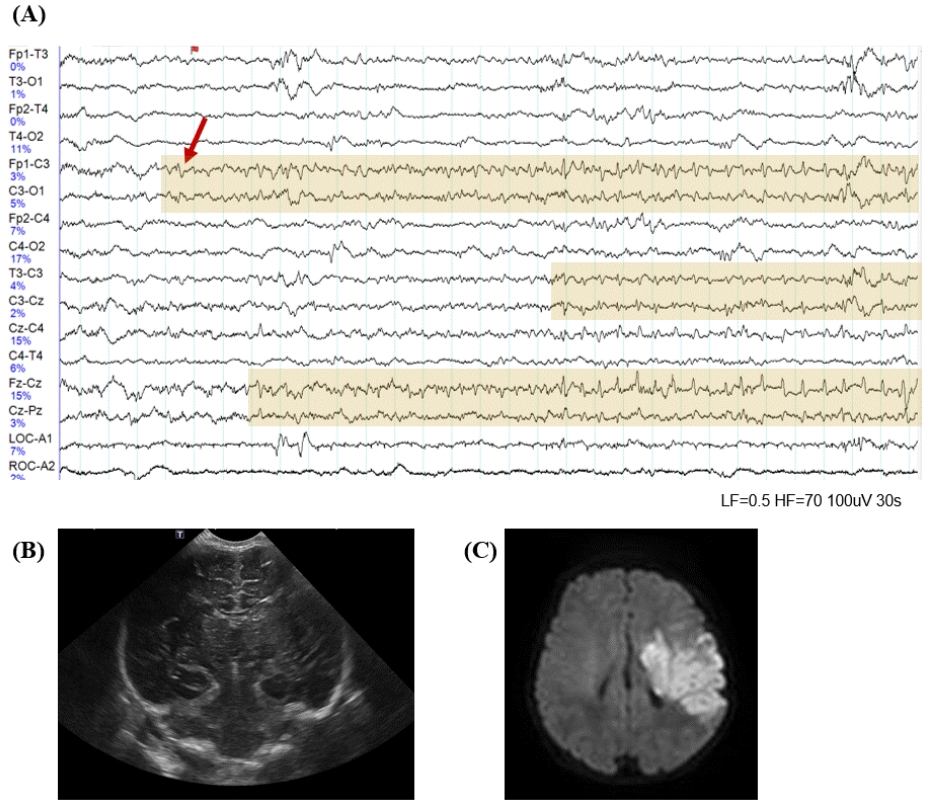
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics and genetic variants of neonatal epilepsy syndromes
Table 2.
Description and clinical considerations of types of neonatal seizure by the 2017 ILAE Classification of Seizures
ILAE, International League Against Epilepsy; EEG, electroencephalography; aEEG, amplitude-integrated EEG; HIE, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; EMG, electromyography; DEE, developmental and epileptic encephalopathy.
Adapted from Pressler et al. Epilepsia 2021;62:615-28 [16], with permission of John Wiley and Sons.
References
1. Lanska MJ, Lanska DJ. Neonatal seizures in the United States: results of the National Hospital Discharge Survey, 1980-1991. Neuroepidemiology 1996;15:117–25.



2. Vasudevan C, Levene M. Epidemiology and aetiology of neonatal seizures. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;18:185–91.


3. Ronen GM, Buckley D, Penney S, Streiner DL. Long-term prognosis in children with neonatal seizures: a population-based study. Neurology 2007;69:1816–22.


4. Uria-Avellanal C, Marlow N, Rennie JM. Outcome following neonatal seizures. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;18:224–32.


5. Andreolli A, Turco EC, Pedrazzi G, Beghi E, Pisani F. Incidence of epilepsy after neonatal seizures: a population-based study. Neuroepidemiology 2019;52:144–51.



6. Ronen GM, Penney S, Andrews W. The epidemiology of clinical neonatal seizures in Newfoundland: a population-based study. J Pediatr 1999;134:71–5.


7. Saliba RM, Annegers JF, Waller DK, Tyson JE, Mizrahi EM. Incidence of neonatal seizures in Harris County, Texas, 1992-1994. Am J Epidemiol 1999;150:763–9.


8. Pisani F, Facini C, Bianchi E, Giussani G, Piccolo B, Beghi E. Incidence of neonatal seizures, perinatal risk factors for epilepsy and mortality after neonatal seizures in the province of Parma, Italy. Epilepsia 2018;59:176473.


9. Soul JS. Acute symptomatic seizures in term neonates: Etiologies and treatments. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2018;23:183–90.



10. Pisani F, Prezioso G, Spagnoli C. Neonatal seizures in preterm infants: a systematic review of mortality risk and neurological outcomes from studies in the 2000's. Seizure 2020;75:7–17.


11. Glass HC. Neonatal seizures: advances in mechanisms and management. Clin Perinatol 2014;41:177–90.

12. Glass HC, Shellhaas RA. Acute symptomatic seizures in neonates. Semin Pediatr Neurol 2019;32:100768.


13. Scher MS, Alvin J, Gaus L, Minnigh B, Painter MJ. Uncoupling of EEG-clinical neonatal seizures after antiepileptic drug use. Pediatr Neurol 2003;28:277–80.


14. Nash KB, Bonifacio SL, Glass HC, Sullivan JE, Barkovich AJ, Ferriero DM, et al. Video-EEG monitoring in newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia. Neurology 2011;76:556–62.



15. Glass HC, Shellhaas RA, Tsuchida TN, Chang T, Wusthoff CJ, Chu CJ, et al. Seizures in preterm neonates: a multicenter observational cohort study. Pediatr Neurol 2017;72:19–24.



16. Pressler RM, Cilio MR, Mizrahi EM, Moshe SL, Nunes ML, Plouin P, et al. The ILAE classification of seizures and the epilepsies: modification for seizures in the neonate. Position paper by the ILAE Task Force on Neonatal Seizures. Epilepsia 2021;62:615–28.



17. Carrasco M, Stafstrom CE. How early can a seizure happen? Pathophysiological considerations of extremely premature infant brain development. Dev Neurosci 2018;40:417–36.



18. Nardou R, Ferrari DC, Ben-Ari Y. Mechanisms and effects of seizures in the immature brain. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;18:175–84.


19. Miller SM, Goasdoue K, Bjorkman ST. Neonatal seizures and disruption to neurotransmitter systems. Neural Regen Res 2017;12:216–7.



20. Rakhade SN, Jensen FE. Epileptogenesis in the immature brain: emerging mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurol 2009;5:380–91.




21. Stafstrom CE, Thompson JL, Holmes GL. Kainic acid seizures in the developing brain: status epilepticus and spontaneous recurrent seizures. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 1992;65:227–36.


22. Rivera C, Voipio J, Payne JA, Ruusuvuori E, Lahtinen H, Lamsa K, et al. The K+/Cl- co-transporter KCC2 renders GABA hyperpolarizing during neuronal maturation. Nature 1999;397:251–5.



23. Shellhaas RA, Wusthoff CJ, Tsuchida TN, Glass HC, Chu CJ, Massey SL, et al. Profile of neonatal epilepsies: characteristics of a prospective US cohort. Neurology 2017;89:893–9.



24. Janackova S, Boyd S, Yozawitz E, Tsuchida T, Lamblin MD, Gueden S, et al. Electroencephalographic characteristics of epileptic seizures in preterm neonates. Clin Neurophysiol 2016;127:2721–7.


25. Hall DA, Wadwa RP, Goldenberg NA, Norris JM. Maternal risk factors for term neonatal seizures: population-based study in Colorado, 19892003. J Child Neurol 2006;21:795–8.



26. Glass HC, Wusthoff CJ, Shellhaas RA, Tsuchida TN, Bonifacio SL, Cordeiro M, et al. Risk factors for EEG seizures in neonates treated with hypothermia: a multicenter cohort study. Neurology 2014;82:1239–44.



27. Glass HC, Shellhaas RA, Wusthoff CJ, Chang T, Abend NS, Chu CJ, et al. Contemporary profile of seizures in neonates: a prospective cohort study. J Pediatr 2016;174:98. –103. e1.



28. Keeney SE, Adcock EW, McArdle CB. Prospective observations of 100 high-risk neonates by high-field (1.5 Tesla) magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system. II. Lesions associated with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics 1991;87:431–8.



29. Grunt S, Mazenauer L, Buerki SE, Boltshauser E, Mori AC, Datta AN, et al. Incidence and outcomes of symptomatic neonatal arterial ischemic stroke. Pediatrics 2015;135:e1220–8.



30. Bruno CJ, Beslow LA, Witmer CM, Vossough A, Jordan LC, Zelonis S, et al. Haemorrhagic stroke in term and late preterm neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2014;99:F48–53.


31. Kirton A, Armstrong-Wells J, Chang T, Deveber G, Rivkin MJ, Hernandez M, et al. Symptomatic neonatal arterial ischemic stroke: the International Pediatric Stroke Study. Pediatrics 2011;128:e1402–10.



32. Castro Conde JR, Fuentes IQ, Campo CG, Sosa AJ, Millan BR, Exposito SH. EEG findings and outcomes of continuous video-EEG monitoring started prior to initiation of seizure treatment in the perinatal stroke. Early Hum Dev 2018;120:1–9.


33. Wong DS, Poskitt KJ, Chau V, Miller SP, Roland E, Hill A, et al. Brain injury patterns in hypoglycemia in neonatal encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2013;34:1456–61.



34. Thomas TC, Smith JM, White PC, Adhikari S. Transient neonatal hypocalcemia: presentation and outcomes. Pediatrics 2012;129:e1461–7.



35. Scher MS, Aso K, Beggarly ME, Hamid MY, Steppe DA, Painter MJ. Electrographic seizures in preterm and full-term neonates: clinical correlates, associated brain lesions, and risk for neurologic sequelae. Pediatrics 1993;91:128–34.



36. Nunes ML, Yozawitz EG, Zuberi S, Mizrahi EM, Cilio MR, Moshe SL, et al. Neonatal seizures: is there a relationship between ictal electroclinical features and etiology? A critical appraisal based on a systematic literature review. Epilepsia Open 2019;4:10–29.




37. Novotny EJ Jr. Early genetic testing for neonatal epilepsy: when, why, and how? Neurology 2017;89:880–1.


38. Perucca P, Perucca E. Identifying mutations in epilepsy genes: impact on treatment selection. Epilepsy Res 2019;152:18–30.


39. El Kosseifi C, Cornet MC, Cilio MR. Neonatal developmental and epileptic encephalopathies. Semin Pediatr Neurol 2019;32:100770.


41. Grinton BE, Heron SE, Pelekanos JT, Zuberi SM, Kivity S, Afawi Z, et al. Familial neonatal seizures in 36 families: clinical and genetic features correlate with outcome. Epilepsia 2015;56:1071–80.


42. Castaldo P, del Giudice EM, Coppola G, Pascotto A, Annunziato L, Taglialatela M. Benign familial neonatal convulsions caused by altered gating of KCNQ2/KCNQ3 potassium channels. J Neurosci 2002;22:RC199.



43. Dehan M, Quillerou D, Navelet Y, D’Allest AM, Vial M, Retbi JM, et al. Convulsions in the fifth day of life: a new syndrome? Arch Fr Pediatr 1977;34:730–42.

44. Okumura A, Watanabe K, Negoro T, Hayakawa F, Kato T, Maruyama K, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with benign partial epilepsy in infancy. Epilepsia 2006;47:181–5.


45. Beal JC, Cherian K, Moshe SL. Early-onset epileptic encephalopathies: Ohtahara syndrome and early myoclonic encephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol 2012;47:317–23.


46. Syrbe S, Zhorov BS, Bertsche A, Bernhard MK, Hornemann F, Mutze U, et al. Phenotypic variability from benign infantile epilepsy to Ohtahara syndrome associated with a novel mutation in SCN2A. Mol Syndromol 2016;7:182–8.




47. Saitsu H, Yamashita S, Tanaka Y, Tsurusaki Y, Nakashima M, Miyake N, et al. Compound heterozygous BRAT1 mutations cause familial Ohtahara syndrome with hypertonia and microcephaly. J Hum Genet 2014;59:687–90.



48. Yamamoto H, Okumura A, Fukuda M. Epilepsies and epileptic syndromes starting in the neonatal period. Brain Dev 2011;33:213–20.


49. Falsaperla R, Sciuto L, La Spina L, Sciuto S, Pratico AD, Ruggieri M. Neonatal seizures as onset of inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs): from diagnosis to treatment. A systematic review. Metab Brain Dis 2021;36:2195–203.




50. Almannai M, El-Hattab AW. Inborn errors of metabolism with seizures: defects of glycine and serine metabolism and cofactor-related disorders. Pediatr Clin North Am 2018;65:279–99.

51. Ficicioglu C, Bearden D. Isolated neonatal seizures: when to suspect inborn errors of metabolism. Pediatr Neurol 2011;45:283–91.


52. Stockler S, Plecko B, Gospe SM Jr, Coulter-Mackie M, Connolly M, van Karnebeek C, et al. Pyridoxine dependent epilepsy and antiquitin deficiency: clinical and molecular characteristics and recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Mol Genet Metab 2011;104:4860.
53. Kuo MF, Wang HS. Pyridoxal phosphate-responsive epilepsy with resistance to pyridoxine. Pediatr Neurol 2002;26:146–7.


54. Mills PB, Footitt EJ, Mills KA, Tuschl K, Aylett S, Varadkar S, et al. Genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy (ALDH7A1 deficiency). Brain 2010;133:2148–59.



55. Gallagher RC, Van Hove JL, Scharer G, Hyland K, Plecko B, Waters PJ, et al. Folinic acid-responsive seizures are identical to pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy. Ann Neurol 2009;65:550–6.


56. Klepper J, Scheffer H, Leiendecker B, Gertsen E, Binder S, Leferink M, et al. Seizure control and acceptance of the ketogenic diet in GLUT1 deficiency syndrome: a 2- to 5-year follow-up of 15 children enrolled prospectively. Neuropediatrics 2005;36:302–8.


57. Mizrahi EM, Kellaway P. Characterization and classification of neonatal seizures. Neurology 1987;37:1837–44.


58. Shellhaas RA. Continuous long-term electroencephalography: the gold standard for neonatal seizure diagnosis. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2015;20:149–53.


60. Murray DM, Boylan GB, Ali I, Ryan CA, Murphy BP, Connolly S. Defining the gap between electrographic seizure burden, clinical expression and staff recognition of neonatal seizures. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008;93:F187–91.


61. Tsuchida TN, Wusthoff CJ, Shellhaas RA, Abend NS, Hahn CD, Sullivan JE, et al. American clinical neurophysiology society standardized EEG terminology and categorization for the description of continuous EEG monitoring in neonates: report of the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society critical care monitoring committee. J Clin Neurophysiol 2013;30:161–73.

62. Fisher RS, Cross JH, D’Souza C, French JA, Haut SR, Higurashi N, et al. Instruction manual for the ILAE 2017 operational classification of seizure types. Epilepsia 2017;58:531–42.



63. Santarone ME, Pietrafusa N, Fusco L. Neonatal seizures: when semiology points to etiology. Seizure 2020;80:161–5.


64. Fernandez-Alvarez E. Transient benign paroxysmal movement disorders in infancy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2018;22:230–7.


65. Besag FM, Hughes EF. Paroxysmal disorders in infancy: a diagnostic challenge. Dev Med Child Neurol 2010;52:980–1.


66. Visser AM, Jaddoe VW, Arends LR, Tiemeier H, Hofman A, Moll HA, et al. Paroxysmal disorders in infancy and their risk factors in a populationbased cohort: the Generation R Study. Dev Med Child Neurol 2010;52:1014–20.


67. Frenkel N, Friger M, Meledin I, Berger I, Marks K, Bassan H, et al. Neonatal seizure recognition--comparative study of continuous-amplitude integrated EEG versus short conventional EEG recordings. Clin Neurophysiol 2011;122:1091–7.


68. Rakshasbhuvankar A, Rao S, Palumbo L, Ghosh S, Nagarajan L. Amplitude integrated electroencephalography compared with conventional video EEG for neonatal seizure detection: a diagnostic accuracy study. J Child Neurol 2017;32:815–22.



69. Kubota T, Kidokoro H, Narahara S, Fukasawa T, Nakata T, Natsume J, et al. Evaluation of interobserver variability in application of the new neonatal seizure classification proposed by the ILAE Task Force. Epilepsy Behav 2020;111:107292.


70. Malone A, Ryan CA, Fitzgerald A, Burgoyne L, Connolly S, Boylan GB. Interobserver agreement in neonatal seizure identification. Epilepsia 2009;50:2097–101.


71. Shah DK, Wusthoff CJ, Clarke P, Wyatt JS, Ramaiah SM, Dias RJ, et al. Electrographic seizures are associated with brain injury in newborns undergoing therapeutic hypothermia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2014;99:F219–24.


72. Shellhaas RA, Chang T, Tsuchida T, Scher MS, Riviello JJ, Abend NS, et al. The American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s guideline on continuous electroencephalography monitoring in neonates. J Clin Neurophysiol 2011;28:611–7.


73. Saliba RM, Annegers FJ, Waller DK, Tyson JE, Mizrahi EM. Risk factors for neonatal seizures: a population-based study, Harris County, Texas, 1992-1994. Am J Epidemiol 2001;154:14–20.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


