Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 65(7); 2022 |
|
Abstract
Background
During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, lung ultrasonography (US) has been gaining importance in pediatric intensive care and emergency settings for the screening, diagnosis, and monitoring of pulmonary pathology.
Purpose
To describe the pattern of lung US changes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and its potential role in monitoring ventilated patients.
Methods
This prospective observational study included children aged 1 month to 12 years with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19. Lung US was performed using a high-frequency linear probe (5ŌĆō12 MHz) in all children with moderate/severe respiratory symptoms within 24 hours of admission and then daily until the patient required oxygen therapy. Lung involvement severity was assessed using lung US scores, while lung aeration improvement or deterioration was measured using lung ultrasound reaeration scores (LUSReS).
Results
Of 85 children with moderate to severe disease, 54 with pulmonary disease were included. Of them, 50 (92.5%) had an interstitial pattern, followed by pleural line abnormalities in 44 (81.5%), reduced or absent lung sliding in 31 (57.4%), and consolidation in 28 (51.8%). A significantly higher lung US score (median, 18; interquartile range [IQR], 11ŌĆō22) was observed in ventilated versus nonventilated patients (median, 9; IQR, 6ŌĆō11). LUSReS improvement after positive end-expiratory pressure titration was positively correlated with improved dynamic lung compliance and oxygenation indices and negatively correlated with the requirement for driving pressure. Successful weaning could be predicted with 100% specificity if loss of LUSReS Ōēż 5.
Conclusion
Interstitial syndrome, fragmented pleural line, and subpleural microconsolidation were the most prevalent lung US findings in children with COVID-19 pneumonia. Thus, lung US may have the ability to monitor changes in lung aeration caused by mechanical ventilation and predict its successful weaning in children with COVID-19.
Graphical abstract
The global community is undergoing austerity due to the catastrophic effect of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) since the emergence of pandemic. Most COVID-19 cases occur in adults, and a subset may progress to severe respiratory illness due to COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome [1]. Severe COVID-19 pneumonia after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) exposure is less common in young adults and children. In a systematic review of 7,480 pediatric patients with confirmed COVID-19, only 2% were severe (e.g., dyspnea, central cyanosis, and hypoxemia), and 0.7% were critical (e.g., acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], respiratory failure, and shock) [2].
Among adults, chest computed tomography (CT) has been shown to be an effective tool for the diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia, as well as a screening tool for the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection in epidemic settings [3]. But in children, Chest CT is not recommended as a screening test in suspected COVID-19 infection. The probable risks include radiation exposure, risk of transport of sick patients, COVID-19 exposure to radiology staff, a potentially nondiagnostic study, and increased imaging equipment/room turnaround time for appropriate cleaning and air turnover [4].
Lung ultrasound (LUS) is a useful diagnostic tool in determining both lung involvement and its severity, thus conceivably plays a role in treatment decisions [5]. Indeed, LUS is a user-friendly, noninvasive real-time tool available at the patientŌĆÖs bedside [6]. Pulmonary changes in COVID-19 are predominantly located peripherally in the lower lobes and thus easily persuadable to evaluation by ultrasound, especially in children owing to their thinner chest wall and better image quality [7]. Several studies draw attention to the applicability of lung US in adults with COVID-19 [8,9], however little published evidence exists regarding its clinical usefulness in children [10].
Considering efficacy of lung US in various pulmonary pathologies we incorporated the practice of this imaging modality in routine management of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in children in our tertiary care COVID referral center. In this study, we describe the lung US pattern of COVID-19 infected children and evaluate its role in daily monitoring and weaning of ventilated patients.
It was a prospective observational study conducted in a tertiary care COVID referral center from September 2020 to June 2021. Children in the age group of 1 month to 12 years with respiratory symptoms on admission in the emergency department, a diagnosis of COVID-19 based on the detection of SARS-CoV-2 by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from the nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swab were included in the study. Institutional Ethics Committee approval (Ref no ŌĆō MC/KOL/IEC/NON-SPON/776/09/20) was obtained for conducting the study. Informed consents were taken from the parents/ legal guardian of the patients.
Patients with preexisting pulmonary pathology like bronchopulmonary dysplasia, bronchiolitis obliterans, active pulmonary tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis were excluded to minimize the possible interference on the LUS evaluation. Patients with confirmed coinfection by other viral or bacterial pathogen detected by culture or multiplex PCR of respiratory samples were also excluded. Children fulfilling the diagnostic criteria of multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) with myocardial dysfunction in echocardiography were also excluded as interstitial edema may be contributed by myocardial dysfunction [11].
LUS was performed in all children with pulmonary symptoms and moderate/severe/critical disease severity within 24 hours of admission and then daily till the patient required oxygen therapy [12]. Chest x-ray was also done in the first 24 hours of hospitalization. Blood culture, sputum or bronchoalveolar fluid culture, and multiplex PCR for other respiratory pathogens were performed. PatientsŌĆÖ demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were captured. Severity of respiratory distress, requirement of oxygen, high flow nasal oxygen, noninvasive ventilation, invasive ventilation, duration of respiratory support, oxygenation status, requirement of antiviral, steroid, other treatments, length of pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) stay, and hospital stay were recorded. Acute severe respiratory distress syndrome was defined and categorized according to the pediatric acute lung injury definition [13].
Transthoracic lung ultrasonography was performed by 4 pediatricians trained in method and practicing point of care LUS for more than 5 years. High-frequency linear probe (4 to 15 MHz) was used to perform LUS. Imaging was done in the supine position and sitting position for patients with moderate severity whereas supine and lateral decubitus position in very sick patients. The depth and frequency were adjusted to set the focal point on the pleural line. By using the anterior & posterior axillary lines, 3 areas per hemithorax were identified (anterior, lateral, posterior). Each area is divided into two, superior and inferior. So, each hemithorax is systemically divided into 6 regions: 2 anterior, 2 lateral, 2 posterior. Finally, for individual patients, 12 chest areas were analyzed. The anterior scans were performed through the midclavicular line, whereas the lateral scans were done through the midaxillary line, and the posterior scans were performed through the scapular line (Fig. 1).
As stated by the International Consensus Conference on LUS for each area we analyzed the following features: presence of interstitial syndrome (B-lines, not confluent or confluent vertical artifacts with white lung), distribution of B-lines (homogeneous or inhomogeneous with spared areas), consolidations and their distribution, pleural line abnormalities (irregular/fragmented, thickened, and/or with subpleural microconsolidation) and their distribution, pleural effusion, and presence of lung sliding (normal, reduced, or absent) [14].
Assessment of severity of lung involvement was done by LUS score [15]. The maximum score could be 36 and the minimum score zero. (Supplementary Table 1A) (Fig. 2)
On daily monitoring of children improvement or deterioration of lung aeration was measured by lung ultrasound reaeration score (LUSReS) proposed by Bouhemad et al. [16] (Supplementary Table 1B). These measurements were performed daily as routine monitoring and also during significant change in oxygenation and ventilation (oxygen saturation [SpO2] fall >5% and/or end tidal carbon dioxide rise >10). For ventilated patients, 2 hours after achieving optimum positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) titration and stable saturation (92%ŌĆō96%), simultaneously LUSReS, change in dynamic lung compliance, improvement of oxygenation index (OI), oxygen saturation index (OSI), partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2)/fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) ratio (PF), SpO2/FiO2 ratio (SF) and driving pressure were measured [13]. Dynamic lung compliance was measured by Open lung tool software in Maquet Servo-I ventilator. Loss of LUS aeration score was monitored during weaning and spontaneous breathing trial (SBT), along with other weaning predictors like respiratory rate (RR), heart rate, blood pressure, PaO2, partial pressure of carbon dioxide, tidal volume, rapid shallow breathing index [RSBI] (breaths/min/mL/kg) [17]. RSBIŌēż8 breaths/min/mL/kg body weight was cutoff for successful weaning. Weaning failure was defined as failed SBT or the need for reintubation within 48 hours following extubation [18].
The primary objective was to describe and compare the pattern of LUS between ventilated and nonventilated group of children suffering from COVID-19 pneumonia and ARDS.
Secondary objectives were ŌĆō (1) to find the correlation between improvement of LUSReS and lung compliance, oxygenation indices, driving pressure requirement, 2 hours after PEEP titration; (2) to determine the performance of loss of LUS aeration score to predict successful weaning.
Data were entered and analyzed using the IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Continuous variables were expressed as median with interquartile range (IQR) and mean with standard deviation, while categorical variables, as numbers and percentages. Comparison of demographics, clinical, laboratory test, and lung imaging data (LUS and x-ray) between the 2 group of patients ŌĆō required mechanical ventilation (MV) (ventilated) and did not require ventilation (nonventilated) category were analyzed by Fischer, Žć2, or Mann-Whitney tests. Correlation between improvement in LUSReS and dynamic compliance and oxygenation indices were tested by Pearson rank correlation test. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was analyzed to assess the predictability of the loss of lung aeration to discriminate between weaning success and failure. Youden index was calculated in MedCalc statistical software to determine the optimal cutoff points of loss of lung aeration score. The area under the curve (AUC) ranges between 0 and 1, and the proximity of AUC to 1 was considered as better performance of that variable. A P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
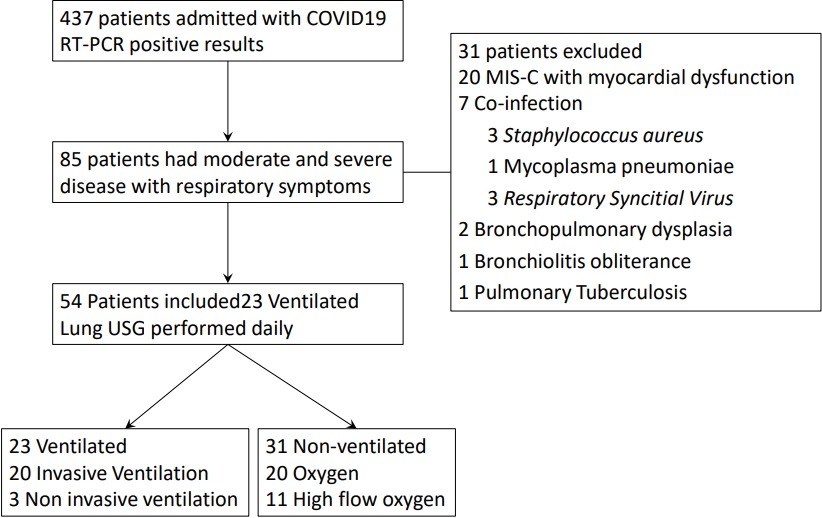
During the study period out of 473 admitted children with COVID-19 RT-PCR positive results, 85 children had moderate or severe respiratory symptoms. Thirty-one patients were excluded (Fig. 3). Out of 54 included patients, 23 (42.6%) required MV and termed as ventilated group, whereas the rest 31 patients were termed as nonventilated group.
Demographic, clinical, laboratory, treatment, and outcome parameters of the whole cohort as well as comparison of the parameters between the 2 groups are shown in Table 1. The median age of the study population was 5.5 years (IQR, 1ŌĆō9). Thirty-one of the cohort (57.4%) were male. Among the clinical characteristics, breathlessness was presenting complaint of 37 patients (77%). Prevalence of comorbidity was greater in the ventilated group (P=0.013). The median duration of fever was 6 days (IQR, 3ŌĆō9.5). RR was significantly high in ventilated patients (42 [IQR, 30ŌĆō56] vs. 32 [IQR, 24ŌĆō46], P=0.022). Significant low SpO2 was noted in the ventilated cohort (87 [IQR, 80ŌĆō92] vs. 92 [IQR, 84ŌĆō96], P=0.013). All patients who required ventilator support fulfilled the criteria of ARDS as compared to 10 patients (32%) in the nonventilated group (P=0.001)
Among the laboratory parameters obtained within first 48 hours of hospital admission, ventilated patients had significantly lower platelet counts compared with nonventilated patients (172 [IQR, 15ŌĆō272]├Ś109/L vs. 216 [IQR, 145ŌĆō288]├Ś109/L, P=0.043). Serum levels of D-dimer and ferritin were significantly elevated among ventilated study group (P=0.031 and P=0.013 respectively). Statistically significantly difference in median interleukin-6 level was noted between ventilated and nonventilated cohort of patients (81.2 [IQR, 35ŌĆō200.5] pg/mL vs. 18.4 [IQR, 12.4ŌĆō69] pg/mL, P=0.002).
Remdesivir was used in 28 patients (54%): 23 (100%) in ventilated group versus 5 (16%) in nonventilated group (P<0.001). Corticosteroids and low molecular weight heparin were administered more often in the ventilated group (P<0.05 for both). Prone positioning was performed in 20 (87%) of ventilated patient. Awake proning was done for 7 patients (22.5 %) in the nonventilated group. Early proning was practiced in patients with predominant posterior and lateral lung area involvement. Forty-three patients (79.6%) needed PICU admission. Median PICU length of stay was significantly prolonged in ventilated cohort (8 [IQR, 5ŌĆō11] vs. 5 [IQR, 3.5ŌĆō7], P=0.024). Two patients in the ventilated group expired.
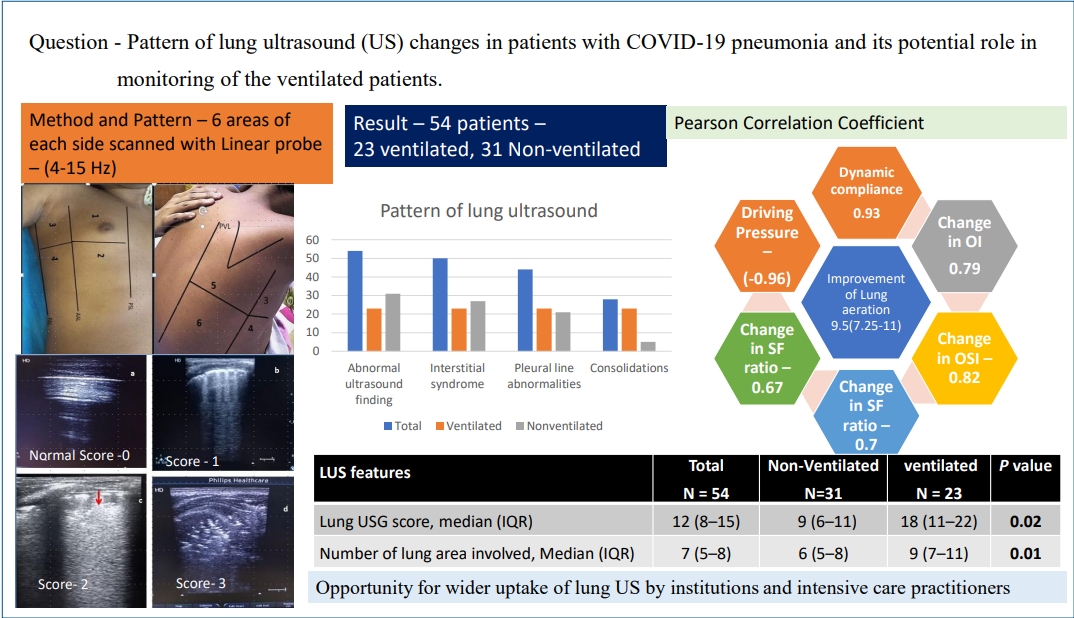
Interstitial syndrome (B-lines) was the most common ultrasound abnormality noticed in 50 patients (92.5%). Bilateral involvement was predominant in the ventilated patients as compared to the nonventilated group: 23 (100%) vs. 6 (19.3%) (P<0.001). Inhomogeneous distribution with spared areas was present in 31 (58%). White lung areas were found in 19 subjects and all were in the ventilated group. Pleural line abnormalities were detected in 44 patients (81.5). It was significantly high in ventilated cohort 23 (100%) versus 21 (67%) (P=0.003). Fragmented pleural line, thickened pleural line, and subpleural microconsolidation were present in 29 (53.7%), 24 (44.4%), and 39 patients (72.2%), respectively. Eighteen patients (86%) in the ventilated group had reduced lung sliding as compared to 3 (9.6) in nonventilated group (P<0.001). Two patients with pneumothorax had absent lung sliding. Consolidation (C profile) was observed in 28 patients (51.8%), with bilateral distribution in 13 patients (24%). Twenty-three ventilated patients (100%) had consolidation, whereas 5 (16.13%) in the nonventilated patient (P<0.001). Pleural effusion was present in 12 patients (22.2%) and 7 had bilateral in distribution. Median LUS score was significantly higher in the ventilated group compared to nonventilated patients (18 [IQR, 11ŌĆō22] vs. 9 [IQR, 6ŌĆō11], P=0.022). Significantly wider lung area was involved in ventilated patients 9 (IQR, 7ŌĆō11) vs. 6 (IQR, 5ŌĆō8) in the nonventilated group (P=0.015).
Overall abnormal CXR findings were observed in 47 of patients (87%). Interstitial pattern, ground glass opacities, and consolidations were detected in a significantly higher percentage in the ventilated group compared to the nonventilated group. Perihilar peribronchial wall thickening pattern was noted in 15 of patients (27.7%) and it was present more frequently in nonventilated patients (12 vs. 3) but did not differ at a statistically significant level.
Among ventilated patients, the median improvement of lung reaeration score was 9.5 (IQR, 7.25ŌĆō11). Improvement of median lung dynamic complex was 2.74 (IQR, 2.15ŌĆō3.6) mL/cmH2O after PEEP titration and it had a strong correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.93, P<0.001) with the LUSReS. All oxygenation indices like OI, OSI, SF ratio, and PF ratio had a good positive correlation with change in lung reaeration score (P=0.001 for all). The median requirement of driving pressure after 2 hours of PEEP titration was 14 (IQR, 11.5ŌĆō18). Driving pressure requirement had a strong negative correlation with improvement of LUSReS (Pearson correlation coefficient: 0.96, P<0.001 (Table 3).
Duration of MV before weaning was significantly longer in weaning failure group as compared to the successful group (7.7┬▒2.5 vs. 5.1┬▒2.0, P=0.033). Weaning failure cohort had greater median loss of LUSReS during SBT (9 [IQR, 7ŌĆō12] vs. 5 [IQR, 3ŌĆō7], P<0.001). Other monitored parameters during weaning process like PO2, FiO2, P/F ratio, SpO2, RR, RSBI, PEEP, and pressure had no significant difference between the 2 groups (Table 4). The ROC curve analysis showed that the AUC of the loss of lung aeration for discrimination between successful or failed weaning was 0.94, (95% CI, 0.85ŌĆō1.00; P=0.001), and the cutoff value of 5 or less had a sensitivity of 79% and specificity of 100% to predict successful weaning in the study population.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a paradigm shift from traditional clinical methods to bedside, noninvasive, rapid, and repeatable imaging-based identification, severity assessment, and prospective monitoring of pulmonary pathology. LUS is being increasingly utilized in adults suffering from COVID-19 pneumonia in critical care settings, triaging, and general inpatient settings [8,9,19].
In this study, we observed that all patients with lower respiratory symptoms had abnormal LUS findings. The most prevalent abnormality was interstitial syndrome found in 50 patients (92.5 %), followed by pleural line abnormalities 44 (81.5%), reduced or absent lung sliding 31 (57.4%), and consolidation 28 (51.8%) respectively. Severe LUS patterns like bilateral confluent interstitial pattern, abolished or reduced lung sliding and consolidation were frequent findings in patients who required MV and it was corroborated by significantly higher LUS score 18 (IQR, 11ŌĆō22) in this group as compared to the nonventilated group 9 (IQR, 6ŌĆō11). Improvement in lung USG reaeration score after PEEP titration had a positive correlation with improvement of dynamic lung compliance, OI, oxygenation saturation index, SpO2/FiO2 ratio, and PaO2/FiO2 ratio, whereas a strong negative correlation was detected with the requirement of driving pressure. Successful weaning could be predicted with 100% specificity if loss of lung aeration scores at or below 5.
In one of the preliminary studies, Musolino et al. [10] from Italy described LUS findings in 10 children with COVID-19 pneumonia. Distinct B-lines (70%), pleural irregularities (60%), areas of white lung (10%), and subpleural consolidations (10%) were major findings of the study. The relevance of LUS as a diagnostic tool in the evaluation of children with (COVID-19) was studied by Hizal et al. [20] Out of 40 patients in this cohort, 10 patients had mild pneumonia and 2 were severe/critical. LUS findings were consistent with a chest CT scan. The performance of LUS as a diagnostic test was found to be good; AUC=0.88 (95% CI, 0.75ŌĆō1.01), sensitivity=83.33%, specificity=93.75%.
Adult studies on lung US in patients with COVID-19 identified similar patterns - interstitial edema, subpleural microconsolidation in an asymmetric multilobar distribution with spared areas involving mainly the lower lobes. Those findings were highly consistent with the CT findings of bilateral, peripheral, and/or subpleural ground glass opacity and/or consolidation on CT [9,16,21,22]. Similarly in a small group of pediatric patients, Giorno et al. [23] showed both the findings and topography of lung compromise on the CT were consistent with the information obtained by lung US.
The frequency of LUS abnormalities was higher in our study population as compared to other pediatric studies. One possible reason is that, we did not screen for asymptomatic patients or patients with only upper respiratory tract symptoms. Chest CT was not done in the study population in acute stage as all patients with lower respiratory tract symptoms had ultrasound changes and also to avoid the risk of transport of sick patients, risk of contamination, avoid unnecessary radiation exposure and difficulty to obtain a good quality image in children.
LUS can play an important role in daily bedside monitoring of ARDS patients in the intensive care unit to assess lung recruitment during PEEP titration. Ultrasonographic assessment of the nonaerated lung area and improvement in aeration score at different levels of PEEP titration and subsequent association with an increase in arterial oxygen partial pressure has been shown in adult study [24]. In a prospective study in 40 ARDS patients, Bouhemad et al. [16] found a significant correlation between PEEP-induced lung recruitment measured by pressure-volume curves and ultrasound reaeration score (Rho=0.88, P=0.001).
As far as we know, the study on daily sonographic monitoring of COVID-19 pneumonia and ARDS patients has not been done previously. Our data revealed that improvement in lung reaeration score had a significant correlation with improvement of dynamic lung compliance and oxygenation indices, whereas a negative correlation was noted with driving pressure requirement. Thus, transthoracic lung sonography might be considered a useful clinical tool in COVID-19 ARDS management. LUS can also guide early prone positioning of patients if lesions are distributed in posterior and lateral lung regions. Clinical assessment and respiratory monitoring by the physicians and nurses are basic fundamental need for tailoring therapy and support to individual patient and LUS can aid in the process in greater way in future. In the COVID-19 era with challenges to perform chest CT and repeated CXR opens the opportunity to explore the utility of LUS.
Weaning from MV is a challenging decision, and more so in patients suffering from COVID-19 infection because both extubation and reintubation are high aerosol-generating procedures and requiring special precautions. In a large pediatric study on 106 children, authors concluded the addition of diaphragmatic and lung US improves the performance for prediction of weaning from invasive MV in PICU patients. At total lung score cutoff at 12, AUC for predicting failure of weaning was 0.934, sensitivity, 85.7%; and specificity, 81.2% [25]. Another study by Soummer et al. [26] found loss of aeration determined by LUS during SBT may accurately predict postextubation distress. We observed that loss of lung aeration score at or below 5 was associated with successful weaning.
Being the only tertiary care referral center of the state, we were able to study all moderate to severe COVID-19 infected children, thus our study population represents the whole cohort of the state. We are presenting the data on the LUS pattern of the largest pediatric population. We excluded patients with chronic pulmonary pathology and myocardial dysfunction to eliminate potential confounders. We explored the possible role of this promising tool in prospective monitoring and weaning from MV of severe/critical COVID-19 infected children, which have not been studied previously.
But there are few limitations of LUS ŌĆō (1) It cannot detect consolidations central in location and perihilar lesions, (2) overdistention of lung during PEEP titration and recruitment cannot be detected. Therefore, we may miss these lesions. We didnot assess diaphragmatic function during weaning, which may be associated with weaning failure.
In conclusion, the study revealed that there is opportunity for wider uptake of LUS by institutions and intensive care practitioners. Interstitial syndrome, fragmented pleural line, and subpleural microconsolidation were the most prevalent LUS finding in children affected by COVID-19. In the PICU, LUS may be utilized to identify areas of poor lung aeration, prospectively monitor changes in lung aeration caused by ventilation and recruitment maneuvers as well as predict successful weaning.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table 1A. Lung ultrasound score
Supplementary Table 1B. Lung ultrasound reareation score
Fig.┬Ā1.
Anatomical landmark and 6 areas of transthoracic lung ultrasound of right side. AAL, anterior axillary line; PAL, posterior axillary line; PSL, parasternal line; PVL, paravertebral line.
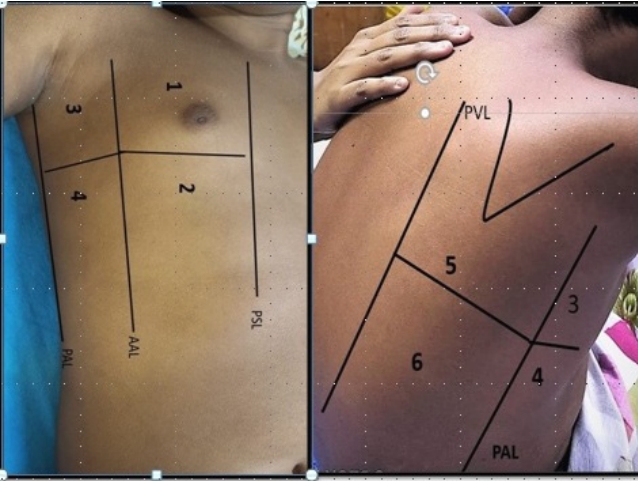
Fig.┬Ā2.
(A) Normal lung ultrasound ŌĆō A profile. (B) Clear number of visible B-lines with horizontal spacing between adjacent B-lines. (C) Multiple B-lines indicative of ŌĆ£white lungŌĆØ with an irregular pleural line and subpleural microconsolidation (arrow). (D) Pulmonary consolidation ŌĆō C profile.

Fig.┬Ā3.
Study flow. Patients with respiratory symptoms and categorization according to need for mechanical ventilation. COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; MIS-C, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children; USG, ultrasonography.
Table┬Ā1.
Demographic, clinical, laboratory, treatment and outcome parameters of the whole cohort and by study group
Table┬Ā2.
Lung US patterns in the whole cohort and by study group
Table┬Ā3.
Correlations between lung ultrasound reaeration score, dynamic lung compliance, oxygenation indices, and driving pressure
IQR, interquartile range; LUSReS, lung ultrasound reaeration score; OI, oxygenation index; OSI, oxygenation saturation index; SF ratio, ratio of oxygen saturation to fraction of inspired oxygen; PF ratio, ratio of partial pressure of oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen.
Boldface indicates a statistically significant difference with P<0.05.
Table┬Ā4.
Loss of lung aeration versus other weaning predictors by weaning failure versus success status
Values are presented as mean┬▒standard deviation or median (interquartile range).
MV, mechanical ventilation; SpO2, oxygen saturation; RR, respiratory rate; PaO2, partial pressure of oxygen; FiO2, fraction of inspired oxygen; OI, oxygenation index; PCO2, partial pressure of carbon dioxide.
Boldface indicates a statistically significant difference with P<0.05.
References
1. Webb BJ, Peltan ID, Jensen P, Hoda D, Hunter B, Silver A, et al. Clinical criteria for COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome: a cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e754ŌĆō63.



2. Liguoro I, Pilotto C, Bonanni M, Ferrari ME, Pusiol A, Nocerino A, et al. SARS-COV-2 infection in children and newborns: a systematic review. Eur J Pediatr 2020;179:1029ŌĆō46.




3. Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, Zhan C, Chen C, Lv W, et al. Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: a report of 1014 cases. Radiology 2020;296:E32ŌĆō40.



4. Foust AM, Phillips GS, Chu WC, Daltro P, Das KM, Garcia-Pe├▒a P, et al. International Expert Consensus Statement on chest imaging in pediatric COVID-19 patient management: imaging findings, imaging study reporting, and imaging study recommendations. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging 2020;2:e200214.



5. Soldati G, Smargiassi A, Inchingolo R, Buonsenso D, Perrone T, Briganti DF, et al. Proposal for international standardization of the use of lung ultrasound for patients with COVID-19: a simple, quantitative, reproducible method. J Ultrasound Med 2020;39:1413ŌĆō9.




6. Vizioli L, Forti P, Bartoli E, Giovagnoli M, Recinella G, Bernucci D, et al. Accuracy of lung ultrasound in patients with acute dyspnea: the influence of age, multimorbidity and cognitive and motor impairment. Ultrasound Med Biol 2017;43:1846ŌĆō52.


7. Wang D, Ju XL, Xie F, Lu Y, Li FY, Huang HH, et al. Clinical analysis of 31 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in children from six provinces (autonomous region) of northern China. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2020;58:269ŌĆō74.

8. Buonsenso D, Pata D, Chiaretti A. COVID-19 outbreak: less stethoscope, more ultrasound. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:e27.



9. Poggiali E, Dacrema A, Bastoni D, Tinelli V, Demichele E, Mateo Ramos P, et al. Can lung US help critical care clinicians in the early diagnosis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia? Radiology 2020;295:E6.



10. Musolino AM, Supino MC, Buonsenso D, Ferro V, Valentini P, Magistrelli A, et al. Lung ultrasound in children with COVID-19: preliminary findings. Ultrasound Med Biol 2020;46:2094ŌĆō8.



11. World Health Organization. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents with COVID-19 [Internet]. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2020 May 15 [2020 May 31]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-and-adolescents-with-covid-19.
12. World Health Organization. Clinical management of COVID-19: interim guidance [Internet]. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2020 May 27 [2020 Jun 28]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/332196.
13. Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference Group. Pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: consensus recommendations from the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2015;16:428ŌĆō39.



14. Volpicelli G, Elbarbary M, Blaivas M, Lichtenstein DA, Mathis G, Kirkpatrick AW, et al. International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med 2012;38:577ŌĆō91.



15. Zhao Z, Jiang L, Xi X, Jiang Q, Zhu B, Wang M, et al. Prognostic value of extravascular lung water assessed with lung ultrasound score by chest sonography in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMC Pulm Med 2015;15:98.




16. Bouhemad B, Brisson H, Le-Guen M, Arbelot C, Lu Q, Rouby JJ. Bedside ultrasound assessment of positive end-expiratory pressure-induced lung recruitment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;183:341ŌĆō7.


17. Thiagarajan RR, Bratton SL, Martin LD, Brogan TV, Taylor D. Predictors of successful extubation in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999;160(5 Pt 1): 1562ŌĆō6.


18. Boles JM, Bion J, Connors A, Herridge M, Marsh B, Melot C, et al. Weaning from mechanical ventilation. Eur Respir J 2007;29:1033ŌĆō56.


19. Volpicelli G, Gargani L. Sonographic signs and patterns of COVID-19 pneumonia. Ultrasound J 2020;12:22.




20. Hizal M, Aykac K, Yayla BCC, Yilmaz A, Altun D, Akkaya HE, et al. Diagnostic value of lung ultrasonography in children with COVID-19. Pediatr Pulmonol 2021;56:1018ŌĆō25.



21. Fiala MJ. A brief review of lung ultrasonography in COVID-19: is it useful? Ann Emerg Med 2020;75:784ŌĆō5.



22. Huang Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zheng C, Zheng Y, et al. A preliminary study on the ultrasonic manifestations of peripulmonary lesions of noncritical novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) [Internet]. Rochester (NY): SSRN; 2020 Feb 26 [cited 2020 Jun 20]. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3544750.
23. Giorno EPC, De Paulis M, Sameshima YT, Weerdenburg K, Savoia P, Nanbu DY, et al. Point-of-care lung ultrasound imaging in pediatric COVID-19. Ultrasound J 2020;12:50.




24. Stefanidis K, Dimopoulos S, Tripodaki ES, Vitzilaios K, Politis P, Piperopoulos P, et al. Lung sonography and recruitment in patients with early acute respiratory distress syndrome: a pilot study. Crit Care 2011;15:R185.








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


