Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 68(12); 2025 |
|
Abstract
Background
The effects of genetic background on the biological effects of vitamin D on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children remain unclear.
Purpose
This study aimed to explore the association between vitamin D-related genetic background and 25-hydroxyvitamin D status and COVID-19 occurrence and severity in children. Here we explored key genetic variants within the vitamin D pathway in pediatric COVID-19 patients in relation to circulating vitamin D binding protein (VDBP).
Methods
Sixty children aged 0–14 years with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and 60 matched controls were genotyped for the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene (FokI, BsmI, TaqI, ApaI), Gc gene of VDBP (rs7041, rs4588), and CYP27B1 promoter (rs10877012) single nucleotide polymorphisms by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism assay.
Results
The FokI FF genotype was more frequently identified among COVID-19 patients than controls, among whom the TaqI TT genotype was prevalent (odds ratio [OR], 2.26; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08–4.73; P=0.02; and OR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.13–0.63; P=0.001, respectively). The Gc1F haplotype was significantly more represented in controls versus COVID-19 patients (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.19–0.81; P=0.01). A 2.04-fold increased risk of COVID-19 was observed in the presence of the VDR FokI F allele (OR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.14–3.64; P=0.01). A multivariate analysis revealed a significant association between the FokI FF genotype and disease severity (OR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.04–0.83; P=0.02). Serum VDBP levels were similar between groups.
Graphical abstract. COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; VDBP, vitamin D binding protein.
Genetic variants in the vitamin D pathway have been linked to children’s susceptibility to viral respiratory infections, suggesting a possible role of vitamin D as an immune modulator [1,2]. Unregulated inflammatory responses and cytokine storm, involved in the pathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection may be therefore associated with vitamin D status and genetic background [3,4]. Genetic susceptibility may predispose to the infection or disease progression and although coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is typically mild in children, serious illness has been reported and very few of them may develop severe complications [5,6].
Recent data have demonstrated the strong effect of vitamin D on the gene expression of antimicrobial peptides, regulating innate and acquired immune responses as well as the inflammatory cascade [1,2]. Its biological actions are executed through the vitamin D receptor (VDR) and the vitamin D binding protein (VDBP), the major vitamin D carrier which binds over 99% of the circulating vitamin D metabolites [1,7]. 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D), the major circulating form of vitamin D, is converted to the active form of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25[OH]2D) through the mitochondrial 1 α-hydroxylase enzyme (CYP27B1) [1,7]. Multiple cell populations of innate immunity, including respiratory epithelial cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, in which these genes are expressed, are required to convert circulating plasma 25(OH)D to the active form 1,25(OH)2D [8]. Moreover, 1,25(OH)2D induces the expression of genes encoding antimicrobial peptides such as the host defence cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide, which is a key component of antiviral responses acting as a regulator of immune response and enhances antimicrobial effects against various pathogens through induction of autophagy [7,9].
Genetic changes in genes involved in the metabolism, transport or binding of vitamin D may result in its deficiency [10]. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the gene encoding VDR (FokI, BsmI, ApaI, TaqI), the Gc gene of VDBP (rs4588 and rs7041) and the CYP27B1-1260 (rs10877012), as well as vitamin D deficiency as a result of low levels of VDBP in plasma have been suggested to be associated with an increased risk of respiratory viral infections in children, which supports the possible role of vitamin D in the immune response to viral respiratory infections [8,10,11].
To date, the role of vitamin D deficiency in the susceptibility of children to COVID-19 is still under investigation but has been linked to clinical severity of the infection in children and higher levels of inflammation markers [12,13]. Recent research in adults has shown that VDR gene polymorphisms might play critical role in the COVID-19 severity [14]. Given the sparse data on the impact of vitamin D pathway components in disease in children, the aim of this study was to investigate the role of the genetic variants related to the status and bioavailability of vitamin D, in the susceptibility of children to COVID-19 and the association of the different genotypes with the disease severity.
This prospective case-control clinical laboratory study included 60 infants, children and adolescents age 1 month to 14 years who were admitted to the hospital from October 2021 through July 2022 due to confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay from nasopharyngeal swab samples. Patients were further categorized into mild, moderate, severe, and critical subgroups according to recently published classifications [15,16], as follows:
Individuals with COVID-19-related symptoms, including fever/chills, cough, vomiting, diarrhea, etc. without signs of pneumonia, abnormal chest imaging, or shortness of breath.
Cases presented with respiratory symptoms, with or without fever, age-specific tachypnea or chest imaging indicating pneumonia. Illness indicative of moderate severity also included dehydration, gastroenteritis and use of intravenous fluids at admission or during hospitalization.
Individuals with dyspnea, hypoxia (SpO2<93%), acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute kidney injury or liver failure, myocarditis, pericarditis, disturbed consciousness and coagulation dysfunction. Patients who required intensive care unit monitoring or support, invasive or noninvasive mechanical ventilation.
Demographic characteristics and medical history of the patients, including age, weight status and body mass index (BMI), vaccination status, time of infection and the presence of comorbidities was obtained. Exclusion criteria included asymptomatic COVID-19 cases and patients with chronic debilitating medical conditions (e.g., malignancy, immunodeficiency, cystic fibrosis, chronic renal disease or patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy). BMI could not be assessed for all participants due to age-related limitations; instead, weight status was evaluated based on available clinical information. Due to limited vaccination coverage during the study period and at the time of patient recruitment, COVID-19 vaccination status was not incorporated into the analysis.
Sixty healthy children of matched age, sex and season of enrolment, who were examined in the context of routine check-ups, hospitalization for noninfectious reasons (e.g., accidents, infantile hemangiomas workup) or preoperative assessment, were recruited as a control group. Only asymptomatic controls, tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR, and for whom there was no history of COVID-19 infection or recent contact with a COVID-19 case at the time of blood sampling, were included.
Data on race and ethnicity was obtained from patients/family report. Analysis did not include distribution of patients according to different ethnic groups.
Peripheral whole blood and serum samples were collected from patients and controls upon admission and were stored at -20℃ until further analysis. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes using the PureLink Genomic DNA Mini Kit (Invitrogen, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and was stored at -20℃ before genotyping. All participants were genotyped for the VDR FokI (rs10735810), BsmI (rs1544410), ApaI (rs7975232), TaqI (rs731236), Gc (rs7041, rs4588) and the CYP27B1-1260 promoter polymorphism (rs10877012), by DNA amplification with PCR and sequence-specific oligonucleotide primers followed by the restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) assay, as previously described [11].
Representative agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR-RFLP products of the studied SNPs are presented in Supplementary Figs. 1-3.
Serum samples were centrifuged and aliquots were stored at -20℃ until further analysis. VDBP concentration was evaluated in the serum of 83 patients in total (40 index and 43 control cases), using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique (Quantikine ELISA kit, Bio-techne R&D Systems, USA). The normal reference range for VDBP levels was considered as 300–600 μg/mL according to published data [17].
Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation. Comparison of independent and continuous parameters was performed using the Mann-Whitney U test. The Kruskal-Wallis test was used for comparison between 3 or more continuous variables. Pearson chi-square test was applied for associations of polymorphisms distribution and allele frequencies of COVID-19 patients and control cases. Variations in the genotype frequencies from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) were assessed in the control group. Logistic regression analysis was used to calculate the odds ratio (OR) with a confidence interval (CI) of 95% for differences in the genotypes of the selected SNPs and to evaluate independent associations between genotypes and COVID-19 susceptibility and severity. Multivariable analysis was applied to further analyze the correlations of the studied parameters with COVID-19 disease and severity after adjusting for the possible confounding factors. Due to the small number of participants with severe COVID-19, they were combined into one group along with those with moderate disease in logistic regression analysis. A P value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant. The sample size was determined with a Sample Size Calculator (G* Power 3.1.9.6).
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics committee and the Institutional Review Board of the University Hospital of Heraklion (19654/01-12-2021). The study was conducted in accordance with relevant regulations. Written parental informed consents were obtained from the participants before enrolment.
In total, 60 patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 and 60 healthy control subjects were enrolled. Demographic characteristics and clinical parameters of the index and control cases are presented in Table 1. Index cases and controls did not differ significantly in the matter of age and sex distribution. Patients’ median age was 5.22±5.47)years, and 33 (55%) were males. Twelve out of 20 patients (60%) with mild disease, were <3 months of age, while 5 out of 10 severe cases were >5 years old. Lowest age in severe COVID-19 group was 2 years. Eleven out of 60 children had comorbidities, such as known asthma, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis (7 patients), type 1 diabetes mellitus (1 patient), history of seizures (2 patients), and hypercholesterolemia (1 patient). Six children were identified as overweight, 2 of whom had coexisting asthma; no cases of obesity were recorded.
Distribution of the VDR (FokI, TaqI, BsmI, ApaI), CYP27B1-1260 (rs10877012) genotype and allele frequencies in addition to the Gc rs7041 and rs4588 variants encoding the 3 major haplotypes (Gc1F, Gc1S, and Gc2) of VDBP in patients and controls are presented in Supplementary Table 1. Comparing genotype distribution of the VDR SNPs between the 2 study groups, a statistically significant difference was found in FokI homozygous FF genotype (OR, 2.26; 95% CI, 1.08–4.73; P=0.02) and TaqI TT genotype cases (OR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.13–0.63; P=0.001). The FokI f and TaqI T alleles were significantly more represented in controls compared to the COVID-19 group (35% vs. 20.8%; OR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.27–0.87; P=0.01), (69.2% vs. 49.2%; OR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.25–0.73; P=0.001), respectively. Gc1F (rs7041T-rs4588C) haplotype was significantly more represented in controls compared to the COVID-19 group (23.3% vs. 10.8%; OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.19–0.81; P=0.01). Patients carrying the CYP27B1-1260 promoter (rs10877012) A allele constitute the 21.7% of COVID-19 cases as opposed to the 33.3% of control cases (OR, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.31–0.98; P=0.04). However, no significant difference was found in the polymorphism genotype distribution between the 2 groups.
Genotype distribution of the studied SNPs was evaluated in terms of COVID-19 clinical severity (Table 2). The FokI FF genotype was found to be more frequent among children with moderate or severe COVID-19 with a statistically significant association noted in the dominant model of analysis (OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.05–0.85; P=0.02). In addition, a moderately significant correlation of Gc (rs7041) polymorphism with COVID-19 severity was observed, in the recessive analysis model (OR, 0.31; 95% CI, 0.10–0.99; P=0.04).
Multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to further test for associations of COVID-19 infection risk and severe disease with the VDR FokI FF genotype, which were demonstrated in the dominant univariable analysis model. The FokI homozygous FF genotype was found to constitute an independent risk factor for COVID-19 clinical severity in the univariable logistic regression analysis and after adjusting for comorbidities (e.g., asthma), age and sex parameters (adjusted OR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.04–0.83; P=0.02) (Table 3). A 2.04-fold increased risk for COVID-19 infection was observed in the case of the VDR FokI F allele (OR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.14–3.64; P=0.01). In addition, the allele was moderately significantly correlated with clinical severity (OR, 3.20; 95% CI, 1.01–10.0; P=0.04) and following the inclusion of additional covariates, this finding was further confirmed in the multivariable analysis (OR, 3.31; 95% CI, 1.02–10.7; P=0.04).
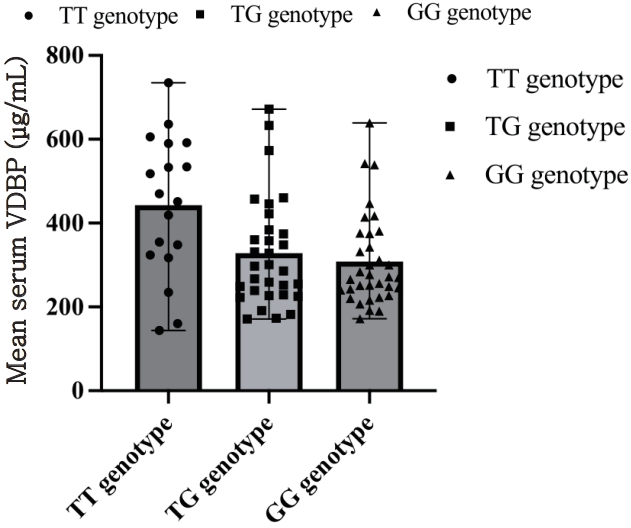
No statistically significant difference was found between serum VDBP levels of the COVID-19 group and the control group (348.90±133.64 μg/mL, and 340.07±147.56 μg/mL respectively, P=0.97). The 3 possible genotypes of Gc SNPs rs7041 and rs4588, were compared regarding the patients’ serum VDBP, and no significant associations were identified according to the analysis between all 3 groups (Kruskal-Wallis H test, P=0.201 for Gc rs7041 and P=0.964 for rs4588). VDBP levels were found slightly higher in patients carrying the rs7041 TT genotype (442.57±167.39 μg/mL) in comparison with the TG (328.18±129.57 μg/mL) and GG genotype (307.81±109.21 μg/mL) (Fig. 1) and there was no significant difference in the comparison between pairs of groups (Mann-Whitney U test, P=0.096 for rs7041 TT vs. TG, GG). The VDBP levels were not correlated with the VDR genotypes of the studied SNPs (Kruskal-Wallis H test, P=0.978 for FokI, P=0.951 for BsmI, P=0.917 for TaqI, P=0.773 for ApaI), or the CYP27B1 promoter polymorphism (P=0.662).
Evidence supports the role of vitamin D as an immunomodulatory agent, which has been shown to balance the inflammatory and macrophage responses, associated with COVID-19 disease [3,4]. SNPs of the VDR locus have been suggested to be associated with an increased risk of lower respiratory infections in children and pathogenesis of immune-mediated diseases [18-21]. Thus, the hypothesis we aimed to explore is that the vitamin D-related genetic background might be associated with the occurrence and severity of a multisystem viral infection, such as COVID-19, in pediatric patients.
The FokI start codon polymorphism in the exon 2 at the 5′ end of the VDR gene has been associated with susceptibility to viral infections, due to changes in transcriptional activity of the VDR protein and possible effects on immune cell behavior [3]. In the case of COVID-19 infection, to date, only one study has investigated the VDR FokI polymorphism solely in pediatric patients, concluding that the homozygous FF genotype may constitute an independent risk factor for susceptibility to COVID-19, whereas the FokI f allele may act as a protective factor for the infection [22]. This finding may be explained by the fact that the FokI f allele encodes a different isoform of VDR protein that results in higher serum levels of 25(OH)D, in contrast to the FokI FF genotype which encodes a less transcriptionally efficient isoform, possibly influencing immune responses [23]. This functional effect may provide a possible basis for the observed association of the FokI FF genotype and disease severity in children, as it may affect host vulnerability to viral infections, such as COVID-19. Together, the aforementioned observations support our results since the FokI FF genotype and the FokI F allele were significantly more frequent among COVID-19 patients as well as patients with moderate or severe disease, whereas the VDR FokI f allele was more represented in the control group. From the logistic regression analysis of the present study the FokI FF genotype was found to constitute an independent risk factor for disease severity, with the FokI F allele associated with both increased susceptibility to COVID-19 and clinical severity. Kotur et al. [24], who assessed the significant effect of the variants associated with poor vitamin D status with severe COVID-19 in 120 Serbian COVID-19 patients recruited during the first peak of COVID-19, found no relationship of the infection risk or severity with pediatric patients. In the same study, however, the vast majority of the study population suffered from mild disease, and as such the analysis of variants was limited to the effect in the risk of symptomatic COVID-19 [24].
Alteration of the VDR gene expression, the protein structure and stability, may have an effect of the exon 9 TaqI polymorphism, leading to reduced signaling and immunomodulatory actions of vitamin D in target cells [11,25]. Data provided by a previous case-control study support the link between the VDR TaqI variant and the susceptibility to viral respiratory tract infections in hospitalized infants when the polymorphism frequency was assessed in comparison with healthy controls [11]. These results are concordant with the findings of our study, in which the TaqI t allele was significantly more represented in COVID-19 patients, compared to the VDR TaqI TT genotype and the TaqI T allele that were more frequent in the control group. A recent single-center case-control study in Greece, exploring the associations of the 4 genetic VDR variants (FokI, BsmI, TaqI, and ApaI) with severity of COVID-19, showed that the TaqI CC (polymorphic) genotype constitutes an independent risk factor for COVID-19 severity [14]. In a similar study investigating the genotypic distributions of FokI and TaqI variants in 300 COVID-19 positive patients in Cyprus, the polymorphic alleles were statistically more represented in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection as opposed to the 300 studied controls [26]. In another cohort study from Turkey, the authors suggested that the VDR gene SNPs including FokI, TaqI, and ApaI, are independent risk factors for severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients [27]. In our study, no significant association was evident between the VDR BsmI or ApaI genotype/allele distribution and COVID-19 risk or, regarding the TaqI polymorphism, the disease severity.
Serum concentration of the 25(OH)D is partly affected by the VDBP phenotypes. Given the multiple functions of the VDBP as part of the actin scavenger system, the neutrophil chemotaxis, as a macrophage activation factor (Gc-MAF) and the protective immunomodulatory effect of vitamin D, the association of these variants with COVID-19 clinical course and complications, have been an area of active research interest [28,29]. Carriers of specific major VDBP alleles, as such the Gc2, have reportedly lower plasma levels of vitamin D metabolites and vitamin D binding protein, which may confer susceptibility to severe COVID-19. Conversely, the Gc1F variant has been found to be more common among healthy infants when compared to infants with acute viral respiratory tract infections [11]. These results are concordant with our findings, regarding the rs7041 TT genotype and the combined Gc1F (rs7041T-rs4588C) haplotype, which was significantly more frequent in healthy controls as opposed to the COVID-19 patients. Besides, recent studies by Speeckaert et al. [29] and Karcioglu Batur and Hekim [30] have retrospectively investigated the impact of the VDBP SNPs at rs7041 and rs4588 loci, with a reported negative correlation of the rs7041 TT genotype and the DBP1 allele frequency with the prevalence and mortality rates of COVID-19, in 10 and 55 countries, worldwide, respectively. These results, may be explained by the differences in vitamin D status and the altered vitamin D affinity due to the effect of VDBP variants.
In an attempt to explain our findings, we explored the circulating levels of VDBP in serum of healthy individuals and COVID-19 patients; however no significant link was found with COVID-19 occurrence, nor in relation to the Gc genetic variants. Laboratory data concerning the effects of vitamin D on host immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children is limited. Recent data have shown that serum VDBP levels have been found significantly decreased in critically ill adult patients with COVID-19, supporting further research focusing on VDBP role in the pathogenesis of the disease [31]. To our knowledge, this is the first study exploring the serological status of VDBP in children with COVID-19 disease in relation to the VDBP polymorphisms, as well as the studied SNPs of VDR and CYP27B1 promoter genes. Despite the fact that no significant associations were evident between serum levels and pediatric COVID-19 disease or the Gc genotypes distribution, we speculate the rs7041 TT genotype, which was more frequent among our control group, and the Gc1F haplotype, notably having the highest affinity for 25(OH) D, may be associated with the circulating levels of 25(OH) D in blood and consequently, the levels of the bioavailable vitamin D [32,33]. Thus, VDBP binding and 25(OH)D affinity along with their potential protective effects could possibly explain our findings regarding the genetic background of the studied population and the VDBP levels, and should be evaluated in further studies addressing their biological influence on COVID-19 disease and severity.
CYP27B1-1260 allelic variation in the promoter region of CYP27B1 hydroxylase, a key enzyme of the vitamin D metabolism, has been associated with Hepatitis C viral infection and endocrine autoimmune diseases in adults, possibly due to the impact on the enzyme activity and the 1,25(OH)2D synthesis [34,35]. As opposed to a previous case-control study investigating the CYP27B1 promoter polymorphism, where no difference was found between infants with viral infections and control subjects [11], the same variant was significantly more common among COVID-19 cases in our study, in comparison with the healthy controls.
To our knowledge, this is the first case-control study to simultaneously investigate key genetic variants within the vitamin D cascade, including the VDR, the VDBP and the CYP27B1-1260 promoter polymorphisms, in a pediatric population with COVID-19. The functional consequences of the polymorphisms involved in the mentioned 3 elements in vitamin D pathway, are reported to have substantial impact on vitamin D levels and based on the data supporting its protective role and immunomodulatory effects, may confer susceptibility to infections. In the case of COVID-19, notably characterized by a complex interaction between the virus and the host response, involving multiple inflammatory pathways, elucidating the genetic background that comprises proneness to the infection, emerges as crucial.
This study has some limitations. It should be acknowledged that the design of the present study did not include quantitative determination of serum 25(OH)D levels, but rather focused on the investigation of genetic determinants of vitamin D pathway and key functional proteins, such as VDBP. Although recent studies demonstrate that vitamin D deficiency is commonly observed between pediatric COVID-19 patients, this approach was based on the common observation that total serum 25(OH)D levels are subject to several variations including environmental factors, nutrition and seasonality and may not consistently correlate with the occurrence and clinical outcomes in pediatric COVID-19. In an attempt to complement our findings indicating that genetic variants in the VDR, the Gc gene of VDBP and the CYP27B1 promoter genes might act as more stable indicators for COVID-19 occurrence and outcomes in children, we opted to quantify the relatively unexplored circulating levels of VDBP in children, which may better reflect the biologically active vitamin D and bioavailable fraction in vitamin D metabolism, especially in the context of genetic variability.
As only a few children with comorbidities were included in the present study, the potential effect of underlying medical conditions such as asthma and obesity—and their possible relation with genetic variants—on COVID-19 clinical severity and disease outcomes could not be fully explored. Larger-scale studies may better elucidate these relationships. A further limitation to consider is that, since SARS-CoV-2 serology testing was not performed in the control group, the number of patients that may have had asymptomatic disease before enrolment, cannot not be acknowledged. Thus, the assessment of risk included the probability in relation to the studied variants, of solely symptomatic COVID-19 disease in the current study. The control group represents the distribution of polymorphisms in the general population, highlighting the need for further studies involving control groups with confirmed exposure and matched risk factors, such as vaccination status—which was limited during our patient recruitment period. It is worth mentioning that, although we explored the 3 crucial loci related to vitamin D metabolism and conducted a comprehensive genetic analysis between the index cases with age- and sex-matched controls, the main limitation of our study that needs to be acknowledged is the small sample size. Even though the included frequencies of the genotype groups were consistent with the HWE, a small number of individuals in the included subgroups, may be unavoidable subject to linkage disequilibrium. Thus, the link between vitamin D-related genetic variants and COVID-19 disease needs to be established in larger cohort studies. In this context, comparison of our allele and genotype frequencies with previously published data from pediatric populations where available, reports VDR polymorphisms (FokI, BsmI, TaqI, ApaI) genotype distributions ranging approximately from 35% to 55% [36]. Data regarding the minor allele frequency for the GC gene polymorphism rs4588 indicate a frequency of approximately 25% [37]. These findings suggest that our control group could be representative, despite sample size limitations.
Nevertheless, our findings, in line with other similar studies, indicate that genetic variants of the VDR, the main plasma carrier of 25(OH)D VDBP and the CYP27B1 promoter gene, could establish genetic markers for COVID-19 occurrence and severe clinical outcome, with the VDR FokI polymorphism possibly constituting an independent risk factor for clinical severity of the disease in children. On the base of COVID-19 infection and the possible manifestations of the disease, such as the multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with it, our results could explain the effect of the vitamin D SNPs in multisystem viral infections in children beyond COVID-19. Moreover, this study may provide insights in the genetic profile of vulnerable children and highlight possible disease subgroups based on the vitamin D genotypes.
To conclude, the VDR FokI, TaqI, the rs7041 of Gc gene and the CYP27B1 promoter polymorphisms might predispose to COVID-19 infection and a more severe clinical course in children. The former might constitute an independent risk factor for disease severity. The effect of genetic variants that mediate vitamin D regulation and metabolism, may extent to viral infections beyond COVID-19 and needs to be further explored.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Figs. 1-3 are available at https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.00577.
Supplementary Table 1.
VDR (FokI, TaqI, BsmI, ApaI), Gc (rs7041 and rs4588) variants encoding the 3 major haplotypes (Gc1F, Gc1S, and Gc2) of VDBP and CYP27B1-1260 (rs10877012) genotype and allele frequencies in patients and controls
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of the vitamin D receptor gene polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism products.
Supplementary Fig. 2.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of the Gc rs7041 and rs4588 polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism products.
Supplementary Fig. 3.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of the CYP27B1-1260 (rs10877012) promoter polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism products.
Footnotes
Funding
This work has been funded by the University of Crete Special Account for Research Funds grant to Chrysoula Perdikogianni (ELKE UOC, Grant No. 4022).
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics and clinical parameters of the COVID-19 versus control cases
Table 2.
Association between VDR FokI, TaqI, Gc (rs7041), and CYP27B1-1260 genotypes and COVID-19 severity
Table 3.
Uni- and multivariate analyses of correlations between VDR FokI genotypes and COVID-19 susceptibility and severity
| Variable |
Univariable analysis |
Multivariable analysis |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI), unadjusted | P value | OR (95% CI), adjusteda) | P value | |
| COVID-19 susceptibility | ||||
| FokI dominant (FF vs. Ff vs. ff) model | 2.269 (1.088-4.733) | 0.028b) | 2.11 (0.957-4.6515) | 0.064 |
| VDR FokI allele (F vs. f) | 2.046 (1.147-3.649) | 0.015b) | 1.9112 (1.0156-3.596) | 0.044 |
| COVID-19 severity | ||||
| FokI Dominant (FF vs. Ff vs. ff) model | 0.215 (0.054-0.854) | 0.028b) | 0.201 (0.049-0.8315) | 0.027 |
| VDR FokI allele (F vs. f) | 3.203 (1.017-10.084) | 0.046b) | 3.316 (1.026-10.709) | 0.045 |
References
1. Gombart AF. The vitamin D-antimicrobial peptide pathway and its role in protection against infection. Future Microbiol 2009;4:1151-65.



2. Bahrami A, Sadeghnia HR, Tabatabaeizadeh SA, Bahrami- Taghanaki H, Behboodi N, Esmaeili H, et al. Genetic and epigenetic factors influencing vitamin D status. J Cell Physiol 2018;233:4033-43.



3. Abdollahzadeh R, Shushizadeh MH, Barazandehrokh M, Choopani S, Azarnezhad A, Paknahad S, et al. Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and clinical/severe outcomes of COVID-19 patients. Infect Genet Evol 2021;96:105098.



4. Peng D, Huang H, Liu Z, Gao Y, Liu Y. Vitamin D levels and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2 in children: a longitudinal cohort study. Front Nutr 2022;9:960859.



5. Ludvigsson JF. Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults. Acta Paediatr 2020;109:1088-95.




6. Kabeerdoss J, Pilania RK, Karkhele R, Kumar TS, Danda D, Singh S. Severe COVID-19, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease: immunological mechanisms, clinical manifestations and management. Rheumatol Int 2021;41:19-32.




7. Ismailova A, White JH. Vitamin D, infections and immunity. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2022;23:265-77.




8. Gunville CF, Mourani PM, Ginde AA. The role of vitamin D in prevention and treatment of infection. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 2013;12:239-45.



9. Aloul KM, Nielsen JE, Defensor EB, Lin JS, Fortkort JA, Shamloo M, et al. Upregulating human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 expression may prevent severe COVID-19 inflammatory responses and reduce microthrombosis. Front Immunol 2022;13:880961.



10. Tomei S, Singh P, Mathew R, Mattei V, Garand M, Alwakeel M, et al. The role of polymorphisms in vitamin D-related genes in response to vitamin D supplementation. Nutrients 2020;12:2608.



11. Zacharioudaki M, Messaritakis I, Galanakis E. Vitamin D receptor, vitamin D binding protein and CYP27B1 single nucleotide polymorphisms and susceptibility to viral infections in infants. Sci Rep 2021;11:13835.




12. Bayramoğlu E, Akkoç G, Ağbaş A, Akgün Ö, Yurdakul K, Selçuk Duru HN, et al. The association between vitamin D levels and the clinical severity and inflammation markers in pediatric COVID-19 patients: single-center experience from a pandemic hospital. Eur J Pediatr 2021;180:2699-705.




13. Yılmaz K, Şen V. Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children? Pediatr Pulmonol 2020;55:3595-601.




14. Tentolouris N, Achilla C, Anastasiou IA, Eleftheriadou I, Tentolouris A, Basoulis D, et al. The association of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity. Nutrients 2024;16:727.



15. Chen ZM, Fu JF, Shu Q, Chen YH, Hua CZ, Li FB, et al. Diagnosis and treatment recommendations for pediatric respiratory infection caused by the 2019 novel coronavirus. World J Pediatr 2020;16:240-6.




16. Forrest CB, Burrows EK, Mejias A, Razzahgi H, Christakis D, Jhaveri R, et al. Severity of acute COVID-19 in children <18 years old March 2020 to December 2021. Pediatrics 2022;149:e2021055765.

17. Blanton D, Han Z, Bierschenk L, Linga-Reddy MV, Wang H, Clare-Salzler M, et al. Reduced serum vitamin D-binding protein levels are associated with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2011;60:2566-70.




18. Han WG, Hodemaekers HM, Nagarajah B, Poelen MM, Helm K, Janssen R, et al. Association of vitamin D receptor polymorphism with susceptibility to symptomatic pertussis. PLoS One 2016;11:e0149576.



19. Roth DE, Jones AB, Prosser C, Robinson JL, Vohra S. Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and the risk of acute lower respiratory tract infection in early childhood. J Infect Dis 2008;197:676-80.


20. Sîrbe C, Rednic S, Grama A, Pop TL. An update on the effects of vitamin D on the immune system and autoimmune diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:9784.



21. Panierakis C, Goulielmos G, Mamoulakis D, Maraki S, Papavasiliou E, Galanakis E. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage might be associated with vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in type 1 diabetes. Int J Infect Dis 2009;13:e437-43.


22. Zeidan NM, Lateef HM, Selim DM, Razek SA, Abd-Elrehim GA, Nashat M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor FokI polymorphism as risk factors for COVID-19. Pediatr Res 2023;93:1383-90.

23. van Etten E, Verlinden L, Giulietti A, Ramos-Lopez E, Branisteanu DD, Ferreira GB, et al. The vitamin D receptor gene FokI polymorphism: functional impact on the immune system. Eur J Immunol 2007;37:395-405.


24. Kotur N, Skakic A, Klaassen K, Gasic V, Zukic B, Skodric- Trifunovic V, et al. Association of vitamin D, zinc and selenium related genetic variants with COVID-19 disease severity. Front Nutr 2021;8:689419.



25. Miyamoto K, Kesterson RA, Yamamoto H, Taketani Y, Nishiwaki E, Tatsumi S, et al. Structural organization of the human vitamin D receptor chromosomal gene and its promoter. Mol Endocrinol 1997;11:1165-79.


26. Mamurova B, Akan G, Mogol E, Turgay A, Tuncel G, Evren EU, et al. Strong association between vitamin D receptor gene and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infectious variants. Glob Med Genet 2023;10:27-33.



27. Apaydin T, Polat H, Dincer Yazan C, Ilgin C, Elbasan O, Dashdamirova S, et al. Effects of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms on the prognosis of COVID-19. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2022;96:819-30.



28. Nagasawa H, Sasaki H, Uto Y, Kubo S, Hori H. Association of the macrophage activating factor (MAF) precursor activity with polymorphism in vitamin D-binding protein. Anticancer Res 2004;24:3361-6.

29. Speeckaert MM, De Buyzere ML, Delanghe JR. Vitamin D binding protein polymorphism and COVID-19. J Med Virol 2021;93:705-7.



30. Karcioglu Batur L, Hekim N. The role of DBP gene polymorphisms in the prevalence of new coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality rate. J Med Virol 2021;93:1409-13.




31. Karakukcu C, Elibol A, Eren E, Saracoglu H, Mutlu Sariguzel F, Gorkem A, et al. Evaluation of vitamin D binding protein and 25-hydroxy vitamin D metabolites in COVID-19 patients. Int J Med Biochem 2023;6:69-74.

32. Randolph AG, Yip WK, Falkenstein-Hagander K, Weiss ST, Janssen R, Keisling S, et al. Vitamin D-binding protein haplotype is associated with hospitalization for RSV bronchiolitis. Clin Exp Allergy 2014;44:231-7.


33. Speeckaert MM, Speeckaert R, Delanghe JR. The biologic importance of the vitamin D binding protein polymorphism in pediatric COVID-19 patients. Eur J Pediatr 2021;180:2707-8.




34. Lange CM, Bojunga J, Ramos-Lopez E, von Wagner M, Hassler A, Vermehren J, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and a CYP27B1-1260 promoter polymorphism are associated with chronic hepatitis C and poor response to interferon-alfa based therapy. J Hepatol 2011;54:887-93.


35. Lopez ER, Zwermann O, Segni M, Meyer G, Reincke M, Seissler J, et al. A promoter polymorphism of the CYP27B1 gene is associated with Addison's disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus in Germans. Eur J Endocrinol 2004;151:193-7.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


