Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 56(2); 2013 |
Abstract
Purpose
It has been reported that 10% to 20% of children with Kawasaki disease (KD) will not respond to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment. In this study, we aimed to identify useful predictors of therapeutic failure in children with KD.
Methods
We examined 309 children diagnosed with KD at the Kyungpook National University Hospital and the Inje University Busan Paik Hospital between January 2005 and June 2011. We retrospectively reviewed their medical records and analyzed multiple parameters in responders and nonresponders to IVIG.
Results
Among the 309 children, 30 (9.7%) did not respond to IVIG. They had significantly higher proportion of neutrophils, and higher levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), total bilirubin, and N-terminal fragment of B-type natriuretic peptide than did responders. IVIG-nonresponders had a significantly longer duration of hospitalization, and more frequently experienced coronary artery lesion, and sterile pyuria. No differences in the duration of fever at initial treatment or, clinical features were noted.
Kawasaki disease (KD) is systemic vasculitis that can cause coronary artery complications, and is the most common cause of pediatric acquired cardiac disease in developed countries. Some cases are recovered naturally without treatment, but around 15% to 25% have complications such as coronary aneurysm and coronary artery ectasia. Such complications may develop into cardiac infarction, sudden death or ischemic heart disease1,2). The use of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and aspirin lowered the frequency of coronary artery complications caused by KD to below 5%, and its morbidity and mortality also went down3). Though its mechanism of action is not clear, immunoglobulin has a systemic anti-inflammatory action, modulating the production of cytokine, neutralizing bacterial superantigen or other etiologic agents, amplifying T-cell suppressor activity, and inhibiting the production of antibody2,3).
However, 10% to 20% of KD patients do not respond to the conventional therapy and have continued fever, and such cases are in need of a different rescue therapy4,5). In the patient group not responding to IVIG and aspirin, the risk of coronary artery complications is very high. For these problems, many studies have been conducted for the early identification of patients who do not respond to IVIG. Many reports have been made particularly in Japan, and they reported involved factors such as pediatric patients' age, duration between the onset of fever and the administration of IVIG, sodium level, proportion of neutrophil, C-reactive protein (CRP), platelet count6), albumin7), total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST)8), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)9), and developed risk-scoring systems using several factors. Nevertheless, there are no agreed factors for predicting patients not responding to IVIG.
Thus, the present authors conducted this study in order to find clinical patterns and laboratory findings important for predicting patients not responding to IVIG.
The subjects of this study were 309 patients diagnosed with KD and treated at the Kyungpook National University Hospital and the Inje University Busan Paik Hospital during the period from January 2005 to June 2011. KD was diagnosed according to the criteria published by American Heart Association in 20042). For all the patients, we collected samples on the day of admission or before immunoglobulin treatment, and measured hemoglobin (Hb), white blood cell, proportion of neutrophil, platelet count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP, AST, ALT, sodium, potassium, total protein, albumin, total bilirubin, total cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein (HDL), and N-terminal fragment of B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP).
All of the patients were administered with IVIG (2 g/kg) and high-dose aspirin (80-100 mg/kg/day). Those who showed improvement in fever and other symptoms after the administration of IVIG were classified as IVIG-responders, and those whose fever continued for over 36 hours or who had recrudescent fever (temperatureŌēź38.0Ōäā axillary or rectally) were classified as IVIG-nonresponders. In addition, echocardiography was performed to measure coronary artery size at diagnosis. Coronary artery lesion was defined as follows; 1) coronary artery diameter had a Z-scoreŌēź2.5, 2) size of coronary artery had 1.5 times larger than other lesions2).
The parameters of Kobayashi score6) are as follows: 1) sodium Ōēż133 mmol/L, 2 points; 2) days of illness at initial treatment Ōēż4 days, 2 points; 3) AST Ōēź100 IU/L, 2 points; 4) % of neutrophilŌēź80, 2 points; 5) CRPŌēź10 mg/dL, 1 point; 6) ageŌēż12 months, 1 point; and 7) platelet countŌēż300├Ś103/mm3, 1 point. The parameters of Egami score9) are as follows: 1) ALTŌēź80 IU/L, 2 points; 2) illness daysŌēż4 days, 1 point; 3) CRPŌēź8 mg/dL, 1 point; 4) ageŌēż6 months, 1 point; and 5) platelet countŌēż300├Ś103/mm3, 1 point. The Sano scoring system8) is as follows: 1) ASTŌēź200 IU/L, 1 point; 2) CRPŌēź7 mg/dL, 1 point; and 3) total bilirubinŌēź0.9 mg/dL, 1 point.
By applying each scoring system to our data, we divided the subjects into low-risk and high-risk groups and obtained sensitivity and specificity.
The groups were compared through Mann-Whitney U-test and Student's t-test. And comparison according to age, weight and gender and the comparison of the frequency of coronary artery lesion were made through chi-square test using SPSS ver. 12.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). We determined significant parameters by univariate analyses, and then the cutoff values of these factors were obtained using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. With these factors in addition to age (not older than 12 months), the duration of fever at the beginning of treatment (not longer than 4 days) and gender (male), which are factors suggested as the predictors of IVIG-resistant KD suggested in the previous reports6-9), we performed multivariable logistic regression analysis. In all analyses, the statistical significance of difference was accepted if P<0.05.
Among the 309 patients, 30 (9.7%) did not respond to IVIG. Between the IVIG-responders and IVIG-nonresponders, no difference was observed in age, gender, and the duration of fever on diagnosis (P=0.987, P=0.195, and P=0.737). The clinical pattern of KD was not different between the two groups, but the frequency of sterile pyuria was higher in the IVIG-nonresponders (19/30, 63.3%) than in the IVIG-responders (67/279, 24.0%), and hospitalization time was also around two times longer in the IVIG-nonresponders (P<0.001). The frequency of coronary artery lesion was 43.3% (13/30) in the IVIG-nonresponders, more frequent than 6.8% (19/279) in the IVIG-responders (P<0.001) (Table 1).
Of the 30 IVIG-nonresponders, 22 were retreated with IVIG (2 g/kg). Six did not respond to IVIG-retreatment were given pulse methylprednisolone (30 mg/kg dose for 3 days), and 2 who did not respond to IVIG and steroid was treated with infliximab (5 mg/kg).
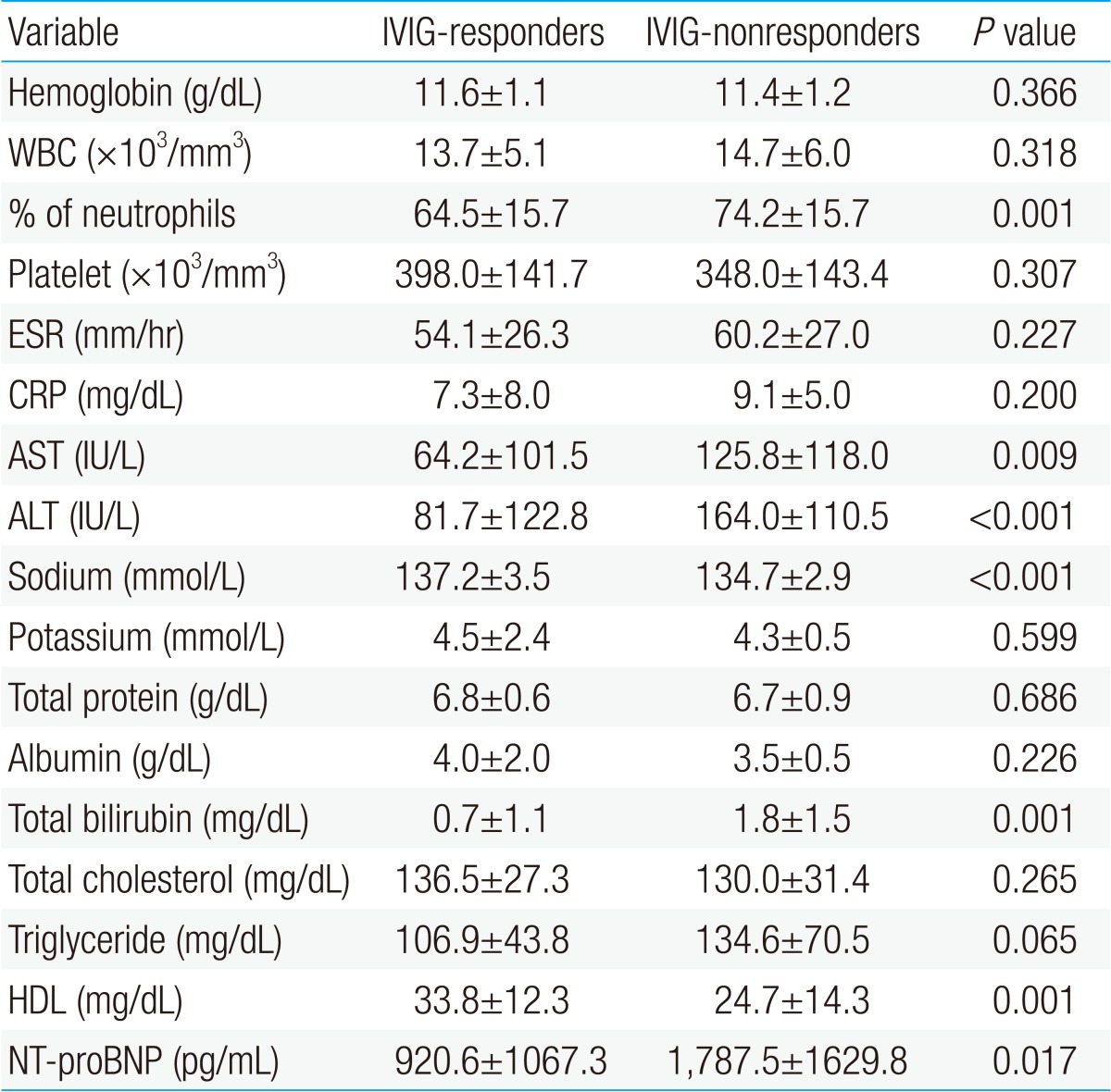
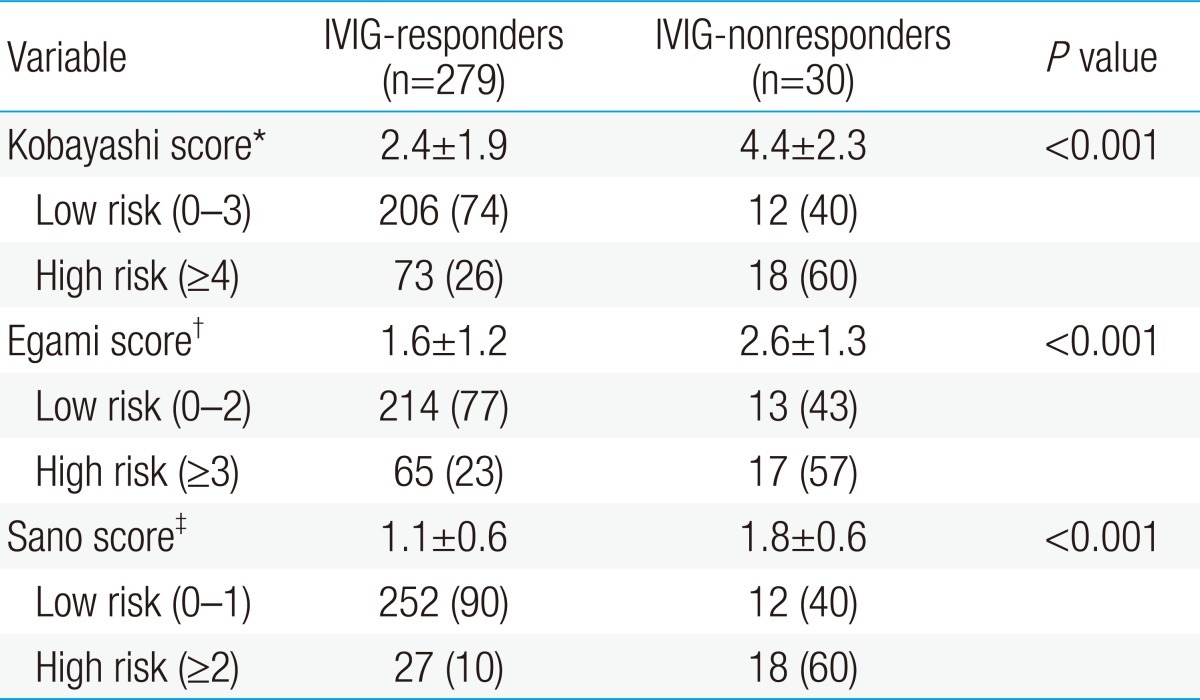
AST, ALT, total bilirubin, % neutrophils, and NT-proBNP were significantly higher in the IVIG-nonresponders than in the IVIG-responders, and sodium level and HDL level were lower in the IVIG-nonresponders than in the IVIG-responders. Previously reported risk factors such as CRP, platelet count, and albumin were not significantly different in this study (Table 2). When data on our patients was applied to Kobayashi score6), Sano score8), Egami score9), and which are risk-scoring systems for predicting IVIG-resistant KD, were significantly higher in the IVIG-nonresponder group. The sensitivity and specificity of the Kobayashi model was 60% and 74%, respectively, and those of the Egami model were 57% and 77%, respectively. The Sano model showed sensitivity of 60% and specificity of 90% (Table 3).
For each biomarker, the cutoff value was decided by the ROC curve. When the cutoff value of % neutrophils for identifying IVIG-nonresponders was set to 76%, the area under the ROC curve was 0.689 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.580 to 0.798), sensitivity was 63%, and specificity was 74%. When the cutoff value of AST was 56 IU/dL, the area under the ROC curve was 0.683 (95% CI, 0.564 to 0.801), sensitivity was 60%, and specificity was 71%. For ALT, at cutoff value of 84 IU/dL, the area under the ROC curve was 0.751 (95% CI, 0.654 to 0.847), sensitivity was 73%, and specificity was 75%. At cutoff value 0.9 mg/dL of total bilirubin, the area under the ROC curve was 0.739 (95% CI, 0.627 to 0.852), sensitivity was 70%, and specificity was 86%. At cutoff value 136 mmol/L of sodium level, the area under the ROC curve was 0.706 (95% CI, 0.626 to 0.786), sensitivity was 70%, and specificity was 59%.
According to the results of multivariable logistic regression analysis, the independent risk factors of IVIG-nonresponders were ALTŌēź84 IU/dL and total bilirubinŌēź0.9 mg/dL. The odds ratio was 3.8 for ALT, and 5.3 for total bilirubin. Having both of the two predictors (ALTŌēź84 IU/dL, total bilirubinŌēź0.9 mg/dL) in laboratory findings showed higher sensitivity and specificity (63% and 90%, respectively) than the existing models in predicting KD patients not responding to initial IVIG (Table 4).
From the results of this study, we found two predictors (ALTŌēź84 IU/dL and total bilirubinŌēź0.9 mg/dL) for KD not responding to initial IVIG treatment. In addition, the frequency of coronary artery lesion was much higher in IVIG-resistant KD, and pulse methylprednisolone and anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-╬▒ monoclonal antibody (infliximab) were found to be useful and effective as rescue therapy.
Research is being made actively for reducing the duration of fever and coronary artery lesions through early detection and treatment of patients not responding to IVIG, who occupy around 10% to 20% of KD. Still, no agreed risk factors have been found. Many of studies on such risk factors were conducted with Japanese patients, and Kobayashi et al.6), Sano et al.8), Egami et al.9), etc. proposed scoring system for predicting IVIG-nonresponders using various parameters. When these risk-scoring systems were applied to the subjects of our study, specificity was high (74% to 90%) but sensitivity was low (57% to 60%), so they had difficulty in screening out high-risk patients who need intensive treatment. After all, there is a problem in applying the risk-scoring systems, which are effective to Japanese pediatric patients, to Korean pediatric patients due to difference in genetic factors between Japanese and Korean patients.
In other studies, Ashouri et al.7) reported risk predictors such as high percent band count, low albumin and the presence of coronary artery lesions. Tremoulet et al.10) mentioned high percent band count, long illness day, high gamma-glutamyl transferase, and low age-adjusted Hb as the risk predictors of IVIG-nonresponders. In Korea as well, Do et al.11) reported that low albumin, low sodium, and high neutrophil proportion were significant in the IVIG-resistant group. Changes in these biomarkers are the effects of diverse cytokines (interleukin [IL]-1╬▓, TNF-╬▒, interferon (IFN)-╬│, IFN-╬▒, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, transforming growth factor-╬▓, matrix metalloproteinase, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) increasing at the early stage2,5). The elevation of VEGF induces the increase of vascular leakage, which in turn, decreases albumin. Furthermore, cytokine-activated natural killer cells accumulate in vascular endothelium and along liver sinusoids. As a result, inflammation of hepatic reticuloendothelial system and biliary tract occurs, that increases liver enzyme and total bilirubin6,12). The accurate pathogenesis of hyponatremia in KD is unknown but is explained by the inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone caused by cerebral vasculitis and the direct renal loss of sodium resulting from the renal involvement of KD13).
As in the previous studies6-9), there were statistical differences in sodium level, liver enzymes (AST, ALT), total bilirubin, and neutrophil proportion in our study. The other parameters mentioned above were not significantly different. Moreover, high frequency of sterile pyuria, low HDL were observed in the IVIG-nonresponder group. KD patients show abnormal urinary findings such as proteinuria, hematuria and sterile pyuria, and severe cases may have interstitial nephritis, acute renal failure, etc., rarely. Sterile pyuria is caused less by urethritis than by renal parenchymal injury and inflammation in KD, and it is also closely associated with cytokines14). KD causes also abnormalities in lipid metabolism due to the effects of cytokines such as TNF-╬▒, IL-1 and IL-6. With the decrease of HDL, triglyceride increases. TNF-╬▒ and IL-1 decreases HDL by damaging the activity of lipoprotein lipase, and increases triglyceride through decreasing circulating lipoprotein and increasing hepatic lipid synthesis15-17). In our study, HDL was significantly different between the two groups, but because the value of lipid profile is affected by diet it may have a limitation as a predictive marker of IVIG-responders and IVIG-nonresponders.
NT-proBNP, a widely used biomarker of cardiovascular disease, is cardiac hormone secreted by the ventricles in response to sheer stress from the overload of body fluid and pressure. It is involved in diuresis, natriuresis, and arterial and venous dilatation and plays the role of regulating myocardial proliferation and hypertrophic response18,19). NT-proBNP is a very important biomarker for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of heart failure in adults, and is a predictor of cardiac functions in patients after cardiac infarction20,21). In pediatric patients as well, NT-proBNP is a significant biomarker for heart failure, congenital heart disease with left-to-right shunt, cyanotic heart disease, right heart disease, secondary right heart disease induced by pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary regurgitation, and allograft disease after heart transplantation22-24). Not as in other febrile illnesses, what is more, it increases at the acute stage of KD and decrease at the convalescent stage, so is useful for diagnosis25). Among cytokines, TNF-╬▒ and IL-1╬▓ accelerate the secretion of NT-proBNP, and secondarily the secretion of NT-proBNP is accelerated by subclinical myocarditis and ischemia in KD26). In this study, NT-proBNP was statistically significantly higher in the IVIG-nonresponder group. Because its variation is large according to age, however, NT-proBNP may be considered clinically but has a limitation in being used as a predictor22).
With excluding parameters which have problems in being used as a predictor, we could obtain the predictors of KD nonresponsive to IVIG using risk factors confirmed from our data and several factors suggested in previous studies. ALTŌēź84 IU/dL and total bilirubinŌēź0.9 mg/dL can be used as important independent risk factors for IVIG-resistant KD. These results imply that severe inflammation spread to the hepatic reticuloendothelial system by the impact of several cytokines and natural killer cells in the IVIG-nonresponder group.
Limitations of this study are that the number of IVIG-nonresponders was too small to represent the sample, and that the study was conducted retrospectively at two medical centers. In addition, echocardiography for diagnosing coronary artery lesions was performed by different examiners.
In conclusion, IVIG and high dose aspirin are established treatment methods of KD. There are still the controversial questions of what risk factors predict patients not responding to IVIG and what additional treatments should be applied to reduce coronary artery lesions. If a large-scale study is conducted with the whole population of KD pediatric patients, we may find the risk factors of KD not responding to IVIG. Then, we may be able to suggest new treatment guidelines different from existing treatment methods and to prevent coronary artery complications caused by KD.
References
2. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 2004;114:1708ŌĆō1733.


3. Royle J, Burgner D, Curtis N. The diagnosis and management of Kawasaki disease. J Paediatr Child Health 2005;41:87ŌĆō93.


4. Rowley AH, Shulman ST. Pathogenesis and management of Kawasaki disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2010;8:197ŌĆō203.



6. Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Takeuchi K, Okada Y, Tamura K, Tomomasa T, et al. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 2006;113:2606ŌĆō2612.


7. Ashouri N, Takahashi M, Dorey F, Mason W. Risk factors for nonresponse to therapy in Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 2008;153:365ŌĆō368.


8. Sano T, Kurotobi S, Matsuzaki K, Yamamoto T, Maki I, Miki K, et al. Prediction of non-responsiveness to standard high-dose gamma-globulin therapy in patients with acute Kawasaki disease before starting initial treatment. Eur J Pediatr 2007;166:131ŌĆō137.



9. Egami K, Muta H, Ishii M, Suda K, Sugahara Y, Iemura M, et al. Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 2006;149:237ŌĆō240.


10. Tremoulet AH, Best BM, Song S, Wang S, Corinaldesi E, Eichenfield JR, et al. Resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 2008;153:117ŌĆō121.



11. Do YS, Kim KW, Chun JK, Cha BH, Namgoong MK, Lee HY. Predicting factors for refractory Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ J 2010;40:239ŌĆō242.



12. Kuo HC, Liang CD, Wang CL, Yu HR, Hwang KP, Yang KD. Serum albumin level predicts initial intravenous immunoglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr 2010;99:1578ŌĆō1583.


13. Watanabe T, Abe Y, Sato S, Uehara Y, Ikeno K, Abe T. Hyponatremia in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Nephrol 2006;21:778ŌĆō781.


14. Watanabe T, Abe Y, Sato S, Uehara Y, Ikeno K, Abe T. Sterile pyuria in patients with Kawasaki disease originates from both the urethra and the kidney. Pediatr Nephrol 2007;22:987ŌĆō991.


15. Chiang AN, Hwang B, Shaw GC, Lee BC, Lu JH, Meng CC, et al. Changes in plasma levels of lipids and lipoprotein composition in patients with Kawasaki disease. Clin Chim Acta 1997;260:15ŌĆō26.


16. Newburger JW, Burns JC, Beiser AS, Loscalzo J. Altered lipid profile after Kawasaki syndrome. Circulation 1991;84:625ŌĆō631.


17. Yun SW, Lee HS, Kim DW, Rhee KW, Jung YS. Changes of lipid and lipoprotein compositions in Kawasaki disease and its impact on cardiac complications. Korean J Pediatr 2005;48:1370ŌĆō1377.
18. Davis GK, Bamforth F, Sarpal A, Dicke F, Rabi Y, Lyon ME. B-type natriuretic peptide in pediatrics. Clin Biochem 2006;39:600ŌĆō605.


20. Newton PJ, Betihavas V, Macdonald P. The role of B-type natriuretic peptide in heart failure management. Aust Crit Care 2009;22:117ŌĆō123.


21. Sullivan DR, West M, Jeremy R. Utility of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) measurement in cardiovascular disease. Heart Lung Circ 2005;14:78ŌĆō84.


22. Nir A, Lindinger A, Rauh M, Bar-Oz B, Laer S, Schwachtgen L, et al. NT-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in infants and children: reference values based on combined data from four studies. Pediatr Cardiol 2009;30:3ŌĆō8.


23. Nasser N, Bar-Oz B, Nir A. Natriuretic peptides and heart disease in infants and children. J Pediatr 2005;147:248ŌĆō253.


24. Nir A, Nasser N. Clinical value of NT-ProBNP and BNP in pediatric cardiology. J Card Fail 2005;11(5 Suppl): S76ŌĆōS80.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


