Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 56(5); 2013 |
Abstract
Purpose
Early diagnosis and treatment of acute pyelonephritis in children is of special importance in order to prevent serious complications. This study was conducted to determine the diagnostic value of serum interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 in children with acute pyelonephritis.
Methods
Eighty-seven patients between 1 month to 12 years old with urinary tract infection (UTI) were divided into 2 groups based on the result of 99m-technetium dimercapto-succinic acid renal scan: acute pyelonephritis (n=37) and lower UTI (n=50) groups. White blood cell (WBC) count, neutrophil (Neutl) count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration, platelet count, and serum IL-6 and IL-8 concentrations of both groups were measured and compared.
Results
There was a significant difference between two groups regarding WBC count, Neutl count, ESR, and CRP concentration (P<0.05). In addition, the difference between the two groups regarding serum IL-6 and IL-8 concentrations was not significant (IL-6, 60 and 35.4 pg/mL and IL-8, 404 and 617 pg/mL, respectively). The sensitivity and specificity of serum IL-6 and IL-8 for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis were 73%, 42% and 78%, 32%, respectively. Sensitivity, specificity, negative and positive predictive values of serum IL-6 and IL-8 were less than those of acute phase serum reactants such as CRP.
Conclusion
This study showed that there was no significant difference between acute pyelonephritis and lower UTI groups regarding serum IL-6 and IL-8 levels. Therefore, despite confirming results of previous studies, it seems that IL-6 and IL-8 are not suitable markers for differentiating between acute pyelonephritis and lower UTI.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is caused by invasion of pathogenic microorganisms into the urinary tract system. The morbidity rate of pediatric UTI in boys and girls is 1.1% and 3%, respectively. The prevalence of UTI in male and female children younger than 6 years old is 1.8% and 6.6%, respectively1-4). UTI is classified into three types: acute pyelonephritis, lower UTI and asymptomatic bacteriuria1,2). The acute pyelonephritis is the most severe type of the disease. Delay in diagnosis and treatment may lead to renal scarring, hypertension and chronic renal failure2). Previous studies have shown that the prevalence of renal scarring due to acute pyelonephritis is 26.5% to 49%5,6). Although clinical symptoms such as fever and common inflammatory markers like erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) can somewhat determine the location of UTI, these symptoms are not always reliable7). Today, 99m-technetium dimercapto-succinic acid (DMSA) renal scan is used as a valuable imaging method for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis1,2). Unfortunately, this imaging device is not available in all medical centers and is accompanied with radiations1,2,8,9). Thus, some studies have stated that rapid diagnostic tests such as cytokines can be used for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis10,11). Interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 are the most prevalent interleukins that are used for differentiation of acute pyelonephritis and lower UTI. To the best of my knowledge, and according to the literature review, few studies document controversy of mentioned test for differentiating acute pyelonephritis and lower UTI10,11). Considering the importance of an early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of acute pyelonephritis, the present study was conducted to determine the diagnostic value of serum IL-6 and IL-8 in children with acute pyelonephritis in children.
This case-control study was conducted at Qazvin Children Hospital affiliated to the Qazvin University of Medical Sciences in Qazvin, Iran in 2011. This hospital is the only children's teaching hospital in Qazvin Province. In this study, 124 children with suspected UTI according to clinical symptoms such as fever, dysuria, flank pain and abnormal urinalysis were evaluated. Among these patients, only those having the following criteria were enrolled in the study: (1) first episode of UTI, (2) positive urine culture (urine culture more than 105 colonies of a single pathogen in a midstream urine sample or clean catch method or 103 colonies of a single pathogen via urinary catheterization, or presence of any number of colonies of an organism in urine culture taken by suprapubic method)1,2). Patients with more than one organism in urine culture, history of more than once episode of UTI, who had received antibiotic therapy or had a concomitant disease such as septicemia, were excluded. Thus, finally 87 patients with a definite diagnosis of UTI were investigated. The age of all patients was between 1 month and 12 years.
All of blood samples were taken before antibiotic therapy. White blood cell (WBC) count, neutrophil (Neutl) count, platelet count, ESR, and CRP concentration were measured as soon as possible. For measuring serum IL-6 and IL-8, four milliliters of blood was taken from peripheral vein and then, the serum was obtained by centrifugation at 3,000 rpm for 5 minutes at 4℃. The serum was then poured into acid-washed tubes and stored in a refrigerator at -20℃ until IL-6 and IL-8 assay. The serum IL-6 and IL-8 were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and commercially available kits (Cat. numbers BMS213/2CE and BMS2o4/3CE, eBioscience, Vienna, Austria).
The ethics committee of the Research Department in the Qazvin University of Medical Sciences (project No.260) approved the study. All parents were provided information regarding the research method in simple language. The children were included in the study after their parents agreed and signed the informed consent form.
Sample size was calculated based on the following parameters: P=65%, α=0/05, 1-α=0.95, d=0.12, β=0.2, 1-β=0.81). Consecutive sampling continued until the desired sample size was reached. Based on the DMSA renal scan result (gold standard), the patients were divided into: acute pyelonephritis and lower UTI groups. In DMSA renal scan, the acute pyelonephritis was diagnosed upon observation of focal or diffuse areas of diminished uptake that are associated with preservation (or at times even bulging) of renal cortical outline1,2).
The two groups were compared with each other in terms of clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of IL-6 and IL-8 were determined and compared with other inflammatory markers such as fever, WBC count, Neutl count, platelet count, ESR, and CRP. Variables of the two groups were compared with each other using chi-square test, t-test, and Mann-Whitney test. The data were analyzed using the SPSS ver. 15 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and statistical methods logistic regression analyses, and odds ratio. P value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
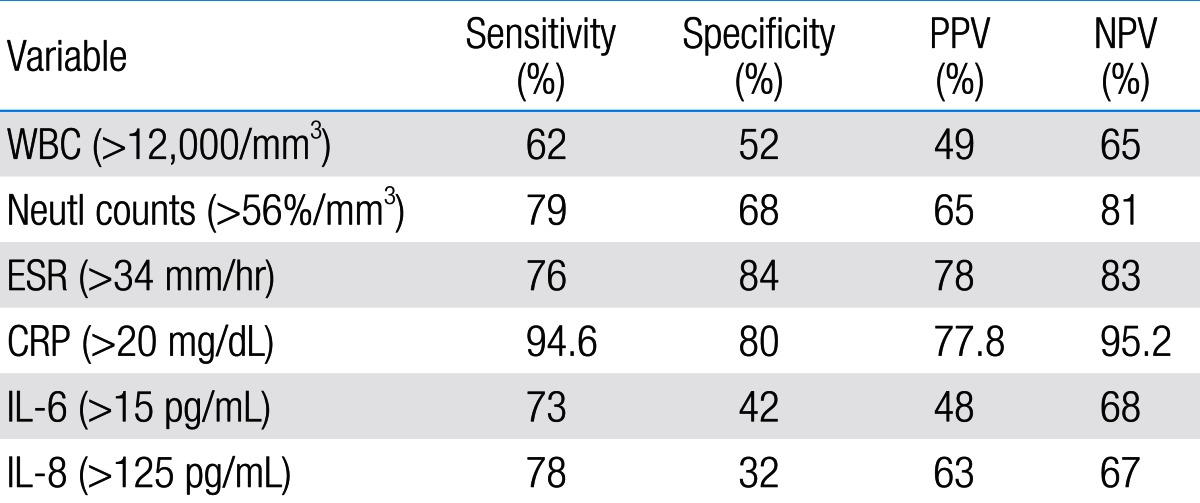
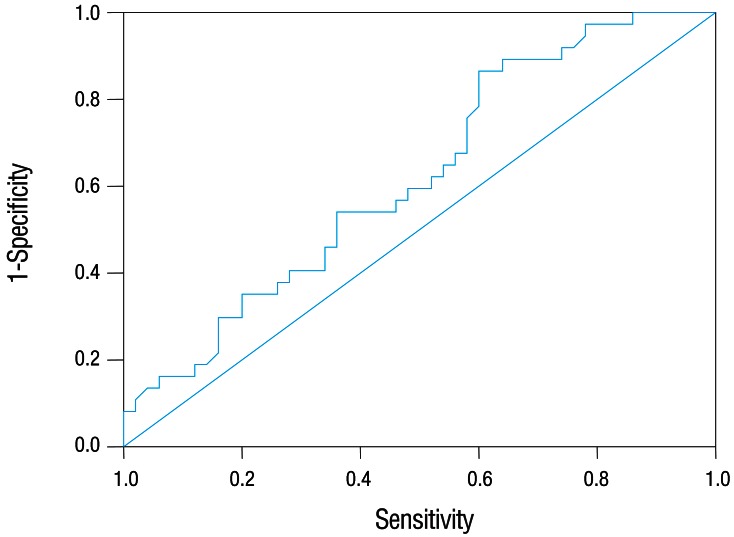
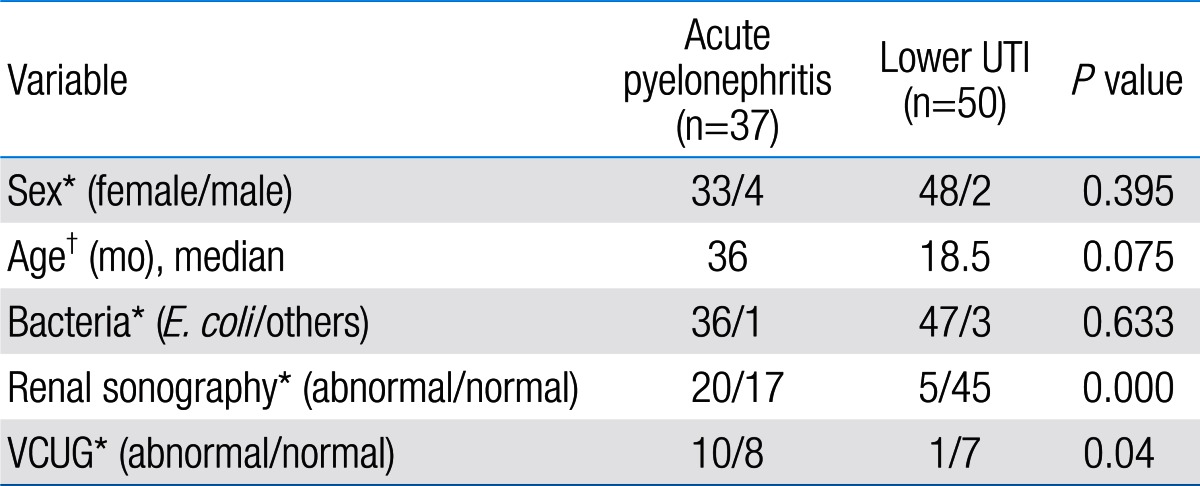
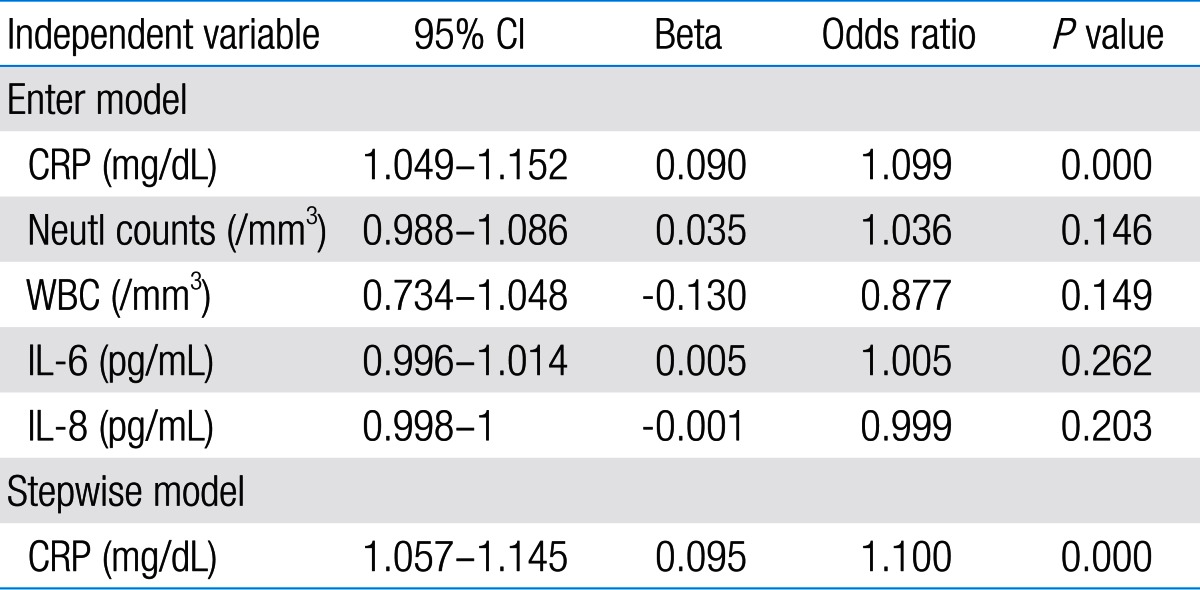
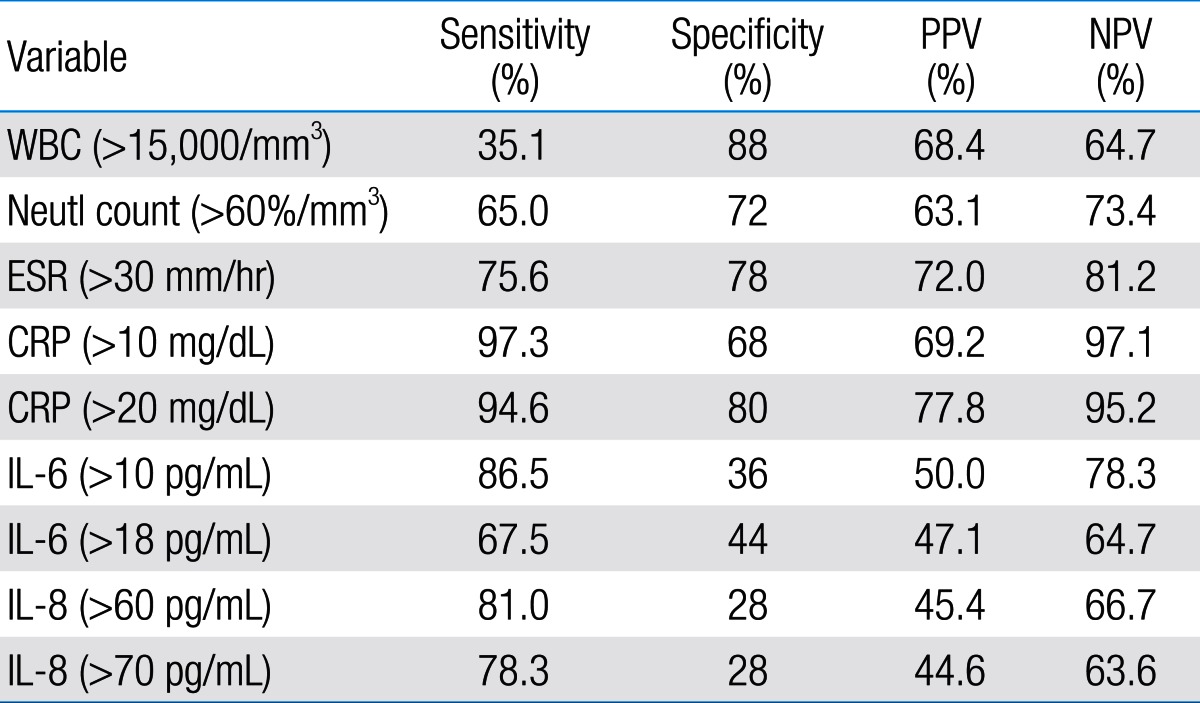
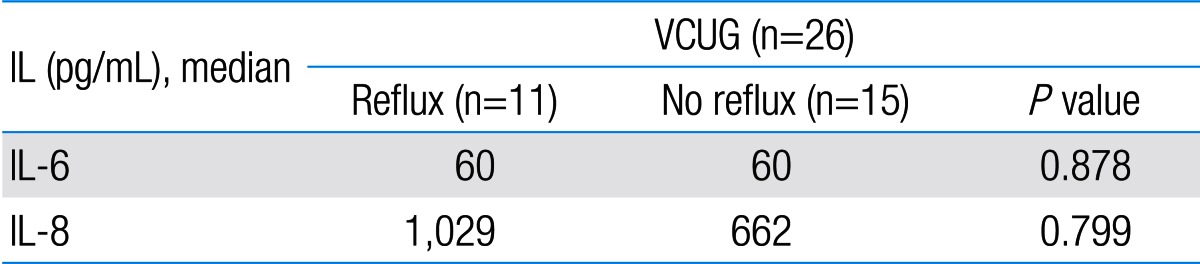
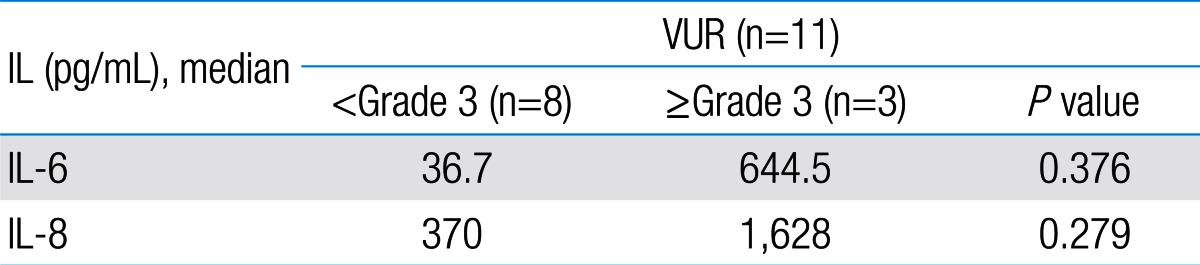
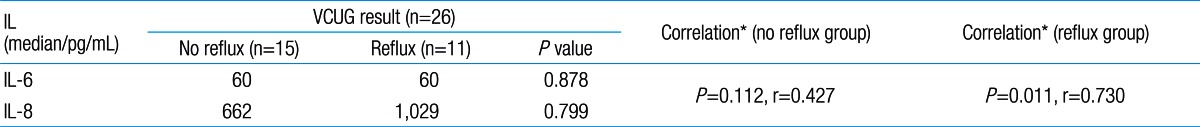
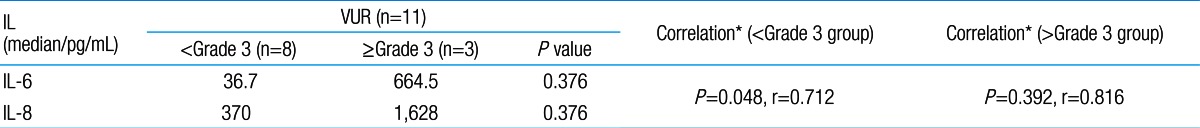
Among 87 children with UTI, 37 children had acute pyelonephritis (33 female and 4 male) and 50 children with lower UTI (48 female and 2 male). There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding sex (P=0.395). Minimum and maximum age of the patients in pyelonephritis group was 3 and 144 months with median of 36, respectively. These values in lower UTI group were 4 and 120 months with median of 18.5, respectively (Table 1). No significant difference was observed between the two groups regarding age (P=0.075). The most frequent clinical symptoms in acute pyelonephritis and lower UTI patients were fever, anorexia and dysuria (Table 2). Escherichia coli was the most common growing organism (P=0.633) (Table 1). The abnormal renal ultrasound was observed in 20 patients with acute pyelonephritis (54%) and 5 patients with cystitis (10%) (P=0.000) (Table 1). The abnormal findings in renal ultrasound in acute pyelonephritis group were dilated pelvicalyceal system (65%), hydronephrosis (25%), and kidney stone (10%). These values in lower UTI group were 80%, 20%, and 0%, respectively. Of 18 voiding cystourethrograms (VCUGs) performed in pyelonephritis group, 10 cases of VUR were observed, while, of 8 VCUGs performed in lower UTI group, 1 case of VUR was observed (P=0.04) (Table 1). There was a significant difference between the two groups in terms of WBC count, Neutl count, and ESR and CRP concentration (Table 3). Although median serum IL-6 in patients with acute pyelonephritis was greater than that in patients with lower UTI, but no significant difference was observed in this regard (P=0.056) (Table 3). There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding median serum IL-8 (P=0.854) (Table 3). Multivariate logistic regression analysis with acute pyelonephritis as a dependent variable and WBC count, Neutl counts, ESR, CRP, IL-6 and IL-8 as independent variables, showed that there is no significant positive correlation between the acute pyelonephritis and IL-6, IL-8 (Table 4). Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of variables were determined with different cutoff points (Tables 5, 6; Figs. 1, 2). Based on the cutoff points determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, values of sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of IL-6 and IL-8 were less than those of CRP (Table 6). There was no significant difference between serum IL-6 and IL-8 concentrations and presence of VUR and severity of VUR (Tables 7, 8). The correlation between serum IL-6 and 8 concentrations according to presence and severity of VUR was shown in Tables 9, 10.
Although DMSA renal scan as a gold standard is used to differentiate acute pyelonephritis from lower UTI, it is not available in all medical centers and is accompanied with radiation, and also it is an expensive method1,2) .Therefore, some researchers suggest rapid diagnostic tests for an early diagnosis and rapid treatment of acute pyelonephritis10-13). Cytokines are examples of such tests10,11,14). Cytokines are hormonal mediators which are produced in response to infectious and inflammatory conditions in different tissues of body. IL-6 and IL-8 are among important cytokines14). IL-6 is an inflammatory cytokine, which is secreted in response to bacterial infections in body. IL-8 is another inflammatory cytokine which is secreted during infectious diseases by monocytes, endothelial cells and neutrophils in response to IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor-α15,16). The study of Sheu et al.10) on children of 1-121 months old with UTI showed that the value of inflammatory markers including CRP, WBC, serum and urinary IL-6 and IL-8 in patients with acute pyelonephritis was higher than that in lower UTI patients. Also, these researches showed that there was a positive significant correlation between acute pyelonephritis, and serum and urinary IL-6, IL-8 and other inflammatory markers. In this study, the sensitivity and specificity of IL-6 and IL-8 were 81%, 83% and 89%, 78%, respectively. Sheu et al.10) concluded that serum IL-6 and IL-8, especially IL-6, are suitable markers for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis. Other studies confirmed the increase in urinary IL-6 and IL-8 in children with febrile UTI17,18). Authors of the above study believe that invasion of lipid A component of endotoxin and P fimbriae present in Escherichia coli and other gram negative bacteria induce inflammation and release of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 cytokines in the invaded area, and consequently, these cytokines increase in urine10,17,18). A study by Gurgoze et al.11) on 76 children with UTI showed that inflammatory markers such as CRP, ESR, WBC count, Neutl count, procalcitonin, IL-6, and IL-1β in patients with acute pyelonephritis were significantly higher than lower UTI. Gurgoze et al.11) showed that there was a positive significant correlation between acute pyelonephritis and IL-1β and procalcitonin, but none with IL-6. In this study, the sensitivity and specificity of IL-6 with cutoff point >18 pg/mL were 88% and 74%, respectively. Researchers concluded that procalcitonin and IL-1β are suitable markers for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis. Krzemien's study on 33 children with UTI revealed that urinary IL-6 and IL-8 are not suitable markers for differentiation of acute pyelonephritis from lower UTI in children up to 2 years old19). Although, in our study the amount of WBC, CRP, ESR, platelet count, Neutl count, and IL-6 in acute pyelonephritis group was higher than that in lower UTI group, the significant differences were observed only for Neutl count; CRP, ESR, and WBC count. Moreover, no positive significant correlation was observed between acute pyelonephritis and IL-6 and IL-8. The only positive significant correlation was observed regarding CRP. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of variables showed various values with different cutoff points. The sensitivity and specificity of IL-6 with cutoff points of 10, 18, 60 and 70 pg/mL were 86.5%, 36%; 67.5%, 44%; 81%, 28%; and 73.8%, 28%, respectively. These values were much lower than those obtained for CRP with cutoff point of 20 mL/dL. Furthermore, PPV and NPV of IL-6 and IL-8 were lower than those obtained for CRP and ESR. Based on ROC curve, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV values of ESR, and CRP were more than those of IL-6 and IL-8. Results of the present study partly agreed with the results of the studies by Gurgoze et al.11) and Krzemien et al.19). The controversy between this study and some previous ones may be due to variables such as time of sampling, age of patients and other factors. Some patients did not accept to follow all the tests that were designed for this research such as VCUG, and this was limitation of the present study. The present study showed that sensitivity and specificity of IL-6 and IL-8 are less than those of acute phase reactants such as CRP. These cytokines are not reliable markers for differentiating acute pyelonephritis from lower UTI.
Acknowledgments
Our thanks and best regards goes to research department of Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, parents of children and Mrs. Shiva Esmaily for their cooperation.
References
1. Hansson S, Jodal U. Urinary tract infection. Avner ED, Harman WE, Niavdet P, editors. Pediatric nephrology. 2004;5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, :1007–1025.
2. Elder JS. Urinary tract infection. Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 2011;19th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, :1829–1838.
4. Buonsenso D, Cataldi L. Urinary tract infections in children: a review. Minerva Pediatr 2012;64:145–157.

5. Ayazi P, Moshiri SA, Mahyar A, Moradi M. The effect of vitamin A on renal damage following acute pyelonephritis in children. Eur J Pediatr 2011;170:347–350.


6. Faust WC, Diaz M, Pohl HG. Incidence of post-pyelonephritic renal scarring: a meta-analysis of the dimercapto-succinic acid literature. J Urol 2009;181:290–297.


7. Ayazi P, Mahyar A, Jahani Hashemi H, Daneshi MM, Karimzadeh T, Salimi F. Comparison of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein tests in children with urinary infection. Iran J Pediatr 2009;19:381–386.
8. Lavocat MP, Granjon D, Allard D, Gay C, Freycon MT, Dubois F. Imaging of pyelonephritis. Pediatr Radiol 1997;27:159–165.


9. Ifergan J, Pommier R, Brion MC, Glas L, Rocher L, Bellin MF. Imaging in upper urinary tract infections. Diagn Interv Imaging 2012;93:509–519.


10. Sheu JN, Chen MC, Lue KH, Cheng SL, Lee IC, Chen SM, et al. Serum and urine levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in children with acute pyelonephritis. Cytokine 2006;36:276–282.


11. Gurgoze MK, Akarsu S, Yilmaz E, Godekmerdan A, Akca Z, Ciftci I, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and procalcitonin in children with acute pyelonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 2005;20:1445–1448.


12. Nikfar R, Khotaee G, Ataee N, Shams S. Usefulness of procalcitonin rapid test for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children in the emergency department. Pediatr Int 2010;52:196–198.


13. Gervaix A, Galetto-Lacour A, Gueron T, Vadas L, Zamora S, Suter S, et al. Usefulness of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein rapid tests for the management of children with urinary tract infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2001;20:507–511.


15. Magudumana MO, Ballot DE, Cooper PA, Trusler J, Cory BJ, Viljoen E, et al. Serial interleukin 6 measurements in the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. J Trop Pediatr 2000;46:267–271.


16. Diepold M, Noellke P, Duffner U, Kontny U, Berner R. Performance of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 serum levels in pediatric oncology patients with neutropenia and fever for the assessment of low-risk. BMC Infect Dis 2008;8:28



17. Jantausch BA, O'Donnell R, Wiedermann BL. Urinary interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatr Nephrol 2000;15:236–240.


Table 2
Comparison of clinical findings between acute pyelonephritis and lower urinary tract infection (UTI) groups
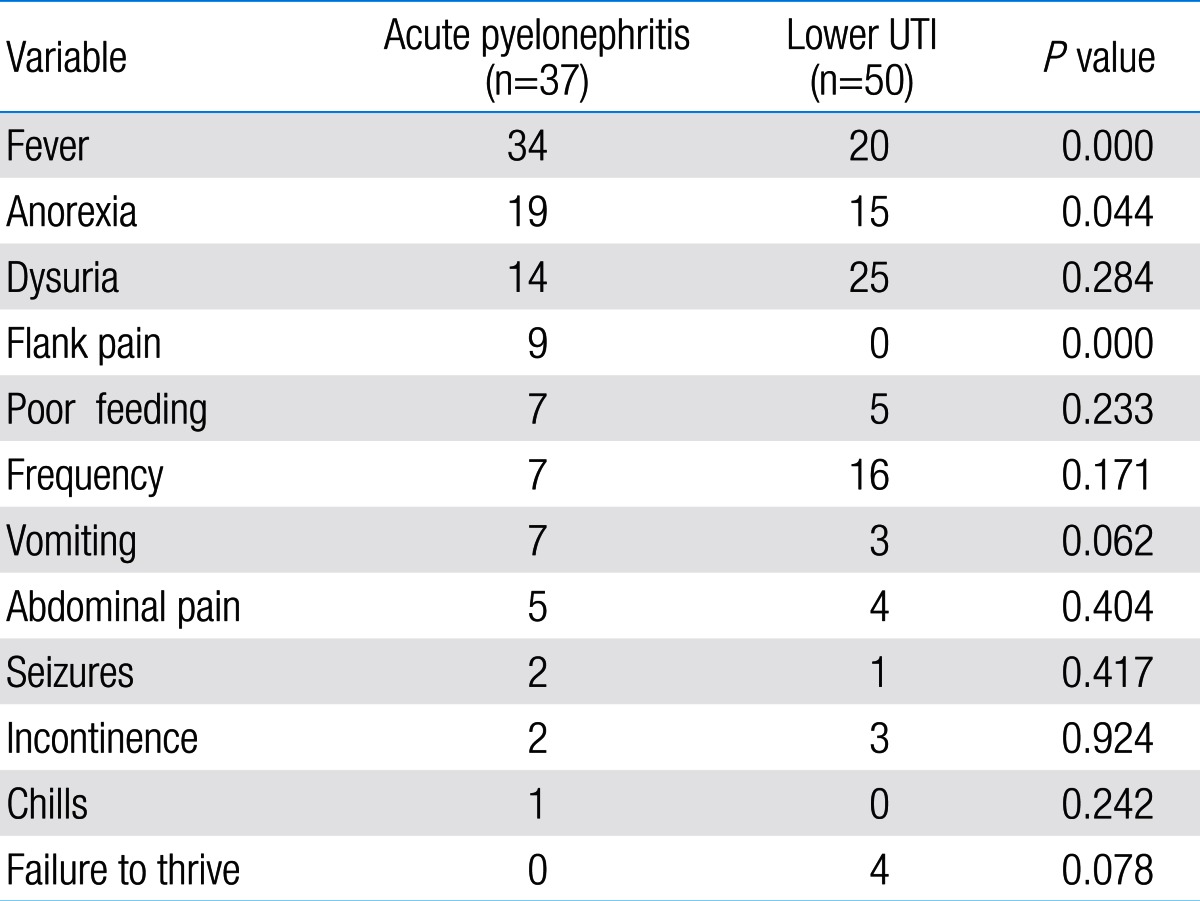
Table 3
Comparison of laboratory findings between acute pyelonephritis and lower urinary tract infection (UTI) groups
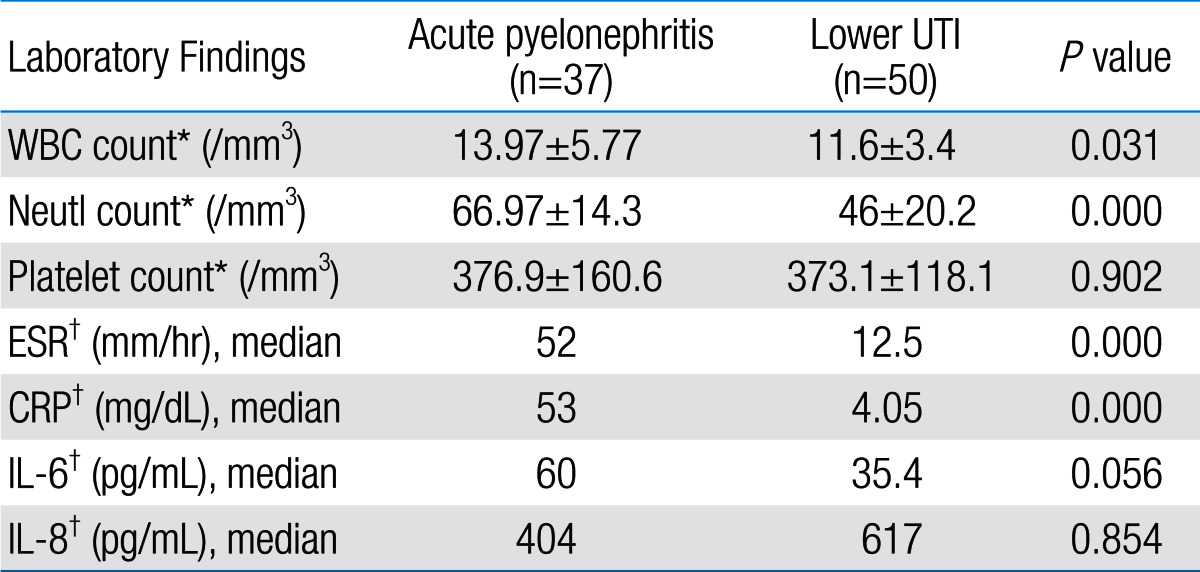
Table 6
Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of IL-6, IL-8 and other variables according to receiver operating characteristic curve




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


