< Previous Next >
Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 57(1); 2014 |
|
Abstract
Channelopathies are a heterogeneous group of disorders resulting from the dysfunction of ion channels located in the membranes of all cells and many cellular organelles. These include diseases of the nervous system (e.g., generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus, familial hemiplegic migraine, episodic ataxia, and hyperkalemic and hypokalemic periodic paralysis), the cardiovascular system (e.g., long QT syndrome, short QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia), the respiratory system (e.g., cystic fibrosis), the endocrine system (e.g., neonatal diabetes mellitus, familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis, and familial hyperaldosteronism), the urinary system (e.g., Bartter syndrome, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease, and hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia), and the immune system (e.g., myasthenia gravis, neuromyelitis optica, Isaac syndrome, and anti-NMDA [N-methyl-D-aspartate] receptor encephalitis). The field of channelopathies is expanding rapidly, as is the utility of molecular-genetic and electrophysiological studies. This review provides a brief overview and update of channelopathies, with a focus on recent advances in the pathophysiological mechanisms that may help clinicians better understand, diagnose, and develop treatments for these diseases.
Channelopathies are diseases that develop because of defects in ion channels caused by either genetic or acquired factors (Fig. 1). Mutations in genes encoding ion channels, which impair channel function, are the most common cause of channelopathies. Consistent with the distribution of ion channels throughout the human body, ion channel defects have been implicated in a wide variety of diseases, including epilepsy, migraine, blindness, deafness, diabetes, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmia, asthma, irritable bowel syndrome, and cancer1-3).
There are remarkable causal heterogeneity (especially genetic) and phenotypic variability in channelopathies, which make the diseases challenging to classify. This review will categorize channelopathies based on the organ system with which they are predominantly associated in both clinical and pathophysiological respects. Nomenclature of genetic diseases described in this article can be found at the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) website: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim.
Ion channels are transmembrane proteins that allow the passive flow of ions, both in and out of cells or cellular organelles, following their electrochemical gradients. Because the flux of ions across a membrane results in electrical currents, ion channels play a key role in generating membrane potential and function in diverse cellular activities, such as signal transduction, neurotransmitter release, muscle contraction, hormone secretion, volume regulation, growth, motility, and apoptosis. Ion channels can be classified according to the types of ions passing through them, the factors of their gating, their tissue expression patterns, and their structural characteristics. Ion channels typically exist in one of the three states: open, inactivated closed (refractory period), and resting closed (Fig. 2). The gating (opening and closing) of ion channels is controlled by diverse factors, such as membrane potential (voltage), ligands (e.g., hormones and neurotransmitters), second messengers (e.g., calcium and cyclic nucleotides), light, temperature, and mechanical changes. Ion channels are formed from either a single protein (e.g., cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, a chloride channel) or, more commonly, from an assembly of several subunits, each a protein encoded by a different gene. More than 400 ion channel genes have been identified4). Further diversity comes from a number of mechanisms, which include the use of multiple promoters, alternative splicing, posttranslational modifications, heteromeric assembly of different principal subunits, and interaction with accessory proteins5).
Ion channels are fundamental in neuronal signaling and thus, channelopathies can be found in a large and growing number of nervous system disorders (Table 1). Among the first genetically characterized and best-understood channelopathies are those that lead to primary skeletal muscle disorders. These muscle disorders exhibit a clinical spectrum ranging from myotonia (muscle hyperexcitability) to flaccid paralysis (muscle hypoexcitability) (Fig. 3). Patients with myotonia congenita present with attacks of extreme muscle stiffness because of delayed relaxation caused by sustained electrical activities in muscle. Both the dominant (Thomsen disease) and the recessive (Becker disease) types of the disease are caused by loss-of-function mutations in a single gene, CLCN1, which encodes the skeletal muscle chloride channel, ClC-1. ClC-1 channels stabilize the resting membrane potential and contribute to membrane repolarization after action potentials in skeletal muscle cells. When action potentials are elicited, potassium ions flow out of the cell and into the extracellular fluid and the transverse tubular system. According to the Nernst equation, the membrane tends to depolarize as extracellular potassium levels rise. Functional loss of ClC-1 channels reduces the inward chloride current required to compensate for the depolarization induced by potassium accumulation in the transverse tubules, thus resulting in spontaneous repetitive firing of action potentials and a slower rate of repolarization7).
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis is an autosomal-dominant disease characterized by recurrent attacks of muscle weakness and mild myotonia with concomitant transient hyperkalemia. The symptoms usually last for minutes to hours and are triggered by fasting, ingestion of potassium-containing foods, or vigorous exercise. Transient normokalemia, or even hypokalemia, can be measured during attacks, thus making the disease occasionally challenging to diagnose8). Gain-of-function mutations in the skeletal muscle voltage-gated sodium channel gene, SCN4A, impair channel inactivation and cause a persistent inward sodium current, which leads to increased membrane excitability and myotonia or reduced excitability with flaccid paralysis depending on the degree of membrane depolarization. Mild membrane depolarization allows wild-type sodium channels to oscillate between recovery from inactivation and reactivation by mutant channels, which results in the repetitive action-potential firing that can lead to myotonia. More severe depolarization inactivates most sodium channels and causes membrane inexcitability and flaccid paralysis7). Prolonged membrane depolarization enhances the activity of voltage-gated potassium channels, which amplifies potassium efflux from muscle cells and thereby increases in serum potassium levels9). Allelic disorders with certain phenotypes overlapping those of hyperkalemic periodic paralysis are potassium-aggravated myotonia and paramyotonia congenita, in which mutations in SCN4A result in a similar gain-of-channel function as described above. Exercise worsens muscle stiffness in paramyotonia congenita, whereas classical myotonia is alleviated by exercise (hence paradoxical myotonia or paramyotonia).
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis is the most common form of periodic paralysis and the majority of the cases are caused by mutations in the skeletal muscle voltage-gated calcium channel gene, CACNA1S, or the sodium channel gene, SCN4A10). Being located at the hypoexcitable end of the spectrum of muscle channelopathies, myotonia is not detected in this disease. The duration of paralytic attacks is longer than that in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (usually for hours and sometimes days). Although respiratory and cardiac muscles generally remain unaffected in hypokalemic periodic paralysis, life-threatening respiratory insufficiency and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported in and out of the country10-12). The mutant channels responsible for hypokalemic periodic paralysis have been known to generate an inward cation leakage current (referred to as the gating-pore current), which renders muscle fibers of patients susceptible to aberrant depolarization in response to low extracellular potassium levels13,14). Alterations in the expression, subcellular localization, and/or kinetics of non-mutated potassium channels, which reduce outward potassium currents, have been implicated in the development of hypokalemia as well as pathological depolarization15-17). The reason why potassium channels are affected by mutations in the CACNA1S or SCN4A gene has long remained elusive. However, given that skeletal muscle fibers from patients with hypokalemic periodic paralysis have been found to possess higher intracellular calcium levels than normal cells17), it now appears that calcium-activated potassium channels hold the key to this conundrum. Indeed, we have recently identified altered subcellular distribution of a calcium-activated potassium channel in skeletal muscle cells of patients with hypokalemic periodic paralysis (in preparation).
Andersen-Tawil syndrome is another example of channelopathies that exhibits dyskalemic (hyper- or, more typically, hypo-kalemic) periodic paralysis together with characteristic dysmorphic features (e.g., craniofacial, dental, and skeletal anomalies) and cardiac arrhythmias by mutations in an inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, Kir2.1. Kir2.1 stabilizes the resting membrane potential in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells and is responsible for terminating the repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. Loss-of-function mutations that alter the kinetics or membrane trafficking of Kir2.1 channels result in sustained depolarization and delayed cardiac repolarization with an increased risk of arrhythmia in Andersen-Tawil syndrome18).
Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a heterogeneous group of genetic disorders of the neuromuscular junction that can arise from presynaptic, synaptic, or postsynaptic defects. Most of the defects are postsynaptic, with the majority of these being caused by mutations in the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), a ligand-gated non-selective cation channel. Activation of nAChRs by acetylcholine released from motor nerve terminals causes sodium influx into muscle cells, which induces cell membrane depolarization and the subsequent cytosolic release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) that is required for muscle contraction. Thus, defects in nAChRs lead to the failure of synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction and the consequent symptoms of congenital myasthenic syndrome, which include fatigable weakness of ocular, bulbar, and limb muscles occurring shortly after birth or in early childhood. Decreased nAChR activity can also result from defective channel assembly caused by mutations in rapsyn (receptor-associated protein of the synapse) or MuSK (muscle-specific kinase)19). Mutations in nAChRs can also cause multiple pterygium syndromes comprising a group of disorders with multiple congenital anomalies, suggesting that the nAChR is vital for organogenesis as well as neuromuscular signal transduction. The phenotypic features of congenital myasthenic syndrome are similar to those of myasthenia gravis, but congenital myasthenic syndrome is not an autoimmune disease. Neurological channelopathies with an autoimmune etiology will be discussed in the section on the immune system.
Channelopathies that primarily affect neurons include certain types of epilepsy, ataxia, migraine, hyperekplexia, blindness, deafness, and peripheral pain syndromes. Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) is a familial epilepsy syndrome that displays a broad spectrum of clinical phenotypes ranging from classical febrile seizures to Dravet syndrome20). Dravet syndrome (also known as severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy) is the most severe form that results from mutations in a voltage-gated sodium channel gene, SCN1A, or a γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor gene, GABRG221). Patients with Dravet syndrome suffer from refractory seizures, ataxia, and severe developmental delay with poor outcomes. The Nav1.1 channel, which is encoded by SCN1A, is one of nine α subtypes (Nav1.1-Nav1.9) of voltage-gated sodium channels and this subtype is preferentially expressed in GABAergic neurons. The GABAA receptor, which is encoded by GABRG2, is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor in the central nervous system (CNS). Dysfunction of Nav1.1 channels or GABAA receptors can lead to reduced excitability of GABAergic neurons, thus resulting in brain hyperexcitability in patients with Dravet syndrome. A correlation between an increase in the severity of Nav1.1 dysfunction and the phenotypic severity in the GEFS+ spectrum has been proposed: mild impairment causes febrile seizures and severe defect leads to Dravet syndrome20). Mutations in GABAA receptors have also been identified in other types of epilepsy, such as juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and childhood absence epilepsy22-25).
Other examples of allelic channelopathies in the CNS include familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 (FHM1), episodic ataxia type 2 (EA2), and spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 (SCA6), each of which is associated with different mutations in the same gene, CACNA1A, that encodes the pore-forming α1 subunit of the P/Q type voltage-gated calcium channel, Cav2.1. Mutations responsible for FHM1 produce gain-of-function effects on Cav2.1 channels, which increase channel activity, synaptic transmission, and susceptibility to cortical spreading depression26), whereas the allelic mutations responsible for EA2 induce a loss-of-channel function, which results in decreased calcium currents through Cav2.127). Cav2.1 is highly expressed in cerebellar Purkinje cells, in which the channel mediates neurotransmitter release. Reduced Cav2.1 channel activity can lead to a decrease in output signals from Purkinje cells and thereby contributes to cerebellar dysfunction in EA2. SCA6 is caused by CAG repeat expansions in CACNA1A that confer a toxic gain-of-function effect: mutant Cav2.1 channels are incompletely degraded and form insoluble aggregates and inclusion bodies within Purkinje cells28).
Familial paroxysmal dyskinesias, which include paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia, paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia, paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesia, and paroxysmal hypnogenic dyskinesia, are an emerging group of channelopathies. Paroxysmal hypnogenic dyskinesia, which is also referred to as autosomal-dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy in certain cases, is a partial epilepsy that is characterized by brief seizures during sleep. The disease has been associated with mutations in neuronal nAChR genes (CHRNA2, CHRNA4, and CHRNB2) and a calcium-activated potassium channel gene (KCNT1)29). Mutations in neuronal nAChR genes result in either increased acetylcholine sensitivity or reduced calcium dependence of the receptor response30).
Hereditary hyperekplexia, also called startle disease or stiff baby syndrome, is one of the first ligand-gated channelopathies to be characterized; this disease is caused by mutations that alter the kinetics or membrane density of the heteromeric α1β glycine receptor chloride channel. Glycine is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS, and glycine receptors are predominantly expressed by the inhibitory interneurons of the spinal cord and brainstem. Impaired function of glycine receptors or associated proteins manifests the characteristic clinical symptoms of hyperekplexia, including exaggerated startle responses and marked hypertonia in response to sudden tactile or auditory stimuli. The onset of the initial episode occurs as early as in the neonatal period and the symptoms tend to resolve with age31).
A multifaceted syndrome called EAST (epilepsy, ataxia, sensorineural deafness, and tubulopathy) or SeSAME (seizures, sensorineural deafness, ataxia, mental retardation, and electrolyte imbalance) was recently described by two independent groups32,33). This syndrome is caused by loss-of-function mutations in an inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, Kir4.1, which has a pivotal role in glial function, neuronal excitability, and systemic potassium homeostasis33).
Pain channelopathies are another emerging class of neurological disorders in which dysfunctional channels represent potential pharmaceutical targets. A number of different channels are widely expressed in nociceptive neurons, and deficits in channels have been found to be associated with diverse steps of defective pain pathways. Familial episodic pain syndrome, primary erythermalgia (or erythromelalgia), and paroxysmal extreme pain disorder, all of which typically begin in childhood or infancy, are known to result from gain-of-function mutations of a voltage-gated sodium channel, Nav1.7, or a transient receptor potential (TRP) cation channel, TRPA1, that cause abnormal electrical firing, thus rendering neurons hyperexcitable34). Conversely, loss-of-function mutations of Nav1.7 lead to congenital indifference to pain35). Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type IIC (also known as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2C), congenital distal spinal muscular atrophy, and scapuloperoneal spinal muscular atrophy are allelic disorders with overlapping phenotypes derived from mutations in a TRP cation channel gene, TRPV4. TRPV4 mutations have also been implicated in skeletal dysplasias that include metatropic dysplasia, spondylometaphyseal dysplasia Kozlowski type, brachyolmia type 3, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia Maroteaux type, familial digital arthropathy with brachydactyly, and parastremmatic dysplasia36). TRP channels are non-selective cation channels that play critical roles in intracellular signaling and homeostasis of calcium and/or magnesium. Mammalian TRP channels belong to six subfamilies: TRP canonical (TRPC), TRP vanilloid (TRPV), TRP melastatin (TRPM), TRP ankyrin (TRPA), TRP polycystin (TRPP), and TRP mucolipin (TRPML). Mutations of the TRPML1 channel (also termed mucolipin 1), a member of the TRPML subfamily, cause mucolipidosis type IV, an autosomal-recessive neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorder that is characterized by severe psychomotor delay and visual impairment worsening over time. Loss-of-function mutations of TRPML1 channels have been shown to disturb calcium permeability and lysosomal acidification in affected cells37), but the precise pathophysiological mechanism underlying the clinical manifestations of the mutations remains to be elucidated.
Cardiac action potentials are generated from a delicate balance of several ionic currents38) (Fig. 4). When this balance is disturbed by ion channel dysfunction, life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias may occur. Cardiac channelopathies are likely responsible for approximately half the sudden arrhythmic death syndrome cases39) and for at least one out of five sudden infant death syndrome cases40). Mutations in calcium, sodium, potassium, and TRP channel genes have been identified to cause a variety of cardiac arrhythmic disorders (Table 2), and polymorphisms have been suggested to be risk factors41).
The first genetically identified cardiac disorder is congenital long QT syndrome (LQTS). Congenital LQTS, the most common form of cardiac channelopathy, is characterized by prolonged ventricular repolarization, predisposing to a high risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias (e.g., torsade de pointes), syncope, and sudden cardiac death. To date, 13 types of LQTS have been linked to mutations in genes that encode ion channels or associated proteins42). LQTS can also be induced by acquired factors, such as acquired diseases, drugs, and electrolyte abnormalities (hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia). Loss-of-function mutations of potassium channel genes (KCNQ1, KCNH2, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNJ2, and KCNJ5) in LQTS reduce the repolarizing currents (IKr, IKs, and IKir) required to terminate the cardiac action potential, leading to a prolongation of the QT interval. Gain-of-function mutations in calcium channel (CACNA1C) and sodium channel genes (SCN5A and SCN4B) in LQTS cause delayed channel closing and inactivation, responsible for prolonged inward currents and depolarization with a resultant increased QT interval. By contrast, loss-of-function mutations in calcium channel genes (CACNA1C, CACNB2, and CACNA2D1) and gain-of-function mutations in potassium channel genes (KCNH2, KCNQ1, and KCNJ2) enhance repolarization, resulting in the abnormal shortening of the cardiac action potential in short QT syndrome43). Loss-of-function mutations in sodium channel genes have been identified to cause Brugada syndrome, familial atrial fibrillation, sick sinus syndrome, familial heart block, and atrial standstill44). It is noteworthy that both gain-of-function mutations (which decrease action potential duration) and loss-of-function mutations (which increase action potential duration) in potassium channel genes predispose to atrial fibrillation45). This demonstrates a precise atrial electrophysiological balance in which minor disturbances in either direction can cause atrial fibrillation.
Hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels contribute to the pacemaker current (If) that is responsible for generating and regulating heart rhythm. Loss-of-function mutations of HCN4, the major HCN channel subunit in pacemaker cells, cause bradycardia46). Moreover, cardiac tachyarrhythmias have also been shown to be associated with dysfunctional HCN4 channels47,48). Although the pathogenic role of HCN channel mutations in cardiac tachyarrhythmias remains to be determined, one of the clues can be found in the suggested function of If in preventing bradycardia-induced ventricular arrhythmias by inhibiting early after-depolarization48).
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is characterized by the development of bidirectional polymorphic ventricular tachycardia upon exposure to adrenergic stimulation in an otherwise normal heart. Experiencing emotional or physical stress can induce dizziness, syncope, and/or sudden cardiac death in patients with CPVT. Manifestations occur in childhood or adolescence, with the average onset at age 7-9 years49). CPVT can be inherited in an autosomal-dominant or recessive manner. The autosomal-dominant form of CPVT (CPVT type 1) is caused by gain-of-function mutations in RYR2, the gene that encodes the cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 (RYR2), a major component of RYR2 channels. RYR2 channels mediate calcium release from the SR into the cytosol upon cell membrane depolarization. Defective closure of RYR2 channels results in intracellular calcium leakage from the SR, which leads to increased potential for delayed after-depolarizations and subsequent ventricular tachycardia50).
There are a number of ion channels expressed in airway cells that have been evaluated, the function of which may contribute to pathogenic conditions, but channelopathies in the respiratory system may not represent common pathologies in Asian populations. This is partly because cystic fibrosis (CF)-the first identified and the most common channelopathy that affects the respiratory system in Western populations-is rarely diagnosed in Asian people. CF is the most prevalent genetic disorder in the Caucasian population, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 2,500 live births51). Patients with CF are vulnerable to severe and chronic pulmonary infections and inflammation, which lead to irreversible airway damage and respiratory failure in most cases. CF exhibits a broad spectrum of symptoms: mild forms can be nearly asymptomatic, being diagnosed in middle age as affecting a single organ, whereas severe forms manifest not only in airways but also in digestive and reproductive systems, with some of the symptoms occurring as early as in the prenatal period51).
CF is caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. CFTR functions as a chloride channel in the apical membrane of epithelia, where the channel controls the volume of liquid on epithelial surfaces by secreting chloride and inhibiting sodium absorption. More than 1,600 mutations in the CFTR gene have been identified51). These mutations, which produce varying functional effects on CFTR, are considered to cause an abnormal transepithelial flux of chloride and sodium, which is accompanied by the passive flow of water and results in liquid depletion on the epithelial surface layer. Depletion of the airway surface liquid, which impairs ciliary function and mucociliary clearance, may lead to recurrent pulmonary infections and chronic inflammation in CF patients52). Increased knowledge of the molecular pathophysiological mechanism underlying CF has led to a variety of active clinical trials to identify targeted treatments, such as channel-specific drugs and gene therapy.
Deficiencies in ion transport have also been implicated in the pathophysiology of asthma. Of particular interest is the role of ion channels in the intracellular calcium homeostasis in asthmatic airways, which may contribute to smooth muscle contraction in the short term and airway remodeling in the long term53). A rise in the cytosolic calcium level ([Ca2+]c) activates almost all cells of the lung, including epithelial, endothelial, and smooth muscle cells, immune cells, and vagal neurons54). Increasing evidence indicates that an altered control of intracellular calcium homeostasis may be the fundamental biochemical basis of asthma. Several TRP channels, which play a critical role in cellular calcium homeostasis, have been associated with bronchial hyper-responsiveness and airway remodeling55-59). Multiple independent genome-wide association studies of childhood asthma revealed a consistent and strong association with ORMDL3, a gene that codes for an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein that regulates ER-mediated calcium homeostasis60). Furthermore, reduced expression of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 2 (SERCA2) has been demonstrated to underlie the abnormal secretory and hyperproliferative phenotype of airway smooth muscle (ASM) in asthma. After ASM cells are activated by an elevation of [Ca2+]c, SERCA2 reuptakes cytosolic calcium into the SR to restore normal [Ca2+]c. Thus, decreased expression and activity of SERCA2 cause a sustained increase in [Ca2+]c, which leads to slower return to the resting state of ASM cells in asthma61).
Respiratory symptoms can also develop in channelopathies associated with other systems, such as life-threatening respiratory insufficiency in hypokalemic periodic paralysis11), congenital myasthenic syndrome62), and long QT syndrome63). Respiratory manifestations typically occur when symptoms of the diseases are severe. Appropriate management of channelopathies thus often requires interdisciplinary approaches.
Electrical activity plays an essential role in insulin secretion from the pancreatic β cell64). Endocrine cells, like neurons and other excitable cells, use the electrical activity of ion channels to maintain or regulate various physiological functions. Defects in ion channels have been increasingly shown to cause endocrine disorders, including those not generally thought of as channelopathies (Table 3).
The adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel is involved in a wide spectrum of insulin secretory disorders ranging from neonatal diabetes mellitus to familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (also known as congenital hyperinsulinism). The KATP channel is a hetero-octameric complex of 4 inwardly-rectifying potassium channel subunits, Kir6.x, that form the pore, and 4 sulfonylurea receptors, SURx, that regulate channel function. KATP channels are found in various organs and/or tissues, such as the pancreas, brain, heart, smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle16,65). In pancreatic β cells, the KATP channel is composed of Kir6.2 and SUR1 subunits and functions as a key regulator of insulin release. ATP and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate directly affect the Kir6.2 subunit, whereas sulfonylurea and Mg-nucleotides control the channel activity through the SUR1 subunit. The intracellular [ATP]/[ADP] ratio primarily determines KATP channel activity. An increase in glucose metabolism leads to elevated intracellular [ATP], and the binding of ATP to Kir6.2 closes KATP channels, which results in membrane depolarization, calcium influx, and insulin secretion. Conversely, when glucose levels are low, Mg-ADP opens KATP channels through the SUR1 subunit, inducing potassium efflux, membrane hyperpolarization, and reduced excitability of pancreatic β cells65). Thus, the KATP channel couples metabolism to electrical activity.
Increased KATP channel activity in pancreatic β cells reduces insulin secretion, whereas decreased channel activity increases insulin secretion. Therefore, defects in KATP channel activity can lead to either a diabetic or a hyperinsulinemic state. Gain-of-function mutations in ABCC8 and KCNJ11, the genes that encode the SUR1 and Kir6.2 subunits of the KATP channel, respectively, keep the channels open and cause neonatal diabetes mellitus. By contrast, loss-of-function mutations in the same genes close KATP channels and cause hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. The mechanism underlying the gain-of-function mutations in neonatal diabetes mellitus is either a reduced sensitivity to the inhibitory action of ATP or an increased sensitivity to the stimulatory action of ADP66). Neonatal diabetes mellitus is usually diagnosed within the first 6 months of life. Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus is differentiated from permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus based on its remission typically within 18 months, with a possible relapse during adolescence. Sulfonylureas act directly on the SUR1 subunit in an ATP-independent manner and can inactivate KATP channels even when mutations are present. Therefore, sulfonylureas provide glycemic control that is as good, or better, than that achieved with insulin therapy in most cases of neonatal diabetes mellitus66,67).
The extent of KATP channel activity has been demonstrated to be correlated with the severity of insulin secretory disorders68) (Fig. 5). Complete loss-of-function mutations of KATP channels lead to a severe phenotype of familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, whereas mutations disrupting channel function only partially result in a less severe phenotype, as in leucine-induced hypoglycemia of infancy. Similarly, the most potent gain-of-function mutations of KATP channels underlie the triad of developmental delay, epilepsy, and neonatal diabetes (DEND) syndrome, the most severe form of diabetic phenotypes69). DEND syndrome is a multi-organ syndromic, permanent form of neonatal diabetes mellitus in which patients exhibit, besides diabetes mellitus, developmental delay, epilepsy, and muscle weakness. Kir6.2 and SUR1 subunits are expressed in extrapancreatic tissues, including the brain (Kir6.2 and SUR1) and skeletal muscle (Kir6.2), which accounts for the neurological symptoms triggered by the overactive KATP channels in DEND syndrome. Mutations that result in smaller functional gain of KATP channels produce a milder phenotype, as in transient neonatal diabetes mellitus68).
Type 2 diabetes is widely recognized to be a polygenic disorder that is associated with polymorphisms in many distinct genes; the combined effect of these polymorphisms contributes to the development of the disease, together with environmental factors, age, and obesity. A single nucleotide polymorphism at codon 23 of the KCNJ11 gene, which causes a glutamic acid-to-lysine substitution (E23K) in Kir6.2, has been strongly associated with an increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes across various ethnic groups, albeit the underlying pathogenic mechanism has yet to be defined69). The E23K variant may possibly cause a reduction in the ATP sensitivity of KATP channels, but the functional effects of individual polymorphisms linked to polygenic disorders are considered to be small.
Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis (TPP) is a sporadic disorder characterized by episodic attacks of flaccid paralysis, hypokalemia, and hyperthyroidism. TPP, which is clinically similar to familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis, is considered as a potentially life-threatening condition because of hypokalemia-induced cardiopulmonary compromise. The pathogenesis of TPP has long been attributed to increased activity of Na+-K+ ATPase stimulated by elevated levels of thyroid hormone, catecholamines, and insulin. Recently, mutations in KCNJ18, the gene that codes for Kir2.6 channels, have been identified in certain TPP patients70). Kir2.6 is an inwardly-rectifying potassium channel that mediates the potassium efflux from skeletal muscle cells. It has been reported that the outward Kir current is low in intercostal muscle fibers of patients with TPP17). Accumulating evidence suggests that loss of Kir2.6 function, together with increased activity of Na+-K+ ATPase, contributes to the development of hypokalemia and paralysis in patients with TPP. Catecholamines and insulin not only stimulate Na+-K+ ATPase but also inhibit Kir channels71). KCNJ18 has a thyroid hormone responsive element in its promoter region, and the expression of this gene is regulated by thyroid hormones at both transcriptional and post-translational levels70). Therefore, the genetic susceptibility resulting from mutations in KCNJ18, combined with thyrotoxicosis, is considered to predispose certain TPP patients to recurrent attacks of hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Mutations in other channel genes associated with the TPP phenotype may be found in patients without KCNJ18 mutations.
Primary aldosteronism (PA) is the most frequent cause of secondary hypertension. Patients with PA exhibit hypertension, high plasma aldosterone levels, low plasma renin activity, and varying degrees of hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis. Aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma and adrenal hyperplasia are common causes of PA. Recently, mutations in KCNJ5, the gene that encodes an inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, Kir3.4, have been shown to be involved in both inherited and acquired PA. Gain-of-function effects of Kir3.4 mutations have been suggested to result in a loss of channel selectivity for potassium and increased sodium conductance, which induce the membrane depolarization responsible for aldosterone secretion and cell proliferation in the adrenal cortex72).
Osteopetrosis is an inherited metabolic bone disease that is characterized by an increased skeletal mass, which is caused by the impaired bone resorption that results from a lack or dysfunction of osteoclasts. Together, osteopetrosis and osteoporosis constitute major human skeletal pathologies caused by the imbalance between bone formation and resorption. Loss-of-function mutations in CLCN7, which encodes the voltage-gated chloride channel 7 (ClC-7), cause autosomal-dominant osteopetrosis type 2 and autosomal-recessive osteopetrosis type 4. Loss-of-function mutations in OSTM1, which codes for the auxiliary β subunit of the ClC-7 channel, give rise to autosomal-recessive osteopetrosis type 5. ClC-7 channels provide the chloride conductance required for extracellular acidification, an essential process for bone resorption by osteoclasts73). Studies have been performed to identify specific ClC-7 ligands that allow selective modulation of ClC-7 channel activity, which can be used to treat osteopetrosis (ClC-7 openers) and osteoporosis (ClC-7 blockers)74).
In the urinary system, there are well-characterized channelopathies affecting the renal tubular system (Table 4). With most of these channelopathies, abnormal endocrinological findings have been reported, but the etiologic origin places these diseases in this category.
Mutations in the renal epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), a heteromeric complex of 3 subunits (α, β, and γ), result in either hereditary hypotension or hypertension. ENaC is located in the apical membrane of epithelial cells predominantly in the kidney, colon, and lung, and the channel plays a major role in sodium reabsorption. Loss-of-function mutations in the α, β, and γ subunits of ENaC cause autosomal-recessive pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 that is characterized by marked hypotension, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, and failure to thrive during the neonatal period. Plasma renin and aldosterone levels are grossly elevated, reflecting a peripheral resistance75). This is a potentially lethal salt-losing disorder in neonates and infants, which persists into adulthood and thus requires lifelong treatment. By contrast, gain-of-function mutations in the β and γ subunits of ENaC result in Liddle syndrome, an autosomal-dominant disorder characterized by hypertension, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis. These mutations enhance ENaC activity by either increasing open probability or increasing channel number in the apical membrane. The overactivity of ENaC leads to excessive sodium reabsorption in the distal part of the renal tubule. Plasma renin and aldosterone levels are low76).
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI), which can be inherited or acquired and is caused by an impaired response of the kidney to the antidiuretic hormone (ADH), results in a decreased ability to concentrate urine, which leads to polyuria and compensatory polydipsia. Over 50 mutations in AQP2, the gene that encodes the water channel aquaporin 2 (AQP2), have been identified to cause autosomal-dominant or recessive forms of hereditary NDI. These mutations affect the function or membrane trafficking of the AQP2. Acquired causes of NDI include drugs, renal diseases, and electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia and hypercalcemia), which have been reported to induce either reduced expression of AQP2 or defective AQP2 trafficking to the apical plasma membrane77).
Bartter syndrome is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of salt-wasting tubulopathies characterized by metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, hyperreninemia and hyperaldosteronemia with varying severity. Bartter syndrome occurs in five types, among which types 2, 3, and 4 result from mutations in ion channel genes. Bartter syndrome type 2 is caused by loss-of-function mutations in KCNJ1 encoding an inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, Kir1.1. Kir1.1 is the apical renal outer medullary potassium channel that mediates potassium secretion from the renal epithelial cells into the tubular lumen, which is essential for sodium chloride reabsorption by the apical sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the Henle loop and which also produces the driving force for paracellular absorption of calcium and magnesium. Patients with Bartter syndrome type 2 uniquely present with initial transient hyperkalemia in the neonatal period, which is because Kir1.1 is involved in distal potassium secretion78). Bartter syndrome type 3 results from loss-of-function mutations in CLCNKB, which codes for kidney chloride channel B (ClC-Kb). On the basolateral membrane of the renal epithelial cells, chloride exits through at least two chloride channels, ClC-Ka (in the thick ascending limb) and ClC-Kb (in the thick ascending limb and distal convoluted tubule). These chloride channels require a β subunit, named barttin, for proper function and membrane localization. Bartter syndrome type 4A is caused by loss-of-function mutations in BSND, which encodes barttin. Heteromeric complexes of the chloride channels (ClC-Ka/ClC-Kb) and barttin are critical for renal salt reabsorption and potassium recycling in the inner ear. Therefore, Bartter syndrome type 4A caused by barttin dysfunction and Bartter syndrome type 4B caused by loss-of-function of both ClC-Ka and ClC-Kb show sensorineural deafness as well as renal salt-wasting tubulopathy78).
Familial hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia (HSH) is an autosomal-recessive disorder resulting from mutations in TRPM6, the gene that encodes the TRPM6 channel. Patients present with severe hypomagnesemia and hypocalcemia, which lead to generalized seizures and tetany shortly after birth, typically during the first month of life. If the disease is left untreated, most patients die or suffer severe neurological damage. Hypocalcemia is secondary to parathyroid failure and parathyroid hormone resistance due to chronic and severe magnesium deficiency. TRPM6 is a magnesium- and calcium-permeable cation channel that is predominantly expressed in intestinal epithelia and kidney tubules. Loss-of-function mutations in TRPM6, which inactivate TRPM6 channel function, have been reported to cause defective intestinal absorption of magnesium and abnormal renal loss in HSH79).
Gain-of-function mutations in TRPC6 channels have been identified to cause an autosomal-dominant form of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), FSGS type 2, which is characterized by proteinuria and progressive decline in renal function. TRPC6, which plays a crucial role in intracellular calcium signaling, is expressed in the glomerular epithelial cells (podocytes) and associates with nephrin and podocin, key components of the glomerular slit diaphragm. TRPC6 activity at the slit diaphragm is considered critical for regulating podocyte structure and function. Foot processes of podocytes and the slit diaphragm form an essential part of the glomerular permeability barrier. In FSGS, the loss of the permeability barrier's integrity results in proteinuria. Dominant gain-of-function effects of TRPC6 mutations have been demonstrated to increase channel activity and calcium influx by altering the channel's gating property or enhancing channel density in the membrane80). Intracellular calcium overload is thought to induce podocyte injury and dysfunction, disrupting the integrity of the permeability barrier.
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), the most common inherited kidney disease, results from mutations in polycystin 1 or 2. Polycystin 2 is the TRPP2 channel, a member of the TRP family, which mediates intracellular calcium signaling and regulates cell growth and differentiation. TRPP2 channels localize to the cilia of renal epithelial cells, where they function as mechano-sensors that allow calcium influx in response to changes in fluid flow. Mutations altering the subcellular localization and/or function of TRPP2 have been described in approximately 15% of patients with ADPKD (designated as PKD type 2). Most of these mutations have gain-of-function effects on TRPP2, which increase channel activity and calcium influx. Enhanced calcium influx in affected cells may lead to impaired cell growth and differentiation, which predispose to tubular cyst formation81). Although the precise mechanism by which increased calcium currents contribute to pathologic manifestations of this disease remains unknown, one of the clues may be found in a recent demonstration that impaired activity and abnormal subcellular localization of non-mutated TRPV4 channels contribute to renal cystogenesis in a rat model of autosomal-recessive polycystic kidney disease82).
Antibodies against ion channels and associated proteins expressed on the surface of neurons or muscle cells have been implicated in a variety of neurological pathologies ranging from myasthenia gravis (MG) to certain forms of encephalitis (Table 5). Typical paraneoplastic antibodies generally target intracellular antigens and are not likely pathogenic. However, antibodies responsible for autoimmune channelopathies, often arising under paraneoplastic conditions, directly affect the kinetics and/or membrane density of ion channels or damage cells expressing the channels, which accounts for the favorable response shown by most patients to immunotherapies. Autoimmune channelopathies have been increasingly found in all age group84).
MG is the prototype of autoimmune channelopathies. Most MG patients have autoantibodies against muscle nAChRs expressed on the postsynaptic membrane of muscle cells. These antibodies reduce functional nAChRs by direct block of function, complement-mediated damage to the cell membrane, and increased receptor endocytosis and degradation (a process referred to as antigenic modulation)85). Antibodies against MuSK, which is required for nAChR clustering, have been identified in a subset of MG patients without nAChR antibodies, reminiscent of the pathogenesis of certain cases of congenital myasthenic syndrome that is a clinically similar but distinct disorder (see p. 5).
Autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy (AAG, also called autoimmune autonomic neuropathy) is an acquired form of autonomic neuropathies in which autoantibodies bind to the α3 subunit of the neuronal nAChR located in ganglionic synapses of sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric nervous systems. Patients present with symptoms of diffuse autonomic failure, such as orthostatic hypotension, hypohidrosis, fixed and dilated pupils, dry eyes and mouth, urinary retention, and constipation or diarrhea. Ganglionic nAChRs mediate fast synaptic transmission in autonomic ganglia. Autoantibodies against ganglionic nAChRs impair cholinergic synaptic transmission, leading to the consequent symptoms of autonomic failure in AAG86).
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a presynaptic disorder that is characterized by proximal muscle weakness, autonomic dysfunction, and areflexia. LEMS results from an autoimmune process in which autoantibodies react against presynaptic P/Q type voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). Presynaptic VGCCs are involved in the depolarization-induced calcium influx that causes neurotransmitter release from nerve terminals. Autoantibodies against VGCCs are known to deplete the channels, reduce calcium influx, and cause a reduction of acetylcholine release. Approximately 50% of patients with LEMS have an underlying malignancy, such as small cell lung cancer (SCLC) in which SCLC cells express VGCCs on their surface, suggesting a cross reactivity of antibodies with presynaptic VGCCs. Accumulating evidence indicates that VGCCs also play a pathogenic role in certain patients with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration associated with SCLC87).
Neuromyotonia (NMT) is a form of peripheral nerve hyperexcitability that is characterized by muscle fasciculations, cramps, pseudomyotonia (slow relaxation following muscle contraction), hyperhidrosis, and variable paraesthesias. NMT can be inherited or acquired. Evidence of a channelopathy can be found in one type of acquired NMT, called Isaac syndrome, in which autoantibodies are directed against α-dendrotoxin (α-DTX)-sensitive voltage-gated potassium channel (VGKC) complexes expressed in motor and sensory nerves. The α-DTX-sensitive VGKC complex consists of a VGKC (a Kv1 tetramer with auxiliary β subunits) and associated proteins, such as leucine-rich glioma inactivated protein 1 (LGI1), contactin-associated protein 2 (CASPR2), and contactin-288). VGKCs help repolarize depolarized cells and prevent repetitive discharges. Autoantibodies against components of VGKC complexes result in loss of functional VGKCs, reduced outward potassium currents, and spontaneous repetitive firing of action potentials, which leads to peripheral nerve hyperexcitability and enhanced muscle contraction89). A combination of NMT and CNS manifestations (e.g., insomnia, confusion, hallucination, delirium, and amnesia) can be detected in Morvan syndrome, in which most patients have VGKC complex antibodies, predominantly against CASPR284). Cramp-fasciculation syndrome is another phenotype of peripheral nerve hyperexcitability that can be caused by VGKC complex antibodies, and this disease is characterized by the occurrence of severe muscle ache, cramps, and twitching in otherwise healthy individuals90).
Limbic encephalitis (LE) is the most common CNS syndrome associated with increased levels of VGKC complex antibodies. LE is characterized by acute or subacute amnesia, confusion, seizures, and personality change or psychosis, with a high signal in the medial temporal lobes on MRI (indicating swelling and/or inflammation). Autoantibodies against ion channels other than VGKC have also been reported in LE patients, including antibodies against α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR), GABAB receptor, and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR)88). LE can arise as a paraneoplastic syndrome. Most LE patients have antibodies against the LGI1 component of VGKC complexes and do not usually have a tumor, whereas a small proportion of LE patients have CASPR2 antibodies and display an increased incidence of thymomas84).
Anti-NMDAR encephalitis is characterized by sequential clinical manifestations that proceed from psychosis, amnesia, confusion, dysphasia, and seizures into dyskinesias, and autonomic and breathing instability, typically requiring management in the intensive care unit. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis is recognized as the most prevalent antibody-associated encephalitis and the second most common immune-mediated encephalitis after acute disseminated encephalomyelitis91). A substantial proportion of patients with this disease are children and young adults with or without an associated tumor. The frequency of underlying tumors (usually ovarian teratoma) depends on age and sex and is lower in younger patients. Patients have antibodies against the NMDAR in blood and cerebrospinal fluid and exhibit high intrathecal synthesis of the antibodies. The NMDAR, a non-selective cation channel, is a glutamate receptor that modulates excitatory neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity in the CNS and plays a critical role in memory, learning, mood, and behavior. Anti-NMDAR antibodies have been demonstrated to lower the membrane density of postsynaptic NMDARs by enhancing receptor internalization and degradation, which can lead to reduced excitability of GABAergic neurons expressing NMDARs at high levels and to the deregulation of excitatory pathways91). In more than 50% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), autoantibodies that react with NMDARs also cause neurological and psychological manifestations, which are often described as neuropsychiatric SLE92).
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) is a severe inflammatory demyelinating disorder that primarily affects the optic nerves and spinal cord. Patients develop symptoms of optic neuritis and transverse myelitis, including blindness, paralysis, sensory defects, and bladder dysfunction, with frequent relapse and increasing disability. Most patients have autoantibodies against aquaporin-4 (AQP4), the main water channel in the CNS that is predominantly expressed on astrocytes93). Astrocytes perform many important functions in the CNS, including the regulation of neurotransmission, immune responses, blood flow, and energy metabolism, and the maintenance of the blood-brain barrier (BBB)94). Autoantibodies against AQP4 have been suggested to induce complement-mediated astrocyte damage, local inflammatory reactions, and BBB disruption. These initial reactions are predicted to lead to oligodendrocyte injury, demyelination, neuronal damage, and the subsequent clinical manifestations of NMO93). Alternative underlying mechanisms for the disorder have also been proposed, including antibody-mediated internalization of AQP4s and glutamate transporters, and antibody-induced activation of effector cells, such as natural-killer cells, which cause cytotoxicity in astrocytes95).
The list of channelopathies is expanding so rapidly because of recent advances in our understanding of the role of ion channels in human physiology and pathophysiology. Emerging topics regarding potential entries to the list include certain types of cancer96), leukemia97), psychiatric disorders98), gastrointestinal diseases3), and additional nervous system disorders99,100). As for disease mechanisms, pathogenic alterations of the expression, localization, and/or function of non-mutated ion channels or proteins that are not ion channels may be found in many channelopathies, as exemplified in familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis and congenital myasthenic syndrome. These mechanisms may provide new targets and approaches for devising novel therapeutic strategies.
Gap junctions are specialized plasma membrane domains in which arrays of channels mediate the passage of ions and small molecules between cells. Although gap junction channels have not yet been classified into specific channel families described in this review, they share ion channel properties and modulate both electrical and metabolic intercellular communication. As predicted, dysfunction of gap junction channels causes a wide range of diseases, including blindness, deafness, hereditary spastic paraplegia, cardiac arrhythmia, X-linked dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, certain integumentary disorders, and craniofacial, dental, and skeletal anomalies. Ongoing research on gap junction physiology may offer novel insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms of channelopathies.
Although most channelopathies affect only one or a few organ systems as described herein, this general theme may not be just because the associated channel subtype has a tissue/organ-specific expression pattern. For example, AQP4 and TRPC6, which are involved in NMO and FSGS type 2, respectively, are also expressed in other tissues or organs, such as the kidney (AQP4) and smooth muscle (TRPC6), in which they do not manifest pathological phenotypes. It is possible that a milieu or associated protein(s) make ion channels at a specific location exhibit increased susceptibility to a pathological condition. Better understanding of the structure and function of ion channels and their related proteins should elucidate the mechanisms that can provide molecular targets for intervention in the pathophysiological process of diseases in this rapidly growing field of medicine.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 12th Seokcheon Research Award funded by the Korean Pediatric Society. The author thanks Moon-Yong Park for assistance with illustrations.
References
2. Valverde MA, Cantero-Recasens G, Garcia-Elias A, Jung C, Carreras-Sureda A, Vicente R. Ion channels in asthma. J Biol Chem 2011;286:32877–32882.



3. Saito YA, Strege PR, Tester DJ, Locke GR III, Talley NJ, Bernard CE, et al. Sodium channel mutation in the irritable bowel syndrome: Evidence for an ion channelopathy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2009;296:G211–G218.


4. Hille B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. 3rd ed. Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates, 2001.
5. Coetzee WA, Amarillo Y, Chiu J, Chow A, Lau D, McCormack T, et al. Molecular diversity of K+ channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999;868:233–285.


6. Berg AT, Berkovic SF, Brodie MJ, Buchhalter J, Cross JH, van Emde Boas W, et al. Revised terminology and concepts for organization of seizures and epilepsies: report of the ILAE Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005-2009. Epilepsia 2010;51:676–685.


7. Lehmann-Horn F, Jurkat-Rott K. Voltage-gated ion channels and hereditary disease. Physiol Rev 1999;79:1317–1372.


8. Song YW, Kim SJ, Heo TH, Kim MH, Kim JB. Normokalemic periodic paralysis is not a distinct disease. Muscle Nerve 2012;46:914–916.


9. Tricarico D, Camerino DC. Recent advances in the pathogenesis and drug action in periodic paralyses and related channelopathies. Front Pharmacol 2011;2:8


10. Kim JB, Kim MH, Lee SJ, Kim DJ, Lee BC. The genotype and clinical phenotype of Korean patients with familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis. J Korean Med Sci 2007;22:946–951.



11. Kil TH, Kim JB. Severe respiratory phenotype caused by a de novo Arg528Gly mutation in the CACNA1S gene in a patient with hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2010;14:278–278.


12. Levitt LP, Rose LI, Dawson DM. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis with arrhythmia. N Engl J Med 1972;286:253–254.


13. Wu F, Mi W, Hernández-Ochoa EO, Burns DK, Fu Y, Gray HF, et al. A calcium channel mutant mouse model of hypokalemic periodic paralysis. J Clin Invest 2012;122:4580–4591.



14. Jurkat-Rott K, Weber MA, Fauler M, Guo XH, Holzherr BD, Paczulla A, et al. K+-dependent paradoxical membrane depolarization and Na+ overload, major and reversible contributors to weakness by ion channel leaks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:4036–4041.



15. Tricarico D, Mele A, Liss B, Ashcroft FM, Lundquist AL, Desai RR, et al. Reduced expression of Kir6.2/SUR2A subunits explains KATP deficiency in K+-depleted rats. Neuromuscul Disord 2008;18:74–80.


16. Kim SJ, Lee YJ, Kim JB. Reduced expression and abnormal localization of the KATP channel subunit SUR2A in patients with familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010;391:974–978.


17. Puwanant A, Ruff RL. INa and IKir are reduced in Type 1 hypokalemic and thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Muscle Nerve 2010;42:315–327.


18. Ballester LY, Benson DW, Wong B, Law IH, Mathews KD, Vanoye CG, et al. Trafficking-competent and trafficking-defective KCNJ2 mutations in Andersen syndrome. Hum Mutat 2006;27:388

19. Engel AG. Current status of the congenital myasthenic syndromes. Neuromuscul Disord 2012;22:99–111.


20. Scheffer IE, Zhang YH, Jansen FE, Dibbens L. Dravet syndrome or genetic (generalized) epilepsy with febrile seizures plus? Brain Dev 2009;31:394–400.


21. Huang X, Tian M, Hernandez CC, Hu N, Macdonald RL. The GABRG2 nonsense mutation, Q40X, associated with Dravet syndrome activated NMD and generated a truncated subunit that was partially rescued by aminoglycoside-induced stop codon read-through. Neurobiol Dis 2012;48:115–123.



22. Maljevic S, Krampfl K, Cobilanschi J, Tilgen N, Beyer S, Weber YG, et al. A mutation in the GABAA receptor α1-subunit is associated with absence epilepsy. Ann Neurol 2006;59:983–987.


23. Hernandez CC, Gurba KN, Hu N, Macdonald RL. The GABRA6 mutation, R46W, associated with childhood absence epilepsy, alters α6β2γ2 and α6β2δ GABAA receptor channel gating and expression. J Physiol 2011;589:5857–5878.



24. Tanaka M, Olsen RW, Medina MT, Schwartz E, Alonso ME, Duron RM, et al. Hyperglycosylation and reduced GABA currents of mutated GABRB3 polypeptide in remitting childhood absence epilepsy. Am J Hum Genet 2008;82:1249–1261.



25. Tian M, Macdonald RL. The intronic GABRG2 mutation, IVS6+2T→G, associated with childhood absence epilepsy altered subunit mRNA intron splicing, activated nonsense-mediated decay, and produced a stable truncated γ2 subunit. J Neurosci 2012;32:5937–5952.



26. Tottene A, Urbani A, Pietrobon D. Role of different voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in cortical spreading depression: specific requirement of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. Channels (Austin) 2011;5:110–114.


27. Rajakulendran S, Graves TD, Labrum RW, Kotzadimitriou D, Eunson L, Davis MB, et al. Genetic and functional characterisation of the P/Q calcium channel in episodic ataxia with epilepsy. J Physiol 2010;588:1905–1913.



28. Unno T, Wakamori M, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Ishikawa K, Kubota H, et al. Development of Purkinje cell degeneration in a knockin mouse model reveals lysosomal involvement in the pathogenesis of SCA6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:17693–17698.



29. Heron SE, Smith KR, Bahlo M, Nobili L, Kahana E, Licchetta L, et al. Missense mutations in the sodium-gated potassium channel gene KCNT1 cause severe autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy. Nat Genet 2012;44:1188–1190.


30. Rodrigues-Pinguet N, Jia L, Li M, Figl A, Klaassen A, Truong A, et al. Five ADNFLE mutations reduce the Ca2+ dependence of the mammalian α4β2 acetylcholine response. J Physiol 2003;550:11–26.



31. Chung SK, Vanbellinghen JF, Mullins JG, Robinson A, Hantke J, Hammond CL, et al. Pathophysiological mechanisms of dominant and recessive GLRA1 mutations in hyperekplexia. J Neurosci 2010;30:9612–9620.



32. Bockenhauer D, Feather S, Stanescu HC, Bandulik S, Zdebik AA, Reichold M, et al. Epilepsy, ataxia, sensorineural deafness, tubulopathy, and KCNJ10 mutations. N Engl J Med 2009;360:1960–1970.



33. Scholl UI, Choi M, Liu T, Ramaekers VT, Häusler MG, Grimmer J, et al. Seizures, sensorineural deafness, ataxia, mental retardation, and electrolyte imbalance (SeSAME syndrome) caused by mutations in KCNJ10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:5842–5847.



34. Kremeyer B, Lopera F, Cox JJ, Momin A, Rugiero F, Marsh S, et al. A gain-of-function mutation in TRPA1 causes familial episodic pain syndrome. Neuron 2010;66:671–680.



35. Cox JJ, Reimann F, Nicholas AK, Thornton G, Roberts E, Springell K, et al. An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain. Nature 2006;444:894–898.



37. Curcio-Morelli C, Zhang P, Venugopal B, Charles FA, Browning MF, Cantiello HF, et al. Functional multimerization of mucolipin channel proteins. J Cell Physiol 2010;222:328–335.


38. Amin AS, Tan HL, Wilde AA. Cardiac ion channels in health and disease. Heart Rhythm 2010;7:117–126.


39. Behr ER, Dalageorgou C, Christiansen M, Syrris P, Hughes S, Tome Esteban MT, et al. Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome: familial evaluation identifies inheritable heart disease in the majority of families. Eur Heart J 2008;29:1670–1680.


40. Wilders R. Cardiac ion channelopathies and the sudden infant death syndrome. ISRN Cardiol 2012;2012:846171


41. Campuzano O, Beltrán-Alvarez P, Iglesias A, Scornik F, Pérez G, Brugada R. Genetics and cardiac channelopathies. Genet Med 2010;12:260–267.


42. Yang Y, Yang Y, Liang B, Liu J, Li J, Grunnet M, et al. Identification of a Kir3.4 mutation in congenital long QT syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2010;86:872–880.



43. Templin C, Ghadri JR, Rougier JS, Baumer A, Kaplan V, Albesa M, et al. Identification of a novel loss-of-function calcium channel gene mutation in short QT syndrome (SQTS6). Eur Heart J 2011;32:1077–1088.



44. Wilde AA, Brugada R. Phenotypical manifestations of mutations in the genes encoding subunits of the cardiac sodium channel. Circ Res 2011;108:884–897.


45. Olson TM, Alekseev AE, Liu XK, Park S, Zingman LV, Bienengraeber M, et al. Kv1.5 channelopathy due to KCNA5 loss-of-function mutation causes human atrial fibrillation. Hum Mol Genet 2006;15:2185–2191.


46. Biel M, Wahl-Schott C, Michalakis S, Zong X. Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels: from genes to function. Physiol Rev 2009;89:847–885.


47. Duhme N, Schweizer PA, Thomas D, Becker R, Schröter J, Barends TR, et al. Altered HCN4 channel C-linker interaction is associated with familial tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome and atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 2013;34:2768–2775.


48. Ueda K, Hirano Y, Higashiuesato Y, Aizawa Y, Hayashi T, Inagaki N, et al. Role of HCN4 channel in preventing ventricular arrhythmia. J Hum Genet 2009;54:115–121.


49. Postma AV, Denjoy I, Kamblock J, Alders M, Lupoglazoff JM, Vaksmann G, et al. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: RYR2 mutations, bradycardia, and follow up of the patients. J Med Genet 2005;42:863–870.



50. van der Werf C, Wilde AA. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: from bench to bedside. Heart 2013;99:497–504.


52. Ratjen FA. Cystic fibrosis: pathogenesis and future treatment strategies. Respir Care 2009;54:595–605.


53. Sweeney M, McDaniel SS, Platoshyn O, Zhang S, Yu Y, Lapp BR, et al. Role of capacitative Ca2+ entry in bronchial contraction and remodeling. J Appl Physiol 2002;92:1594–1602.


55. Xiao JH, Zheng YM, Liao B, Wang YX. Functional role of canonical transient receptor potential 1 and canonical transient receptor potential 3 in normal and asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2010;43:17–25.


56. Sel S, Rost BR, Yildirim AO, Sel B, Kalwa H, Fehrenbach H, et al. Loss of classical transient receptor potential 6 channel reduces allergic airway response. Clin Exp Allergy 2008;38:1548–1558.


57. Vennekens R, Olausson J, Meissner M, Bloch W, Mathar I, Philipp SE, et al. Increased IgE-dependent mast cell activation and anaphylactic responses in mice lacking the calcium-activated nonselective cation channel TRPM4. Nat Immunol 2007;8:312–320.


58. Lee LY, Gu Q. Role of TRPV1 in inflammation-induced airway hypersensitivity. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2009;9:243–249.



59. Caceres AI, Brackmann M, Elia MD, Bessac BF, del Camino D, D'Amours M. . A sensory neuronal ion channel essential for airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:9099–9104.



60. Akhabir L, Sandford AJ. Genome-wide association studies for discovery of genes involved in asthma. Respirology 2011;16:396–406.


61. Mahn K, Hirst SJ, Ying S, Holt MR, Lavender P, Ojo OO, et al. Diminished sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) expression contributes to airway remodeling in bronchial asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:10775–10780.



62. Webster R, Maxwell S, Spearman H, Tai K, Beckstein O, Sansom M, et al. A novel congenital myasthenic syndrome due to decreased acetylcholine receptor ion-channel conductance. Brain 2012;135:1070–1080.


63. Pyo JY, Joh DH, Park JS, Lee SJ, Lee H, Kim W, et al. Ventricular tachyarrhythmias in a patient with Andersen-Tawil syndrome. Korean Circ J 2013;43:62–65.



64. Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 1989;54:87–143.


65. Vivaudou M, Moreau CJ, Terzic A. Structure and function of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Kew J, Davies C, editors. Ion channels: from structure to function. 1st ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009;:454–473.
66. Babenko AP, Polak M, Cavé H, Busiah K, Czernichow P, Scharfmann R, et al. Activating mutations in the ABCC8 gene in neonatal diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2006;355:456–466.


67. Kong JH, Kim JB. Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus caused by a de novo ABCC8 gene mutation. Korean J Pediatr 2011;54:179–182.



68. Koster JC, Permutt MA, Nichols CG. Diabetes and insulin secretion: the ATP-sensitive K+ channel (KATP) connection. Diabetes 2005;54:3065–3072.


69. Ashcroft FM. ATP-sensitive potassium channelopathies: focus on insulin secretion. J Clin Invest 2005;115:2047–2058.



70. Ryan DP, da Silva MR, Soong TW, Fontaine B, Donaldson MR, Kung AW, et al. Mutations in potassium channel Kir2.6 cause susceptibility to thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Cell 2010;140:88–98.



71. Ruff RL. Insulin acts in hypokalemic periodic paralysis by reducing inward rectifier K+ current. Neurology 1999;53:1556–1563.


72. Scholl UI, Nelson-Williams C, Yue P, Grekin R, Wyatt RJ, Dillon MJ, et al. Hypertension with or without adrenal hyperplasia due to different inherited mutations in the potassium channel KCNJ5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:2533–2538.



73. Del Fattore A, Cappariello A, Teti A. Genetics, pathogenesis and complications of osteopetrosis. Bone 2008;42:19–29.


74. Schaller S, Henriksen K, Sveigaard C, Heegaard AM, Hélix N, Stahlhut M, et al. The chloride channel inhibitor NS3736 [corrected] prevents bone resorption in ovariectomized rats without changing bone formation. J Bone Miner Res 2004;19:1144–1153.


75. Riepe FG. Clinical and molecular features of type 1 pseudohypoaldosteronism. Horm Res 2009;72:1–9.


76. Butterworth MB. Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by membrane trafficking. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010;1802:1166–1177.



77. Moeller HB, Rittig S, Fenton RA. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: essential insights into the molecular background and potential therapies for treatment. Endocr Rev 2013;34:278–301.



78. Kleta R, Bockenhauer D. Bartter syndromes and other salt-losing tubulopathies. Nephron Physiol 2006;104:p73–p80.


79. Schlingmann KP, Waldegger S, Konrad M, Chubanov V, Gudermann T. TRPM6 and TRPM7-Gatekeepers of human magnesium metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007;1772:813–821.


80. Dryer SE, Reiser J. TRPC6 channels and their binding partners in podocytes: role in glomerular filtration and pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2010;299:F689–F701.



81. Miyakawa A, Ibarra C, Malmersjö S, Aperia A, Wiklund P, Uhlén P. Intracellular calcium release modulates polycystin-2 trafficking. BMC Nephrol 2013;14:34



82. Zaika O, Mamenko M, Berrout J, Boukelmoune N, O'Neil RG, Pochynyuk O. TRPV4 dysfunction promotes renal cystogenesis in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2013;24:604–616.



83. Kleopa KA. Autoimmune channelopathies of the nervous system. Curr Neuropharmacol 2011;9:458–467.



85. Verschuuren JJ, Huijbers MG, Plomp JJ, Niks EH, Molenaar PC, Martinez-Martinez P, et al. Pathophysiology of myasthenia gravis with antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor, muscle-specific kinase and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4. Autoimmun Rev 2013;12:918–923.


86. Winston N, Vernino S. Recent advances in autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy. Curr Opin Neurol 2010;23:514–518.


87. Titulaer MJ, Lang B, Verschuuren J. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: from clinical characteristics to therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:1098–1107.


88. Vincent A, Bien CG, Irani SR, Waters P. Autoantibodies associated with diseases of the CNS: new developments and future challenges. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:759–772.


89. Tomimitsu H, Arimura K, Nagado T, Watanabe O, Otsuka R, Kurono A, et al. Mechanism of action of voltage-gated K+ channel antibodies in acquired neuromyotonia. Ann Neurol 2004;56:440–444.


90. Liewluck T, Klein CJ, Jones LK Jr. Cramp-fasciculation syndrome in patients with and without neural autoantibodies. Muscle Nerve 2014;49:351–356.


91. Dalmau J, Lancaster E, Martinez-Hernandez E, Rosenfeld MR, Balice-Gordon R. Clinical experience and laboratory investigations in patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:63–74.



92. Lauvsnes MB, Omdal R. Systemic lupus erythematosus, the brain, and anti-NR2 antibodies. J Neurol 2012;259:622–629.


93. Ratelade J, Verkman AS. Neuromyelitis optica: aquaporin-4 based pathogenesis mechanisms and new therapies. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2012;44:1519–1530.



94. Jensen CJ, Massie A, De Keyser J. Immune players in the CNS: the astrocyte. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2013;8:824–839.


95. Saikali P, Cayrol R, Vincent T. Anti-aquaporin-4 auto-antibodies orchestrate the pathogenesis in neuromyelitis optica. Autoimmun Rev 2009;9:132–135.


96. Pedersen SF, Stock C. Ion channels and transporters in cancer: pathophysiology, regulation, and clinical potential. Cancer Res 2013;73:1658–1661.


97. Morelli MB, Liberati S, Amantini C, Nabissi M, Santoni M, Farfariello V, et al. Expression and function of the transient receptor potential ion channel family in the hematologic malignancies. Curr Mol Pharmacol 2013;7 08 [Epub].

98. Imbrici P, Camerino DC, Tricarico D. Major channels involved in neuropsychiatric disorders and therapeutic perspectives. Front Genet 2013;4:76


Fig. 3
Diagram showing a clinical spectrum of muscle channelopathies ranging from myotonia to flaccid paralysis.

Fig. 4
Major ionic currents that contribute to the cardiac myocyte action potential in relation to the surface electrocardiogram. Ito1, transient outward potassium current; ICa,L, L-type inward calcium current; IKr, rapid delayed-rectifier potassium current; IKs, slow delayed-rectifier potassium current; IK1, inwardly-rectifying potassium current.
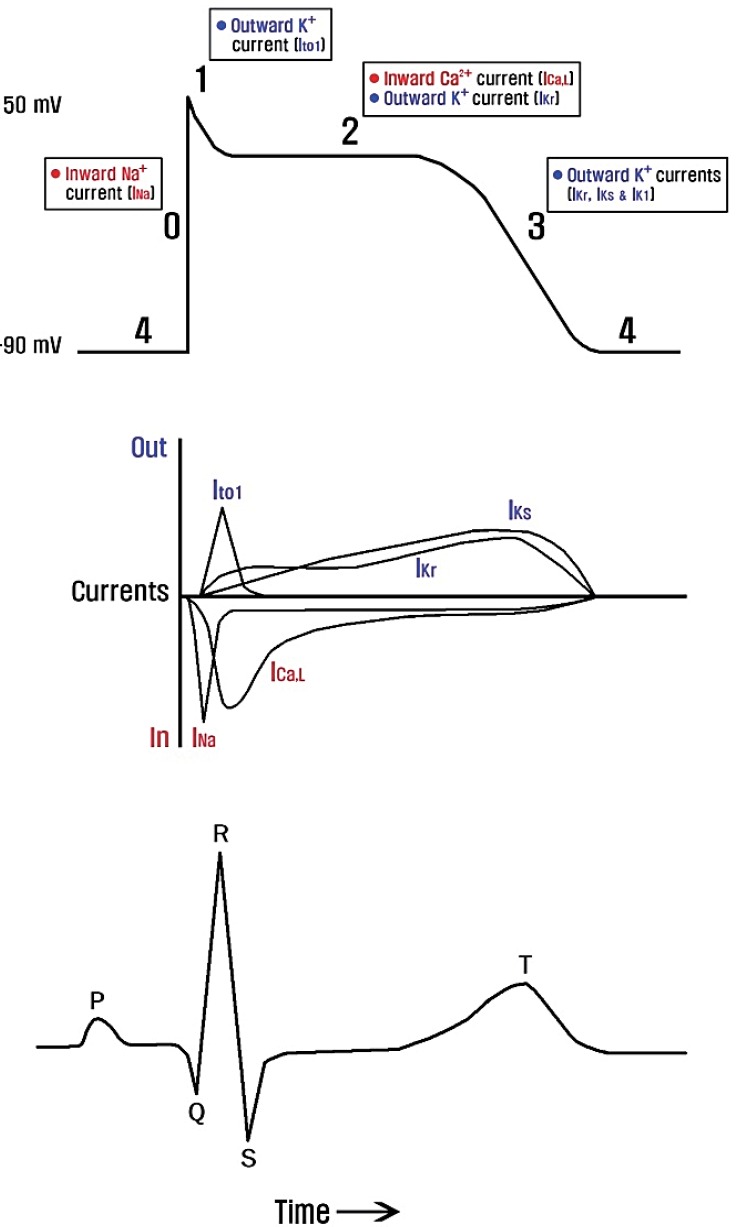
Fig. 5
Diagram illustrating the relationship between KATP channel activity and insulin secretory disorders.
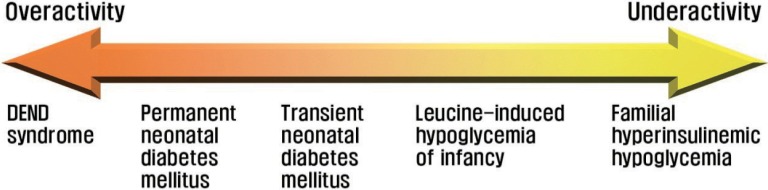
Table 1
Nervous system channelopathies
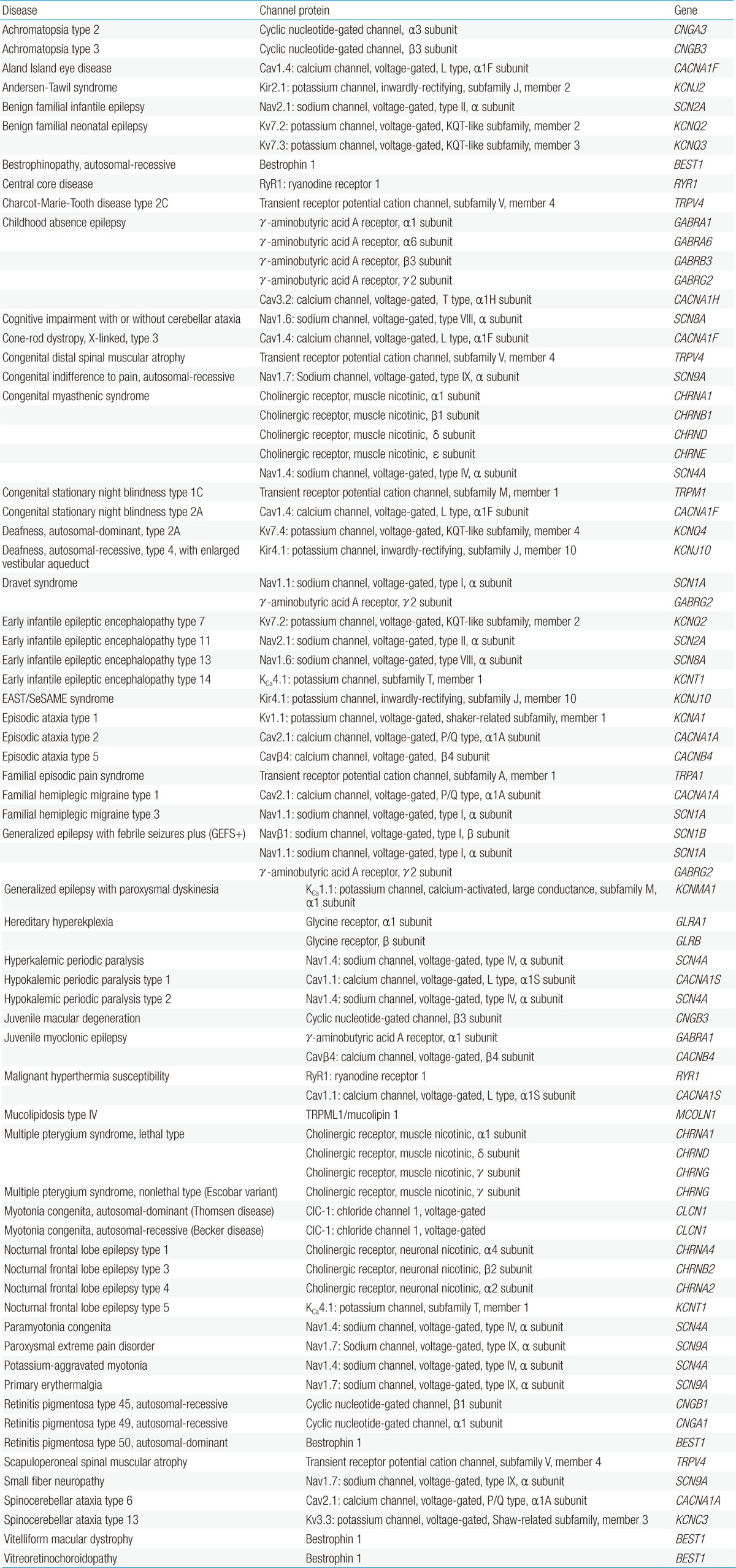
Nomenclature is based on the OMIM and the current report of the International League Against Epilepsy Commission6).








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


