|
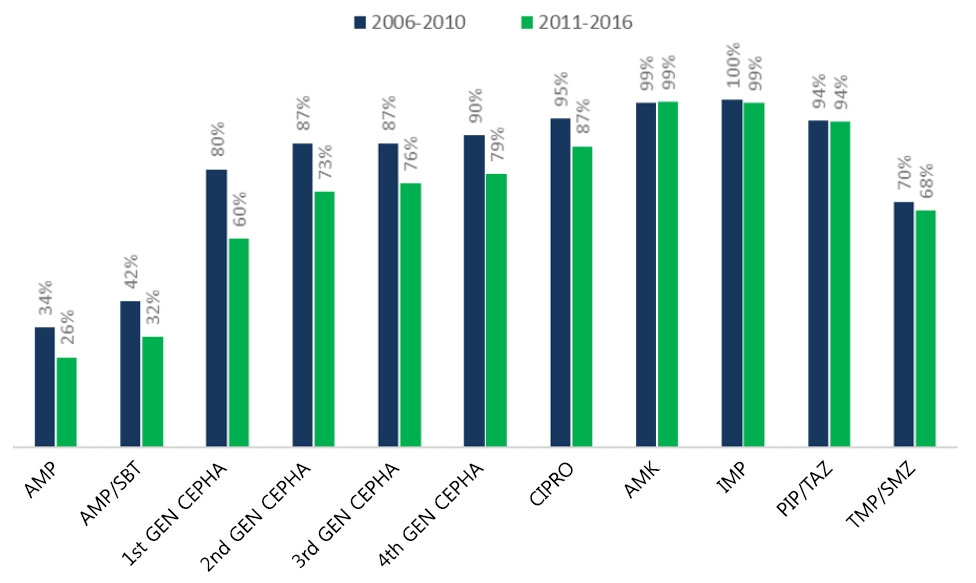
Question: How has the antibiotic susceptibility of urinary pathogens changed and what does it imply?
Finding: A yearly increase in multidrug-resistant and extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)–producing pathogens was observed. A higher recurrence rate was observed in cases of febrile urinary tract infection caused by ESBL producers in patients with underlying vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
Meaning: The initial empirical antibiotic should reflect the changing susceptibility patterns and underlying VUR status. |


