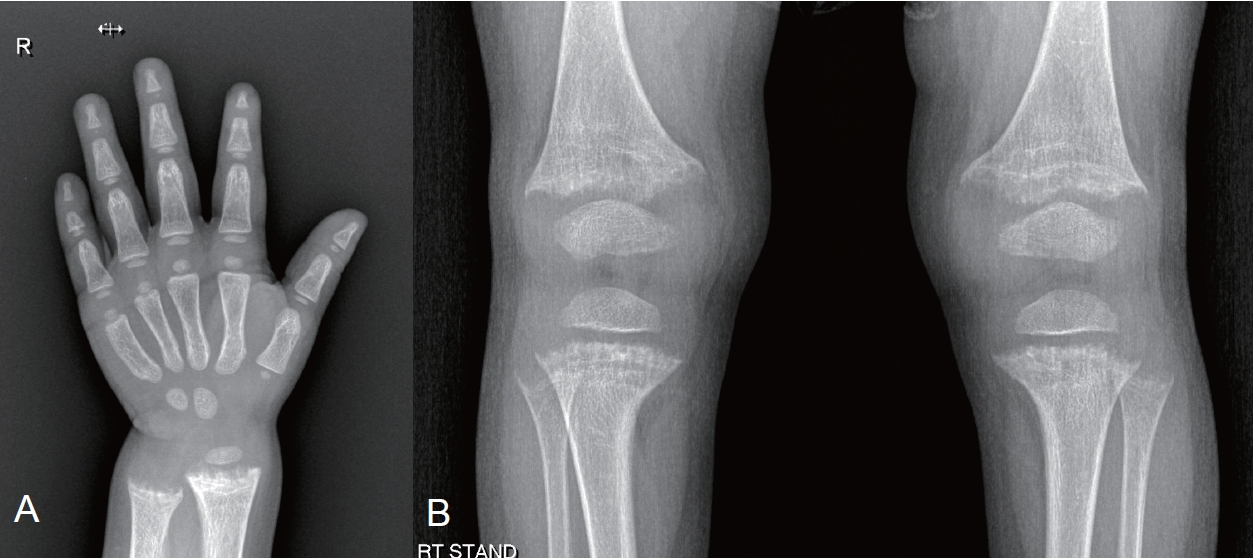
|
· X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), the most common cause of hypophosphatemic rickets, affects 1/20,000 people.
· XLH is caused by a loss-of-function mutation of the PHEX gene.
· Its main pathogenesis is elevated fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) level.
· Burosumab, an FGF23 inhibitor, was developed in the early 2000s.
· Burosumab was approved in Korea in 2020 for XLH patients aged 1+ years with radiographic evidence of bone disease. |


