Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 54(2); 2011 |
Abstract
Vitamin D is present in two forms, ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) produced by plants and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) produced by animal tissues or by the action of ultraviolet light on 7-dehydrocholesterol in human skin. Both forms of vitamin D are biologically inactive pro-hormones that must undergo sequential hydroxylations in the liver and the kidney before they can bind to and activate the vitamin D receptor. The hormonally active form of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D], plays an essential role in calcium and phosphate metabolism, bone growth, and cellular differentiation. Renal synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D from its endogenous precursor, 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD), is the rate-limiting and is catalyzed by the 1╬▒-hydroxylase. Vitamin D dependent rickets type I (VDDR-I), also referred to as vitamin D 1╬▒-hydroxylase deficiency or pseudovitamin D deficiency rickets, is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized clinically by hypotonia, muscle weakness, growth failure, hypocalcemic seizures in early infancy, and radiographic findings of rickets. Characteristic laboratory features are hypocalcemia, increased serum concentrations of parathyroid hormone (PTH), and low or undetectable serum concentrations of 1,25(OH)2D despite normal or increased concentrations of 25OHD. Recent advances have showed in the cloning of the human 1╬▒-hydroxylase and revealed mutations in its gene that cause VDDR-I. This review presents the biology of vitamin D, and 1╬▒-hydroxylase mutations with clinical findings.
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D] is one of the principle hormonal regulators of calcium and phosphorus metabolism in the body and is critically important for normal growth and mineralization of bone. Renal synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D from its endogenous precursor, 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD), is the rate-limiting, hormonally regulated step in the bioactivation of vitamin D and is catalyzed by the mitochondrial cytochrome P450 enzyme, 25OHD-1╬▒-hydroxylase (1╬▒-hydroxylase, P450c1╬▒)1, 2). Vitamin D dependent rickets type I (VDDR-I), also referred to as vitamin D 1╬▒-hydroxylase deficiency or pseudovitamin D deficiency rickets, is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations of the 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene3-5). Characteristic laboratory features are hypocalcemia, increased serum concentrations of parathyroid hormone (PTH), and low or undetectable serum concentrations of 1,25(OH)2D despite normal or increased concentrations of 25OHD. Physiological doses of 1╬▒ (OH) vitamin D3 (1╬▒-OHD) or 1,25(OH)2D3 induce remission of the clinical and laboratory abnormalities3). This review presents the biology of vitamin D, and 1╬▒-hydroxylase mutations with clinical findings.
Vitamin D exists as either ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) produced by plants, or cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) produced by animal tissues and by the action of ultraviolet radiation (290-310 nm) on 7-dehydrochoesterol in human skin6, 7). Vitamin D2 differs from D3 only in having a 22, 23 double bond and having an additional methyl group attached to carbon 24. Both forms of vitamin D are biologically inactive pro-hormones that must undergo successive hydroxylations at carbons 25 and 1 before they can bind to and activate the vitamin D receptor. The 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D occurs primarily in the liver, catalyzed by the mitochondrial cytochrome P450 enzyme, P450c25. The activity of the hepatic 25-hydroxylase is not under tight physiologic regulation, and thus the circulating concentration of 25OHD is determined primarily by one's dietary intake of vitamin D and amount of sunlight exposure. Although 25OHD is the most abundant form of vitamin D in the blood, it has minimal capacity to bind to the vitamin D receptor and elicit a biological response8). The active form of vitamin D, 1,25(OH)2D, is produced in the proximal renal tubule by the 1╬▒-hydroxylation of 25OHD. The circulating concentration of 1,25(OH)2D primarily reflects its synthesis in the kidney. The 1╬▒-hydroxylase is the rate-limiting step in the bioactivation of vitamin D, and enzyme activity in the kidney is tightly regulated by PTH, calcium, phosphorus, and 1,25(OH)2D itself9, 10).
The human 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene has been cloned and mapped to the chromosome 12q13.1-q13.3 at the same locus11-14) as the autosomal recessive VDDR-I. It is approximately 5 Kb and is composed of nine exons13). Furthermore, several laboratories have characterized mutations in the 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene in patients with VDDR-I14-23). VDDR-I is characterized by failure to thrive, muscle weakness, hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and the bony changes of rickets3). The hallmarks of the diseases are greatly reduced serum concentration of 1,25(OH)2D despite normal or increased concentrations of 25OHD, and the reversal of clinical and laboratory abnormalities by administration of physiologic amounts of 1,25(OH)2D3-5). To date, a total of 36 mutations in the 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene have been identified in patients with VDDR-I22). All but one of the frameshift and premature translation-arrest mutations described eliminate the heme-binding site of P450c1╬▒, hence the resultant protein cannot have 1╬▒-hydroxylase activity. Two mutations described in 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene are relatively more common than the others. Deletion of guanine 958 (958delG), as numbered from the gene's transcriptional start site13), was found on 20 French Canadian alleles16, 17); microsatellite haplotype analysis showed that these arose from a single founder17, 24). A 7 nucleotide insertion in exon 8 was found in 14 affected alleles16-18); these arose from various ethnic groups with different microsatellite haplotypes17).
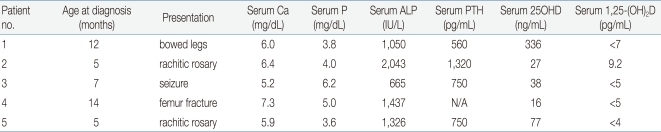
So far, 5 Korean patients with VDDR-I have been studied at a molecular genetic level and 3 distinct mutations have been identified22). The clinical data for these patients were summarized in Table 1. Patient 1 presented with bowing of the legs at 12 months of age. He had a prominent forehead with craniotabes, rachitic rosary, and genu varus. Laboratory data revealed hypocalcemia, high serum alkaline phosphatase and PTH concentrations, and radiographic features of rickets. Treatment with 1a-OHD resulted in improvement of clinical, radiographic, and laboratory abnormalities. Patient 2 developed recurrent seizures at 5 months of age. At 15 months of age she was found to have kyphosis, prominent rachitic rosary, a widely open anterior fontanel, varus deformity of the elbow, and x-ray findings of severe rickets with fractures of both fibulae. Laboratory data revealed hypocalcemia, high serum alkaline phosphatase and PTH concentrations, and low 1,25(OH)2D concentration. She was successfully treated with 1a-OHD. Patient 3 presented with a hypocalcemic seizure at 5 months of age. At 25 months of age he was found to have a prominent forehead, rachitic rosary, and bowing of the legs. Laboratory evaluation showed hypocalcemia, high serum alkaline phosphatase activity, and low 1,25(OH)2D concentration. Radiographs revealed features of severe rickets. She responded well to 1a-OHD. Patient 4 presented with a femur fracture after minor trauma at the age of 14 months. He had hypocalcemia, high alkaline phosphatase activity, low 1,25(OH)2D concentration, and rachitic changes on x-ray. Administration of 1a-OHD resulted in normalization of clinical, radiographic, and laboratory abnormalities. Patient 5 presented with a hypocalcemic seizure at 5 months of age and was treated with calcium and vitamin D. At 17 months of age he was noted to have rachitic rosary, prominent forehead, and enlargement of wrists and ankles. Laboratory data revealed hypocalcemia, high serum alkaline phosphatase concentration, and rachitic changes on x-ray. Serum concentration of 25OHD was above the normal range whereas that of 1, 25-(OH)2D was not detectable. He responded well to administration of 1╬▒-OHD.
On molecular genetic studies, patient 1 was homozygous for a splice site mutation, substitution of an adenine for a guanine in the first nucleotide of intron 3 (IVS3+1 G>A). This mutation disrupts the splice donor site resulting in retention of intron 3. The retained intron would create a frameshift after codon 196 and a translational termination signal 63 bp downstream from the end of exon 3, resulting in a severely truncated protein that cannot have enzymatic activity. Patient 2 was homozygous for a 7 nucleotide insertion in exon 8; this mutation alters the reading frame downstream of codon 442 and creates a premature TGA stop signal at codon 44617). Patients 3 and 4 were compound heterozygous for the two mutations detected in patients 1 and 2. Patient 5 was compound heterozygous for the mutation detected in patient 1, IVS3+1 G>A, and for a novel nonsense mutation, 2561G>A in exon 6 that creates a premature TAG stop signal at codon 328. Analysis of the family members showed that the asymptomatic parents and the brother of patient 1 were heterozygous for the IVS3+1 G>A mutation. The mother and the brother of patient 2 were heterozygous for the 7 nucleotide insertion in exon 8; DNA from the father was not available for study. The mother of patient 3 was heterozygous for IVS3+1 G>A, and the father and sister were heterozygous for the 7 nucleotide insertion in exon 8. The mother of the patient 4 was heterozygous for the 7 nucleotide insertion in exon 8; the father was not studied. The mother and brother of patient 5 were heterozygous for the IVS3+1 G>A, and the father was heterozygous for the 2651G>A mutation in exon 6.
There are two common mutation sites in 5 Korean patients with VDDR-I (Table 2). The splice site mutation, IVS3+1 G>A, occurred in 5 of 10 alleles. Guanine to adenine substitution in the first nucleotide of an intron is a common mutation in many genes and usually results in skipping of the 5'-exon or activation of potential splice sites25). However, in short introns, retention of the intron may also occur as has been demonstrated for IVS3+1 G>A in the 1╬▒-hydroxylase19, 25). The retention of intron 3 causes altered translation and a premature stop codon 63 bp downstream from the end of exon 3. The resulting truncated 1╬▒-hydroxylase would have only 197 of 508 amino acids, would lack the heme-binding domain, and hence would have no enzyme activity. The 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene contains the normally duplicated sequence 5'-CCCACCC CCCACCC-3' in exon 8, which encodes residues 438-442 (Pro-Thr-Pro-His-Pro). Korean patients showed triplication rather than duplication of this 7 nucleotide sequence on 4 alleles. This 7 nucleotide insertion alters the reading frame downstream of codon 442 and creates a premature TGA stop signal at codon 446; this is upstream from the heme-binding domain, hence the resulting truncated protein is devoid of activity17). Wang et al.17) previously reported that six families of widely divergent ethnic backgrounds (Filipino, Polish, Chinese, Caucasian American, African American, and Hispanic) carried this 7 nucleotide insertion in association with four different microsatellite haplotypes. Thus, the ethnic and haplotype diversity associated with the 7 nucleotide insertion suggests that it has risen by several independent de novo events, probably as the result of a slipped-strand mispairing mechanism during meiosis26). Kitanaka et al.19) found 10 different 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene mutations in 20 Japanese alleles, suggesting that there is no founder effect in that ethnic group. By contrast, Korean patients revealed only three different mutations in ten alleles, suggesting that in Korean ethnic group, the genetic defect in the 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene is more homogeneous.
The main hormonal regulator of bone mineralization is vitamin D. Dietary deficiency of vitamin D and genetic disorders of vitamin D biosynthesis and action can cause rickets. The patients with VDDR-I have mutations in the gene encoding renal 1╬▒-hydroxylase. A total of 36 mutations in the 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene have been identified. Two mutations (958delG, 7 nucleotide insertion in exon 8) described in 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene are relatively more common than the others. Until now, 5 Korean patients with VDDR-I have been studied and 3 distinct mutations have been identified. There are two common mutation sites; IVS3+1 G>A and 7 nucleotide insertion in exon 8. Japanese patients with VDDR-I revealed 10 different 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene mutations in 20 alleles. By contrast, Korean patients showed only three different mutations in ten alleles, suggesting that the genetic defect in the 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene is more homogeneous in Korean ethnic group.
References
1. Fraser DR, Kodicek E. Unique biosynthesis by kidney of a biologically active vitamin D metabolite. Nature 1970;228:764ŌĆō766.


2. Brunette MG, Chan M, Ferriere C, Roberts KD. Site of 1,25(OH)2 vitaminD3 synthesis in the kidney. Nature 1978;276:287ŌĆō289.


3. Fraser D, Kooh SW, Kind HP, Holick MF, Tanaka Y, DeLuca HF. Pathogenesis of hereditary vitamin-D-dependent rickets. An inborn error of vitamin D metabolism involving defective conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to 1╬▒,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. N Engl J Med 1973;289:817ŌĆō822.


4. Scriver CR, Reade TM, DeLuca HF, Hamstra AJ. Serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels in normal subjects and in patients with hereditary rickets or bone disease. N Engl J Med 1978;299:976ŌĆō979.


5. Delvin EE, Glorieux FH, Marie PJ, Pettifor JM. Vitamin D dependency: replacement therapy with calcitriol? J Pediatr 1981;99:26ŌĆō34.


6. Feldman D, Malloy PJ, Gross C. Marcus R, Feldman D, Kelsey J,Vitamin D: metabolism and action. editors. Osteoporosis. 1996;1st ed. San Diego: Academic Press, :205ŌĆō235.
7. Strewler GJ, Rosenblatt M. Felig P, Baxter JD, Frohman LA,Mineral metabolism. editors. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1995;3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, :1407ŌĆō1516.
8. Portale AA, Miller WL. Human 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1╬▒-hydroxylase: cloning, mutations, and gene expression. Pediatr Nephrol 2000;14:620ŌĆō625.


9. Breslau NA. Normal and abnormal regulation of 1,25(OH)2D synthesis. Am J Med Sci 1988;296:417ŌĆō425.


11. St-Arnaud R, Messerlian S, Moir JM, Ombdahl JL, Glorieux FH. The 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase gene maps to the pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets (PDDR) disease locus. J Bone Miner Res 1997;12:1552ŌĆō1559.


12. Monkawa T, Yoshida T, Wakino S, Shinki T, Anazawa H, DeLuca HF, et al. Molecular cloning of cDNA and genomic DNA for human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1╬▒-hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997;239:527ŌĆō533.


13. Fu GK, Portale AA, Miller WL. Complete structure of the human gene for the vitamin D 1╬▒-hydroxylase, P450c1╬▒. DNA Cell Biol 1997;16:1499ŌĆō1507.


14. Kitanaka S, Takeyama K, Murayama A, Sato T, Okumura K, Nogami M, et al. Inactivating mutations in the 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene in patients with pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets. N Engl J Med 1998;338:653ŌĆō661.


15. Fu GK, Lin D, Zhang MY, Bikle DD, Shackleton CHL, Miller WL, et al. Cloning of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1╬▒-hydroxylase and mutations causing vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1. Mol Endocrinol 1997;11:1961ŌĆō1970.


16. Yoshida T, Monkawa T, Tenenhouse HS, Goodyer P, Shinki T, Suda T, et al. Two novel 1╬▒-hydroxylase mutations in French-Canadians with vitamin D dependency rickets type 1. Kidney Int 1998;54:1437ŌĆō1443.


17. Wang JT, Lin CJ, Burridge SM, Fu GK, Labuda M, Portale AA, et al. Genetics of vitamin D 1╬▒-hydroxylase deficiency in 17 families. Am J Hum Genet 1998;63:1694ŌĆō1702.



18. Smith SJ, Rucka AK, Berry JL, Davies M, Mylchreest S, Paterson CR, et al. Novel mutations in the 1╬▒-hydroxylase (P450c1) gene in three families with pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets resulting in loss of functional enzyme activity in blood-derived macrophages. J Bone Miner Res 1999;14:730ŌĆō739.


19. Kitanaka S, Murayama A, Sakaki T, Inouye K, Seino Y, Fukumoto S, et al. No enzyme activity of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene product in pseudovitamin D deficiency rickets, including that with mild clinical manifestation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:4111ŌĆō4117.


20. Wang X, Zhang MYH, Miller WL, Portale AA. Novel gene mutations in patients with 1╬▒-hydroxylase deficiency that confer partial enzyme activity in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:2424ŌĆō2430.


21. Porcu L, Meloni A, Casula L, Asunis I, Marini MG, Cao A, et al. A novel splicing defect (IVS6+1GT) in a patient with pseudovitamin D deficiency rickets. J Endocrinol Invest 2002;25:557ŌĆō560.


22. Kim CJ, Kaplan LE, Perwad F, Huang N, Sharma A, Choi Y, et al. Vitamin D 1╬▒-hydroxylase gene mutations in patients with 1╬▒-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:3177ŌĆō3182.


23. Alzahrani AS, Zou M, Baitei EY, Alshaikh OM, Al-Rijjal RA, Meyer BF, et al. A novel G102E mutation of CYP27B1 in a large family with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;95:4176ŌĆō4183.


24. Labuda M, Labuda D, Korab-Laskowska M, Cole DE, Zietkiewicz E, Weissenbach J, et al. Linkage disequilibrium analysis in young populations: pseudo-vitamin D-deficiency rickets and the founder effect in French Canadians. Am J Hum Genet 1996;59:633ŌĆō643.


25. Cooper DN, Krawczak M, Antonaratis SE. Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D,The nature and mechanism of human gene mutation. editors. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. 1995;7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, :259ŌĆō291.
Table┬Ā2
1╬▒-hydroxylase Gene Mutations in 5 Korean Patients (10 alleles) with Vitamin D Dependent Rickets Type I

*Nucleotide numbers refer to genomic DNA and are numbered from the transcription start site 13). The reference sequence is available on the NCBI, Entrez, Nucleotide database: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Entrez; accession number AF 027152.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


