Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 54(6); 2011 |
Abstract
Purpose
Long-term survivors of childhood cancer appear to have an increased risk for the metabolic syndrome, subsequent type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in adulthood compared to healthy children. The purpose of this study was to investigate the frequency of the metabolic syndrome and associated factors in childhood cancer survivors at a single center in Korea.
Methods
We performed a retrospective review of medical records of 98 childhood cancer survivors who were diagnosed and completed anticancer treatment at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea between Jan. 1996 and Dec. 2007. Parameters of metabolic syndrome were evaluated between Jan. 2008 and Dec. 2009. Clinical and biochemical findings including body fat percentage were analyzed.
Results
A total of 19 (19.4%) patients had the metabolic syndrome. The median body fat percentage was 31.5%. The body mass index and waist circumference were positively correlated with the cranial irradiation dose (r=0.38, P<0.001 and r=0.44, P<0.00, respectively). Sixty-one (62.2%) patients had at least one abnormal lipid value. The triglyceride showed significant positive correlation with the body fat percentage (r=0.26, P=0.03). The high density lipoprotein cholesterol showed significant negative correlation with the percent body fat (r=-0.26, P=0.03).
Conclusion
Childhood cancer survivors should have thorough metabolic evaluation including measurement of body fat percentage even if they are not obese. A better understanding of the determinants of the metabolic syndrome during adolescence might provide preventive interventions for improving health outcomes in adulthood.
Improved diagnostic tools and treatment modalities including surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, as well as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation have dramatically increased childhood cancer survival over the last 30 years1). As the number of childhood cancer survivors grows, quality of life issues over the long term have become important.
The metabolic syndrome is a cluster of features including: dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, hypertension and obesity, especially central obesity. The metabolic syndrome is a risk factor for the subsequent development of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Many investigators have reported adolescent prevalence data for the metabolic syndrome using numerous diagnostic criteria. Although agreement is lacking on the criteria for diagnosing the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents, the diagnostic criteria typically involve the same five risk factors identified in adults including abdominal obesity, high triglyceride, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), high blood pressure and high fasting glucose with modification of the cut-off values2-4).
According to a statement by the American Heart Association, post-cancer treatment survivors were classified as tier III, which means increased cardiovascular risk factors with epidemiological evidence for manifest cardiovascular disease early in adult life5).
In 1996, Talvensaari et al.5) reported that long-term survivors of childhood cancer appeared to have an increased risk for the metabolic syndrome compared to age and gender matched healthy control children.
In Korea, a recent report revealed that the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the general childhood population was around 10%6). However, study of the metabolic syndrome in childhood cancer survivors has not been performed. The purpose of this study was to investigate the frequency of the metabolic syndrome and associated factors in childhood cancer survivors at a single center in Korea.
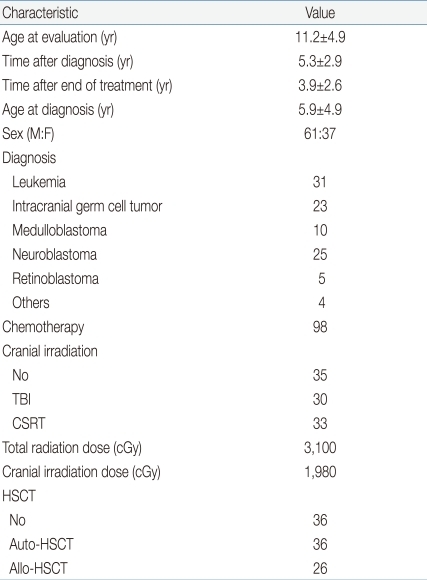
All surviving 98 subjects who visited endocrinology clinic and were examined for parameters of metabolic syndrome between January 2008 and December 2009 were enrolled in this study. All subjects were diagnosed and treated for childhood cancer of less than 18 years of age at the Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, between 1996 and 2007. The clinical characteristics of the patients are listed in Table 1. At the time of the examination, all survivors were disease free. The study was approved by the institutional review board at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
The medical records were reviewed for the clinical history. The patients were interviewed and a physical examination was performed. The height and weight were measured. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated as the weight in kilograms divided by the height in meters squared. Height, weight and BMI standard deviation score (SDS) were assessed using the Korean standard growth charts7). Pubertal development was assessed according to Tanner and Whitehouse stage8). Waist and hip circumferences were measured to the nearest millimeter. The BMI at or above the 85th percentile and below 95th percentile was considered overweight. The BMI above the 95th percentile was considered obese6). The physical examination included blood pressure, measured using an automated hemadynamometer. Fat mass and percent body fat were determined by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA, Hologic Delphi W, software 12.4.2, Hologic Inc., Bedford, MA, USA). The precision of the fat assessments was approximately 1%.
Laboratory samples were collected in the morning after overnight fasting. The tests included plasma triglycerides, plasma total cholesterol, serum HDL-C, serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), blood glucose, serum insulin, plasma uric acid, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), triiodothyronine, free thyroxine, and thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Standard growth hormone provocation test was performed after overnight fasting with at least two separate stimuli with insulin, glucagon, clonidine or levodopa. Human-growth hormone (hGH) was measured in serial blood samples with 30 minute interval during 2 hours by commercial radioimmunoassay kit (Immunotech S.A.S., Marseille Cedex, France). Growth hormone deficiency (GHD) was diagnosed when all provocated hGHs were less than 10 ng/mL with at least two stimuli.
The definition reported by the National Cholesterol Education Program/Adult Treatment Panel III was used to determine the diagnosis of the metabolic syndrome9). The findings of at least three of the following five criteria were required to diagnose the metabolic syndrome: Central obesity with a waist circumference at or over 90th percentile for age, gender, and height; Low HDL-C levels, Ōēż40 mg/dL; high triglyceride (TG) levels, Ōēź110 mg/dL; high fasting glucose, Ōēź110 mg/dL; elevated systolic or diastolic blood pressure, at or above the 90th percentile for age, gender, and height.
Continuous data were analyzed using an independent sample t-test or analysis of variance in the case of normally distributed data and the Mann-Whitney U-test or Kruskal-Wallis test for skewed distribution or ordinal variables. Categorized data were analyzed using Fisher's exact test and the chi-square test as appropriate. To determine independent association of clinical parameters and metabolic syndrome prevalence, data were analyzed using multiple logistic regression test. A P value <0.05 was considered significant; all statistical analyses were performed using SPSS ver. 15.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago. IL, USA).
A total of 19 (19.4%) patients had the metabolic syndrome (Table 2). Fourteen were males and five were females. Their median age was 15 years. The median BMI SDS was 0.71. The median body fat percent was 31.5%. Among them, seven (36.8%) were overweight or obese. Therefore, half of them had the metabolic syndrome even though they were not overweight or obese. Seventeen (89.5%) patients had cranial irradiation. Four (21%) patients had GHD, which was diagnosed by a growth hormone stimulation test. All four patients with GHD had cranial irradiation.
By multivariate analyses BMI SDS (P=0.03), the presence of GHD (P=0.04), and the type of cranial irradiation (P<0.001) were found associated with metabolic syndrome prevalence.
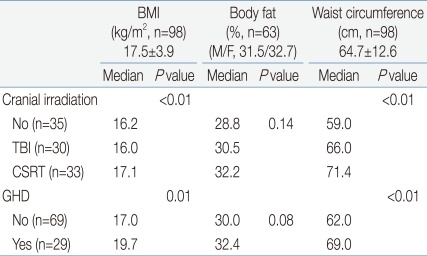
Seventeen (17.3%) patients were overweight or obese. Thirteen (13.3%) patients were overweight and 4 (4%) were obese. Central obesity was found in 13 (13.3%) patients. Subgroups classified according to the type of cranial irradiation showed significant differences in the BMI and waist circumference. However, there was no significant difference in the BMI SDS, waist circumference percentile or body fat percent (Table 3). Patients with GHD had higher BMI and increased waist circumference (Table 3). Among the parameters of obesity, the BMI and waist circumference were positively correlated with the cranial irradiation dose (r=0.38, P<0.001 and r=0.44, P<0.001, respectively, Fig. 1).
All 98 patients showed euthyroid state which include 24 patients with levo-thyroxine therapy at the time of the present study due to overt hypothyroidsm. The level of mean serum IGF-1 was 226┬▒169 ng/mL and IGF-1 SDS was -0.13┬▒1.59. The mean IGF-1 SDS of patients with GHD was not significantly lower than that of patients without GHD (-0.54┬▒2.15 vs. 0.03┬▒1.26, respectively, P=0.18).
The percent of whole body fat was measured in 63 patients (42 males and 21 females). The median body fat percent was 31.5%. The median body fat percent in males and females was 31.5% (26.6 to 35.6) and 32.7% (27.3 to 34.8) respectively (Table 3). The percent body fat tended to be higher in patients that had cranial irradiation with higher doses. In addition, the percent body fat tended to be higher in patient with GHD compared to patients without GHD (Table 3).
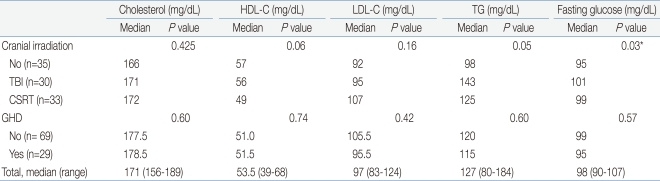
In total, 61 (62.2%) patients had at least one abnormal lipid value. Twenty two (21.4%) patients had hypercholesterolemia (total cholesterol Ōēź200 mg/dL), 14 (14.3%) had raised LDL-C (LDL-C Ōēź130 mg/dL), 25 (25.5%) had reduced HDL-C (HDL-C Ōēż40 mg/dL) and 57 (58.2%) had hypertriglyceridemia (TG Ōēź110 mg/dL) (Table 2).
There was no significant difference in the lipid profile between patients with and without cranial irradiation. The TG showed significant positive correlation with the percent body fat (r=0.26, P=0.03, Fig. 2A). Moreover, the HDL-C showed significant negative correlation with the percent body fat (r=-0.26, P=0.03, Fig. 2B).
The fasting glucose was above 110 mg/dL in 19 (19.4%) patients. Subgroups classified according to the type of cranial irradiation showed significant differences in the fasting glucose level (Table 4).
Twenty six (26.5%) patients had increased blood pressure (Table 2). Eighteen were males and eight were females. Their median age was 12.2 years (5.3 to 15). The median age at diagnosis was 3.8 years (1.5 to 9.6). The median BMI SDS was 0.23 (-0.43 to 0.79). The median percent body fat was 31.8% (28.9 to 34.3). Sixteen (61.5%) had cranial irradiation.
The metabolic syndrome is an important health issue in children and adolescents with regard to the long term implications of cardiovascular morbidity and type 2 diabetes. This is one of a few reports to examine the frequency and factors associated with the metabolic syndrome among childhood cancer survivors in Korea. The results of this study showed that the frequency of the metabolic syndrome in childhood cancer survivors was 19.4%. This is about twice the frequency in the general population of children according to a study conducted by the Korean national health and nutrition survey10).
Several studies have reported an increased prevalence of overweight or obese childhood cancer survivors1,11,12). The reported prevalence of overweight or obese childhood cancer survivors has varied from 16 to 50%5,13,14). In this study, 17.3% were overweight or obese, which is consistent with previous studies. This is a higher frequency compared to the prevalence in the general Korean population, which has recently been reported to be around 10%6). Moreover, our results show that BMI SDS was positively associated with prevalence of metabolic syndrome. Therefore, continuous surveillance of BMI in childhood cancer survivor is crucial for early detection of metabolic syndrome in these patients.
The basic feature of the metabolic syndrome is central obesity. An appropriate definition of central obesity for children and adolescents is challenging. Central obesity was found in 13.2% of the patients reported here, which is consistent with previous studies15). In this study, the BMI and waist circumference percentiles were correlated with the cranial irradiation dose, which could have caused hypothalamic/pituitary damage that manifested as hormonal problems. Growth hormone has been implicated not only in linear growth, but also in metabolism. The results of this study showed that the percent body fat of patients with GHD tended to be higher than in patients without GHD.
The amount of fat and lean body mass, and the distribution of fat are important risk factors for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes16,17). Unfortunately, there is no Korean reference data for body composition in this age group. Therefore, the reported reference data of percent body fat was used12,18). Higgins et al.19) reported that an upper cut-off point of 33% body fat is an indicator of cardiovascular disease risk in children. In this study, 41.2% (26/63) of the patients had a percent fat that was above 33%, despite a median BMI SDS of 0.14 (-0.71 to 0.9). This may suggest that the body composition of childhood cancer survivors should be considered even if they are not overweight or obese.
About half of the patients in this study had at least one abnormal lipid profile. The percent body fat was positively correlated with the triglyceride and negatively correlated with the HDL-C. Vatanparast et al.20) reported that DXA-derived fat mass indices can be used for predicting blood lipid profiles in postmenopausal women. Although studies in children are lacking, our findings suggest the importance of the percent fat in predicting the lipid profile.
In childhood cancer survivors, the frequency of the metabolic syndrome appears to be increased. This finding was associated with BMI SDS, presence of GHD, and cranial irradiation. The notable fact was that the body composition of childhood cancer survivors was metabolically unfavorable even if they were not obese. Therefore, childhood cancer survivors should have thorough metabolic evaluation including measurement of the percent body fat even if their BMI is in the normal range. Furthermore, more intense surveillance and education is necessary for the patients who had cranial irradiation and GHD.
The major limitations of this study are as follows: a cross-sectional setting, small sample size from a single center and lack of optimal comparison group. Thereafter, a prospective long-term cohort study is needed to reproduce the results of this study.
In Korea, the number of childhood cancer survivors increased to approximately 20,000 to 25,00021). However, there are no large cohort studies in Korea like The Childhood Cancer Survivor Study of USA or British Childhood Cancer Survivor Study of United Kingdom. In 2008, Children's Oncology Group published the update of Long-Term Follow-up Guidelines for Survivors of Childhood, Adolescent, and Young Adult Cancers22) for screening and management of late effects resulting from therapeutic exposures during the treatment of malignancies. The guideline recommends annual physical examination of height, weight, BMI, blood pressure for screening metabolic syndrome. Moreover, laboratory tests including fasting blood glucose, insulin, and lipid profile are recommended every 2 years if the patient is overweight or every 5 years if the patient is in normal weight22). Now, we need the Korean cancer survivor cohort and follow-up guidelines. The primary preventive interventions for the patients with risk factors of metabolic syndrome include education of the patients and parents about the diet modification and adequate physical activities for maintaining normal BMI and body fat percent.
In conclusion, a better understanding of the determinants of the metabolic syndrome during adolescence might provide insights into preventive interventions for improving health outcomes and reducing the incidence of cardiovascular disease in adults.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project; Grant sponsor: Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea; Grant number: A080588; Grant sponsor: Samsung Biomedical Research Institute; Grant numbers: C-A9-240-2 Grant sponsor: In-Sung Foundation for Medical Research.
References
1. Hoffman KE, Derdak J, Bernstein D, Reynolds JC, Avila NA, Gerber L, et al. Metabolic syndrome traits in long-term survivors of pediatric sarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2008;50:341ŌĆō346.


2. Johnson WD, Kroon JJ, Greenway FL, Bouchard C, Ryan D, Katzmarzyk PT. Prevalence of risk factors for metabolic syndrome in adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2001-2006. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2009;163:371ŌĆō377.


3. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S, et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: an IDF consensus report. Pediatr Diabetes 2007;8:299ŌĆō306.


5. Talvensaari KK, Lanning M, Tapanainen P, Knip M. Long-term survivors of childhood cancer have an increased risk of manifesting the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996;81:3051ŌĆō3055.


6. Park MJ. Epidemiology of the metabolic syndrome among Korean children and adolescents. Korean J Pediatr 2008;51:564ŌĆō568.

7. Lee SY, Kim JH, Oh KW, Kim YN, Kang YJ. Development of growth curves and the criteria of obesity in Korean children and adolescents, final report. 2007;Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare.
8. Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH. Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stages of puberty. Arch Dis Child 1976;51:170ŌĆō179.



9. Cook S, Weitzman M, Auinger P, Nguyen M, Dietz WH. Prevalence of a metabolic syndrome phenotype in adolescents: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2003;157:821ŌĆō827.


10. Kim HM, Park J, Kim HS, Kim DH, Park SH. Obesity and cardiovascular risk factors in Korean children and adolescents aged 10-18 years from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1998 and 2001. Am J Epidemiol 2006;164:787ŌĆō793.


11. Pietil├ż S, M├żkipernaa A, Siev├żnen H, Koivisto AM, Wigren T, Lenko HL. Obesity and metabolic changes are common in young childhood brain tumor survivors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2009;52:853ŌĆō859.


12. Jarfelt M, Lannering B, Bosaeus I, Johannsson G, Bjarnason R. Body composition in young adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur J Endocrinol 2005;153:81ŌĆō89.


13. Didi M, Didcock E, Davies HA, Ogilvy-Stuart AL, Wales JK, Shalet SM. High incidence of obesity in young adults after treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood. J Pediatr 1995;127:63ŌĆō67.


14. Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA, Yasui Y, Fears T, Stovall M, et al. Obesity in adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:1359ŌĆō1365.


15. Taskinen M, Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Hovi L, Lipsanen-Nyman M. Impaired glucose tolerance and dyslipidaemia as late effects after bone-marrow transplantation in childhood. Lancet 2000;356:993ŌĆō997.


16. Sardinha LB, Teixeira PJ, Guedes DP, Going SB, Lohman TG. Subcutaneous central fat is associated with cardiovascular risk factors in men independently of total fatness and fitness. Metabolism 2000;49:1379ŌĆō1385.


17. Bj├Črntorp P. Body fat distribution, insulin resistance, and metabolic diseases. Nutrition 1997;13:795ŌĆō803.


18. van der Sluis IM, de Ridder MA, Boot AM, Krenning EP, de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM. Reference data for bone density and body composition measured with dual energy x ray absorptiometry in white children and young adults. Arch Dis Child 2002;87:341ŌĆō347.



19. Higgins PB, Gower BA, Hunter GR, Goran MI. Defining health-related obesity in prepubertal children. Obes Res 2001;9:233ŌĆō240.


20. Vatanparast H, Chilibeck PD, Cornish SM, Little JP, Paus-Jenssen LS, Case AM, et al. DXA-derived abdominal fat mass, waist circumference, and blood lipids in postmenopausal women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009;17:1635ŌĆō1640.


Fig.┬Ā1
Correlation of cranial irradiation and obesity. The body mass index (BMI) (A) and waist circumference (B) were positively correlated with the cranial irradiation dose (r=0.38, P<0.001 and r=0.44, P<0.001, respectively).
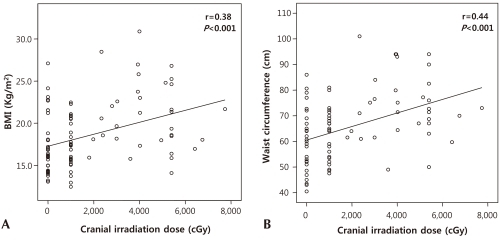
Fig.┬Ā2
(A) Correlation of body fat percentage and triglyceride. The triglyceride showed significant positive correlation with the body fat percentage. (B) Correlation of body fat percentage and triglyceride. The high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) showed significant negative correlation with the body fat percentage.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


