Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 61(3); 2018 |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Frequent desaturation due to immature incoordination of suck-swallow-breathing in preterm infants can influence multiple organs such as the heart, lungs, and brain, which can then affect growth and development. Most notably in preterm infants, feeding desaturation may even affect pulmonary function during gavage feeding. Because respiratory muscle activities may reflect the work required during respiration, we evaluated the differences in these activities between full-term and preterm infants with feeding desaturation, and investigated the correlations with clinical variables.
Methods
Nineteen preterm infants with feeding desaturation (group 1) and 19 age-matched full-term infants (group 2) were evaluated. Oromotor function was evaluated using video recording. The root-mean-squre (RMS) envelope of the electromyography signal was calculated to quantify the activities of muscles involved in respiration. The differences in RMS between both groups and the correlation with clinical variables including gestational age (GA), birth weight (BW), and Apgar scores (AS) at 1 and 5 minutes after birth were evaluated.
Results
The RMS values of the diaphragm (RMS-D) and rectus abdominis (RMS-R) were significantly greater in group 1 compared to group 2, and the 1- and 5-min AS were significantly lower in group 1 compared to group 2. RMS-D and RMS-R were inversely correlated with GA, BW, 1- and 5-min AS in all infants.
Coordination of the rhythms of suck, swallow, and breathing is an essential component for successful suckle feeding in premature infants.1,2) There are high risks of desaturation during feeding due to immature coordination, gastroesophageal reflux, immature oral structures and combined diseases.3,4,5,6,7,8,9) Clinically significant oxygen desaturation events were defined as any decrease in oxygen saturation below 90% for greater than or equal to 1 second.10) While preterm infants may also have compromised pulmonary functions during gavage feeding, more frequent desaturation can occur during bottle feeding, especially when bottle-fed with an extant gavage tube.3,11,12,13,14) All these feeding techniques are frequently performed in premature infants. Frequent desaturation due to immature incoordination of suck-swallow-breathing can influence multiple organs such as the heart, lungs, and the brain, which can then affect the growth and development of the infants.15,16,17,18)
There is some evidence that diaphragmatic fatigue has a role in the pathophysiology of desaturation in premature infants.19,20,21) Due to their highly compliant chest wall, preterm infants are disadvantaged with regards to their respiratory mechanics. Chest wall distortion, which manifests as paradoxical breathing, is common in infants and is particularly visible in preterm infants.4) Studies have suggested that this distortion increases the volume displacement of the diaphragm during inspiration and requires additional effort and significant calorie expenditure while inducing diaphragmatic fatigue and desaturation. Gewolb and Vice22) reported that the duration and severity of hypoxemic episodes were associated with the number of concurrent abdominal muscle contractions in preterm infants after mechanical ventilation. The delay in lung inflation after contraction of the abdominal muscles eventually results in a decreased lung volume that is below the baseline. To the best of our knowledge, no previous study has attempted to explore the association between feeding desaturation and abdominal muscle contraction in preterm infants who have not received mechanical ventilation.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the differences in the activities of respiratory muscles between full-term and preterm infants with feeding desaturation, and investigate their correlation with clinical variables such as gestational age (GA), birth weight (BW), and Apgar score at 1 and 5 minutes after birth (1- and 5-m AS). In addition, differences in oromotor function and the activities of respiratory muscles between bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and a non-BPD group were also evaluated.
This is a nonrandomized cross-sectional study. Nineteen preterm infants with feeding desaturation (group 1) and 19 GA-matched full-term infants without feeding desaturation (group 2) were recruited. Significant feeding desaturation in this study was defined as arterial oxygen saturation levels below 85% for more than 2 seconds (moderate to severe desaturation).10,16,23) All infants were bottle-fed and had no concurrent sepsis and no craniofacial anomalies. Gavage-fed infants were excluded from the study. They were bottle-fed by a skilled nurse who had more than 2 or 3 years experiences at neonatal intensive care unit during their scheduled feeding times. Small size nipple for infants under 3 months (Aissok, Greenmom, Anyang, Korea) was used for each feeding. Ten of 19 infants in group 1 had BPD, 4 had brain lesions including 3 periventricular leukomalacia and 1 grade III intraventricular hemorrhages. Group 1 was further subdivided into BPD and non-BPD groups. The preterm infants who needed oxygen supplementation for at least 28 postnatal days were classified as the BPD group.24) The Institutional Review Board and Ethics Committee of Daegu Catholic University Medical Centre approved the study protocol (CR-15-113). A waiver of written informed consent was granted.
Swallowing behavior was recorded for five minutes and data from the entire feed were used. The swallowing function was measured by a physician who had 10 years of experience in pediatric rehabilitation medicine. A “swallow run” was defined as 3 swallows with interswallow intervals of 2 seconds. Rhythmic stability/variability was quantified using the coefficient of variation (COV: the standard deviation of the mean interval divided by the mean interval). Swallow-breath (SW-BR) intervals and COVs were similarly calculated using only the swallows in runs. Breath-breath (BR-BR) intervals and COVs were calculated for breaths that occurred during swallow runs with at least 3 swallowing events. Simultaneous or near simultaneous SW-BR intervals (<0.1 second) were not used in the analysis. The percentage of apneic swallows was also determined (swallows in runs of three that were not associated with breathing movements divided by total swallow runs). The assessment of oromotor function was performed during bottle feeding as previously described, which included quantifying the COV of BR-BR and SW-BR, as well as the proportion of apneic swallows.22,25)
Electromyographic (EMG) activities of respiratory muscles, such as the diaphragm and rectus abdominis muscles, were recorded via surface electrodes using a 4-channel electrophysiology unit (Medelec, Company of Oxford, Oxford, UK). Surface electrodes for diaphragm muscles were placed in the eighth intercostal space between the midclavicular and mid-axillary line. For rectus abdominis muscles, surface electrodes were attached 2 cm laterally to the umbilicus (Fig. 1).26) EMG activities of the respiratory muscles were recorded at resting state for an hour after feeding. The root-mean-square (RMS) envelope of the EMG signal was calculated to quantify the activities of the respiratory muscles. RMS values were averaged over 10 measurements. The correlations between RMS-D and RMS-R with GA, BW, 1- and 5-m AS were also evaluated.
An independent t test was used to assess the differences in RMS of respiratory muscles between the groups 1 and 2. One-way analysis of variance was used to assess differences in RMS of respiratory muscles between the BPD, non-BPD, and full-term groups. Post hoc test was performed by using Tukey and Dunnett T3. The relationship between RMS and clinical variables was assessed suing the Pearson correlation coefficient. The level of significance was set at P<0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 19.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA).
Nineteen preterm infants and the corresponding full-term infants were investigated, their characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Although infants in group 1 weighed less at birth and had lower GAs compared to group 2, postconceptional age (PCA) and weight at the time of study did not significantly differ between both groups. However, the 1- and 5-m AS in group 1 were significantly lower than those in group 2 and rectus abdominis (RMS-R) muscles in group 1 were also significantly greater than those in group 2. RMS-D and RMS-R were inversely correlated with GA, BW, 1- and 5-m AS in all infants (Table 2).
As high RMS value are suggestive of increased breathing work,27) the presence of BPD can affect RMS value. To correct for potential bias, group 1 was subdivided into BPD and non-BPD subgroups Full details regarding the BPD and non-BPD subgroups are summarized in Table 3. GA, BW, and 1-m AS in the BPD group were lower compared to the non-BPD group. The PCA at the time of study was older in the BPD group compared to non-BPD, suggesting that the infants in the former group were included in the study at an older age. The trends for 5-m AS and weight at the time of study were similar. There was no difference in the history of respiratory distress syndrome between both groups, but the duration of invasive and noninvasive ventilation was longer in the BPD group compared to other groups. At the time of study, there was no observed difference in the duration of oxygen supplementation or the number of infants on supplemental oxygen during feeding.
There was no difference in RMS values among the BPD, non-BPD and full-term groups (Fig. 2). These results suggest that the presence of BPD did not affect the RMS value. In addition, we evaluated the oromotor function of preterm infants (Table 4), and the COV of BR-SW was similar in both groups (BPD, 0.23±0.05 vs. non-BPD, 0.20±0.06). However, the COV of BR-BR was less rhythmic in the BPD group (0.18±0.05 vs. 0.13±0.02, P<0.05), while apneic swallowing was higher in the BPD group than in the non-BPD (6.4±1.3 vs. 3.8±0.7, P<0.01). These results reflect more irregular and immature breathing pattern in the BPD group compared to the non-BPD group, however, latter group showed relatively mature breathing patterns and increased breathing work during feeding.
Surface EMG signals can evaluate the neuronal respiratory drive and help evaluate respiratory muscle function.28) Although potentially contaminated by other muscle activities, it may be a safe and noninvasive method to monitor respiratory function in neonates.26,29)
We found that RMS-D and RMS-R in preterm infants with feeding desaturation were higher than those in full-term infants. During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and moves inferiorly, thus enlarging the volume of the thoracic cavity, which then reduces intrathoracic pressure. When the diaphragm relaxes, air is exhaled by elastic recoiling of the lung. This is supported by contraction of the tissues lining the thoracic cavity, as well as abdominal muscle contractions, since the abdominal muscle acts as an antagonist that is paired with the diaphragm's contraction. This phenomenon is termed the thoracoabdominal synchrony.26,30)
It has been postulated that contractions of the abdominal muscles in preterm infants can result in forced exhalation that reduces lung volume and imposes a substantial load on inspiratory muscles as they must overcome an increase in workload before being able to effectively inspire using the diaphragm. In addition, the diaphragm in preterm infants maintains less than 10% of type I muscle fibers and low percentages of type IIb muscle fibers.31,32) The paucity of fatigue-resistant type I muscle fibers, the high proportion of fatigue-susceptible type IIc muscle fibers, and a low oxidative capacity of the neonatal diaphragm all suggest that the diaphragm muscle is relatively prone to fatigue.19,20,31)
Therefore, an increase in the diaphragmatic breathing work may represent a significant expenditure of calories and contribute to the development of diaphragmatic fatigue and ventilatory failure. Consequently, an imbalance between an imposed load and the capacity of inspiratory muscles results in desaturation symptoms in preterm infants. Thus, the increase in RMS suggests that work-of-breath and thoracoabdominal asynchrony were increased in preterm infants.
Respiration is the last component to be integrated into the coordination of suck-swallow-breathing for successful sucking in preterm infants.22) It has been shown that even full-term infants had unstable respiration compared to sucking or swallowing during feeding.33) The stabilization of respiration correlated with postmenopausal age (PMA) rather than postnatal age. This study showed that RMS values were inversely correlated with GA and BW and breathing during feeding was unstable and immature in preterm infants.
Several studies have reported that preterm infants, especially ones with BPD, had some form of impairment in maturation sequence and breathing control.6,34,35) However, RMS-D and RMS-R in the BPD group were not different from those in the non-BPD group. Several studies have shown that feeding desaturation occurs frequently in BPD infants;34) however, Thoyre and Carlson10) reported that feeding desaturation was less in very low birth weight infants who may have chronic lung disease. They explained that this was due to higher PMA and concomitant oxygen supplementation and suggested close monitoring for desaturation. All but one preterm infant did not require continuous oxygen supplementation in this study. Even infants with oxygen supplementation at the time of study required oxygen supplementation intermittently during feeding. Oxygen supplementation during feeding did not differ in both groups. Although the COV of SW-BR did not differ statistically, the COV of BR- BR was significantly higher in the BPD group indicating less rhythmic respiration. This suggested that the BPD group has high risks of feeding desaturation due to irregular respiration and frequent apneic swallows. These results were consistent with the previous study.35) However, it is noteworthy that the RMS-D and RMS-R were also increased in the non-BPD groups. Even preterm infants without BPD had high risks for feeding desaturation due to increased work of breath. It has been reported that oxygen supplementation can have positive effects including improvement in ventilation-perfusion matching, which then leads to end-expiratory lung volume.18) Therefore, regardless of BPD, all preterm infants should be carefully monitored for incoordination and feeding desaturation and provided the necessary means such as rehabilitation and proper oxygen supplementation.
Given the small number of subjects, further investigations with a larger population are needed to assess the usefulness of abdominal and diaphragm muscle activities as a means of treating feeding desaturation in preterm infants.
This study indicated that the activities of respiratory muscles in preterm infants with feeding desaturation were greater than those in full-term infants and were inversely correlated with clinical variables according to prematurity. In the case of preterm infants experiencing feeding desaturation, it is important to assess oromotor function and the activities of respiratory muscles altogether. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report that evaluates abdominal and diaphragm muscle activities in preterm infants with feeding desaturation.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1D1A1B01014260).
Notes
Conflicts of interest:
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Bosma JF. Development of feeding. Clini Nutr 1986;5:210–218.
2. Lau C, Smith EO, Schanler RJ. Coordination of suck-swallow and swallow respiration in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 2003;92:721–727.


3. Shivpuri CR, Martin RJ, Carlo WA, Fanaroff AA. Decreased ventilation in preterm infants during oral feeding. J Pediatr 1983;103:285–289.


4. Heldt GP. Development of stability of the respiratory system in preterm infants. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988;65:441–444.


5. Mathew OP. Respiratory control during nipple feeding in preterm infants. Pediatr Pulmonol 1988;5:220–224.


6. Rosen CL, Glaze DG, Frost JD Jr. Hypoxemia associated with feeding in the preterm infant and full-term neonate. Am J Dis Child 1984;138:623–628.


7. Nugent ST, Finley JP. Spectral analysis of the EMG and diaphragmatic muscle fatigue during periodic breathing in infants. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985;58:830–833.


8. Choi HW, Park HW, Kim HY, Lim G, Koo SE, Lee BS, et al. Feeding Desaturation and Effects of Orocutaneous Stimulation in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol 2010;17:193–200.

9. Poets CF, Langner MU, Bohnhorst B. Effects of bottle feeding and two different methods of gavage feeding on oxygenation and breathing patterns in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 1997;86:419–423.


10. Thoyre SM, Carlson J. Occurrence of oxygen desaturation events during preterm infant bottle feeding near discharge. Early Hum Dev 2003;72:25–36.



11. Blondheim O, Abbasi S, Fox WW, Bhutani VK. Effect of enteral gavage feeding rate on pulmonary functions of very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 1993;122(5 Pt 1): 751–755.


12. Shiao SY. Comparison of continuous versus intermittent sucking in very-low-birth-weight infants. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 1997;26:313–319.


13. Shiao SY, Youngblut JM, Anderson GC, DiFiore JM, Martin RJ. Nasogastric tube placement: effects on breathing and sucking in very-low-birth-weight infants. Nurs Res 1995;44:82–88.

14. Chen CH, Wang TM, Chang HM, Chi CS. The effect of breast- and bottle-feeding on oxygen saturation and body temperature in preterm infants. J Hum Lact 2000;16:21–27.


15. Farahani R, Kanaan A, Gavrialov O, Brunnert S, Douglas RM, Morcillo P, et al. Differential effects of chronic intermittent and chronic constant hypoxia on postnatal growth and development. Pediatr Pulmonol 2008;43:20–28.


16. Garg M, Kurzner SI, Bautista DB, Keens TG. Clinically unsuspected hypoxia during sleep and feeding in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 1988;81:635–642.

17. Gewolb IH, Vice FL. Neonatal rhythmic feeding score correlates with short-term neurodevelopmental outcome in premature infants ≤33 weeks gestation [abstract]. Pediatr Res 2005;57:3290
18. Samuels MP, Poets CF, Southall DP. Abnormal hypoxemia after life-threatening events in infants born before term. J Pediatr 1994;125:441–446.


19. Le Souëf PN, England SJ, Stogryn HA, Bryan AC. Comparison of diaphragmatic fatigue in newborn and older rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988;65:1040–1044.


20. Lopes JM, Muller NL, Bryan MH, Bryan AC. Synergistic behavior of inspiratory muscles after diaphragmatic fatigue in the newborn. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 1981;51:547–551.


21. Muller N, Gulston G, Cade D, Whitton J, Froese AB, Bryan MH, et al. Diaphragmatic muscle fatigue in the newborn. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 1979;46:688–695.


22. Gewolb IH, Vice FL. Abnormalities in the coordination of respiration and swallow in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Dev Med Child Neurol 2006;48:595–599.


23. Wang LY, Luo HJ, Hsieh WS, Hsu CH, Hsu HC, Chen PS, et al. Severity of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and increased risk of feeding desaturation and growth delay in very low birth weight preterm infants. Pediatr Pulmonol 2010;45:165–173.


25. Gewolb IH, Fishman D, Qureshi MA, Vice FL. Coordination of suck-swallow-respiration in infants born to mothers with drug-abuse problems. Dev Med Child Neurol 2004;46:700–705.


27. Jolley CJ, Luo YM, Steier J, Reilly C, Seymour J, Lunt A, et al. Neural respiratory drive in healthy subjects and in COPD. Eur Respir J 2009;33:289–297.


28. Estrada L, Torres A, Sarlabous L, Jane R. Evaluating respiratory muscle activity using a wireless sensor platform. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2016;2016:5769–5772.
29. Farina D, Enoka RM. Surface EMG decomposition requires an appropriate validation. J Neurophysiol 2011;105:981–982.


30. Lunardi AC, Porras DC, Barbosa RC, Paisani DM, Marques da, Tanaka C, et al. Effect of volume-oriented versus flow-oriented incentive spirometry on chest wall volumes, inspiratory muscle activity, and thoracoabdominal synchrony in the elderly. Respir Care 2014;59:420–426.


31. Keens TG, Bryan AC, Levison H, Ianuzzo CD. Developmental pattern of muscle fiber types in human ventilatory muscles. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 1978;44:909–913.


32. Sieck GC, Fournier M, Blanco CE. Diaphragm muscle fatigue resistance during postnatal development. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991;71:458–464.


33. Bamford O, Taciak V, Gewolb IH. The relationship between rhythmic swallowing and breathing during suckle feeding in term neonates. Pediatr Res 1992;31:619–624.


34. Gewolb IH, Bosma JF, Vice FL. Maturational changes in the coordination of respiration and swallow in premature infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) [abstract]. Pediatr Res 2002;51.
Fig. 1
Recording sites for surface electrodes. E1–E2, diaphragm; E3–E4, rectus abdominis; a, midclavicular line; b, midaxillary line.
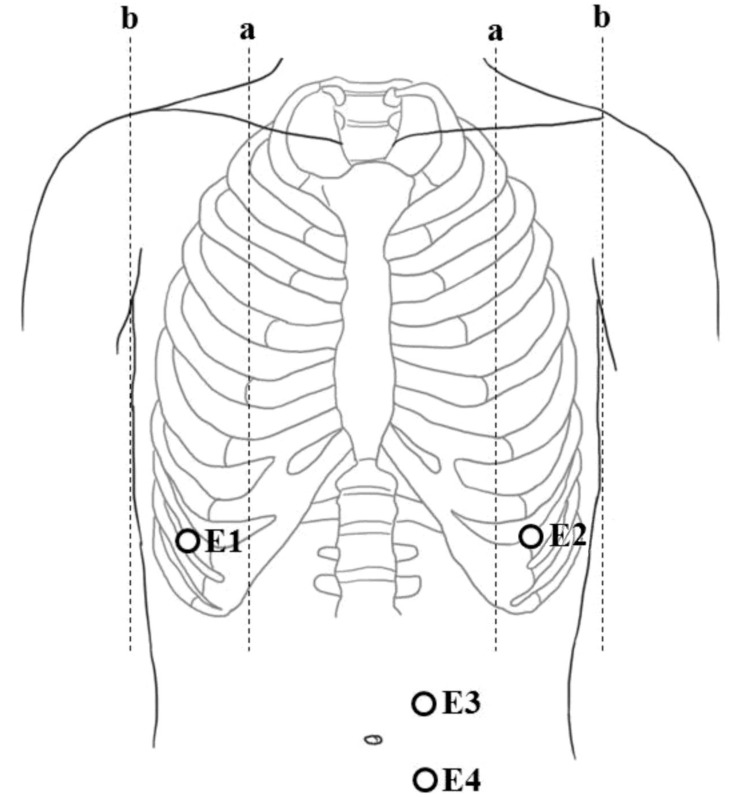
Fig. 2
Respiratory muscle activities in non-BPD, BPD, and Group 2. (A) RMS-D. (B) RMS-R. RMS-D, root mean square of diaphragm; RMS-R, root mean square of rectus abdominis; BPD, bronchopulmonary dysplasia.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


