Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 65(1); 2022 |
|
Abstract
The prevalence of developmental disabilities is increasing worldwide over time. Developmental issues in infancy or early childhood may cause learning difficulties or behavioral problem in school age, further adversely affecting adolescent quality of life, which finally lead to low socioeconomic status in family, increase in medical expenses, and other relevant issues in various ways. Early childhood has brain plasticity, which means there is high chance of recovering from developmental issues by early detection and timely intervention. Pediatricians are placed an ideal position to meet with young children till 6 years of age, of which age range is the time applicable to early intervention. Determining child’s developmental status can be made by 2 pathways such as developmental surveillance and developmental screening tests. For better results, pediatricians should update their knowledge about developmental issues, risk factors, and screening techniques through varying educational program or other relevant educating materials. This paper will update reports on the prevalence of developmental disabilities and review the recent results of the Korean developmental screening test and discuss relevant issues. Finally, it will be addressed the pediatrician’s role in early detecting developmental issues and timely intervention.
Graphical abstract. Overall flow of developmental evaluation
Development in childhood is dynamic in nature and a complex process accompanying biological and psychological changes along with physical growth. Early childhood, which usually refers to the first 5 years of life, is the fastest period of growth. During that period, the developing brain is most sensitive to stimulation and nurturing [1]. Therefore, in such sensitive periods, various factors can positively or negatively affect to development in early childhood [2].
Developmental delay (DD) in childhood has been adversely related to academic achievement in adolescence. The term of “developmental disorder” or “developmental disabilities” (DDs) refers to a heterogeneous group of sharing mental or physical impairments that result in substantial functional limitations in overall life activities [3,4]. They are chronic conditions that give rise to physical, psychological, and economic burdens for families and societies resulting in high medical expenses and low labor productivity. Increasing the prevalence of DDs is the common phenomenon occurring worldwide, although there are some variations of rate of prevalence depending on countries (Table 1). Therefore, the increasing trend of DDs has aroused attention of the societies, and is relevant with an increasing number of epidemiological studies for DDs [5,6].
Early detection and proper intervention can reduce the chances of future developmental disorders and prevent secondary sequelae [7]. A first necessary step in order to plan for early intervention should start with knowing the estimated prevalence of DD and features of various types of delays [8]. Up-to-date reporting of DDs prevalence is important for understanding populations with disabilities, efficiently targeting such populations, administering interventions, making relevant policies, and finally monitoring their effectiveness [6].
DD can be developed within various domains, which are not mutually exclusive. In addition, it is not unusual for one of these areas to be unnoticed often [9]. Furthermore, the wide normal variation among children often makes parents or primary care pediatricians easily miss subtle findings which can be the clue of DD [10]. A strategy of developmental surveillance and periodic developmental screening test (DST) may help pediatricians more efficiently find such subtle clinical issues.
Early detection of DD requires comprehensive judgements of medical history, developmental evaluation, physical and neurological examination along with a DST. Most of them have been described in many literatures. Therefore, this paper will limit the scope to review the estimated prevalence of DDs in the recent literature worldwide and update the results of the Korean DST, finally addressing the pediatrician’s role in early detecting developmental issues and timely intervention.
Although direct comparison of the prevalence of DDs among worldwide countries is not possible due to many reasons such as methods, diagnostic criteria, ethnicity, age differences of population, and socioeconomic status, the increasing tendency of the prevalence of DDs is a globally common phenomenon (Table 1). For instances, the World Health Organization estimated that 8% of all children under 5 years of age have some types of developmental deficit [11]. In the United States, the prevalence of DDs among children between ages 3 and 17 increased by more than 2%, from 12.84% to 15.04% over a period of 12 years ranging from 1997 to 2008, and then 1.5% more increased during next 9 years till 2017 [5,6]. The same phenomenon is found in Asian and other countries (Table 1).
Recently, Rah et al. [12] reported a population-based epidemiological study of the prevalence and incidence of DDs in South Korea. That study shows an evident increase over the 15-year period in both the incidence rate and prevalence of 8 types of DDs among the younger population in South Korea as follows: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), cerebral palsy (CP), DD, intellectual disability (ID), language disorder, learning disorder, and special sensory disorder [12]. The prevalence of DDs steadily increased by more than 4 times (from 0.6 to 2.5) from 2003 to 2017 (Table 1). Boys had higher incidence than girls throughout the period, during which the gap increased from 19.1% to 31.4%.
The increase in medical cost or other expenses in children with DDs makes societies or countries focus on the importance of early detection and timely intervention. Therefore, many countries have implemented health screening programs for younger populations to early identify affected children to secure healthy national population and to lessen future medical expenses or other socioeconomic costs, starting from early 2000s.
In 2001, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) policy statement called for pediatricians to screen all children for DDs during routine well-child visits [13]. In 2004, by the Individuals With Disabilities Education Improvement Act, child health professionals are mandated to provide early identification and intervention for children with DDs through “medical home,” which is a community-based collaborative systems [3]. The medical home provides a triad of key primary care services including preventive care, acute illness management, and chronic condition management [3]. In 2006, the AAP released guidelines for developmental surveillance at every well-child visit and use of a standardized screening tool at the 9-, 18-, and 24- or 30-month well-child visits [3,13]. In 2016, 63% of pediatricians have been reported to use standardized developmental screening tools [14]. The Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ), Parents’ Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS), and Denver II test along with the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers were widely adopted as standardized developmental screening tools. The frequency of use is ASQ, PEDS, and Denver II in order. However, still, one-third of pediatricians are not applying standardized screening test tools in United States due to several causes such as time limitation, inadequate reimbursement, and lack of treatment options for positive screening results [14].
In Singapore, every well child is scheduled to be seen by trained nurses or doctors for a developmental screening at specific ages for 6 rounds between the ages of one month and 4–6 years [15]. The developmental checklist is based on the Denver Developmental Screening Test (DDST-Singapore) [15].
In Taiwan, under the Enforcement Rules of the Children and Youth Welfare Law of Taiwan, the Taipei City Developmental Checklist for Preschoolers, a second version has been used as the assessment tool to identify children with DD [16]. The government of Taiwan further promotes the early intervention of DD at the Child Developmental Assessment Center under the laws of the “Protection of Children and Youths Welfare and Rights Act.” The main scope of their responsibilities is to screen children at risk, provide transdisciplinary assessments, diagnose the children with DD, and write assessment and therapy recommendation reports [17]. Developmental surveillance has been conducted in children aged 2–3 years and 4–6 years, and clinicians have been requested to report results via the internet when children with abnormal development are found. Doctors are paid Taiwan Dollar (TWD) 80 National Taiwan dollar for each report and in advance if the child is diagnosed with DD, and awarded another TWD 800 as an encouragement for the screening effort. This efficient strategy has increased the rates of eligibility for access to early intervention services and should thus encourage other early intervention professionals [17].
In Norway, the public health system provides free medical, mental, and dental services for all children and youth from 0–18 years, and close to 100% of parents with young infants come regularly to local well-baby clinics from birth and up to 5 years of age for weight control, vaccination and developmental checkups of their infant [8]. Checkups and developmental monitoring are conducted by public health nurses and general practitioners based on clinical judgement, not using standardized screening tools. The health providers’ clinical judgement, along with parental concerns are the primary bases for decision-making.
Netherlands has administered preventive child healthcare (PCH), which is a community-based well-childcare. PCH is offered to all children from birth until adolescence with free of charge [18]. Recently, researchers from Dutch developed a prediction model to identify children at risk of future DD at age 4 in a population-based setting, which showed good performance with an area under the curve of 0.84 [18].
Estonia offers comprehensive health coverage. Infants receive monthly health monitoring as well as at least 3 appointments with a nurse during their first year. During these appointments, the nurse provides families with information on child nutrition, safety, and others. Before attending to primary school at age 6, all children receive a school readiness health checkup to address any health or developmental issues. Primary care is free, and school nurses generally provide health screenings at grades 1, 3, 7, and 11. They refer families to a primary care physician or specialist when needed [19]. In Finland, all prenatal and perinatal care is free of charge, as are annual checkups for children up to age 7 [20].
DDs typically persist throughout a child's life and therefore require significant resources and planning for support services over the life span for optimal health, education, and functioning [21]. As compared to children without disabilities, children with at least one developmental disability need higher rates of hospital visit, personal carers, special education, and increased prescribed medication use [22]. Therefore, timely surveillance of DDs is crucial for developing effective programs and policies, and providing early intervention to maximize health and well-being.
Developmental surveillance is a systematic approach aiming to early detect children who may be at risk of future DD and plan next steps such as making referral to subspecialty or scheduling next appointment [23]. Dworkin defined it as “a flexible, continuous process whereby knowledgeable professionals perform skilled observations of children during the provision of health care.” [24] Its components include hearing or asking about parents’ concerns of their child development, taking developmental history, skilled observations of children, identifying risk and protective factors, and offering parents anticipatory guidance on health and developmental issues with consultation with other relevant professionals [3,25].
Surveillance begins by eliciting and addressing parents’ concerns at every well-child visit [23]. It is a longitudinal process designed to help clinicians focus on identification and intervention into the early stage of problems in order to potentially prevent them [26].
When pediatricians are heard of parents’ concern about developmental issue, most of it are found to be within normal variation. Therefore, clinicians may answer to parents simply for reassurance [10]. However, pediatricians should cautiously use the phrase “The child will grow out of it,” a kind of “wait and see” approach [10]. Just waiting without objective evidence and only relying on clinical judgement may cause late recognition, finally resulting in parental dissatisfaction, anxiety, and loss of the benefits from early identification and intervention [3].
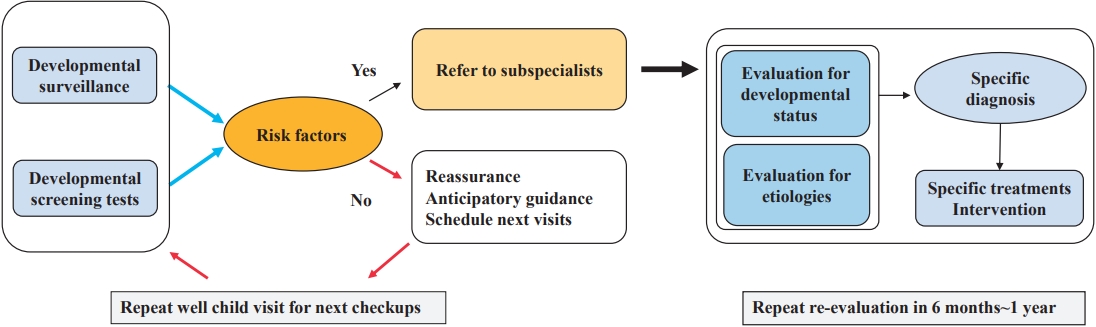
Along with eliciting parents’ developmental concerns, systematic history taking is followed. It includes pre-/peri-/postnatal histories, milestones, 3-generation pedigree in family history relating to DD or other neurologic disorders, and socioeconomical backgrounds (Fig. 1). When taken history, it should be made based on the presence of identifiable risk factors, which are as followings; biologic risk (prenatal or perinatal insult), environmental risk (familial circumstances such as financial issue, alcohol, and abuse), and established risk (previously diagnosed neurological disorders) [10,27,28].
In addition, clinical judgement may lead to miss mild phenotype of DD depending on variable causes such as the degree of pediatrician’s experience, time constraints, and attitude attempting to focus on developmental issues. DST can help physicians identify potential issues more efficiently, which are not yet progressing to be overt.
Developmental screening is one of several strategies in the prevention and amelioration of DDs and complications [2]. DST is “a brief assessment procedure designed to identify children who should receive more intensive diagnosis or assessment.” [29]
Korean government launched the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children (NHSPIC) on November 2007 to perform the serial assessment and management of the growth and development of infants and children as a health checkup program [7]. It started with body measurement and DST. Educational sessions and dental checkups were added in 2010. In 2012, 7th checkup for the group aged 66–71 months was added in Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) [30].
When DST was conducted first at November 2007, Korean ASQ (K-ASQ) or Denver II test was used. However, Denver II test needed skillful practitioner’s effort and time. K-ASQ test did not reflect cultural difference and some items showed low specificity. Finally, K-DST was developed and has been used as a first edition since September, 2014. Since then, all test results are stored and managed in the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) web server, which allows parents and clinicians to look all serial data. In 2017, first edition of K-DST was revised as a second edition, which was more sophisticated with high sensitivity and specificity [7].
K-DST is a parent-reported screening test that allows parents to directly monitor the development of their children, taking less time and is able to quickly and effectively identify varying domains of DD in primary care institutions [7]. Although it is based on parental reports, its reliability and validity as a screening test have been confirmed because its results are highly correlated with those of the Korean Bayley Scales of Infant Development-II and Korean Weschler Preschool and Primary Scales of Intelligence, the most widely used test tools for confirming neurodevelopmental disorders [7].
According to the NHIS database maintained by the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, an estimated 3 million children are scheduled to visit to primary care clinics or hospitals for serial health checkups annually. The number of participants is slightly decreasing over time (from 3,200,486 in 2012 to 2,712,089 in 2019), a trend that is in line with the decreasing birth rate (Table 2). This test was first administered to recipients with health insurance. In 2015, it was applied to infants or children of all families, which is the reason why the data increased since then (Figs. 2, 3).
The overall checkup rate is gradually increasing yearly. In 2012, the participation rate was 55%; it had increased to 78% by 2019 (Table 2). In other words, an estimated 20% still did not participate in checkup programs in 2019. The overall nonparticipation rate was decreasing over time, but it increased with age within the same year (Table 2, Fig. 4). Specifically, the nonparticipation rate peaked in the group of children aged 66–71 months at nearly 40% in 2019 (Fig. 4). Among regions or provinces in South Korea, in 2019, the nonparticipation rate ranged from 15% to 25%; based on NHIS data, the highest rate was observed in Jeollabuk-do province, while the lowest rate was observed at Jeju province.
Rah et al. [12] reported in a national study that children with higher economic status showed a higher tendency to visit clinics for checkups. They suggested that the government’s financial support should not be limited to providing the free screening program but that it also needs to expand to support affordability of time to ameliorate the health inequalities caused by economic status [12]. In another national study, Shin et al. [31] reported that time limitations for work or other reasons were the main constraint causing parents to miss their children’s checkups.
The results of developmental evaluations of the K-DST subitems are described in 4 categories: good, follow-up test, further evaluation, and on-going care. “Good” refers to screening “negative” while the other 2 categories are considered as screening “positive” except for “on-going care,” which means already having known DDs (Table 2). In the details, “follow-up test” means that clinicians cannot determine whether children are developmentally normal or abnormal at the time of the checkup. Therefore, it needs to be done for short-term follow-up for re-evaluation. More specifically, among them, children younger than 2 years of age are recommended to visit the clinic to repeat the K-DST in 2 months after taking it the first time. Children who are 2 years old or older should be retested in 3 months after the initial checkup (Fig. 1). “Further evaluation” indicates the need for a referral to a subspecialist such as a pediatric neurologist, pediatric psychiatrist, or pediatric rehabilitation medicine doctor to address suspected developmental issues (Fig. 1).
Based on NHIS data regarding the results of K-DST, the screening “negative” result has gradually decreased to 86%, while the screening “positive” result has increased (Table 2). The “follow-up” and “further evaluation” groups have gradually increased to 12% and 2%, respectively (Table 2).
By sex ratio, the “good” category showed similar proportions in both sexes. However, boys consistently showed a higher proportion than girls in the “follow-up” and “further evaluation” groups (Fig. 2B, C). The sex ratio (male:female) in both groups has been found to be consistently 1.7 from 2017 to 2019. Those findings are in line with other relevant studies. In the Taiwan study, the prevalence of DD in boys is 2.13 times (2.09–2.18 for 1997–2008) that of girls [17] and Boyle et al. [5] reported that it was 1.78.
Many theories have been proposed to explain the sex difference, including both biological and sociological factors. Biologically, the higher risk in boys is often attributed to hereditary factors such as X-linked conditions [32,33]. The central nervous system of young boys is also found to be more susceptible to various damage [32]. In terms of social factors, in Asian countries, families generally display a male gender preference, and thus pay more attention to boys [32,33]. Moreover, boys are more likely to demonstrate impulsive and aggressive behaviors than girls and therefore are more likely to be referred for diagnosis. Furthermore, it can be also explained by the concept of “female protective model”, which shows higher mutation burden in females protects them from the disease and explains the increased male prevalence in many neurodevelopmental disorders [34].
In the section of additional question, parents can answer the questions only in a “yes or no.” There is high chance of false-positive cases situation. Parents would answer a “yes” even in the case of only once observation in their children’s activities. This can lead to the result of high positive rate for the “peer” and “high-level” groups. It needs to be more specified in choosing choices in those questions [30].
Further, feedback system is needed for pediatricians or other clinicians when they refer children who are finally categorized as a “further evaluation” group to subspecialists to raise clinical experience regarding it. Sharing with the web service for reporting consultation results of subspecialists can be one of the solution [30].
Although clinicians recommend that parents of children who screen positive visit subspecialists, only some parents actually do so. Still, no further specific and consistent system has been available to provide follow-up action according to the results of the DST. When NHSPIC examinations are performed at tertiary medical centers, it is easier to refer the “further evaluation” group for a consultation with subspecialists at the same medical institution. However, most patients visit primary care institutions; thus, the “further evaluation” group often does not undergo further assessment and management due to many barriers such as parents disagreeing with the referral, family denial, lack of understanding of the need of further evaluation, the mother’s poor mental health, and other family-related environmental factors [35]. The first step toward ameliorating this issue is for the clinician to ensure that the parents understand the need for the intervention.
For France, the Netherlands, Estonia, and Finland, monthly developmental evaluations are provided for the first 6 months of age, but the NHSPIC does not include developmental evaluations for the same period [12,31]. Further studies are needed for the efficacy of the DST in very young infants in South Korea.
The current NHSPIC incudes evaluations for gross motor, fine motor, cognition, language, social, and self-help skills along with additional questions regarding CP and ASD. However, it has not evaluated the coexistence of other psychiatric problems. The 5 developmental domains are not mutually exclusive. There can be a high probability of coexistence with psychiatric problems in infants and children who screen positive on developmental assessments. Therefore, a secondary evaluation is needed to screen for psychiatric problems among infants and children at risk of developmental issues following the previous screening test.
To meet that need, in South Korea, short-term national project conducted under the title of “development of the comprehensive assessment inventory for differential diagnosis and the evaluation of comorbidity of DD kids under 7 years old” from September 2015 to August 2017. It started with the purpose of providing a secondary screening tool to evaluate further for “follow-up” group and “further evaluation” group following initial screening by K-DST to enhance developmental screening efficiency [36]. Finally, after benchmarking the electronic preschool age psychiatric assessment (ePAPA), Korean-ePAPA was developed. And then “Infant Comorbidity Evaluation for Neurodevelopmental Delay” tool was developed on April 2017 and was registered for patent registration on February 2018. However, since the final report regarding it on 2017, there has been no further progression due to several reasons such as the termination of study period and lack of research fund. It requires more research of the formal utility on screening infants and children at-risk following first screening test under the cooperation by multidisciplinary teams with national research fund.
Speech and language delays are the most common developmental problem among preschool children. Its prevalence is estimated to be 5%–12% in children 2 to 5 years of age [37]. Among them, expressive language delay is one of the most common reasons that young children are referred for further evaluation [38]. Language is linked to both cognitive and emotional development and is served to guide cognition and behavior [39]. Children with receptive language delay are fairly likely to have continuing language delay, as well as being at risk for later learning, behavioral, and emotional problems [40]. Therefore, impaired language learning is correlated with poor outcomes in academic achievement, reading, comprehension, socio-behavioral development, and self-esteem [41]. So, language delay may be the 1st indication of ID, ASD, and child neglect [39].
Children with having future ID usually show different pattern of DD in early childhood according to their age. In early infancy, a lack of visual or auditory responsiveness, abnormal muscle tone (hypo- or hypertonia), and feeding difficulties are observed. Between 6 and 18months of age, gross motor delay is the most common complaint. Language delay and behavioral problems are common concerns after 18months [39]. In infants and toddlers, motor and language milestones are often the best substitute for cognitive assessments [10]. Accordingly, ID can be mostly manifested as language or behavioral problems since 18 months of age before definite diagnosis of ID after 6 years of age.
The term “late talkers” (LT) refers to young children aged 18–35 months who have limited expressive vocabulary and/or receptive language in the absence of neurodevelopmental disabilities [40,42]. Several studies reported that 9% to 20% of 2- to 3-year-old children are late talkers [41,43]. Longitudinal studies revealed that many of LT catch up to their normal peers within 4 years of age [44,45]. However, 6% to 44% of late talkers have persistent language impairments [46].
The large and prospective study reported that 3 protective factors associated with late talking were identified: book reading, play opportunities, and formal childcare experiences at child care centers [41]. They are all examples of stimulation activities for language-based social interaction with various communication partners [41]. Especially, reading aloud to children is a powerful strategy to promote language development, vocabulary, and parent-child relationship [39].
If there are family histories of LT of parents, no other accompanying neurologic deficits, and no social/behavioral problem along with the result of “follow-up recommendation,” pediatricians should recommend the retest of K-DST in 2 months or 3 months following the initial K-DST according to their ages with stimulation activities and perform close observation of children’s language development over time (Fig. 1).
Sensory development such as auditory, visual, tactile, and proprioception is the crucial neurodevelopmental process helping children experience and control their environments. Through sensory experiences, children’s brains mature as new neuronal pathways are reorganized interplaying with environmental exposure along with strengthening of existing pathways [39]. Therefore, sensory deprivation at the stage of reorganization of synapses such as preservation and pruning has led to adverse effects in early childhood development. About 30% of hearing-impaired children have at least one other neurological disability such as ID, CP, and craniofacial anomalies [39]. Therefore, vision and hearing evaluation are essential to detect and treat for sensory impairments.
Based on the report regarding global trend of prevalence of DDs between 1990 and 2016, vision loss and hearing loss were most common among 6 types of DDs such as ID, ADHD, epilepsy, ASD, hearing loss, and vision loss [11]. Pediatricians can find 2 questions asking about hearing and visual function on the first page of K-DST sheets. It is essential to check the status of hearing and vision at the checkup [11].
Maximum brain development occurs within the first 3 years of a child’s life [15]. Each neuron develops on average 15,000 synapses by that age [39]. During early childhood, through preservation of frequently used synapses pathways and pruning of less-used ones, reorganization of neuronal circuits occurs. It acts important roles in brain plasticity, which is the ability of the brain to be shaped by experience, continuing into adolescence [37]. Neuronal plasticity makes the central nervous system reorganize its networks depending on features of environmental stimulants in positive or negative ways [39]. Therefore, the critical period of treatment for DD is before the child reaches 3 years of age [47]. There is a high chance of catch-up growth by early intervention performed during the periods of plasticity. However, if its periods close without early intervention, more permanent deficits may occur [39].
Previous literature reported that early identification of DD and intervention can positively alter a child’s long-term trajectory through brain plasticity [1,48-50]. For example, for children who have communication problems, more than 65% can be improved when intervention happens before 3 years of age [51]. Del Tufo et al. [52] reported that early intervention decreased risk of poorer comprehension by almost 40%. In addition, they reported a positive association between receiving early intervention and expressive language development [52].
Children can have appropriate developmental progress despite childhood trauma through resilience. Resilience is the ability to withstand, adapt to, and recover from adversities. It is possible through strong connections within supportive families. Even children with biologic risk factors may do well developmentally in supportive family environment [39]. Pediatricians should be aware of that fact and attempt to level up resilience in their patients and families [3,39].
Biological factors are influenced by environmental factors. By the time children start talking, language learning abilities depend on how well biological variables and their linguistic environment are interplayed [40]. Therefore, through providing language enrich environment, early intervention can help improve their language abilities. Further, when related with significant environmental neglect or abuse, it is important to intervene in order to provide more supportive and stimulating environments to children [40].
In primary care settings, children with DD are normally identified through 3 major channels: during routine developmental surveillance or screening; parental concern; and third parties’ reports by such as school teachers or nursery carers [35]. Pediatricians should play an important role not only in the first channel, but also should be alert on parental or third parties’ concerning reports.
Early recognition of delays requires in-depth knowledge of child development [53]. The efficacy of surveillance and screening test depends on the clinician’s experience in being capable of taking adequate physical and neurologic examination, right reading of developmental screening results, and knowledge of developmental milestones [54]. Adequate knowledge of developmental milestones is essential for the primary care physician to be able to provide anticipatory guidance and suggest appropriate activities to the parents or caregivers so that they can facilitate the next stage of development (Fig. 1).
In relevant with this, the Red flag table can be used a criterion for making referral to subspecialists to make sure that children are on the right path of their own development (Table 3). If your child shows 2 or more these signs, it is recommended making referral to subspecialty (Table 3). In addition, pediatricians also can see some questions suggestive of red flags in K-DST. The additional question section is regarding the possibility of CP, language delay, and ASD. These questions can be the clue of early signs of future DDs. Pediatricians need to pay attention to the answers of the questions [56].
As shown in Fig. 1, if showing normal developmental status through surveillance and screening test, it indicate that the child is at low risk of a developmental disorder, reassurance can be offered to parents with recommendation of next follow-up visit [3]. In reassuring parents, the pediatrician should emphasize the importance of serial surveillance and screening [3]. Physicians should also be aware of other reversible factors affecting development, such as sleep, diet, and caregiver’s stress of childcare [15].
Mothers are the primary environment for their children. They have close relationships both in good or bad ways. Some authors reported mother's depression and stress as significant factors for children's development [57,58]. Major depression that arises during pregnancy or in the postpartum period threatens the mother–child relationship. It is a risk factor for later cognitive and behavioral problems. Persistent maternal depression has been linked to decreases in child intelligence quotient scores at school entry [39]. Therefore, pediatricians need to check familial environment, especially parental emotional stress such as depression and anxiety, which easily can be evaluated by self-reporting test [59]. The information about parental emotion and stress level facilitates referral for therapy, which may provide long-term benefits to the child [39].
Knowledge regarding development and quality of training varies among pediatricians. Various educational programs should be regularly held for general pediatricians to conduct surveillance and screening test properly. Pediatricians should maintain and update their knowledge about developmental issues, risk factors, and screening techniques through varying educational program or other relevant educating materials
During sensitive periods for brain development, early detection and intervention for DD in children are important because a child’s development has lifelong implications for health, learning, and well-being. For successful early identification, it requires pediatricians to be skillful of screening techniques, actively to address parental concerns about development, and make connections with available community resources.
Based on these efforts, primary care pediatricians should conduct systematic approach to detect children with suspicious DD through developmental surveillance, K-DST, along with acknowledgement of red flags.
Repeated developmental assessments over time are more informative than one time assessment in planning investigations and management. A continuing, on-going relationship between pediatricians, parents, and preschool teachers will guarantee better good neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Fig. 1.
Flowchart shows algorithm approach to developmental screening and surveillance. K-DST, Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children; N, normal; A, abnormal; SD, standard deviation; HC, head circumference; DS, developmental surveillance.

Fig. 2.
Gender ratio according to the results of developmental screening tests in the National Health Insurance Service database. (A) Good. (B) Follow-up test. (C) Further evaluation.

Fig. 3.
Yearly trend of the rate of “screening positive” at developmental screening tests according to age group in the National Health Insurance Service database. (A) Follow-up group. (B) Further evaluation group.

Fig. 4.
Nonparticipation rate according to participants’ age in the National Health Screening program for Infants and Children in South Korea in the NHIS database. NHIS, National Health Insurance Service.
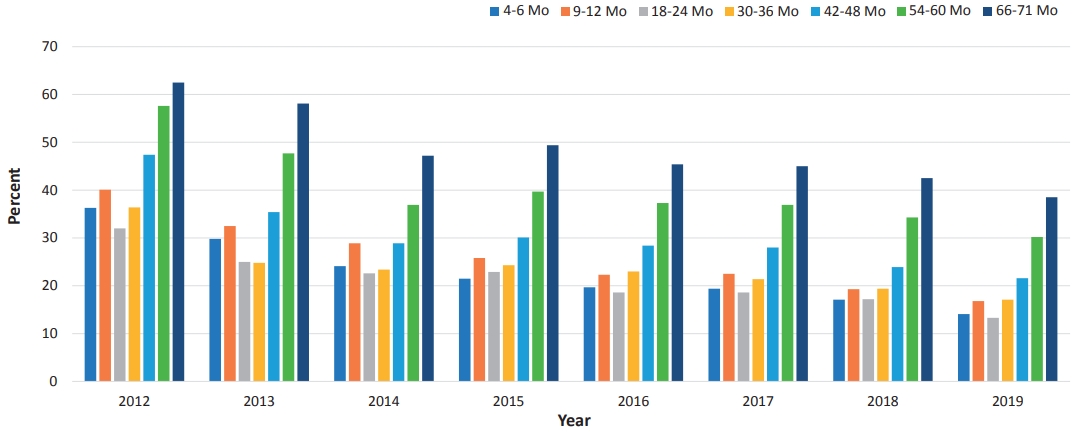
Table 1.
Prevalence rate of developmental disabilities worldwide
| Study | Country | No. of population | Age | Tool | Subjects | Prevalence (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global research [11] | Global | 52,856,396 | <5 yr | GATHER | ADHD, ASD, hearing loss, vision loss, epilepsy, ID | 1990 | 2016 |
| 8.9 | 8.4 | ||||||
| Rah et al. [12] | South Korea | 754,972 | 0–6 yr | NHIS database | 8 DDs: ADHD, ASD, CP, DD, ID, language disorder, learning disorder, special sensory disorder | 2003 | 2017 |
| 0.6 | 2.5 | ||||||
| Kuo et al. [17] | Taiwan | 2,308,790 | <6 yr | NHIS database | DD | 1997 | 2008 |
| 0.16 | 3.25 | ||||||
| Boyle et al. [5] | USA | No mention | 3–17 yr | NHIS, survey | 10 DDs: ADHD, autism, CP, MR, other DD, hearing loss, seizure, stuttering, blindness, learning disability | 1997 | 2008 |
| 12.84 | 15.04 | ||||||
| Zablotsky et al. [6] | USA | 88,530 | 3–17 yr | NHIS, survey | Same as above | 2009 | 2017 |
| 16.22 | 17.76 | ||||||
| Valla et al. [8] | Norway | 1,555 | 4–12 mo | ASQ, version 2 | Communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem solving, and personalsocial | 2011 May–2012 May | |
| 5.7–7 | |||||||
| Sajedi et al. [60] | Iran | 10,516 | 4–60 mo | ASQ | Same as above | 2013 | |
| 3.67–4.31 | |||||||
| Correia et al. [61] | Brazil | 3,566 | 2–72 mo | ASQ, version 3 | Same as above | 2017 | |
| 9.2 | |||||||
GATHER, Guidelines for Accurate and Transparent Health Estimates Reporting; NHIS, National Health Insurance Service; ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; ASD, autism spectrum disorder; ID, intellectual disability; DDs, developmental disabilities; DD, developmental delay; CP, cerebral palsy; MR, mental retardation; NHIS, National health interview surveys; ASQ, Ages and Stage Questionnaires.
Table 2.
Time trend of the results in the Korean developmental screening test in the NHIS database
Table 3.
Red flags suggestive of suspected delayed development in infant and early childhood
Adapted and modified from www.cdc.gov/milestones. [10,55]
References
1. From neurons to neighborhoods: the science of early childhood development. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2000.
2. Anderson LM, Shinn C, Fullilove MT, Scrimshaw SC, Fielding JE, Normand J, et al. The effectiveness of early childhood development programs. A systematic review. Am J Prev Med 2003;24:32-46.

3. Council on Children With Disabilities; Section on Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics; Bright Futures Steering Committee; Medical Home Initiatives for Children With Special Needs Project Advisory Committee. Identifying infants and young children with developmental disorders in the medical home: an algorithm for developmental surveillance and screening. Pediatrics 2006;118:405-20.



4. Petersen MC, Kube DA, Palmer FB. Classification of developmental delays. Semin Pediatr Neurol 1998;5:2-14.


5. Boyle CA, Boulet S, Schieve LA, Cohen RA, Blumberg SJ, Yeargin-Allsopp M, et al. Trends in the prevalence of developmental disabilities in US children, 1997-2008. Pediatrics 2011;127:1034-42.


6. Zablotsky B, Black LI, Maenner MJ, Schieve LA, Danielson ML, Bitsko RH, et al. Prevalence and trends of developmental disabilities among children in the United States: 2009-2017. Pediatrics 2019;144:e20190811.


7. Chung HJ, Yang D, Kim GH, Kim SK, Kim SW, Kim YK, et al. Development of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST). Clin Exp Pediatr 2020;63:438-46.



8. Valla L, Wentzel-Larsen T, Hofoss D, Slinning K. Prevalence of suspected developmental delays in early infancy: results from a regional population-based longitudinal study. BMC Pediatr 2015;15:215.



10. First LR, Palfrey JS. The infant or young child with developmental delay. N Engl J Med 1994;330:478-83.


11. Global Research on Developmental Disabilities Collaborators. Developmental disabilities among children younger than 5 years in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Glob Health 2018;6:e1100-21.



12. Rah SS, Hong SB, Yoon JY. Prevalence and incidence of developmental disorders in Korea: a nationwide population-based study. J Autism Dev Disord 2020;50:4504-11.


13. Sand N, Silverstein M, Glascoe FP, Gupta VB, Tonniges TP, O'Connor KG. Pediatricians' reported practices regarding developmental screening: do guidelines work? Do they help? Pediatrics 2005;116:174-9.


14. Lipkin PH, Macias MM, Baer Chen B, Coury D, Gottschlich EA, Hyman SL, et al. Trends in pediatricians' developmental screening: 2002-2016. Pediatrics 2020;145:e20190851.


15. Choo YY, Yeleswarapu SP, How CH, Agarwal P. Developmental assessment: practice tips for primary care physicians. Singapore Med J 2019;60:57-62.



16. Lai DC, Tseng YC, Guo HR. Characteristics of young children with developmental delays and their trends over 14 years in Taiwan: a population-based nationwide study. BMJ Open 2018;8:e020994.



17. Kuo HT, Muo CH, Chang YT, Lin CK. Change in prevalence status for children with developmental delay in Taiwan: a nationwide population-based retrospective study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2015;11:1541-7.


18. Siderius EJ, Carmiggelt B, Rijn CS, Heerkens YF. Preventive child health care within the framework of the Dutch health care system. J Pediatr 2016;177S:S138-41.


19. National Center on Education and the Economy (NCEE). Estonia [Internet]. Washington, DC: NCEE; 2021 [cited 2021 Jun 24]. Available from: https://ncee.org/country/estonia/.
20. National Center on Education and the Economy (NCEE). Finland [Internet]. Washington, DC: NCEE; 2021 [cited 2021 Jun 24]. Available from: https://ncee.org/country/finland/.
21. McGuire DO, Tian LH, Yeargin-Allsopp M, Dowling NF, Christensen DL. Prevalence of cerebral palsy, intellectual disability, hearing loss, and blindness, National Health Interview Survey, 2009-2016. Disabil Health J 2019;12:443-51.



22. Boulet SL, Boyle CA, Schieve LA. Health care use and health and functional impact of developmental disabilities among US children, 19972005. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2009;163:19-26.


23. Glascoe FP, Robertshaw NS. New AAP policy on detecting and addressing developmental and behavioral problems. J Pediatr Health Care 2007;21:407-12.


24. Dworkin PH. Detection of behavioral, developmental, and psychosocial problems in pediatric primary care practice. Curr Opin Pediatr 1993;5:531-6.


25. Dworkin PH. British and American recommendations for developmental monitoring: the role of surveillance. Pediatrics 1989;84:1000-10.

26. Blair M, Hall D. From health surveillance to health promotion: the changing focus in preventive children's services. Arch Dis Child 2006;91:730-5.



27. Bennett FC, Guralnick MJ. Effectiveness of developmental intervention in the first five years of life. Pediatr Clin North Am 1991;38:1513-28.


28. Zuckerman B, Bresnahan K. Developmental and behavioral consequences of prenatal drug and alcohol exposure. Pediatr Clin North Am 1991;38:1387-406.


29. Meisels SJ, Provence S. Screening assessment: guidelines for identifying young disabled and developmentally vulnerable children and their families. Washington, DC: National Center for Clinical Infant Program, 1989.
30. Suh CR, Sohn SY, Kim GH, Jung SK, Eun BL. Single-center experience of the Korean-Developmental Screening Test for infants and children. Korean J Pediatr 2016;59:483-9.



31. Shin SM, Choi BM, Choi JE. Problem analysis and the improvement plan for the national health screening program for infants and children. Sejong (Korea): Ministry of Health and Welfare, 2017.
32. Leonard H, Wen X. The epidemiology of mental retardation: challenges and opportunities in the new millennium. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2002;8:117-34.


33. Munro JD. Epidemiology and the extent of mental retardation. Psychiatr Clin North Am 1986;9:591-624.

34. Jacquemont S, Coe BP, Hersch M, Duyzend MH, Krumm N, Bergmann S, et al. A higher mutational burden in females supports a "female protective model" in neurodevelopmental disorders. Am J Hum Genet 2014;94:415-25.



35. Choo YY, Agarwal P, How CH, Yeleswarapu SP. Developmental delay: identification and management at primary care level. Singapore Med J 2019;60:119-23.



36. Bahn GH, Lee KS. Development of the comprehensive assessment inventory for differential diagnosis and the evaluation of comorbidity of developmental delay kids under 7 years old [Internet]. Seoul (Korea): Korea Mental Health Technology R&D Project; 2017 [cited 2021 Jun 24]. Available from: http://www.mhrnd.re.kr/xe/apply_list/1208.
37. Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C. Prevalence and natural history of primary speech and language delay: findings from a systematic review of the literature. Int J Lang Commun Disord 2000;35:165-88.


38. Rescorla L LE. Language impairments in young children. In: Layton T, Wastson L, editors. Handbook of early language impairment in children. I: Nature. New York: Delmar Publishing Company, 2000:1-38.
39. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW III, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 21th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Inc., 2020.
40. Rescorla L. Late talkers: do good predictors of outcome exist? Dev Disabil Res Rev 2011;17:141-50.


41. Collisson BA, Graham SA, Preston JL, Rose MS, McDonald S, Tough S. Risk and protective factors for late talking: an epidemiologic investigation. J Pediatr 2016;172:168-74; e1.


42. Hawa VV, Spanoudis G. Toddlers with delayed expressive language: an overview of the characteristics, risk factors and language outcomes. Res Dev Disabil 2014;35:400-7.


43. Zubrick SR, Taylor CL, Rice ML, Slegers DW. Late language emergence at 24 months: an epidemiological study of prevalence, predictors, and covariates. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2007;50:1562-92.


44. Dale PS, Price TS, Bishop DV, Plomin R. Outcomes of early language delay: I. Predicting persistent and transient language difficulties at 3 and 4 years. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2003;46:544-60.


45. Chilosi AM, Pfanner L, Pecini C, Salvadorini R, Casalini C, Brizzolara D, et al. Which linguistic measures distinguish transient from persistent language problems in late talkers from 2 to 4 years? A study on Italian speaking children. Res Dev Disabil 2019;89:59-68.


46. Hart KI, Fujiki M, Brinton B, Hart CH. The relationship between social behavior and severity of language impairment. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2004;47:647-62.


47. Grantham-McGregor S, Cheung YB, Cueto S, Glewwe P, Richter L, Strupp B, et al. Developmental potential in the first 5 years for children in developing countries. Lancet 2007;369:60-70.



48. Scherzer AL, Chhagan M, Kauchali S, Susser E. Global perspective on early diagnosis and intervention for children with developmental delays and disabilities. Dev Med Child Neurol 2012;54:1079-84.


49. Hebbeler K, Spiker D, Baily D, Scarborough AA, Mallik S, Simeonsson RJ. Early intervention for infants and toddlers with disabilities and their families: participants, services, and outcomes. Menlo Park: SRI International, 2007.
50. Barger B, Rice C, Wolf R, Roach A. Better together: developmental screening and monitoring best identify children who need early intervention. Disabil Health J 2018;11:420-6.



51. Mulrine C, Kollia B. Speech, language, hearing delays: time for early intervention? J Fam Pract 2015;64:E1-9.
52. Del Tufo SN, Earle FS, Cutting LE. The impact of expressive language development and the left inferior longitudinal fasciculus on listening and reading comprehension. J Neurodev Disord 2019;11:37.



53. Developmental surveillance and screening of infants and young children. Pediatrics 2001;108:192-6.



55. Horridge KA. Assessment and investigation of the child with disordered development. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2011;96:9-20.


56. Eun BL, Chung HJ. Korean-development screening test for infants and children. Cheongju (Korea): Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014.
57. Beck CT. Maternal depression and child behaviour problems: a meta-analysis. J Adv Nurs 1999;29:623-9.


58. Burchinal MR, Roberts JE, Hooper S, Zeisel SA. Cumulative risk and early cognitive development: a comparison of statistical risk models. Dev Psychol 2000;36:793-807.


59. Valicenti-McDermott M, Lawson K, Hottinger K, Seijo R, Schechtman M, Shulman L, et al. Parental stress in families of children with autism and other developmental disabilities. J Child Neurol 2015;30:1728-35.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


