Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 66(1); 2023 |
|
Abstract
Background
Although preterm infants often experience desaturation or bradycardia during oral feeding, specific guidelines for its management are lacking.
Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effects of a commercial thickened formula (TF) on oxygen saturation and heart rate stabilization during oral feeding in preterm infants.
Methods
This retrospective study included 122 infants born at a median (interquartile range [IQR]) 31+6 weeks (29+4 −34+6 weeks) of gestation weighing 1,725 g (1,353–2,620 g) and fed commercial cornstarch-containing TF due to feeding-associated desaturation or bradycardia. We excluded infants fed TF to treat symptomatic regurgitation. Desaturation and bradycardia events were compared between 3 days prior to the change and 3 days after the change to TF. Desaturation and bradycardia were defined as SpO2 <85% and heart rate <100 beats/min during or immediately after oral bottle feeding, respectively.
Results
The median (IQR) postmenstrual age and weight were 36+1 weeks (34+6–38+0 weeks) and 2,395 g (2,160–2,780 g), respectively, at the time of change to TF. The frequency of desaturation significantly decreased after TF feeding (median [IQR]: 2.3 [1.3–3.3] events/day vs. 0.3 [0–1.7] events/day, P< 0.001). Bradycardia also decreased after TF feeding (0.3 [0–1] events/day vs. 0 [0–0.7] events/day, P=0.006). There were no cases of diarrhea or electrolyte abnormalities after TF feeding. Defecation frequency decreased (P=0.037), and polyethylene glycol was prescribed to 27% of the TF-fed infants. In a subgroup analysis of 16 infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia, the frequency of desaturation was reduced (2.3 [1.8–3.8] events/day vs. 0.5 [0–1.5] events/day, P=0.042), and weight gain improved (22.5 [3.1–36.3] g/day vs. 41.3 [28.1–55.1] g/day, P=0.019), after TF feeding.
Graphical abstract
Competent oral feeding in preterm infants is essential for hospital discharge readiness. The overall prevalence of problematic neonatal feeding is 25%–40%, which increases as the infant is more premature [1-5]. With respect to various feeding problems, desaturation or bradycardia associated with oral feeding often delays the discharge of preterm infants from a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and repeated episodes may be harmful to the developing brain [1-3,6,7]. The mechanisms attributed to unstable cardiorespiratory vital signs during oral feeding include poor coordination of the suck-swallow-breath cycle, immature sucking power, immature oral structures, gastroesophageal reflux, and associated lung or airway diseases [8-15]. Given the diversity of the underlying etiologies and clinical manifestations of feeding problems in neonates, the lack of standardized diagnostic definitions and therapeutic strategies is challenging.
A thickened formula (TF) refers to any modified formula with the addition of thickening agents to increase viscosity aiming to decrease regurgitation [16]. Cornstarch-containing TF is widely used in infants with gastroesophageal reflux and is recognized as harmless [16,17]. Although the mechanism is not fully understood, TFs are frequently used in infants with dysphagia or feedingassociated desaturation, or bradycardia [18-20]. However, there are a limited number of studies investigating the efficacy and safety of TFs in premature infants. Thus, we aimed to demonstrate how these TFs improve hemodynamic stability during oral feeding in preterm infants. We also evaluated the safety of a commercial TF in this population.
This retrospective study was conducted in the NICU of Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea. Among infants admitted to the NICU from October 2018 to December 2020, preterm infants born before 37 weeks of gestation and fed a commercial TF (Novalac AR, Novalac United Pharmaceuticals, Paris, France) because of desaturation or bradycardia during or immediately after oral feeding were included. We excluded infants who were fed TF due to symptomatic regurgitation without desaturation or bradycardia. Also, infants who required any medication for apnea or symptomatic heart failure were excluded. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Inha University Hospital (IRB No. 2022–05–031). The requirement for informed consent was waived by the board due to the retrospective nature of this study.
Neonatal data were collected from medical records. A percutaneous pulse oximeter sensor (Nellcor N-200; Nellor Inc., Hayward, CA, USA) was used to measure oxygen saturation (SpO2) and heart rate. Flexible skin electrocardiogram electrodes (Ambu BlueSensor BRS, Ambu Inc., Ballerup, Denmark) were used to monitor heart rate. Desaturation and bradycardia were defined as SpO2 <85% and heart rate <100 beats/min during or immediately after oral bottle feeding, respectively. The number of desaturation and bradycardia events was compared between 3 days before and after the change of milk to TF. Comorbidities and the type of milk before changing to TF were investigated. Respiratory distress syndrome was diagnosed by the attending physician based on respiratory symptoms, chest radiography, and blood gas analysis. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) was defined as oxygen dependency at a postmenstrual age of 36 weeks with oxygen treatment for at least the first 28 days of life. Subgroup analyses were performed for infants having BPD. For safety evaluation, we collected data on weight gain, stool frequency, diarrhea, and serum electrolytes during the 5 days before and after TF feeding. In addition, parental compliance with continued TF feeding at the 1-month follow-up after discharge was also investigated.
Continuous data were assessed for normality using the ShapiroWilk test, and a paired t test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare the data before and after formula change. A statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 27.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Variables were expressed as median (interquartile range [IQR]) or numbers (%). A P value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
A total of 122 preterm infants were included in this study. The median (IQR) gestational age and birth weight were 31+6 weeks (29+4−34+6 weeks) and 1,725 g (1,353–2,620 g), respectively. Respiratory distress syndrome and BPD were diagnosed in 29 (23.8%) and 16 patients (13.1%), respectively. Twelve infants (9.8%) experienced intraventricular hemorrhage (grade ≥2) and 2 of them had a history of seizures. At the time of change to TF, only 1 infant was administered one anticonvulsant with a seizure-free state. Eighty-one infants (66.4%) were breastfed wholly or partially, and 41 infants (33.6%) received only formula milk (Table 1).
The median (IQR) postnatal age, postmenstrual age, and body weight at the time of change to TF were 22 days (6−38 days), 36+1 weeks (34+6–38+0 weeks), and 2,395 g (2,160–2,780 g), respectively. After the change to TF, median (IQR) bradycardia decreased from 0.3 event/day (0–1 event/day) to 0 event/day (0–0.7 event/day) (P=0.006). The frequency of desaturation was also significantly reduced from 2.3 event/day (1.3–3.3 event/day) to 0.3 event/day (0–1.7 event/day) (P<0.001) (Fig. 1, Table 2). In most patients, feeding-associated bradycardia and desaturation dramatically decreased immediately after the change to TF (Fig. 2).
The median (IQR) weight gain for 5 days after the change to TF was 28.8 g (0.7–42.5 g) per day and did not differ from that of 5 days before TF feeding (P=0.092). When we analyzed the change in weight gain based on the type of milk previously fed, more premature infants who were fed preterm formula showed significantly improved weight gain after TF feeding than those who were fed term formula or breastmilk (Supplementary Table 1). There were no cases of diarrhea or hyperkalemia, and serum electrolytes concentrations did not differ before and after the change to TF. Stool frequency decreased from 3 (2–4.6) to 2.7 (2–3.5) (P=0.037). Polyethylene glycol (Forlax, Ahngook Pharm., Seoul, Korea) was prescribed to 27.1% of patients (n=33) due to symptoms suggesting constipation after TF feeding, such as hard stools or problems in passing stools. However, no case had stopped to continue TF feeding due to constipation. At the 1-month follow-up after discharge, 92.6% of patients continued TF feeding without any complications. Discontinuation of TF feeding was decided by the clinician differently during 1 and 6 month-of-corrected age depending on each infant’s condition and parents’ wishes.
Table 3 shows subgroup analyses for 16 infants with BPD, median (IQR) postnatal age, postmenstrual age, and body weight at the time of change to TF were 5 days 8 (53−63 days), 36+0 weeks (35+1–36+5 weeks), and 2,465 g (2,298–2,623 g), respectively. After the change to TF, median (IQR) frequency of desaturation was significantly reduced from 2.3 event/day (1.8–3.8 event/day) to 0.5 event/day (0–1.5 event/day) (P=0.042). There was no difference in the frequency of bradycardia or defecation. The median (IQR) weight gain for 5 days after the change to TF was significantly higher as 41.3 g (28.1–55.1 g) per day compared to 22.5 g (3.1–36.3 g) per day for 5 days before the change to TF (P=0.019). Polyethylene glycol (Forlax, Ahngook Pharm) was prescribed to 25% (n=4) of patients after TF feeding.
This study showed that the number of desaturation and bradycardia events significantly decreased with TF feeding, suggesting that TFs can be helpful for preterm infants having feeding desaturation and bradycardia. As there are no specific guidelines for infants with feeding problems, our results are meaningful for building clinical practice evidence. Although the mechanisms involved in the improvement of feeding desaturation or bradycardia were not investigated in this study, several possibilities can be assumed.
First, TFs may be effective in stabilizing SpO2 and heart rate through reducing the frequency or amount of hidden or combined gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroesophageal reflux is very common in infants, affecting 50%–85% of infants at least once a day [17]. Reflux that appears immediately after eating is usually nonacidic, but can cause esophageal distension, leading to central apnea [21]. In the case of acid reflux that occurs during the postprandial period when the stomach is partially empty, acid stimulation of laryngeal chemoreceptors induces reflexes that protect the airways from aspiration, such as laryngeal contractions, obstructive apnea and bradycardia [21]. Studies have shown that the use of feed thickeners effectively reduces the frequency and severity of gastroesophageal regurgitation [17]. In this regard, TFs designed for antiregurgitation may effectively alleviate feedingassociated desaturation and bradycardia by reducing hidden or combined gastroesophageal reflux.
Second, TFs may be effective in stabilizing SpO2 and heart rate through enhancing coordination of the suck-swallow-breathe cycle in preterm infants. Independent oral feeding requires sophisticated control of numerous phases, including sucking, swallowing, breathing, maturation of respiratory function to endure short pauses of ventilation during swallowing, and coordination of the suck-swallow-breathe cycle [9,10,22,23]. Studies have shown that 50%–60% of preterm infants with feeding desaturation exhibit swallowing dysfunction in video-fluoroscopic swallowing tests at term-equivalent age [11,24]. Further, thickened liquids were slower to reach the hypopharynx and remained there for a shorter period of time, improving swallowing function and safety in neurologically impaired patients such as those with cerebral palsy, brain damage, and neurodegenerative diseases [25-27]. In addition, adapting the flow rate has been shown to have positive effects on sucking patterns and suck-swallow-breathe coordination [28,29]. Therefore, TFs may assist preterm infants with immature physiological functions to achieve more competent rhythmic oral feeding.
Preterm infants with BPD are at a higher risk of developing feeding problems and issues with breathing control during feeding [11,30]. During oral feeding, respiratory frequency decreases, the airway is closed while swallowing, and the following inhalation has a shorter inspiratory time with compensatory larger tidal volume [13,22,31]. Infants with BPD may not be able to decrease their respiratory rate to interdigitate with suck-swallow rhythms without compromising oxygenation and ventilation. Studies have shown that apnea, desaturation, bradycardia, or disruption of the suck-swallow rhythm during feeding were more frequent in infants with BPD than in those without BPD [11,30]. As we studied pre- and post-TF feeding changes, we did not compare the effects of TF feeding between infants with and without BPD. However, as shown in subgroup analyses, TF feeding effectively decreased feeding desaturation in infants with BPD. And, interestingly, their weight gains improved after TF feeding. This result might be related to decreased work of breathing during TF feeding; however, the number of infants was too small to draw conclusion.
Various TFs are available on the market. Among these, cornstarch-containing TFs are widely used and considered safe for infants less than 6 months of age [16,17]. There have been concerns about delayed gastric emptying or absorption interference of minerals and nutrients because of casein curds [16]. However, weight gain was favorable, and there were no cases of hyperkalemia or metabolic acidosis after the change to Novalac AR, the cornstarch-containing TF, in our study. Feed thickeners added to the formula can sometimes cause changes in stool consistency or frequency. There were no cases of diarrhea; however, 27.1% of infants in our study showed symptomatic constipation. When we prescribed polyethylene glycol, constipation was effectively controlled, and parental compliance to continue Novalac AR was as high as 92.6%.
This study has several limitations. There was no control group and the long-term effects of TFs were not investigated. Additionally, this was a retrospective study. However, we observed specific changes in the desaturation and bradycardia associated with oral feeding before and after TF feeding in a relatively large group of preterm infants (n=122). Despite the lack of clear guidelines for the use of TFs, a Canadian study reported that 71% of clinicians recommended TFs containing cornstarch instead of thickeners in infants with feeding difficulties [20]. Further research to accumulate additional concrete evidence and develop systematic intervention strategies is warranted to guide clinicians in caring for infants with feeding difficulties.
In this study, we observed that TF decreased the frequency of desaturation and bradycardia during oral feeding in preterm infants. To our knowledge, no previous study has evaluated the effect of TFs on the improvement in feeding desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants. TFs may help stabilize SpO2 and heart rate in newborns with hidden gastroesophageal regurgitation or difficulty in coordinating sucking, swallowing, and breathing. Constipation should be monitored in TF-fed infants and appropriate medications could be administered if necessary.
Supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1 can be found via https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2022.00780.
Supplementary Table 1.
Comparison before and after feeding with a thickened formula (TF) according to previous type of milk
Fig. 1.
Box plots of frequency of bradycardia and desaturation before versus after the change to a thickened formula. The median (interquartile range [IQR]) frequency of bradycardia decreased from 0.3 (0–1) events/day to 0 (0–0.7) events/day (P =0.006). The frequency of desaturation also significantly decreased from 2.3 (1.3–3.3) events/day to 0.3 (0–1.7) events/day (P <0.001). The box represents IQR and the line across the box indicates the median. The vertically extending lines denote the minimum and maximum values within 1.5× IQR, while the outlier dots denote observations outside the range of the adjacent value (1.5× IQR). Bradycardia and desaturation were defined as heart rate <100 beats/min and SpO2 <85% during or immediately after oral bottle feeding, respectively.

Fig. 2.
Representative vital sign trend showing improved bradycardia and desaturation after change to a thickened formula.
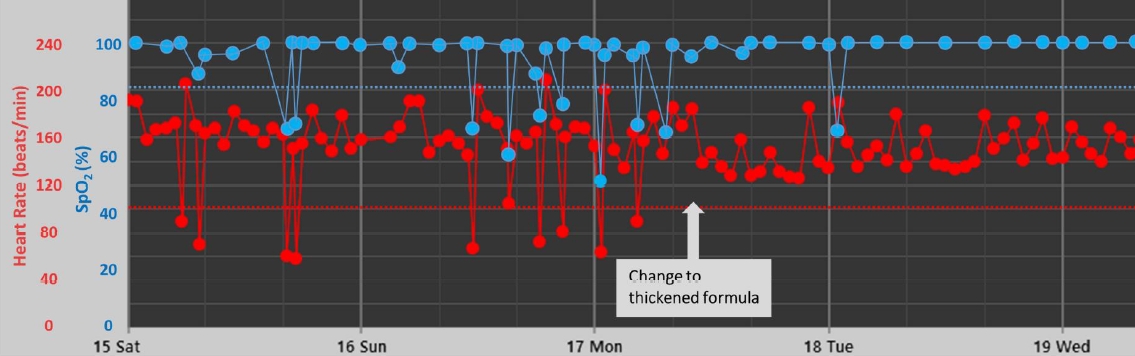
Table 1.
Patients’ baseline characteristics (N=122)
Table 2.
Comparison of variables before and after feeding of a thickened formula (TF) (N=122)
| Variable | Before TF | After TF | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bradycardiaa) frequency (event/day) | 0.3 (0–1) | 0 (0–0.7) | 0.006 |
| Desaturationb) frequency (event/day) | 2.3 (1.3–3.3) | 0.3 (0–1.7) | <0.001 |
| Serum sodium (mEq/L) | 138 (137–140) | 138 (136–139) | 0.207 |
| Serum potassium (mEq/L) | 4.6 (4.2–5.0) | 4.7 (4.4–5.0) | 0.195 |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 89 (81–103) | 89 (78–98) | 0.152 |
| Weight gain (g/day) | 20.0 (7.5–34.4) | 28.8 (0.7–42.5) | 0.092 |
| Defecation (stool number/day) | 3 (2–4.6) | 2.7 (2–3.5) | 0.037 |
Table 3.
Comparison of variables before and after feeding of a thickened formula (TF) among infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (N=16)
| Variable | Before TF | After TF | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bradycardiaa) frequency (event/day) | 0.5 (0–1.0) | 0.3 (0–0.9) | 0.637 |
| Desaturationb) frequency (event/day) | 2.3 (1.8–3.8) | 0.5 (0–1.5) | 0.042 |
| Serum sodium (mEq/L) | 138 (137–140) | 138 (136–139) | 0.300 |
| Serum potassium (mEq/L) | 4.8 (4.2–5.0) | 4.7 (4.4–4.8) | 0.977 |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 99 (89–111) | 96 (84–105) | 0.244 |
| Weight gain (g/day) | 22.5 (3.1–36.3) | 41.3 (28.1–55.1) | 0.019 |
| Defecation (stool number/day) | 2.2 (1.3–4.3) | 2.3 (1.3–3.0) | 0.364 |
References
1. Motion S, Northstone K, Emond A. Persistent early feeding difficulties and subsequent growth and developmental outcomes. Ambul Child Heal 2001;7:231–7.

2. Pados BF, Hill RR, Yamasaki JT, Litt JS, Lee CS. Prevalence of problematic feeding in young children born prematurely: a meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr 2021;21:100.




3. Eichenwald EC, Blackwell M, Lloyd JS, Tran T, Wilker RE, Richardson DK. Inter-neonatal intensive care unit variation in discharge timing: Influence of apnea and feeding management. Pediatrics 2001;108:928–33.



4. Rommel N, De Meyer AM, Feenstra L, Veereman-Wauters G. The complexity of feeding problems in 700 infants and young children presenting to a tertiary care institution. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2003;37:75–84.


5. Jadcherla SR, Wang M, Vijayapal AS, Leuthner SR. Impact of prematurity and co-morbidities on feeding milestones in neonates: a retrospective study. J Perinatol 2010;30:201–8.




6. Hoogewerf M, ter Horst HJ, Groen H, Nieuwenhuis T, Bos AF, van Dijk MWG. The prevalence of feeding problems in children formerly treated in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Perinatol 2017;37:578–84.



7. Lau C, Bhat K, Potak D, Schanler RJ. Oral feeding assessment predicts length of hospital stay in late preterm infants. J Pediatr Mother Care 2015;1:102.



8. Kamity R, Kapavarapu PK, Chandel A. Feeding problems and long-term outcomes in preterm infants—a systematic approach to evaluation and management. Children 2021;8:1158.



9. Viswanathan S, Jadcherla S. Feeding and swallowing difficulties in neonates: developmental physiology and pathophysiology. Clin Perinatol 2020;47:223–41.


10. Gulati IK, Sultana Z, Jadcherla SR. Approach to feeding difficulties in neonates and infants: a comprehensive overview. Clin Perinatol 2020;47:265–76.


11. Han C, Shin J, Jeon GW. Development of swallowing function in infants with oral feeding difficulties. Int J Pediatr 2020;2020:5437376.




12. Chen CT, Wang LY, Wang YL, Lin BS. Quantitative real-time assessment for feeding skill of preterm infants. J Med Syst 2017;41:95.



14. Sakalidis VS, McClellan HL, Hepworth AR, Kent JC, Lai CT, Hartmann PE, et al. Oxygen saturation and suck-swallow-breathe coordination of term infants during breastfeeding and feeding from a teat releasing milk only with vacuum. Int J Pediatr 2012;2012:130769.




15. Vice FL, Gewolb IH. Respiratory patterns and strategies during feeding in preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol 2008;50:467–72.


16. Salvatore S, Savino F, Singendonk M, Tabbers M, Benninga MA, Staiano A, et al. Thickened infant formula: what to know. Nutrition 2018;49:51–6.


17. Kwok TC, Ojha S, Dorling J. Feed thickener for infants up to six months of age with gastro-oesophageal reflux. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;12:CD003211.



18. Ng V, Bogaardt H, Tzannes G, Collins S, Docking K. Thickened formulas used for infants with dysphagia: Influence of time and temperature. Dysphagia 2022;37:923–32.



19. Cichero JAY, Nicholson TM, September C. Thickened milk for the management of feeding and swallowing issues in infants: a call for interdisciplinary professional guidelines. J Hum Lact 2013;29:132–5.



20. Dion S, Duivestein JA, St Pierre A, Harris SR. Use of thickened liquids to manage feeding difficulties in infants: a pilot survey of practice patterns in Canadian pediatric centers. Dysphagia 2015;30:457–72.



22. Lau C. Development of infant oral feeding skills: what do we know? Am J Clin Nutr 2016;103:616S–621S.



23. Lau C, Smith EO, Schanler RJ. Coordination of suck-swallow and swallow respiration in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr Int J Paediatr 2003;92:721–7.

24. Davis NL, Liu A, Rhein L. Feeding immaturity in preterm neonates: risk factors for oropharyngeal aspiration and timing of maturation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2013;57:735–40.


25. Clavé P, De Kraa M, Arreola V, Girvent M, Farré R, Palomera E, et al. The effect of bolus viscosity on swallowing function in neurogenic dysphagia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006;24:1385–94.


26. Inamoto Y, Saitoh E, Okada S, Kagaya H, Shibata S, Ota K, et al. The effect of bolus viscosity on laryngeal closure in swallowing: kinematic analysis using 320-row area detector CT. Dysphagia 2013;28:33–42.



27. Rempel G, Moussavi Z. The effect of viscosity on the breath-swallow pattern of young people with cerebral palsy. Dysphagia 2005;20:108–12.



28. Jenik A, Fustiñana C, Marquez M, Mage D, Fernandez G, Mariani G. A new bottle design decreases hypoxemic episodes during feeding in preterm infants. Int J Pediatr 2012;2012:531608.




29. Kao HM, Lin CH, Chang YJ. Feeding with cross-cut teats has better sucking effects and oxygenation in preterm infants with chronic lung disease. J Clin Nurs 2010;19:3016–22.








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


