Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 66(6); 2023 |
|
Abstract
Gastrointestinal (GI) allergies are broadly associated with food allergies and divided into groups based on the degree of allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) involvement: IgE-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, and mixed. Non-IgE-mediated GI food allergies are mostly observed in neonates and infants and include food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome (FPIES), food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis (FPIAP), and food protein-induced enteropathy (FPE). In addition to the classical phenotype, unique phenotypes such as vomiting and bloody stool, suspected sepsis, and overlapping eosinophilic GI disorders (EGIDs) have increased in Japan over the past 2 decades. Some of these cases were defined as having chronic FPIES. More recently, cases of hen’s-egg FPIES in Japan have increased dramatically since 2018, albeit for unknown reasons. Typical mixed-type food allergies are EGIDs, characterized by prominent eosinophil infiltration in the GI tract leading to GI symptoms. EGIDs are broadly classified into eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and non-EoE EGIDs that involve the GI tract with the exception of the esophagus. Of the EGIDs, EoE is the best known, as the number of cases has increased dramatically in Western countries, whereas pediatric EoE remains rare in Asia and non-EoE EGIDs may be more prevalent in Japan. A recent Japanese national survey showed that pediatric non-EoE EGIDs were persistent and severe compared to those in adults, possibly requiring further effective therapeutic options. Among the EGIDs, FPIAP is pathologically diagnosed as an infantile form of eosinophilic colitis. In addition, recent FPIES and FPE cases also involved eosinophilic inflammation. Recent cases of GI allergies may be associated with type 2 inflammation. A better understanding of the interactions between GI allergies and type 2 inflammation may clarify the pathogenesis of the recent increase in GI allergies.
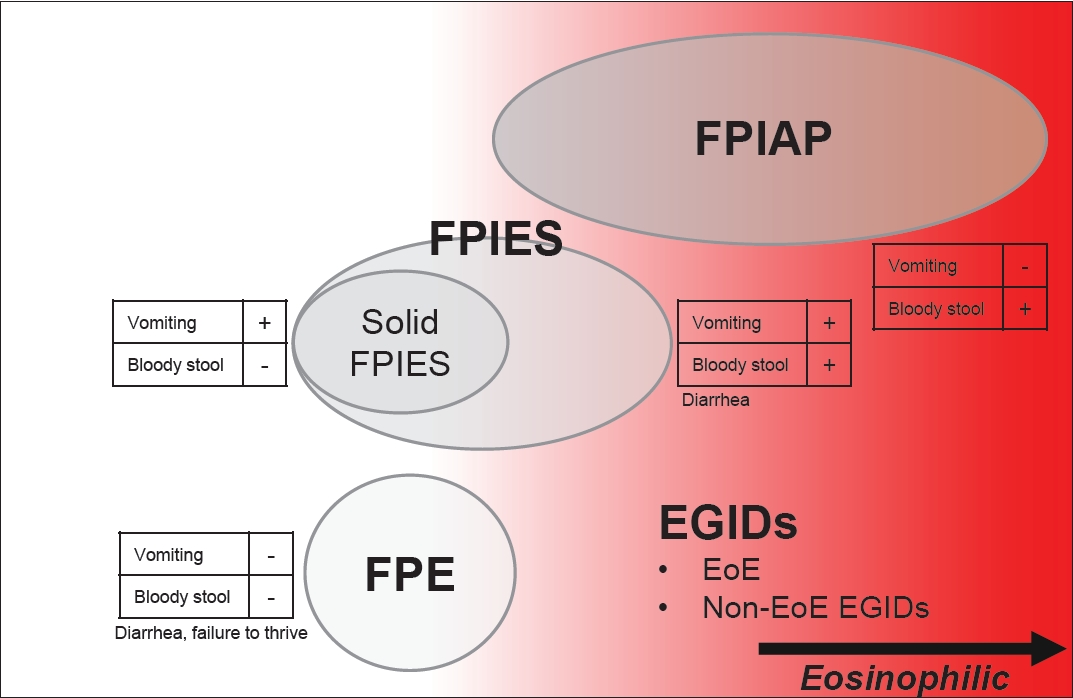
Graphical abstract. Relationship between non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies and eosinophilic inflammation. Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies (non-IgE-GIFAs) are classified as classical 3-disease entities. In addition, non-IgE-GIFAs is also divided into 4 groups according to the presence or absence of bloody stool and vomiting (indicated by small tables). Recently, more patients with non-IgEGIFAs possess eosinophilic inflammation resembling EGIDs. FPIES, food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome; FPIAP, food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis; FPE, food protein-induced enteropathy; EGIDs, eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders; EoE, eosinophilic esophagitis; Non-EoE EGIDs, non-eosinophilic esophagitis eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders.
Since the late 1990s, neonates and infants with vomiting and bloody stool associated with cow’s milk protein–based formulas have often been observed in Japan [1,2]. These infants were considered to have a type of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome (FPIES) that might differ from the classical type. Such a unique phenotypic FPIES sometimes shows marked eosinophilic infiltration, indicating its overlap with eosinophilic gastrointestinal (GI) disorders (EGIDs) [2]. EGIDs, except for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), may be more common in Japan [3,4], even from an international perspective. Subsequently, some cases were defined as chronic FPIES according to published international consensus guidelines [5]. These guidelines also state that chronic FPIES is more common in Korea and Japan. During the same period, the number of patients with EoE rapidly increased in Western countries [6]. GI food allergies have recently attracted increasing attention worldwide. This review briefly discusses the features of non-immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated GI food allergies (non-IgE-GIFAs), including recent unique Japanese FPIES and EGIDs.
Adverse reactions to foods vary and include non-immune and immune reactions indicating food allergies (Fig. 1) [7]. Toxic reactions, such as toxic mushrooms and puffer toxins, are first excluded by differential diagnosis before investigations into the broader category of food allergies. Thus, neither toxic nor immune-mediated reactions, such as food intolerance (e.g., lactose intolerance) and reactions to pharmacologically active food substances (e.g., vasoactive amines such as serotonin and histamine from fruits and fish, respectively), are distinguished from immune-mediated reactions, a broad category of food allergies. In particular, GI food allergies are the focus of digestive symptoms. GI food allergies are divided into 3 categories based on the involvement of allergen-specific IgEs: IgE-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, and mixed types [8]. The most common IgEmediated GI food allergy is the immediate type, termed “food allergies,” in the presence of GI symptoms. Non-IgE-mediated types, collectively called non-IgE-GIFAs, are mostly observed in neonates and infants. This category includes FPIES, food proteininduced allergic proctocolitis (FPIAP), and food protein-induced enteropathy (FPE) [9]. Typical mixed-type GI allergies that fall between IgE- and non-IgE-mediated types are EGIDs, which are characterized by aberrant eosinophil infiltration in the GI tract, leading to GI symptoms. EGIDs were recently broadly classified into EoE and non-EoE, which involve the GI tract except for the esophagus [9]. Although EGIDs have been observed in persons of all ages, pediatric EGIDs occur mainly after school age.
Japanese pediatricians have observed an increase in the unique phenotype of non-IgE-GIFAs since the late 1990s [1,2]. The incidence of non-IgE-GIFAs, including FPIES, FPIAP, FPE, and unclassified, was 0.21% (approximately 0.13% of the cases were considered FPIES after excluding cases of suggested FPIAP) in a national survey of neonatal care units at that time [1]. In the United States, the percentage was 0.023% in the 2005–2009 survey [10], lower than that in Japan. However, it increased to 0.42% in patients born in 2015–2018, and the cumulative total increased to 0.14% between 2000 and 2018 [10]. In recent years, the incidence of FPIAP has also increased in the United States [11], reaching the same levels as in Japan. More interestingly, although its etiology remains unknown, the number of patients with solid FPIES, especially boiled egg yolk FPIES, has drastically increased in Japan over the past few years [12,13].
The rapidly increasing Japanese phenotype of non-IgE-GIFAs in the 2000s comprised both unexplained and classical phenotypes, resulting in these types of non-IgE-GIFAs being treated as a single entity in Japan [2]. The overall picture of non-IgE-GIFA in Japan over the past 2 decades is discussed below [2,14]. Non-IgE-GIFAs occur mostly from the neonatal period to early infancy. They are nonimmediate allergies (onset within 24 hours) that are mainly caused by cow’s milk protein and characterized by vomiting and subsequent diarrhea with occasional bloody stool. They can also be caused by breast milk.
Cluster classification based on the presence or absence of vomiting and/or bloody stool in Japanese cases has been performed [2]. In addition, a mixed type of FPIES and FPIAP, characterized by bloody stool and vomiting [15], as well as a sepsis-like group with fever and elevated C-reactive protein levels, have also attracted attention. Eosinophilic inflammation, peripheral blood eosinophilia, and Th2-skewed cytokine profiles are frequently observed. Although approximately 30% of patients show allergen-specific IgE positivity [2,16,17], Specific IgEs are generally undetectable; therefore, the allergy is categorized as the non-IgEmediated type. To confirm allergen sensitization, the allergenspecific lymphocyte stimulation test (ALST) has been conducted almost exclusively in Japan [18]. In the ALST, the stimulation index (% of stimulated cells) is calculated as lymphocyte proliferation in a culture of peripheral blood mononuclear cells after stimulation with a food antigen that reflects the activation and expansion of allergen-specific memory T cells [19]. This can be a useful approach when allergen-specific IgEs are undetectable owing to non-IgEmediated allergies [8]. The elimination of causative foods is highly effective. The vast majority of cases develop tolerance by 3 years of age at the latest [20].
Bloody stool is often the only symptom of FPIAP, which is generally mild [17,20]. The histopathological findings are characterized by eosinophil infiltration, which is recognized as infantile eosinophilic colitis (EC) [21]. In addition to those fed cow’s milk formula, exclusively breastfed infants can develop this type of allergy. A physician-supervised oral food challenge (OFC) test is not necessary in mild cases [17]. The elimination of causative foods improves symptoms and allows patients to develop tolerance relatively early, indicating a good prognosis. The incidence of this disease seems to have increased in Japan [15] ahead of that in Western countries. A recent report showed that the prospectively defined incidence of FPIAP in the United States was markedly higher than that previously reported [11].
FPE, characterized by diarrhea lasting for 2 weeks or more, poor weight gain, and failure to thrive due to impaired digestion and nutrient malabsorption [17], is relatively rare. It may take 1–2 weeks to improve after the avoidance of causative foods. The histopathological findings of FPE, such as villus atrophy of the small intestinal mucosa, crypt hyperplasia, and lymphocyte infiltration, are well-known and should be of definitive diagnostic value. FPE is generally diagnosed by improvement after the elimination of causative foods and characteristic pathological findings. An OFC test after a period of avoidance cannot result in acute symptoms, unlike in chronic FPIES, meaning that interpreting the OFC test results may be difficult. Additionally, FPE can develop after infectious gastroenteritis [22].
FPIES is the most well-recognized non-IgE-GIFA, and its new classifications were presented in international guidelines in 2017 [5]. FPIES is characterized by protracted repetitive vomiting, pallor, and lethargy, beginning within 1–4 hours of ingestion of the causative food. Subsequent diarrhea can occur within approximately 5–10 hours, occasionally with bloody stools. This condition was defined as “acute FPIES” in the new classification. Cow’s milk or soy formula (nonsolid foods)-induced FPIES is typically present in early infancy (<6 months) compared with solid food allergies [5]. The FPIES (6–12 months) reflects the introduction of solid foods.
In contrast, newly classified chronic FPIES occurs with the daily ingestion of triggering foods and presents as chronic or intermittent emesis, watery diarrhea, and failure to thrive [5]. Chronic FPIES generally develops in infants younger than 4 months of age fed cow’s milk or soy formula (nonsolid foods). Chronic FPIES should be diagnosed by the improvement of symptoms within days after the avoidance of the offending foods and acute symptoms that resemble acute FPIES by the reintroduction (OFC test) of offending foods. Surprisingly, chronic FPIES is a relatively rare condition that is encountered more frequently in Korea and Japan than elsewhere [5,7,23], although the reason remains undetermined.
In addition to the classification of symptom timing and duration, novel detailed classifications have been shown in guidelines based on age at onset, severity, and IgE positivity (Fig. 1) [5]. Unlike in IgE-mediated immediate food allergies, oral or intravenous saline bolus infusions—not intramuscular adrenaline injection—effectively treat acute FPIES episodes [5]. International guidelines address clinical issues, resulting in better practices for FPIES.
The remaining issues that should be addressed are as follows [7]. First, tests that prove the sensitization of specific foods to determine immunologic mechanisms, such as the ALST in Japan, should be established; otherwise, the diagnosis is just clinical. Second, although chronic FPIES is a meaningful concept to explain some unique phenotypes, some cases have not yet been categorized (unclassified). For example, some patients show GI inflammation soon after birth before feeding, although this may be similar to FPIAP [24]. In addition, there are suspected cases of chronic FPIES that do not show acute symptoms upon the reintroduction of suspected foods, suggesting that they might be a clinical condition that falls between FPIES and FPE or FPIAP [2,15,16].
Among patients with mixed phenotypes of FPIES and FPIAP [15], sepsis-like phenotypes [25] were included in the unclassified group. Although cow’s milk is the most common cause of FPIES, solid FPIES is another controversial entity [26]. Causative foods for solid FPIES vary geographically, with most internationally reported solid FPIES cases being caused by rice and oats [26,27]. Fish-induced FPIES is more common in Italy [28] and Spain [29]. In Japan, soybeans, wheat, rice, and hen’s eggs have been mentioned as causative foods, but the mention of egg yolks has been notably increasing [30].
An overall increase in solid FPIES was observed in Japan [30]. Of them, there has been a dramatic increase in the cases of hen’segg FPIES in Japan since 2018 [12,13,31,32]. Although the diagnosis of milk FPIES may be complicated, as mentioned above, solid FPIES can be clearly diagnosed according to international guidelines. Although better awareness of solid FPIES appeared affected by the increase, it may be unable to explain it. One report speculated that this increase may be associated with a change in policy regarding the early introduction of hen’s eggs to infants at high risk of food allergies [12]. However, such an early introduction could be used in a relatively confined location owing to the uneven distribution of allergists in Japan [33], implying the possibility of other reasons. Most cases of boiled or cooked hen’s-egg FPIES have been associated with egg yolks rather than egg whites. Compared to cow’s milk-induced nonIgE-GIFAs, including FPIES, those of hen’s eggs are exclusively typical FPIES and rarely accompanied by bloody stool and peripheral blood eosinophilia [31,32]. Interestingly, patients generally experience a normal consumption of boiled egg yolks before onset [31]. Tolerance acquisition earlier than the generally recommended timing of an OFC test has been reported in boiled egg yolk FPIES, suggesting better prognosis [31].
EGIDs occurring at all ages are clinicopathological diseases characterized by allergic/eosinophilic inflammation leading to GI dysfunction [34]. EGID is a typical mixed-type GI allergy with both IgE- and non-IgE-mediated characteristics [7]. EGIDs consist of EoE and EGIDs observed in areas other than the esophagus. Although pediatric EGIDs (pEGIDs) have been observed mainly in children older than school age as mentioned above, FPIES (nonsolid), FPE, and FPIAP have often been associated with eosinophilic inflammation in Japanese neonates and early infants [14,35]. EoE is a relatively common disease with a prevalence of 0.05%–0.10% in Western countries [36]. In contrast, more EGIDs, except for EoE, have been reported in Japan [4]. However, transcriptome analyses of EoE in Japan are not very different from those in Western countries [37]; recently, the incidence of EoE has been increasing in Japanese adults [34,38]. However, pediatric EoE (pEoE) is rare in Asian children.
EGIDs include GI eosinophilic inflammation secondary to various underlying diseases as a broad category [39]. Primary EGID is a GI allergic inflammatory disease. It develops at all ages and is more common in children after school than in infants [4,34]. EGIDs are classified according to the affected site and mainly include EoE, eosinophilic gastritis, eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE), and EC. EGE was used as an umbrella term for EGIDs, except for EoE, by some experts [7,34]. However, since the majority of EGIDs are EoE in Western countries, and EoE is clearly identified from other EGIDs, as an international agreement, a novel classification of EGID was published in 2022 [9], in which EGIDs are divided into 2 categories: EoE and non-EoE EGID, which means EGID other than EoE. This classification can be applied not only to adults but also to children. Non-EoE EGID have also been classified into predominant mucosal, muscular, and subserosal depending on the degree of eosinophil infiltration in layers of the bowel wall, although these 3 types can often be mixed [40].
Most EGIDs in Western countries are EoEs. The number of patients with EoE has increased rapidly over the past 2 decades [36], resulting in a well-known disease in Western countries. A meta-analysis comparing pediatric and adult EoE reported a higher pooled incidence in adults versus children (7/100,000 vs. 5/100,000) in North America, Europe, and Australia [41]. In contrast, EoE is less prevalent in Asia than in Western countries [38]. In addition, more patients had non-EoE than EoE EGIDs in Japan in a national survey conducted among adults 10 years ago [3]. Moreover, pEoE was extremely rare in Japanese children at the time (unpublished data [42]) according to another national survey. Even with the recent advanced awareness of EoE, the proportion of children and adults with EoE, as per Japanese national EGIDs surveys, was 11.8% and 62.2%, respectively [4]. In addition, 95% of patients with EoE were adults [4]. Nevertheless, its prevalence in Asia has been increasing, especially among adults [34,38]. EoE has a strong male predominance with a prevalence of approximately 0.05%–0.10% internationally [36].
The symptoms of EoE are due to esophageal stenosis and dysfunction. Symptoms in children vary depending on age because infants and toddlers may not fully complain [43]. The main symptoms are a broad category of feeding disorders in infants and toddlers, vomiting and abdominal pain in early childhood, and dysphagia in late childhood and adolescence. Food impaction and dysphagia in adults have been observed in teens and young adults [43]. Interestingly, food impaction is extremely rare in Asian adults; dysphagia is the predominant symptom, and heartburn and epigastric or chest pain are relatively common. Most Asian cases, in individuals of all ages, do not progress severely [38]. Moreover, the detection of asymptomatic esophageal eosinophilia during medical examinations in adults has been a controversial issue in Japan [44]. Although the natural history of Japanese EoE and asymptomatic esophageal eosinophilia remains unclear, one report demonstrated that 62.1% of patients with asymptomatic esophageal eosinophilia developed progressive diseases [45], implying that more attention should be paid to the potential presence of pEoE.
EoE is suspected due to the presence of esophageal symptoms, and histopathological assessments using biopsies are essential for its diagnosis, even in children. Its diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and histopathological findings of clinicopathologic disease [46,47]. Notably, peripheral blood eosinophilia is uncommon. EoE shows extremely specific endoscopic findings such as edema, esophageal rings, linear furrows, whitish exudates, and strictures. Histopathological findings showed an increased number of eosinophils in the esophageal mucosal epithelium (defined as ≥15 eosinophils/high-power field [HPF]) with basal epithelial cell hyperplasia. Guidelines recommend that at least 4–6 biopsies be obtained from different locations [48] with focus on areas with characteristic endoscopic findings to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Since EoE now encompasses a concept, proton-pump inhibitor (PPI)-responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE) and PPIs have become its first-line therapy, although PPI therapy is a diagnostic tool for EoE that excludes patients with PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE) [46,49]. PPI therapy is more effective in Asian than Western adults. When treated with PPIs, 73% of patients showed clinical and histological remission [50]. Patients who do not respond significantly to a standard dose of PPIs can achieve remission with double doses of PPIs or vonoprazan. Indeed, unlike in Western countries, where there are many more severe cases, most adult patients in Japan have been controlled with standard or double doses of PPIs or vonoprazan [50]. According to the results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, the efficacy of PPIs for histological remission and symptom improvement did not significantly differ based on patient age, study design, or PPI type assessed [51]. PPIs can generally be used at doses higher than the usual pediatric dose. Topical steroid therapy (steroid swallowing) is recommended for nonresponders to acid blockers, while systemic steroid therapy is considered only in severe cases [46,47].
Dietary therapies, including elemental and elimination diets, are also effective and can occasionally be definitive [52], which may be recommended for nonresponders to PPIs. Among the elimination diets, an empirical elimination diet has sometimes been chosen. In this dietary modification, the most common trigger foods for food allergies are eliminated until remission is achieved and then gradually reintroduced [53]. Although pediatricians certainly have to consider the disadvantages, the success rates of dietary modifications in children were 90%, 72%, and 45%–77% using elemental, empiric elimination, and targeted elimination diets based on allergy testing, respectively [54]. Balloon dilatation was performed in patients with esophageal fibrotic stenosis [55].
Non-EoE EGIDs are relatively rare in Western countries, with a prevalence of approximately 0.018% [56] in individuals of all ages. However, more cases have been reported in Japan than in other countries. In fact, 5.5 times more patients had non-EoE EGIDs than EoE among Japanese adults approximately 10 years ago [3], and a recent nationwide Japanese survey showed that 41% of patients with non-EoE EGIDs were children. In addition, the number of pediatric patients with non-EoE EGIDs is 7.5 times higher than that of pediatric patients with EoE [4].
These symptoms are nonspecific and depend on the affected GI site and degree of eosinophil infiltration in the layers of the bowel wall [40]. Eosinophil infiltration localized to the mucosa can induce vomiting, diarrhea, and malabsorption. Muscular eosinophil infiltration may cause obstructive symptoms, and ascites can be observed in eosinophil infiltration on the serosal side. Restricted activity, weight loss, surgery, and hypoproteinemia are more frequent in pediatric patients with non-EoE EGIDs compared to in adult patients and those with EoE, resulting in persistent and severe disease [4].
Unlike EoE, peripheral blood eosinophilia is observed at a high rate in non-EoE EGIDs [3], providing clues to suspect non-EoE EGIDs. However, when peripheral blood eosinophilia is detected, it is important to distinguish non-EoE EGIDs from secondary GI eosinophilia because of systemic eosinophilic disease. Making the diagnosis of non-EoE EGIDs may be more difficult than that of EoE EGIDs. One reason is that, unlike EoE, endoscopic findings are nonspecific, such as edema, redness, and erosion [34]. Another reason is that physiological tissue eosinophils are observed exclusively in the GI tract except for the esophagus [52]. They sometimes even exhibit degranulation. Twenty eosinophils per HPF should be the lowest number to suspect non-EoE EGIDs during screening [57]. There was a clear trend in the physiological distribution of GI eosinophils: they were detectable in the stomach, rose toward the anus, peaked in the ascending colon, and decreased toward the anus [58,59]. This trend in children was similar to that observed in adults [59]. More recently, Pesek’s criteria for tissue eosinophilia of the GI tract were used: stomach ≥30 eosinophils/HPF, small intestine ≥50 eosinophils/HPF, and colon ≥60 eosinophils/HPF [4,60]. Taken together, the clinicopathological diagnosis is more important in non-EoE EGID.
Although there are cases of improvement with temporary fasting or no treatment, systemic steroids are the first-line therapy. However, non-EoE EGIDs relapse in approximately 60% of patients after treatment with systemic steroids [61,62]. A trial using montelukast for pediatric non-EoE EGIDs was the only randomized controlled study [63] according to a systematic literature search using the PubMed and Cochrane databases until 2016 in the Japanese guidelines for EGIDs [61] and showed symptomatic improvement. Therefore, patients with pediatric non-EoE EGID in the absence of severe or rapidly progressive conditions can be treated with montelukast as first-line therapy in Japanese guidelines [61]. The therapeutic effects of food elimination and elemental diets have been reported in many cases [64,65]. However, further research is required because of the lack of well-designed high-quality studies based on the results of a systematic review in which approximately 90% of patients were children [66]. A large-scale Japanese national survey reported that most pediatric cases of non-EoE EGIDs were persistent and severe, as their restricted activity, weight loss, surgery, and hypoproteinemia were more frequent than those of adult patients [4]. Further effective therapeutic options, such as molecular targeting approaches, are required for this condition.
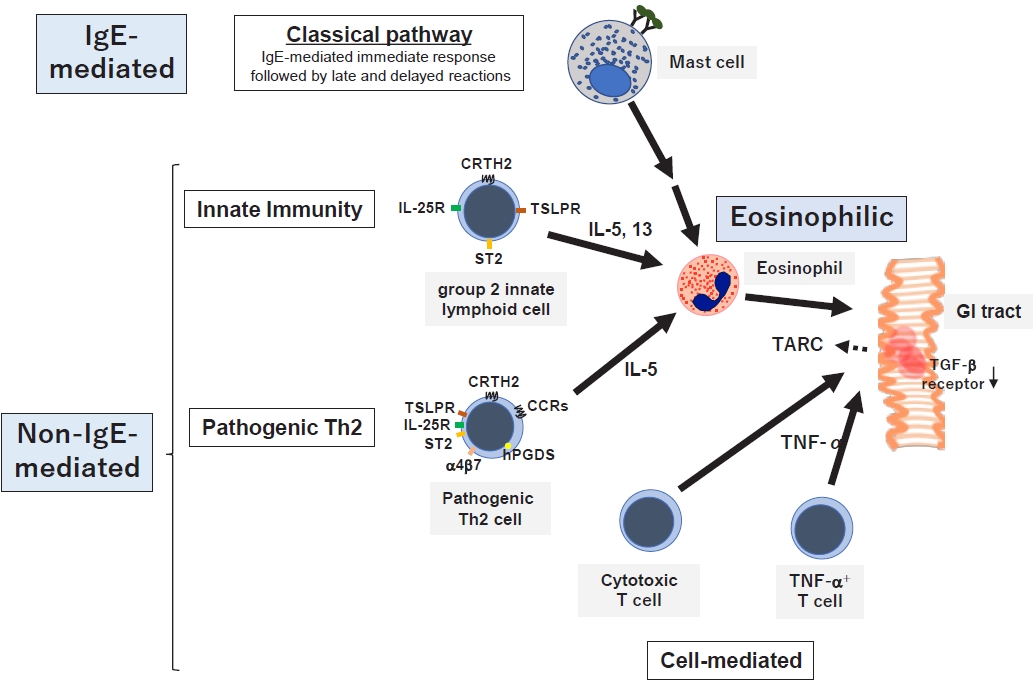
For a comprehensive understanding of the pathophysiology of GI allergy, the latter should be approached from 2 angles: the strength of involvement of the IgE-mediated mechanism and eosinophilic inflammation (Fig. 2) [7]. Classical eosinophilic/allergic inflammation is a common pathophysiological feature of allergic disorders and consists of 3 temporal phases: IgE-mediated early, eosinophil-associated late, and delayed-phase reactions resulting in chronic inflammation [67]. This is also known as late and delayed type I allergic hypersensitivity reactions characterized by the interaction of mast cells and Th2 cells with eosinophils that are recruited later [67].
Among GI allergies, EGIDs are also allergic inflammation, while FPIAP, a type of non-IgE-GIFA, is infantile EC [21]. In addition, specific IgEs have been detected in approximately 30% of non-IgE-GIFA cases, including FPIES [2,16,17]. Interestingly, 0.16% of patients who received oral immunotherapy (OIT) for IgE-mediated immediate food allergies developed EGIDs, the most common adverse reactions other than immediate allergic reactions [68]. The prevalence of EoE after the initiation of OIT in Western countries is 2.7%–30% in patients with digestive symptoms resembling EoE [69,70]. In addition, most patients do not undergo biopsy, leading to possible underestimation of the diagnosis. Therefore, a concept termed OITIGER (OIT-induced GI and eosinophilic response) has been proposed for GI symptoms experienced during OIT [71]. Taken together, IgE-mediated immediate food allergies, non-IgE-GIFAs, and EGIDs may not be independent; rather, they may overlap.
Classical mechanisms as well as various novel mechanisms associated with innate immunity or the pathogenic Th2 response have been proposed in GI allergies to date. Elevated serum levels and GI tissue mRNA expression of interleukin (IL)-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) were demonstrated in infants with non-IgE-GIFAs along with EGIDs [72], suggesting that non-IgE-GIFAs may be associated with type 2 innate lymphocytes (ILC2). In addition, the levels of eosinophil-derived neurotoxins in fecal mucus are increased in patients with FPIES [73] and FPE [74]. Moreover, the cow’s milk-induced production of Th2 cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 was significantly greater in patients with cow’s milk FPIES with versus without bloody stool [75]. Taken together, non-IgE-GIFA, at least when accompanied by bloody stool, may be associated with type 2 inflammation.
Among the EGIDs, EoE has been elucidated in detail. Consistent with this mechanism, the identified genetic variants are associated with epithelial barrier dysfunction (FLG, DSG1, CAPN14, SPINK5, and SPINK7) and Th2-mediated immune responses (CCL26, POSTN, and TSLP) [76]. Notably, ILC2 may also play a pathogenic role in pediatric EGIDs via type 2 cytokine production induced by epithelium-derived cytokines [77,78]. Pathogenic Th2 cells were defined as CRTH2+hPGDS+CD161hi CD4+ T cells, detectable in the antrum, duodenum, and esophagus of patients with EGID 18–60 years of age [79]. However, other mechanisms, in addition to type 2 inflammation, are known in non-IgE-GIFAs, which include heterogeneous subtypes. Increased tumor necrosis factor-α-producing cells and decreased transforming growth factor-β receptor expression have long been observed in the pathology of FPIES [80], and increased intestinal intraepithelial cytotoxic CD8+ T cells can be detected in FPE [81].
With regard to other allergic/eosinophilic inflammatory diseases, the prevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis with type 2 inflammation has dramatically increased in several Asian countries, following Western countries, over the last 20 years. Zhang et al. [82] named this condition “eosinophilic shift.” This condition is associated with Staphylococcus aureus, and the same may apply to GI allergies. Notably, the number of patients with EoE has also increased in Western countries over the past 2 decades [36], followed by Asian adults [38]. Presumably, this increase could not be explained only by improved awareness of this disease entity but could also be associated with other etiologies. Especially in children, non-IgE-GIFAs, at least when induced by cow’s milk, FPIES, FPE, and FPIAP are involved in eosinophilic inflammation [2]. Even FPIAP, which clearly overlaps with EGIDs, has recently increased in the United States [11]. In addition to non-IgE or mixed allergies, IgE-mediated food allergies can induce EGIDs as complications of OIT, implying that they are more eosinophilic in children [68]. The cause of the “eosinophilic shift” in the GI tract remains a mystery, which is speculated to result from an increased number of patients with allergies and/or stronger interactions between eosinophils and pathogens such as bacteria, leading to dysbiosis [83]. A better understanding of the eosinophilic shift may provide clues to clarify the pathogenesis of the recent increase in GI allergy.
Footnotes
Funding
This project was supported by Research on Intractable Diseases, Health, and Labour Sciences research grants (H29-Nanchi-ippan-042 and 20FC1016 to Y.Y.) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, and by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research C ((16K11358 and 21K07833 to Y.Y.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Acknowledgments
This review was based on the content presented at the Annual Congress of the Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease (KAPARD) on October 23, 2020, by a speaker of the JSPACI-KAPARD exchange program. I am grateful to Professors Soo-Jong Hong and Kangmo Ahn for providing this opportunity and thank Ms. Kyoko Iwasaki (Gunma Children’s Medical Center) for her excellent office work.
Fig. 1.
Adverse reactions to foods. Differential diagnoses of adverse reactions to food. Among the adverse food reactions, toxic reactions and non-immune-mediated reactions should be excluded from the diagnoses of allergies. GI allergies are schematized by locating the point defined by IgE detectability on the abscissa and the involvement of eosinophilic inflammation on the ordinate. In terms of FPIES, detailed classifications based on international consensus guidelines is presented. EC, eosinophilic colitis; EG, eosinophilic gastritis; EGE, eosinophilic gastroenteritis; EGIDs, eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders; EoE, eosinophilic esophagitis; FA, food allergy; GI, gastrointestinal; IgE, immunoglobulin E; FPE, food protein-induced enteropathy; FPIAP, food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis; FPIES, food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome; Non-IgE-GIFAs, non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies; sIgE, specific IgE.

Fig. 2.
Mechanisms of gastrointestinal allergies. GI allergies are associated with the IgE-mediated pathway followed by chronic eosinophilic inflammation, innate immunity, pathogenic Th2 cells, and cell-mediated mechanisms. GI, gastrointestinal; IgE, immunoglobulin E; IL, interleukin; CRTH2, chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells; TSLPR, thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor; ST2, suppression of tumorigenicity 2; CR, chemokine receptor; hPGDS, hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TARC, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine.
References
1. Miyazawa T, Itahashi K, Imai T. Management of neonatal cow's milk allergy in high-risk neonates. Pediatr Int 2009;51:544–7.


2. Nomura I, Morita H, Hosokawa S, Hoshina H, Fukuie T, Watanabe M, et al. Four distinct subtypes of non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies in neonates and infants, distinguished by their initial symptoms. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;127:685–8.e1-8.


3. Kinoshita Y, Furuta K, Ishimaura N, Ishihara S, Sato S, Maruyama R, et al. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis. J Gastroenterol 2013;48:333–9.



4. Yamamoto M, Nagashima S, Yamada Y, Murakoshi T, Shimoyama Y, Takahashi S, et al. Comparison of nonesophageal eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders with eosinophilic esophagitis: a nationwide survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021;9:3339–49.e8.


5. Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Chehade M, Groetch ME, Spergel JM, Wood RA, Allen K, et al. International consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome: Executive summary-Workgroup Report of the Adverse Reactions to Foods Committee, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017;139:1111–26.e4.


6. Spergel JM, Brown-Whitehorn TF, Beausoleil JL, Franciosi J, Shuker M, Verma R, et al. 14 years of eosinophilic esophagitis: clinical features and prognosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009;48:30–6.


7. Yamada Y. Unique features of non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy during infancy in Japan. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2020;20:299–304.


8. Calvani M, Anania C, Cuomo B, D'Auria E, Decimo F, Indirli GC, et al. Non-IgE- or mixed IgE/non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies in the first years of life: old and new tools for diagnosis. Nutrients 2021;13:226.



9. Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Abonia JP, Alexander JA, Arva NC, Atkins D, et al. International consensus recommendations for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease nomenclature. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;20:2474. –84. e3.


10. Ruffner MA, Wang KY, Dudley JW, Cianferoni A, Grundmeier RW, Spergel JM, et al. Elevated atopic comorbidity in patients with food protein-induced enterocolitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2020;8:1039–46.



11. Martin VM, Virkud YV, Seay H, Hickey A, Ndahayo R, Rosow R, et al. Prospective assessment of pediatrician-diagnosed food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis by gross or occult blood. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2020;8:1692–9.e1.



12. Akashi M, Hayashi D, Kajita N, Kinoshita M, Ishii T, Tsumura Y, et al. Recent dramatic increase in patients with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome (FPIES) provoked by hen's egg in Japan. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2022;10:1110–2.e2.


13. Nishino M, Sato S, Nagakura KI, Takahashi K, Asaumi T, Ogura K, et al. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome triggered by egg yolk and egg white. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2021;32:618–21.



14. Nomura I, Morita H, Ohya Y, Saito H, Matsumoto K. Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies: distinct differences in clinical phenotype between Western countries and Japan. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2012;12:297–303.



15. Kimura M, Shimomura M, Morishita H, Meguro T, Seto S. Serum Creactive protein in food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome versus food protein-induced proctocolitis in Japan. Pediatr Int 2016;58:836–41.



16. Miyazawa T, Itabashi K, Imai T. Retrospective multicenter survey on food-related symptoms suggestive of cow's milk allergy in NICU neonates. Allergol Int 2013;62:85–90.


17. Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Katz Y, Mehr SS, Koletzko S. Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;135:1114–24.


18. Kimura M, Oh S, Narabayashi S, Taguchi T. Usefulness of lymphocyte stimulation test for the diagnosis of intestinal cow's milk allergy in infants. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2012;157:58–64.



19. Sachs B, Fatangare A, Sickmann A, Glassner A. Lymphocyte transformation test: history and current approaches. J Immunol Methods 2021;493:113036.


20. Labrosse R, Graham F, Caubet JC. Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies in children: an update. Nutrients 2020;12:2086.



21. Mennini M, Fiocchi AG, Cafarotti A, Montesano M, Mauro A, Villa MP, et al. Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis in infants: Literature review and proposal of a management protocol. World Allergy Organ J 2020;13:100471.



22. Iyngkaran N, Robinson MJ, Sumithran E, Lam SK, Puthucheary SD, Yadav M. Cows' milk protein-sensitive enteropathy. An important factor in prolonging diarrhoea of acute infective enteritis in early infancy. Arch Dis Childhood 1978;53:150–3.



23. Hwang JB, Park MH, Kang YN, Kim SP, Suh SI, Kam S. Advanced criteria for clinicopathological diagnosis of food protein-induced proctocolitis. J Korean Med Sci 2007;22:213–7.



24. Mori M, Ohtsuka Y, Ishida A, Yamazaki S, Jimbo K, Inage E, et al. Outcome of infants presenting rectal bleeding: a retrospective study in a single institution. Pediatr Int 2014;56:884–90.



25. Kimura M, Ito Y, Tokunaga F, Meguro T, Shimomura M, Morishita H, et al. Increased C-reactive protein and fever in Japanese infants with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Pediatr Int 2016;58:826–30.



26. Ruffner MA, Ruymann K, Barni S, Cianferoni A, Brown-Whitehorn T, Spergel JM. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome: insights from review of a large referral population. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2013;1:343–9.


27. Ocak M, Akarsu A, Sahiner UM, Soyer O, Sekerel BE. Phenotypes and natural history of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome in the east Mediterranean region. Allergy Asthma Proc 2020;41:420–7.


28. Sopo SM, Giorgio V, Dello Iacono I, Novembre E, Mori F, Onesimo R. A multicentre retrospective study of 66 Italian children with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome: different management for different phenotypes. Clin Exp Allergy 2012;42:1257–65.


29. Vila L, Garcia V, Rial MJ, Novoa E, Cacharron T. Fish is a major trigger of solid food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome in Spanish children. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2015;3:621–3.


30. Okura Y, Shimomura M, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi I. Usefulness of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine in solid food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2022;33:e13677.



31. Watanabe Y, Sakai H, Nihei M, Miura K, Kumaki S. Early tolerance acquisition in hen's egg yolk-associated food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021;9:2120–2.e2.


32. Toyama Y, Ishii T, Morita K, Tsumura Y, Takahashi T, Akashi M, et al. Multicenter retrospective study of patients with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome provoked by hen's egg. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021;9:547–9.e1.


33. Nakamura Y. The roles and training system of new specialists for allergy in internal medicine. Arerugi 2017;66:1139–47.

34. Kinoshita Y, Oouchi S, Fujisawa T. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases - pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Allergol Int 2019;68:420–9.


35. Kimura M, Shimomura M, Morishita H, Meguro T, Seto S. Eosinophilia in infants with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome in Japan. Allergol Int 2017;66:310–6.


36. Dellon ES, Hirano I. Epidemiology and natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018;154:319–32.e3.



37. Shoda T, Morita H, Nomura I, Ishimura N, Ishihara S, Matsuda A, et al. Comparison of gene expression profiles in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) between Japan and Western countries. Allergol Int 2015;64:260–5.


38. Ishimura N, Shimura S, Jiao D, Mikami H, Okimoto E, Uno G, et al. Clinical features of eosinophilic esophagitis: differences between Asian and Western populations. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;30 Suppl 1:71–7.



39. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004;113:11. –28. quiz 29.


40. Klein NC, Hargrove RL, Sleisenger MH, Jeffries GH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1970;49:299–319.


41. Arias A, Perez-Martinez I, Tenias JM, Lucendo AJ. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016;43:3–15.

42. Yamada Y. Research on grasping the overall picture of patients with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis (pEoE) and establishment of diagnostic and treatment guidelines of pEoE - Overall research report (2010-2013) [Internet]. Saitama (Japan): National Institute of Public Health; 2011 [202 2 Dec 31]. Available from: https://mhlw-grants.niph.go.jp/project/20123.
44. Ishimura N, Sumi S, Okada M, Mikami H, Okimoto E, Nagano N, et al. Is asymptomatic esophageal eosinophilia the same disease entity as eosinophilic esophagitis? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;17:1405–7.


45. Ishibashi F, Fukushima K, Onizuka R, Tanaka R. Risk of progression to eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with asymptomatic esophageal eosinophilia: a retrospective pilot study. JGH Open 2020;4:422–8.




46. Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, Furuta GT, Spergel JM, Zevit N, et al. Updated international consensus diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: proceedings of the AGREE conference. Gastroenterology 2018;155:1022–33.e10.



47. Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias A, von Arnim U, Bredenoord AJ, Bussmann C, et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidencebased statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Europ Gastroenterol J 2017;5:335–58.




48. Nielsen JA, Lager DJ, Lewin M, Rendon G, Roberts CA. The optimal number of biopsy fragments to establish a morphologic diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:515–20.



49. Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, Attwood SE, Bonis PA, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128:3. –20.e6. quiz 21-2.


50. Okimoto E, Ishimura N, Ishihara S. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Digestion 2021;102:33–40.



51. Lucendo AJ, Arias A, Molina-Infante J. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor drugs for inducing clinical and histologic remission in patients with symptomatic esophageal eosinophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;14:13–22.e1.


52. Liacouras CA. Clinical presentation and treatment of pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2011;7:264–7.


53. Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, Hess T, Nelson SP, Emerick KM, et al. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:1097–102.


54. Barni S, Arasi S, Mastrorilli C, Pecoraro L, Giovannini M, Mori F, et al. Pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: a review for the clinician. Ital J Pediatr 2021;47:230.




55. Dougherty M, Runge TM, Eluri S, Dellon ES. Esophageal dilation with either bougie or balloon technique as a treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2017;86:581–91.e3.



56. Jensen ET, Martin CF, Kappelman MD, Dellon ES. Prevalence of eosinophilic gastritis, gastroenteritis, and colitis: estimates from a national administrative database. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2016;62:36–42.



57. Kato M, Kephart GM, Talley NJ, Wagner JM, Sarr MG, Bonno M, et al. Eosinophil infiltration and degranulation in normal human tissue. Anat Rec 1998;252:418–25.


58. Matsushita T, Maruyama R, Ishikawa N, Harada Y, Araki A, Chen D, et al. The number and distribution of eosinophils in the adult human gastrointestinal tract: a study and comparison of racial and environmental factors. Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:521–7.

59. DeBrosse CW, Case JW, Putnam PE, Collins MH, Rothenberg ME. Quantity and distribution of eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract of children. Pediatr Dev Pathol 2006;9:210–8.



60. Pesek RD, Reed CC, Muir AB, Fulkerson PC, Menard-Katcher C, Falk GW, et al. Increasing rates of diagnosis, substantial co-occurrence, and variable treatment patterns of eosinophilic gastritis, gastroenteritis, and colitis based on 10-year data across a multicenter consortium. Am J Gastroenterol 2019;114:984–94.



61. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorder research group of the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare in Japan. Japanese clinical practice guidelines for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in preschool children to adults [Internet]. Tokyo (Japan), Japan Council for Quality Health Care. [cited 2022 Aug 19]. Available online: https://minds.jcqhc.or.jp/n/med/4/med0445/G0001228.
62. Pineton de Chambrun G, Gonzalez F, Canva JY, Gonzalez S, Houssin L, Desreumaux P, et al. Natural history of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;9:950–6.e1.


63. Friesen CA, Kearns GL, Andre L, Neustrom M, Roberts CC, AbdelRahman SM. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of montelukast in dyspeptic children with duodenal eosinophilia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2004;38:343–51.


64. Yamada Y, Kato M, Isoda Y, Nishi A, Jinbo Y, Hayashi Y. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis treated with a multiple-food elimination diet. Allergol Int 2014;63 Suppl 1:53–6.


65. Okimoto E, Ishimura N, Okada M, Mikami H, Sonoyama H, Ishikawa N, et al. Successful food-elimination diet in an adult with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. ACG Case Rep J 2018;5:e38.



66. Lucendo AJ, Serrano-Montalban B, Arias A, Redondo O, Tenias JM. Efficacy of dietary treatment for inducing disease remission in eosinophilic gastroenteritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2015;61:56–64.


67. Akdis CA, Sicherer SH. Allergy and the immunologic basis of atopic disease. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme J, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2020:1170–4.e1.
68. Sato S, Sugizaki C, Yanagida N, Ito K, Ohshima Y, Shimojo N, et al. Nationwide questionnaire-based survey of oral immunotherapy in Japan. Allergol Int 2018;67:399–404.


69. Lucendo AJ, Arias A, Tenias JM. Relation between eosinophilic esophagitis and oral immunotherapy for food allergy: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2014;113:624–9.


70. Petroni D, Spergel JM. Eosinophilic esophagitis and symptoms possibly related to eosinophilic esophagitis in oral immunotherapy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2018;120:237–40.e4.


71. Goldberg MR, Nachshon L, Levy MB, Elizur A, Katz Y. Risk factors and treatment outcomes for oral immunotherapy-induced gastrointestinal symptoms and eosinophilic responses (OITIGER). J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2020;8:125–31.


72. Shoda T, Matsuda A, Arai K, Shimizu H, Morita H, Orihara K, et al. Sera of patients with infantile eosinophilic gastroenteritis showed a specific increase in both thymic stromal lymphopoietin and IL-33 levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016;138:299–303.


73. Wada T, Toma T, Muraoka M, Matsuda Y, Yachie A. Elevation of fecal eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in infants with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2014;25:617–9.


74. Wada T, Matsuda Y, Muraoka M, Toma T, Yachie A. Fecal eosinophilderived neurotoxin in cow's milk-sensitive enteropathy: a case report. Allergol Int 2015;64:99–100.


75. Morita H, Nomura I, Orihara K, Yoshida K, Akasawa A, Tachimoto H, et al. Antigen-specific T-cell responses in patients with non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy are predominantly skewed to T(H)2. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013;131:590–2.e1-6.


76. Lyles J, Rothenberg M. Role of genetics, environment, and their interactions in the pathogenesis of eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr Opin Immunol 2019;60:46–53.



77. Doherty TA, Baum R, Newbury RO, Yang T, Dohil R, Aquino M, et al. Group 2 innate lymphocytes (ILC2) are enriched in active eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;136:792–4.e3.



78. Judd LM, Heine RG, Menheniott TR, Buzzelli J, O'Brien-Simpson N, Pavlic D, et al. Elevated IL-33 expression is associated with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis, and exogenous IL-33 promotes eosinophilic esophagitis development in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2016;310:G13–25.


79. Mitson-Salazar A, Yin Y, Wansley DL, Young M, Bolan H, Arceo S, et al. Hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase defines a proeosinophilic pathogenic effector human T(H)2 cell subpopulation with enhanced function. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016;137:907–18.e9.


80. Chung HL, Hwang JB, Park JJ, Kim SG. Expression of transforming growth factor beta1, transforming growth factor type I and II receptors, and TNF-alpha in the mucosa of the small intestine in infants with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;109:150–4.

81. Ohtsuka Y, Yamashiro Y, Maeda M, Oguchi S, Shimizu T, Nagata S, et al. Food antigen activates intraepithelial and lamina propria lymphocytes in food-sensitive enteropathy in mice. Ped Res 1996;39:862–6.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


