Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 68(9); 2025 |
|
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed pediatric healthcare by supporting diagnostics, personalized treatment strategies, and prognosis predictions. Although it offers significant promise in these areas, its application in pediatric settings poses distinct challenges compared with that in adults due to variable developmental status, the limited availability of pediatric data, and ethical concerns regarding bias and transparency. This narrative review summarizes the key concepts of AI and its clinical applications across clinical fields in the treatment of children and adolescents. Here we highlight the emerging role of large language models in performing administrative tasks and clinical documentation and supporting decision-making. We also address the evolving impact of AI integration in surgical care as an example while exploring ongoing concerns regarding reliability and diagnostic safety. Furthermore, we survey AI-enabled medical devices and discuss the current regulatory frameworks relevant to pediatric care. This review provides a balanced overview of opportunities and challenges from a pediatrician's standpoint and aims to facilitate effective alignment and collaboration with key stakeholders in pediatric healthcare. Pediatricians must implement AI solutions cautiously and accountably to avoid unintended harm and realize their potential.
Data-driven innovations that enhance disease prevention, diagnostics, treatment, outcomes, and the prediction of clinical courses are transforming pediatric healthcare. Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI), fueled by increasing computing power and extensive data availability, is rapidly advancing, with innovative approaches and algorithms continuously emerging. Nevertheless, pediatric AI applications face distinct challenges. For instance, variability in children’s developmental stages and the limited availability of high-quality data pose significant obstacles to developing robust AI models [1].
This review provides contextual background, clarifies key terminology, explores current clinical applications, and discusses the challenges of implementing AI in pediatrics. While here we do not attempt to offer a comprehensive or fully up-to-date catalog, we incorporate diverse perspectives from all key stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem, including patients, parents or guardians, physicians, hospitals, insurance providers, and industrial partners developing AI-based medical devices. By bridging the gap between technological innovation and clinical practice, we provide an unbiased assessment of the opportunities and challenges surrounding AI-enabled pediatric healthcare, which ultimately aims to enhance patient outcomes and overall well-being.
AI is a field of interdisciplinary research that spans computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and other areas [2]. It focuses on developing methods that enable machines to perceive their environment, learn from data, store knowledge, and make decisions to achieve defined goals [3].
Modern AI research can be traced back to 1956, when John McCarthy used the term “artificial intelligence” during the Dartmouth Summer Research Project. Early successes, such as the Logic Theorist [4], a program capable of proving mathematical theorems, generated optimism about its potential. During the 1980s, AI experienced a resurgence with the development of expert systems, which applied expert knowledge to complex decision-making tasks. A notable example is MYCIN, developed at Stanford University that recommend effective antibiotics for bacterial infections [5]. However, despite their initial promise and successful implementations, these expert systems struggled to adapt to new situations and proved costly to maintain and update their knowledge bases [6].
The field advanced rapidly with the rise of machine learning (ML), a branch of AI focused on training algorithms to recognize patterns and make decisions accordingly. ML enables computers to solve problems without requiring explicit programming. ML methods fall into three broad categories: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning (see Table 1 for brief descriptions).
The current advent of AI stems from deep learning (DL) [7], pioneered by Hinton et al. [8,9] through deep neural networks. DL is a subset of ML methods that utilize artificial neural networks (Table 1), typically featuring large layered networks of processing units with millions to billions of adjustable parameters. DL models, such as large language models (LLMs) like the generative pretrained transformer (GPT) behind ChatGPT [10,11], are trained on vast amounts of text data (Fig. 1 left). These LLMs are examples of so-called foundation models: large, general-purpose models that can be adapted to various domains. While most current foundation models are based on the transformer architecture with LLMs as their most popular examples, the concept extends to other architecture and data modalities such as images, audio, and multimodal data. Because foundation models were initially trained for general purposes, they often undergo fine-tuning using smaller, domain-specific datasets to specialize them for specific tasks (Fig. 1 right). For example, ChatGPT is a fine-tuned model built upon the GPT foundation model and optimized for conversation.
The combination of enhanced computing power and large volumes of multimodal data has driven AI’s recent exponential growth, thereby impacting various sectors including healthcare [6,12]. These technologies have demonstrated success performing diagnostic tasks [12], predicting patient outcomes [13], and assisting with surgical procedures [14]. Understanding the fundamental concepts of AI will help healthcare professionals navigate emerging technologies and leverage these tools to deliver better patient care [2,15].
AI technologies are increasingly integrated into various aspects of pediatric care, thereby offering potential benefits while also presenting unique challenges.
AI and ML are transforming pediatric subspecialties by augmenting specific clinical tasks such as early detection, precision diagnostics, and outcome predictions. AI-driven early warning systems are particularly valuable in time-sensitive conditions such as pediatric sepsis. These models leverage biosignal data to predict deterioration and guide timely interventions, potentially improving survival rates [1,16,17]. Furthermore, in pediatric allergy and immunology, ML models incorporating environmental data have shown promise in forecasting allergen exposure, thereby helping prevent acute exacerbations [18,19]. In pediatric neurology and oncology, DL models trained on multimodal inputs including genetic, neuroimaging, and clinical data have enhanced diagnostic precision for complex conditions such as pediatric brain tumors [20,21]. Similarly, in pediatric cardiology, DL models applied to echocardiograms and electrocardiograms have demonstrated strong ability to detect biventricular dysfunction and ventricular dilation, which are often challenging to assess using traditional methods [22].
Beyond diagnostics, AI models also contribute to postoperative risk assessments. For instance, an interpretable ML model like optimal classification trees has been successfully used to predict the clinical outcomes of patients with a history of undergoing congenital heart surgery despite non-linear data relationships [23,24]. These tools can help clinicians tailor follow-up care and surveillance strategies based on individual risk profiles. These examples demonstrate how AI models both enhance accuracy and efficiency in pediatric care and enable more proactive and personalized clinical management.
LLMs may help streamline administrative tasks, enhance doctor–patient communication, and support clinical decisions. LLMs can be utilized in tasks that requires their natural language processing capacity, such as generating clinical notes from conversations. Moreover, they can be integrated into electronic medical records systems to assist with patient summaries, discharge instructions, and personalized education efforts [25]. LLM tools can rapidly produce medical documentation of comparable quality to that of physician-written notes, significantly reducing physicians' administrative burdens [26]. LLMs can also aid communication with caregivers by generating contextually relevant and patient-specific responses to common parental questions in the pediatric intensive care unit [27].
In terms of clinical decision support, LLMs have shown potential for diagnostic assistance, treatment planning, and information retrieval [28]. They demonstrated high accuracy and significantly faster responses at pediatric drug dosage calculations [29]. LLMs showed diagnostic performance comparable to that of pediatricians in supporting the differential diagnosis of common presentations in primary care [30]. As LLMs evolve to handle more complex interactions, such as comprehensive history-taking and open-ended questioning, their use might improve diagnostic accuracy [31].
Despite growing enthusiasm for their clinical use, LLMs have primarily been evaluated through medical examination questions, with limited assessments of their real-world clinical performance [32]. In recent stress tests using clinically based prompts, GPT-4o demonstrated a 16% inappropriate response rate. Notably, 21.5% of responses previously considered acceptable with GPT-3.5 were subsequently deemed inappropriate when reassessed with newer models [33]. These findings highlight the need for continuous and rigorous model assessments in clinical applications, especially in pediatric populations, where limited age-specific data may exacerbate the risk of biased or underperforming LLMs.
Other significant risks include hallucinations and biases, which raise serious questions about these models’ accuracy and reliability because they can produce misinformation, distort context, and strengthen bias. Data privacy is also a major concern. Uploading patient information into external LLMs (like public versions of Chat GPT) carries considerable risk, as input data might be used for model training that potentially exposes identifiable health information.
These risks and concerns require that pediatricians and caregivers exercise caution when using these tools.
AI/ML technologies embedded in medical devices are increasingly used in direct clinical interventions, necessitating a closer examination of their approval processes, safety, and pediatric-specific challenges. While the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorized the first AI-enabled device in 1995, the number of AI/ML-based medical devices, including software, has risen sharply only over the past decade [34].
Table 2 summarizes representative cases based on their specific patient care step they aim to address: prevention, diagnosis, treatment, or prediction. These devices can analyze vast amounts of medical data and detect subtle changes in patterns that may be overlooked by clinicians, facilitating faster and more accurate diagnoses. Predictive analytics powered by AI/ML can estimate a patient's disease risk and likelihood of hospital readmission [35]. Patient treatment can be personalized using these devices, such as smart insulin pumps, which autonomously adjust insulin delivery in response to real-time patient data [36]. Wearable devices and sensors integrated with AI/ML enable continuous monitoring, allowing for timely interventions [37]. Furthermore, AI-enhanced robotic surgery systems improve operative precision and safety [38].
Most currently approved AI/ML medical devices are categorized as class I or II, indicating low and moderate risk, respectively, and authorized through the 510(k) pathway, which requires demonstrating substantial equivalence to a previously approved device [39]. This regulatory approach often reflects incremental improvements to existing technologies rather than breakthrough innovations, with approval processes that may not require new clinical trials but instead rely on comparisons to predicate devices. Developers may attempt to bypass the complexities of full regulatory approval by initially launching their products as wellness apps to collect patient data for a future regulatory approval application, potentially compromising safety and data sharing [40,41].
Unlike static (“locked”) algorithms, AI/ML systems evolve using new data. While this allows ongoing optimization, it raises concerns about postmarket safety and reliability. These changes may introduce unexpected risks, particularly in pediatric populations, if not supported by robust validations. Recognizing these challenges, the FDA has proposed a lifecycle-based regulatory framework that includes pre-market reviews, algorithm change protocols, and postmarket surveillance to allow ongoing updates while ensuring sustained safety and effectiveness [42,43].
AI/ML medical devices for pediatric healthcare face unique development and implementation challenges. Medical technology for children has traditionally lagged behind that for adults [44]. AI/ML technologies are no exception to this trend. This systematic delay often places pediatric clinicians in the position of using adult devices for children without adequate evidence of safety or efficacy in off-label applications. The unique characteristics of the pediatric population (i.e., children are not "small adults") make the extension of algorithms developed for adult populations to children risky due to fundamental differences in physiology, disease presentation, and care requirements.
Moreover, children are frequently underrepresented in test cohorts used to validate these technologies. The limited financial incentive due to the smaller market size further delays developing pediatric-specific AI/ML applications. Despite children comprising approximately 23% of the U.S. population, they account for only 10% of total healthcare expenditures [45]. Consequently, only a small fraction (17%; 149 devices in 1995–2024) of FDA-approved AI/ML devices are labeled for pediatric use, primariliy in the radiology, cardiology, and neurology [46].
Therefore, when considering the use of these technologies for vulnerable pediatric populations, pediatricians and related specialists must balance the potential benefits of AI/ML medical devices against their current limitations and regulatory uncertainties.
Minimally invasive surgery is a surgical care area that actively adopted AI early on [47,48]. Due to the complex and delicate anatomical structures of pediatric patients, conventional surgical approaches require high technical expertise. However, the integration of AI technologies like ML, LLMs, and computer vision may contribute to improved surgical outcomes in peditric patients by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, surgical planning, intraoperative guidance, and postoperative monitoring [48,49]. The real-time identification of critical anatomical structures assisted by AI-based image analysis can minimize unnecessary tissue damage and potentially accelerating postoperative recovery [50]. An automated analysis of surgical procedures enables the generation of surgical documentation without manual input [51]. In robotic surgery, AI improves outcomes by stabilizing instruments, enhancing visualization, identifying critical anatomical structures, providing early warnings of intraoperative risks, and enabling partial automation of robotic control [52,53]. Despite this potential, challenges include a lack of pediatric-sized robotic instruments, high implementation costs, and limited or biased pediatric datasets trained primarily on adult populations that hinder model generalizability and reduce clinical reliability in children [49].
Of note, digital twin technology is increasingly being explored within surgical fields. Digital twin-assisted surgery (DTAS), enhanced by AI and DL, creates patient-specific virtual replicas that dynamically reflect intraoperative conditions, offering real-time guidance. By integrating live physiological data with predictive modeling, DTAS can improve surgical precision, for example by accurately delineating tumor margins and identifying critical anatomical structures to minimize collateral damage and ensure complete resection. Clinically, this approach has been associated with reduced operative times, fewer complications, and improved patient outcomes [54]. Moreover, DTAS serves as a powerful educational tool by allowing trainees to practice with highly realistic simulations of complex procedures within a safe and controlled environment [54]. While DTAS contributes to enhanced surgical precision, its performance is highly dependent on the quality and accuracy of the real-world anatomical data used to construct the virtual models. Given the rarity and low volume of pediatric surgical cases, collaborative multicenter efforts are essential to the development and curation of training datasets.
Like with all AI tools in healthcare, those used in pediatric surgery must undergo rigorous validation for safety and transparency, during which processes pediatric surgeons should play a pivotal role to ensure their clinical reliability [55].
Implementing AI in healthcare places healthcare providers at the center of a network of interactions with insurers/payers, patients/caregivers, and the healthcare industry (Fig. 2).
Healthcare providers benefit from AI through enhanced diagnostic accuracy and speed, streamlined workflows, and access to up-to-date medical information, leading to better patient care and outcomes. For example, AI can assist with the diagnosis of pediatric conditions, thereby enabling timely interventions. However, providers face increased responsibility in validating AI outputs. Conflicts between AI recommendations and clinical judgment can create legal and ethical uncertainties [56].
In their interactions with insurers and payers, healthcare providers leverage AI to improve operational efficiency and cost optimization. By accurately detecting fraudulent claims, providers help insurers reduce financial losses, leading to more affordable healthcare plans. However, both parties must address challenges such as the initial investment required for AI implementation and ensuring that the algorithms are free from bias to maintain fairness in patient care [57,58].
Healthcare providers also play a crucial role in addressing patient and caregiver concerns. While AI can aid the early detection of health issues, reduce medical errors, and enhance overall care quality, providers must ensure that patient data are protected during such usage to address privacy concerns and maintain trust. They need to manage the cost of AI technologies to avoid burdening patients and caregivers with increased expenses. Providers must also work to overcome resistance to adopting AI by educating and reassuring their patients about its benefits and safety.
In the broader industry, healthcare providers contribute to market differentiation and utilization of the transformative potential of AI in healthcare. They may ensure regulatory compliance by integrating only those AI tools that meet industry standards. However, providers must navigate challenges such as the scarcity of pediatric data for training AI models and the complexity of integrating AI with existing systems while addressing ethical considerations related to AI use, such as ensuring patient consent and transparency in AI’s decision-making. Incentive structures surrounding reimbursement policies vary across countries and influence AI adoption in clinical care [59].
By effectively managing these interactions and challenges, healthcare providers can leverage AI to improve healthcare outcomes, enhance patient experiences, and drive healthcare innovations. Balancing the benefits and challenges of AI implementation is crucial to maximizing its potential and ensuring responsible use across all stakeholders.
Integrating AI into pediatric practice presents substantial challenges that necessitate careful consideration of ethical implications and robust policy oversight. One primary challenge is the "black box" problem. Many AI systems operate without transparency, making it difficult for clinicians to understand and trust their recommendations [60,61]. This lack of transparency hinders their adoption in pediatric healthcare, in which clinical decisions require explicit justification and caregiver confidence. Without sufficient explainability, clinicians may hesitate to adopt AI-driven advice, particularly in sensitive pediatric contexts. Thus, advancing explainable AI (XAI; Table 1) methods is essential for building clinician trust and AI reliability [62]. Nonetheless, current XAI technologies remain in early development and require substantial research and validation.
Bias in healthcare AI models can lead to disparities in diagnostics, treatment, and resource allocation, disproportionately affecting underserved populations. Such bias stems from data bias and algorithmic bias. Data bias occurs when training data are unrepresentative or reflect existing inequalities. For example, AI dermatology tools trained mostly on light-skinned patients performed poorly for those with darker skin tones [63]. On the other hand, algorithmic bias emerges from the model’s design and assumptions regardless of data quality. Models can unintentionally discriminate despite data balance. For instance, using health costs to predict medical needs can underestimate needs of groups with limited access, such as Black patients, who spend less in healthcare [64].
Another significant challenge involves false-positive alerts from AI-based diagnostic and monitoring tools [65]. Frequent false alarms can cause alert fatigue in clinicians, diminishing their responsiveness to genuine clinical emergencies. In pediatric care, in which timely decisions and interventions are crucial, reduced clinician vigilance can have particularly serious consequences [66]. Moreover, false-positive alerts trigger unnecessary medical interventions, including unwarranted diagnostic tests and treatments, increasing healthcare costs and excessive resource utilization. Such unnecessary interventions also raise ethical concerns, as pediatric patients are exposed to avoidable stress and risks from procedures, while their families experience unnecessary anxiety. To address this, stakeholders should prioritize the development of AI algorithms that balance sensitivity with specificity. Thus, the rigorous validation of AI systems tailored explicitly for pediatric populations is essential. Furthermore, healthcare institutions and regulatory bodies must establish standards that ensure the clinical relevance of AI-generated alerts to ultimately enhance patient safety, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Financial incentives also pose an additional significant challenge preventing AI integration in pediatric healthcare. Economic factors can subtly influence diagnostic thresholds—known as “biomarkup”—leading AI systems to detect minor or borderline conditions that prompt unnecessary but billable interventions [57,67]. Such subtle bias toward profitability over clinical necessity risks compromising patient-centered care. To mitigate this risk, stakeholders, including AI developers, healthcare institutions, and insurers, must commit to observing transparent practices and aligning AI deployment strictly for patient benefit. Robust oversight, clear regulatory guidelines, and independent audits are required to ensure that AI technologies serve pediatric populations equitably, ethically, and effectively and prioritize clinical benefit over financial gain.
Liability issues arising from AI integration in clinical care present complex challenges beyond those encountered in traditional practice. When AI-driven decisions cause patient harm, evaluating responsibility across clinicians, developers, and healthcare institutions raises intricate legal and ethical questions [57]. Additionally, while reliance on incomplete or biased datasets can produce inaccurate outputs, proving the connection between AI errors and patient harm with sufficient or acceptable evidence may be difficult due to issues including AI explainability and its evolving nature [56].
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among pediatric clinicians, data scientists, ethicists, patient advocates, regulatory authorities, and lawyers. Rigorous oversight and ethical governance of AI applications will allow the medical community to safely integrate AI into pediatric care. Such an approach will enable clinicians to leverage the transformative potential of AI, ultimately improving patient outcomes while preserving patient welfare and trust.
Persistent concerns about data quality, algorithmic transparency, limited explainability, and ethical considerations including bias and financial incentives in AI integration emphasize the need for sustained research, cross-disciplinary collaboration, and robust governance. As AI increasingly integrates into pediatric clinical practice, clinicians must develop core competencies with these technologies to effectively deliver their evolving functions. However, the current limitations of LLMs, including concerns regarding reliability, hallucinations, data bias, and insufficient validation within pediatric contexts, suggest that their widespread clinical application may still be premature. Pediatricians are well-positioned to guide the thoughtful adoption of AI to improve the health outcomes of children and adolescents. Therefore, cautious and accountable implementation is crucial to preventing unintended harm induced by AI and realizing its potential.
Footnotes
Funding
This work was supported by the Gyeongsang National University Fund for Professors on Sabbatical Leave 2024 (TP) and by the NIH R01NS129188 and U54HG01 2513 (SWK).
Fig. 1.
Basic concepts in modern artificial intelligence (AI). (Left) The hierarchy of AI, machine learning, deep learning, and foundation models. These concepts are independent of data types such as text, image, or audio. (Right) An example showing how large language models (LLMs; foundation models for text data) are trained on vast amounts of text data (hundreds of billions of words). These models are then fine-tuned for specific tasks, such as generating responses to users’ prompts. The figure shows only a subset of popular applications. GPT, generative pretrained transformer; LLaMA, large language model meta AI.
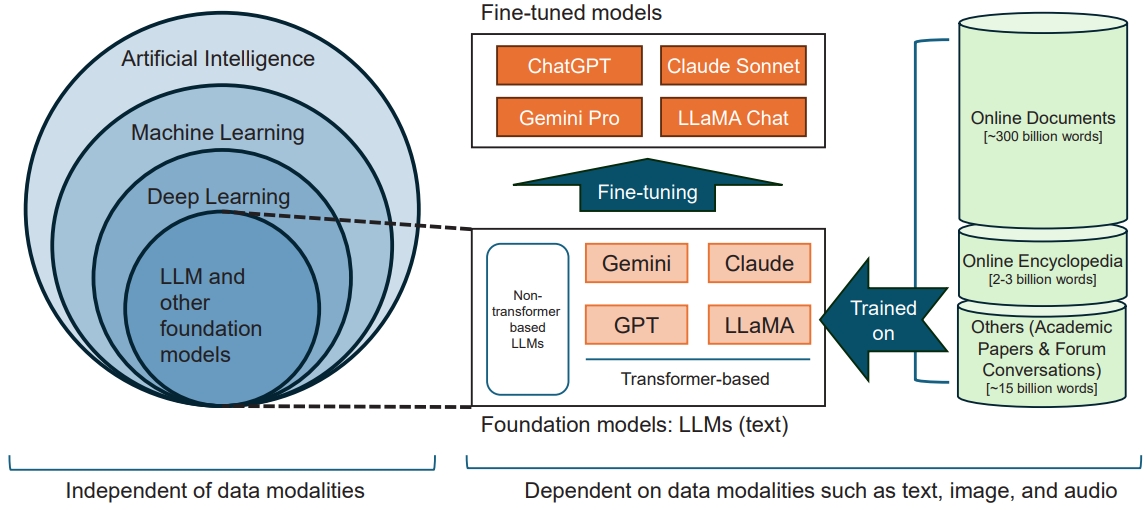
Fig. 2.
Key areas for artificial intelligence in healthcare, highlighting interactions between stakeholders. Healthcare providers gain diagnostic accuracy and streamlined workflows. Insurers improve efficiency and detect fraud but face investment challenges. Patients benefit from early detection and better care, but privacy concerns persist. The industry sees market differentiation but faces data and integration issues. Balancing these aspects is crucial for effective artificial intelligence implementation. PHI, protected health information.
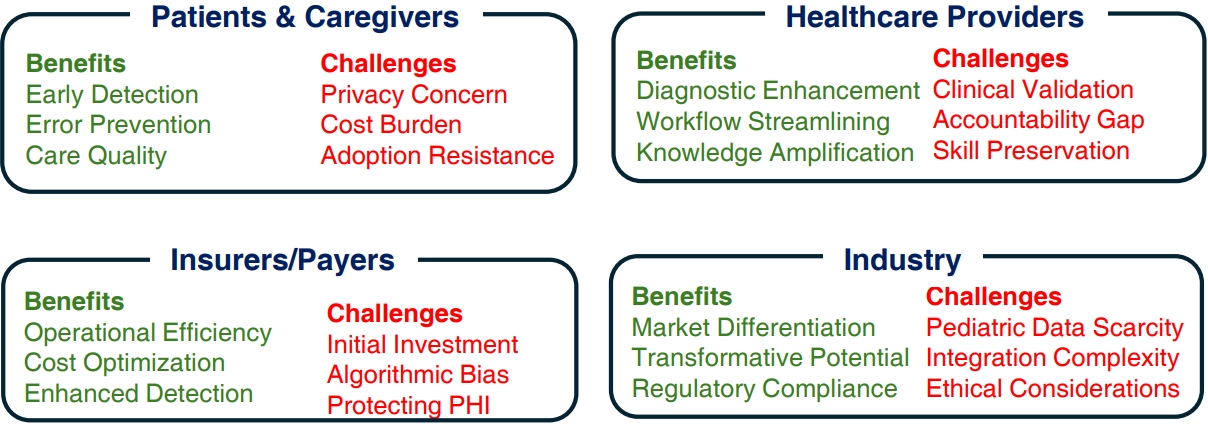
Table 1.
Glossary of terms
| Artificial intelligence (AI) | A branch of computer science that focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, for example, understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, and making decisions. [68] |
| Machine learning (ML) | A subset of AI that involves developing algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to perform specific tasks without explicit instructions by learning from data. [69] There are different ML approaches (e.g., supervised and unsupervised learning) depending on whether the training data is labeled with correct answers. |
| Supervised learning | A machine learning paradigm where a model learns from a labeled dataset: each training example comes with an input and its correct output (label). During training, the model makes predictions, while an algorithm adjusts the model’s parameters to reduce errors between predictions and labels. Repeating this process, the model gradually learns to map inputs to their correct outputs. |
| Unsupervised learning | A machine learning approach that uses unlabeled data. The algorithm analyzes input data to find hidden structures or patterns without any explicit correct outputs. Common unsupervised learning tasks include clustering. Generative models are better suited for unsupervised task as they learn data structure and can create new examples, unlike discriminative models which require labels to distinguish between groups. |
| Reinforcement learning | A machine learning paradigm where an agent interacts with its environment and learns to make decisions through trial and error, guided by feedback (rewards or penalties). Unlike supervised learning, the agent learns from the consequences of its actions: receiving rewards for good choices and penalties for poor ones. Through iterations, the agent refines its decision-making policy. |
| Deep learning | One of the advanced approaches in machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn and extract highly complex features and patterns from raw input data. [7] The term “deep” refers to the many layers, which enable the network to learn high-level data representations. |
| Artificial neural networks (ANN) | A subset of machine learning models inspired by the structure of the human brain. They consist of interconnected layers of nodes (called “neurons”) - an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. The network learns by adjusting weights assigned to each connection between nodes. [70] |
| Foundation models | A large-scale machine learning model trained on broad data that can be adapted for diverse downstream tasks. [71] These models typically contain billions of parameters and are pretrained on expansive datasets from diverse types of data. For language processing, these foundation models are known as large language models (LLMs), with most built on transformers. |
| Large language models (LLMs) | The foundation models specifically designed to analyze, generate, and manipulate human language. These models typically contain billions of parameters that should be learned from training data, requiring vast amounts of diverse text data. [72] generative pretrained transformers (GPT), Gemini, [73] Claude, [74] and LLaMA [75,76] are examples of LLMs. |
| Transformers | A type of neural network model that perform well at processing and learning relationships between long sequences of data, such as sentences and paragraphs, by focusing on different parts of the sequence to make predictions (the mechanism known as attention). [77] Unlike older models like recurrent neural networks, Transformers can analyze entire sentences at once, which makes them faster to train and better at understanding long-range context. They also handle larger datasets more efficiently and can retain context across long passages. The GPT is a foundation model built on the transformer architecture. |
| Explainability, interpretability, and explainable AI (XAI) | One of the major issues in large and complex AI models is the difficulty to understand how they work (interpretability) or why they made a specific output (explainability). In healthcare, it is particularly crucial to build trust in AI by allowing clinicians to verify that AI’s reasoning aligns with established medical knowledge and specific patient cases. Explainable AI (or XAI) aims to make the decision-making processes of complex AI models understandable to humans. [78] Chain-of-thought prompting is suggested to improve the explainability of LLMs by making them to generate intermediate reasoning steps, allowing humans to better understand how the conclusions are reached. [79] |
Table 2.
Summary of selected U.S. Food and Drug Administration/Conformité Européenne approved artificial intelligence-based medical devices (pediatric applications preferred)
| Device/software name | Category | Technology domain | Intended purpose | Regulatory status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeRO Infant ICU Monitor (MPSC) [35,80] | Prevention | Predictive analytics on vital signs (proprietary statistical/ML “heart rate characteristics” algorithm) | Monitors NICU patients’ heart rate variability in real time to generate a HeRO score that indicates risk of sepsis or clinical deterioration | FDA-cleared as Class II (Circa 2009) |
| Owlet Dream Sock [81] | Prevention | Wearable sensor with algorithmic monitoring (pulse oximetry analysis) | Continuous at-home surveillance of infant vital signs to help prevent SIDS/infant distress | FDA De Novo clearance (2023) |
| Empatica Embrace2 [37] | Prevention | Wearable ML-based physiological analysis (accelerometer/EDA) | Real-time seizure detection using accelerometer and electrodermal data | FDA 510(k) cleared as Class II (ages 6+); CE Mark for home or hospital use |
| Etiometry IVCO2 Index [82] | Prevention | ICU analytics software | Analyzes ventilator, vital signs, and lab data to detect risk of hypercapnia in critically ill infants/children | FDA 510(k) cleared (Class II)—first for pediatric ICU (2019), extended for neonates <2 kg (2023); CE Marked in EU |
| BoneXpert (Visiana) [83] | Diagnosis | Computer vision-based radiograph analysis | Automatically calculates pediatric bone age from hand x-rays | CE Mark (Class I medical software) in Europe; not FDA-cleared in US |
| Gleamer BoneView [84] | Diagnosis | Deep learning computer vision (fracture detection) | Flags possible fractures, dislocations, or lesions in trauma radiographs | FDA 510(k) cleared in 2023 for adult and pediatric fracture detection (age >2) |
| AZmed Rayvolve [85] | Diagnosis | Deep learning computer vision (fracture detection) | Automates x-ray fracture detection and highlights suspicious findings | CE Mark (Class IIa) under EU MDR (2021); FDA 510(k) in 2022 |
| Canvas Dx [86] | Diagnosis | Machine learning diagnostic algorithm (multisource data fusion) | Integrates parent surveys, clinician input, and short home videos to help diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder | FDA De Novo authorized (2021), Class II with special controls |
| Eko Murmur Analysis Software (EMAS) [87] | Diagnosis | Audio signal AI (digital stethoscope analyzed with ML algorithm) | Analyzes heart sounds (± ECG) to detect and classify heart murmurs | FDA 510(k) cleared in 2022; integrated under FDA’s “Electronic Stethoscope” category (Class II) |
| BrightHeart Prenatal Cardiac AI [88] | Diagnosis | Deep learning image analysis (obstetric ultrasound AI) | Examines prenatal ultrasound to identify fetal congenital heart defects | FDA 510(k) cleared (late 2024); CE Mark pending |
| PainChek Infant [89] | Diagnosis | Computer vision (facial expression analysis) | Utilizes facial microexpression recognition to infer infant pain level | CE Marked in EU; not FDA-cleared |
| Tandem Control-IQ [36] | Treatment | Predictive glucose control (insulin pump automation) | Adjusts insulin delivery continuously based on glucose trend predictions | FDA De Novo clearance (2019); classified as Class II |
| Akili EndeavorRx [90] | Treatment | Digital therapeutic (video game with adaptive cognitive training) | Prescription game-based therapy targeting children with ADHD | FDA De Novo authorization (2020); Class II digital therapeutic |
| Luminopia One [91] | Treatment | VR-based therapy (computer-vision–modified binocular content) | Delivers VR content to treat amblyopia in children by balancing visual input to each eye | FDA De Novo clearance (2021); Class II |
| Da Vinci Surgical System – AI enhancement | Treatment | Robotic surgical system with AI-driven automation | Uses AI-driven feedback, force sensing, and computer vision-assisted positioning for enhanced precision | FDA-cleared since 2000; AI features (e.g., force sensing) cleared via iterative 510(k) submissions |
| CergenX Ltd. [92] | Prognosis | AI-driven EEG analysis in neonates | Real-time screening for abnormal newborn brain activity to enable early interventions (antiseizure meds, therapeutic hypothermia, etc.) | FDA Breakthrough Device (2025), TAP fast-track program (not yet cleared) |
| i-ROP DL (ROP Prognosis) [93] | Prognosis | Deep learning analysis of retinal images | Detects and stages retinopathy of prematurity to prevent blindness in preterm infants | FDA Breakthrough Device (2020); under clinical validation, not yet marketed |
CE, Conformité Européenne; EDA, electrodermal activity; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; MDR, Medical Device Regulation; ML, machine learning; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; TAP, Total Product Lifecycle Advisory Program; HeRO, heart rate observation; SIDS, sudden infant death syndrome; ICU, intensive care unit; US, United States; AI, artificial intelligence; ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; VR, virtual reality; EEG, electroencephalogram.
References
1. Ramgopal S, Sanchez-Pinto LN, Horvat CM, Carroll MS, Luo Y, Florin TA. Artificial intelligence-based clinical decision support in pediatrics. Pediatr Res 2023;93:334–41.




2. Meskó B, Görög M. A short guide for medical professionals in the era of artificial intelligence. NPJ Digit Med 2020;3:126.


3. Russell SJ, Norvig P. Artificial Intelligence: a modern approach. 4th ed. Pearson, 2021.
4. McCorduck P. Machines who think. 2nd ed. A. K. Peters, 2004.
5. Amsterdam D. Perspective: limiting antimicrobial resistance with artificial intelligence/machine learning. BME Front 2023;4:0033.



8. Hinton GE, Osindero S, Teh YW. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput 2006;18:1527–54.


9. Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006;313:504–7.


10. Brown TB, Mann B, Ryder N, Subbiah M, Kaplan J, Dhariwal P, et al. Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv: 2005.14165v4 [Preprint] 2020 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.14165.

11. Ouyang L, Wu J, Jiang X, Almeida D, Wainwright CL, Mishkin P, et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv:2203.02155v1 [Preprint] 2022 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.02155.

12. Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017;542:115–8.




13. Yu KH, Zhang C, Berry GJ, Altman RB, Ré C, Rubin DL, et al. Predicting non-small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated microscopic pathology image features. Nat Commun 2016;7:12474.




14. Shademan A, Decker RS, Opfermann JD, Leonard S, Krieger A, Kim PCW. Supervised autonomous robotic soft tissue surgery. Sci Transl Med 2016;8:337ra64.


16. Sullivan BA, Beam K, Vesoulis ZA, Aziz KB, Husain AN, Knake LA, et al. Transforming neonatal care with artificial intelligence: challenges, ethical consideration, and opportunities. J Perinatol 2024;44:1–11.




17. Tennant R, Graham J, Kern J, Mercer K, Ansermino JM, Burns CM. A scoping review on pediatric sepsis prediction technologies in healthcare. NPJ Digit Med 2024;7:353.




18. Shamji MH, Ollert M, Adcock IM, Bennett O, Favaro A, Sarama R, et al. EAACI guidelines on environmental science in allergic diseases and asthma - Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to develop a causality model in exposomics. Allergy 2023;78:1742–57.



19. Zhou C, Shuai L, Hu H, Ung COL, Lai Y, Fan L, et al. Applications of machine learning approaches for pediatric asthma exacerbation management: a systematic review. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2025;25:170.




20. Steyaert S, Qiu YL, Zheng Y, Mukherjee P, Vogel H, Gevaert O. Multimodal deep learning to predict prognosis in adult and pediatric brain tumors. Commun Med (Lond) 2023;3:44.




21. Haddadi Avval A, Banerjee S, Zielke J, Kann B, Mueller S, Rauschecker AM. Applications of artificial intelligence and advanced imaging in pediatric diffuse midline glioma. Neuro Oncol 2025;20:1–15.
22. Mayourian J, Gearhart A, La Cava WG, Vaid A, Nadkarni GN, Triedman JK, et al. Deep learning-based electrocardiogram analysis predicts biventricular dysfunction and dilation in congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2024;84:815–28.



23. Bertsimas D, Zhuo D, Dunn J, Levine J, Zuccarelli E, Smyrnakis N, et al. Adverse outcomes prediction for congenital heart surgery: a machine learning approach. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg 2021;12:453–60.



24. Sarris GE, Zhuo D, Mingardi L, Dunn J, Levine J, Tobota Z, et al. Congenital heart surgery machine learning-derived in-depth benchmarking tool. Ann Thorac Surg 2024;118:199–206.


25. Fraile Navarro D, Coiera E, Hambly TW, Triplett Z, Asif N, Susanto A, et al. Expert evaluation of large language models for clinical dialogue summarization. Sci Rep 2025;15:1195.


26. Lee C, Britto S, Diwan K. Evaluating the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on clinical documentation efficiency and accuracy across clinical settings: a scoping review. Cureus 2024;16:e73994.



27. Hunter RB, Thammasitboon S, Rahman SS, Fainberg N, Renuart A, Kumar S, et al. Using ChatGPT to provide pa2tient-specific answers to parental questions in the PICU. Pediatrics 2024;154:e2024066615.

28. Vrdoljak J, Boban Z, Vilovic M, Kumric M, Bozic J. A review of large language models in medical education, clinical decision support, and healthcare administration. Healthcare (Basel) 2025;13:603.



29. Levin C, Orkaby B, Kerner E, Saban M. Can large language models assist with pediatric dosing accuracy? Pediatr Res 2025;Mar 8 doi: 10.1038/s41390-025-03980-8. [Epub].


30. Mansoor M, Ibrahim AF, Grindem D, Baig A. Large language models for pediatric differential diagnoses in rural health care: Multicenter retrospective cohort study comparing GPT-3 with pediatrician performance. JMIRx Med 2025;6:e65263.



31. Johri S, Jeong J, Tran BA, Schlessinger DI, Wongvibulsin S, Barnes LA, et al. An evaluation framework for clinical use of large language models in patient interaction tasks. Nat Med 2025;31:77–86.



32. Bedi S, Liu Y, Orr-Ewing L, Dash D, Koyejo S, Callahan A, et al. Testing and evaluation of health care applications of large language models: a systematic review. JAMA 2025;333:319–28.



33. Chang CT, Farah H, Gui H, Rezaei SJ, Bou-Khalil C, Park YJ, et al. Red teaming ChatGPT in medicine to yield real-world insights on model behavior. NPJ Digit Med 2025;8:149.


34. Fera B, Sullivan JA, Varia H, Shukla M. Building and maintaining health care consumers’ trust in generative AI. Deloitte Insights 2024;Jun 6.
35. Swanson JR, King WE, Sinkin RA, Lake DE, Carlo WA, Schelonka RL, et al. Neonatal intensive care unit length of stay reduction by heart rate characteristics monitoring. J Pediatr 2018;198:162–7.


36. Fisker S, Christensen M, Bach E, Bibby BM, Hansen KW. Long-term performance of two systems for automated insulin delivery in adults with type 1 diabetes: an observational study. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 2025;8:e70043.



37. Onorati F, Regalia G, Caborni C, LaFrance WC Jr, Blum AS, Bidwell J, et al. Prospective study of a multimodal convulsive seizure detection wearable system on pediatric and adult patients in the epilepsy monitoring unit. Front Neurol 2021;12:724904.



38. Zhang C, Hallbeck MS, Salehinejad H, Thiels C. The integration of artificial intelligence in robotic surgery: a narrative review. Surgery 2024;176:552–7.


39. Muehlematter UJ, Bluethgen C, Vokinger KN. FDA-cleared artificial intelligence and machine learning-based medical devices and their 510(k) predicate networks. Lancet Digit Health 2023;5:e618–26.


40. Torous J, Stern AD, Bourgeois FT. Regulatory considerations to keep pace with innovation in digital health products. NPJ Digit Med 2022;5:121.




41. Simon DA, Shachar C, Cohen IG. Skating the line between general wellness products and regulated devices: strategies and implications. J Law Biosci 2022;9:lsac015.




42. Santra S, Kukreja P, Saxena K, Gandhi S, Singh OV. Navigating regulatory and policy challenges for AI enabled combination devices. Front Med Technol 2024;6:1473350.



43. Warraich HJ, Tazbaz T, Califf RM. FDA Perspective on the regulation of artificial intelligence in health care and biomedicine. JAMA 2025;333:241–7.


44. Bourgeois FT, Espinoza JC. Advancing equity in medical device development for children. JAMA Pediatr 2023;177:561–2.


45. Sheet NF. NHE fact sheet. Baltimore (MD): U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, 2024.
46. Brewster RCL, Nagy M, Wunnava S, Bourgeois FT. US fda approval of pediatric artificial intelligence and machine learning-enabled medical devices. JAMA Pediatr 2025;179:212–4.



47. Elahmedi M, Sawhney R, Guadagno E, Botelho F, Poenaru D. The state of artificial intelligence in pediatric surgery: a systematic review. J Pediatr Surg 2024;59:774–82.


48. Arakaki S, Takenaka S, Sasaki K, Kitaguchi D, Hasegawa H, Takeshita N, et al. Artificial intelligence in minimally invasive surgery: current state and future challenges. JMA J 2025;8:86–90.



49. Tsai AY, Carter SR, Greene AC. Artificial intelligence in pediatric surgery. Semin Pediatr Surg 2024;33:151390.


50. Ryu S, Goto K, Kitagawa T, Kobayashi T, Shimada J, Ito R, et al. Real-time artificial intelligence navigation-assisted anatomical recognition in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 2023;27:3080–2.




51. Khanna A, Wolf T, Frank I, Krueger A, Shah P, Sharma V, et al. Enhancing accuracy of operative reports with automated artificial intelligence analysis of surgical video. J Am Coll Surg 2025;240:739–46.


52. Saeidi H, Opfermann JD, Kam M, Wei S, Leonard S, Hsieh MH, et al. Autonomous robotic laparoscopic surgery for intestinal anastomosis. Sci Robot 2022;7:eabj2908.



53. Kim JW, Zhao TZ, Schmidgall S, Deguet A, Kobilarov M, Finn C, et al. Surgical robot transformer (SRT): Imitation learning for surgical tasks. arXiv:2407.12998v1 [Preprint] 2024 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.12998.

54. Asciak L, Kyeremeh J, Luo X, Kazakidi A, Connolly P, Picard F, et al. Digital twin assisted surgery, concept, opportunities, and challenges. NPJ Digit Med 2025;8:32.




55. Chouffani El Fassi S, Abdullah A, Fang Y, Natarajan S, Masroor AB, Kayali N, et al. Not all AI health tools with regulatory authorization are clinically validated. Nat Med 2024;30:2718–20.



56. Mello MM, Guha N. Understanding Liability risk from using health care artificial intelligence tools. N Engl J Med 2024;390:271–8.


57. Mello MM, Rose S. Denial-artificial intelligence tools and health insurance coverage decisions. JAMA Health Forum 2024;5:e240622.


58. Mello MM, Roberts JL. Antidiscrimination law meets artificial intelligence-new requirements for health care organizations and insurers. JAMA Health Forum 2024;5:e243397.


60. Karako K, Tang W. Applications of and issues with machine learning in medicine: Bridging the gap with explainable AI. Biosci Trends 2025;18:497–504.


62. La Bella S, Gupta L, Venerito V. AI am the future: artificial intelligence in pediatric rheumatology. Curr Opin Rheumatol Mar 12. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000001087. [Epub].
63. Adamson AS, Smith A. machine learning and health care disparities in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol 2018;154:1247–8.


64. Obermeyer Z, Powers B, Vogeli C, Mullainathan S. Dissecting racial bias in an algorithm used to manage the health of populations. Science 2019;366:447–53.


65. Michard F, Mulder MP, Gonzalez F, Sanfilippo F. AI for the hemodynamic assessment of critically ill and surgical patients: focus on clinical applications. Ann Intensive Care 2025;15:26.




66. Herrera H, Wood D. Battling alarm fatigue in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am 2023;35:347–55.


67. Mandl KD. Unseen commercial forces could undermine artificial intelligence decision support. NEJM AI 2025;2(3): DOI: 10.1056/AIp2400922.

68. Topol EJ. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med 2019;25:44–56.



69. Obermeyer Z, Emanuel EJ. Predicting the future - big data, machine learning, and clinical medicine. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1216–9.



70. Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A. Deep learning. The MIT Press, 2016.
71. Bommasani R, Hudson DA, Adeli E, Altman R, Arora S, von Arx S, et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv:2108.07258v3 [Preprint] 2021 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv. 2108.07258.

72. Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: Pretraining of deep bidirectional Transformers for language understanding. arXiv:1810.04805v2 [Preprint] 2018 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805.

73. Gemini T, Anil R, Borgeaud S, Alayrac JB, Yu J, Soricut R, et al. Gemini: a family of highly capable multimodal models. arXiv:2312.11805v54 [Preprint] 2023 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.11805.

74. Bai Y, Kadavath S, Kundu S, Askell A, Kernion J, Jones A, et al. Constitutional AI: harmlessness from AI feedback. arXiv:2212.08073v [Preprint] 2023 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2212.08073.

75. Touvron H, Lavril T, Izacard G, Martinet X, Lachaux MA, Lacroix T, et al. LLaMA: open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv:2302.13971v1 [Preprint] 2023 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.13971.

76. Touvron H, Martin L, Stone K, Albert P, Almahairi A, Babaei Y, et al. Llama 2: open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv:2307.09288v2 [Preprint] 2023 [cited 2025 Feb 3. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv. 2307.09288.

77. Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, et al. Attention is all you need. arXiv:1706.03762v7 [Preprint] 2017 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762.

78. Adadi A, Berrad M. Peeking inside the black-box: a survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 2018;6:52138–60.

79. Wei J, Wang X, Schuurmans D, Bosma M, Ichter B, Xia F, et al. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. arXiv:2201.11903v6 [Preprint] 2022 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2201.11903.

80. Moorman JR, Carlo WA, Kattwinkel J, Schelonka RL, Porcelli PJ, Navarrete CT, et al. Mortality reduction by heart rate characteristic monitoring in very low birth weight neonates: a randomized trial. J Pediatr 2011;159:900. –6. e1.



81. FDA clearance [Internet]. Lehi (UT): Owlet US; 2023 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://owletcare.com/pages/fda-response.
82. Asfari A. Artificial intelligence role and clinical decision support system extubation readiness trail and etiometry scoring system. Biomed J Sci Tech Res 2021;35:27291–3.

83. Yigit MH, Eviz E, Hatun S, Yesiltepe Mutlu G. Automatic bone age determination in adult height prediction for girls with early variants puberty and precoccious puberty. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 2025;Feb 20 doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2025.2024-7-24. [Epub].

84. Shelmerdine SC, Pauling C, Allan E, Langan D, Ashworth E, Yung KW, et al. Artificial intelligence (AI) for paediatric fracture detection: a multireader multicase (MRMC) study protocol. BMJ Open 2024;14:e084448.



85. AZmed Secures FDA 510(k) Clearance for Rayvolve in Pediatric Fracture Detection AI [Internet]. Paris (France): AZMED; 2024 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://www.azmed.co/news-post/azmed-secures-fda-510-kclearance-for-rayvolve-in-pediatric-fracture-detection-ai.
86. Cognoa. Cognoa receives FDA marketing authorization for first-of-its-kind autism diagnosis aid [Internet]. Cognoa 2021 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/cognoa-receives-fda-marketingauthorization-for-first-of-its-kind-autism-diagnosisaid-301304351.html?target=_blank&rel=noopener%20noreferrer.
87. Stagg A, Giglia TM, Gardner MM, Shustak RJ, Natarajan SS, Hehir DA, et al. Feasibility of digital stethoscopes in telecardiology visits for interstage monitoring in infants with palliated congenital heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol 2023;44:1702–9.




88. BrightHeart. BrightHeart’s AI for prenatal heart defect detection receives FDA clearance [Internet]. Paris (France): BrightHeart; 2025 [cited 2025 Feb 3]. Available from: https://www.brightheart.ai/press/20250131-femtechinsider.
89. Hughes JD, Chivers P, Hoti K. The clinical suitability of an artificial intelligence-enabled pain assessment tool for use in infants: feasibility and usability evaluation study. J Med Internet Res 2023;25:e41992.



90. Shaikh TA, Dar TR, Sofi S. A data-centric artificial intelligent and extended reality technology in smart healthcare systems. Soc Netw Anal Min 2022;12:122.




91. Koc I, Bagheri S, Chau RK, Hoyek S, Shousha NA, Mahmoudinezhad G, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of digital therapeutics for amblyopia. Ophthalmology 2025;132:654–60.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


