Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 68(10); 2025 |
|
Abstract
Background
Breastfeeding has nutritional, immunological, and psychological benefits for infants. However, breastfeeding rates have recently declined in South Korea.
Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the breastfeeding trends and determinants in a nationwide birth cohort.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study used claims data from the National Health Insurance Service from 2007–2022. Infants born between 2007 and 2021 who underwent at least one National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children examination were included in this study. Breastfeeding rates were analyzed across eight age-specific sessions, and logistic regression models were used to identify factors associated with breastfeeding practices.
Results
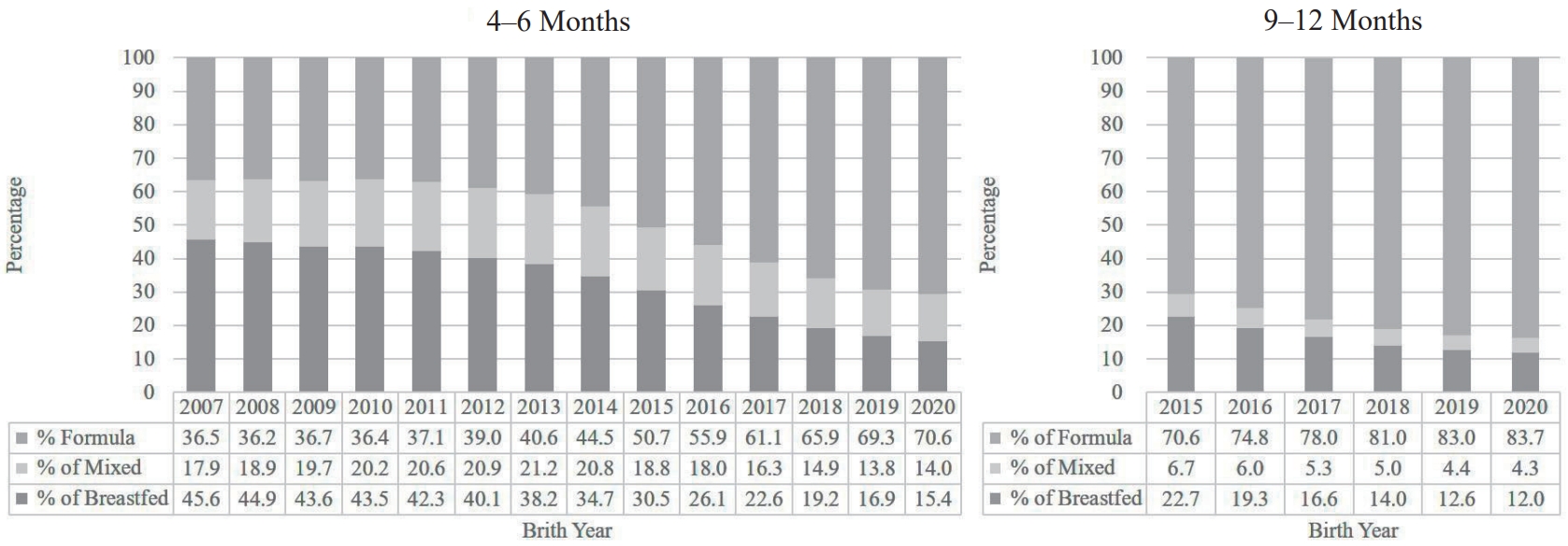
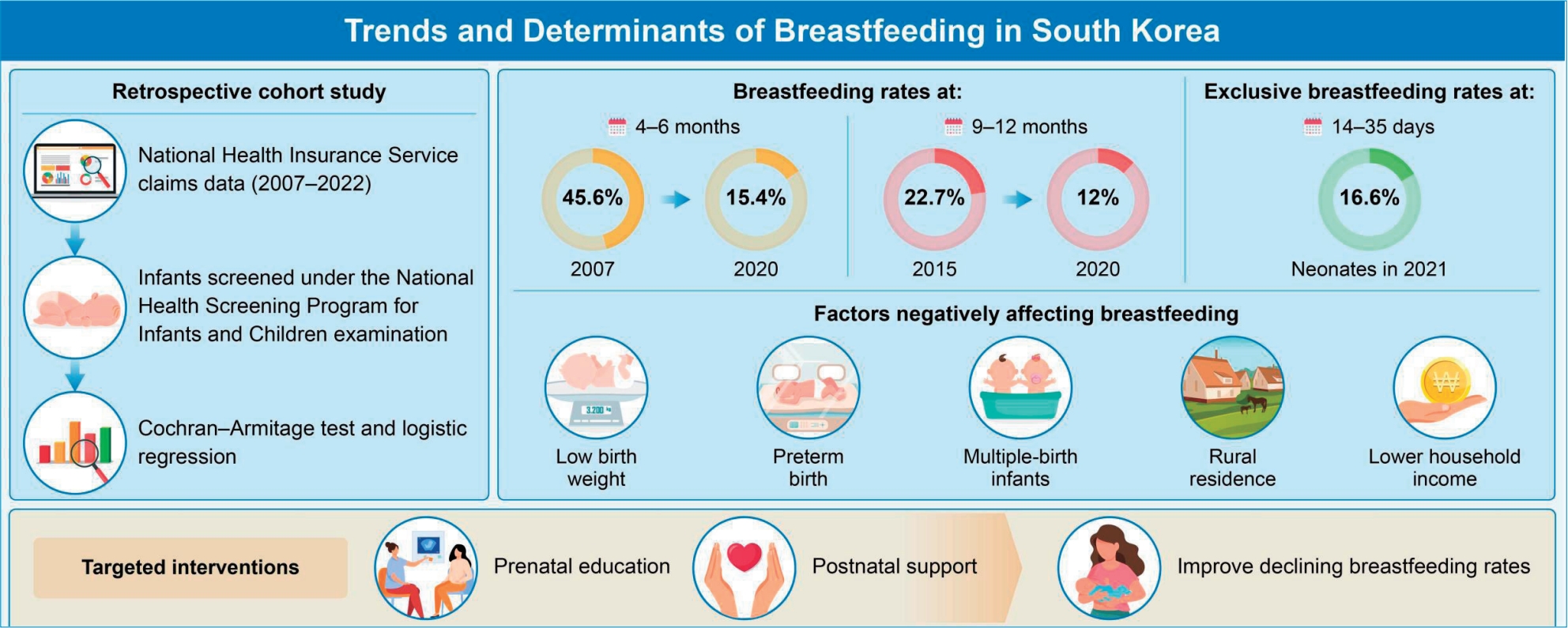
At 4–6 months, the prevalence of breastfeeding decreased from 45.6% in 2007 to 15.4% in 2020, whereas that of formula feeding increased from 36.5% to 70.6%. Similarly, the breastfeeding rate at 9–12 months decreased from 22.7% in 2015 to 12.0% in 2020. In 2021, only 16.6% of neonates were exclusively breastfed at 14–35 days of life, and the rate of exclusive breastfeeding at 6 months further declined from 10.0% in 2020 to 8.8% in 2021. Factors negatively affecting breastfeeding were low birth weight (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.636; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.607–0.667), preterm birth (aOR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.687–0.754), multiple births (aOR, 0.603; 95% CI, 0.570–0.638), rural residence (aOR, 0.788; 95% CI, 0.771–0.805), and lower household income (aOR, 0.783; 95% CI, 0.748–0.819) (P<0.001).
Conclusion
Breastfeeding rates in South Korea have declined significantly over the past decade, with disparities observed in preterm, low birth weight, and multiple-birth infants as well as and rural or lower-income households. Targeted interventions including enhanced prenatal education, postnatal support, and community-based initiatives are necessary to improve breastfeeding rates.
Graphical abstract. Trends and determinants of breastfeeding among Korean infants (2007–2021).
Beyond its role as a primary nutritional source, breastfeeding plays a crucial role in shaping the infant microbiome, supporting immune system maturation, and providing psychological comfort [1,2]. Breastfeeding is associated with a reduced risk of various pediatric illnesses, including otitis media, infectious gastroenteritis, respiratory tract infections, asthma, sudden infant death syndrome, and childhood obesity [3,4]. Recognizing these benefits, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the World Health Organization recommend exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) for the first 6 months, followed by continued breastfeeding alongside consumption of complementary foods, with breastfeeding continuation for 2 year or longer, as mutually desired by the mother and infant [4,5].
Monitoring breastfeeding trends is essential for assessing and improving breastfeeding promotion. Recently, breastfeeding rates have declined in South Korea. According to a 2021 survey conducted by the Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs (KIHSA) [6], the EBF rate was 36.9% at 3 months and 20.1% at 6 months, which are both below the global average of 44% of children under 6 months being exclusively breastfed in 2021. Additionally, the rate of any breastfeeding continuation up to 12 months declined to 16.8%, which is below the global average of 65% of continued breastfeeding (12–23 months) [7]. These findings are consistent with those of previous Korean studies based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), which have reported a decline in long-term breastfeeding rates (≥12 months) over the past decade, with breastfeeding becoming rare beyond 18 months in South Korea [8].
To support infant health and nutrition, the Korean Society of Pediatrics introduced the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children (NHSPIC) in 2007 as part of a national health initiative [9]. The program includes an age-specific nutritional questionnaire addressing breastfeeding practices. In response to the growing demand for neonatal assessment and enhanced breastfeeding education, the program was revised and implemented in 2021. Although nationwide cohort studies using the NHSPIC data have primarily focused on the protective effects of breastfeeding against diseases, research exploring breastfeeding trends and their determinants in South Korea is limited.
Therefore, this study aimed to investigate factors influencing breastfeeding practices and trends using a population-based nationwide birth cohort in South Korea.
This study used claims data from the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database between January 1, 2007 and December 31, 2022. South Korea operates a universal, single-payer healthcare system, and the NHIS maintains nationwide records of inpatient and outpatient visits, procedures, and prescriptions [10]. We identified infants born between January 1, 2007 and December 31, 2021, who underwent at least one NHSPIC examination by 2022. Based on the national birth statistics [11], our cohort represented 79.2% (4,806,520 of 6,070,270) of all births in South Korea during this period. The first neonatal examination was introduced in 2021, and our analysis covered 66.0% (172,813 of 260,562) of the national births for that year. Infants with missing or incorrect birth dates, missing checkup dates, or incomplete breastfeeding-related questionnaire responses were excluded. After applying these criteria, 4,539,662 participants were finally included (Fig. 1).
This study was approved by the Korea University Guro Hospital Institutional Review Board (approval number 2023GR0251), NHIS (No. NHIS-2024-1-113) and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The requirement for informed consent was waived because the study used anonymized, deidentified data.
The NHIS database includes four primary datasets as follows: (1) insurance eligibility, (2) medical treatment, (3) medical care institutions, and (4) infant and child health examinations. The medical treatment dataset provides details on inpatient and outpatient visits, procedures, and prescriptions reimbursed by the NHIS, coded using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision and Korean Drug and Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical codes [12].
The NHSPIC is a national health screening program initiated in November 2007 by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and the National Health Insurance Corporation. Health- and growth-related data were systematically collected across eight age-specific sessions: (1st, 14–35 days; 2nd, 4–6 months; 3rd, 9–12 months; 4th, 18–24 months; 5th, 30–36 months; 6th, 42–48 months; 7th; 54–60 months; and 8th, 66–71 months after birth). In January 2021, the first neonatal screening session (15–35 days) was introduced, which incorporated a questionnaire on EBF. From 2007 to 2020, the second and third NHSPIC surveys included a breastfeeding question: “What do you primarily feed your child?” The response options were (1) breast milk only, (2) formula only, and (3) mixed breast milk and formula. In 2021, the NHSPIC questionnaire was revised to include a more detailed assessment of breastfeeding practices. The updated survey collected information on the duration of EBF from birth, whether breastfeeding was continued in the third NHSPIC session, and the total duration of breastfeeding in the fifth NHSPIC session.
Additionally, infant-related factors, including low birth weight (LBW), <2,500 g vs. ≥2,500 g), prematurity, and multiple births, were extracted from the NHSPIC data. Demographic characteristics, such as sex, residential area, and household income level, were obtained from the NHIS claims data. Residential areas were classified as urban or rural based on a population threshold of 500,000 and further categorized by administrative district. Household income levels were divided into four groups based on insurance premium percentiles as follows: Medicaid recipients (eligible for medical aid and exempt from insurance premiums), low-income group (1st–30th percentile), middle-income group (31st–70th percentile), and high-income group (>70th percentile).
We calculated the number and percentage of children breastfed by birth year, which was confirmed through NHSPIC screening sessions. Trends in breastfeeding rates were analyzed using the Cochran–Armitage trend test. Logistic regression was used to identify the determinants of breastfeeding and calculate odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed, incorporating significant variables from the univariate analysis. Additionally, we examined the duration of EBF at 12 and 36 months of age. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS ver. 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., USA).
The prevalence of breastfeeding among Korean infants aged 4–6 months declined from 45.6% in 2007 to 15.4% in 2020, whereas the prevalence of formula feeding significantly increased from 36.5% in 2007 to 70.6% in 2020 (Fig. 2). Breastfeeding rates stratified by infant characteristics and birth year are presented in Supplementary Table 1. Across all demographic and clinical subgroups, breastfeeding rates consistently decreased over time (P<0.001). The adjusted ORs (aORs) for breastfeeding according to the independent variables are presented in Table 1. Factors significantly associated with a lower likelihood of breastfeeding included later birth years, LBW (<2,500 g), preterm birth, multiple births, residence in rural areas, and lower household income (P<0.001). Compared to infants born in 2007, those born in 2020 had a significantly lower likelihood of breastfeeding (aOR, 0.219; 95% CI, 0.215–0.224; P<0.001). A consistent declining trend was observed across birth years, with aORs progressively decreasing (e.g., 2010: aOR, 0.921; 95% CI, 0.907–0.935 vs. 2015: aOR, 0.529; 95% CI, 0.521–0.537). Infants with LBW had 43% lower odds of breastfeeding than those with normal birth weight (aOR, 0.564; 95% CI 0.555–0.573). Similarly, infants born preterm (aOR, 0.649; 95% CI, 0.639–0.660) and those born from multiple births (aOR, 0.173; 95% CI, 0.167–0.180) had a significantly lower likelihood of breastfeeding than their counterparts. Infants from rural areas were less likely to breastfeed at 4–6 months of age than those from urban areas (aOR, 0.972; 95% CI, 0.967–0.977). Additionally, infants from Medicaid-recipient households had significantly lower odds of breastfeeding, even after adjusting for demographic factors (aOR, 0.783; 95% CI, 0.748–0.819).
Among infants aged 9–12 months, the breastfeeding rate has declined from 22.7% in 2015 to 12.0% in 2020, and the prevalence of formula feeding has increased from 70.6% in 2007 to 83.7% in 2020 (Fig. 2, Supplementary Table 2). The likelihood of breastfeeding significantly decreased in subsequent years compared to that in 2015, with infants born in 2020 having the lowest likelihood of breastfeeding (aOR, 0.467; 95% CI, 0.455–0.480; P<0.001) (Table 1).
Unlike the 4–6 month group, in which rural residence was associated with a lower likelihood of breastfeeding, infants living in rural areas had slightly higher odds of continued breastfeeding at 9–12 months than those in urban regions (aOR, 1.014; 95% CI, 1.004–1.024; P<0.01). Although household income was significantly associated with the likelihood at 4–6 months, it was not a significant factor at 9–12 months.
Among the 90,746 infants born in 2021, 16.6% were exclusively breastfed during the neonatal period (14–35 days after birth) as assessed in the first newly established NHSPIC examination. Table 2 presents the EBF rates and adjusted odds according to infant characteristics. Similar to the 4–6-and 9–12-month age groups, LBW, prematurity, multiple births, and rural residence were associated with a lower likelihood of EBF. The largest difference was observed in the multiple-birth group, which had significantly lower odds of EBF than the other groups (aOR, 0.236; 95% CI, 0.188–0.297).
Ever EBF was reported by 49.8% of the respondents among infants aged 9–12 months, with a median duration of 3 months (Table 3). The proportion of infants who were exclusively breastfed for 6 months decreased from 10.0% in 2020 to 8.8% in 2021. The distribution of breastfeeding duration among exclusively breastfed infants differed significantly between 2020 and 2021 (P<0.001). Among them., the percentage of participants exclusively breastfeeding for 1–3 months was slightly increased across the years (63.7% in 2020 vs. 67.4% in 2021), although the rate for durations exceeding 3 months was lower in 2021 than in 2020 (36.3% in 2020 vs. 32.6% in 2021, P<0.001).
The prevalence of any breastfeeding declined from 88.1% in 2018 to 84.7% in 2020 (Table 4). Breastfeeding likelihood consistently declined over time, with multiple-birth infants having the lowest likelihood of breastfeeding (aOR, 0.603; 95% CI, 0.570–0.638). Additionally, Medicaid-recipient households had significantly lower odds of breastfeeding, even after adjusting for potential confounders (aOR, 0.189; 95% CI, 0.168–0.213).
Any breastfeeding was reported by 87.1% of the respondents among infants aged 30–36 months and the median duration of breastfeeding was only 3 months. The proportion of infants who were never breastfed increased from 11.9% in 2018 to 13.3% in 2019 and 15.3% in 2020 (P<0.001). (Supplementary Table 3). The proportion of infants breastfed for 1–6 months showed minimal variation, whereas the proportion continuing breastfeeding at 7–12 months declined from 18.6% in 2018 to 15.5% in 2020.
This study examining the trends and determinants of breastfeeding in South Korea highlights a significant decline in breastfeeding prevalence over time. The breastfeeding rate at 4–6 months decreased from 45.6% in 2007 to 15.4% in 2020, whereas formula feeding increased from 36.5% in 2007 to 70.6% in 2020. Similarly, the prevalence of breastfeeding at 9–12 months declined from 22.7% in 2015 to 12.0% in 2020. In 2021, newly collected data showed that 16.6% of infants were exclusively breastfed during the neonatal period, and the prevalence of EBF at 6 months further declined from 10.0% in 2020 to 8.8% in 2021. The rate of breastfeeding also decreased from 88.1% in 2018 to 84.7% in 2022, and only 17.0% of infants continued breastfeeding at 7–12 months. The key factors negatively associated with EBF include LBW, prematurity, multiple births, and rural residency.
Breastfeeding rates vary significantly between countries. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States, 83.2% of infants initiate breastfeeding, with 24.9% exclusively breastfed at 6 months. Unlike South Korea, the U.S. has shown a relatively steady increase in breastfeeding rates from 2007 to 2022 [13]. Similarly, a study in Japan has reported an EBF prevalence of 37.4% at 6 months between 2011 and 2014 [14]. European countries also exhibit variations in breastfeeding rates; immediately after birth, 56%–98% of infants receive human milk, with 38%–71% continuing breastfeeding and 13%–39% exclusively breastfeeding at 6 months [15]. By contrast, the present study noted that in South Korea, only 16.6% of infants were exclusively breastfed at 1 month, and approximately 8.8% at 5–6 months in the infants born in 2021. Recent data from this study indicate that while the EBF rate at 3 months and the any breastfeeding rate up to 6 months have remained relatively stable, there is a declining trend in EBF beyond 3 months and overall breastfeeding beyond 6 months. These figures are significantly lower than international public health recommendations and demonstrate a continuous decline in breastfeeding practices. This trend is consistent with those in previous reports from the KIHSA [6] and KNHANES [8], reflecting a distinct pattern in South Korea. Therefore, it is essential to promote continued breastfeeding beyond 6 months, even after the introduction of solid foods.
This large-scale cohort study identified the key factors influencing breastfeeding rates in South Korea. LBW, preterm, and multiple-birth infants were less likely to be breastfed at 4–6 months, which is consistent with the findings of previous studies. Despite South Korea’s declining birth rate, the proportion of preterm births (<37 weeks of gestation) increased from 6.5% in 2013 to 9.7% in 2020 [16], largely owing to an increase in high-risk pregnancies and multiple births [17]. EBF is recommended for preterm and LBW infants as it is for full-term infants. EBF is strongly recommended for preterm and LBW infants because of its role in preventing morbidity, improving growth, and supporting developmental outcomes. However, in this study, breastfeeding rates among these high-risk groups were significantly lower, likely owing to feeding difficulties, immaturity, and other complications [18]. Previous studies have indicated that breastfeeding rates in moderate-to-late preterm infants are lower than those in full-term infants, a trend that is also observed in South Korea [19]. The current national breastfeeding promotion programs may remain insufficient, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to support multiple-birth, preterm, and LBW infants. Breastfeeding multiple-birth infants is significantly more challenging than breastfeeding a single infant and requires greater physical and emotional resilience. Future Korean research should explore targeted interventions and conduct longitudinal studies to assess the impact of different support measures on breastfeeding success in multiple births [20]. Infants in rural areas were less likely to initiate breastfeeding and continue breastfeeding for 4–6 months, which may be attributable to the sociodemographic differences between urban and rural populations. These regional disparities in breastfeeding rates have important public health implications and highlight the need for community-based breastfeeding education programs. Such efforts should not be limited to healthcare institutions, but should also involve household- and community-level interventions to promote breastfeeding awareness and support. Infants from Medicaid-recipient households were more likely to never initiate breastfeeding and had lower breastfeeding continuation rates at 4–6 months. This is consistent with previous Korean studies, which have reported that the poorest socioeconomic groups had the lowest breastfeeding rates between 2010 and 2012 [21]. These disparities may be influenced by maternal occupation, education level, and access to lactation support, suggesting that improving access to lactation counseling and workplace accommodations could help mitigate these barriers [22].
Despite global efforts to promote breastfeeding, South Korea continues to experience challenges in maintaining optimal breastfeeding practices, with rates falling short of international recommendations [23]. To improve breastfeeding rates, comprehensive strategies at the individual, community, and policy levels must be implemented. The key measures include enhancing prenatal education, expanding breastfeeding-friendly hospital policies, such as the Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative, extending postnatal support, promoting workplace accommodation, and strengthening community-based interventions. Although Korean pediatricians generally had a positive attitude toward breastfeeding, the provision of breastfeeding counseling was limited, highlighting the need for policy support to establish structured counseling programs and ultimately improve breastfeeding rates [24]. Special attention should be directed toward populations with historically low breastfeeding rates, including low-income families and mothers of LBW, preterm, or multiple-birth infants. Standardized data collection on breastfeeding practices is essential to track national trends and optimize breastfeeding support programs. The U.S. Breastfeeding Report Card, introduced by the CDC [13] in 2007, serves as a model for monitoring and promoting breastfeeding practices in response to declining rates.
This study has some limitations. First, because breastfeeding data were self-reported at the time of the NHSPIC examinations, the responses may have been subject to recall bias, affecting the accuracy of the reported breastfeeding duration and exclusivity. Second, inconsistencies in breastfeeding definitions over time limit the comparability of the findings across different study periods. Before 2021, the NHSPIC questionnaire categorized feeding methods as breast milk, formula, or mixed feeding, making it difficult to distinguish between exclusive and partial breastfeeding methods. In the NHSPIC database, information on infant feeding practices is collected at specific time points, but detailed data regarding the introduction of complementary foods or other dietary supplements are limited. To avoid misinterpretation, this study used the term "breastfeeding" instead of "exclusive breastfeeding" when reporting findings based on this category before 2021. Given these limitations, we chose to use the broader term "breastfeeding" to more accurately reflect the data collected and to prevent potential misunderstanding among readers. Since 2021, the questionnaire has explicitly classified EBF, improving data accuracy but reducing comparability with previous years. Additionally, the classification of infant age groups in the NHSPIC program presents a challenge in accurately assessing breastfeeding rates. While EBF under 6 months is defined as breastfeeding up to 6 months (0–5 months of age), the 4–6 months category in the NHSPIC data includes infants up to 6 months and 29 days, leading to potential classification discrepancies. Third, age classification inconsistencies in the national infant health screening program may have affected the accuracy of reported breastfeeding rates. For instance, the 9–12 months and 30–36 months categories include cases where the exact number of months is not standardized, potentially introducing discrepancies in the reported data. To obtain more precise national breastfeeding statistics, it is essential to ensure a more consistent and clearly defined age classification in future surveys. Fourth, as this study has an observational design, establishing causal relationships between breastfeeding practices and associated factors was not possible. Key maternal factors that could influence breastfeeding behaviors—such as maternal health, age, education level, mode of delivery, and workplace policies—were not included in the analysis. These unmeasured variables may contribute to breastfeeding disparities and should be explored in future studies. Fifth, the potential influence of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on breastfeeding practices was not fully examined. The pandemic may have affected maternal healthcare access, hospital policies, and breastfeeding support services, which could have influenced breastfeeding rates during this period. Future studies should assess post-pandemic breastfeeding trends to determine any long-term impacts. Given these limitations, future research should focus on improving data collection methods, refining age classifications in national surveys, and revising the NHSPIC questionnaire to establish a more accurate and standardized assessment of breastfeeding rates. These efforts will help provide more reliable data to inform breastfeeding promotion policies in South Korea.
In conclusion, this study demonstrated a persistent decline in breastfeeding rates in South Korea over time, with substantial disparities according to infant characteristics and socioeconomic factors. Our findings underscore the urgent need for comprehensive national strategies to promote and support breastfeeding, particularly among vulnerable populations. Strengthening breastfeeding education, support systems, and policy initiatives will be essential to reversing current trends and improving child health outcomes.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Tables 1-3 are available at https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.00857.
Supplementary Table 1.
Research flow chart. FFQ, food frequency questionnaire; NT-pro-BNP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; TD, thiamin deficiency; TPPE, thiamin pyrophosphate effect.
Supplementary Table 2.
Trends in the prevalence of breastfeeding among infants aged 9–12 months from 2007 to 2020
Supplementary Table 3.
Periods of breastfeeding among infants aged 30–36 months
Footnotes
Table 1.
Determinants of breastfeeding among infants born in 2007–2020 by study subgroup
| Variable | Prevalence rate (%) |
Breastfeeding at 4–6 months |
Prevalence rate (%) |
Breastfeeding at 9–12 months |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Univariable |
Mutivariable |
Univariable |
Mutivariable |
|||
| OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | |||
| Birth year | ||||||
| 2007 | 45.6 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 2008 | 44.9 | 0.974 (0.959–0.989)*** | 0.973 (0.958–0.989)*** | |||
| 2009 | 43.6 | 0.925 (0.910–0.939)*** | 0.927 (0.912–0.941)*** | |||
| 2010 | 43.5 | 0.918 (0.905–0.932)*** | 0.921 (0.907–0.935)*** | |||
| 2011 | 42.3 | 0.875 (0.862–0.888)*** | 0.878 (0.865–0.892)*** | |||
| 2012 | 40.1 | 0.801 (0.789–0.813)*** | 0.806 (0.794–0.819)*** | |||
| 2013 | 38.2 | 0.738 (0.727–0.749)*** | 0.742 (0.731–0.754)*** | |||
| 2014 | 34.7 | 0.633 (0.624–0.643)*** | 0.638 (0.628–0.647)*** | |||
| 2015 | 30.5 | 0.524 (0.517–0.532)*** | 0.529 (0.521–0.537)*** | 22.7 | 1 | 1 |
| 2016 | 26.1 | 0.422 (0.416–0.429)*** | 0.425 (0.419–0.432)*** | 19.3 | 0.813 (0.803–0.823)*** | 0.812 (0.802–0.823)*** |
| 2017 | 22.6 | 0.349 (0.344–0.354)*** | 0.352 (0.347–0.358)*** | 16.7 | 0.681 (0.672–0.690)*** | 0.681 (0.672–0.69)*** |
| 2018 | 19.2 | 0.283 (0.279–0.288)*** | 0.286 (0.282–0.291)*** | 14.0 | 0.556 (0.548–0.564)*** | 0.558 (0.55–0.566)*** |
| 2019 | 16.9 | 0.243 (0.239–0.247)*** | 0.246 (0.242–0.250)*** | 12.6 | 0.490 (0.483–0.498)*** | 0.491 (0.484–0.499)*** |
| 2020 | 15.4 | 0.217 (0.213–0.221)*** | 0.219 (0.215–0.224)*** | 12.0 | 0.465 (0.453–0.477)*** | 0.467 (0.455–0.48)*** |
| LBW infant | ||||||
| No | 33.5 | 1 | 1 | 17.8 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 16.8 | 0.402 (0.397–0.408)*** | 0.564 (0.555–0.573)*** | 8.4 | 0.422 (0.411–0.432)*** | 0.6 (0.583–0.619)*** |
| Preterm infant | ||||||
| No | 33.3 | 1 | 1 | 17.7 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 16.7 | 0.402 (0.396–0.407)*** | 0.649 (0.639–0.66)*** | 8.3 | 0.421 (0.41–0.433)*** | 0.661 (0.64–0.682)*** |
| Multiple-birth infant | ||||||
| No | 33.2 | 1 | 1 | 17.6 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 5.7 | 0.122 (0.118–0.126)*** | 0.173 (0.167–0.18)*** | 4.6 | 0.225 (0.214–0.237)*** | 0.301 (0.285–0.318)*** |
| Residential area | ||||||
| Urban | 32.9 | 1 | 1 | 17.2 | 1 | 1 |
| Rural | 32.1 | 0.966 (0.961–0.970)*** | 0.972 (0.967–0.977)*** | 17.3 | 1.009 (1.000–1.018) | 1.014 (1.004–1.024)** |
| Household income | ||||||
| High | 32.3 | 1 | 1 | 17.2 | 1 | 1 |
| Middle | 33.2 | 1.041 (1.036–1.046)*** | 0.977 (0.972–0.982)*** | 17.3 | 1.003 (0.994–1.013) | 0.984 (0.975–0.994) |
| Low | 31.7 | 0.975 (0.968–0.982)* | 0.934 (0.927–0.941)* | 17.0 | 0.985 (0.970–0.999) | 0.987 (0.972–1.001) |
| Medicaid | 28.8 | 0.850 (0.816–0.885)*** | 0.783 (0.748–0.819)*** | 17.0 | 0.981 (0.907–1.062) | 1.036 (0.957–1.123) |
Table 2.
Determinants of exclusive breastfeeding among infants aged 14–35 days in 2021 by study subgroup
Table 3.
Duration of exclusive breastfeeding among infants aged 9–12 months
Table 4.
Determinants of any breastfeeding among newborn infants in 2018–2020
References
2. Ip S, Chung M, Raman G, Chew P, Magula N, DeVine D, et al. Breastfeeding and maternal and infant health outcomes in developed countries. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 2007;(153):1–186.
3. Horta BL, Bahl R, Martines JC, Victora CG. Evidence on the long-term effects of breastfeeding: systematic review and meta-analyses. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization, 2007;:1–51.
5. Alayón S, Varela V, Mukuria-Ashe A, Alvey J, Milner E, Pedersen S, Yourkavitch J. Exclusive breastfeeding: measurement to match the global recommendation. Matern Child Nutr 2022;18:e13409.


6. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. The 2021 National Family and Fertility Survey. Seoul (Korea): Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs, 2021.
7. United Nations Children’s Fund. The state of the World’s Children 2021: on my mind — promoting, protecting and caring for children’s mental health. New York: United Nations Children’s Fund, 2021.
8. Hong J, Chang JY, Oh S. The current status of prolonged breastfeeding and its related factors in Korean infants and their mothers: a Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. J Korean Med Sci 2023;38:e261.




9. Moon JS, Kim JY, Chang SH, Hae CK, Yang HR, Seo JK, et al. Development of a nutrition questionnaire and guidelines for the Korea National Health Screening Program for infants and children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2008;11:42–55.


10. Lee J, Lee JS, Park SH, Shin SA, Kim YY. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46:e15.


11. Statistics Korea. Birth statistics [Internet]. Daejeon (Korea): Statistics Korea; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 3]. Available from: https://www.index.go.kr/unity/potal/indicator/IndexInfo.do?clasCd=10&idxCd=F0008.
12. Bae CC, Maresso A. Republic of Korea: health system review. Health Syst Transit 2009;11:1–184.
13. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Breastfeeding report card [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 3]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding-data/breastfeeding-report-card/index.html.
14. Inano H, Kameya M, Sasano K, Matsumura K, Tsuchida A, Hamazaki K, et al. Factors influencing exclusive breastfeeding rates until 6 months postpartum: the Japan Environment and Children's Study. Sci Rep 2021;25;11:6841.




15. Theurich MA, Davanzo R, Busck-Rasmussen M, Díaz-Gómez NM, Brennan C, Kylberg E, et al. Breastfeeding rates and programs in Europe: a survey of 11 National Breastfeeding Committees and Representatives. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2019;68:400–7.


16. Statistics Korea. Birth and fertility statistics [Internet]. Daejeon (Korea): Statistics Korea; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 3]. Available from: https://kosis.kr/search/search.do?query=%EC%B6%9C%EC%83%9D%EC%95%84%EC%88%98.
17. Cho H, Lee YW. Multiple births and low birth weight: evidence from South Korea. Am J Hum Biol 2022;34:e23648.



18. Keir A, Rumbold A, Collins CT, McPhee AJ, Varghese J, Morris S, et al. Breastfeeding outcomes in late preterm infants: a multi-centre prospective cohort study. PLoS One 2022;17:e0272583.



19. Radtke JV. The paradox of breastfeeding-associated morbidity among late preterm infants. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 2011;40.1:9–24.



20. Bhardwaj G, Smitha MV, Jelly P, Stephen S, Cook JE, Panda S. Breastfeeding challenges experienced by mothers following multiple births—a systematic review and metasynthesis of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods studies. Breastfeed Med 2025;20:219–30.


21. Huh Y, Kim YN, Kim YS. Trends and determinants in breastfeeding among Korean women: a nationwide population-based study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18:13279.



-
METRICS

-
- 1 Web of Science
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 4,414 View
- 83 Download






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation

