Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 57(5); 2014 |
|
Abstract
Pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia (PHP Ia) is a disorder characterized by multiform hormonal resistance including parathyroid hormone (PTH) resistance and Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO). It is caused by heterozygous inactivating mutations within the Gs alpha-encoding GNAS exons. A 9-year-old boy presented with clinical and laboratory abnormalities including hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, PTH resistance, multihormone resistance and AHO (round face, short stature, obesity, brachydactyly and osteoma cutis) which were typical of PHP Ia. He had a history of repeated convulsive episodes that started from the age of 2 months. A cranial computed tomography scan showed bilateral calcifications in the basal ganglia and his intelligence quotient testing indicated mild mental retardation. Family history revealed that the patient's maternal relatives, including his grandmother and 2 of his mother's siblings, had features suggestive of AHO. Sequencing of the GNAS gene of the patient identified a heterozygous nonsense mutation within exon 11 (c.637 C>T). The C>T transversion results in an amino acid substitution from Gln to stop codon at codon 213 (p.Gln213*). To our knowledge, this is a novel mutation in GNAS.
Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP) is a disorder of end-organ resistance primarily affecting the actions of parathyroid hormone (PTH)1). It is characterized by hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia in association with increased secretion of PTH due to decreased target tissue responsiveness to PTH. Patients with PHP Ia are not only resistant to PTH, but also to other hormones that bind to receptors coupled to stimulatory G protein (Gs alpha)2). The GNAS gene is located on chromosome 20q13.11 and consists of 13 exons and 12 introns3). PHP-Ia is caused by heterozygous mutations affecting one of the 13 GNAS exons encoding Gs alpha4).
We report here a 9-yr-old boy with PHP Ia with a nonsense mutation of c.637 C>T in the GNAS gene, which is novel.
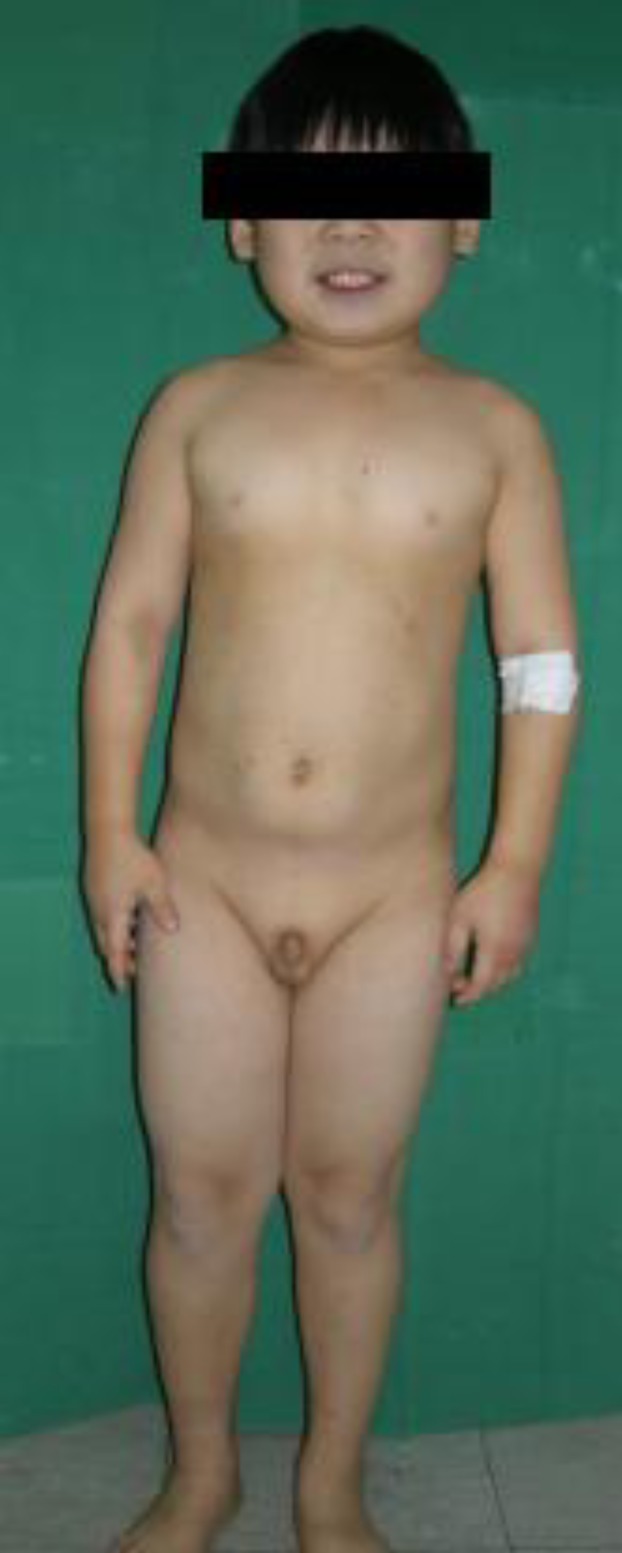
9-year-old boy was admitted to Hallym University Medical Center with painful subcutaneous soft tissue masses with calcifications on the right toes and posterior chest wall. He had a history of repeated convulsive episodes from the age of 2 months. Physical examination showed short stature (120 cm, 3rd percentile), round face (Fig. 1), brachydactyly with short metacarpals (Fig. 2) and subcutaneous ossifications on the 2nd toe tip and 1st web space of the right foot and the left lower posterior chest wall (Fig. 3). His weight was 30 kg (50th percentile), thus having a normal body mass index (20.83 kg/m2, 85th-90th percentile).
He was the first child of nonconsanguinous Korean parents. He was born at full term by cesarean section with a birth weight of 3.3 kg. Family history revealed that his maternal grandmother had features suggestive of AHO, such as short stature, round face, obesity and brachydactyly. His mother had normal appearance apart from short stature, but two of her siblings had short stature, round face and obesity. We could not make further investigation because the patient lost contact with his mother and maternal family after his parents got divorced.
Laboratory tests revealed hypocalcemia (4.2 mg/dL; normal range, 8.8-10.8 mg/dL), hyperphosphatemia (8.9 mg/dL; normal range, 3.7-5.6 mg/dL) and elevated serum PTH (146.5 pg/mL; normal range, 9-65 pg/mL). He also showed elevated plasma thyroid-stimulating hormone (6.978 µIU/mL; normal range, 0.5-4.8 µIU/mL), follicle stimulating hormone (5.6 µIU/mL; normal range, 0.26-3.0 µIU/mL), and luteinizing hormone (1.2 µIU/mL; normal range, 0.02-0.3 µIU/mL), which suggest multiple hormone resistance. Urinary phosphorous and cyclic adenosine monophosphate response after infusion of synthetic human PTH (teriparatide acetate) was attenuated (Ellsworth-Howard test) (Table 1). Cranial computed tomography scan demonstrated bilateral calcifications in the basal ganglia (Fig. 4). His intellegence scale (Korean Educational Development Institute - Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children) indicated mild mental retardation (intelligence quotient, 67).
He was diagnosed as having PHP Ia based on physical and laboratory findings; hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, PTH resistance, presence of AHO, multiple hormone resistance and mental retardation. He was started on phosphate-binding substance (aluminum hydroxide, 80 mg/kg/day), vitamin D (alfacalcidol, 1 mcg/day) and calcium carbonate (50 mg/kg/day). Three months later, his serum calcium was elevated from 4.2 to 6.0 mg/dL, and phosphorus was decreased from 8.9 to 8.6 mg/dL. The patient's clinical symptoms of pain, seizure and hyperactivity were reduced.
To support the diagnosis of PHP Ia, we performed DNA analysis of the GNAS gene.
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes using the Wizard Genomic DNA Purification kit following the manufacturer's instructions (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). All coding exons and their flanking introns of the GNAS gene were amplified using primer sets designed by the authors. Polymerase chain reaction was performed with a thermal cycler (model 9700, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) as follows: 32 cycles of denaturation at 94℃ for 30 seconds, annealing at 60℃ for 30 seconds, and extension at 72℃ of 30 seconds. After treatment of amplicon (5 uL) with 10 U shrimp alkaline phosphatase and 2 U exonuclease I (USB Co., Cleveland, OH, USA), direct sequencing was performed with the BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction kit (Applied Biosystems) on the ABI Prism 3100×1 genetic analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
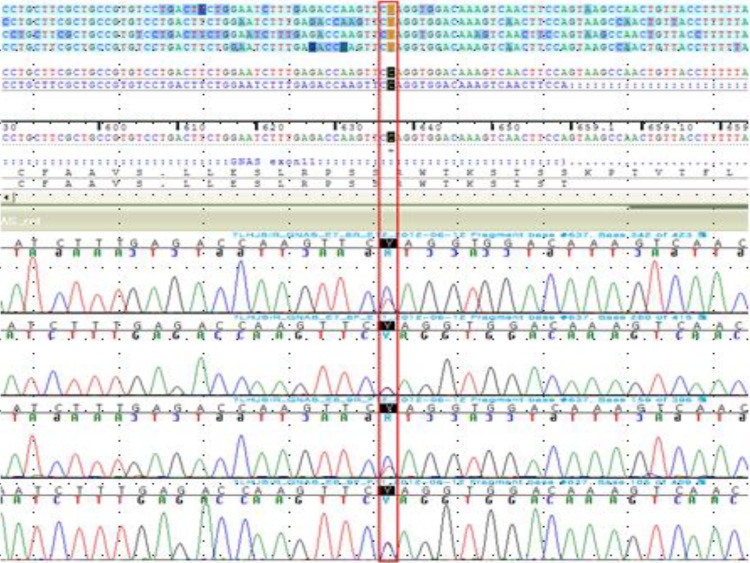
Sequencing of the amplified GNAS genomic DNA fragments revealed a heterozygous nonsense mutation within exon 11 (c.637 C>T) (Fig. 5). The C>T transversion results in an amino acid substitution from Gln to stop codon at codon 213 (p.Gln213*). To our knowledge, this is a novel mutation in GNAS. We also performed DNA sequencing of the GNAS gene of his father, but no mutation was detected.
PHP is a heterogeneous disease characterized by PTH resistance and classified as types Ia, Ib, Ic, and II, according to its different pathogenesis and phenotype5). In contrast to the situation in hypoparathyroidism, in PHP the parathyroid glands are normal or hyperplastic and they can synthesize and secrete PTH6).
Heterozygous inactivating mutations within Gs alpha-encoding GNAS exons are found in patients with PHP-Ia, who also show resistance to other hormones and a constellation of physical features called AHO. Patients who exhibit AHO features without evidence for hormone resistance, who are said to have pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism (PPHP), also carry heterozygous inactivating Gs alpha mutations1,7). There is some evidence to suggest that the Gs alpha mutation is paternally transmitted in patients with PPHP and maternally transmitted in patients with PHP-Ia. The gene may be imprinted in a tissue-specific manner6,8,9).
In our case, the patient presented the characteristics of AHO and hormone resistance. DNA sequencing of the patient and his father revealed that only the patient had mutations. The presence of slight AHO in the mother's side of the patient may suggest that the mutation came from his mother, but we were unable to confirm this because the DNA of the patient's mother or maternal family was not available at the time of the study. Although we could not obtain molecular data from the maternal family of the patient, considering variation of phenotypes due to genomic imprinting, we were able to explain that the patient had the genotype and phenotype of PHP Ia. In the maternal family of the patient, his mother had milder features suggestive of AHO, whereas her mother and two siblings had characteristics that were more strongly suggestive of AHO. We can suspect the possibility of a hypofunctioning GNAS mutation like mosaicism, but it was impossible to validate.
Mutational analysis of GNAS gene is a useful method for identifying genetic abnormalities as well as making diagnosis and differentiation of various subtypes of PHP10). There are previous reports of Korean patients with PHP Ia and PPHP who were confirmed by genetic analysis. Park et al.11) reported a nonsense mutation of c.94A>T (p.K32X) and a frame shift mutation of c.344_345insT (p.V117RfsX23) in patients with PHP Ia, of which the former was novel. In a study of patients with PHP Ia and PPHP, Jin et al.10) identified two novel mutations; c.569_570del mutation (p.Tyr190CysfsX19) and a splicing mutation (c.659+1G>A). GNAS has been termed one of the most complex gene loci in the human genome3). Although many mutations have been identified in GNAS, c.637 C>T nonsense mutation is deemed novel. This identification stresses that GNAS gene analysis is important for the diagnosis of PHP. Further investigation is required to determine the various genotypes of PHP.
References
2. Winter J, Hiort O, Hermanns P, Thiele S, Pohlenz J. A new heterozygous mutation (D196N) in the Gs alpha gene as a cause for pseudohypoparathyroidism type IA in a boy who had gallstones. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2011;24:297–301.

3. Miao ZM, Wang C, Wang BB, Meng DM, Su DM, Cheng Z, et al. Identification of a novel mutation in a pseudohypoparathyroidism family. Int J Endocrinol 2011;2011:509549


4. Jüppner H, Bastepe M. Different mutations within or upstream of the GNAS locus cause distinct forms of pseudohypo-parathyroidism. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2006;19(Suppl 2): 641–646.

5. Ngai YF, Chijiwa C, Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S, Stewart L, Yong SL, Robinson WP, et al. Pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a and the GNAS p.R231H mutation: Somatic mosaicism in a mother with two affected sons. Am J Med Genet A 2010;152A:2784–2790.


6. Doyle DA. Pseudohypoparathyroidism. Kliegman RM, editor. Nelson textbook of Pediatrics. 19th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2011;:1919–1920.
7. Lubell T, Garzon M, Anyane Yeboa K, Shah B. A novel mutation causing pseudohypoparathyroidism 1A with congenital hypothyroidism and osteoma cutis. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 2009;1:244–247.



8. Martin J, Tucker M, Browning JC. Infantile osteoma cutis as a presentation of a GNAS mutation. Pediatr Dermatol 2012;29:483–484.


9. Reis MT, Cattani A, Mendonca BB, Correa PH, Martin RM. A novel GNAS mutation in an infant boy with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia and normal serum calcium and phosphate levels. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2010;54:728–731.


Fig. 2
The patient's hands (A) and an x-ray of right hand (B) show brachydactyly with short metacarpals.
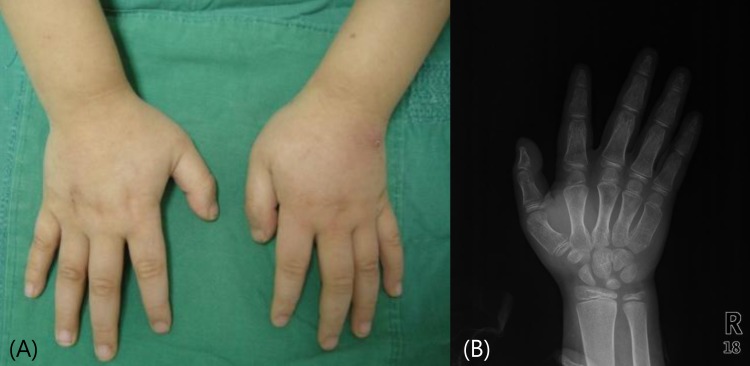
Fig. 3
(A) The patient's posterior chest wall with subcutaneous ossifications and (B) a whole body bone scan show irregular increased activity in the area of calcification. (C) An x-ray of the patient's right foot shows calcification of subcutaneous tissue of 1st web space (long arrow) and 2nd toe tip (short arrow).
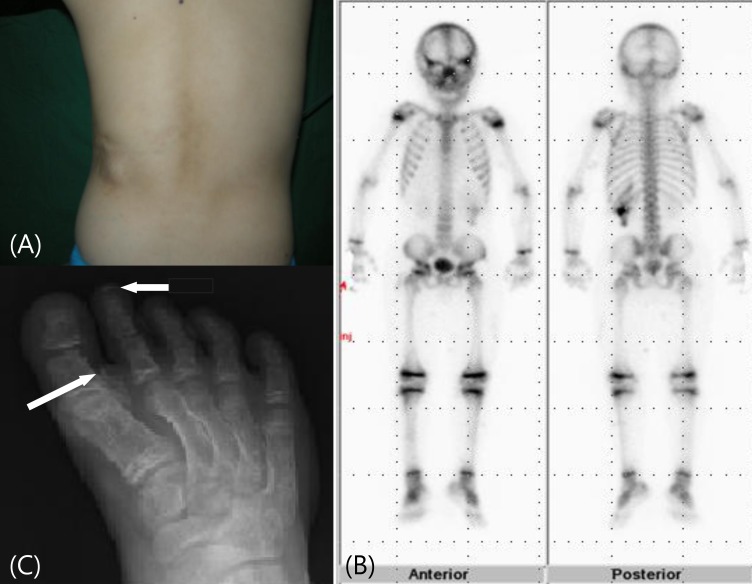
Fig. 4
(A, B) Cranial computed tomography scan shows multiple calcifications in basal ganglia and cerebral subcortex.
Table 1
The results of Ellsworth-Howard test
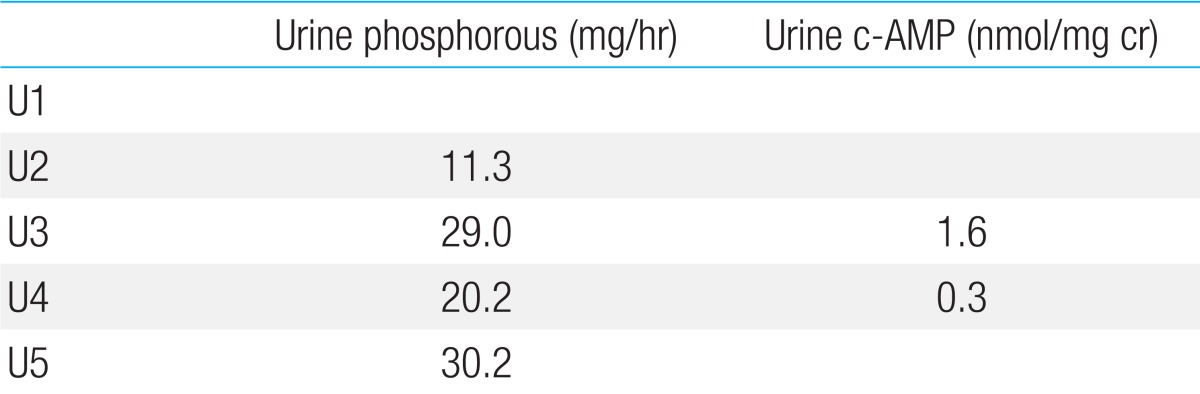
The urine sample obtained 2 hours before administration of human PTH (Fosteo, teriparatide) was designated U1, and samples collected thereafter at 1-hour interval were disignated U2, U3, U4, and U5. PTH was injected at the time between U3 and U4.
Phosphaturic response: (urinary phosphate U4+urinary phosphate U5)-(urinary phosphate U2+urinary phosphate U3). cAMP response: Urinary cAMP U4-urinary cAMP U3.
In this case, phosphaturic response (0.25 fold) was blunted (normal range, 10 folds) and urinary cAMP excretion was not increased.
PTH, parathyroid hormone; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


